Realistic Environmental Exposure of Microplastics in European Flat Oyster, Ostrea edulis: Evaluation of Accumulation and Depuration Under Controlled Conditions and Molecular Assessment of a Set of Reference Genes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
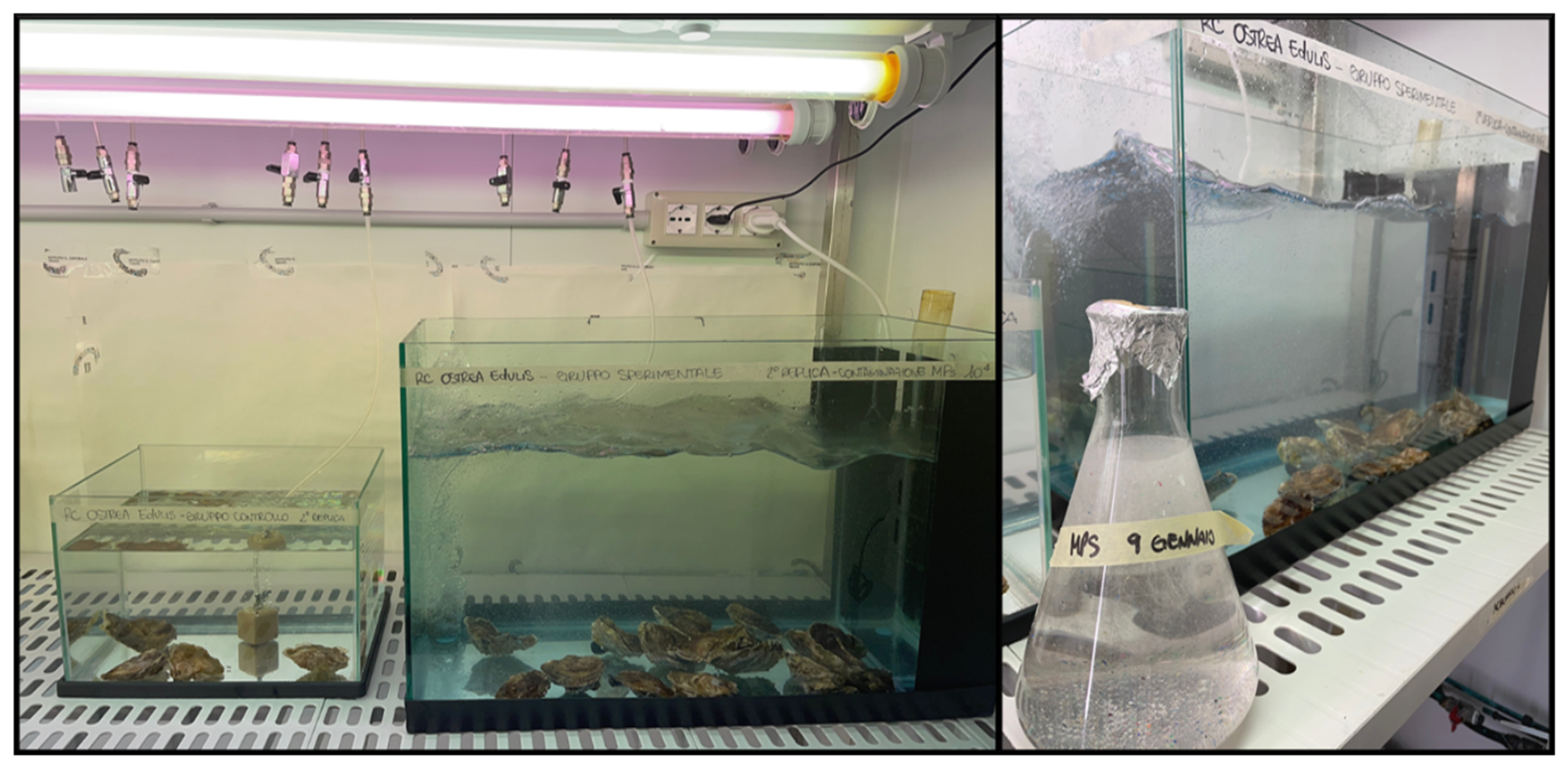
2.1. Ostrea Edulis and Experimental Set-Up
2.2. MPs’ Preparation and Ageing
2.3. MPs’ Exposure and Accumulation Phase
2.4. Gene Expression
2.4.1. RNA Extraction
2.4.2. cDNA Synthesis
2.4.3. Gene Expression Analysis
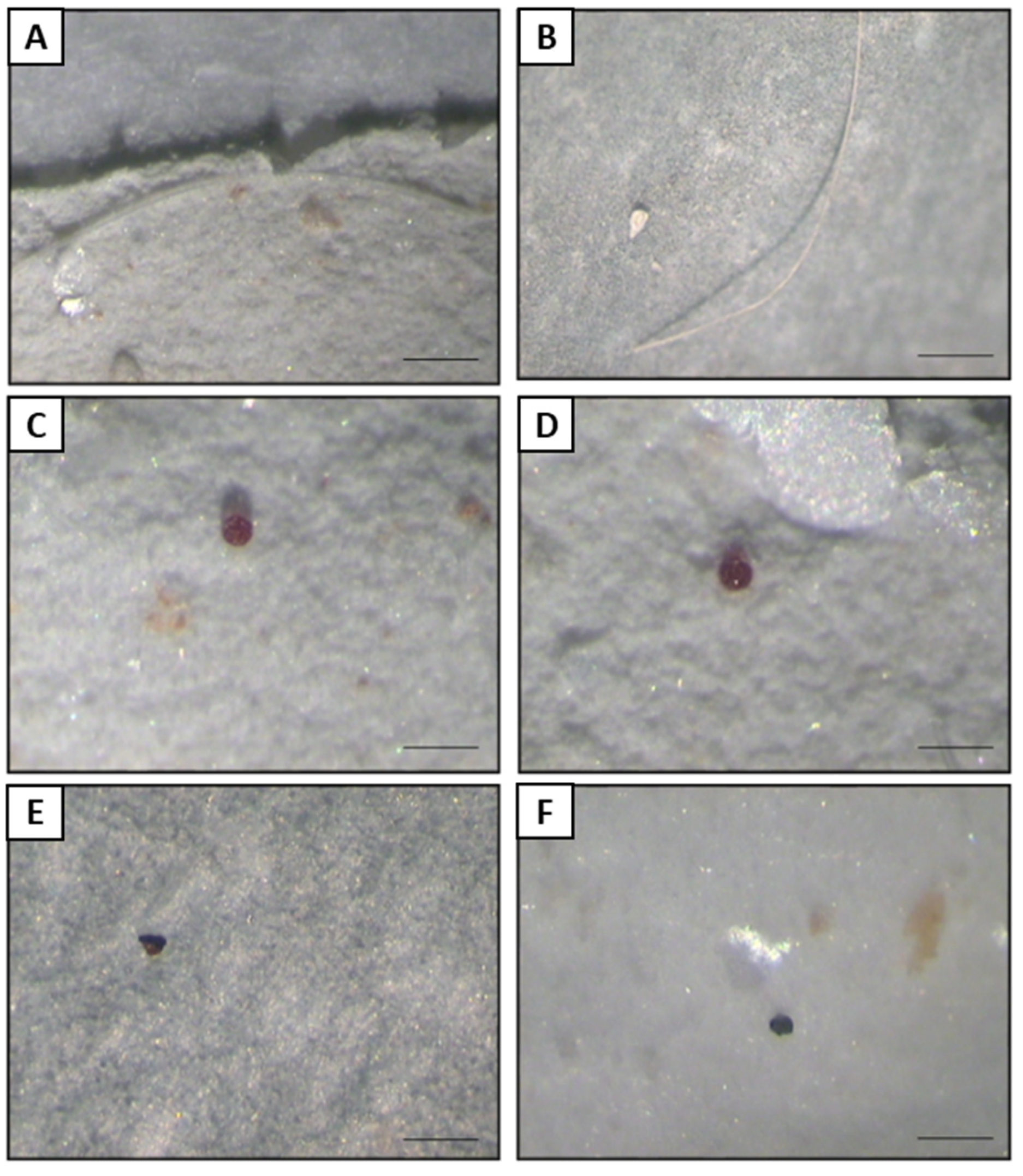
2.5. Depuration, Sample Digestion and Stereomicroscope Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
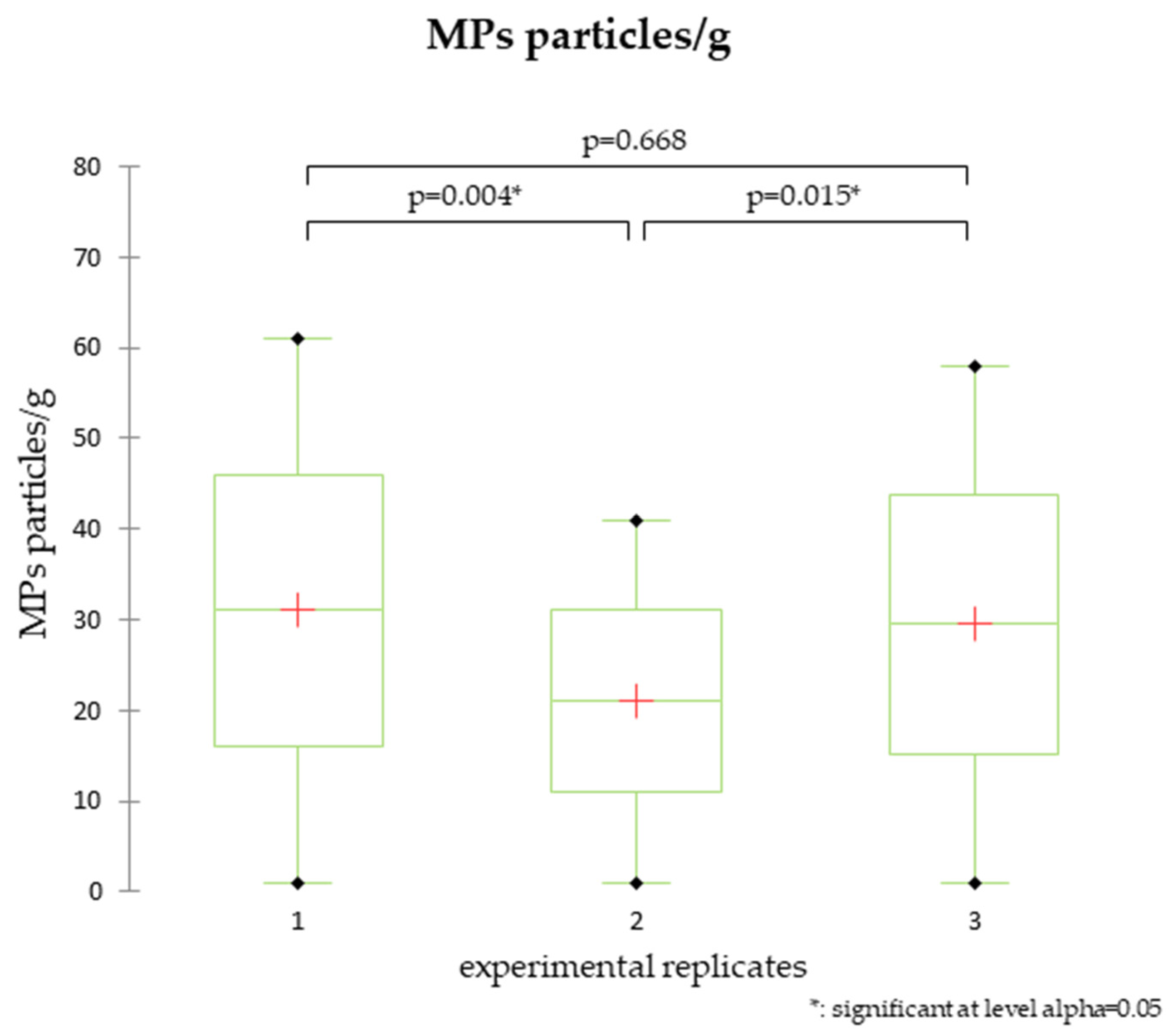
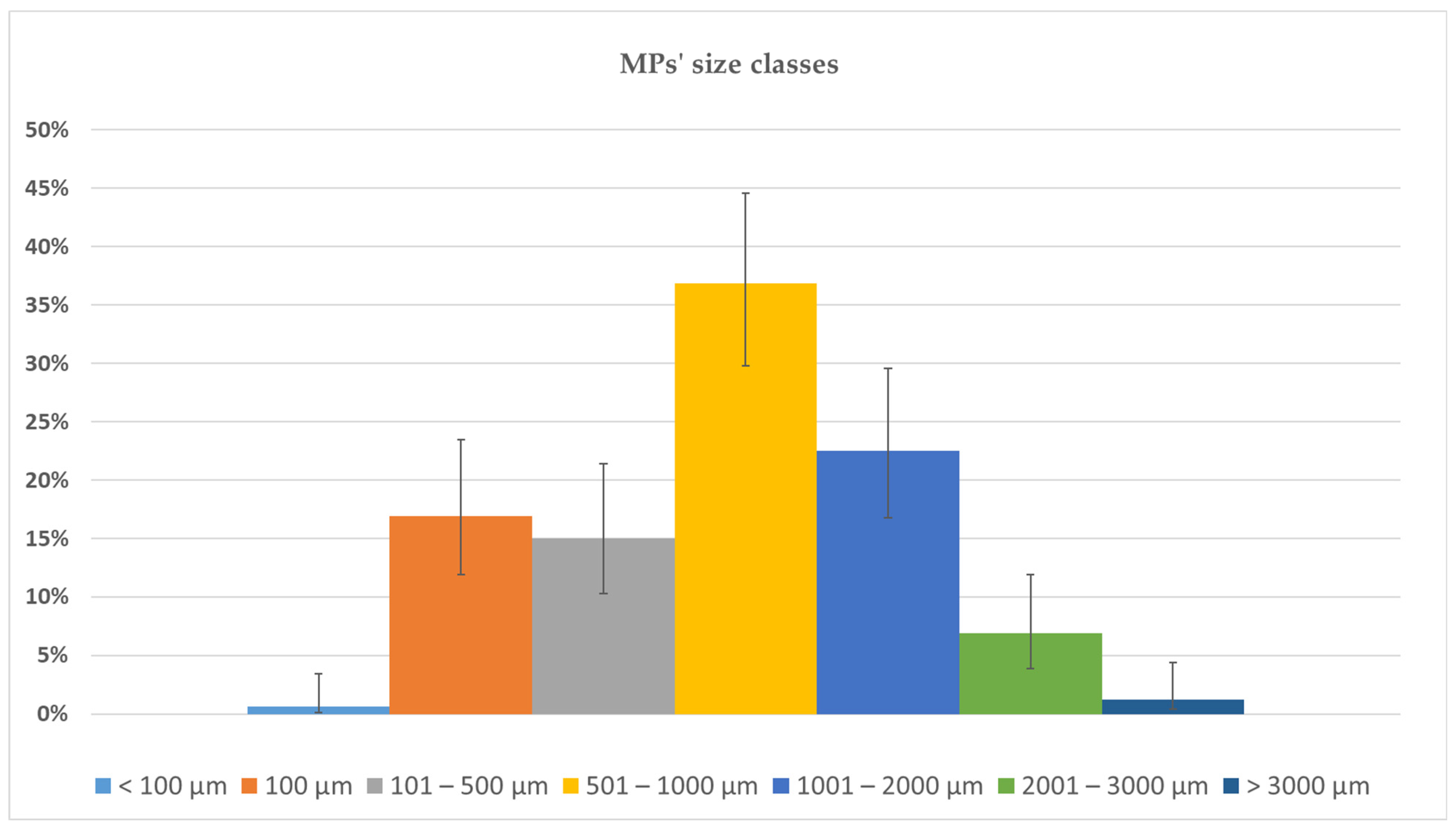
3.1. Bioaccumulation of MPs in Ostrea edulis
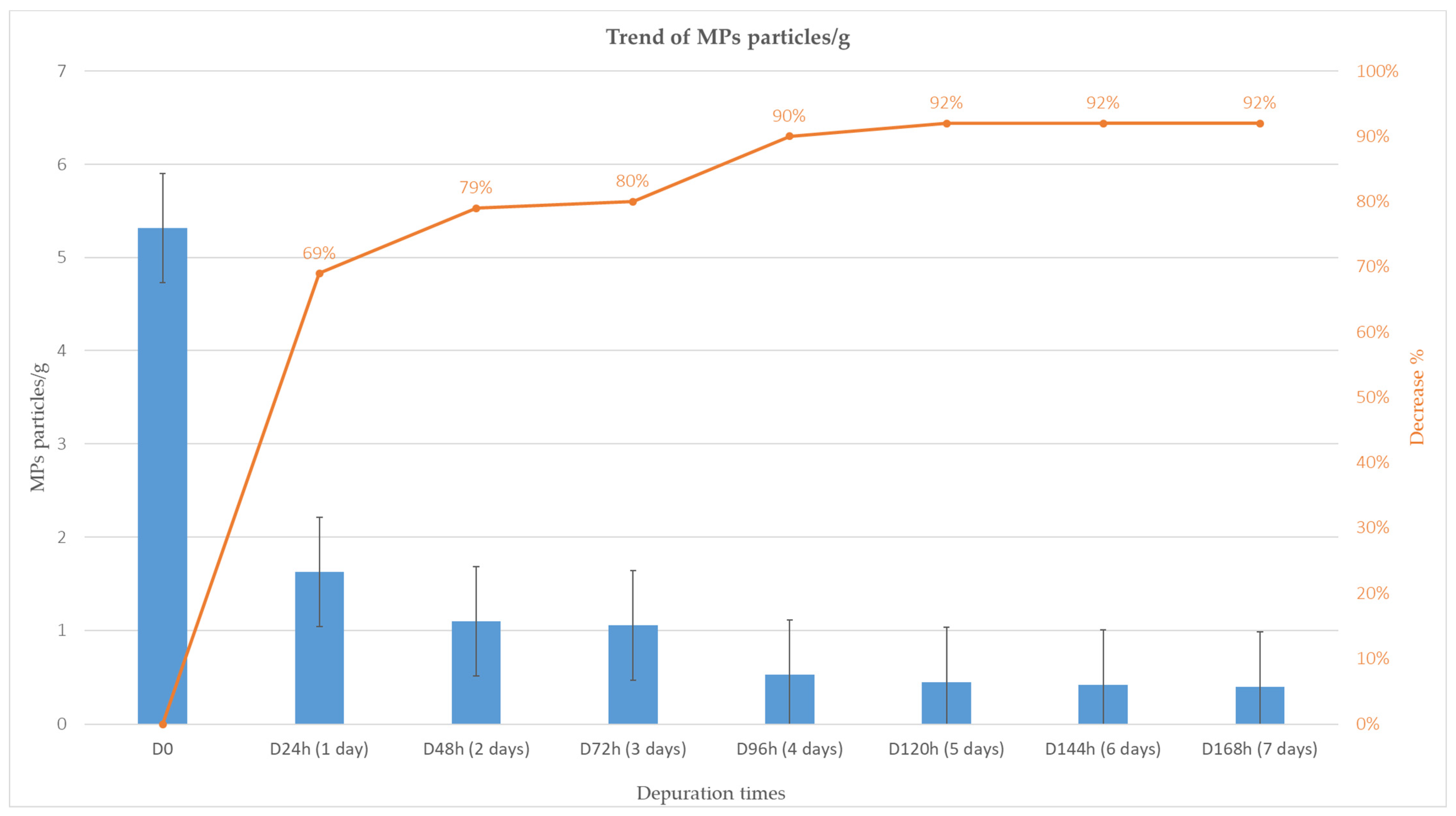
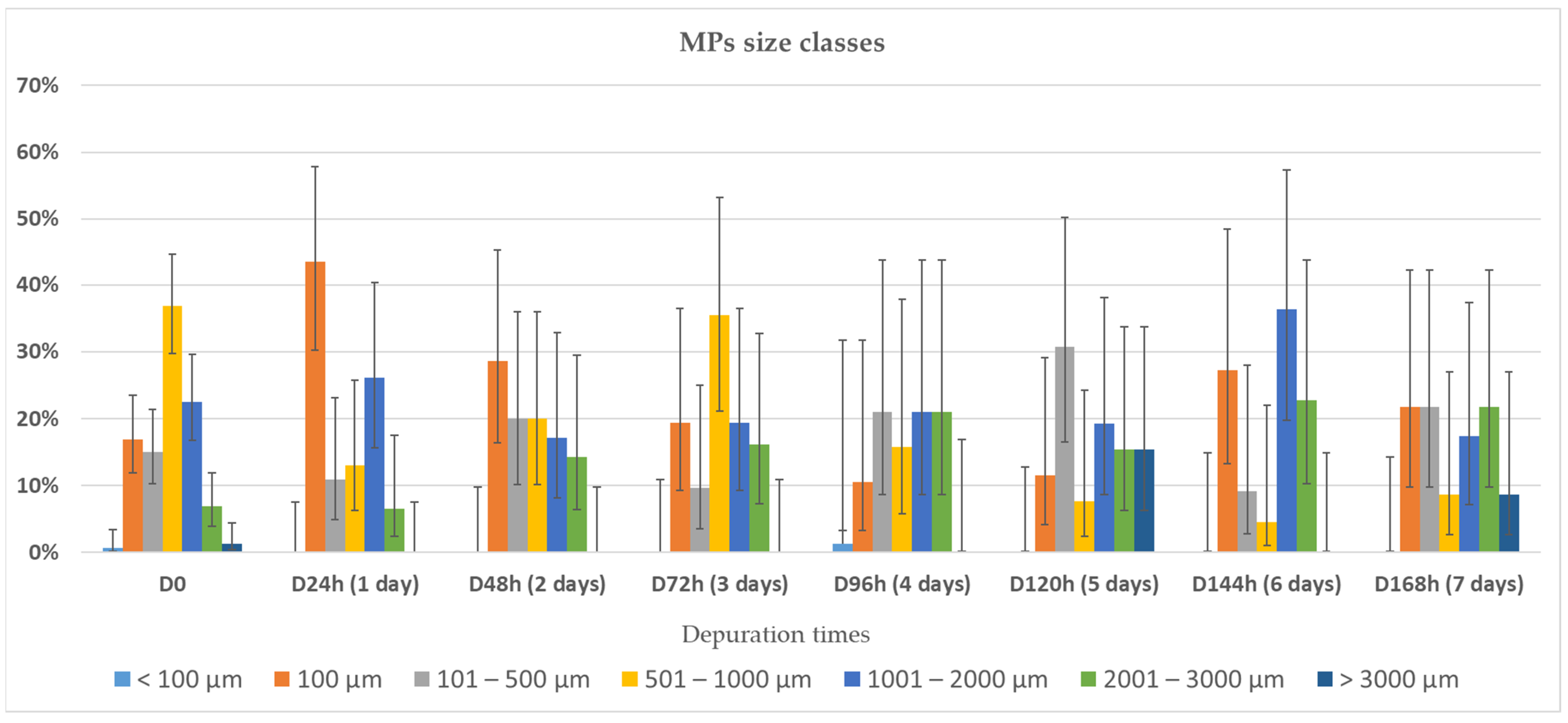
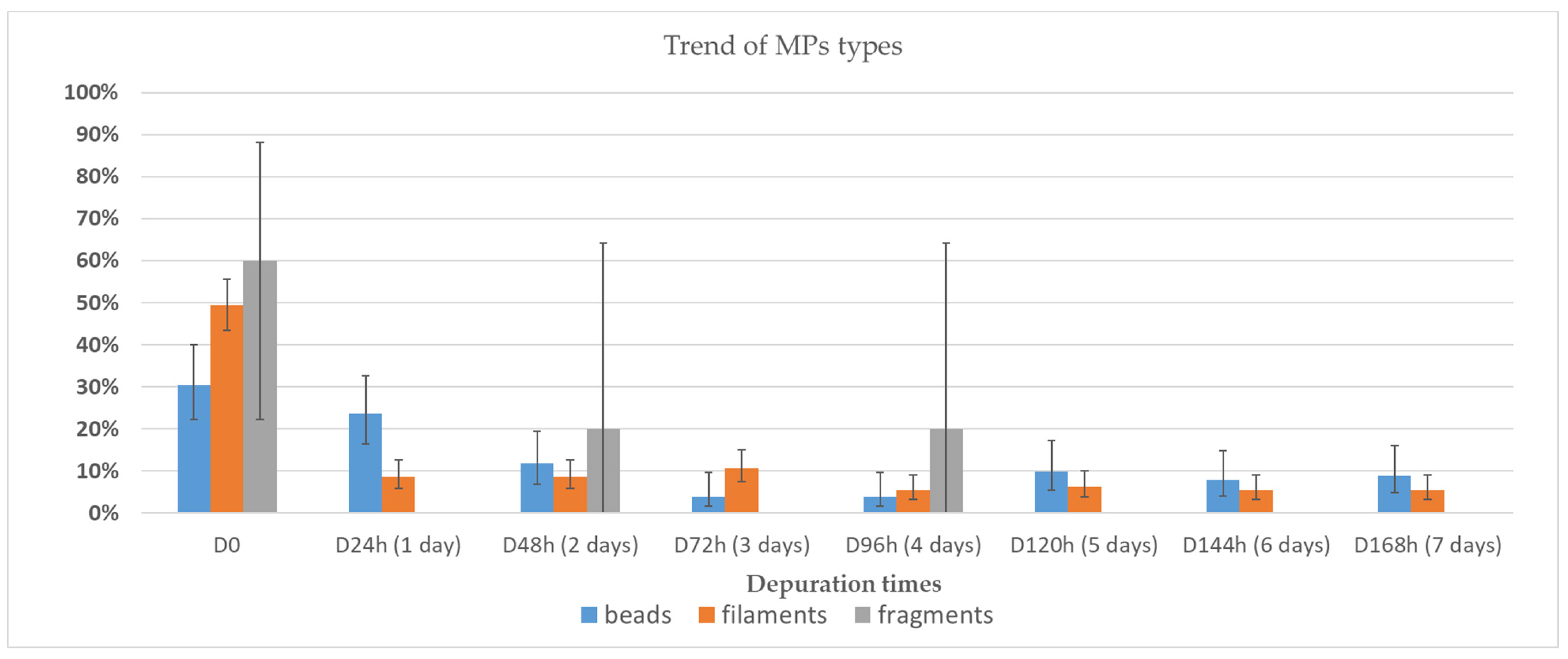
3.2. Depuration and Elimination of MPs in Ostrea edulis
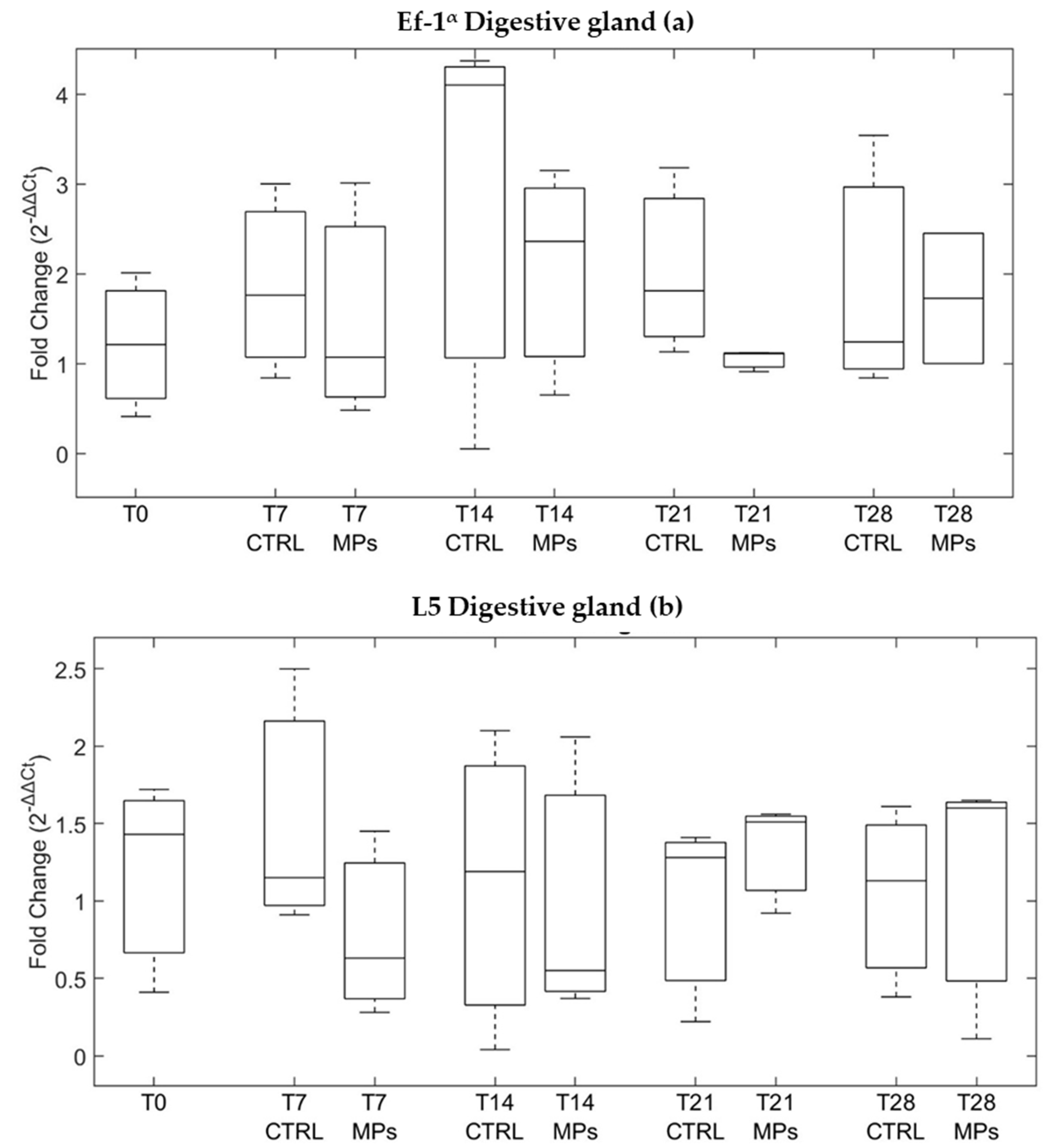
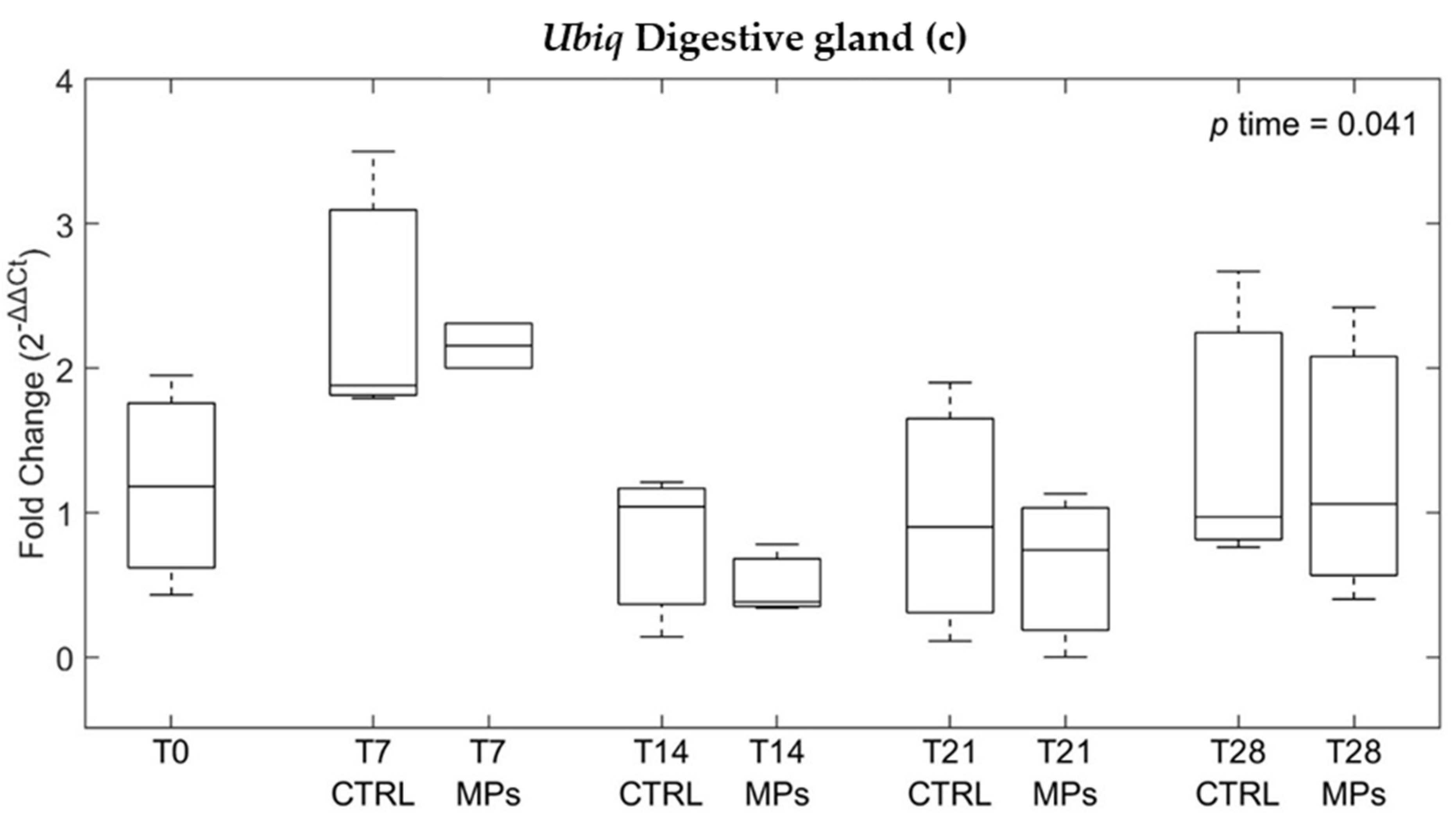
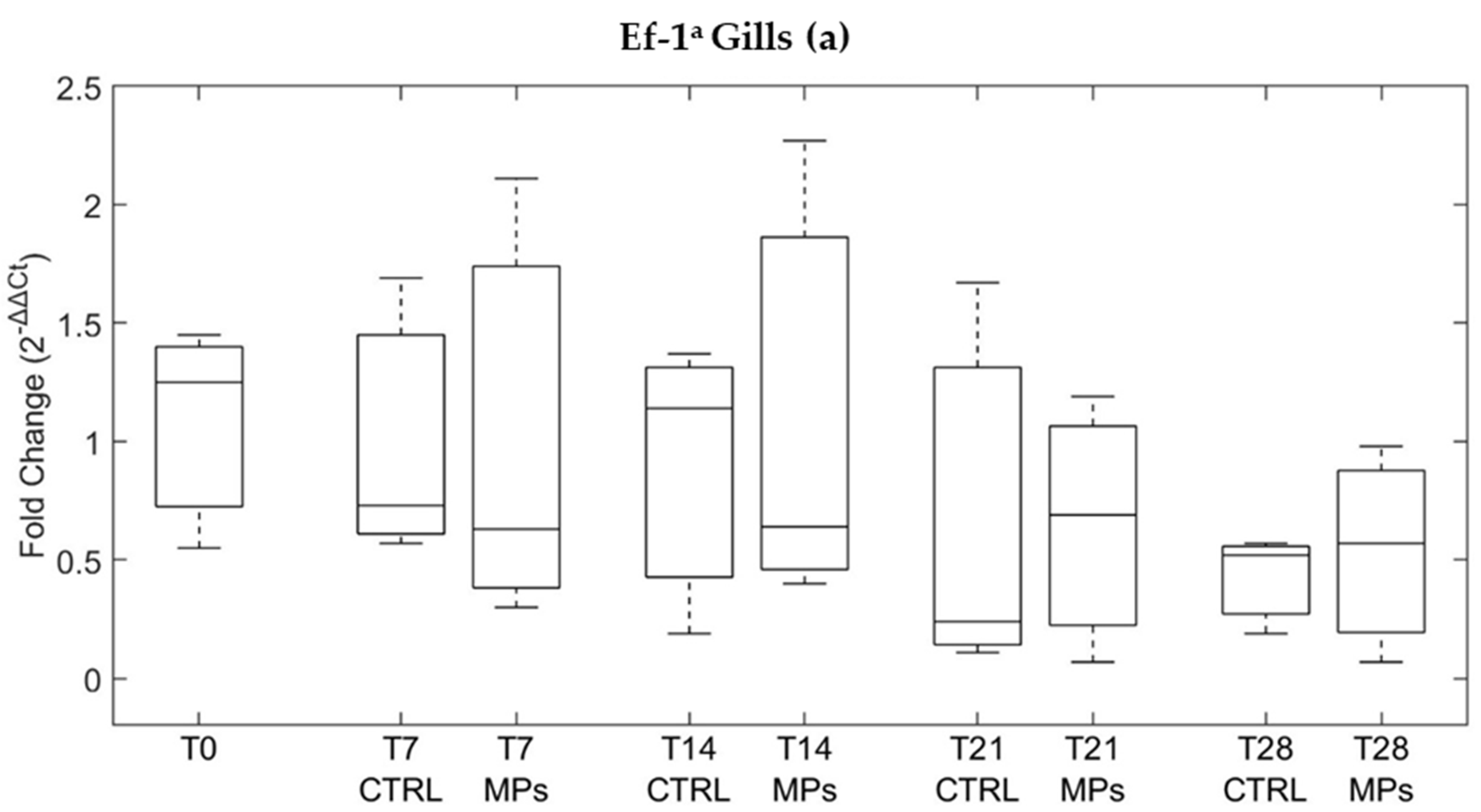
3.3. Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, S.; Ma, J.; Ji, R.; Pan, K.; Miao, A.J. Microplastics in aquatic environments: Occurrence, accumulation, and biological effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, X.; Shan, E.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Q. Toxic effects of exposure to microplastics with environmentally relevant shapes and concentrations: Accumulation, energy metabolism and tissue damage in oyster Crassostrea gigas. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GESAMP. Guidelines or the Monitoring and Assessment of Plastic Litter and Microplastics in the Ocean; Kershaw, P.J., Turra, A., Galgani, F., Eds.; IMO/FAO/UNESCO-IOC/UNIDO/WMO/IAEA/UN/UNEP/UNDP/ISA Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection. Reports and Studies GESAMP No. 99; GESAMP: London, UK, 2019; 130p. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, R.C.; Moore, C.J.; vom Saal, F.S.; Swan, S.H. Plastics, the environment and human health: Current consensus and future trends. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2153–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, P.; Nelson, K. Trophic level transfer of microplastic: Mytilus edulis (L.) to Carcinus maenas (L.). Environ. Pollut. 2013, 177, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setälä, O.; Fleming-Lehtinen, V.; Lehtiniemi, M. Ingestion and transfer of microplastics in the planktonic food web. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzetti, E.; Sureda, A.; Tejada, S.; Faggio, C. Microplastic in marine organism: Environmental and toxicological effects. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 64, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouin, T. Toward an Improved Understanding of the Ingestion and Trophic Transfer of Microplastic Particles: Critical Review and Implications for Future Research. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 39, 1119–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Diab, H.; Thompson, J. Microplastic Pollution: Chemical Characterization and Impact on Wildlife. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Hernández, E.A.; Ramírez-Álvarez, N.; Rios Mendoza, L.M.; Macías-Zamora, J.V.; Sánchez-Osorio, J.L.; Hernández-Guzmán, F.A. Microplastic concentrations in cultured oysters in two seasons from two bays of Baja California, Mexico. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, D.; Li, L.; Jabeen, K.; Shi, H. Microplastics in commercial bivalves from China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 207, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salini, R.; Tora, S.; Filipponi, F.; Conte, A.; Giansante, C.; Ippoliti, C. Analyzing trend and heatwaves of 15 Years of Sea Surface Temperature Variations along the Italian Adriatic Coast. Vet. Ital. 2024, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCCCOS. Coastal Science Website. 2023. Available online: https://coastalscience.noaa.gov (accessed on 25 November 2023).
- OSPAR. Joint assessment and monitoring programme (JAMP) 2017–2023. OSPAR Comission—Agreement 2014-2. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mathalon, A.; Hill, P. Microplastic fibers in the intertidal ecosystem surrounding Halifax Harbor, Nova Scotia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 81, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Su, L.; Li, H.; Liang, M.; Shi, H. Assessing the relationship between the abundance and properties of microplastics in water and in mussels. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hantoro, I.; Löhr, A.J.; van Belleghem, F.G.A.J.; Widianarko, B.; Ragas, A.M.J. Microplastics in coastal areas and seafood: Implications for food safety. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 674–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, V.; Böhmert, L.; Lisicki, E.; Block, R.; Cara-Carmona, J.; Pack, L.K.; Selb, R.; Lichtenstein, D.; Voss, L.; Henderson, C.J.; et al. Uptake and effects of orally ingested polystyrene microplastic particles in vitro and in vivo. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 1817–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poma, A.; Vecchiotti, G.; Colafarina, S.; Zarivi, O.; Aloisi, M.; Arrizza, L.; Chichiriccò, G.; Di Carlo, P. In Vitro Genotoxicity of Polystyrene Nanoparticles on the Human Fibroblast Hs27 Cell Line. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, S.; Domenech, J.; Barguilla, I.; Cortés, C.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. Genotoxic and immunomodulatory effects in human white blood cells after ex vivo exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 3431–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.D.; Chen, C.W.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, H.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lin, C.H. Polystyrene microplastic particles: In vitro pulmonary toxicity assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çobanoğlu, H.; Belivermiş, M.; Sıkdokur, E.; Kılıç, Ö.; Çayır, A. Genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of polyethylene microplastics on human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Expósito, N.; Rovira, J.; Sierra, J.; Gimenez, G.; Domingo, J.L.; Schuhmacher, M. Levels of microplastics and their characteristics in molluscs from North-West Mediterranean Sea: Human intake. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 181, 113843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, X.; Shan, E.; Wang, Q. Oxidative stress biomarkers, physiological responses and proteomic profiling in oyster (Crassostrea gigas) exposed to microplastics with irregular-shaped PE and PET microplastic. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringer, A.; Cachot, J.; Dubillot, E.; Prunier, G.; Huet, V.; Clérandeau, C.; Evin, L.; Thomas, H. Intergenerational effects of environmentally-aged microplastics on the Crassostrea gigas. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 294, 118600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, H.; Chen, L.; Teng, X.; Xue, C.; Li, Z. An overview of microplastics in oysters: Analysis, hazards, and depuration. Food Chem. 2023, 422, 136153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardon, T.; Morvan, L.; Huvet, A.; Quillien, V.; Soyez, C.; le Moullac, G.; le Luyer, J. Microplastics induce dose-specific transcriptomic disruptions in energy metabolism and immunity of the pearl oyster Pinctada margaritifera. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhao, J.; Teng, J.; Ren, J.; Shan, E.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Hou, C.; Wang, Q. Combined effects of salinity and polystyrene microplastics exposure on the Pacific oysters Crassostrea gigas: Oxidative stress and energy metabolism. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 193, 115153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Teng, X.; Chen, L.; Wu, S.; Xue, C.; Li, Z. Changes in Flavor-Related Biomarkers in Pacific Oysters (Crassostrea gigas) Following Microplastic Exposure. Foods 2024, 13, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringer, A.; Thomas, H.; Prunier, G.; Dubillot, E.; Bossut, N.; Churlaud, C.; Clérandeau, C.; le Bihanic, F.; Cachot, J. High density polyethylene (HDPE) microplastics impair development and swimming activity of Pacific oyster D-larvae, Crassostrea gigas, depending on particle size. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felici, A.; Vittori, S.; Meligrana, M.C.T.; Roncarati, A. Quality traits of raw and cooked cupped oysters. Eur. Food J. Technol. Res. 2020, 246, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, S.; Chen, L.; Teng, X.; Shi, H.; Xue, C.; Li, Z. Metabolic profiles and protein expression responses of Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) to polystyrene microplastic stress. Food Chem. 2025, 462, 140961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.; Lovatelli, A.; Ababouch, L. Bivalve depuration: Fundamental and practical aspects. In FAO Fisheries Technical Paper (Arabic Edition); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Shi, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xue, C. Molecular mechanism of protein dynamic change in Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) during depuration at different salinities uncovered by mass spectrometry-based proteomics combined with bioinformatics. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anon. Regulation (EC) No. 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 laying down specific hygiene rules for food of animal origin. 2004. [Google Scholar]
- van Cauwenberghe, L.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastics in bivalves cultured for human consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 193, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnstiel, S.; Soares-Gomes, A.; da Gama, B.A.P. Depuration reduces microplastic content in wild and farmed mussels. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, B.; Albentosa, M. Dynamic of small polyethylene microplastics (≤10 μm) in mussel’s tissues. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, B.; Albentosa, M. Insights into the uptake, elimination and accumulation of microplastics in mussel. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, P.; Palazzo, L.; Andrea de Lucia, G.; Telfer, T.C.; Baroli, M.; Carboni, S. Microplastics uptake and egestion dynamics in Pacific oysters, Magallana gigas (Thunberg, 1793), under controlled conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, Y.; An, Y.-J. Effects of food presence on microplastic ingestion and egestion in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.E.; Zhao, S.; Holohan, B.A.; Mladinich, K.M.; Griffin, T.W.; Wozniak, J.; Shumway, S.E. Selective Ingestion and Egestion of Plastic Particles by the Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis) and Eastern Oyster (Crassostrea virginica): Implications for Using Bivalves as Bioindicators of Microplastic Pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8776–8784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covernton, G.A.; Dietterle, M.; Pearce, C.M.; Gurney-Smith, H.J.; Dower, J.F.; Dudas, S.E. Depuration of anthropogenic particles by Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas): Feasibility and efficacy. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 181, 113886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Im, D.-H.; Park, Y.-H.; Lee, J.-W.; Yoon, S.-J.; Hwang, U.-K. Ingestion and egestion of polystyrene microplastic fragments by the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 307, 119217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, J.E.; Ertel, B.M.; Gray, A.D. Accumulation and depuration of microplastic fibers, fragments, and tire particles in the eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica: A toxicokinetic approach. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Expósito, N.; Barrientos-Riosalido, A.; Santini, S.; Cincinelli, A.; Alcalde, L.; Castell, V.; Nadal, M.; Sierra, J.; Rovira, J. Microplastics levels in cultured or harvested mollusks non-depurated and commercially depurated at different times. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 212, 117568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Milan, M.; Benedetti, M.; Fattorini, D.; d’Errico, G.; Pauletto, M.; Bargelloni, L.; Regoli, F. Pollutants bioavailability and toxicological risk from microplastics to marine mussels. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 198, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandts, I.; Teles, M.; Gonçalves, A.P.; Barreto, A.; Franco-Martinez, L.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Martins, M.A.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Tort, L.; Oliveira, M. Effects of nanoplastics on Mytilus galloprovincialis after individual and combined exposure with carbamazepine. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revel, M.; Châtel, A.; Perrein-Ettajani, H.; Bruneau, M.; Akcha, F.; Sussarellu, R.; Rouxel, J.; Costil, K.; Decottignies, P.; Cognie, B.; et al. Realistic environmental exposure to microplastics does not induce biological effects in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroom, R.J.E.; Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Halsband, C. Aging of microplastics promotes their ingestion by marine zooplankton. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albentosa, M.; Sánchez-Hernández, M.; Campillo, J.A.; Moyano, F.J. Relationship between physiological measurements (SFG -scope for growth-) and the functionality of the digestive gland in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2012, 163, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collignon, A.; Hecq, J.-H.; Glagani, F.; Voisin, P.; Collard, F.; Goffart, A. Neustonic microplastic and zooplankton in the North Western Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, E.E.; Boxall, A.B.A. Microplastics in the aquatic environment: Evidence for or against adverse impacts and major knowledge gaps. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 2776–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, Ö.; Belivermiş, M.; Sıkdokur, E.; Sezer, N.; Aksüt, Y.; Pekmez, M.; Kösesakal, T.; Gerçek, Y.C. The combined effects of polyethylene microplastics and benzoanthracene on Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Chemosphere 2023, 329, 138664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzurro, F.; Nerone, E.; Ancora, M.; Di Domenico, M.; Mincarelli, L.F.; Cammà, C.; Salini, R.; Di Renzo, L.; Di Giacinto, F.; Corbau, C.; et al. Exposure of Mytilus galloprovincialis to Microplastics: Accumulation, Depuration and Evaluation of the Expression Levels of a Selection of Molecular Biomarkers. Animals 2023, 14, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morga, B.; Arzul, I.; Faury, N.; Renault, T. Identification of genes from flat oyster Ostrea edulis as suitable housekeeping genes for quantitative real time PCR. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.-P.; Chiu, C.-C.; Huang, H.-W. Assessment of microplastics in oysters in coastal areas of Taiwan. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Review of the Methods Used for Identification and Quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 22 January 2024).
- RefFinder. Available online: https://blooge.cn/RefFinder/ (accessed on 27 December 2023).
- Xie, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B. RefFinder: A web-based tool for comprehensively analyzing and identifying reference genes. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2023, 23, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiafico, S. Package ‘rcompanion’. Cran Repos 2017, 20, 1–71. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rcompanion (accessed on 22 January 2024).
- Grubbs, F.E. Procedures for Detecting Outlying Observations in Samples. Technometrics 1969, 11, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, M.J.; Nixon, G.J.; Foy, C.A.; Harris, N. Standardisation of data from real-time quantitative PCR methods—Evaluation of outliers and comparison of calibration curves. BMC Biotechnol. 2005, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, C.; Coquillé, V.; Guyomarch, J.; Auffret, M.; Moraga, D. A selection of reference genes and early-warning mRNA biomarkers for environmental monitoring using Mytilus spp. as sentinel species. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 86, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul-Pont, I.; Lacroix, C.; González Fernández, C.; Hégaret, H.; Lambert, C.; le Goïc, N.; Frère, L.; Cassone, A.-L.; Sussarellu, R.; Fabioux, C.; et al. Exposure of marine mussels Mytilus spp. to polystyrene microplastics: Toxicity and influence on fluoranthene bioaccumulation. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, J.; Shumway, S.E. Separating the grain from the chaff: Particle selection in suspension- and deposit-feeding bivalves. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2024, 300, 83–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Rotchell, J.M.; Shen, X.; Li, Q.; Zhu, J. Where are we? Towards an understanding of the selective accumulation of microplastics in mussels. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, F.; Garcia, A.R.; Pereira, B.P.; Fonseca, M.; Mestre, N.C.; Fonseca, T.G.; Ilharco, L.M.; Bebianno, M.J. Microplastics effects in Scrobicularia plana. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, W.A.; Zammit, A.; Dove, M.C.; Stevenson, G.; Taylor, M.D. First observations of perfluorooctane sulfonate occurrence and depuration from Sydney Rock Oysters, Saccostrea glomerata, in Port Stephens NSW Australia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittinger, C.A.; Buikema, A.L.; Hornor, S.G.; Young, R.W. Variation in tissue burdens of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in indigenous and relocated oysters. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1985, 4, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Albores, A.; Lopez-Santamarina, A.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Ibarra, I.S.; Mondragón, A.d.C.; Miranda, J.M.; Lamas, A.; Cepeda, A. Complementary Methods to Improve the Depuration of Bivalves: A Review. Foods 2020, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Su, Y.-C.; Liu, C.; Oscar, T.; DePaola, A. Efficacy of Vibrio parahaemolyticus depuration in oysters (Crassostrea gigas). Food Microbiol. 2019, 79, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuvasate, S.; Chen, M.-H.; Su, Y.-C. Reductions of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas) by depuration at various temperatures. Food Microbiol. 2012, 31, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistini, R.; Masotti, C.; Listorti, V.; Suffredini, E.; Maurella, C.; Garcia-Vozmediano, A.; Costa, E.; Iacona, F.; Orlandi, M.; Ercolini, C.; et al. Norovirus Persistence in Oysters to Prolonged Commercial Purification. Pathogens 2021, 10, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker-Austin, C.; Trinanes, J.A.; Taylor, N.G.H.; Hartnell, R.; Siitonen, A.; Martinez-Urtaza, J. Emerging Vibrio risk at high latitudes in response to ocean warming. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolandhasamy, P.; Su, L.; Li, J.; Qu, X.; Jabeen, K.; Shi, H. Adherence of microplastics to soft tissue of mussels: A novel way to uptake microplastics beyond ingestion. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doré, W.J.; Lees, D.N. Behavior of Escherichia coli and male-specific bacteriophage in environmentally contaminated bivalve molluscs before and after depuration. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 2830–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lees, D. Viruses and bivalve shellfish. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 59, 81–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Regulation (EC) n. 854/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 laying down specific rules for the organisation of official controls on products of animal origin intended for human consumption. 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Barrientos, M.; Vásquez Lavín, F.; Ponce Oliva, R.D.; Nayga, R.M., Jr.; Gelcich, S. Microplastics in seafood: Consumer preferences and valuation for mitigation technologies. Food Res. Int. 2024, 187, 114342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finley, D. An alternative to destruction. Nature 2001, 412, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.; Pereira, P.; Taylor, A.; Liang, J.N.; Reddy, V.N.; Szweda, L.I.; Shang, F. Ubiquitin-dependent lysosomal degradation of the HNE-modified proteins in lens epithelial cells. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1424–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, M.T.; Siah, A.; Mateo, D.; Markham, F.; McKenna, P.; Johnson, G.; Berthe, F.C.J. Selection and evaluation of housekeeping genes for haemocytes of soft-shell clams (Mya arenaria) challenged with Vibrio splendidus. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2008, 99, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubero-Leon, E.; Ciocan, C.M.; Minier, C.; Rotchell, J.M. Reference gene selection for qPCR in mussel, Mytilus edulis, during gametogenesis and exogenous estrogen exposure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 2728–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| ID | Depuration Time (Days) | MPs Particles/ Individual | MPs/g | Decrease % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D0 | 53.3 | 5.3 | ||
| D24h | 1 | 15.3 | 1.6 | 69% |
| D48h | 2 | 12.0 | 1.1 | 79% |
| D72h | 3 | 10.3 | 1.1 | 80% |
| D96h | 4 | 9.0 | 0.5 | 90% |
| D120h | 5 | 8.7 | 0.5 | 92% |
| D144h | 6 | 7.9 | 0.4 | 92% |
| D168h | 7 | 7.7 | 0.4 | 92% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pizzurro, F.; Nerone, E.; Di Domenico, M.; Ancora, M.; Mincarelli, L.F.; Salini, R.; Di Renzo, L.; Fazio, S.; Recchi, S. Realistic Environmental Exposure of Microplastics in European Flat Oyster, Ostrea edulis: Evaluation of Accumulation and Depuration Under Controlled Conditions and Molecular Assessment of a Set of Reference Genes. Water 2025, 17, 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071063
Pizzurro F, Nerone E, Di Domenico M, Ancora M, Mincarelli LF, Salini R, Di Renzo L, Fazio S, Recchi S. Realistic Environmental Exposure of Microplastics in European Flat Oyster, Ostrea edulis: Evaluation of Accumulation and Depuration Under Controlled Conditions and Molecular Assessment of a Set of Reference Genes. Water. 2025; 17(7):1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071063
Chicago/Turabian StylePizzurro, Federica, Eliana Nerone, Marco Di Domenico, Massimo Ancora, Luana Fiorella Mincarelli, Romolo Salini, Ludovica Di Renzo, Simone Fazio, and Sara Recchi. 2025. "Realistic Environmental Exposure of Microplastics in European Flat Oyster, Ostrea edulis: Evaluation of Accumulation and Depuration Under Controlled Conditions and Molecular Assessment of a Set of Reference Genes" Water 17, no. 7: 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071063
APA StylePizzurro, F., Nerone, E., Di Domenico, M., Ancora, M., Mincarelli, L. F., Salini, R., Di Renzo, L., Fazio, S., & Recchi, S. (2025). Realistic Environmental Exposure of Microplastics in European Flat Oyster, Ostrea edulis: Evaluation of Accumulation and Depuration Under Controlled Conditions and Molecular Assessment of a Set of Reference Genes. Water, 17(7), 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071063






