Biochar–Sponge Iron Modified Bioretention System Improved Nitrogen Removal Efficiency for Aquaculture Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
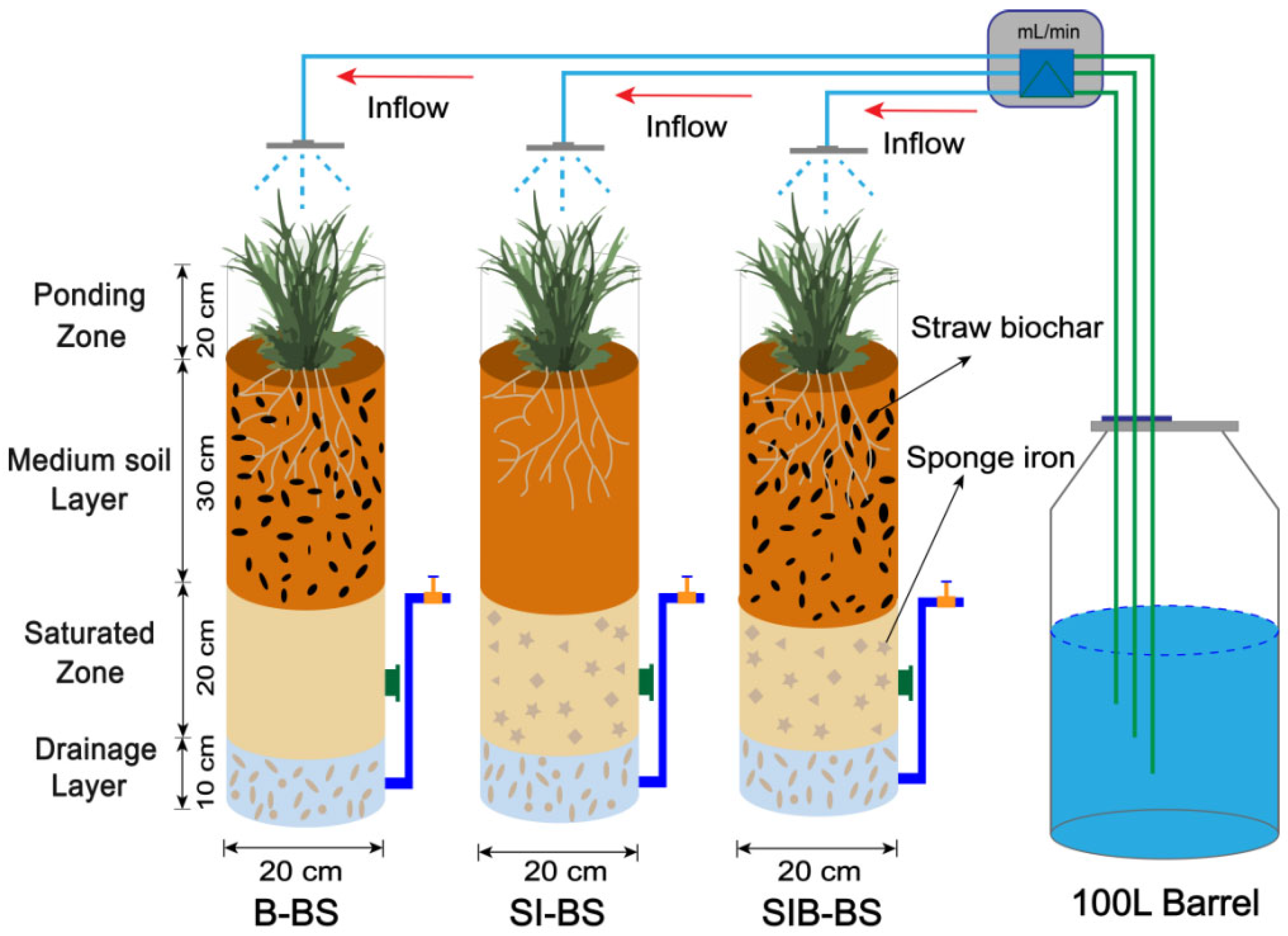
2.1. Experimental System Construction
2.2. Formulation of Aquaculture Wastewaters
2.3. Operation of the System
2.4. Water Quality Measurement
2.5. Characterization and Determination of Physicochemical Properties
2.6. Metagenomic Analysis
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
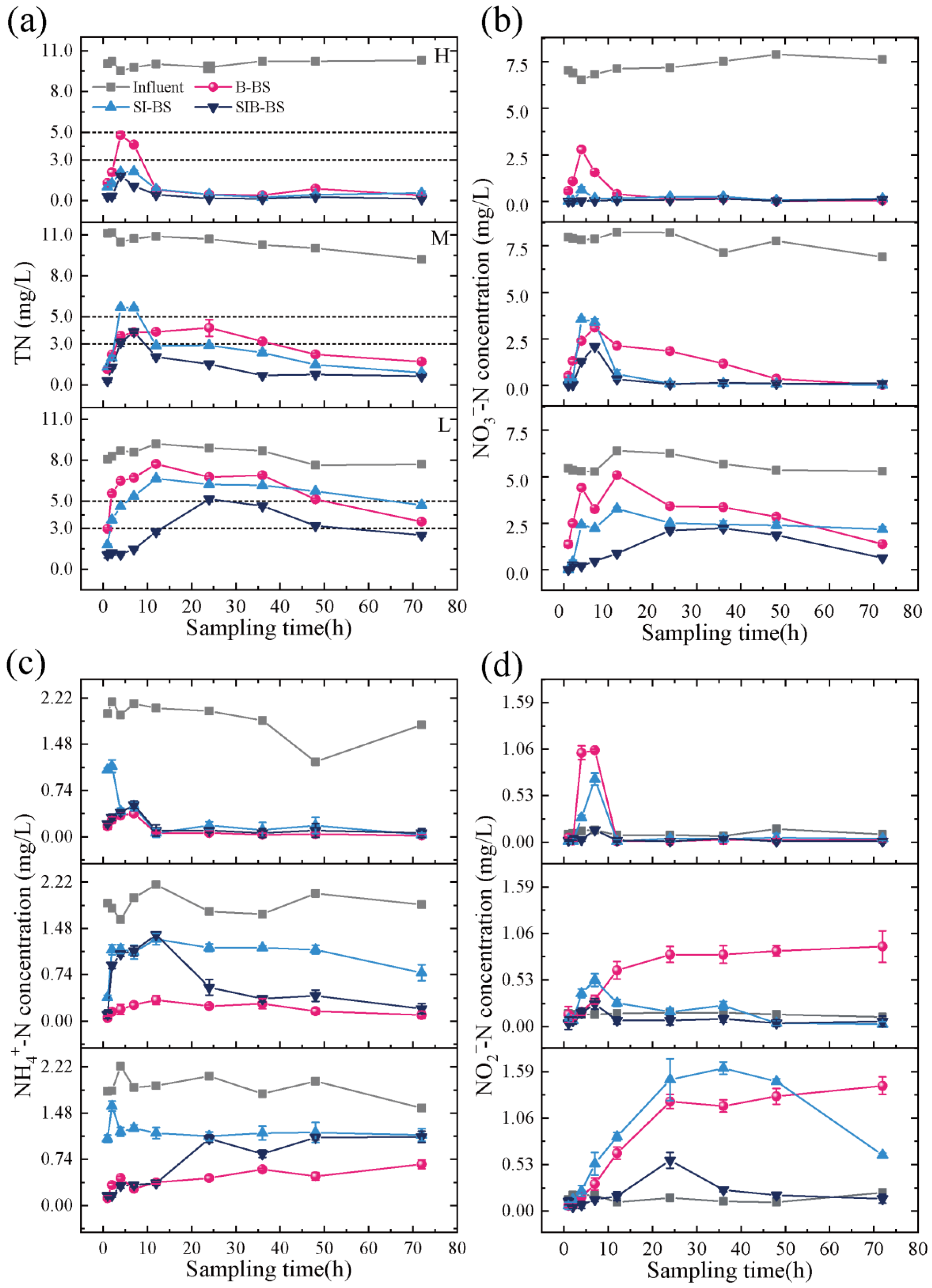
3.1. Nitrogen Removal Efficacy of Bioretention Systems Operated Intermittently at Different Influent Concentrations
3.2. Nitrogen Removal Efficacy of Bioretention Systems Operating Continuously at Different Influent Temperatures
3.3. Interfacial Effects of Biochar–Sponge Iron Modified Media
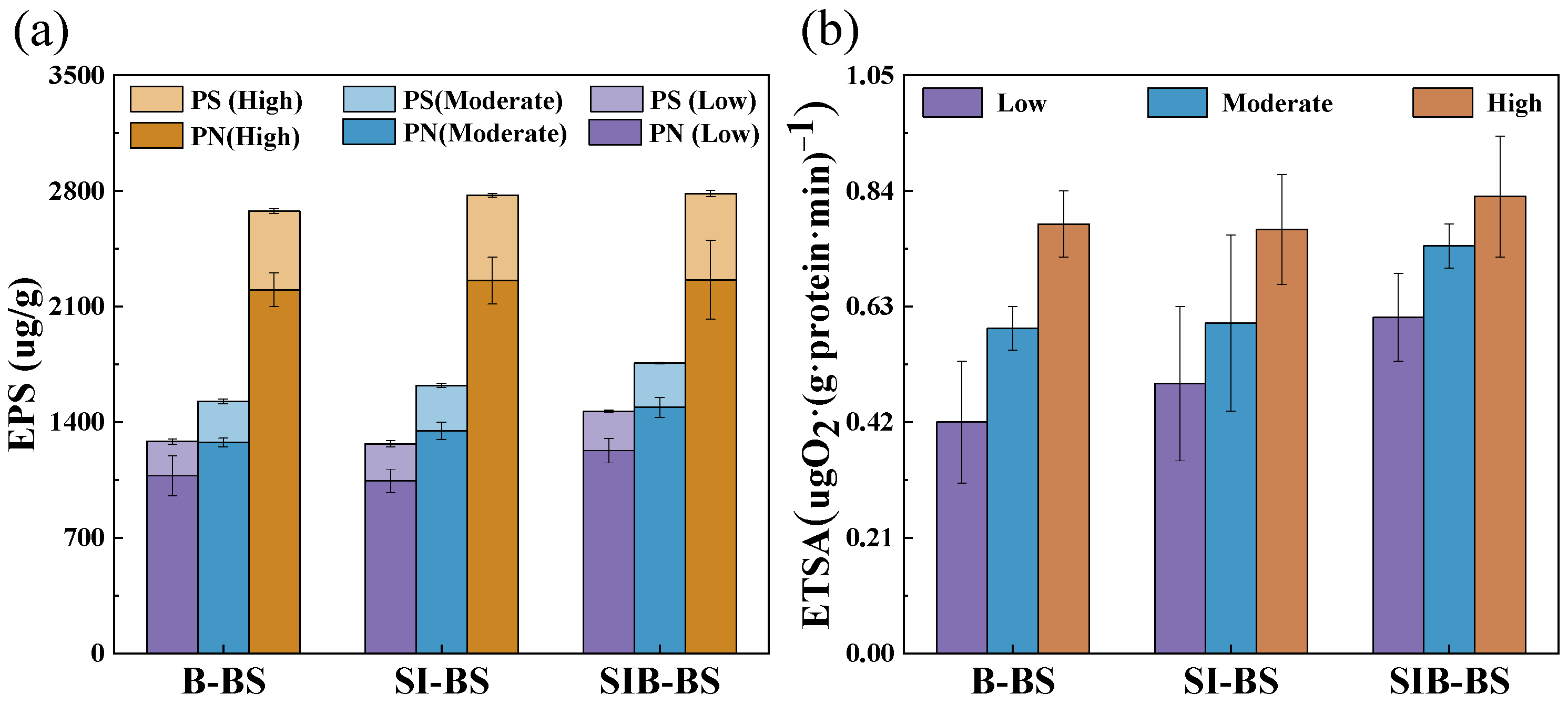
3.3.1. Physicochemical Effects
3.3.2. Biochemical Effect
3.4. Mechanism of Nitrogen Removal by Biochar–Sponge Iron Synergistic Enhancement of Bioretention System
3.4.1. Effect of Biochar–Sponge Iron on Microbial Composition
3.4.2. Effect of Biochar–Sponge Iron on Denitrification Genes
3.5. Nitrogen Removal Process by Biochar–Sponge Iron Bioretention System
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Three bioretention systems exhibited good nitrogen removal efficiency during intermittent inflow, and SIB-BS performed best. At 8.0–12.8 °C, at influent TN concentrations of 9.5 ± 0.3 mg/L and 31.1 ± 0.4 mg/L, respectively, SIB-BS had effluent TN concentrations of 1.9 ± 0.1 mg/L and 4.2 ± 0.1 mg/L, respectively, with TN removal rates of 79.7% and 86.4%.
- (2)
- Under continuous inflow conditions, SIB-BS had lower TN concentrations in the effluent than B-BS and SI-BS at varying temperatures (8–26.3 °C). At low temperature (8–12.8 °C), the SIB-BS’s TN concentration (2.6 ± 1.5 mg/L) was significantly lower than that of B-BS (5.6 ± 1.6 mg/L) and SI-BS (5.0 ± 1.5 mg/L). (p < 0.05).
- (3)
- The combination of biochar and sponge iron promoted the enrichment of denitrifying genera (Hydrogenophaga, Thauera, etc.), boosting denitrification genes (narG/H, napA/B, etc.) and facilitating nitrate/nitrite denitrification.
- (4)
- Biochar and sponge iron addition promoted the secretion of EPS, optimized the electron transfer pathway mediated by Fe2+, accelerated electron transfer efficiency, and enhanced the low-temperature nitrogen removal stability of bioretention systems.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, K.; Jiang, R.T.; Qiu, J.Q.; Liu, J.L.; Shao, L.; Zhang, J.H.; Liu, Q.G.; Jiang, Z.J.; Wang, H.; He, W.H.; et al. How to control pollution from tailwater in large scale aquaculture in China: A review. Aquaculture 2024, 590, 741085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.-G.; Nguyen, M.-K.; Nguyen, H.-L.; Thai, V.-A.; Le, V.-R.; Vu, Q.M.; Asaithambi, P.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D. Ecotoxicological response of algae to contaminants in aquatic environments: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 919–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Xu, G.; Yu, H. Overview of strategies for enhanced treatment of municipal/domestic wastewater at low temperature. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Zhao, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Jin, P.; Zheng, Z. Enhanced nitrogen removal from low-temperature wastewater by an iterative screening of cold-tolerant denitrifying bacteria. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 45, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Ding, L.; Wei, X.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z.; Han, S.; Huang, T.; Wang, B.; et al. Physiological responses to heat stress in the liver of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) revealed by UPLC-QTOF-MS metabolomics and biochemical assays. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 242, 113949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordignon, F.; Birolo, M.; Fanizza, C.; Trocino, A.; Zardinoni, G.; Stevanato, P.; Nicoletto, C.; Xiccato, G. Effects of water salinity in an aquaponic system with rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), black bullhead catfish (Ameiurus melas), Swiss chard (Beta vulgaris), and cherry tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Aquaculture 2024, 584, 740634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santigosa, E.; Constant, D.; Prudence, D.; Wahli, T.; Verlhac-Trichet, V. A novel marine algal oil containing both EPA and DHA is an effective source of omega-3 fatty acids for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. World Aquac. Soc. 2020, 51, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C.; Qian, Q.; Liang, Z.; Liang, J.; Wen, L.; Jiang, L.; Wang, S. Enhanced Nitrogen Removal from Aquaculture Wastewater Using Biochar-Amended Bioretention Systems. Water 2025, 17, 2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Singh, V.; Cheng, L.; Hussain, A.; Ormeci, B. Nitrogen removal from wastewater: A comprehensive review of biological nitrogen removal processes, critical operation parameters and bioreactor design. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Han, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Shi, P.; Pan, Y.; Li, A. Occurrence, distribution and potential environmental risks of pollutants in aquaculture ponds during pond cleaning in Taihu Lake Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 939, 173610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, M.; Traenckner, J. Development of Decay in Biofilms under Starvation Conditions-Rethinking of the Biomass Model. Water 2020, 12, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burut-Archanai, S.; Ubertino, D.; Chumtong, P.; Mhuantong, W.; Powtongsook, S.; Piyapattanakorn, S. Dynamics of Microbial Community During Nitrification Biofilter Acclimation with Low and High Ammonia. Mar. Biotechnol. 2021, 23, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Song, Y.Q.; Xu, M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Ma, H.Y.; Zhi, Y.; Shao, Z.Y.; Chen, L.; Yuan, Y.S.; et al. Multi-media interaction improves the efficiency and stability of the bioretention system for stormwater runoff treatment. Water Res. 2024, 250, 121017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansar, H.; Duan, H.F.; Mark, O. Unit-scale- and catchment-scale-based sensitivity analysis of bioretention cell for urban stormwater system management. J. Hydroinform. 2023, 25, 1471–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Sage, J.; Técher, D.; Gromaire, M.-C. Hydrological performance of bioretention in field experiments and models: A review from the perspective of design characteristics and local contexts. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 965, 178684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-X.; Chen, S.-J.; Hong, X.-Y.; Wang, L.-Z.; Wu, H.-M.; Tang, Y.-Y.; Gao, Y.-Y.; Hao, G.-F. Plant exudates-driven microbiome recruitment and assembly facilitates plant health management. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2025, 49, fuaf008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afridi, M.S.; Kumar, A.; Javed, M.A.; Dubey, A.; de Medeiros, F.H.V.; Santoyo, G. Harnessing root exudates for plant microbiome engineering and stress resistance in plants. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 279, 127564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Søberg, L.C.; Viklander, M.; Blecken, G.-T. Nitrogen removal in stormwater bioretention facilities: Effects of drying, temperature and a submerged zone. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 169, 106302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.K.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Tsen-Tieng, D.L.; Balasubramanian, R. Biochar-based bioretention systems for removal of chemical and microbial pollutants from stormwater: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Q.; Zhangsun, X.; Cao, J.; Zhang, F.; Huang, T. Water-lifting aerator coupled with sponge iron-enhanced biological aerobic denitrification to remove nitrogen in low C/N water source reservoirs: Effect and mechanism. Environ. Res. 2025, 277, 121557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Song, Y.; Shao, Z.; Chai, H. Biochar-pyrite bi-layer bioretention system for dissolved nutrient treatment and by-product generation control under various stormwater conditions. Water Res. 2021, 206, 117737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-J.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Qi, Y. An anaerobic two-layer permeable reactive biobarrier for the remediation of nitrate-contaminated groundwater. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5977–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, M.; Cun, D.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chang, J. Agricultural runoff treatment by constructed wetlands filled with iron-carbon composites in winter: Performance augmentation by organic solids and denitrifying bacteria addition. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 387, 129692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Wang, Z.; Shi, C.; Li, N.; Bai, M.; Yao, J.; Hrynsphan, D.; Qian, H.; Hu, S.; Wei, J.; et al. Enhanced denitrification performance via biochar-mediated electron shuttling in Pseudomonas guariconensis: Mechanistic insights from enzymatic and electrochemical analyses. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 382, 126667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xie, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhang, M.; Yan, P.; Xu, F.; Tang, L.; He, S. Efficient nitrogen removal through coupling biochar with zero-valent iron by different packing modes in bioretention system. Environ. Res. 2023, 223, 115375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathishkumar, K.; Li, Y.; Sanganyado, E. Electrochemical behavior of biochar and its effects on microbial nitrate reduction: Role of extracellular polymeric substances in extracellular electron transfer. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 395, 125077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Song, X.; Cheng, M.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, Y. Enhancing the pollutant removal performance and biological mechanisms by adding ferrous ions into aquaculture wastewater in constructed wetland. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 293, 122003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, B.; Zhu, L.; Xing, B. Effects and mechanisms of biochar-microbe interactions in soil improvement and pollution remediation: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cao, X.; Zhao, J.; Dai, Y.; Cui, N.; Li, Z.; Cheng, S. Performance of biofilter with a saturated zone for urban stormwater runoff pollution control: Influence of vegetation type and saturation time. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 105, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashem, A.H.M.; Das, P.; Hawari, A.H.; Mehariya, S.; Thaher, M.I.; Khan, S.; Abduquadir, M.; Al-Jabri, H. Aquaculture from inland fish cultivation to wastewater treatment: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio Technol. 2023, 22, 969–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ke, H.; Xie, J.; Tan, H.; Luo, G.; Xu, B.; Abakari, G. Characterizing the water quality and microbial communities in different zones of a recirculating aquaculture system using biofloc biofilters. Aquaculture 2020, 529, 735624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Luo, G.; Tan, H.; Sun, D. Effects of sludge retention time on water quality and bioflocs yield, nutritional composition, apparent digestibility coefficients treating recirculating aquaculture system effluent in sequencing batch reactor. Aquac. Eng. 2016, 72–73, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wen, X.; Cao, Z.; Cheng, R.; Qian, Y.; Mi, J.; Wang, Y.; Liao, X.; Ma, B.; Zou, Y.; et al. Modified cornstalk biochar can reduce ammonia emissions from compost by increasing the number of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and decreasing urease activity. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Li, N. Remediation of nitrogen polluted water using Fe–C microelectrolysis and biofiltration under mixotrophic conditions. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Chi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Jin, X.; Jin, P. Diversified metabolism makes novel Thauera strain highly competitive in low carbon wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2021, 206, 117742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Tu, Q.; Chen, X. Achieving enhanced denitrification via hydrocyclone treatment on mixed liquor recirculation in the anoxic/aerobic process. Chemosphere 2017, 189, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Qu, T.; Ran, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, A. Effect of extracellular polymeric substances removal and re-addition on anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 57, 104702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Cheng, X.; Wang, C.; Kang, L.; Chen, P.; He, Q.; Zhang, G.; Ye, J.; Zhou, S. Extracellular polymeric substances trigger an increase in redox mediators for enhanced sludge methanogenesis. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, C.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, N. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) promoted by pyrogenic biochar: Deciphering the interaction with extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xu, F.; Yang, C.; Su, X.; Guo, F.; Xu, Q.; Peng, G.; He, Q.; Chen, Y. Highly efficient nitrate removal in a heterotrophic denitrification system amended with redox-active biochar: A molecular and electrochemical mechanism. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Xu, F.; Cai, R.; Li, D.; Xu, Q.; Yang, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; He, Q.; Ao, L.; et al. Enhancement of denitrification in biofilters by immobilized biochar under low-temperature stress. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, T.; Gao, C.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, A. Effect of extracellular polymeric substances removal and re-addition on the denitrification performance of activated sludge: Carbon source metabolism, electron transfer and enzyme activity. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhuang, W.-Q. Functional bacteria and their genes encoding for key enzymes in hydrogen-driven autotrophic denitrification with sulfate loading. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 440, 140901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tang, M.; He, L.; Xiao, X.; Yang, F.; He, Q.; Sun, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; et al. Exploring the impact of fulvic acid on electrochemical hydrogen-driven autotrophic denitrification system: Performance, microbial characteristics and mechanism. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 412, 131432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, L.; Xing, G.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhang, Y. Interspecies electron transfer and microbial interactions in a novel Fe (II)-mediated anammox coupled mixotrophic denitrification system. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 403, 130852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, A.; Szewzyk, U.; Ma, F. Improvement of biological nitrogen removal with nitrate-dependent Fe (II) oxidation bacterium Aquabacterium parvum B6 in an up-flow bioreactor for wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.-Y.; Zhou, L.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, J. Hydrogen-driven microbial biogas upgrading: Advances, challenges and solutions. Water Res. 2021, 197, 117120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Li, W.; Ren, S.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, M.; Guo, K.; Xie, H.; Li, J. Use of sponge iron as an indirect electron donor to provide ferrous iron for nitrate-dependent ferrous oxidation processes: Denitrification performance and mechanism. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 357, 127318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, X.; Yang, T.; Zhu, H.; He, Z.; Zhao, R.; Chen, Y. Sponge iron enriches autotrophic/aerobic denitrifying bacteria to enhance denitrification in sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 407, 131097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teal, T.K.; Lies, D.P.; Wold, B.J.; Newman, D.K. Spatiometabolic stratification of Shewanella oneidensis biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 7324–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Cha, D.K. Effect of low temperature on abiotic and biotic nitrate reduction by zero-valent Iron. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Ni, J.; Ma, T.; Li, C. Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification at low temperature by a newly isolated bacterium, Acinetobacter sp HA2. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 139, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Winkler, M.K.H.; Volcke, E.I.P. Elucidating the Competition between Heterotrophic Denitrification and DNRA Using the Resource-Ratio Theory. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 13953–13962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Chen, P.; Yang, G.; Niu, R.; Bai, Y.; Cheng, K.; Huang, G.; Liu, T.; Li, X.; Li, F. Fe(II) Oxidation Shaped Functional Genes and Bacteria Involved in Denitrification and Dissimilatory Nitrate Reduction to Ammonium from Different Paddy Soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 21156–21167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luz Cayuela, M.; Angel Sanchez-Monedero, M.; Roig, A.; Hanley, K.; Enders, A.; Lehmann, J. Biochar and denitrification in soils: When, how much and why does biochar reduce N2O emissions? Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Zhao, W.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bai, M.; Su, S.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Z. Ammonia-oxidizing activity and microbial structure of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria, ammonia-oxidizing archaea and complete ammonia oxidizers in biofilm systems with different salinities. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 423, 132248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, M.; Chaudhari, N.; Thamdrup, B.; Overholt, W.A.; Bristow, L.A.; Taubert, M.; Kuesel, K.; Jehmlich, N.; von Bergen, M.; Herrmann, M. Differential contribution of nitrifying prokaryotes to groundwater nitrification. ISME J. 2023, 17, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Huo, Y.; Qi, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Qiao, M. Biochar-supported microbial systems: A strategy for remediation of persistent organic pollutants. Biochar 2025, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Xin, X.; Li, S.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, T.; Mueller, C.; Cai, Z.; Wright, A.L. Effects of Fe oxide on N transformations in subtropical acid soils. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, srep08615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Hao, J.; Feng, Y. Differences in the efficiency and mechanisms of different iron-based materials driving synchronous nitrogen and phosphorus removal. Environ. Res. 2025, 268, 120706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, B.; Boddicker, A.M.; Roane, T.M.; Mosier, A.C. Nitrifier Gene Abundance and Diversity in Sediments Impacted by Acid Mine Drainage. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelino, V.R.; Verbruggen, H. Multi-marker metabarcoding of coral skeletons reveals a rich microbiome and diverse evolutionary origins of endolithic algae. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; He, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yang, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, R.; Li, Y.-Y. Biochar mediated microbial synergy in Partial nitrification-anammox systems: Enhancing nitrogen removal efficiency and stability. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2025, 19, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulatti, A.; Zhao, B.; Xie, F.; Cui, Y.; Yue, X. Approach enhancing nitrate removal from actual municipal wastewater by integrating electric-magnetic field with Fe0 in UMSR reactor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 333, 125646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Zhou, Q.W.; Wang, L.L.; Wan, B.; Yang, Q.N. How Biochar Addition Affects Denitrification and the Microbial Electron Transport System (ETSA): A Meta-Analysis Based on a Global Scale. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.Y.; Savio, F.; Kjaergaard, C.; Jensen, M.M.; Kovalovszki, A.; Smets, B.F.; Valverde-Pérez, B.; Zhang, Y.F. Inorganic bioelectric system for nitrate removal with low N2O production at cold temperatures of 4 and 10 °C. Water Res. 2025, 274, 123061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Huang, Y.T.; Ji, H.F.; Nie, X.J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Ge, C.; Luo, A.C.; Chen, X. Treatment of turtle aquaculture effluent by an improved multi-soil-layer system. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2015, 16, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yu, J.X.; Chen, Y.C.; Li, X.J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Xiao, C.Q.; Fang, Z.; Chi, R. The adsorption mechanism of NH4+ on clay mineral surfaces: Experimental and theoretical studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayadi, M.; Farasati, M.; Mahmoodlu, G.M.; Rostamicharati, F. Removal of Nitrate, Ammonium, and Phosphate from Water Using Conocarpus and Paulownia Plant Biochar. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. Int. Engl. Ed. 2020, 39, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Wang, B.; Hassan, M.; Xu, H.; Wang, X. Removal mechanisms of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in biochar and its effects on plant growth. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 158, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, G.; Dong, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. Inhibitory Effects of Biochar on N2O Emissions through Soil Denitrification in Huanghuaihai Plain of China and Estimation of Influence Time. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Bao, Z.; Meng, J.; Chen, T.; Liang, X. Biochar Makes Soil Organic Carbon More Labile, but Its Carbon Sequestration Potential Remains Large in an Alternate Wetting and Drying Paddy Ecosystem. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Mu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Deng, L.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Tabassum, S.; Liu, H. A comprehensive review on nature-inspired redox systems based on humic acids: Bridging microbial electron transfer and high-performance supercapacitors. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2026, 156, 101563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Huang, D.; Xu, X.; Yang, F. Optimal algae species inoculation strategy for algal-bacterial granular sludge: Sludge characteristics, performance and microbial community. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 123011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Duan, J.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, F.; Sand, W.; Hou, B. Extracellular Polymeric Substances and Biocorrosion/Biofouling: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Jiang, W.; Wen, L.; Zhang, C.; Liang, J.; Jiang, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, S. Biochar–Sponge Iron Modified Bioretention System Improved Nitrogen Removal Efficiency for Aquaculture Wastewater Treatment. Water 2026, 18, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18020270
Wang J, Jiang W, Wen L, Zhang C, Liang J, Jiang L, Yang X, Wang S. Biochar–Sponge Iron Modified Bioretention System Improved Nitrogen Removal Efficiency for Aquaculture Wastewater Treatment. Water. 2026; 18(2):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18020270
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiang, Wenqiang Jiang, Luting Wen, Chengcai Zhang, Junneng Liang, Linyuan Jiang, Xueming Yang, and Shumin Wang. 2026. "Biochar–Sponge Iron Modified Bioretention System Improved Nitrogen Removal Efficiency for Aquaculture Wastewater Treatment" Water 18, no. 2: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18020270
APA StyleWang, J., Jiang, W., Wen, L., Zhang, C., Liang, J., Jiang, L., Yang, X., & Wang, S. (2026). Biochar–Sponge Iron Modified Bioretention System Improved Nitrogen Removal Efficiency for Aquaculture Wastewater Treatment. Water, 18(2), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18020270




