Abstract
Constructed wetlands (CWs) are cost-effective and sustainable systems for wastewater treatment, but their hydraulic performance remains a critical challenge. In this study, a lab-scale baffled horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland was modeled using Computational Fluid Dynamics to investigate the effects of aeration strategies on hydraulic performance, focusing on aeration rates and positions. A gas–liquid two-phase flow system was modeled using the Euler–Euler approach with the Darcy–Forchheimer model in OpenFOAM, simulating 15 cases with varying aeration rates (0.1–0.3 m3/day) and positions (middle of channels vs. bends at the ends of baffles). Results show that the introduction of aeration influenced hydraulic efficiency (HE) and the Morrill Dispersion Index (MDI). Without aeration, the baseline HE was already high (HE = 0.9297) due to the optimized baffle configuration. However, aeration further improved performance, with HE increasing to 0.9594 and MDI decreasing from 1.6087 to 1.4000 when aeration was applied at bends (Position C) at 0.3 m3/day. Aeration at bends was more effective than mid-channel aeration, promoting uniform flow distribution and reducing short-circuiting. These findings highlight the importance of aeration positioning and provide insights for optimizing CW design to balance energy consumption and hydraulic performance.
1. Introduction
Constructed wetlands (CWs) have been globally recognized as cost-effective and sustainable solutions for wastewater treatment. Their ability to integrate natural processes with engineered systems enables the removal of various pollutants, such as organic matter, nitrogen, and phosphorus, while promoting biodiversity and environmental conservation [1,2]. However, the hydraulic performance of CWs is still a critical challenge, as poor hydraulic performance often leads to short-circuiting and uneven pollutant removal, reducing the overall treatment efficiency.
To address this issue, researchers have examined how hydraulic behavior affects treatment outcomes under different design and operational parameters. These include influent modes [3], hydraulic loading rate [4], and system configurations like baffle designs and hydraulic residence time [5]. These structural modifications help reduce dead zones and enhance contact between pollutants and reactive surfaces, thereby improving treatment efficiency [6].
Aeration has been demonstrated as a promising approach to improve the treatment performance of CWs by improving oxygen transfer, promoting microbial activity, and accelerating pollutant degradation [7,8,9]. The installation of baffles in aerated CWs can better facilitate the formation of multistage Anaerobic-Oxic (AO) zones within the system. Such a multistage system, through segmented treatment, can effectively avoid the problem of excessive load on a single stage, thereby achieving more efficient organic matter removal [10]. Additionally, it increases the frequency of nitrification and denitrification reactions, leading to enhanced TN removal efficiency [11]. However, the impact of aeration on hydraulic behavior, especially in baffled CW systems, remains insufficiently understood. Parameters such as aeration rate and aeration position may have an influence on the RTD within the wetland system, potentially affecting both hydraulic and treatment efficiencies.
Recent studies have attempted to address these gaps using different design strategies. For example, Hua, Liu [2] investigated cascading aeration in spiral wetlands and reported improved hydraulic behavior and pollutant removal due to enhanced mixing and reduced short-circuiting. Wu, Fan [12] studied intermittently aerated vertical flow CWs and showed that aeration rate and timing significantly affected treatment efficiency and hydraulic distribution. These findings indicate that aeration strategy design plays a key role in optimizing system performance. However, these works primarily focused on pollutant removal rather than detailed hydraulic behavior.
Furthermore, the configuration of aerators has been shown to impact flow patterns. Alvarado, Vesvikar [13] showed that while additional aerators can improve flow uniformity, the gains plateau beyond a certain number, highlighting the trade-off between hydraulic performance and energy use. Additionally, optimizing aeration strategies in CWs has significant implications for energy conservation. Aeration is often one of the most energy-intensive processes in wastewater treatment systems, accounting for up to 75% of the total energy expenditure [14]. Improper aeration strategies can lead to unnecessary energy consumption without corresponding improvements in treatment performance. Therefore, a deeper understanding of these interactions is crucial for the optimal design and operation of aerated CWs.
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) has emerged as a powerful tool for simulating complex multiphase flow systems in CWs, which enables the analysis of key factors affecting hydraulic performance under various operating conditions. In recent years, many studies have successfully applied CFD modeling to explore the effects of changes in design parameters, including the inlet–outlet configuration [15], vegetation distribution [16], and clogging effects [17,18]. Our previous research [19] also demonstrated the effectiveness of baffle design in improving HE through CFD simulations. While these studies confirm CFD’s utility in analyzing hydraulic performance, they rarely address how aeration configurations interact with flow dynamics in baffled systems.
To address these gaps, this study employs a gas–liquid two-phase CFD model to systematically evaluate how different aeration rates and positions influence RTD in a baffled horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland (HSFCW). Unlike previous studies that primarily focused on pollutant removal, our research emphasizes hydraulic dynamics under varied aeration conditions. The novelty of this work lies in
- (1)
- the application of a two-phase CFD model to simulate aeration-driven hydraulic behavior in baffled systems;
- (2)
- the investigation of aeration configuration (rate and position) as design variables affecting RTD and HE;
- (3)
- the provision of actionable insights for optimizing aeration strategies that balance treatment performance and energy use.
These findings will contribute to a deeper understanding of the interplay between aeration and hydraulic processes, providing practical guidance for the sustainable design and operation of aerated CWs.
2. Description of the CFD Model
2.1. Modeling Setup
A lab-scale rectangular HSFCW with seven baffles (0.5 m in length) was investigated under different aeration strategies in this study. The reactor, measuring 1.2 m in length, 0.6 m in width, and 0.6 m in depth (Figure 1), was modeled. Based on the physical characteristics of our laboratory-scale reactor [6], the water depth was maintained at 0.4 m, and the reactor was filled with a filter medium with a porosity of 45%, resulting in an effective pore volume of approximately 162 L. Based on a constant flow rate of 2.7 L/h, the nominal residence time of the system was calculated as 48 h. Our earlier study [19] demonstrated that this baffle configuration, featuring seven baffles of 0.5 m in length, significantly enhanced the HE of CWs, increasing it from 59% in a system without baffles to 95%. This configuration was selected for its ability to achieve high HE while also promoting the formation of multistage AO zones in aerated CWs, which is beneficial for pollutant removal. Two aeration parameters were considered, i.e., aeration rates and aeration positions (Figure 2), the combinations of which are shown in Table 1. The values of aeration rates were determined via the literature [12] and the scale of the reactor. The inlet–outlet configuration, flow rate, and porosity were kept constant for all cases. The inlet was set at 0.3 m from the base of the reactor and outlet was set at 0.4 m. Consequently, 15 cases were simulated to evaluate the effect of different aeration strategies on the hydraulic performance of CWs.
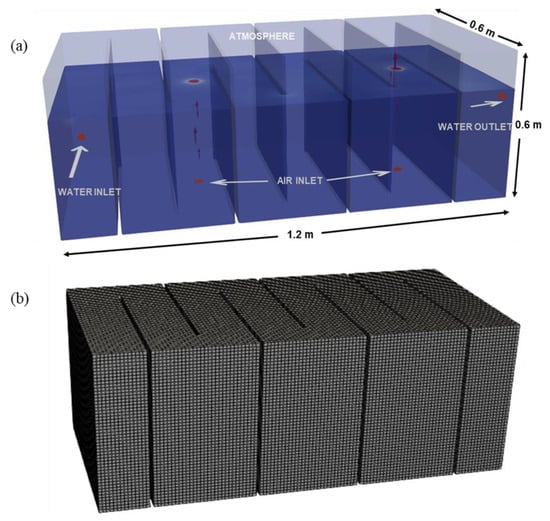
Figure 1.
Sketch of the simulated aerated baffled CW: (a) overview of the geometry and (b) mesh.
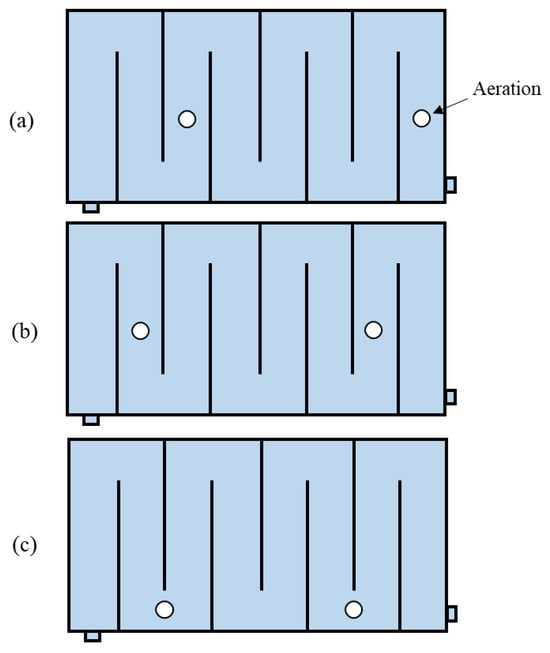
Figure 2.
Top view of the aeration layout: (a) Position A, (b) Position B, and (c) Position C.

Table 1.
Combinations of aeration strategies investigated in simulations.
To determine an appropriate mesh size for the simulations, the computational domain was initially discretized using structured cubes measuring 1 × 1 × 1 cm. A grid independence study was then conducted by comparing the results obtained with this 1 cm cell size to those generated using a finer 0.5 cm cell size. The outcome showed that the mean velocity and pressure predicted using the 1 cm cell differ less than 1% from those of the 0.5 cm cells. Therefore, the computational domain was divided into 421,150 structural meshes with a size of 1 × 1 × 1 (cm) for subsequent simulations. The three-dimensional mesh for the computational domain is shown in Figure 1b.
The boundary conditions for the CFD simulation in OpenFOAM were set to replicate the flow and aeration processes within the CW system shown in Figure 1a. Both the water and air inlets were defined using the flowRateInletVelocity boundary condition to specify the respective inflow rates for the liquid and gas phases. The top surface, which is open to the atmosphere, was modeled using the pressureInletOutletVelocity condition to allow for free movement of the gas phase and interaction with the environment. The water outlet was assigned a zeroGradient pressure boundary condition to enable free outflow while maintaining pressure balance. No-slip boundary conditions were applied to all solid surfaces, including the baffles, side walls, and bottom surface, to account for frictional effects on the liquid phase. The filter medium was additionally modeled with a porous resistance term using the Darcy–Forchheimer equation to simulate flow resistance through the porous structure. The parameters defining the fluids and pollutant transport used in the model simulations (Table 2) are based on empirical values, pertinent literature, and experimental tests. The filter medium is considered to be gravel with a nominal particle size of 8 mm.

Table 2.
Parameters of CWs used in the simulations.
2.2. Modeling of Internal Flows
In this study, the HSFCW system was created as a three-dimensional model and simulated using OpenFOAM v2312, which is a free and open-source CFD software developed primarily by OpenCFD Ltd. (Bracknell, UK) since 2004. The twoPhaseEulerFoam was selected as the solver for this study to simulate the effects of aeration process in the baffled CW. This solver is specifically designed for gas–liquid two-phase flow systems using the Euler–Euler approach, which treats both phases as interpenetrating continua. Its capability to model large-scale multiphase interactions makes it particularly suitable for analyzing aerated flow dynamics in a porous medium like CW. The choice of twoPhaseEulerFoam is driven by its ability to efficiently handle multiphase flow in porous environments without explicitly tracking individual gas bubble shapes or interfaces. This is essential for studying the global impacts of aeration, such as gas distribution, interphase momentum exchange, and their influence on hydraulic performance.
The gas–liquid two-phase flow system was modeled using the Euler–Euler approach, which is governed by the mass conservation equation (Equation (1)), and the momentum conservation equation (Equation (2)) for each phase.
where is the volume fraction of phase ( = liquid, gas), is the density of the phase , is the velocity of the phase in the -direction, and the subscript .
In considering the porous structure within the wetland, the Darcy–Forchheimer model was used to add a porosity zone to the fluid domain by adding a momentum loss source term to the momentum equation to simulate the hindering effect of the substrates on the internal fluid [21].
in which and represents the velocity of phase in - and -directions, respectively; is the pressure shared by both phases; and are the viscous and turbulent stress, since the flow in CWs is generally classified as laminar (Re < 600) [22]; is equal to 0; is the gravitational acceleration; is the surface tension; is the momentum loss source term described using the Darcy–Forchheimer equation (Equation (3)); and the subscripts i, j = 1, 2, 3:
where is the fluid viscosity, and the coefficients C1 and C2 must be specified in OpenFOAM, which can be calculated by solving the following equations [23]:
in which is the mean particle size of the filter and is the porosity of the substrates. Furthermore, the fluid domain is considered as equivalent to being spatially averaged in the process of solving the porous media model [17]. Hence, the porosity value used in the simulation is the spatial average value determined by the experiment.
2.3. Simulating Tracer Transport
To simulate tracer transport in the CW system, a scalar field was introduced to represent the concentration of the tracer. This was achieved by adding a scalarTransport function to the controlDict file in OpenFOAM. The scalarTransport function enables the solution of an additional scalar transport equation alongside the existing flow fields, capturing the behavior of the tracer as it is transported and diffuses through the domain. The convection–diffusion equation is as follows [24]:
where is the transported scalar, is the fluid velocity, and is the diffusion coefficient divided by the fluid density; both are supposed to be constant. Then RTD functions can be obtained by monitoring the value of scalar at the outlet.
2.4. The RTD Model
The time it takes for individual fluid particles to pass through a tank (or reactor) varies based on the specific hydraulic pathways they follow [25]. This duration is commonly referred to as the exit age or residence time. The RTD curve, typically represented as E(t), describes the statistical distribution of the exit ages for all fluid particles passing through the reactor. The RTD curve is expressed in units of the inverse of time and is characterized by the following equation:
where is the flow rate at time t, represents both the outlet tracer concentration at time t and the value of the outlet scalar at time t, and is the sampling time interval.
From the RTD analysis, the following key parameters were derived to evaluate the hydraulic performance:
The parameter HE enables for a comparison of various systems. This parameter is a measure of the CW’s ability to evenly distribute flow throughout the occupied water volume, as well as to provide proper mixing or recirculation [26]. HE was calculated with Equation (9) [27]:
where is the nominal residence time.
The Morrill Dispersion Index (MDI) is a widely used parameter to evaluate the HE and flow uniformity of CW. It is defined as the ratio of the time required for 90% of the tracer to exit the system () to the time required for 10% of the tracer to exit () [27,28]:
This index provides insight into the degree of mixing, short-circuiting, and dead zones within the system. An MDI value close to one indicates near-ideal plug flow, where fluid particles move uniformly through the system, maximizing HE. Conversely, a higher MDI value suggests significant dispersion and poor flow uniformity, often associated with short-circuiting or stagnant zones.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. RTD Analysis
Based on the results of the CFD models, the normalized value of the passive transport scalar was collected at the outlet to generate RTD curves for all cases. The RTD curves for the aerated CW system are shown in Figure 3a–c for three aeration positions (A, B, and C) under varying aeration rates (A1–A5, B1–B5, C1–C5), and with no aeration as a control. The findings indicate a consistent trend across positions: as the aeration was integrated in the system, the shape of the RTD curve became slightly taller and narrower compared to the control group (no aeration). However, there was no significant change in the RTD shape with increasing aeration rate. This pattern suggests that higher aeration rates have very limited impact on the RTD.
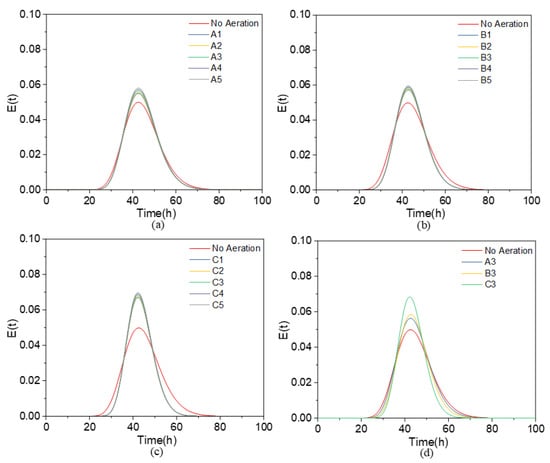
Figure 3.
Simulated RTD curves for the aerated CW system: (a) Position A under different aeration rates, (b) Position B under different aeration rates, (c) Position C under different aeration rates, (d) comparison of different aeration positions at the same aeration rate (0.2 m3/day).
Figure 3d presents the comparison of RTD curves for three different aeration positions under a fixed aeration rate (0.2 m3/day). It can be observed that the location of the aeration point has a more significant impact on the RTD curves than the aeration rate, particularly when the aeration point is positioned at the bend at the end of the baffles (Position C). This indicates that aeration at the bend promotes a more uniform flow distribution and a longer mean residence time, resulting in flow patterns closer to ideal plug flow. In contrast, the RTD curves for the two scenarios where the aeration points were placed in the middle of the channels (Positions A and B) show some improvement compared to the non-aerated control group, but the differences between these two positions are not significant.
The reasons for this phenomenon can be better understood through flow field diagrams (Figure 4). Positioning aeration points at the center of each baffle section enhances local flow uniformity and mixing, as seen in case (Figure 4a), where high-velocity regions are concentrated around the aeration point, promoting localized mixing. However, the effect of aeration is limited to the surrounding aera of the aeration point, and this localized improvement fails to address issues such as short-circuiting and dead zones in the corners. Low flow velocity problems persist in these areas. In contrast, relocating the aeration point to the bend at the end of the baffles (as shown in Figure 4b) creates a wider, high-velocity zone that extends over a larger area of the wetland. This configuration targets the transitional flow zones, significantly reducing flow stagnation and resulting in a more uniform velocity distribution across the system. In Case C3 (Figure 4b), the transitions between baffle sections become smoother, allowing the flow to more closely approximate ideal plug flow conditions, ensuring a more consistent RTD. Consequently, this aeration layout effectively optimizes the HE, making it a more robust strategy for improving the overall performance of the wetland system.
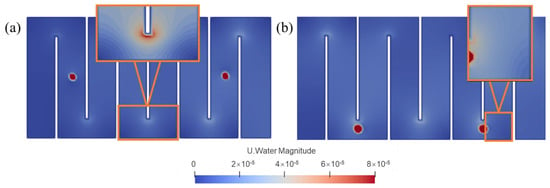
Figure 4.
Velocity fields for cases (a) B3 and (b) C3 in a horizontal plane at depth h = 0.2 m.
3.2. Hydraulic Performance Analysis
Table 3 presents four evaluation indicators used to assess the hydraulic performance of CWs, including a short-circuit indicator , a mixing indicator MDI, the mean residence time , and HE λ. MDI and HE are the most commonly used and reliable indicators for evaluating hydraulic performance of CWs, but they focus on different aspects [29]. MDI assesses the flow uniformity and degree of mixing within a system, which is particularly useful for identifying short-circuiting and dead zones. In contrast, HE evaluates the overall system efficiency by comparing the mean residence time to the nominal residence time , making it more suitable for determining how effectively the system utilizes its design capacity. In general, the larger the value of and the smaller the value of MDI (≥1), the closer the wetland flow is to the plug flow. Additionally, the closer the value of is to , and the larger the value of λ (≤1), the closer the flow characteristics are to ideal plug flow.

Table 3.
Values of parameters defining the hydraulic performance of HSFCWs.
The overall trends in Table 3 indicate that both increasing aeration rates and changing aeration positions can improve the hydraulic performance of CW. As the aeration rate increases from 0 to 0.3 m3/day, there is a consistent improvement in HE and a reduction in MDI across all positions. This is consistent with previous findings. For example, Hua, Liu [2] demonstrated that a cascading aeration design significantly enhanced the effective volume ratio and ammonia removal by improving hydraulic behavior and reducing short-circuiting in spiral flow wetlands. A similar trend was observed in previous studies. Butterworth, Dotro [30] pointed out that aeration enable easy water transport through settled solids in the CW system and ameliorated the HE value of CW.
Moreover, the results of Hreiz, Potier [31] confirm that the spatial layout of aerators critically affects RTD and turbulence in channel reactors. Their study showed that sidewall and distributed aeration generated more uniform mixing and flow patterns than central configurations. Notably, the impact of aeration becomes more pronounced when the aeration point is placed at the bend, with Position C consistently achieving the highest λ values and the lowest MDI values at all aeration rates. At an aeration rate of 0.3 m3/day, HE increases from 0.9297 without aeration to 0.9423 for Position A, 0.9444 for Position B, and 0.9594 for Position C, highlighting the superior performance of aeration at bends compared to mid-channel positions. Similarly, the mixing indicator MDI, which reflects flow uniformity, decreases from 1.6087 in the control to 1.4823, 1.4792, and 1.4000 for Positions A, B, and C, respectively, under the same aeration rate. These results emphasize that aeration at bends not only reduces short-circuiting more effectively but also enhances the RTD closer to ideal plug flow. Moreover, while increasing the aeration rate from 0.1 to 0.3 m3/day improves λ across all positions, the improvement is most pronounced for Position C, demonstrating its effectiveness in optimizing hydraulic performance. This finding underlines the critical role of aeration positioning in achieving enhanced HE in wetland systems. This spatial effect aligns with findings by Hreiz, Potier [31], who emphasized the role of aeration-induced turbulence in shaping plug-flow-like behavior.
On the other hand, with increasing aeration rates, the hydraulic performance improved across all cases, albeit to a limited extent. Specifically, HE increased and MDI decreased. This outcome is consistent with the conclusions drawn by Munoz, Drizo [32], who reported that aeration increases HE by improving water mixing and dispersion, as evidenced by changes in tracer response curves and higher numbers of continuously stirred tank reactors (CSTRs). This improvement helps reduce preferential flow paths and short-circuiting. However, as also demonstrated by Alvarado, Vesvikar [13], over-aeration does not necessarily lead to proportional hydraulic benefits. Their CFD-based scenario analysis in a full-scale aerated pond found that running more aerators increased energy use without significantly improving RTD performance. This supports our observation that continuously increasing the aeration rate does not benefit treatment efficiency. Wu, Fan [12] explored the optimization of organics and nitrogen removal in intermittently aerated vertical flow CWs, focusing on aeration times ranging from 1 to 10 h per day and aeration rates from 0.1 to 2.0 L/min. The results identified 4 h per day at an aeration rate of 1.0 L/min as the optimal condition, achieving removal efficiencies of 97.2% for COD, 98.4% for NH₄⁺-N, and 90.6% for TN. However, increasing the aeration rate to 2.0 L/min led to a decline in TN removal efficiency due to excessive oxygen reducing the anoxic zones necessary for effective denitrification, underscoring the need to balance oxygen supply for simultaneous nitrification and denitrification. Additionally, Alvarado, Vesvikar [13] emphasized that energy-efficient operation is achievable with fewer aerators, reinforcing the importance of identifying the threshold at which aeration becomes energetically inefficient or even hydraulically disruptive. Moreover, further increasing the aeration rate could potentially induce turbulence, disrupting the original plug flow pattern and transforming the CW into a completely mixed flow system, resembling a CSTR. Therefore, it can be inferred that there is a threshold for improving hydraulic efficiency by increasing the aeration rate. This threshold requires further investigation under different design conditions, particularly through tracer studies and multiphase CFD modeling, to define optimal energy–performance tradeoffs. Additionally, since aeration is an energy-intensive process, a comprehensive cost–benefit analysis is recommended to evaluate the specific benefits of increased aeration.
In this study, a configuration with seven baffles was used to create multi-stage AO conditions that better reflect practical applications. However, the numerical improvements in HE achieved (92.97–95.94% improvement across all scenarios simulated) through aeration appeared relatively limited. This may because the hydraulic performance without aeration was already highly optimized due to the baffles, with HE and MDI values approaching those of ideal plug flow conditions. Therefore, to determine whether the aeration strategy has the same impact on CWs with different HE, and also to identify the threshold for aeration rate, future studies should simulate a broader range of scenarios. These should include configurations with varying baffle configurations and aeration rates, and these simulations should be validated with tracer experiments.
3.3. Future Study
While this study provides insights into the hydraulic effects of aeration rate and positioning in baffled CWs using CFD modeling, there are several limitations. First, the simulations are based on an idealized, lab-scale system with fixed boundary conditions and do not account for factors such as influent variability, temperature fluctuations, or long-term clogging. Second, the model does not incorporate biofilm growth, oxygen gradients, or microbial kinetics, which are critical to understanding pollutant degradation. Third, no experimental validation such as tracer studies or in situ measurements of microbial activity was performed, which limits the generalizability of the findings.
Therefore, further experimental work could include an investigation of biofilm communities, as the positioning and intensity of aeration may influence biofilm development and composition. Key areas to assess include the rate of biofilm formation, its stability under shear stress, and its microbial diversity. Understanding these dynamics could help determine whether changes in biofilm characteristics correspond to variations in treatment efficiency or process type. Sampling within different reactor stages could provide insights into the type of treatment occurring in specific zones, offering a deeper understanding of how biofilm communities contribute to pollutant degradation.
Moreover, future studies should explore how aeration positioning affects microbial activity and substrate degradation. While HRT reflects the potential for contact between pollutants and bacteria, it does not fully capture spatial differences in air–bacteria interactions. Uneven air distribution may result in localized oxygen gradients, potentially influencing microbial metabolism and digestion rates in different zones of the wetland. Experimental work incorporating microbial sampling and spatial oxygen profiling would provide valuable data to assess how aeration position impacts actual treatment mechanisms.
Another area to be explored is the economic feasibility of these configurations. A cost–benefit analysis could evaluate whether the HE and treatment efficiency improvements achieved by aeration justify the associated energy consumption. This analysis should extend across a broader range of scenarios to identify conditions where baffles alone are cost-effective, where they become cost-prohibitive, and where aeration—or a combination of both—may be necessary to meet more stringent legislative standards or achieve zero-discharge objectives.
4. Conclusions
This study evaluated the effects of aeration rates and positions on the hydraulic performance of baffled HSFCWs using CFD simulations. The results demonstrate that aeration has positive effects on hydraulic parameters, with improvements observed in HE and a decrease observed in MDI. Without aeration, the baseline hydraulic performance was already high (λ = 0.9297, MDI = 1.6087) due to the presence of seven optimally configured baffles. Increasing aeration rates consistently improved hydraulic performance, but the magnitude of improvement was not significant. Aeration further enhanced performance, with λ increasing to 0.9594 (2.97% improvement on non-aerated baffled CW) and MDI decreasing to 1.4000 when applied at the end of a baffle where the flow “bends” around a corner into a new flow channel (Position C) with an aeration rate of 0.3 m3/day. “Bend” aeration proved to be more effective than mid-channel aeration (Positions A and B), as it facilitated better mixing, reduced short-circuiting, and promoted uniform flow patterns throughout the wetland. In contrast, mid-channel aeration resulted in smaller improvements at the same aeration rate because the aeration in the middle of the channel does not affect the low-velocity areas at the corners. These findings indicate that the combination of bend aeration and high aeration rates is crucial for achieving both efficient pollutant removal and improved hydraulic performance. However, considering energy consumption and the design requirements for pollutant removal, designers should adjust the aeration rate based on practical conditions.
Author Contributions
J.W.: Conceptualization, methodology, and original draft preparation. S.C.: Supervision, review, editing of the manuscript, funding acquisition, and project administration. J.K.: Supervision, review, and editing of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank David Morgan and John Ryan at UCD School of Civil Engineering for providing support in CW fabrication. The first author also acknowledges financial support from the China Scholarship Council and University College Dublin, Ireland.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Stottmeister, U.; Wiessner, A.; Kuschk, P.; Kappelmeyer, U.; Kastner, M.; Bederski, O.; Muller, R.A.; Moormann, H. Effects of plants and microorganisms in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Biotechnol. Adv. 2003, 22, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, G.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Xing, Z.; Wu, L.; Xu, X. Aeration and hydraulic efficiency in spiral wetlands via waterfall design. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 67, 106228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Ding, Y.; Niu, R.; Zhao, X.; Yan, D. The impact of influent mode on nitrogen removal in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands: A simple analysis of hydraulic efficiency and nutrient distribution. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 60, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir, R.; Gidirislioglu, A.; Cebi, U. A study on the effects of different hydraulic loading rates (HLR) on pollutant removal efficiency of subsurface horizontal-flow constructed wetlands used for treatment of domestic wastewaters. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 164, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, H.C.; Lim, P.E.; Seng, C.E.; Nawi, M.A. Newly developed baffled subsurface-flow constructed wetland for the enhancement of nitrogen removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 104, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Cotterill, S.; Keenahan, J. Investigating the treatment efficiency of a baffled horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland with diverse hydraulic efficiency. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 379, 124864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, X.; Peng, S.; Wu, Q.; Yan, L. Effects of aeration position on organics, nitrogen and phosphorus removal in combined oxidation pond-constructed wetland systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uggetti, E.; Hughes-Riley, T.; Morris, R.H.; Newton, M.I.; Trabi, C.L.; Hawes, P.; Puigagut, J.; Garcia, J. Intermittent aeration to improve wastewater treatment efficiency in pilot-scale constructed wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 559, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, L.; Wei, C.; Wu, W.; Zhao, X.; Lu, T. Enhanced nitrogen removal using solid carbon source in constructed wetland with limited aeration. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248 Pt B, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, J.; Bian, D.; Nie, Z.; Ai, S.; Tian, X.; Wang, H. Effect of hydraulic residence time and inlet flow distribution ratio on the pollutant removal of low-temperature municipal wastewater in multistage AO process. Water Environ. J. 2020, 34, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Dong, W.; Wang, H.; Jiang, S. Biological nutrient removal and molecular biological characteristics in an anaerobic-multistage anaerobic/oxic (A-MAO) process to treat municipal wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Fan, J.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Hu, Z.; Lv, J. Optimization of organics and nitrogen removal in intermittently aerated vertical flow constructed wetlands: Effects of aeration time and aeration rate. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 113, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, A.; Vesvikar, M.; Cisneros, J.F.; Maere, T.; Goethals, P.; Nopens, I. CFD study to determine the optimal configuration of aerators in a full-scale waste stabilization pond. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4528–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpinska, A.M.; Bridgeman, J. Towards a robust CFD model for aeration tanks for sewage treatment—A lab-scale study. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2017, 11, 371–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabokrouhiyeh, N.; Bottacin-Busolin, A.; Savickis, J.; Nepf, H.; Marion, A. A numerical study of the effect of wetland shape and inlet-outlet configuration on wetland performance. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 105, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savickis, J.; Bottacin-Busolin, A.; Zaramella, M.; Sabokrouhiyeh, N.; Marion, A. Effect of a meandering channel on wetland performance. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Lu, M.; Bian, H.; Sheng, L.; He, C. Effects of clogging on hydraulic behavior in a vertical-flow constructed wetland system: A modelling approach. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 109, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, G.; Kong, J.; Ji, Y.; Li, M. Influence of clogging and resting processes on flow patterns in vertical flow constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Cotterill, S.; Keenahan, J. Optimizing the hydraulic performance of a baffled horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland through computational fluid dynamics modelling. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Cui, Y.; Shi, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liu, F.; Wan, D.; Ma, Z. Improved test to determine design parameters for optimization of free surface flow constructed wetlands. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 280, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengers, E.E.; Silva, J.B.d.; Paulo, P.L.; Janzen, J.G. Hydraulic performance of a modified constructed wetland system through a CFD-based approach. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2016, 12, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefe, S.H.; Barber, L.B.; Runkel, R.L.; Ryan, J.N.; McKnight, D.M.; Wass, R.D. Conservative and reactive solute transport in constructed wetlands. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, W01201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Hai, R.; Lu, Z. CFD study on hydraulic performance of subsurface flow constructed wetland: Effect of distribution and catchment area. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 26, 1272–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colli, A.N.; Bisang, J.M. Time-dependent mass-transfer behaviour under laminar and turbulent flow conditions in rotating electrodes: A CFD study with analytical and experimental validation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 137, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manenti, S.; Todeschini, S.; Collivignarelli, M.C.; Abbà, A. Integrated RTD−CFD Hydrodynamic Analysis for Performance Assessment of Activated Sludge Reactors. Environ. Process. 2018, 5, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, J.; Somes, N.L.G.; Wong, T.H.F. Hydraulics efficiency of constructed wetlands and ponds. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodin, H.; Mietto, A.; Ehde, P.M.; Persson, J.; Weisner, S.E.B. Tracer behaviour and analysis of hydraulics in experimental free water surface wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 49, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylward, L.; Bonner, R.; Sheridan, C.; Kappelmeyer, U. Hydraulic study of a non-steady horizontal sub-surface flow constructed wetland during start-up. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 880–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dong, B.; Zhou, W.; Qian, Z. Optimal selection of hydraulic indexes with classical test theory to compare hydraulic performance of constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 143, 105687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, E.; Dotro, G.; Jones, M.; Richards, A.; Onunkwo, P.; Narroway, Y.; Jefferson, B. Effect of artificial aeration on tertiary nitrification in a full-scale subsurface horizontal flow constructed wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 54, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hreiz, R.; Potier, O.; Wicks, J.; Commenge, J.M. CFD Investigation of the effects of bubble aerator layouts on hydrodynamics of an activated sludge channel reactor. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 2657–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, P.; Drizo, A.; Cully Hession, W. Flow patterns of dairy wastewater constructed wetlands in a cold climate. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3209–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).