Antecedent Rainfall Duration Controls Stage-Based Erosion Mechanisms in Engineered Loess-Filled Gully Beds: A Laboratory Flume Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
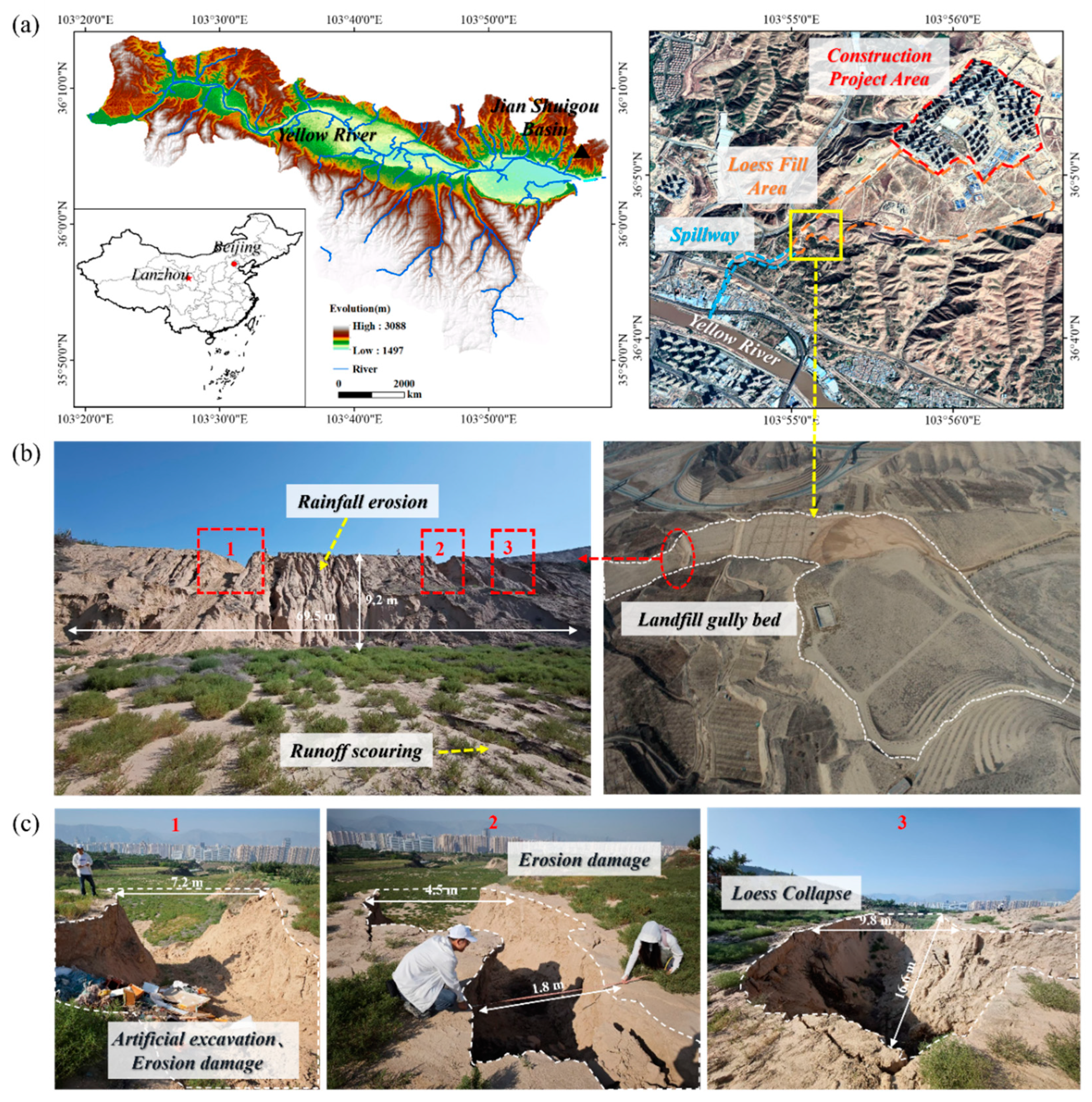
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Physical Properties of the Materials
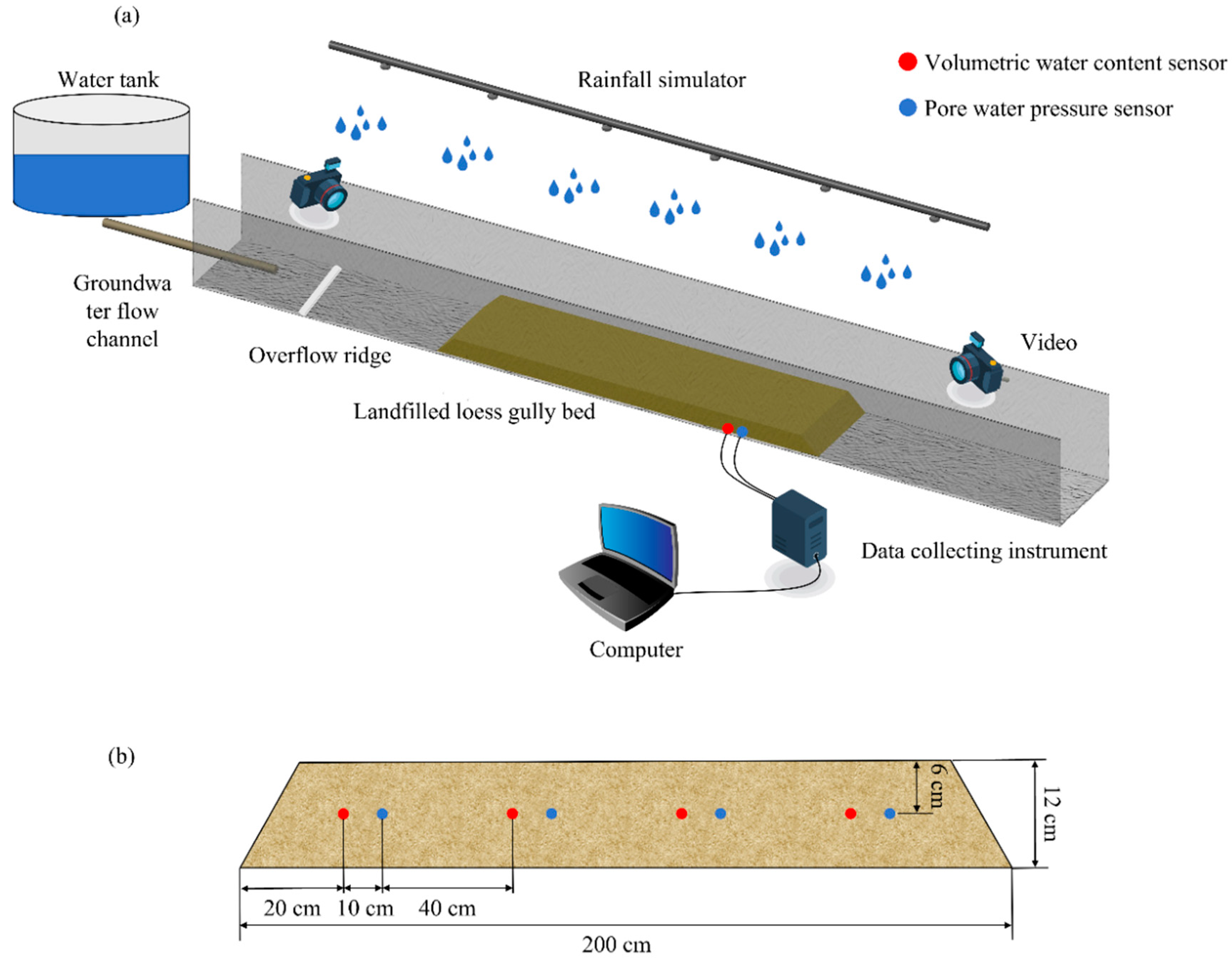
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Experimental Apparatus
3. Experimental Observations
3.1. Phased Evolution of Infilled Loess Gully Bed Erosion Under Antecedent Rainfall Regulation
3.1.1. Raindrop Impact Phase
3.1.2. Intermission Phase
3.1.3. Runoff Scouring–Gully Evolution Phase
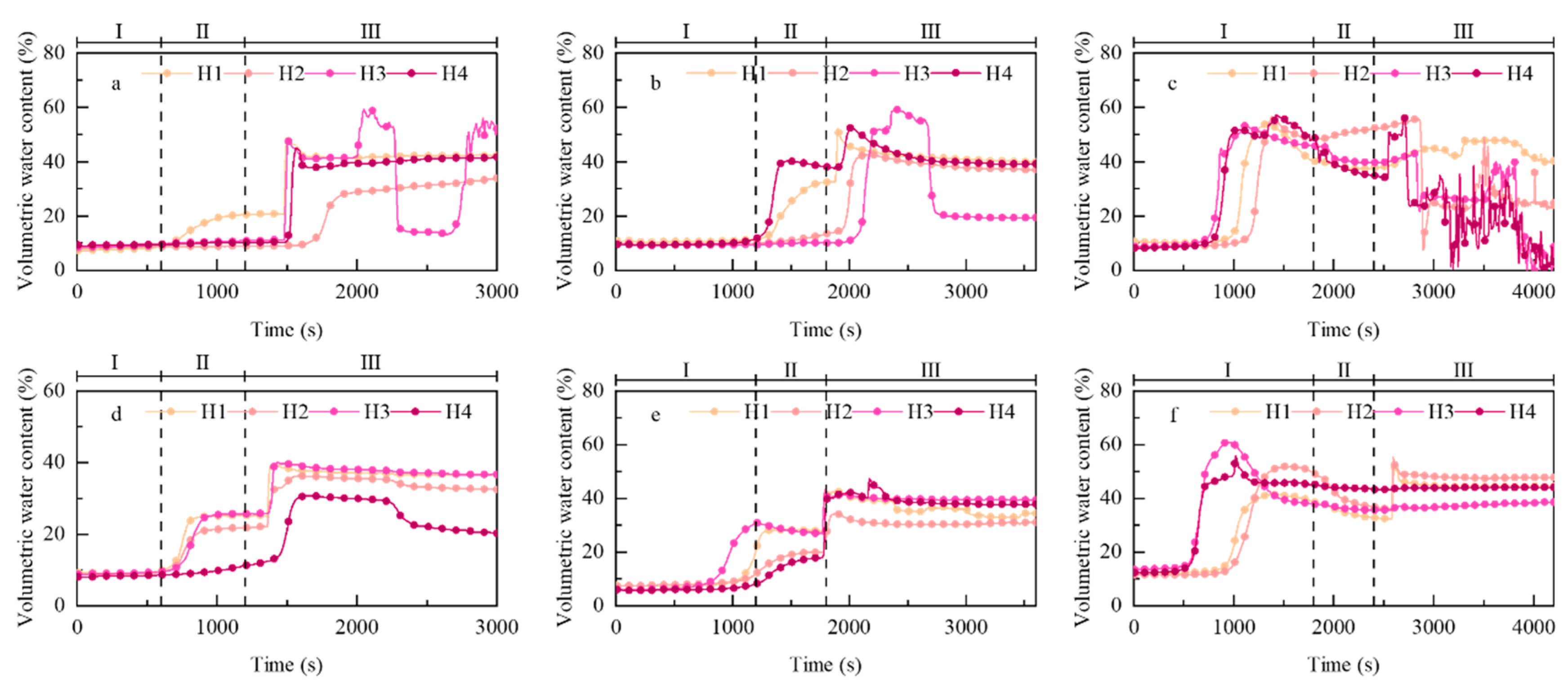
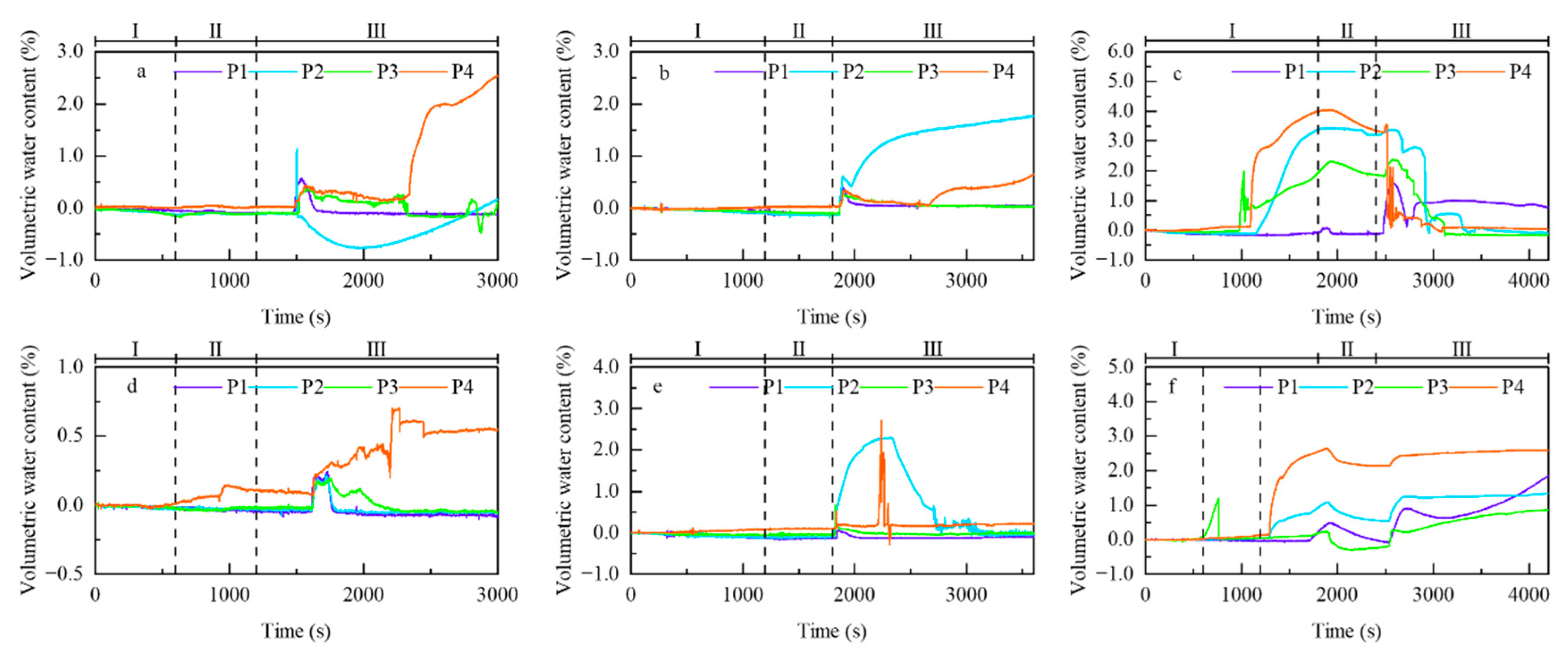
3.2. Soil Hydrological Response Patterns
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Regulation of Macro-Scale Phased Evolution
4.2. Micro-Scale Hydromechanical Mechanisms
4.3. Scaling Relationships and Significance of Antecedent Rainfall Pre-Regulatory Effects
4.4. Insights from Experimental Results into the Fragility of Anthropogenically Modified Landforms
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greminger, P.J.; Sud, Y.K.; Nielsen, D.R. Spatial Variability of Field-measured Soil-water Characteristics. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzjohn, C.; Ternan, J.L.; Williams, A.G. Soil Moisture Variability in a Semi-Arid Gully Catchment: Implications for Runoff and Erosion Control. CATENA 1998, 32, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eekhout, J.P.C.; De Vente, J. Global Impact of Climate Change on Soil Erosion and Potential for Adaptation through Soil Conservation. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 226, 103921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kwon, J.-H.; Om, J.-S.; Lee, T.; Kim, G.; Kim, H.; Heo, J.-H. Increasing Extreme Flood Risk under Future Climate Change Scenarios in South Korea. Weather Clim. Extremes 2023, 39, 100552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Takhellambam, B.S.; Srivastava, P.; Lamba, J.; McGehee, R.P.; Kumar, H.; Tian, D. Projected Mid-Century Rainfall Erosivity under Climate Change over the Southeastern United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimonti, G.; Mariani, L. Is the Number of Global Natural Disasters Increasing? Environ. Hazards 2024, 23, 186–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, D.; Wu, Z.; Cao, Z. Extreme Rainfall Erosivity: Research Advances and Future Perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Matthews, F.; Liakos, L.; Bezak, N.; Diodato, N.; Ballabio, C. Global Rainfall Erosivity Projections for 2050 and 2070. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Casasnovas, J.A.; Ramos, M.C.; Ribes-Dasi, M. Soil Erosion Caused by Extreme Rainfall Events: Mapping and Quantification in Agricultural Plots from Very Detailed Digital Elevation Models. Geoderma 2002, 105, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shellberg, J.G.; Brooks, A.P.; Rose, C.W. Sediment Production and Yield from an Alluvial Gully in Northern Queensland, Australia. Earth Surf. Process Landf. 2013, 38, 1765–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, H.; Moussavi, A.; Ghadiri, H.; Rose, C.W. Flow-Driven Soil Erosion Processes and the Size Selectivity of Sediment. J. Hydrol. 2011, 406, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B.; Ye, Y. Natural and Anthropogenic Rates of Soil Erosion. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2017, 5, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutchler, C.K. Splash Droplet Production by Waterdrop Impact. Water Resour. Res. 1971, 7, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjmand Sajjadi, S.; Mahmoodabadi, M. Sediment Concentration and Hydraulic Characteristics of Rain-Induced Overland Flows in Arid Land Soils. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Song, Y.-K.; Kim, Y.T. Slope stability characteristic of unsaturated weathered granite soil in inje considering antecedent rainfall. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2012, 12, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durukan, S. Evaluation of the Antecedent Saturation and Rainfall Conditions on the Slope Failure Mechanism Triggered by Rainfalls. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahardjo, H.; Leong, E.C.; Rezaur, R.B. Effect of Antecedent Rainfall on Pore-water Pressure Distribution Characteristics in Residual Soil Slopes under Tropical Rainfall. Hydrol. Process 2008, 22, 506–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Domínguez, J.D.; García-Aristizábal, E.F.; Vega-Posada, C.A. Effect of Rainfall Infiltration on the Hydraulic Response and Failure Mechanisms of Sandy Slope Models. Rev. Fac. Ing. 2016, 25, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, A.; Rahardjo, H.; Leong, E.-C. Effect of Antecedent Rainfall Patterns on Rainfall-Induced Slope Failure. J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental Eng. 2011, 137, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Ma, J.; Guo, J.; Qi, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, P. Effects of Rainfall on Surface Environment and Morphological Characteristics in the Loess Plateau. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 37455–37467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tuo, X.; Zhang, G.; Peng, F. Panzhihua Airport Landslide (Oct. 3rd 2009) and an Emergency Monitoring and Warning System Based on the Internet of Things. J. Mt. Sci. 2013, 10, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, B.; Fan, H.; Meng, M. Study on the Destruction of Backfilled Loess Slopes by Short-Term Extreme Rainfall Erosion. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Huang, F.; Huang, J.; Jiang, S.-H.; Zhou, C.; Zhu, L. Experimental Study of the Failure Mode and Mechanism of Loess Fill Slopes Induced by Rainfall. Eng. Geol. 2021, 280, 105941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y. Model Experimental Study on the Failure Mechanisms of a Loess-Bedrock Fill Slope Induced by Rainfall. Eng. Geol. 2023, 313, 106979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, R.B.; Poesen, J. Laboratory Experiments on the Influence of Slope Length on Runoff, Percolation and Rill Development. Earth Surf. Process Landf. 1989, 14, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogan, J.; Gratchev, I. A Study on the Effect of Rainfall and Slope Characteristics on Landslide Initiation by Means of Flume Tests. Landslides 2019, 16, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Qian, H.; Wu, J. Environment: Accelerate Research on Land Creation. Nature 2014, 510, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Sui, L.; Ma, T.; Dan, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, R.; Qiang, X. GEE-Based Ecological Environment Variation Analysis under Human Projects in Typical China Loess Plateau Region. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, C.H.; Dijkstra, T.; Wasowski, J.; Meng, X. Loess Geohazards Research in China: Advances and Challenges for Mega Engineering Projects. Eng. Geol. 2019, 251, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Peng, J.; Zhuang, J.; Feng, L.; Huo, A.; Mu, X.; Wang, W. Gully Erosion and Expansion Mechanisms in Loess Tablelands and the Scientific Basis of Gully Consolidation and Tableland Protection. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2023, 66, 821–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Guo, B.; Ma, Z.; Li, X.; Ye, X.; Yu, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, S.; et al. Magnetostratigraphic Age and Monsoonal Evolution Recorded by the Thickest Quaternary Loess Deposit of the Lanzhou Region, Western Chinese Loess Plateau. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 139, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanmaercke, M.; Poesen, J.; Van Mele, B.; Demuzere, M.; Bruynseels, A.; Golosov, V.; Bezerra, J.F.R.; Bolysov, S.; Dvinskih, A.; Frankl, A.; et al. How Fast Do Gully Headcuts Retreat? Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 154, 336–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Qin, W.; Guo, Q.; Yin, Z.; Duan, X. The Gully Erosion Rates in the Black Soil Region of Northeastern China: Induced by Different Processes and Indicated by Different Indexes. CATENA 2019, 182, 104146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Meng, X.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Response of a Loess Landslide to Rainfall: Observations from a Field Artificial Rainfall Experiment in Bailong River Basin, China. Landslides 2018, 15, 895–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Dong, Y.; Su, X.; Wang, X. Debris Flow Disaster Induced by Artificial Accumulation Site in Loess Area: An Instance of Jianshui Valley, Lanzhou City. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 22, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Dai, F.C.; Tham, L.G.; Tu, X.B.; Min, H.; Zhou, Y.F.; Wu, C.X.; Xu, K. Field Testing of Irrigation Effects on the Stability of a Cliff Edge in Loess, North-West China. Eng. Geol. 2011, 120, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Huang, H.; Liu, D.; Hui, X. Study on Permeability and Collapsibility Characteristics of Sandy Loess in Northern Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-R.; Huang, L.-J. Infiltration and Failure Behavior of an Unsaturated Soil Slope under Artificial Rainfall Model Experiments. Water 2023, 15, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarinejad, A.; Akca, D.; Springman, S.M. Precursors of Instability in a Natural Slope Due to Rainfall: A Full-Scale Experiment. Landslides 2018, 15, 1745–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Horn, R.; Ren, T. Soil Structure Effects on Deformation, Pore Water Pressure, and Consequences for Air Permeability during Compaction and Subsequent Shearing. Geoderma 2022, 406, 115452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Ma, Y. Change Characteristics of Soil and Water Parameters of Loess Landfill Slopes during Rainfall Scouring. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. Trans. CSAE 2023, 39, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Lu, M. Study on Pore-Water Pressure Variation and Deformation Characteristics of Warm Frozen Soils under Confined Dynamic Loading. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2023, 214, 103968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, N.; Shen, H. Progressive Deformation and Failure Mechanism of Loess Fill Slopes Induce by Rainfall: Insights from Flume Model Tests. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Vanapalli, S.; Li, T. Review of Collapse Triggering Mechanism of Collapsible Soils Due to Wetting. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2016, 8, 256–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, D.G.; Vanapalli, S.K. 2.7 Shear Strength of Unsaturated Soils; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; Volume 60. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Laflen, J.M.; Bradford, J.M. Evaluation of the Detachment-Transport Coupling Concept in the WEPP Rill Erosion Equation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annandale, G.W. Scour Technology: Mechanics and Engineering Practice; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.L.; Rowntree, K.M.; Roux, J.J.L. An Interrogation of Research on the Influence of Rainfall on Gully Erosion. Catena 2021, 206, 105482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimov, V.; Sheshukov, A.; Barnes, P. Impact of Precipitation and Runoff on Ephemeral Gully Development in Cultivated Croplands. Proc. IAHS 2015, 367, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.V.; Cullum, R.F.; Römkens, M.J.M. Ephemeral Gully Erosion by Preferential Flow through a Discontinuous Soil-Pipe. Catena 2008, 73, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J.; Nachtergaele, J.; Verstraeten, G.; Valentin, C. Gully Erosion and Environmental Change: Importance and Research Needs. Catena 2003, 50, 91–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yibeltal, M.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Adgo, E.; Meshesha, D.T.; Aklog, D.; Masunaga, T.; Tsubo, M.; Billi, P.; Vanmaercke, M.; et al. Analysis of Long-Term Gully Dynamics in Different Agro-Ecology Settings. Catena 2019, 179, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayas, A.; Vanwalleghem, T.; Laguna, A.; Peña, A.; Giráldez, J.V. Reconstructing Long-Term Gully Dynamics in Mediterranean Agricultural Areas. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezelsofloo, A.A.; Maghrebi, M.; Daroughe, F. Identification of Expansion Rate in Active Gullies using Remote Sensing. J. Water Sustain. Dev. 2018, 5, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, K. Spatial Variation in Gully Expansion Rate in a Loess-Covered Tableland Region Based on Systematic Sampling and High-Resolution Image Interpretation. Catena 2024, 236, 107756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Ma, X.; Jiao, J.; Zhao, W.; Ling, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, X. Magnitude and Hotspots of Soil Erosion Types during Heavy Rainstorm Events on the Loess Plateau: Implications for Watershed Management. Catena 2024, 246, 108365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korup, O.; Densmore, A.L.; Schlunegger, F. The Role of Landslides in Mountain Range Evolution. Geomorphology 2010, 120, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wu, H.; Zhou, S.; Guo, D.; Chen, R. Land Subsidence in Coastal Reclamation with Impact on Metro Operation under Rapid Urbanization: A Case Study of Shenzhen. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 970, 179020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, S.Y.; Tan, M.L.; Tew, Y.L.; Sim, Y.K.; Yee, J.C.; Chong, A.K.M. Between the Devil and the Deep Blue Sea: Trends, Drivers, and Impacts of Coastal Reclamation in Malaysia and Way Forward. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Xu, S.; Shi, B.; Gu, K.; Cheng, G.; Jia, L. Observation and Evaluation of Soil Stratum Deformation in Reclamation Area under Ocean Tides. Can. Geotech. J. 2025, 62, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jo, H.; Oh, J. Application of Drone LiDAR Survey for Evaluation of a Long-Term Consolidation Settlement of Large Land Reclamation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokker, P.A.; Gunnink, J.L.; Koster, K.; De Lange, G. Disentangling and Parameterizing Shallow Sources of Subsidence: Application to a Reclaimed Coastal Area, Flevoland, the Netherlands. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2019, 124, 1099–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, C.; Liu, Q.; Liu, G. Accretion–Erosion Dynamics of the Yellow River Delta and the Relationships with Runoff and Sediment from 1976 to 2018. Water 2020, 12, 2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayas, A.; Gómez, J.A. Modelling of Gully Widening, a Review. Implications for Research on Gully Evolution and Restoration. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2024, 255, 104836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Feng, M.; Jing, H.; Yang, R. The Impact of Changes in Water–Sediment Relationships at River Confluences on the Evolution of River Bars. J. Hydrol. 2024, 645, 132212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, P.; Xu, Q.; Yunus, A.P.; Dong, X.; Pu, C.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Z. Micro-Topographic Assessment of Rill Morphology Highlights the Shortcomings of Current Protective Measures in Loess Landscapes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqua, S.; Bigdeli, A.; Cherian, C. Effect of Pore Fluid pH on the Collapse Behaviour and Microstructural Evolution of a Loess. Environ. Geotech. 2023, 10, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
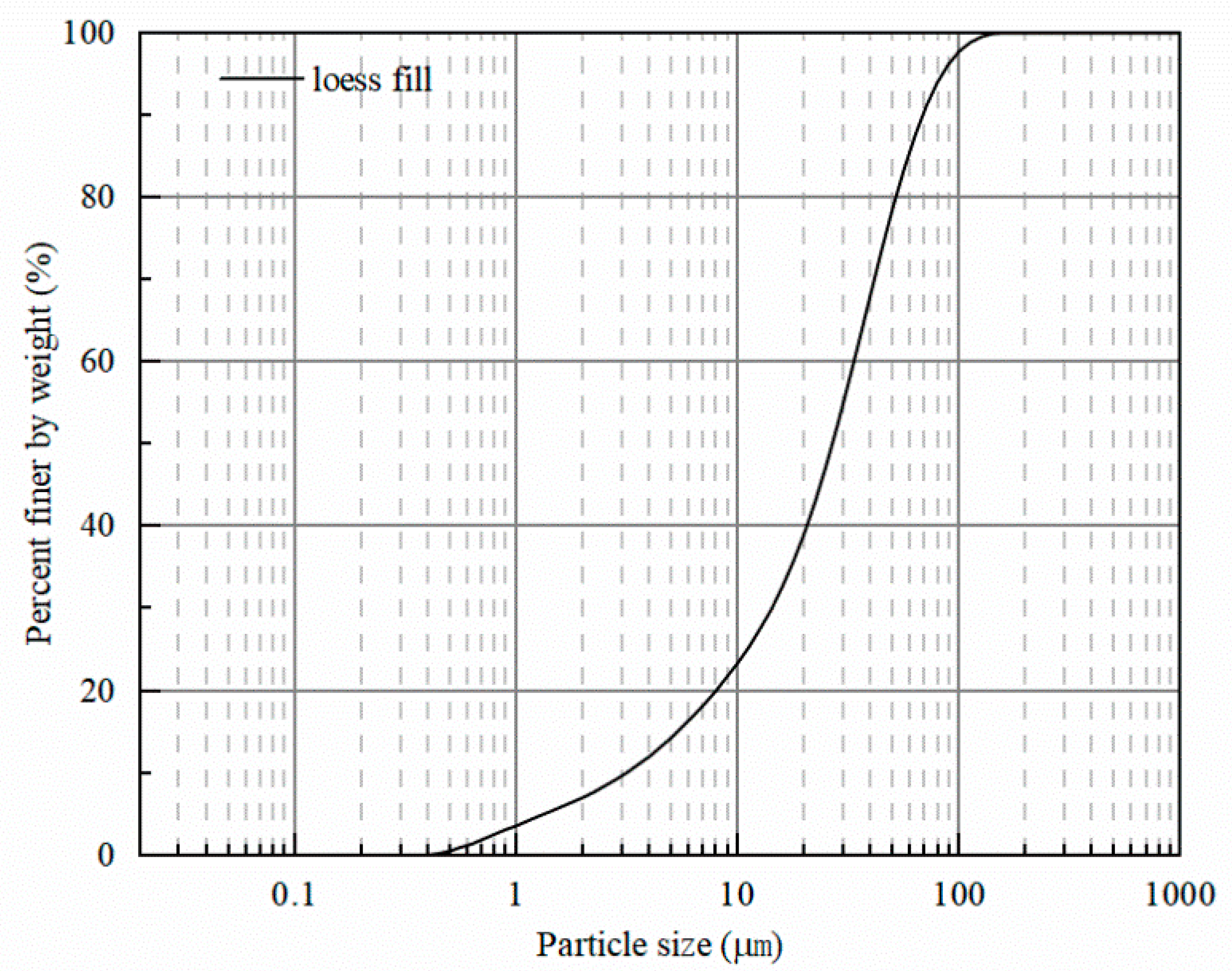


| Natural Density (g·cm−3) | Natural Water Content (%) | Plastic Limit (%) | Liquid Limit (%) | Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity (cm·min−1) | Saturated Water Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.38 | 8–10 | 16 | 26 | 0.03 | 45 |
| Test Number | Groove Width (cm) | Slope (°) | Rainfall Intensity (mm/h) | Rainfall Duration (min) | Runoff Flow Rate (L/min) | Runoff Duration (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 50 | 9 | 78 | 10 | 15 | 30 |
| T2 | 20 | |||||
| T3 | 30 | |||||
| T4 | 12 | 10 | ||||
| T5 | 20 | |||||
| T6 | 30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Liu, X.; Shu, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, Q.; Xiao, Z. Antecedent Rainfall Duration Controls Stage-Based Erosion Mechanisms in Engineered Loess-Filled Gully Beds: A Laboratory Flume Study. Water 2025, 17, 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091290
Ma Y, Liu X, Shu H, Wang Y, Huang J, Li Q, Xiao Z. Antecedent Rainfall Duration Controls Stage-Based Erosion Mechanisms in Engineered Loess-Filled Gully Beds: A Laboratory Flume Study. Water. 2025; 17(9):1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091290
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yanjie, Xingrong Liu, Heping Shu, Yunkun Wang, Jinyan Huang, Qirun Li, and Ziyang Xiao. 2025. "Antecedent Rainfall Duration Controls Stage-Based Erosion Mechanisms in Engineered Loess-Filled Gully Beds: A Laboratory Flume Study" Water 17, no. 9: 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091290
APA StyleMa, Y., Liu, X., Shu, H., Wang, Y., Huang, J., Li, Q., & Xiao, Z. (2025). Antecedent Rainfall Duration Controls Stage-Based Erosion Mechanisms in Engineered Loess-Filled Gully Beds: A Laboratory Flume Study. Water, 17(9), 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091290





