Cumulative Risk of Heavy Metals in Long-Term Operational Rain Garden
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
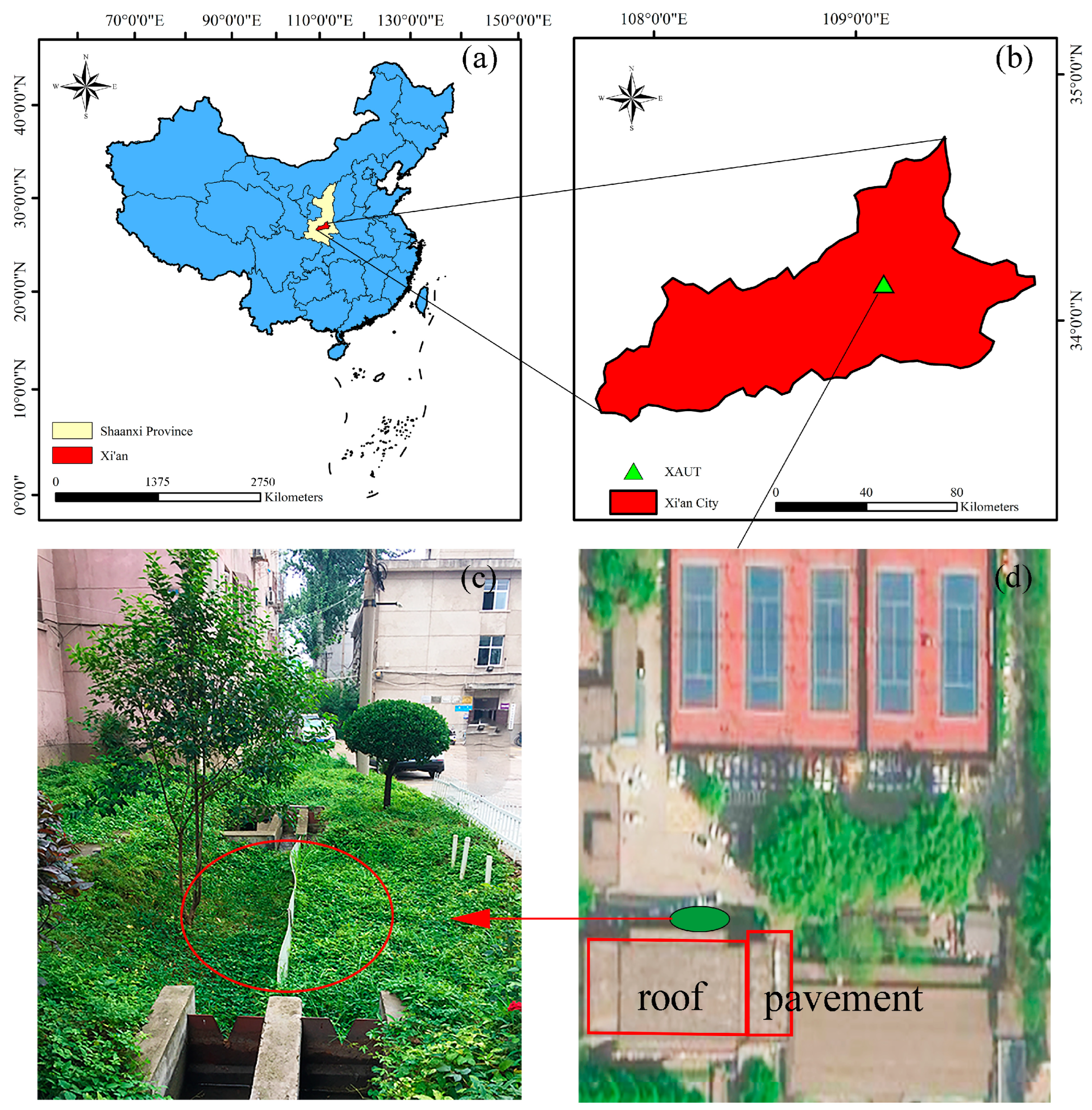
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Sample Collection
2.3. Soil Sample Testing Method
2.4. Trend Analysis
2.5. Evaluation Method of Soil HM Pollution
2.5.1. Enrichment Factor
2.5.2. Geo-Accumulation Index
2.5.3. Potential Ecological Risk Index (ER)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatial Variation of Soil HMs
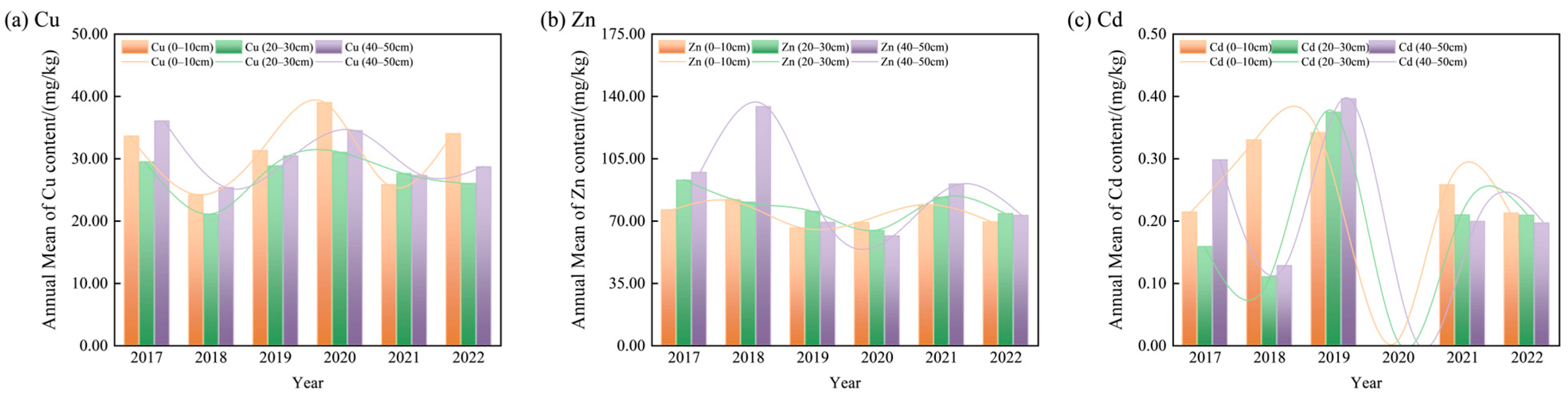
3.2. Temporal Variation of Soil HMs
3.3. Evaluation of HM Cumulative Effect
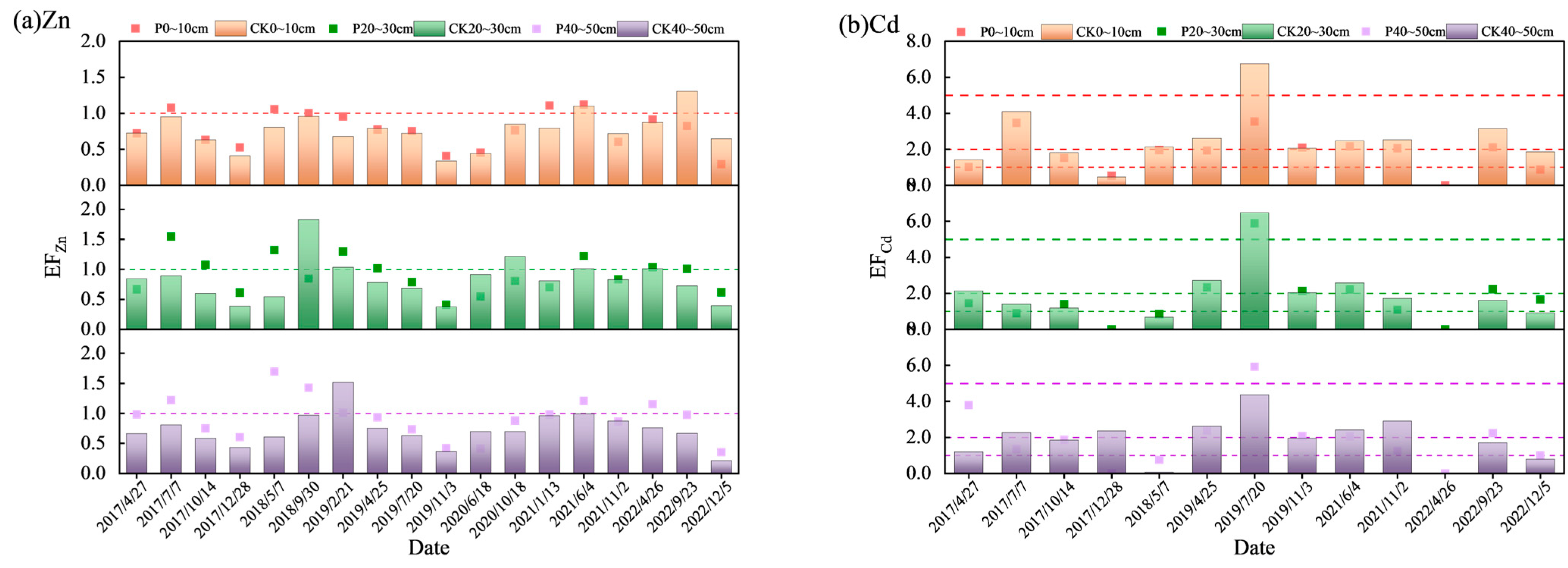
3.3.1. Evaluation Result of Enrichment Factor Method
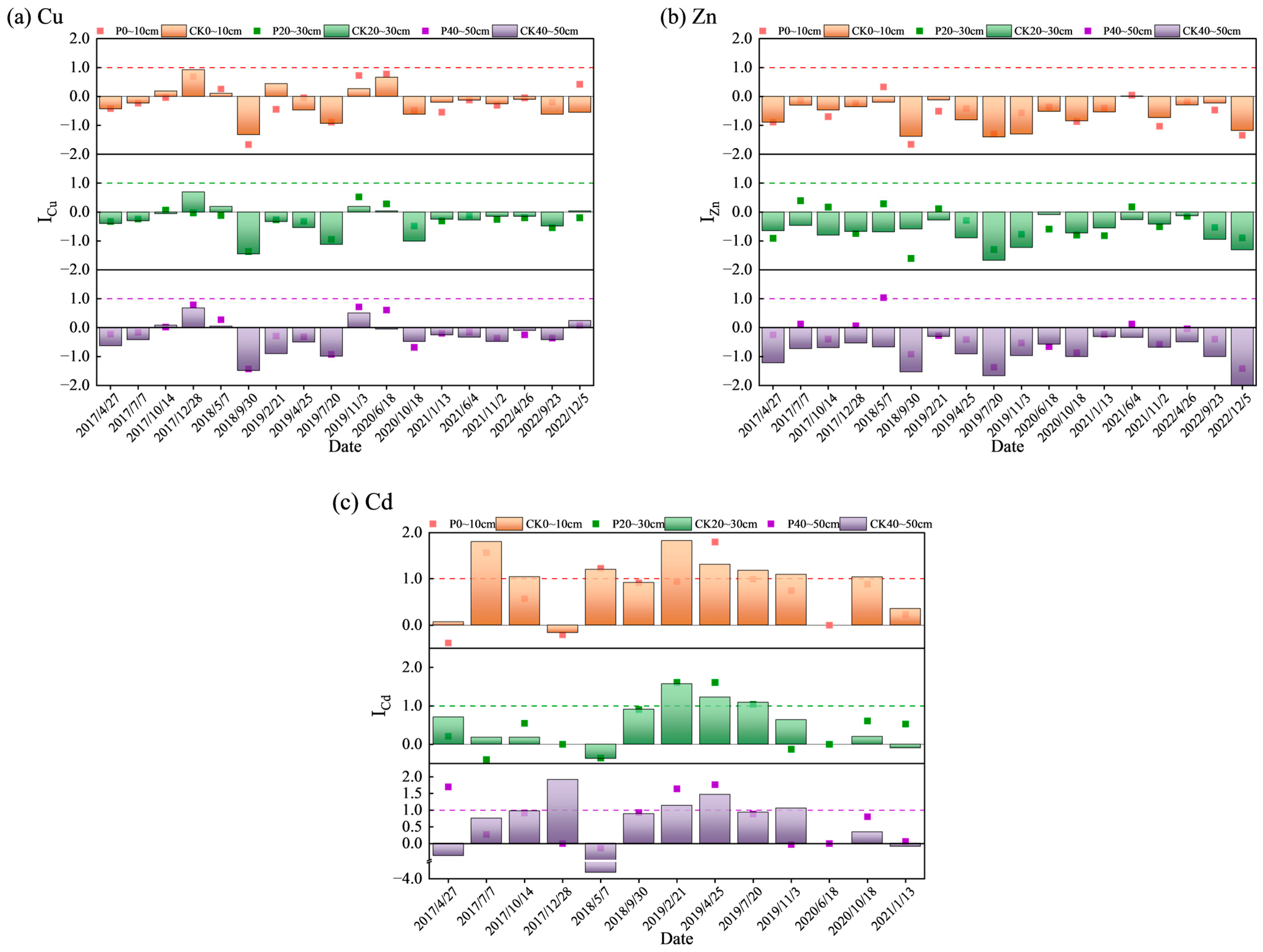
3.3.2. Evaluation Result of Geo-Accumulation Index
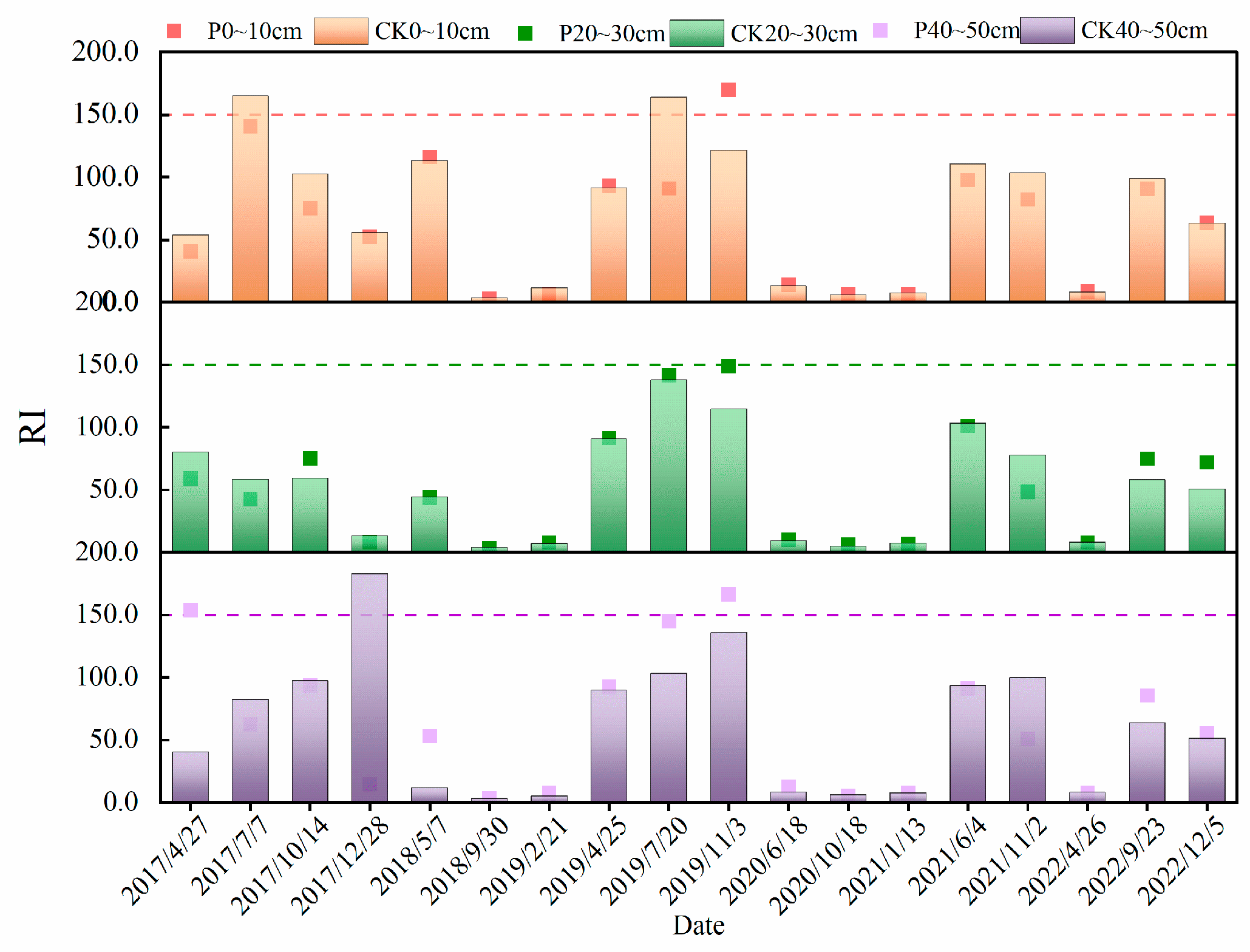
3.4. Ecological Risk Assessment of HM Pollutants
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fletcher, T.D.; Shuster, W.; Hunt, W.F.; Ashley, R.; Butler, D.; Arthur, S.; Trowsdale, S.; Barraud, S.; Semadeni-Davies, A.; Bertrand-Krajewski, J.L.; et al. SUDS, LID, BMPs, WSUD and more—The evolution and application of terminology surrounding urban drainage. Urban Water J. 2015, 12, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Luo, W.; Jia, Z.; Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, M. Effect of rain gardens on storm runoff reduction. Adv. Water Sci. 2015, 26, 787–794. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Wu, S.; Tang, S.; Luo, W.; Xu, Q.; Shao, Z. Influences of focused recharge from rain gardens on groundwater level and water quality. Adv. Water Sci. 2018, 29, 221–229. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Luo, W.; Jia, Z.; Tang, S.; Xu, Q.; Yin, X. Influence of rainwater garden infiltration on water content in unsaturated soil and groundwater. J. Yangzhou Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2020, 23, 63–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lefevre, G.H.; Paus, K.H.; Natarajan, P.; Gulliver, J.S.; Hozalski, R.M. Review of Dissolved Pollutants in Urban Storm Water and Their Removal and Fate in Bioretention Cells. J. Environ. Eng. 2015, 141, 04014050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Davis, A.P. Urban Particle Capture in Bioretention Media. I: Laboratory and Field Studies. J. Environ. Eng. 2008, 134, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, T.; Weiss, L.G.; Gulliver, J.S. Contamination of Soil and Groundwater Due to Stormwater Infiltration Practices; University of Minnesota Stormwater Assessment Project; University of Minnesota: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Winiarski, T.; Bedell, J.P.; Delolme, C.; Perrodin, Y. The impact of stormwater on a soil profile in an infiltration basin. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedoldi, D.; Chebbo, G.; Pierlot, D.; Kovacs, Y.; Gromaire, M.C. Impact of runoff infiltration on contaminant accumulation and transport in the soil/filter media of Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems: A literature review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 904–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meland, S. Ecotoxicological Effects of Highway and Tunnel Wash Water Runoff; Norwegian University of Life Sciences: Ås, Norway, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sultan, M.B.; Choudhury, T.R.; Alam, M.N.; Doza, M.B.; Rahmana, M.M. Soil, dust, and leaf-based novel multi-sample approach for urban heavy metal contamination appraisals in a megacity, Dhaka, Bangladesh. J. Environ. Adv. 2022, 7, 100154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Liu, Y.; Feng, X.; Mao, P.; Wang, M. Pollution effect assessment of industrial activities on potentially toxic metal distribution in windowsill dust and surface soil in central China. J. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 144023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ameri, M.; Hatt, B.; Coustumer, L.S.; Fletcher, T.; Payne, E.; Deletic, A. Accumulation of heavy metals in stormwater bioretention media: A field study of temporal and spatial variation. J. Hydrol. 2018, 567, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Shokouhian, M.; Ni, S. Loading estimates of lead, copper, cadmium, and zinc in urban runoff from specific sources. Chemosphere 2001, 44, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatt, B.E.; Fletcher, T.D.; Deletic, A. Hydraulic and pollutant removal performance of fine media stormwater filtration systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2535–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthanna, T.M.; Viklander, M.; Blecken, G.; Thorolfsson, S.T. Snowmelt pollutant removal in bioretention areas. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4061–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nightingale, H.I. Lead, zinc, and copper in soils of urban storm-runoff retention basins. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1975, 67, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, R.A. Potential for Chemical Transport Beneath a Stormwater Runoff Recharge (Retention) Basin for an Industrial Catchment in Fresno, California; Water-resources Investigations Report 93–4140; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1995.
- Jones, P.S.; Davis, A.P. Spatial accumulation and strength of affiliation of heavy metals in bioretention media. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 139, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluge, B.; Markert, A.; Facklam, M.; Sommer, H.; Kaiser, M.; Pallasch, M.; Wessolek, G. Metal accumulation and hydraulic performance of bioretention systems after long-term operation. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Wang, S.; Li, J. Accumulation characteristics and risk of heavy metals and microbial community composition in bioretention systems: A case study of a university campus. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 193, 106996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 491-2019; Soil and Sediment—Determination of Copper, Zinc, Lead, Nickel and Chromium—Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. China Environmental Publishing Group: Beijing, China, 2019.
- GB/T 17141-1997; Soil Quality—Determination of Lead, Cadmium—Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1997.
- Wei, F. Modern Analytical Methods of Soil Elements; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1992; pp. 74–88. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, S.; Bai, X.; Luo, G.; Wu, L.; Cao, Y.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Z.; et al. Variation trend of global soil moisture and its cause analysis. Ecol. Ind. 2020, 110, 105939–105949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Li, S.; Yang, W.; Liu, L.; Shi, Y.; Lai, Y.; Yu, P.; Yang, Z.; Luo, K.; Zhou, T.; et al. Spatio-temporal changes in global root zone soil moisture from 1981 to 2017. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Chen, J.; Huang, R.; Yang, Y.; You, H.; Han, X. Spatial and Temporal Variation in Alpine Vegetation Phenology and Its Response to Climatic and Topographic Factors on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Yang, J.; Liang, Y. Research on assessment methods of heavy metal pollution in soil—Taking Guangzhou as an example. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 1329–1337. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Yin, A.; Huang, Z.; Yao, D.; Dai, W.; Wang, N.; Wang, H. Assessment of heavy metal pollution of farmland soil around an abandoned silicon plant in Yunnan. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2022, 41, 785–793. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Tan, F.; Dong, X.; Zhang, N.; Bao, L. Heavy Metal Characteristics and Comprehensive Quality Index Evaluation of Soil-Crop System in 11 Cities of Yunnan Province, China. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2022, 10, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, I.; Whitworth, K.W.; Christensen, B.; Afshar, M.; Han, H.A.; Rammah, A.; Oluwadairo, T.; Symanski, E. Heavy metal pollution of soils and risk assessment in Houston, Texas following Hurricane Harvey. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 296, 118717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, C.; Zou, L. Characteristics of heavy metals and Pb isotopic signatures in sediment cores collected from typical urban shallow lakes in Nanjing, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dai, L.; Li, L.; Liang, T. Multivariable cokriging prediction and source analysis of potentially toxic elements (Cr, Cu, Cd, Pb, and Zn) in surface sediments from Dongting Lake, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fu, R.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, M.; Xiao, K.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, C.; Xiong, Y. Heavy metal contamination in surface sediments: A comprehensive, large–scale evaluation for the Bohai Sea. China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhou, H.; Qi, Z. Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution with Principal Component Analysis and Geo-accumulation Index. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 1946–1952. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, A.B.; Kabir, S.; Reza, A.H.M.S.; Zaman, M.N.; Ahsan, A.; Rashid, M. Enrichment factor and geo-accumulation index of trace metals in sediments of the ship breaking area of Sitakund Upazilla (Bhatiary–Kumira), Chittagong, Bangladesh. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 125, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Guo, L.; Deng, Z.; Wang, D.; Liu, L. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and water quality characteristics of the reservoir control reaches in the middle Han River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Wang, L.; Yang, R.; Hou, W.; Zhang, S.; Guo, X.; Zhao, W. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil of a construction waste landfill site. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 70, 101700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, J.; Bao, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, M.; Sun, X.; Jin, F. Characteristics and Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Soil of Baotou Iron Mine Area, Inner Mongolia. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 32, 3099–3105. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Onkal-Engin, G.; Demir, I.; Hiz, H. Assessment of urban air quality in Istanbul using fuzzy synthetic evaluation. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3809–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Lu, W.; Yang, W.; Li, J. Application of fuzzy mathematics and pollution index method in soil heavy metal pollution. J. Soil 2008, 2, 212–215. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Chen, C.; Han, Y.; Cheng, C.; Luo, Y.; Xu, W.; Chen, Q.; Ren, S. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in sewage irrigated soil in Dunhua Irrigation District of Taiyuan City based on fuzzy mathematics. Huanjing Huaxue 2010, 29, 1152–1157. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chabukdhara, M.; Nema, A.K. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in Hindon River sediments: A chemometric and geochemical approach. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, R.A. Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A seal approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Li, Y. Influences of stormwater concentration infiltration on the heavy metal contents of soil in rain gardens. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.P.; Shokouhian, M.; Sharma, H.; Minami, C.; Winogradoff, D. Water quality improvement through bioretention: Lead, copper, and zinc removal. Water Environ Res. 2003, 75, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X. Study on Pollution Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Atmosphere, Soil and Precipitation in Xi’an City. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi’an, China, 2013. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M. Study on the Characteristics of Heavy Metal and PAHs of Road Runoff of Xi’an City. Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2016. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. Contamination Characteristics of Surface Runoff in Densely Populated Areas in Downstream Yangtze River, China. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 3304–3315. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Chen, X.; Wei, X.; Zhao, Z. Characteristics of Heavy Metal Pollution in Road Runoff in Urumqi City. Huanjing Gongcheng 2014, 32, 105–110. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Shan, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, K.; Teng, H.; Jiang, Q. Effects of winter warming on the migration characteristics and pollution risk assessment of Zn, Cu, and Pb in the snow-soil continuum in seasonal snow cover area. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 31, 103159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q. Experimental Study on Adsorption and Migration of Heavy Metals Cu, Cd, Zn, Pb in Soil. Master’s Thesis, Qingdao University, Qingdao, China, 2008. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, Y. Research progress in heavy metal pollution and phytoremediation in soil. J. Agric. 2023, 13, 20–23+32. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, M.; Ma, Y. Mitigation of heavy metal stress in the soil through optimized interaction between plants and microbes. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 11872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wu, M.; Fang, F.; Wu, J.; Ma, K. Characteristics and influencing factors of heavy metal pollution in surface dust from driving schools of Wuhu, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 12, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wi, E.; Park, E.; Shin, H.; Hong, J.; Jeong, S.; Kwon, J.T.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y. Overall distribution of tire-wear particles, nano carbon black, and heavy metals in size-fractionated road dust collected from steel industrial complexes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 884, 163878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesilonis, I.D.; Pouyat, R.V.; Neerchal, N.K. Spatial distribution of metals in soils in Baltimore, Maryland: Role of native parent material, proximity to major roads, housing age and screening guidelines. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Qiu, L.; Wei, Z.; Yang, C.; He, B. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in the bioretention systems of sponge cities. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 4127–4135. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Chao, X.; Hao, S.; Song, K. Study on accumulation and pollution risk of heavy metals in rain garden soil. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2021, 41, 3359–3365. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Zheng, P.; Li, X.; Wang, X. Four season pollution characteristics of heavy metals in runoff rainwater from different underlying road surfaces in Xi’an City. J. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 23, 1170–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezuglova, O.S.; Gorbov, S.N.; Tischenko, S.A.; Aleksikova, A.S.; Tagiverdiev, S.S.; Sherstnev, A.K.; Dubinina, M.N. Accumulation and migration of heavy metals in soils of the Rostov region, south of Russia. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Dong, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Chen, G.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhou, T. Heavy metal pollution in urban river sediment of different urban functional areas and its influence on microbial community structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Yan, P.; Yu, H.; Yang, S.; Xu, J.; Liu, X. Spatiotemporal modeling of soil heavy metals and early warnings from scenarios-based prediction. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Liao, Q.; Hua, M.; Wu, X.; Bi, K.; Yan, C.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X. Survey of heavy metal pollution and assessment of agricultural soil in Yangzhong district, Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 2148–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, Q.; Wang, W.; Yan, J.; Liu, Y.; Kuang, S.; Lu, J. Determining priority control factors for heavy metal management in urban road dust based on source-oriented probabilistic ecological-health risk assessment: A study in Xi’an during peak pollution season. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 369, 122105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Tang, H.; Sima, W.; Wang, H.; Zou, D.; Qiu, B.; Qu, J.; Liang, R.; Dong, J.; Liao, Y.; et al. Heavy metal pollution level and potential ecological risk assessment of sludge landfill. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2022, 41, e13795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xu, Z.; Yan, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, D. Characteristics of Heavy Metal Pollution and Ecological Risk Evaluation of Indoor Dust from Urban and Rural Areas in Taiyuan City During the Heating Season. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 2143–2152. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhao, W.; Huang, T.; Cheng, S.; Yu, L.; Yin, Y. Seasonal Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in PM10 Around Electroplating Plants. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 18–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X. Characteristics of Heavy Metal Removal and Migration Accumulation in Residual Sludge Matrix Bioretention Facility. Master’s Thesis, Hebei University of Engineering, Handan, China, 2022. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metal accumulation in typical bioretention facilities. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 3608–3622. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Boivin, P.; Saadé, M.; Pfeiffer, H.R.; Hammecker, C.; Degoumois, Y. Depuration of highway runoff water into grass-covered embankments. Environ. Technol. 2008, 29, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legret, M.; Demare, D.; Balades, J.D.; Madiec, M. Study of heavy metal pollution in a storm water infiltration area. In Proceedings of the Novatech ’92, International Conference on Innovative Technologies in the Domain of Urban Stormwater Drainage, Lyon, France, 3–5 November 1992; pp. 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Lind, B.; Karro, E. Stormwater infiltration and accumulation of heavy metals in roadside green areas in Goteborg, Sweden. Ecol. Eng. 1995, 5, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Class | Enrichment status | Class | Sediment quality | ||
| I | ≤1 | No enrichment | II | ≤0 | No enrichment |
| II | 1~2 | Slight enrichment | III | 0~1 | Slight enrichment |
| III | 2~5 | Moderate enrichment | IV | 1~2 | Moderate enrichment |
| IV | 5~20 | Severe enrichment | V | 2~3 | Moderately strong enrichment |
| V | 20~40 | Very severe enrichment | VI | 3~4 | Strong enrichment |
| VI | >40 | Extremely severe enrichment | VI | 4~5 | Quite strong enrichment |
| VII | >5 | Extremely strong enrichment | |||
| Potential ecological risk for monomial factor | Potential ecological risk for multinomial factor | ||||
| <40 | Low ecological risk | <150 | Low ecological risk | ||
| 40~80 | Moderate ecological risk | 150~300 | Moderate ecological risk | ||
| 80~160 | Considerable ecological risk | 300~600 | Considerable ecological risk | ||
| 160~320 | High ecological risk | ≥600 | Very high ecological risk | ||
| ≥320 | Very high ecological risk | ||||
| HM Elements | Soil Layer/cm | Mean mg/kg | FEB/% | FER/% | CV/% | Sk | bk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | 0–10 cm | 31.42 | 88.89 | 61.11 | 39.46 | 0.65 | −0.10 |
| 20–30 cm | 27.67 | 88.89 | 61.11 | 26.94 | 0.45 | 1.90 | |
| 40–50 cm | 30.74 | 83.33 | 77.78 | 37.99 | 0.88 | 0.45 | |
| Zn | 0–10 cm | 32.94 | 61.11 | 61.11 | 75.30 | 0.48 | 0.39 |
| 20–30 cm | 34.19 | 50.00 | 55.56 | 89.49 | 0.54 | −0.92 | |
| 40–50 cm | 39.00 | 72.22 | 94.44 | 99.55 | 2.10 | 6.61 | |
| Cd | 0–10 cm | 0.26 | 77.78 | 15.38 | 43.85 | 0.54 | 0.28 |
| 20–30 cm | 0.22 | 72.22 | 50.00 | 52.29 | 0.94 | −0.04 | |
| 40–50 cm | 0.26 | 66.67 | 53.85 | 52.65 | 0.63 | −0.93 |
| Element | Cu | Zn | Cd | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | P | CK | P | CK | P | |
| EMC/(ug/L) | 5.45 | 52.18 | 72.14 | 115.40 | 0.32 | 46.09 |
| Pollutant concentration/(ug/L) | 2.05~12.16 | 16.50~70.44 | 16.94~273.46 | 0.80~558.6 | 0.10~1.31 | 5.96~372.20 |
| Dry deposition flux/(mg/m2) | 13.80 | 13.80 | 627.58 | 627.58 | 1.09 | 1.09 |
| Wet deposition flux/(mg/m2) | 19.16 | 19.16 | 268.16 | 268.16 | 1.27 | 1.27 |
| Total pollutant amount/(mg) | 0 | 14,284.52 | 0 | 31,591.28 | 0 | 12,617.08 |
| Cu | Zn | Cd | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 cm | 20–30 cm | 40–50 cm | 0–10 cm | 20–30 cm | 40–50 cm | 0–10 cm | 20–30 cm | 40–50 cm | |
| β | 0.2600 | −0.1020 | −0.1568 | −0.3746 | −0.6700 | −2.0138 | 0.0043 | 0.0058 | −0.0044 |
| Zc | 0.3788 | −0.1136 | −0.4924 | −0.2273 | −0.6818 | −1.3636 | 0.0686 | 0.8563 | −0.7785 |
| HM Elements | Soil Layer/cm | EiP | EiCK | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | ||
| Cu | 0–10 | 2.36 | 12.85 | 7.34 | 3.00 | 14.27 | 7.12 |
| 20–30 | 2.91 | 10.77 | 6.46 | 2.74 | 12.15 | 6.46 | |
| 40–50 | 2.78 | 12.96 | 7.18 | 2.68 | 11.99 | 6.46 | |
| Zn | 0–10 | 0.47 | 1.89 | 1.05 | 0.57 | 1.51 | 1.01 |
| 20–30 | 0.49 | 1.97 | 1.15 | 0.47 | 1.41 | 0.97 | |
| 40–50 | 0.56 | 3.08 | 1.24 | 0.37 | 1.22 | 0.86 | |
| Cd | 0–10 | 34.47 | 156.38 | 83.83 | 40.21 | 159.57 | 95.49 |
| 20–30 | 34.15 | 137.23 | 73.90 | 34.79 | 134.04 | 72.16 | |
| 40–50 | 40.85 | 153.19 | 87.07 | 3.19 | 169.79 | 79.83 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, D.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Jiang, C.; Jia, B.; Cheng, B. Cumulative Risk of Heavy Metals in Long-Term Operational Rain Garden. Water 2025, 17, 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070955
Yan D, Li H, Li J, Jiang C, Jia B, Cheng B. Cumulative Risk of Heavy Metals in Long-Term Operational Rain Garden. Water. 2025; 17(7):955. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070955
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Dandan, Huaien Li, Jiake Li, Chunbo Jiang, Binkai Jia, and Bo Cheng. 2025. "Cumulative Risk of Heavy Metals in Long-Term Operational Rain Garden" Water 17, no. 7: 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070955
APA StyleYan, D., Li, H., Li, J., Jiang, C., Jia, B., & Cheng, B. (2025). Cumulative Risk of Heavy Metals in Long-Term Operational Rain Garden. Water, 17(7), 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070955







