Assessing the Impact of Often Overlooked Snowfall on the Hydrological Balance of Apennine Mountain Aquifers in Central Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Hydrogeological Overview
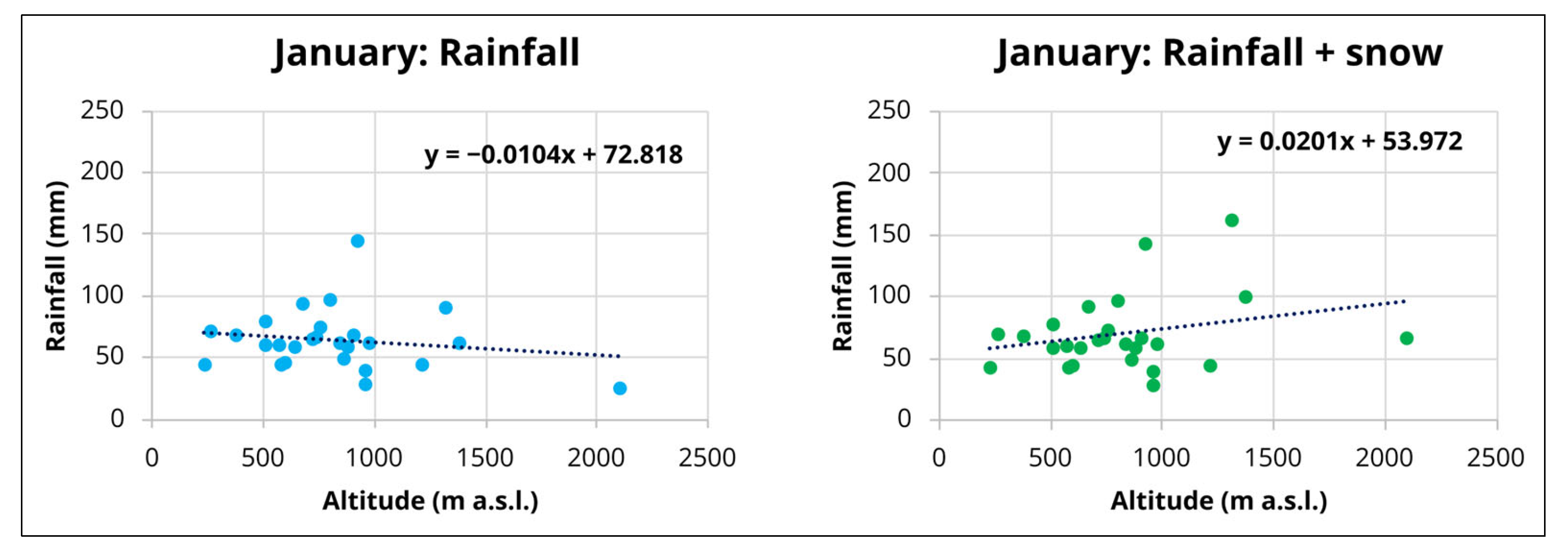
2.2. Hydrological Balance and Data Elaboration
3. Results and Discussion
- The reference periods are different from those of the present study, and some are referred to periods of the last century with thermometric and pluviometric regimes, even if averaged over many years, that are different from those of the present study.
- The duration of the periods analyzed varies from a few dozen years to a few years,
- The number of analyzed springs varies from author to author.
- In many balances, only the basal springs with flow rates higher than tens of L/s are considered, while those, even if numerous, with flow rates lower than tens of L/s are excluded from the calculation.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grossi, G.; Lendvai, A.; Peretti, G.; Ranzi, R. Snow Precipitation Measured by Gauges: Systematic Error Estimation and Data Series Correction in the Central Italian Alps. Water 2017, 9, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán-Tejeda, E.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Beniston, M. The Changing Roles of Temperature and Precipitation on Snowpack Variability in Switzerland as a Function of Altitude. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2131–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, A.J.; Kuenzer, C.; Gessner, U.; Dech, S. Remote Sensing of Snow—A Review of Available Methods. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 4094–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagnati, A.; Crepaz, A.; Macelloni, G.; Pampaloni, P.; Ranzi, R.; Tedesco, M.; Tomirotti, M.; Valt, M. Study of the Snow Melt–Freeze Cycle Using Multi-Sensor Data and Snow Modeling. J. Glaciol. 2004, 50, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celico, P. Schema Idrogeologico Dell’Appennino Carbonatico Centro-Meridionale. Mem. E Note Dell’istituto Di Geol. Appl. Dell’università Di Napoli 1979, 14, 5–97. [Google Scholar]
- Mastrorillo, L.; Baldoni, T.; Banzato, F.; Boscherini, A.; Cascone, D.; Checcucci, R.; Petitta, M.; Boni, C. Quantitative Hydrogeological Analysis of the Carbonate Domain of the Umbria Region (Central Italy). Ital. J. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2009, 1, 137–156. [Google Scholar]
- Mastrorillo, L.; Petitta, M. Effective Infiltration Variability in the Umbria-Marche Carbonate Aquifers of Central Italy. J. Mediterr. Earth Sci. 2010, 2, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanni, T.; Desiderio, G.; Fochi Vici, C.; Petitta, M.; Ruggieri, G.; Rusi, S.; Tallini, M.; Vivalda, P.M. Schema Idrogeologico Dell’Italia Centro-Adriatica. Scala 1:250.000; CNR GNDCI: Perugia, Italy, 2011; ISBN 9788890652912. [Google Scholar]
- The KARMA Project Mediterranean Karst Aquifer Map. Available online: https://download.bgr.de/bgr/grundwasser/MEDKAM/pdf/MEDKAM_v1.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Taylor, C.J.; Greene, E.A. Hydrogeologic Characterization and Methods Used in the Investigation of Karst Hydrology. In Field Techniques for Estimating Water Fluxes Between Surface Water and Ground Water; Rosenberry, D.O., LaBaugh, J.W., Eds.; U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2008; pp. 71–114. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, A.; Mudarra, M.; Andreo, B.; Marín, A.; Wagener, T.; Lange, J. Modeling Spatiotemporal Impacts of Hydroclimatic Extremes on Groundwater Recharge at a Mediterranean Karst Aquifer. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 6507–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Gleeson, T.; Wada, Y.; Wagener, T. Enhanced Groundwater Recharge Rates and Altered Recharge Sensitivity to Climate Variability through Subsurface Heterogeneity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2842–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Mata, L.J.; Arnell, N.W.; DÖLL, P.; Jimenez, B.; Miller, K.; Oki, T.; ŞEN, Z.; Shiklomanov, I. The Implications of Projected Climate Change for Freshwater Resources and Their Management. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2008, 53, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, R.L.; Moratiel, R.; Song, Z.; Swelam, A.; Jomaa, I.; Shapland, T. Evapotranspiration Response to Climate Change. Acta Hortic. 2011, 922, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtew, W.; Melesse, A. Climate Change and Evapotranspiration. In Evaporation Evapotranspiration; Springer: Dordrecht, The Ntherlands, 2013; pp. 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanke, J.; Liesch, T. Quantification and Possible Causes of Declining Groundwater Resources in the Euro-Mediterranean Region from 2003 to 2020. Hydrogeol. J. 2022, 30, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, V.; Sbarbati, C.; Banzato, F.; Lacchini, A.; Petitta, M. Recharge Assessment of the Gran Sasso Aquifer (Central Italy): Time-Variable Infiltration and Influence of Snow Cover Extension. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 41, 101090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, V.; Barberio, M.D.; Sbarbati, C.; Petitta, M. Groundwater Recharge Distribution Due to Snow Cover in Shortage Conditions (2019–22) on the Gran Sasso Carbonate Aquifer (Central Italy). Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scozzafava, M.; Tallini, M. Net Infiltration in the Gran Sasso Massif of Central Italy Using the Thornthwaite Water Budget and Curve-Number Method. Hydrogeol. J. 2001, 9, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitta, M.; Banzato, F.; Lorenzi, V.; Matani, E.; Sbarbati, C. Determining Recharge Distribution in Fractured Carbonate Aquifers in Central Italy Using Environmental Isotopes: Snowpack Cover as an Indicator for Future Availability of Groundwater Resources. Hydrogeol. J. 2022, 30, 1619–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanni, T.; Rusi, S. Idrogeologia Del Massiccio Carbonatico Della Montagna Della Majella (Appennino Centrale). Boll. Soc. Geol. Ital. 2003, 122, 173–202. [Google Scholar]
- Chiaudani, A.; Di Curzio, D.; Rusi, S. The Snow and Rainfall Impact on the Verde Spring Behavior: A Statistical Approach on Hydrodynamic and Hydrochemical Daily Time-Series. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Curzio, D.; Di Giovanni, A.; Lidori, R.; Marzano, F.S.; Rusi, S. Investigating the Feasibility of Using Precipitation Measurements from Weather RaDAR to Estimate Potential Recharge in Regional Aquifers: The Majella Massif Case Study in Central Italy. Acque Sotter. Ital. J. Groundw. 2022, 11, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Curzio, D.; Di Giovanni, A.; Lidori, R.; Montopoli, M.; Rusi, S. Comparing Rain Gauge and Weather RaDAR Data in the Estimation of the Pluviometric Inflow from the Apennine Ridge to the Adriatic Coast (Abruzzo Region, Central Italy). Hydrology 2022, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, C.; Bono, P.; Capelli, G. Schema Idrogeologico Dell’Italia Centrale. Mem. Della Soc. Geol. Ital. 1986, 35, 991–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Percopo, C.; Brandolin, D.; Canepa, M.; Capodaglio, P.; Cipriano, G.; Gafà, R.; Iervolino, D.; Marcaccio, M.; Mazzola, M.; Mottola, A.; et al. Criteri Tecnici per Lo Stato Quantitativo e Il Monitoraggio Dei Corpi Idrici Sotterranei; ISPRA—Manuali e Linee Guida 157/2017; ISPRA: Rome, Italy, 2017; pp. 10–30. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings, K.S.; Winchell, T.S.; Livneh, B.; Molotch, N.P. Spatial Variation of the Rain-Snow Temperature Threshold across the Northern Hemisphere. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusi, S.; Di Curzio, D.; Di Giovanni, A. Hydrodynamic Characterization of Carbonate Aquifers Using Atypical Pumping Tests without the Interruption of the Drinking Water Supply. Water 2024, 16, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, A.; García-Ortega, E.; Merino, A.; Sánchez, J.L.; Tapiador, F.J. Orographic Biases in IMERG Precipitation Estimates in the Ebro River Basin (Spain): The Effects of Rain Gauge Density and Altitude. Atmos. Res. 2020, 244, 105068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turc, L. Le Bilan d’eau Des Sols: Relation Entre Les Précipitations, l’évaporation et l’écoulement. Journées L’hydraulique 1954, 3, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Thornthwaite, C.W.; Mather, J.R. Instruction and Tables for Computing Potential Evapotranspiration and Water Balance. Climatology 1957, 10, 185–311. [Google Scholar]
- Celico, P. Prospezioni Idrogeologiche; Liguori Editore: Naples, Italy, 1988; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- Cassa per il Mezzogiorno; Celico, P. Idrogeologia Dell’Italia Centro-Meridionale. Progetti Speciali per Gli Schemi Idrici Nel Mezzogiorno. Quad. Della Cassa Per Il Mezzog. 1983, 4, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Autorità di Bacino Distrettuale dell’Appennino Centrale (AUBAC). Schede Monografiche Dei Corpi Idrici Sotterranei Del Distretto Dell’Appennino Centrale; Autorità di Bacino Distrettuale dell’Appennino Centrale (AUBAC): Rome, Italy, 2021; pp. 4–526.
- Petitta, M.; Tallini, M. Idrodinamica Sotterranea Del Massiccio Del Gran Sasso (Abruzzo): Nuove Indagini Idrologiche, Idrogeologiche e Idrochimiche (1994–2001). Boll. Della Soc. Geol. Ital. 2002, 121, 343–363. [Google Scholar]
- Regione Abruzzo. Piano Di Tutela Delle Acque (PTA)—Relazione Idrogeologica (Elab. A1.2); 2008. Available online: https://www.regione.abruzzo.it/pianoTutelaacque/docs/elaboratiPiano/A1_2/A1_2RelazioneIdrogeologica.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Conese, M.; Nanni, T.; Peila, C.; Rusi, S.; Salvati, R. Idrogeologia Della Montagna Del Morrone (Appennino Abruzzese): Dati Preliminari. Mem. Della Soc. Geol. 2001, 56, 181–196. [Google Scholar]
- Boni, C.; Ruisi, M. Carta Idrogeologica Della Marsica Orientale (M. Marsicano—M.Gna Grande) Scala 1:50.000; Pubblicazione GNDCI-CNR: Rome, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]

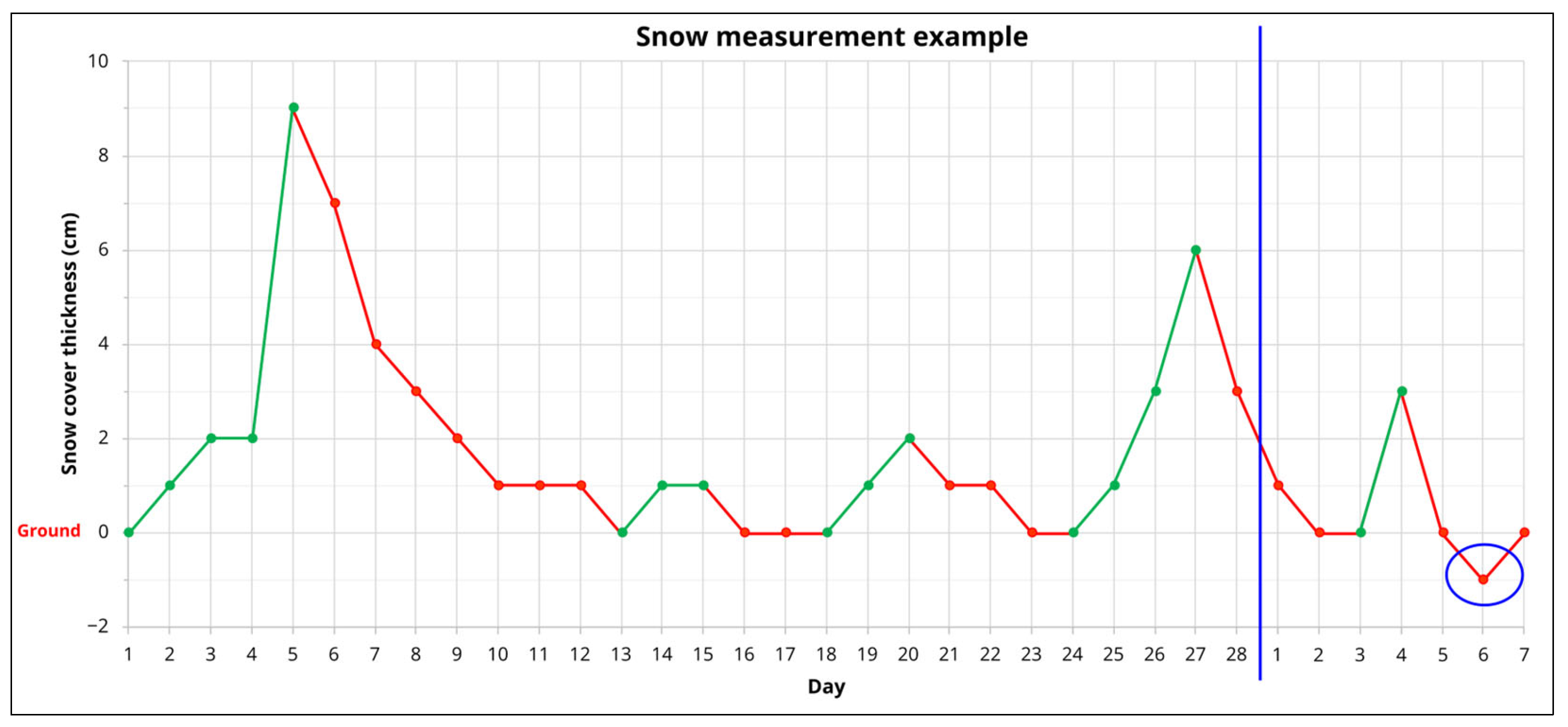
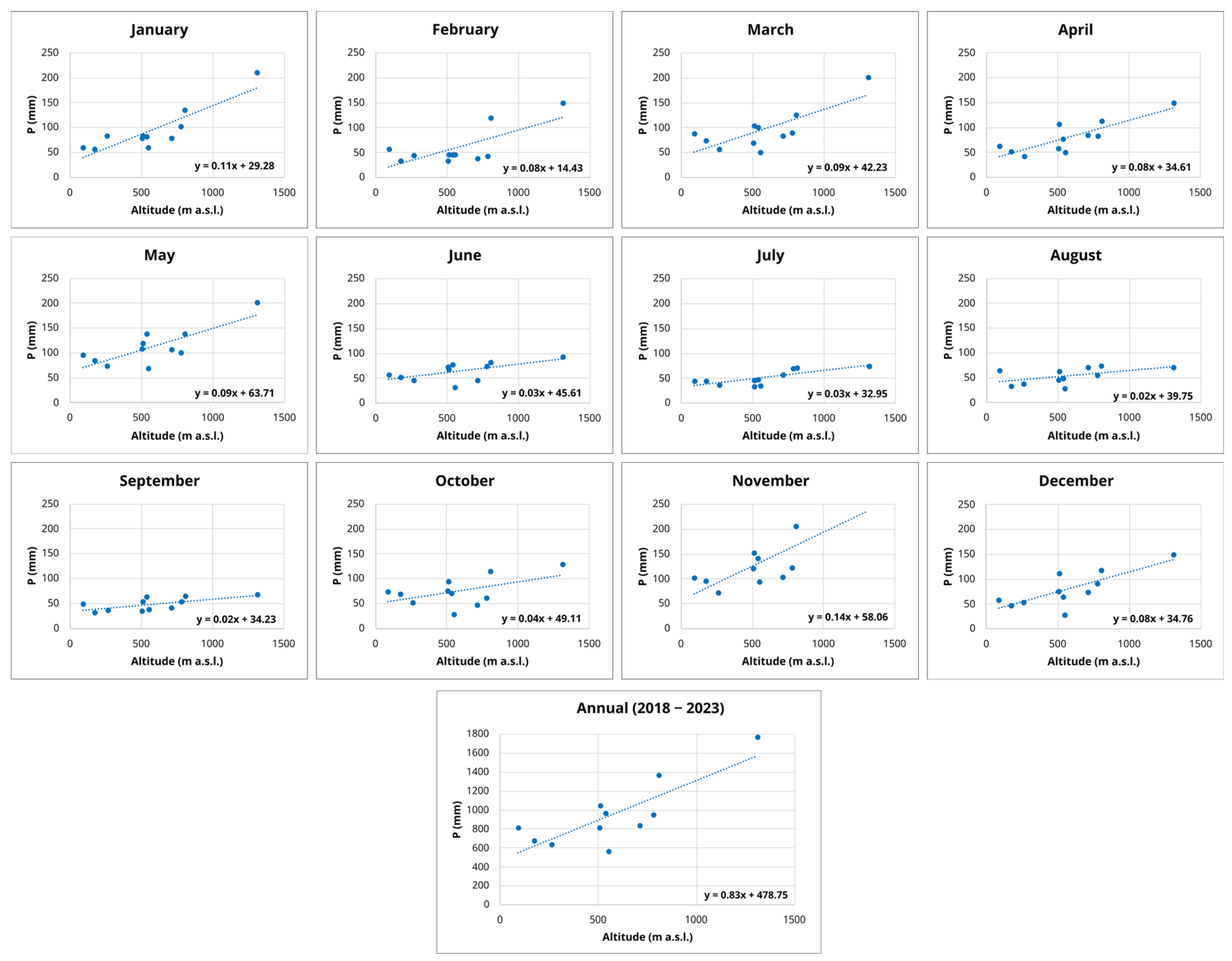

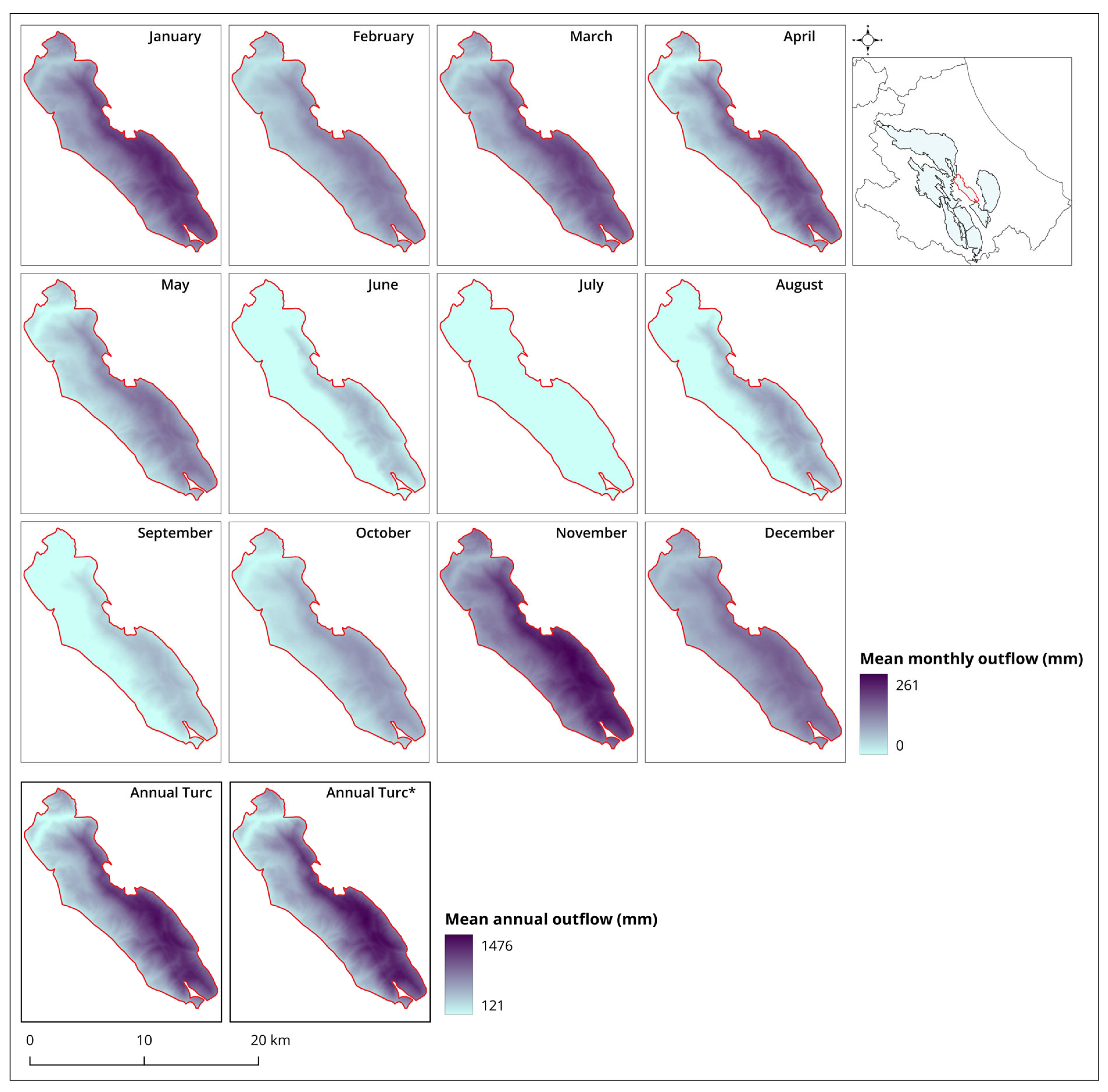
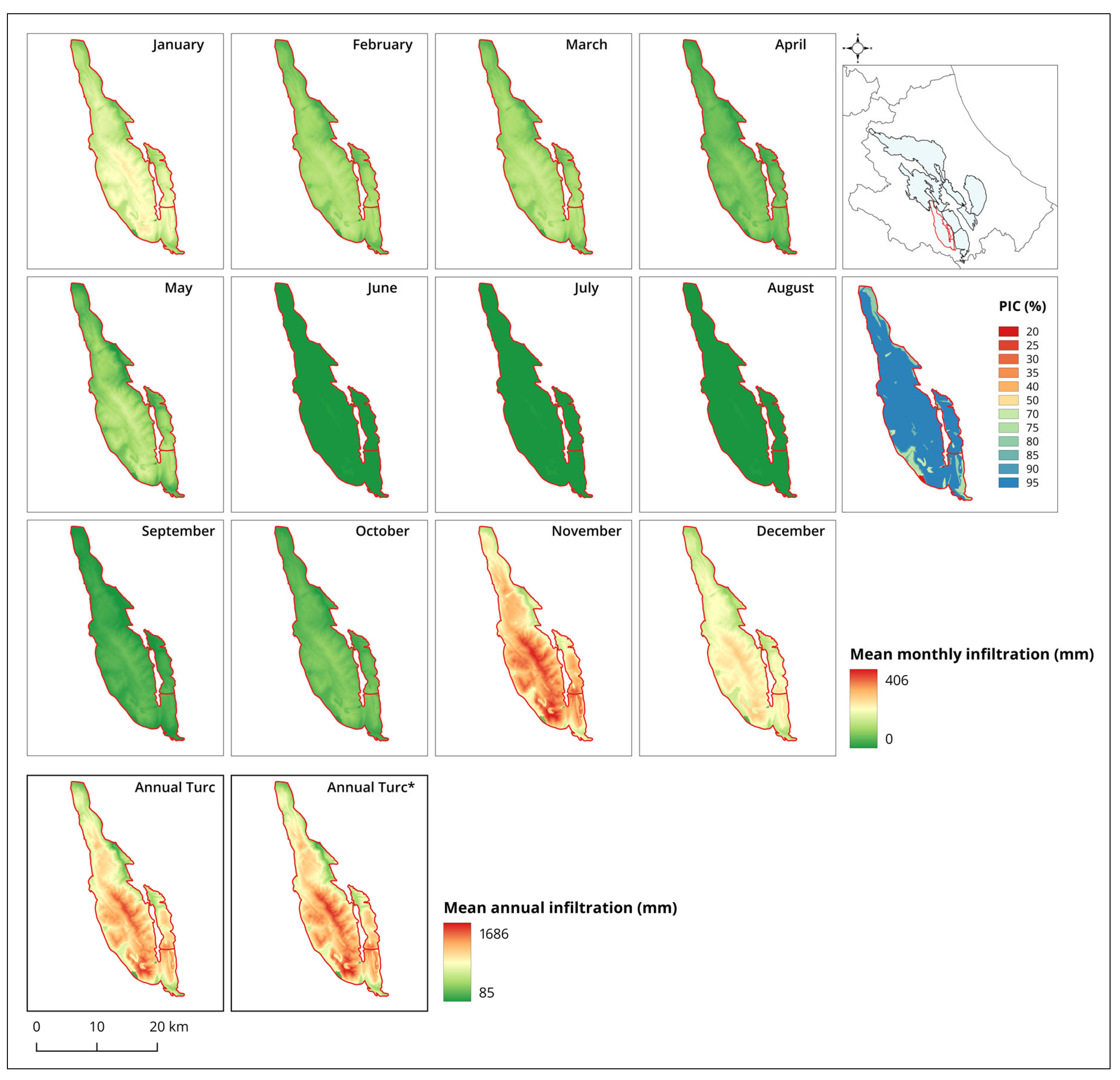
| Station Name | Altitude (m a.s.l.*) | Mean Annual Value (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Campotosto Diga | 1313 | 215 |
| Caramanico Terme | 805 | 92 |
| L’Aquila, Campo Imperatore | 2094 | 256 |
| Ovindoli | 1375 | 150 |
| Pretoro, Passo Lanciano | 1310 | 256 |
| Roccaraso | 1231 | 140 |
| Scanno, Passo Godi | 1542 | 212 |
| Majella Infiltration | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfall and Snow Inflow | Only Rainfall Inflow | |||||||||||||
| mm | L/s | mm | L/s | |||||||||||
| Min | Max | Mean | Std. Dev | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Std. Dev | Min | Max | Mean | |
| Thornth | 1090 | 494 | 9903 | 844 | 357 | 7671 | ||||||||
| Turc | 19 | 2279 | 1069 | 523 | 173 | 20,701 | 9710 | 28 | 1713 | 822 | 385 | 254 | 15,560 | 7467 |
| Turc* | 25 | 2346 | 1107 | 534 | 227 | 21,310 | 10,055 | 33 | 1752 | 846 | 391 | 300 | 15,914 | 7685 |
| Monte Morrone Infiltration | ||||||||||||||
| Thornth | 780 | 382 | 2637 | 716 | 339 | 2242 | ||||||||
| Turc | 47 | 1346 | 634 | 322 | 159 | 4555 | 2145 | 48 | 1209 | 579 | 284 | 162 | 4090 | 1959 |
| Turc* | 54 | 1402 | 668 | 331 | 181 | 4741 | 2261 | 54 | 1236 | 602 | 286 | 186 | 4181 | 2036 |
| Monte Marsicano Infiltration | ||||||||||||||
| Thornth | 1016 | 274 | 7535 | 893 | 218 | 6623 | ||||||||
| Turc | 86 | 1620 | 973 | 284 | 637 | 12,009 | 7215 | 85 | 1374 | 855 | 230 | 630 | 10,108 | 6340 |
| Turc* | 92 | 1686 | 1019 | 293 | 683 | 12,502 | 7556 | 91 | 1416 | 889 | 234 | 675 | 10,500 | 6592 |
| Gran Sasso Infiltration | ||||||||||||||
| Thornth | 457 | 140 | 18,197 | 391 | 93 | 15,558 | ||||||||
| Turc | 35 | 997 | 409 | 154 | 1405 | 39,683 | 16,270 | 44 | 743 | 342 | 105 | 1751 | 29,564 | 13,608 |
| Turc* | 39 | 1027 | 427 | 157 | 1560 | 40,845 | 16,994 | 48 | 772 | 361 | 109 | 1910 | 30,718 | 14,364 |
| Genzana–Greco Infiltration | ||||||||||||||
| Thornth | 688 | 121 | 6036 | 610 | 82 | 5354 | ||||||||
| Turc | 110 | 937 | 630 | 122 | 965 | 8224 | 5530 | 110 | 765 | 556 | 83 | 965 | 6714 | 4880 |
| Turc* | 117 | 978 | 662 | 126 | 1027 | 8584 | 5810 | 116 | 787 | 579 | 83 | 1018 | 6908 | 5082 |
| Monte Porrara Infiltration | ||||||||||||||
| Thornth | 490 | 124 | 1447 | 460 | 110 | 1360 | ||||||||
| Turc | 76 | 765 | 443 | 131 | 226 | 2226 | 1309 | 71 | 679 | 403 | 113 | 210 | 2007 | 1191 |
| Turc* | 81 | 787 | 462 | 132 | 239 | 2326 | 1367 | 76 | 701 | 423 | 115 | 225 | 2072 | 1250 |
| Majella | Variation |
| Thornthwaite | 29% |
| Turc | 30% |
| Turc* | 31% |
| Monte Morrone | Variation |
| Thornthwaite | 14% |
| Turc | 14% |
| Turc* | 15% |
| Monte Marsicano | Variation |
| Thornthwaite | 9% |
| Turc | 10% |
| Turc* | 11% |
| Gran Sasso | Variation |
| Thornthwaite | 17% |
| Turc | 20% |
| Turc* | 18% |
| Genzana–Greco | Variation |
| Thornthwaite | 13% |
| Turc | 13% |
| Turc* | 14% |
| Monte Porrara | Variation |
| Thornthwaite | 7% |
| Turc | 10% |
| Turc* | 9% |
| Majella | ||
| Data Source | Mean infiltration (L/s) | Mean infiltration (mm) |
| Thornthwaite | 9903 | 1089 |
| Turc | 9710 | 1069 |
| Turc* | 10,055 | 1107 |
| Data Source | Discharge (L/s) | Discharge (mm) |
| Abruzzo Region [36] | 8773 | 966 |
| Monte Morrone | ||
| Data Source | Infiltration (L/s) | Mean infiltration (mm) |
| Thornthwaite | 2637 | 780 |
| Turc | 2145 | 634 |
| Turc* | 2261 | 668 |
| Data Source | Discharge (L/s) | Discharge (mm) |
| Conese et al. [37] | 1475 | 436 |
| Monte Marsicano | ||
| Data Source | Infiltration (L/s) | Mean infiltration (mm) |
| Thornthwaite | 7535 | 1016 |
| Turc | 7215 | 973 |
| Turc* | 7556 | 1019 |
| Data Source | Discharge (L/s) | Discharge (mm) |
| Boni & Ruisi [38] | 7900 | 1065 |
| Monte Porrara | ||
| Data Source | Infiltration (L/s) | Mean infiltration (mm) |
| Thornthwaite | 1447 | 490 |
| Turc | 1309 | 443 |
| Turc* | 1367 | 462 |
| Data Source | Discharge (L/s) | Discharge (mm) |
| Abruzzo Region [36] | 1460 | 494 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rusi, S.; Di Giovanni, A. Assessing the Impact of Often Overlooked Snowfall on the Hydrological Balance of Apennine Mountain Aquifers in Central Italy. Water 2025, 17, 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060864
Rusi S, Di Giovanni A. Assessing the Impact of Often Overlooked Snowfall on the Hydrological Balance of Apennine Mountain Aquifers in Central Italy. Water. 2025; 17(6):864. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060864
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusi, Sergio, and Alessia Di Giovanni. 2025. "Assessing the Impact of Often Overlooked Snowfall on the Hydrological Balance of Apennine Mountain Aquifers in Central Italy" Water 17, no. 6: 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060864
APA StyleRusi, S., & Di Giovanni, A. (2025). Assessing the Impact of Often Overlooked Snowfall on the Hydrological Balance of Apennine Mountain Aquifers in Central Italy. Water, 17(6), 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060864








