Laboratory Experiments of Surge Pressure Loads Acting on Downstream Dams and Reservoir Banks Caused by Landslides in Narrow, Elongated Reservoirs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup and Methodology
2.1. Flume Setup and Instrumentation
2.2. Experimental Conditions and Procedure
2.3. Data Analysis Techniques
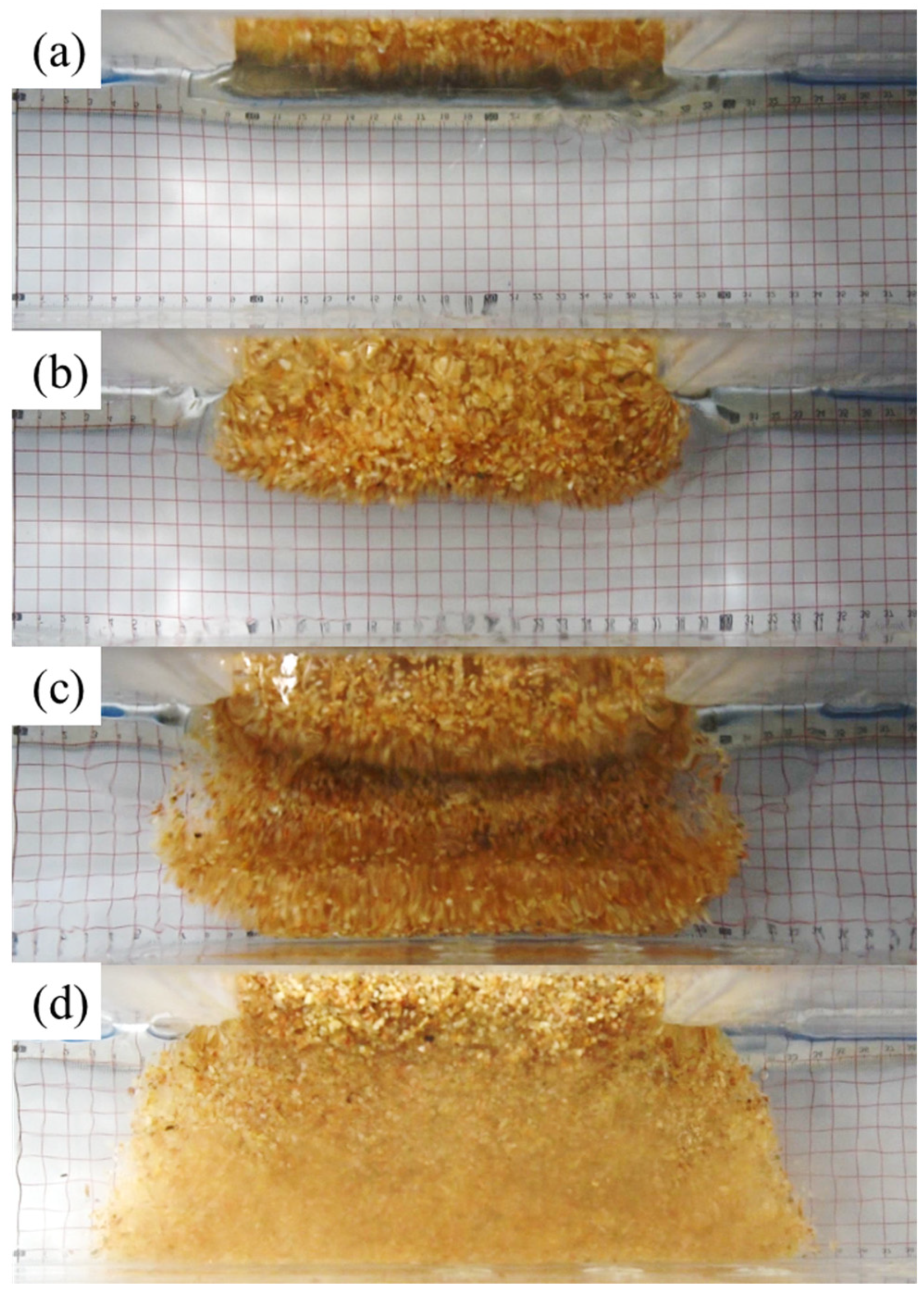
3. Results
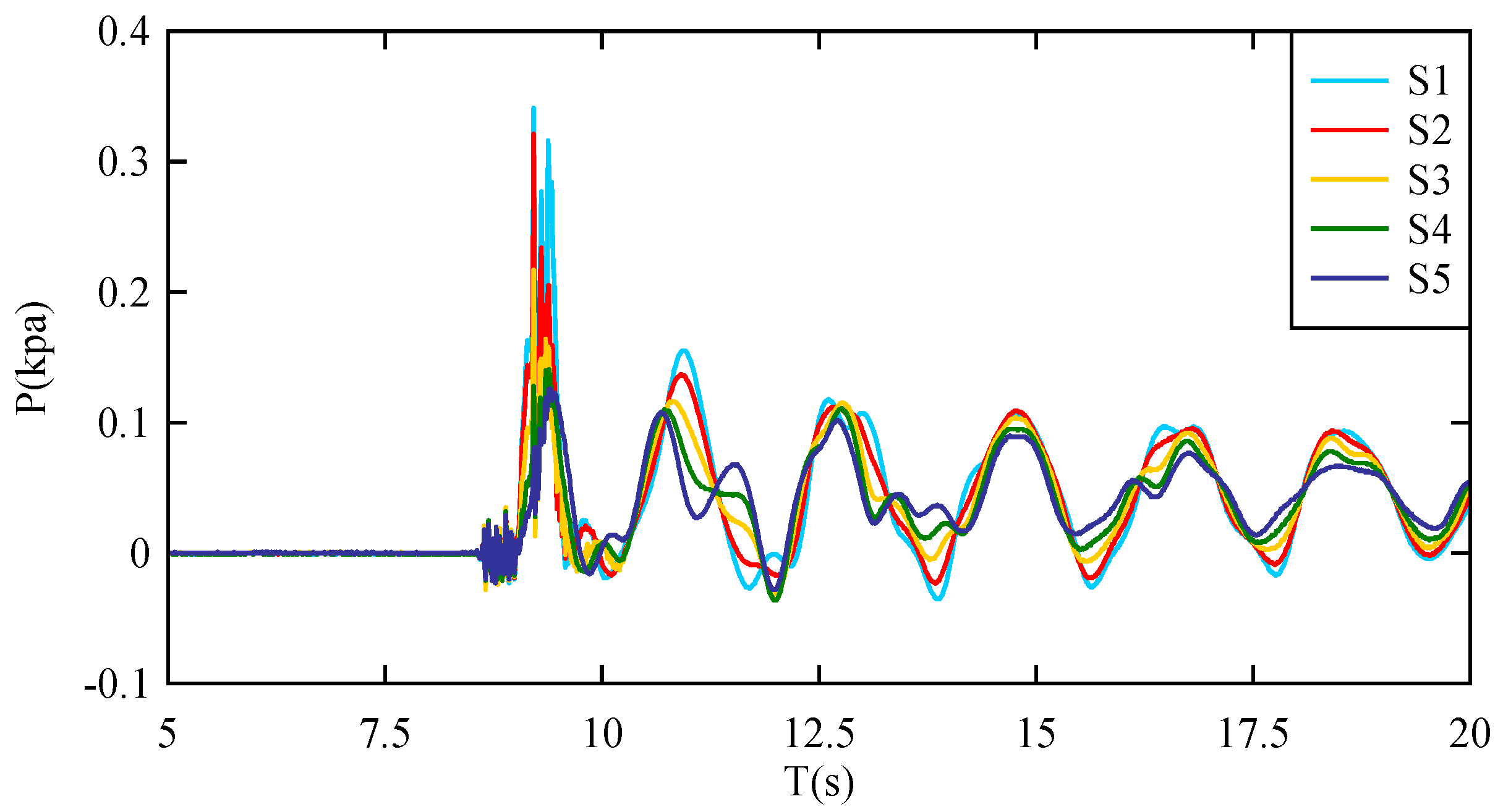
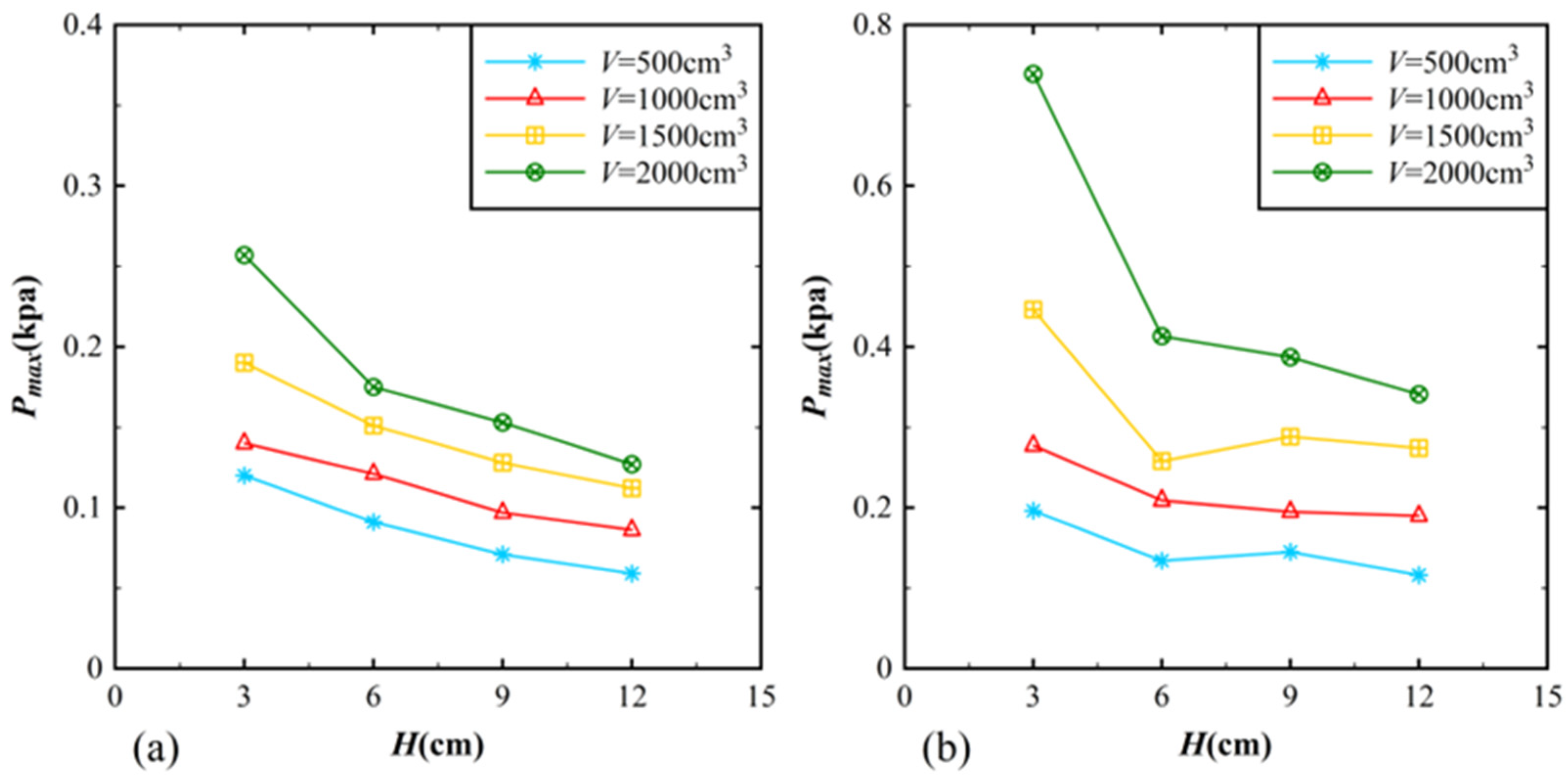
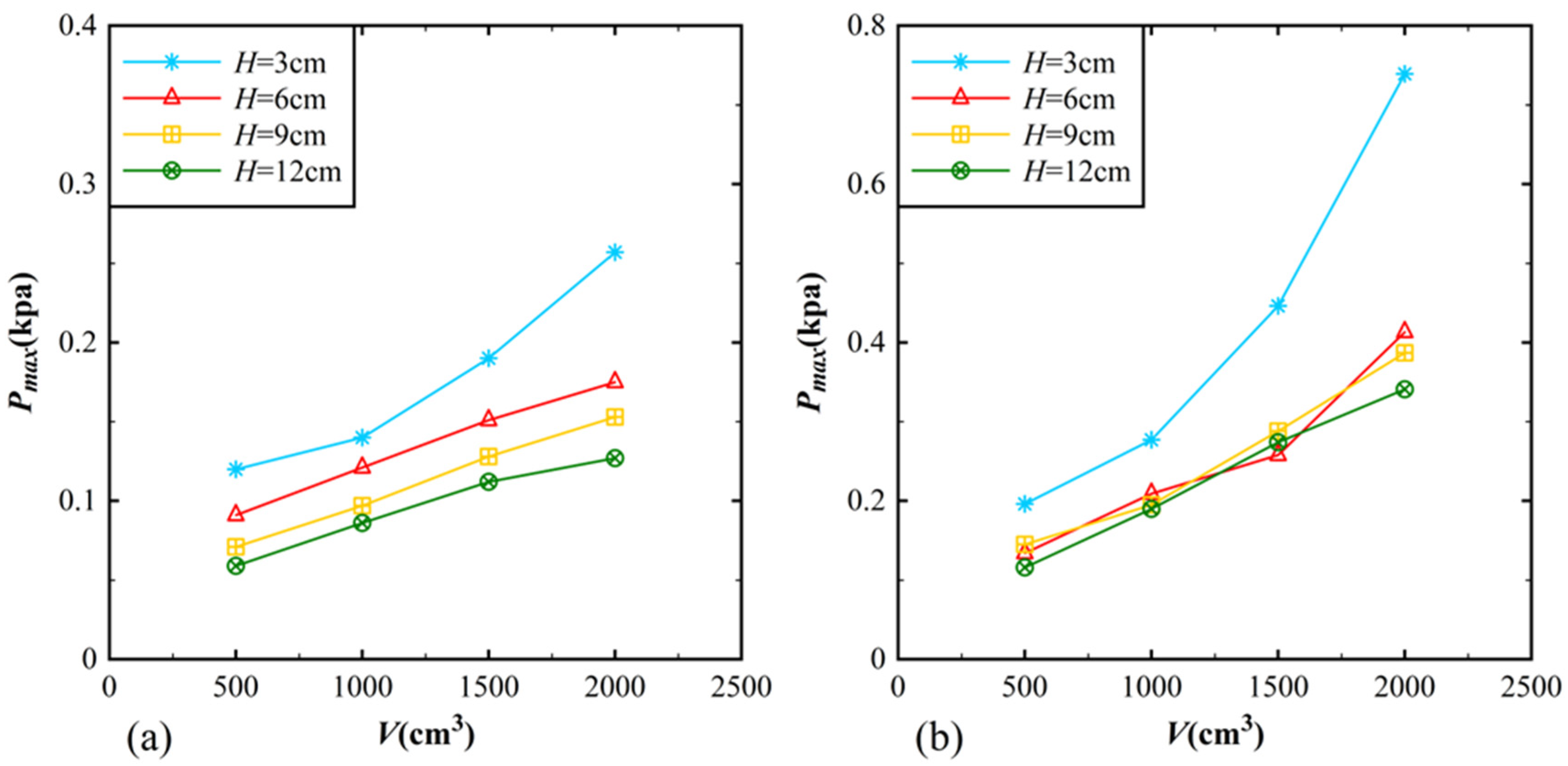
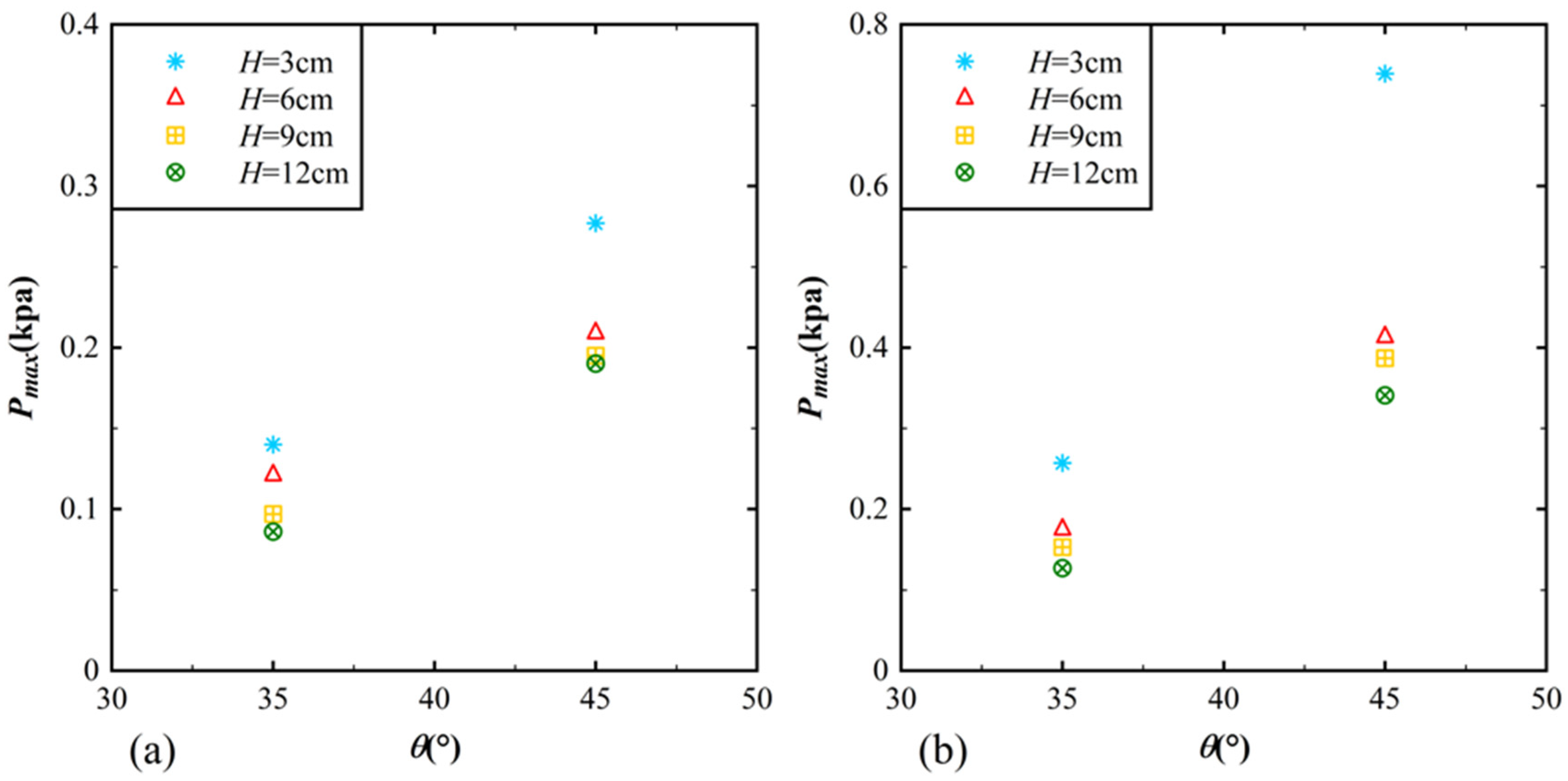
3.1. Impact Pressure Distribution on the Reservoir Bank
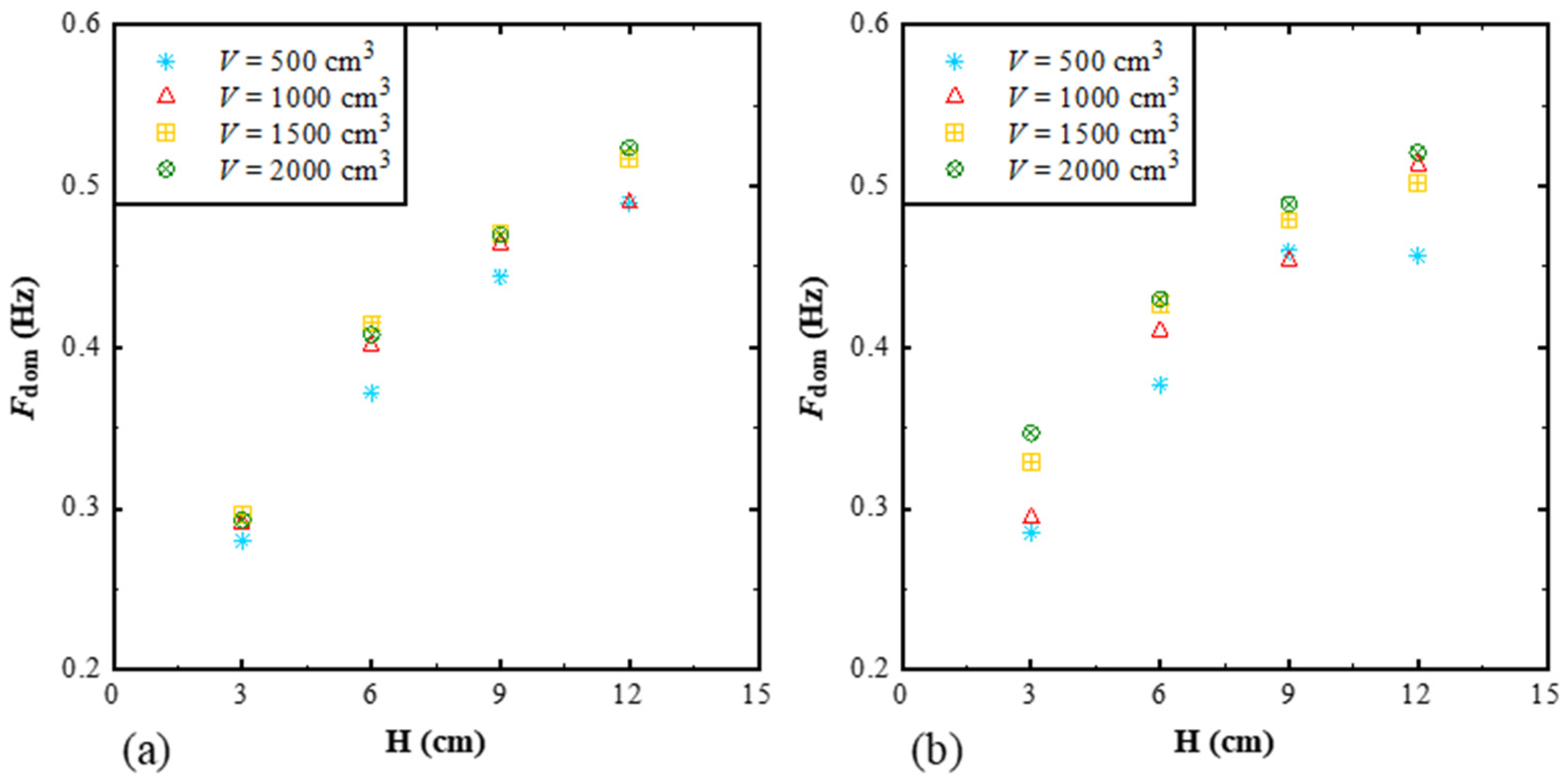
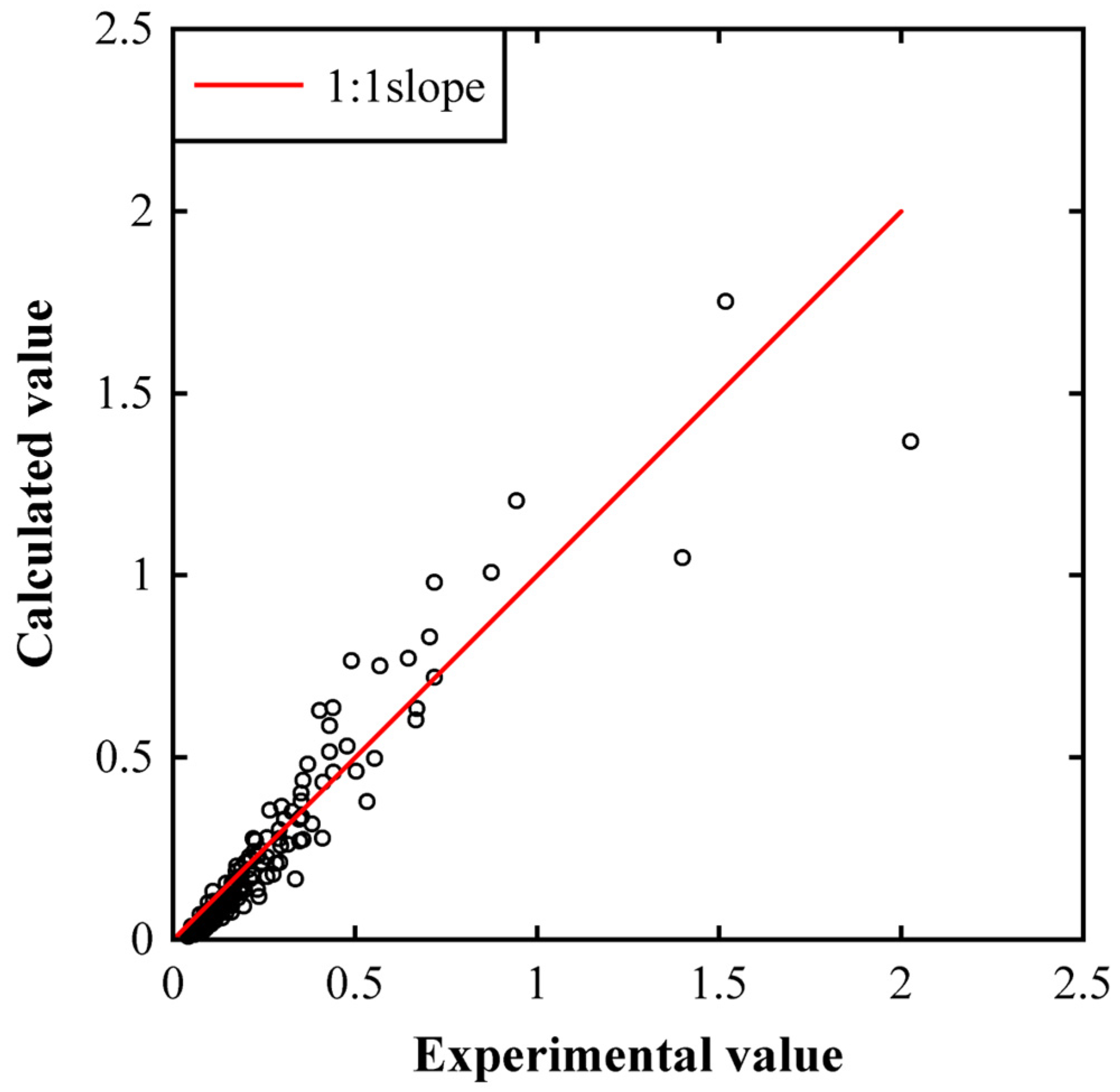
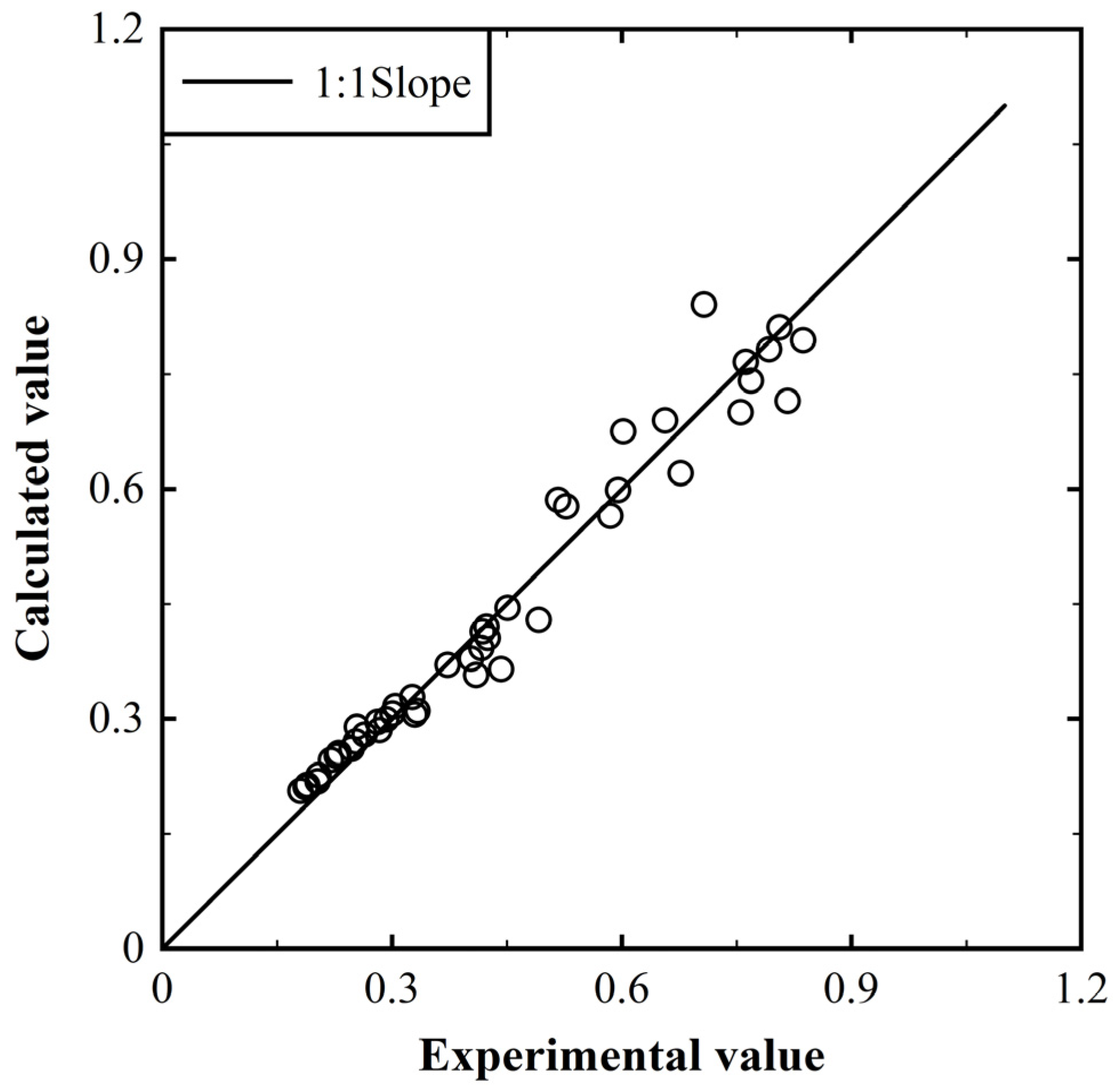
3.2. Empirical Equation for Predicting Impact Pressure on the Reservoir Bank
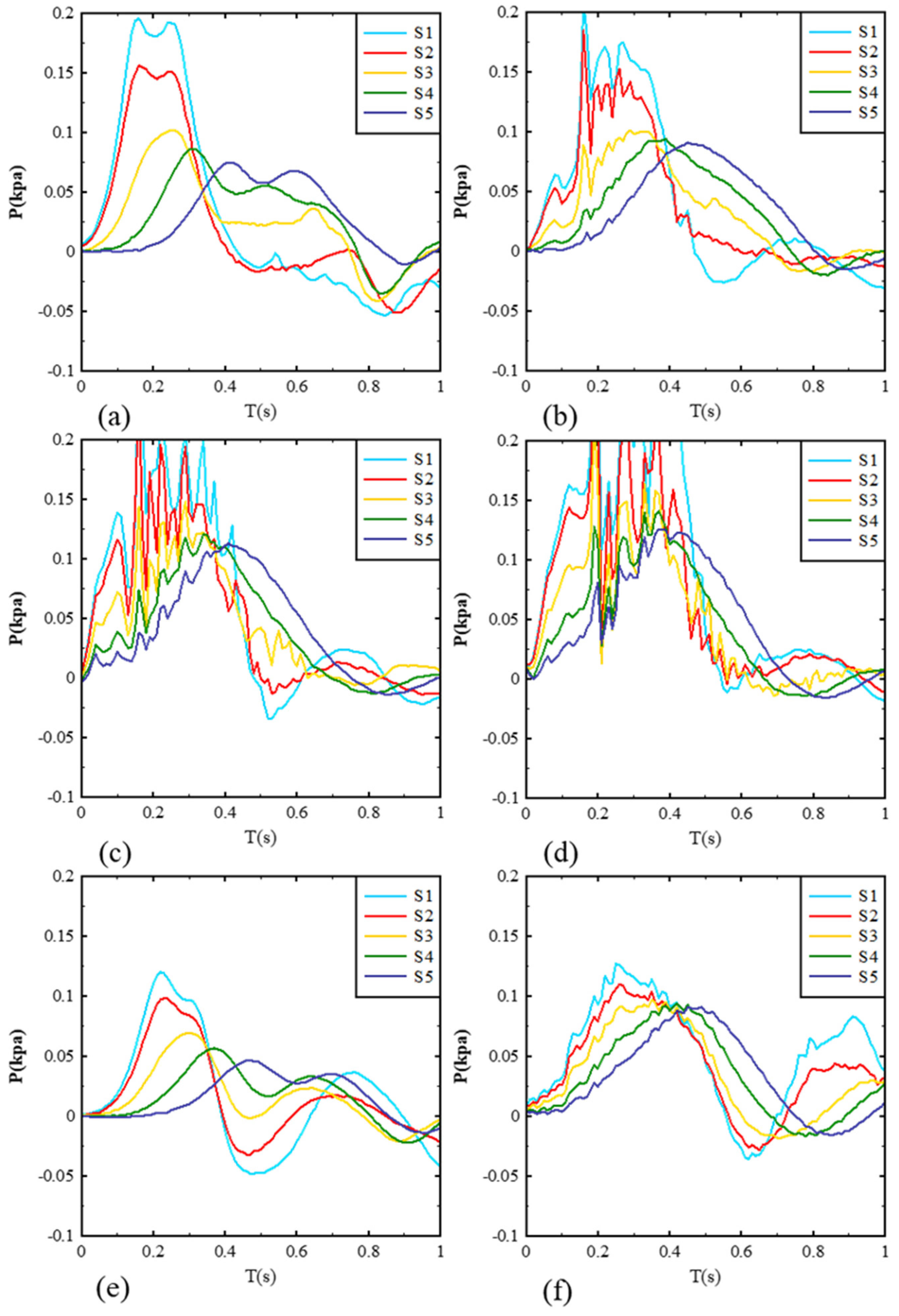
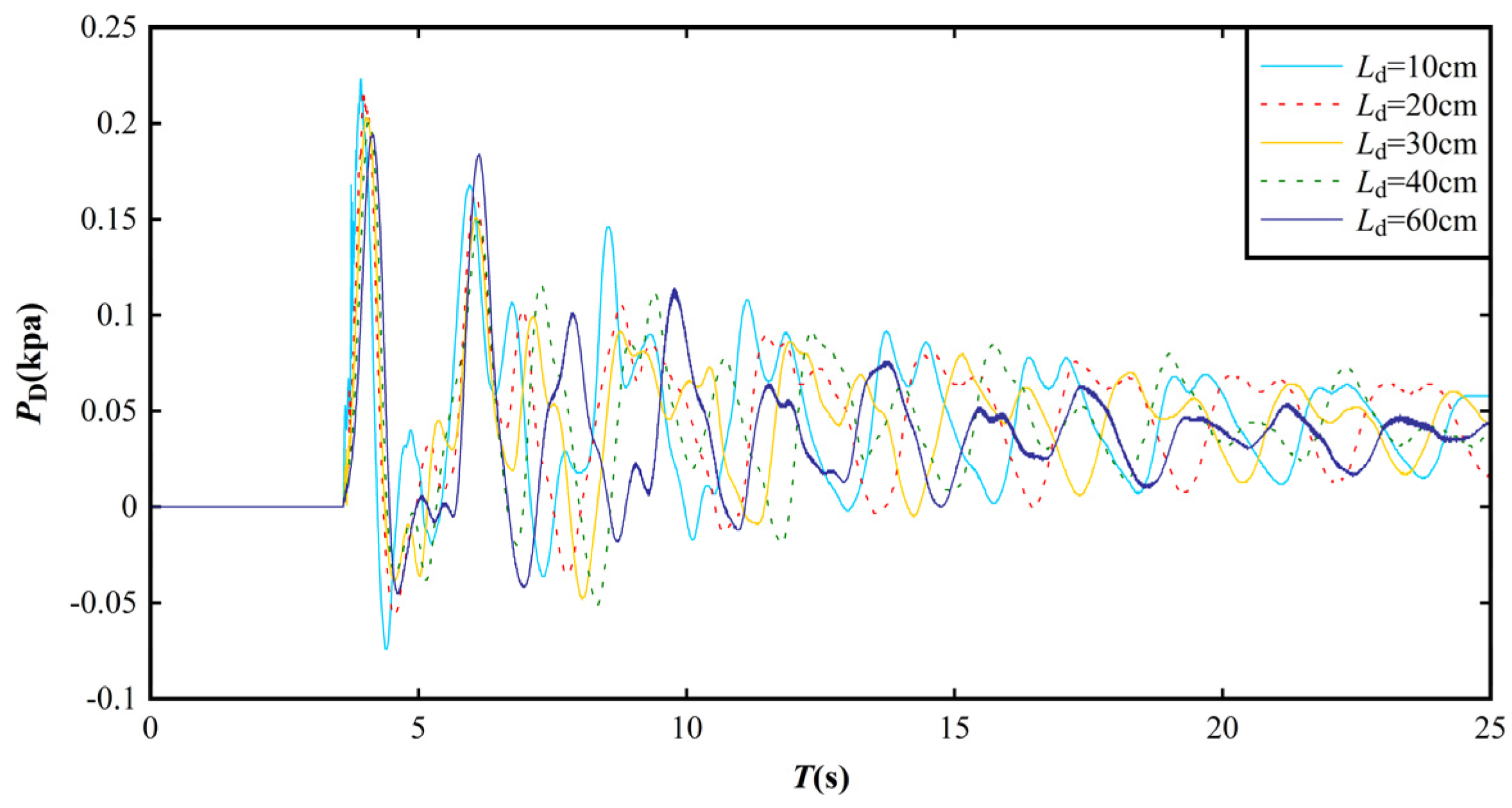
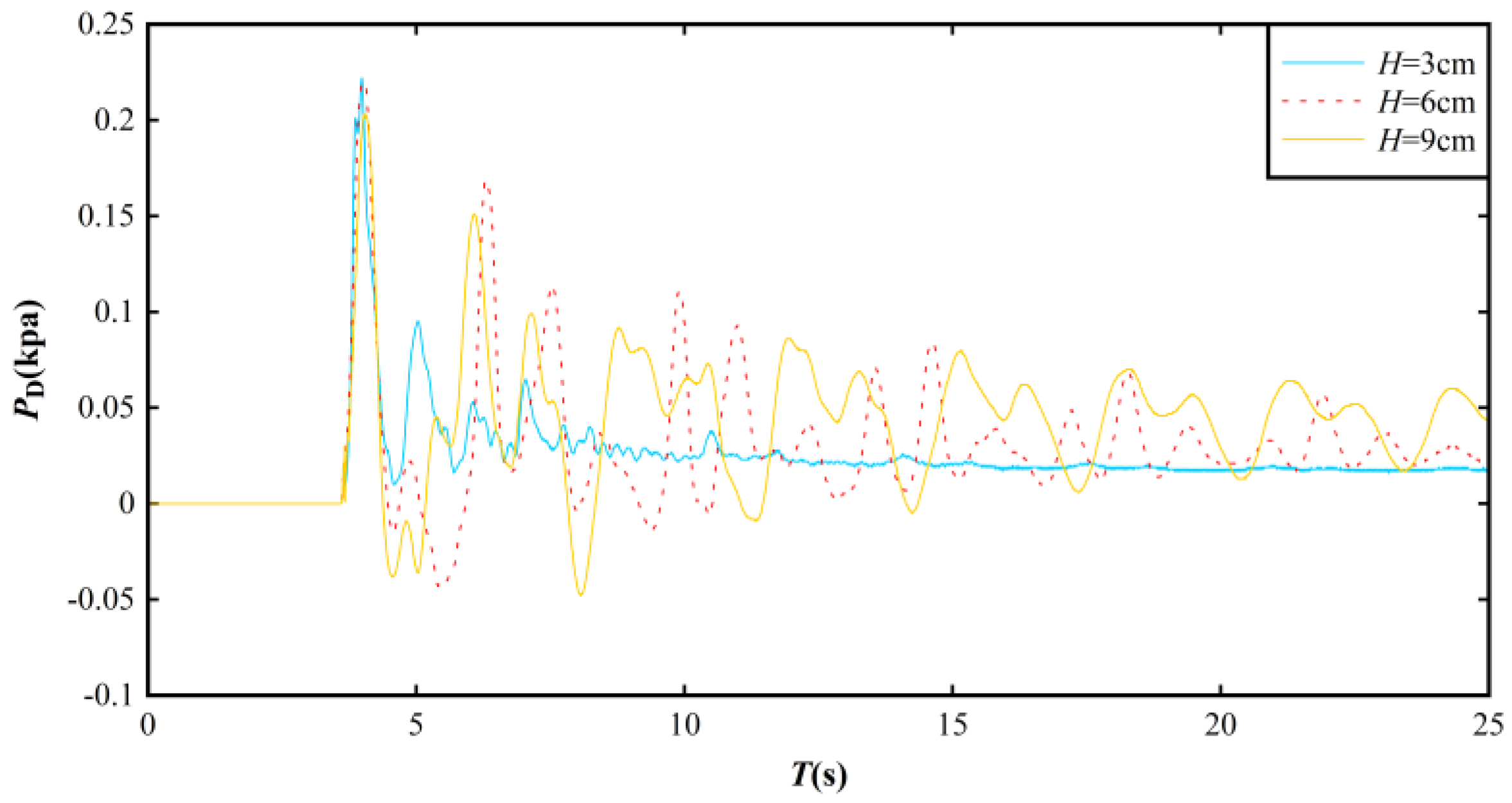
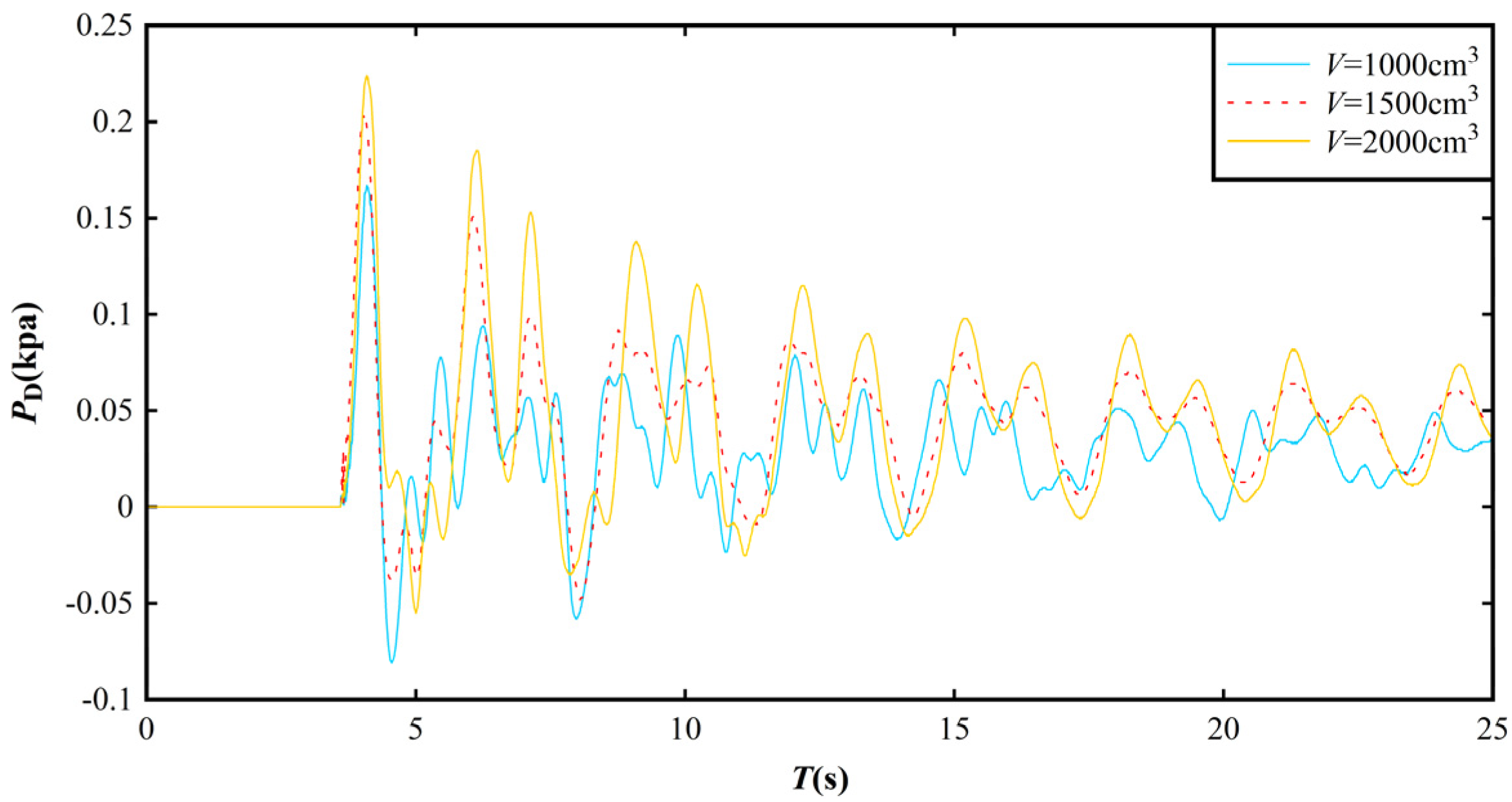
3.3. Impact Pressure Distribution on the Dam Surface
3.4. Empirical Equation for Predicting Impact Pressure on the Dam Surface
4. Discussion
4.1. Practical Applicability of Developed Equations
4.2. Implications for Dam Safety and Reservoir Management
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, R.; Fan, X. The landslide story. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froude, M.J.; Petley, D.N. Global fatal landslide occurrence from 2004 to 2016. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 18, 2161–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Tu, X.; Gao, W. The Impact of Reservoir Fluctuations on Reactivated Large Landslides: A Case Study. Geofluids 2019, 2019, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel, E.; Parra, N. Stability of a slope to the filling of a reservoir, understanding the behavior of a fractured rock mass. In Proceedings of the 8th South American Congress on Rock Mechanics, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 15–18 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Li, X.; Yan, X. The landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China and the effects of water storage and rain on their stability. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Huang, B.; Wang, W. Reservoir-induced landslides and risk control in Three Gorges Project on Yangtze River, China. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2016, 8, 577–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manenti, S.; Salis, N.; Todeschini, S. 3D WCSPH modelling of landslide-water dynamics during 1963 Vajont disaster. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykes, A.P.; Bromhead, E.N. Hazards from lakes and reservoirs: New interpretation of the Vaiont disaster. J. Mt. Sci. 2022, 19, 1717–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.C.; Deng, J.H.; Tham, L.G.; Law, K.T.; Lee, C.F. A large landslide in Zigui County, Three Gorges area. Can. Geotech. J. 2004, 41, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizzo, A.; De Girolamo, P.; Petaccia, A. Forecasting impulse waves generated by subaerial landslides. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2005, 110, C12025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, V.; Hager, W.H. Impulse product parameter in landslide generated impulse waves. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2010, 136, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, F.; Fritz, H.M. Physical modeling of tsunamis generated by three-dimensional deformable granular landslides. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2012, 117, C11015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindstrøm, E.K.; Pedersen, G.K.; Jensen, A.; Glimsdal, S. Experiments on slide generated waves in a 1:500 scale fjord model. Coast. Eng. 2014, 92, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Nik-Khah, A. Impulsive waves caused by subaerial landslides. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2008, 8, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweifel, A.; Hager, W.H.; Minor, H.E. Plane impulse waves in reservoirs. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2006, 132, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, V.; Spinneken, J. Improved landslide-tsunami prediction: Effects of block model parameters and slide model. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 1489–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Bellotti, G.; Risio, M.D. Wavenumber-frequency analysis of the landslide-generated tsunamis at a conical island. Coast. Eng. 2013, 81, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitti, G.; Ancey, C.; Postacchini, M.; Brocchini, M. Impulse waves generated by snow avalanches: Momentum and energy transfer to a water body. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2016, 121, 2399–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, V.; Hager, W.H.; Minor, H.E. Landslide Generated Impulse Waves in Reservoirs: Basics and Computation; ETH Zürich: Zürich, Switzerland, 2009; pp. 1–172. [Google Scholar]
- Fritz, H.M.; Hager, W.H.; Minor, H.E. Near field characteristics of landslide generated impulse waves. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2004, 130, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, F.M.; Hager, W.H.; Boes, R.M. Spatial impulse wave generation and propagation. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2019, 145, 04019011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Cui, P.; Chen, X.Q.; Zhu, X.H.; Zhou, G.G.D. Laboratory experiments of water pressure loads acting on a downstream dam caused by ice avalanches. Landslides 2015, 12, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffini, G.; Heller, V.; Briganti, R. Numerical modelling of landslide-tsunami propagation in a wide range of idealised water body geometries. Coast. Eng. 2019, 153, 103518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Yavari-Ramshe, S. Numerical simulation of wave generated by landslide incidents in dam reservoirs. Landslides 2011, 8, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisacik, D.; Troch, P.; Van Bogaert, P. Experimental study of pressure distributions due to the breaking wave impacts on a vertical wall with an overhanging horizontal cantilever slab. Ocean Eng. 2019, 177, 142–154. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, J.H.; Hussain, K.; Shao, S.D.; Huang, Y.F. Shallow sediment transport flow computation using time-varying sediment adaptation length. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2014, 29, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hofland, B.; Altomare, C.; Oosterlo, P.; Uijttewaal, W. Forces on a vertical wall on a dike crest due to overtopping flow. Coast. Eng. 2015, 95, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, G.; Allsop, W.; Bruce, T.; Pearson, J. Breaking wave loads at vertical seawalls and breakwaters. Coast. Eng. 2010, 57, 424–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindar, R.; Sriram, V.; Schimmels, S.; Stagonas, D. Characterization of breaking wave impact on vertical wall with recurve. ISH J. Hydraul. Eng. 2019, 25, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugni, C.; Brocchini, M.; Faltinsen, O.M. Wave impact loads: Wave impact loads: The role of the flip-through. Phys. Fluids 2006, 18, 122101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oumeraci, H.; Klammer, P.; Partenscky, H.W. Classification of breaking wave loads on vertical structures. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1993, 119, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkgöz, M.S. Breaking wave impact on vertical and sloping coastal structures. Ocean Eng. 1995, 22, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, M.; Arami, A.; Yui, T. Wave impact pressure on vertical walls under breaking waves of various types. Coast. Eng. 1994, 22, 79–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| d50 (mm) | θ = 35° | θ = 45° | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H (cm) | V (cm3) | H (cm) | V (cm3) | |
| 2.5 | 3 | 500 | 3 | 500 |
| 3 | 1000 | 3 | 1000 | |
| 3 | 1500 | 3 | 1500 | |
| 3 | 2000 | 3 | 2000 | |
| 6 | 500 | 6 | 500 | |
| 6 | 1000 | 6 | 1000 | |
| 6 | 1500 | 6 | 1500 | |
| 6 | 2000 | 6 | 2000 | |
| 9 | 500 | 9 | 500 | |
| 9 | 1000 | 9 | 1000 | |
| 9 | 1500 | 9 | 1500 | |
| 9 | 2000 | 9 | 2000 | |
| 12 | 500 | 12 | 500 | |
| 12 | 1000 | 12 | 1000 | |
| 12 | 1500 | 12 | 1500 | |
| 12 | 2000 | 12 | 2000 | |
| d50 (mm) | θ (°) | H = 3 cm | H = 6 cm | H = 9 cm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V (cm3) | Ld (cm) | V (cm3) | Ld (cm) | V (cm3) | Ld (cm) | ||
| 2.5 | 45 | 1000 | 10 | 1000 | 10 | 1000 | 10 |
| 1000 | 20 | 1000 | 20 | 1000 | 20 | ||
| 1000 | 30 | 1000 | 30 | 1000 | 30 | ||
| 1000 | 40 | 1000 | 40 | 1000 | 40 | ||
| 1000 | 60 | 1000 | 60 | 1000 | 60 | ||
| 1500 | 10 | 1500 | 10 | 1500 | 10 | ||
| 1500 | 20 | 1500 | 20 | 1500 | 20 | ||
| 1500 | 30 | 1500 | 30 | 1500 | 30 | ||
| 1500 | 40 | 1500 | 40 | 1500 | 40 | ||
| 1500 | 60 | 1500 | 60 | 1500 | 60 | ||
| 2000 | 10 | 2000 | 10 | 2000 | 10 | ||
| 2000 | 20 | 2000 | 20 | 2000 | 20 | ||
| 2000 | 30 | 2000 | 30 | 2000 | 30 | ||
| 2000 | 40 | 2000 | 40 | 2000 | 40 | ||
| 2000 | 60 | 2000 | 60 | 2000 | 60 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Zhao, W.; Niu, Z.; Yang, H. Laboratory Experiments of Surge Pressure Loads Acting on Downstream Dams and Reservoir Banks Caused by Landslides in Narrow, Elongated Reservoirs. Water 2025, 17, 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081133
Wang H, Zhao W, Niu Z, Yang H. Laboratory Experiments of Surge Pressure Loads Acting on Downstream Dams and Reservoir Banks Caused by Landslides in Narrow, Elongated Reservoirs. Water. 2025; 17(8):1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081133
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hantao, Weiyang Zhao, Zhipan Niu, and Hang Yang. 2025. "Laboratory Experiments of Surge Pressure Loads Acting on Downstream Dams and Reservoir Banks Caused by Landslides in Narrow, Elongated Reservoirs" Water 17, no. 8: 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081133
APA StyleWang, H., Zhao, W., Niu, Z., & Yang, H. (2025). Laboratory Experiments of Surge Pressure Loads Acting on Downstream Dams and Reservoir Banks Caused by Landslides in Narrow, Elongated Reservoirs. Water, 17(8), 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081133






