A Novel Halophilic Bacterium for Sustainable Pollution Control: From Pesticides to Industrial Effluents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Medium and Reagents
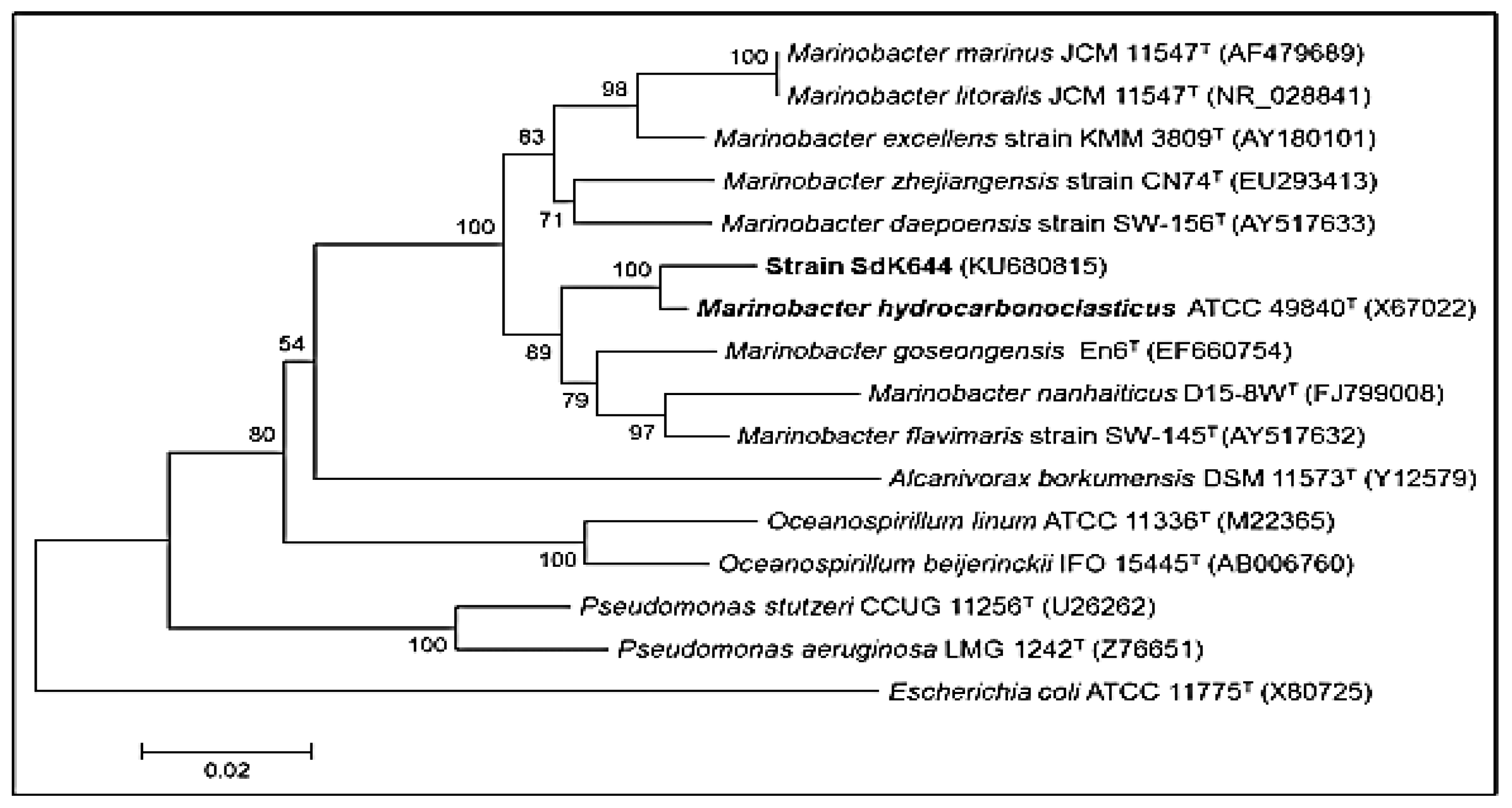
2.2. Preparation of Bacterial Strains
2.3. Samples
2.4. Monitoring Bacterial Growth in the Presence of Metribuzin
2.5. Optimization of Growth Conditions and Metribuzin Biodegradation
- Metribuzin Concentration: Various concentrations of metribuzin (2, 20, 50, and 100 mg/L) were added to the MSM, and the bacterial growth was monitored by OD600 measurements over a period of 144 h. This was used to identify the concentration range that allowed for optimal bacterial growth and metribuzin degradation.
- pH Levels: The pH of the medium was adjusted to different values (4.0, 7.0, and 9.0) using HCl and NaOH to assess how the pH affects the growth and degradation efficiency of the strain.
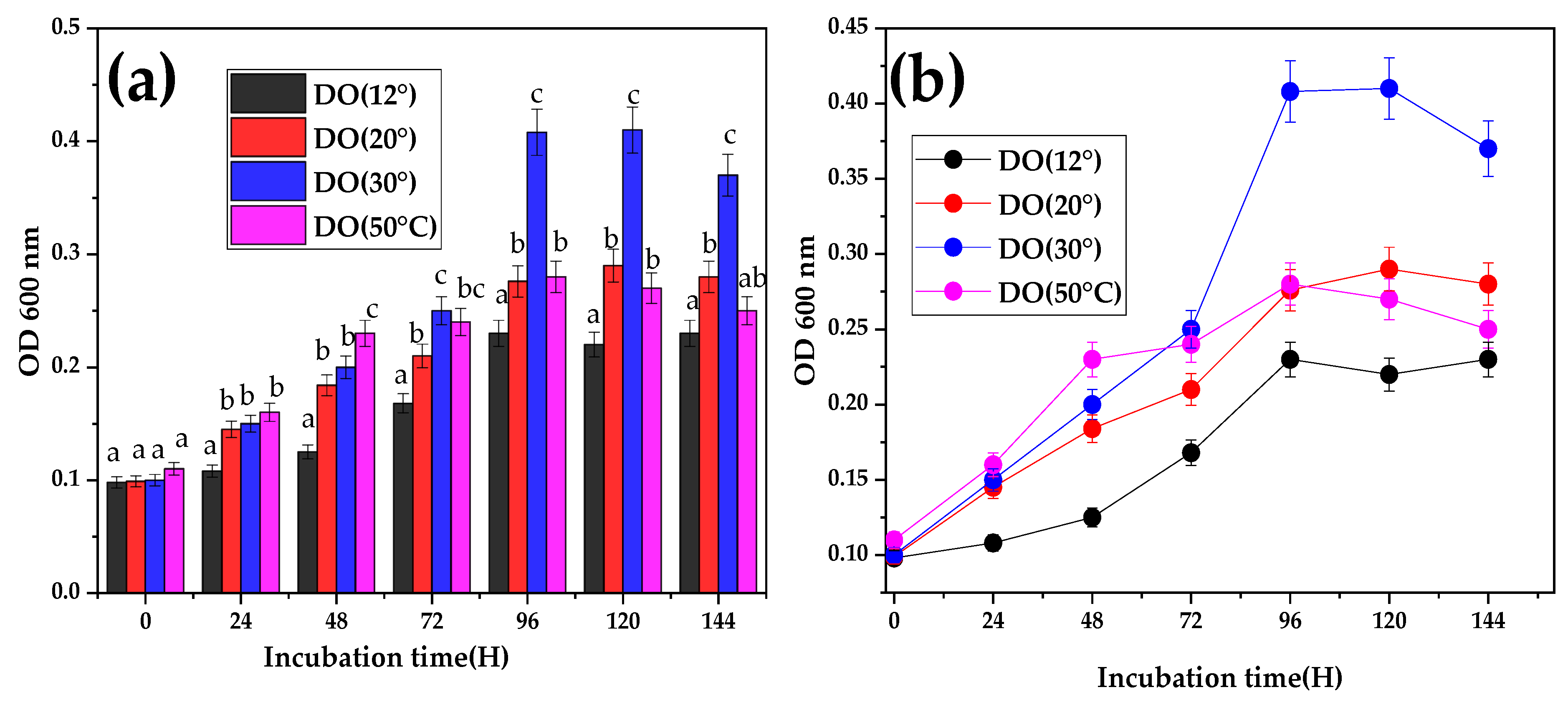
- Temperature: The bacterial cultures were incubated at various temperatures (12 °C, 20 °C, 30 °C, and 45 °C) to identify the temperature range in which the strain exhibited the best growth rate and metribuzin degradation capacity.
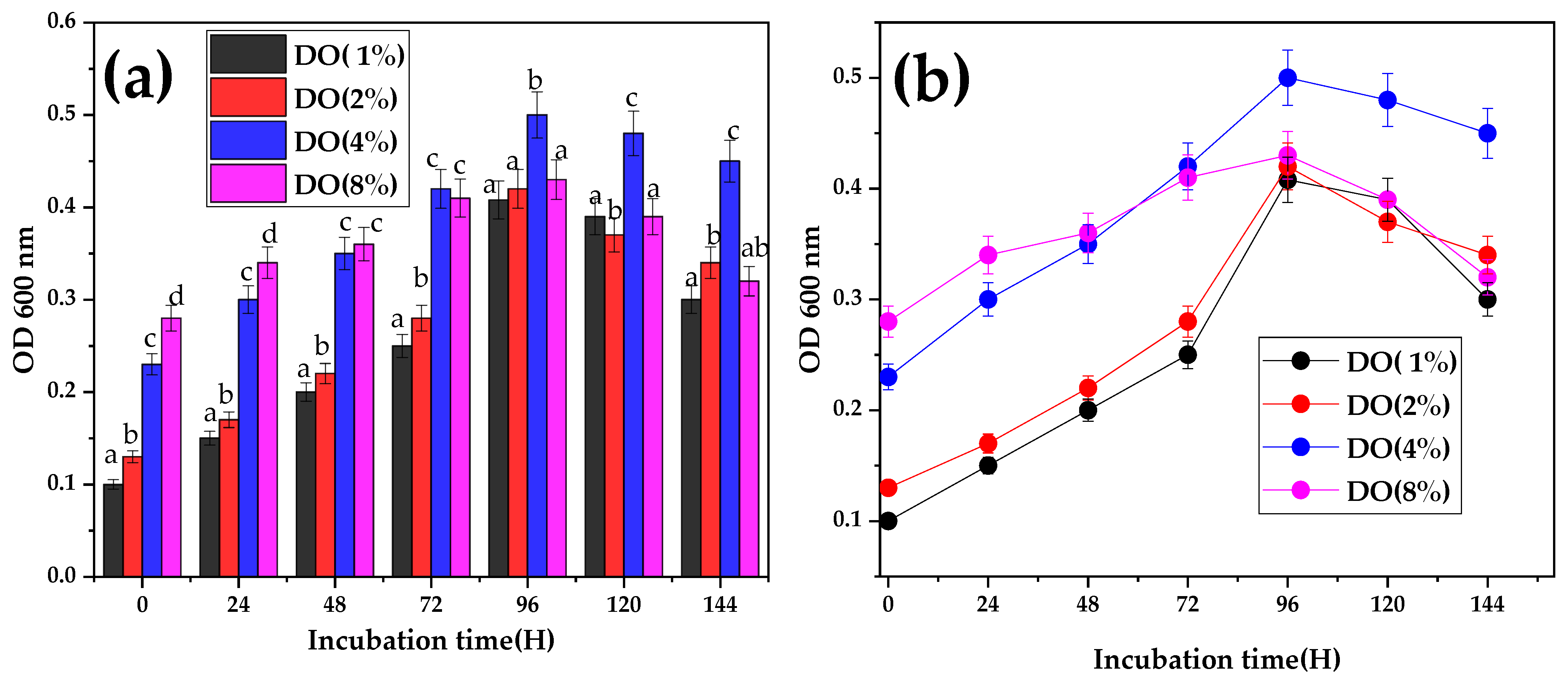
- Inoculum Volume: Different inoculum volumes (1%, 2%, 4%, and 8% v/v) were tested to determine the optimal inoculum size for efficient growth and degradation.
2.6. Degradation of Metribuzin by SDK644
2.7. Treatment of Slaughterhouse Effluent
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Different Concentrations of Metribuzin on Cell Growth
3.2. Effect of pH on Cell Growth
3.3. Effect of Temperature on Bacterial Growth
3.4. Effect of Inoculum Concentration on Bacterial Growth
3.5. Degradation of Metribuzin by Strain SDK644
3.6. Treatment of Slaughterhouse Effluent
3.7. Comparative Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toumi, S.; Lekmine, S.; Touzout, N.; Moussa, H.; Elboughdiri, N.; Boudraa, R.; Benslama, O.; Kebir, M.; Danish, S.; Zhang, J. Harnessing Deep Learning for Real-Time Water Quality Assessment: A Sustainable Solution. Water 2024, 16, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalfaoui, B.; Meniai, A.H.; Borja, R. Removal of Copper from Industrial Wastewater by Raw Charcoal Obtained from Reeds. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1995, 64, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNECA; UNECE; UNECLAC; UNESCAP; UNESCWA; World Health Organization (WHO). Water and Climate Change; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2020; ISBN 92-3-100371-2. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Yan, G.; Huo, Z.; Mo, Y.; Wen, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhou, H.; Yan, B.; Lin, Z. Thallium’s Threat to Aquatic Life: Stage-Specific Toxicity in Zebrafish Embryos and Larvae. Environ. Health 2024, 2, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.K.; Kumar, U.; Kumar, I.; Dwivedi, A.; Singh, P.; Mishra, S.; Seth, C.S.; Sharma, R.K. Critical Review on Toxic Contaminants in Surface Water Ecosystem: Sources, Monitoring, and Its Impact on Human Health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 56428–56462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S. Water Quality Prospective in Twenty First Century: Status of Water Quality in Major River Basins, Contemporary Strategies and Impediments: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- du Plessis, A.; du Plessis, A. Primary Water Quality Challenges, Contaminants and the World’s Dirtiest Places. In Water as an Inescapable Risk: Current Global Water Availability, Quality and Risks with a Specific Focus on South Africa; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 79–114. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Hernández, M.L.; Sánchez-Salinas, E.; Olvera-Velona, A.; Folch-Mallol, J.L. Pesticides in the Environment: Impacts and Their Biodegradation as a Strategy for Residues Treatment; Stoytcheva, M., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 551–574. [Google Scholar]
- Garnier, J.; Marescaux, A.; Guillon, S.; Vilmin, L.; Rocher, V.; Billen, G.; Thieu, V.; Silvestre, M.; Passy, P.; Raimonet, M. Ecological Functioning of the Seine River: From Long-Term Modelling Approaches to High-Frequency Data Analysis. In Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Science and Business Media Deutschland: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 189–216. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; Mao, J.; Xia, H.; Song, S.; Chen, W.; Zhao, D. Effect of Wastewater Treatment Plant Discharge on the Bacterial Community in a Receiving River. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 239, 113641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, T.; Yu, K.; Chai, B.; Tang, Q.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; He, L.; Lei, X.; Li, Y.; Meng, Y. Microplastics Increase the Microbial Functional Potential of Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Water Pollution in a Freshwater Lake: A Metagenomic Study. Environ. Res. 2024, 257, 119250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Chai, B.; Zhuo, T.; Tang, Q.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; He, L.; Lei, X.; Chen, B. Hydrostatic Pressure Drives Microbe-Mediated Biodegradation of Microplastics in Surface Sediments of Deep Reservoirs: Novel Findings from Hydrostatic Pressure Simulation Experiments. Water Res. 2023, 242, 120185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Ullah, M.I.; Sajjad, A.; Shakeel, Q.; Hussain, A. Environmental and Health Effects of Pesticide Residues. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 48: Pesticide Occurrence, Analysis and Remediation Vol. 2 Analysis; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 311–336. [Google Scholar]
- Varjani, S.; Joshi, R.; Srivastava, V.K.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. Treatment of Wastewater from Petroleum Industry: Current Practices and Perspectives. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 27172–27180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Bisht, B.; Joshi, V.; Singh, A.; Talwar, A. Physical, Chemical and Bacteriological Study of Water from Rivers of Uttarakhand. J. Hum. Ecol. 2010, 32, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; He, X.; Song, Y.; Tian, L.; Wu, H. Improving Aerobic Digestion of Food Waste by Adding a Personalized Microbial Inoculum. Curr. Microbiol. 2024, 81, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, C.; Hu, X. Biochar-Bacteria Coupling System Enhanced the Bioremediation of Phenol Wastewater-Based on Life Cycle Assessment and Environmental Safety Analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Liang, L.; Shi, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, L.; Xiao, J.; Huang, N.; Zhao, A.; Xia, Y.; Hou, J. Biofilms in Plastisphere from Freshwater Wetlands: Biofilm Formation, Bacterial Community Assembly, and Biogeochemical Cycles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 134930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azubuike, C.C.; Chikere, C.B.; Okpokwasili, G.C. Bioremediation Techniques–Classification Based on Site of Application: Principles, Advantages, Limitations and Prospects. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.-R.; Shang-Guan, P.-K.; Li, S.-H.; Zhang, C.-H.; Lou, J.-M.; Guo, L.; Liu, L.; Lu, Y. The Influence of Carbon Dioxide on Fermentation Products, Microbial Community, and Functional Gene in Food Waste Fermentation with Uncontrol pH. Environ. Res. 2025, 267, 120645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xia, Y.; Chen, L.; Yan, W.; Liu, B.; Jin, S. Full Recovery of Brines at Normal Temperature with Process-Heat-Supplied Coupled Air-Carried Evaporating Separation (ACES) Cycle. npj Clean Water 2024, 7, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitha, T.; Satyaprakash, M.; Vani, S.S.; Sadhana, B.; Padal, S. A Review on Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Their Transport, Fate and Biodegradation in the Environment. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci 2017, 6, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar]
- Navacharoen, A.; Vangnai, A.S. Biodegradation of Diethyl Phthalate by an Organic-Solvent-Tolerant Bacillus Subtilis Strain 3C3 and Effect of Phthalate Ester Coexistence. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2011, 65, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, G.-F.; Lu, H.; Jin, R.-F.; Zhou, J.-T.; Lei, T.-M. Biodegradation of Acid Orange 7 and Its Auto-Oxidative Decolorization Product in Membrane-Aerated Biofilm Reactor. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2012, 67, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doolotkeldieva, T.; Konurbaeva, M.; Bobusheva, S. Microbial Communities in Pesticide-Contaminated Soils in Kyrgyzstan and Bioremediation Possibilities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 31848–31862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Wu, S.; Zhu, W.; Liang, B.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J. Enhanced Geopolymerization of MSWI Fly Ash through Combined Activator Pretreatment: A Sustainable Approach to Heavy Metal Encapsulation and Resource Recovery. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Pandit, J.; Gautam, V.; Shirkot, P. Optimization of Culture Conditions for Maximizing Extracellular Organophosphorus Hydrolase Activity in Pseudomonas Strains with Chlorpyrifos Degradation Potential. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2019, 8, 322–326. [Google Scholar]
- Gangola, S.; Bhatt, P.; Kumar, A.J.; Bhandari, G.; Joshi, S.; Punetha, A.; Bhatt, K.; Rene, E.R. Biotechnological Tools to Elucidate the Mechanism of Pesticide Degradation in the Environment. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 133916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.; Iqbal, S.; Rauf, S.; Khalid, Z.M. Characteristics of Phenol Biodegradation in Saline Solutions by Monocultures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas pseudomallei. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Jiang, S.; Ou, J.; Kouadio, K.L.; Xiong, B. Multifaceted Anomaly Detection Framework for Leachate Monitoring in Landfills. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 368, 122130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Sun, X.; Yan, C.; Mao, M.; Lin, Z.; Liu, W. Stabilization of Arsenic Sulfide Sludge to Form Stable Johnbaumite by Alkaline-Oxidative Hydrothermal Treatment. ACS ES&T Eng. 2024, 4, 1657–1667. [Google Scholar]
- Odukkathil, G.; Vasudevan, N. Toxicity and Bioremediation of Pesticides in Agricultural Soil. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio. Technol. 2013, 12, 421–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Lin, D.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, Y.; Cai, L.; Fang, H.; Yu, Y. Biodegradation of DDT by Stenotrophomonas Sp. DDT-1: Characterization and Genome Functional Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, A.; Singh, J. Biodegradation of DDT. J. Text. Sci. Eng. 2015, 5, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Murugesan, A.; Jeyasanthi, T.; Maheswari, S. Isolation and Characterization of Cypermethrin Utilizing Bacteria from Brinjal Cultivated Soil. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 4, 010–013. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza, J.; Perea, Y.; Salvador, J. Bacterial Biodegradation of Permetrina and Cipermetrina Pesticides in a Culture Assemblage. Av. Cienc. Ing. 2011, 2, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Bordjiba, O.; Steiman, R.; Kadri, M.; Semadi, A.; Guiraud, P. Removal of Herbicides from Liquid Media by Fungi Isolated from a Contaminated Soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitte, I.; Duran, R.; Hernandez-Raquet, G.; Mounier, J.; Jézéquel, R.; Bellet, V.; Balaguer, P.; Caumette, P.; Cravo-Laureau, C. Dynamics of Metabolically Active Bacterial Communities Involved in PAH and Toxicity Elimination from Oil-Contaminated Sludge during Anoxic/Oxic Oscillations. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 4199–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anh, H.T.H.; Shahsavari, E.; Bott, N.J.; Ball, A.S. Bioaugmentation of Seafood Processing Wastewater Enhances the Removal of Inorganic Nitrogen and Chemical Oxygen Demand. Aquaculture 2021, 542, 736818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zi, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Gao, H.; Hu, N. Marinobacter hydrocarbonoclasticus NY-4, a Novel Denitrifying, Moderately Halophilic Marine Bacterium. SpringerPlus 2013, 2, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X.-Y.; Ai, G.-M.; Miao, L.-L.; Liu, Z.-P. Characterization of a Marine Origin Aerobic Nitrifying–Denitrifying Bacterium. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 114, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenati, B.; Chebbi, A.; Badis, A.; Eddouaouda, K.; Boutoumi, H.; El Hattab, M.; Hentati, D.; Chelbi, M.; Sayadi, S.; Chamkha, M. A Non-Toxic Microbial Surfactant from Marinobacter Hydrocarbonoclasticus SdK644 for Crude Oil Solubilization Enhancement. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 154, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javaid, M.M.; Mahmood, A.; Bhatti, M.I.N.; Waheed, H.; Attia, K.; Aziz, A.; Nadeem, M.A.; Khan, N.; Al-Doss, A.A.; Fiaz, S. Efficacy of Metribuzin Doses on Physiological, Growth, and Yield Characteristics of Wheat and Its Associated Weeds. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 866793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Authority, E.F.S.; Álvarez, F.; Arena, M.; Auteri, D.; Leite, S.B.; Binaglia, M.; Castoldi, A.F.; Chiusolo, A.; Cioca, A.; Colagiorgi, A. Peer Review of the Pesticide Risk Assessment of the Active Substance Metribuzin. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e08140. [Google Scholar]
- Samir, D.; Selma, R.M.O.; Asma, S. The Effect of Herbicide Metribuzin on Environment and Human: A Systematic Review. Pharm. Biosci. J. 2020, 8, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Heidrich, E.S.; Dolfing, J.; Jarvis, A.P. Determination of the Relationship between the Energy Content of Municipal Wastewater and Its Chemical Oxygen Demand. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 15705:2002; Water Quality—Determination of the Chemical Oxygen Demand Index (ST-COD)—Small-Scale Sealed-Tube Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Mirzavand, S.; Aeini, M.; Najafgholi, H.M.; Rezamahalleh, H.M. Identification and Characterization of Bacterial Strains Capable of Degrading Atrazine and Metribuzin Herbicides in Sugarcane Fields. Sugar Tech 2024, 26, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, G.K.; Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Datta, S.; Singh, J. Toxicity, Monitoring and Biodegradation of Organophosphate Pesticides: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 1135–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, T.; Boopathy, R. Biotransformation of Metribuzin under Various Electron Acceptor Conditions. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2022, 32, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahla, A.Q.; Iqbal, S.; Anwar, S.; Firdous, S.; Mueller, J.A. Optimizing the Metribuzin Degrading Potential of a Novel Bacterial Consortium Based on Taguchi Design of Experiment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Zaidi, A.; Saghir Khan, M. Modulations in Growth, Structure, Cell Viability and Antioxidant Enzyme of a Nodule Bacterium Mesorhizobium Ciceri Induced by Pesticides. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 4103–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamleh, A.A.; Danish, M.; Al-Dosary, M.A.; El-Zaidy, M.; Ali, S. Physiological and Oxidative Stress Responses of Solanum lycopersicum (L.) (Tomato) When Exposed to Different Chemical Pesticides. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 7237–7252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Yadav, A.N.; Saxena, R.; Paul, D.; Tomar, R.S. Biodiversity of Pesticides Degrading Microbial Communities and Their Environmental Impact. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 101883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.; Srivastava, P.; Devi, R.S.; Bhadouria, R. Influence of Synthetic Fertilizers and Pesticides on Soil Health and Soil Microbiology. In Agrochemicals Detection, Treatment and Remediation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 25–54. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, V.M.; Verma, V.K.; Rawat, B.S.; Kaur, B.; Babu, N.; Sharma, A.; Dewali, S.; Yadav, M.; Kumari, R.; Singh, S. Current Status of Pesticide Effects on Environment, Human Health and It’s Eco-Friendly Management as Bioremediation: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 962619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushchak, V.I.; Matviishyn, T.M.; Husak, V.V.; Storey, J.M.; Storey, K.B. Pesticide Toxicity: A Mechanistic Approach. EXCLI J. 2018, 17, 1101. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, M.; Khan, M.S.; Singh, U.B. Pesticide-Tolerant Microbial Consortia: Potential Candidates for Remediation/Clean-up of Pesticide-Contaminated Agricultural Soil. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebai, H.; Sholkamy, E.N.; Abdelhamid, M.A.; Prakasam Thanka, P.; Aly Hassan, A.; Pack, S.P.; Ki, M.-R.; Boudemagh, A. Soil Actinobacteria Exhibit Metabolic Capabilities for Degrading the Toxic and Persistent Herbicide Metribuzin. Toxics 2024, 12, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essa, A.; Reyad, A.M.; Radwan, T.; Ibrahim, W.M. Biodegradation of the Organophosphorus Insecticide Diazinon by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Isolated from Agricultural Drainage Ditches. Egypt. J. Bot. 2016, 56, 353–370. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Hao, Z.H.; Zhang YuBin, Z.Y.; Hou ZhiGuang, H.Z.; Wu Xian, W.X.; Gao HeNan, G.H.; Sun, F.; Pan HongYu, P.H. Biodegradation of Triazine Herbicide Metribuzin by the Strain Bacillus sp. N1. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2014, 49, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, G.; Tafese, T.; Abda, E.M.; Kamaraj, M.; Assefa, F. Factors Influencing the Bacterial Bioremediation of Hydrocarbon Contaminants in the Soil: Mechanisms and Impacts. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 9823362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanang, M.; Fuad, N.; Didik, R.; Topo, S.; Panuwun, J. Effect of Alkaline Fluids to Blood pH and Lactic Acid Changes on Sub Maximal Physical Exercise; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 197, p. 012049. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, M.S.; Thangadurai, T.D.; Manjubaashini, N.; Nataraj, D. Walnut Shell Biomass Waste Derived Excitation-Dependent CQDs for Toxic Insecticide Sensing and Protein Denaturation Inhibition–An Ecofriendly and Sustainable Approach. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 136, 110021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, N.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, W.; Ma, Y.; Niu, Z. Colonization Characteristics of Bacterial Communities on Plastic Debris Influenced by Environmental Factors and Polymer Types in the Haihe Estuary of Bohai Bay, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10763–10773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Ran, X.; Liu, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhong, X.; Jiao, N. Effectiveness of Chemical Oxygen Demand as an Indicator of Organic Pollution in Aquatic Environments. Ocean.-Land-Atmos. Res. 2024, 3, 0050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahraoui, H.; Toumi, S.; Boudoukhani, M.; Touzout, N.; Sid, A.N.E.H.; Amrane, A.; Belhadj, A.-E.; Hadjadj, M.; Laichi, Y.; Aboumustapha, M. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Coagulation–Flocculation Treatment Using Aluminum Sulfate on a Polluted Surface Water Source: A Year-Long Study. Water 2024, 16, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Ahmad, H.W. Investigation of the Persistence, Toxicological Effects, and Ecological Issues of S-Triazine Herbicides and Their Biodegradation Using Emerging Technologies: A Review. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutua, G.K.; Ngigi, A.N.; Getenga, Z.M. Degradation Characteristics of Metribuzin in Soils within the Nzoia River Drainage Basin, Kenya. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2016, 98, 800–813. [Google Scholar]
- García-Prieto, J.C.; González-Burciaga, L.A.; Proal-Nájera, J.B.; García-Roig, M. Study of Influence Factors in the Evaluation of the Performance of a Photocatalytic Fibre Reactor (TiO2/SiO2) for the Removal of Organic Pollutants from Water. Catalysts 2022, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svierzoski, N.D.S.; Matheus, M.C.; Bassin, J.P.; Brito, Y.D.; Mahler, C.F.; Webler, A.D. Treatment of a Slaughterhouse Wastewater by Anoxic–Aerobic Biological Reactors Followed by UV-C Disinfection and Microalgae Bioremediation. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, J.; Huiliñir, C.; Salazar, R. Removal of Organic Matter Contained in Slaughterhouse Wastewater Using a Combination of Anaerobic Digestion and Solar Photoelectro-Fenton Processes. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 210, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameters | Values | Limit Values |
|---|---|---|
| COD (mg/L) | 1700 | 800 |
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 1600 | 250 |
| pH | 8 | 6.5–8.5 |
| T (°C) | 11.5 | 30 |
| Polluants | Optic Density (600 nm) | Operating Condition | Efficiency (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrène | 1.8 | C0 = 100 mg/L T = 30 °C pH = 7 inoculation = 2% Time = 14 day | 38 | [42] |
| Anthracène | 1.6 | 31 | ||
| Naphtalène | 1.1 | Low effeciency | ||
| Phénanthrène | 0.3 | |||
| Metribuzine | 0.5 | C0 = 20 mg/L T = 30 °C pH = 7 inoculation = 4% Time = 6 day | 80 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mihoubi, N.; Ferhat, S.; Nedjhioui, M.; Zenati, B.; Lekmine, S.; Boudraa, R.; Ola, M.S.; Zhang, J.; Amrane, A.; Tahraoui, H. A Novel Halophilic Bacterium for Sustainable Pollution Control: From Pesticides to Industrial Effluents. Water 2025, 17, 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060888
Mihoubi N, Ferhat S, Nedjhioui M, Zenati B, Lekmine S, Boudraa R, Ola MS, Zhang J, Amrane A, Tahraoui H. A Novel Halophilic Bacterium for Sustainable Pollution Control: From Pesticides to Industrial Effluents. Water. 2025; 17(6):888. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060888
Chicago/Turabian StyleMihoubi, Nadia, Samira Ferhat, Mohamed Nedjhioui, Billal Zenati, Sabrina Lekmine, Reguia Boudraa, Mohammad Shamsul Ola, Jie Zhang, Abdeltif Amrane, and Hichem Tahraoui. 2025. "A Novel Halophilic Bacterium for Sustainable Pollution Control: From Pesticides to Industrial Effluents" Water 17, no. 6: 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060888
APA StyleMihoubi, N., Ferhat, S., Nedjhioui, M., Zenati, B., Lekmine, S., Boudraa, R., Ola, M. S., Zhang, J., Amrane, A., & Tahraoui, H. (2025). A Novel Halophilic Bacterium for Sustainable Pollution Control: From Pesticides to Industrial Effluents. Water, 17(6), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060888










