Hydrochemical Processes, Mineral Scaling and Water Quality of Geothermal Waters in Sichuan Basin, Southwestern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological and Geothermal Setting
3. Materials and Methods
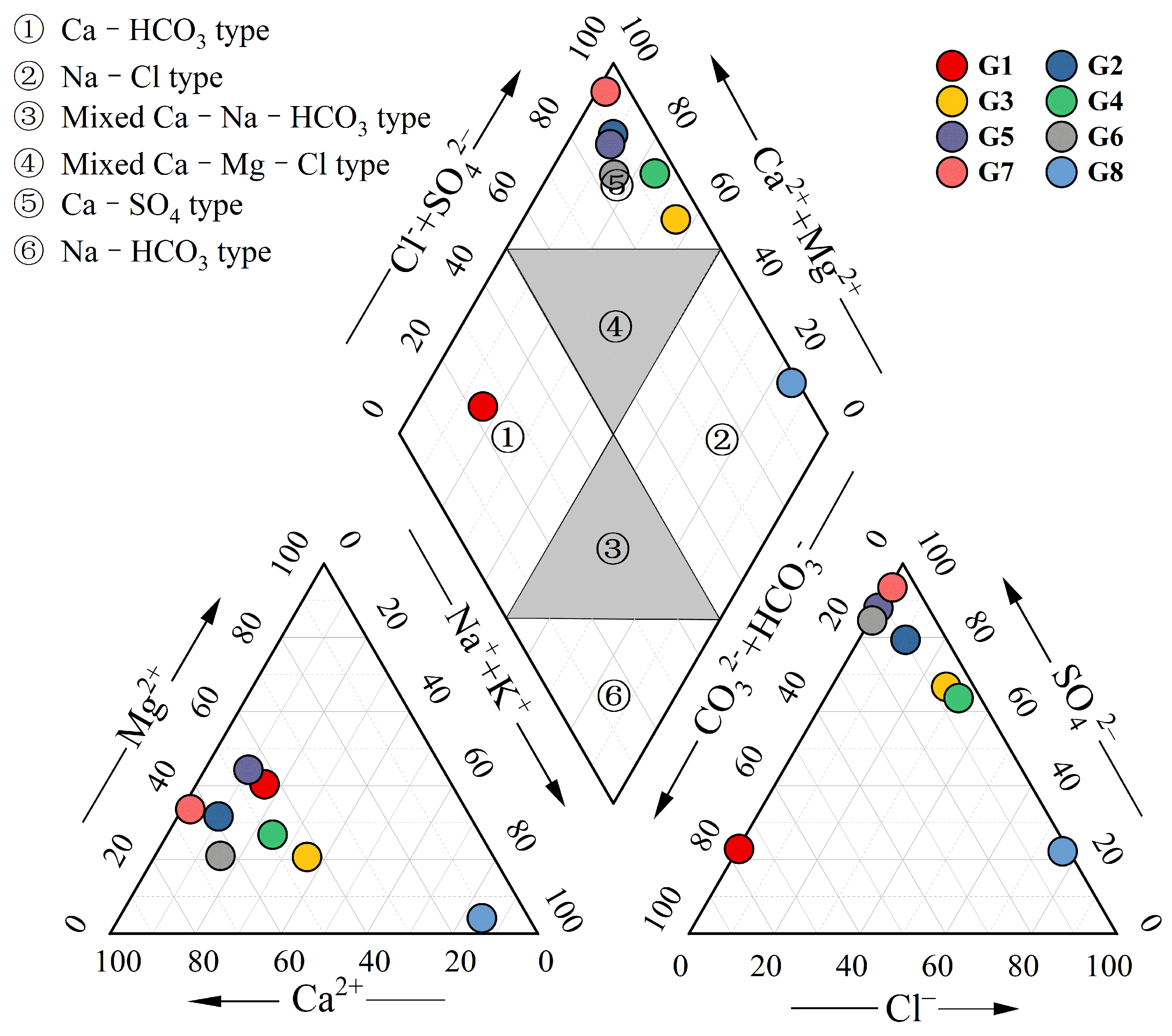
4. Hydrochemical Results
5. Discussion
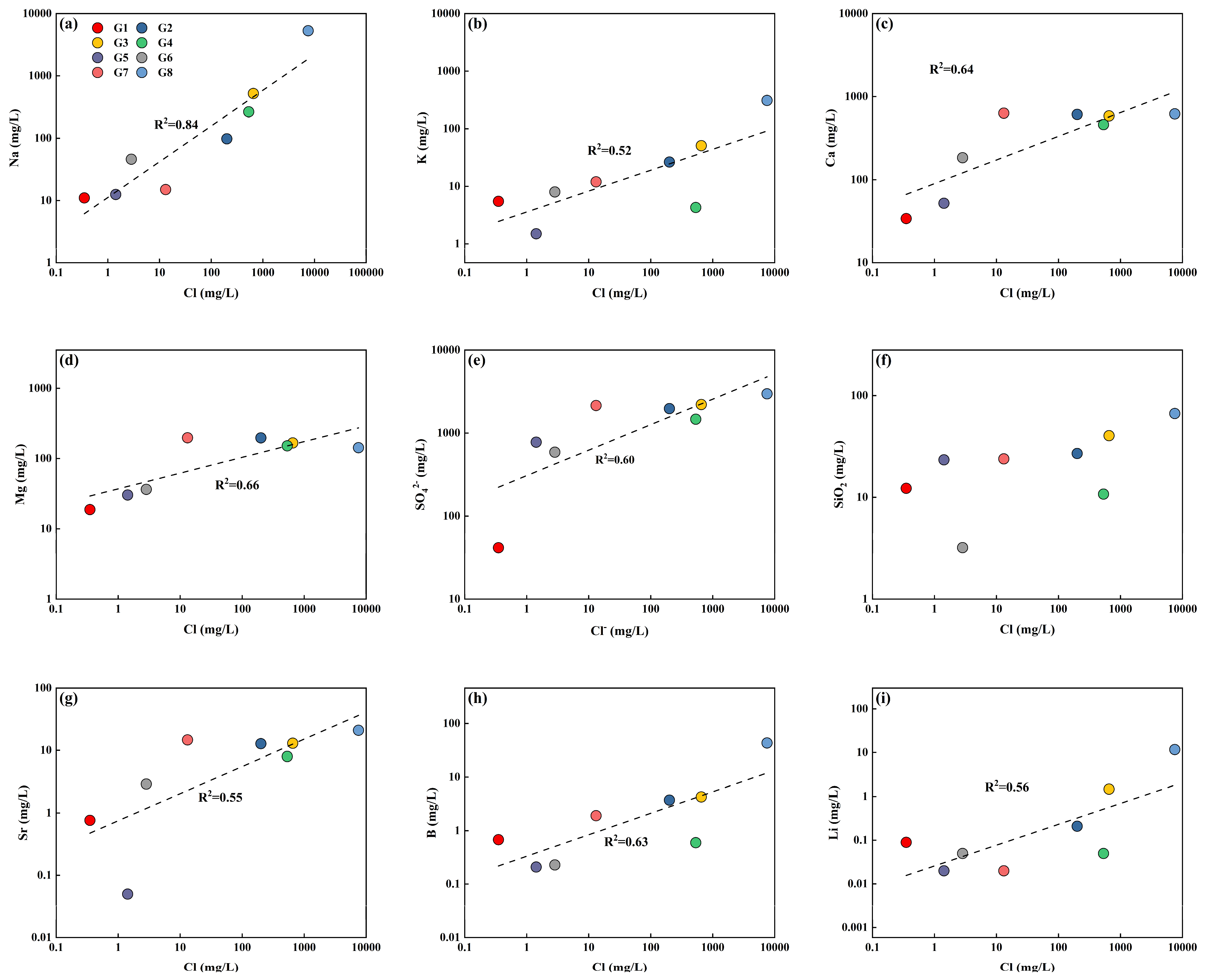
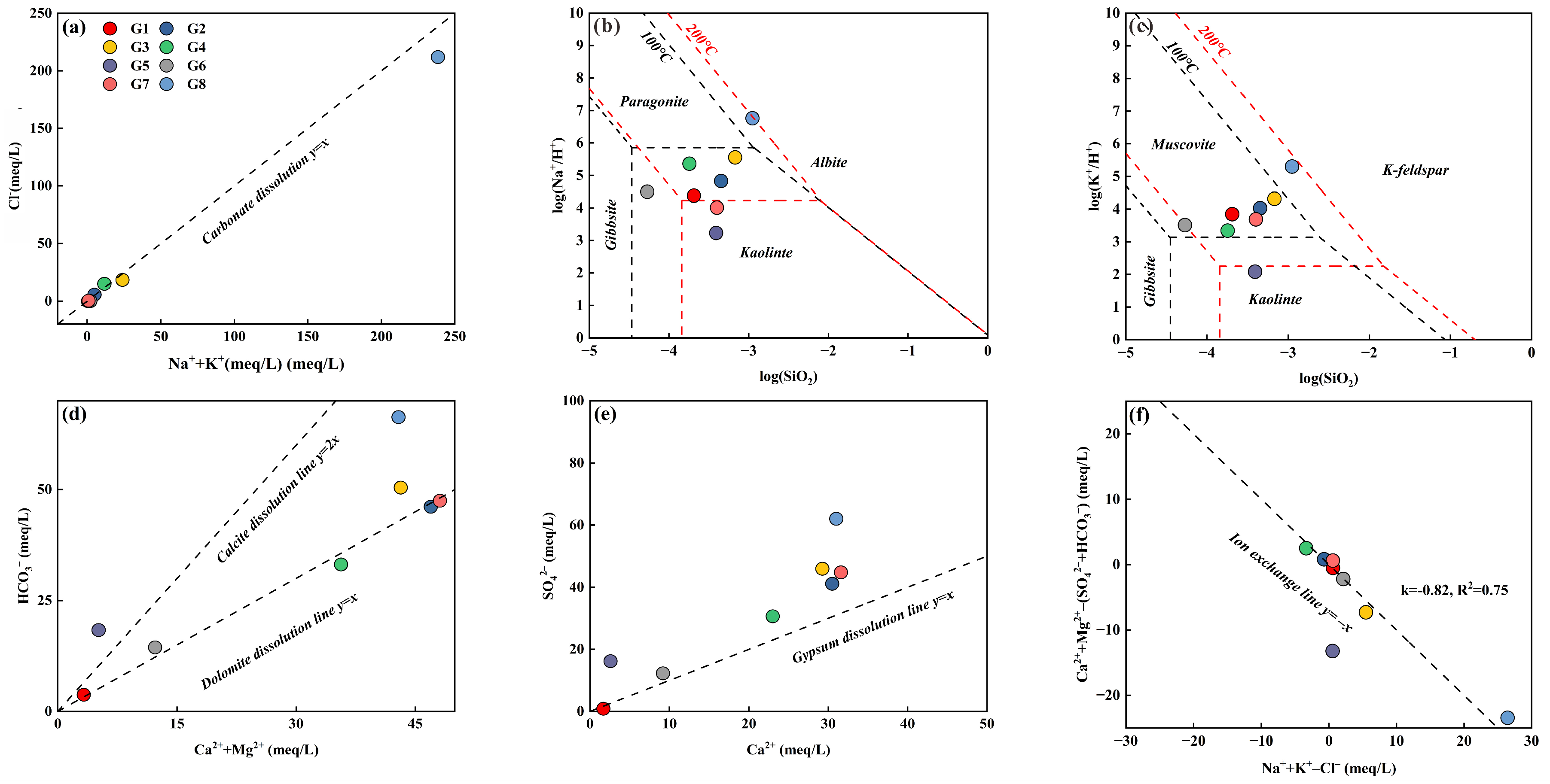
5.1. Main Processes Affecting Hydrochemistry
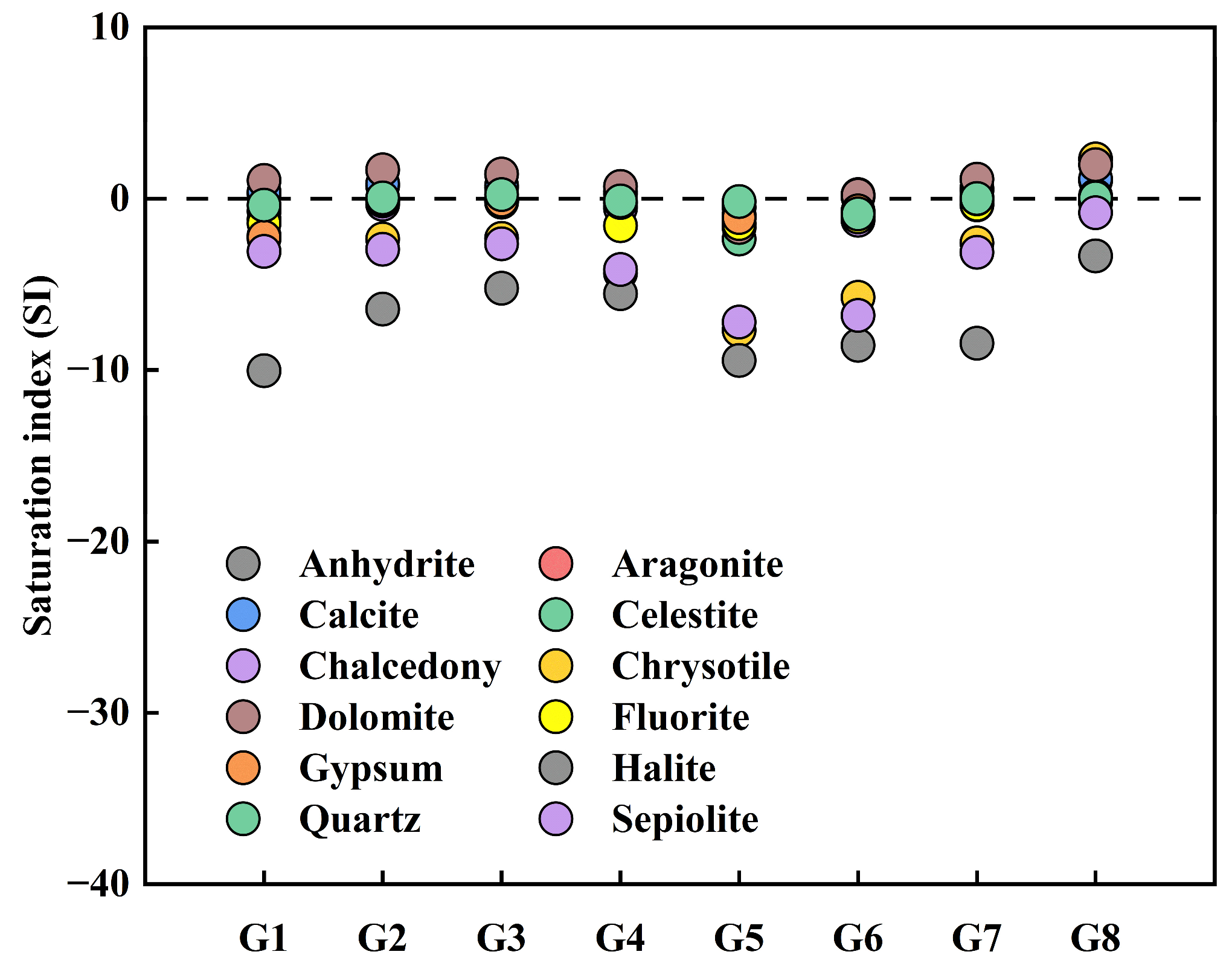
5.2. Mineral Equilibrium Status of Geothermal Waters
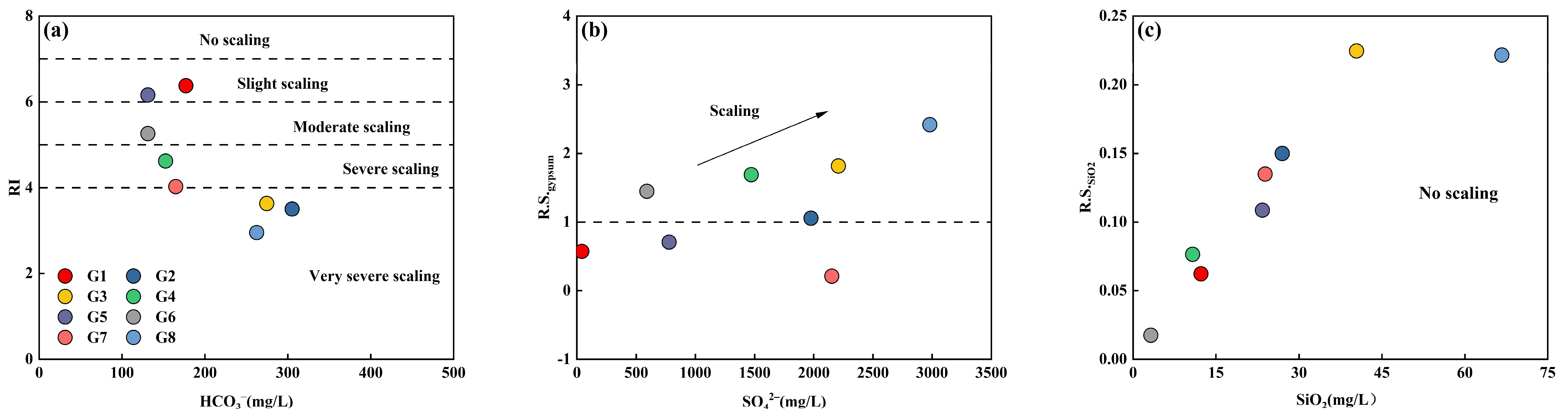
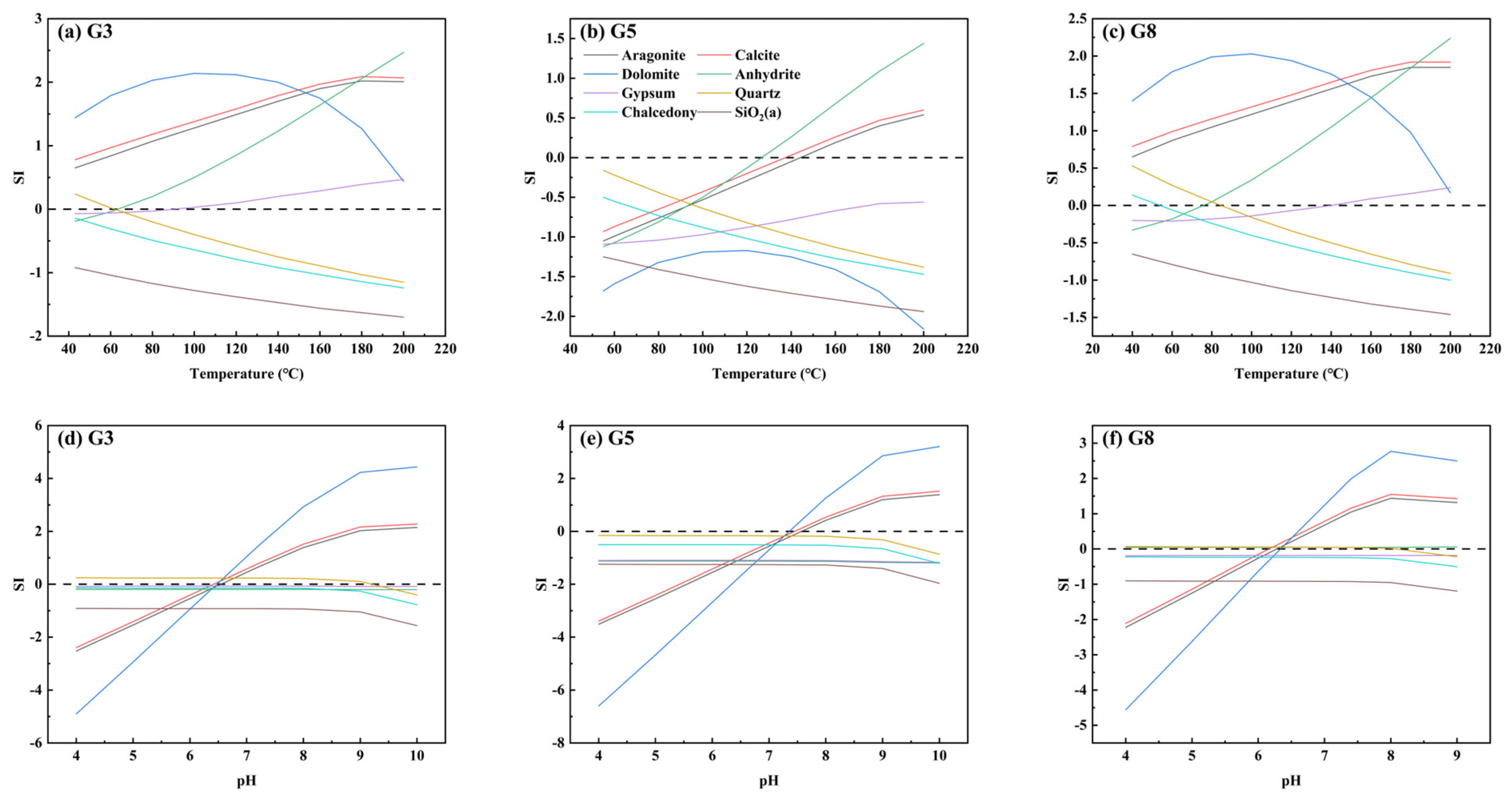
5.3. Mineral Scaling Trends of Geothermal Waters
5.3.1. Index Analysis Method
5.3.2. Hydrogeochemical Modeling Using PHREEQC
5.3.3. Descaling and Prevention
5.4. Drinking Water Quality Evaluation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EWQI | Entropy-weighted water quality index |
| SI | Saturation indices |
| CAI | Choro-alkaline indices |
References
- Guo, Q. Hydrogeochemistry of high-temperature geothermal systems in China: A review. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Wen, H.; Hao, Y. Geochemical evidence for the nonexistence of supercritical geothermal fluids at the Yangbajing geothermal field, southern Tibet. J. Hydrol. 2022, 604, 127243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemperer, S.L.; Zhao, P.; Whyte, C.J.; Darrah, T.H.; Crossey, L.J.; Karlstrom, K.E.; Liu, T.; Winn, C.; Hilton, D.R.; Ding, L. Limited underthrusting of India below Tibet: 3He/4He analysis of thermal springs locates the mantle suture in continental collision. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2113877119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, D.J.; Broadley, M.W.; Halldórsson, S.A.; Ranta, E.; Ricci, A.; Tyne, R.L.; Stefánsson, A.; Ballentine, C.J.; Barry, P.H. The use of noble gas isotopes to trace subsurface boiling temperatures in Icelandic geothermal systems. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2021, 560, 116805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libbey, R.B.; Williams–Jones, A.E.; Melosh, B.L.; Backeberg, N.R. Characterization of geothermal activity along the North American–Caribbean Plate boundary in Guatemala: The Joaquina geothermal field. Geothermics 2015, 56, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.K.; Chandrasekharam, D.; Raju, N.J.; Ranjan, S. Geothermal energy potential in relation to black carbon reduction and CO2 mitigation of Himalayan geothermal belt—A review. Geothermics 2024, 119, 102962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Duo, J.; Huang, X.; Sun, M.; Lv, G. Hydrochemical, D–O–Sr isotopic and electromagnetic characteristics of geothermal waters from the Erdaoqiao area, SW China: Insights into genetic mechanism and scaling potential. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 158, 105486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Kuang, X.; Hao, Y.; Wang, C.; Feng, Y.; Zou, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zheng, C. Magmatic fluid input controlling the geochemical and isotopic characteristics of geothermal waters along the Yadong–Gulu rift, southern Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2023, 619, 129196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Stefánsson, A.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Xing, L.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X. Geochemistry of thermal fluids and the genesis of granite–hosted Huangshadong geothermal system, Southeast China. Geothermics 2023, 109, 102647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, J.W.; Toth, A.N. Direct utilization of geothermal energy 2020 worldwide review. Geothermics 2021, 90, 101915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Wood, D.A. A holistic review of geosystem damage during unconventional oil, gas and geothermal energy recovery. Fuel 2018, 227, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozau, E.; Häußler, S.; van Berk, W. Hydrogeochemical modelling of corrosion effects and barite scaling in deep geothermal wells of the North German Basin using PHREEQC and PHAST. Geothermics 2015, 53, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotsika, E. H–O–C–S isotope and geochemical assessment of the geothermal area of Central Greece. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 150, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Guan, L.; Liu, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, B.; Xu, S.; Sano, Y. Fluid geochemistry and geothermal anomaly along the Yushu–Ganzi–Xianshuihe fault system, eastern Tibetan Plateau: Implications for regional seismic activity. J. Hydrol. 2022, 607, 127554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, M.; Xie, X.-G.; Chen, B.; Dan, Z.; Ellam, R.M.; Xu, S. Assessing magmatic contributions to rift–related geothermal systems in collisional orogens: Insights from the Sangri–Cona rift, southern Tibetan Plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2024, 270, 106193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pang, Z.; Galeczka, I.M. Quantitative assessment of calcite scaling of a high temperature geothermal well in the Kangding geothermal field of Eastern Himalayan Syntax. Geothermics 2020, 87, 101844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbaş, H.A.; Bozdağ, A. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and evaluation of the geothermal fluids in the Gazlıgöl geothermal field (Afyonkarahisar), Western Anatolia, Turkey. Geothermics 2022, 105, 102543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Malik, A.; Mohan, D.; Sinha, S. Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)—A case study. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3980–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Pei, Q. Hydrochemistry, quality and potential health risk appraisal of nitrate enriched groundwater in the Nanchong area, southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Hu, X.; Guo, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, S.; Yang, B. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion reveals the typical geothermal structure of Yanggao geothermal field in Datong Basin, northern China. Geothermics 2022, 105, 102505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allis, R.; Moore, J.; Blackett, B.; Gwynn, M.; Kirby, S.; Sprinkel, D. The Potential for Basin-Centered Geothermal Resources in the Great Basin. Geotherm. Resour. Counc. Trans. 2011, 35, 683–688. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Cao, Q.; Fang, C.; Zhu, C. Characteristics of geothermal field and evaluation of geothermal resource potential in the Yingjiang Basin. Energy Geosci. 2023, 4, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Cui, G.; Linyou, Z.; Qingda, F.; Zhang, Z.; Niu, W.; Xu, X.; Deng, L. Hydrogeochemical evidence for the geothermal origin of sedimentary hot dry rock in Gonghe Basin, Northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 549.541–549.513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bédard, K.; Comeau, F.-A.; Raymond, J.; Malo, M.; Nasr, M. Geothermal Characterization of the St. Lawrence Lowlands Sedimentary Basin, Québec, Canada. Nat. Resour. Res. 2017, 27, 479–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Operacz, A.; Józef, C. Perspectives of geothermal water use in the Podhale Basin according to geothermal step distribution. Geol. Geophys. Environ. 2018, 44, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, S.E.; Burns, E.R. Three-dimensional temperature maps of the Williston Basin, USA: Implications for deep hot sedimentary and enhanced geothermal resources. Geothermics 2025, 125, 103196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuanqing, Z.; Ming, X.; Yusong, Y.; Yongqing, Z.; JingNan, S. Palaeogeothermal response and record of the effusing of Emeishan basalts in the Sichuan basin. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 55, 949–956. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Cui, L.; Kalogirou, S.A. Geothermal resource evaluation in the Sichuan Basin and suggestions for the development and utilization of abandoned oil and gas wells. Renew. Energy 2024, 225, 120362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Y. Geochemistry of hot springs in the Tengchong hydrothermal areas, Southwestern China. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2012, 215–216, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qi, J.; Yi, L.; Xu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, Y. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of geothermal waters in the eastern Himalayan syntaxis geothermal field, southern Tibet. Geothermics 2021, 97, 102233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, X.; Liao, X.; Zhang, Y. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Conceptual Model of the Geothermal Waters in the Xianshuihe Fault Zone, Southwestern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, G.; Xing, L.; Li, T.; Zhao, J. Geochemical response of deep geothermal processes in the Litang region, Western Sichuan. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2019, 37, 626–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, X.; Yu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Genetic Mechanism of Geothermal Springs in the Aba Area, Western Sichuan Province, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Pang, Z.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, T.; Kong, Y.J.G. Geochemistry of geothermal fluids with implications on the sources of water and heat recharge to the Rekeng high-temperature geothermal system in the Eastern Himalayan Syntax. Geothermics 2018, 74, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Li, X.; Qi, J.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, R. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Natural Water System: A Case Study in Kangding County, Southwestern China. Water 2018, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, M.; Wei, C.; Huang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Qin, L.; Pei, Q. Hydrochemistry and Entropy-Based Groundwater Quality Assessment in the Suining Area, Southwestern China. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 5591892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.A.I.; Jingwen, S.U.; Zhuang, L.I.; Hongfeng, S.H.I.; Rui, W.; Yang, Y.; Yong, D. Study on the chemical characteristics and hydrogeochemistry process of groundwater in the upper reaches of Xin’an River Basin. East. China Geol. 2023, 44, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. User’s Guide to PHREEQC (Version 2): A Computer Program for SPECIATION, batch-Reaction, One-dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations (No. 99-4259); US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1999.
- Chauhan, V.; Saevarsdottir, G.; Tesfahunegn, Y.A.; Asbjornsson, E.; Gudjonsdottir, M.J.G. Computational study of two-phase flashing flow in a calcite scaled geothermal wellbore. Geothermics 2021, 97, 102239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Liu, S.L.; Bian, Q.Y.; Yan, B.; Liu, X.F.; Liu, J.X.; Bu, X.B. Scaling Analysis of Geothermal Well from Ganzi and Countermeasures for Anti-scale. Adv. New Renew. Energy 2015, 3, 202–206. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, P.F.I. Review of Shell-and-Tube Heat Exchanger Fouling and Corrosion In Geothermal Power Plant Service; Radian Corp.: Austin, TX, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, M.H.; Tian, T.; Sun, Y.D.; Li, X. A study of the scaling trend of thermal groundwater in Kangding county of Sichuan. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2012, 39, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, T.E.; Sollo, F.W., Jr. Loss in Water Main Carrying Capacity. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1967, 59, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, Q.; Liu, M.; Luo, J.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, M.; Guo, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, C. Hydrogeochemical processes occurring in the hydrothermal systems of the Gonghe–Guide basin, northwestern China: Critical insights from a principal components analysis (PCA). Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.K.; Kumar, A.; Shashtri, S.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P.; Mallick, J. Multivariate statistical analysis and geochemical modeling for geochemical assessment of groundwater of Delhi, India. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 175, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sampling Number | pH | TDS | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Li | Br |
| G1 | 7.7 | 300.5 | 11 | 5.5 | 34.07 | 18.85 | 0.09 | 0.15 |
| G2 | 7.2 | 3443.8 | 98 | 26.5 | 611.2 | 197.6 | 0.21 | 1.57 |
| G3 | 7.2 | 4503.6 | 520 | 51 | 586.2 | 167.2 | 1.48 | 6.46 |
| G4 | 7.3 | 2973.5 | 265 | 4.3 | 460.9 | 152 | 0.05 | 0.59 |
| G5 | 6.5 | 368.8 | 12.5 | 1.5 | 52.1 | 30.4 | 0.02 | 0.15 |
| G6 | 7.2 | 938.6 | 46 | 8 | 184.4 | 36.48 | 0.05 | 0.15 |
| G7 | 7.2 | 3218.7 | 15 | 12 | 633.3 | 198.3 | 0.02 | 0.15 |
| G8 | 7.4 | 17,223.6 | 5300 | 310 | 621.2 | 142.9 | 11.7 | 115 |
| Sampling Number | Sr | NH4+ | HCO3− | SO42− | Cl− | F− | SiO2 | B |
| G1 | 0.76 | 0.17 | 177 | 41.6 | 0.35 | 1.18 | 12.28 | 0.68 |
| G2 | 12.81 | 0.02 | 305.1 | 1976 | 200.4 | 2.4 | 26.98 | 3.75 |
| G3 | 13.02 | 0.03 | 274.6 | 2208 | 654.1 | 2.51 | 40.41 | 4.30 |
| G4 | 8.02 | 0.02 | 152.5 | 1472 | 531.9 | 0.39 | 10.77 | 0.60 |
| G5 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 131.2 | 778 | 1.42 | 1.37 | 23.39 | 0.21 |
| G6 | 2.92 | 0.13 | 131.2 | 590 | 2.84 | 0.98 | 3.21 | 0.23 |
| G7 | 14.75 | 0.02 | 164.8 | 2152 | 13.12 | 1.85 | 23.9 | 1.91 |
| G8 | 21 | 2.48 | 262.4 | 2980 | 7516 | 5.6 | 66.7 | 43.18 |
| Serial Number | CAI-I (No Unit) | CAI-II (No Unit) |
|---|---|---|
| G1 | −61.70942 | −0.161724 |
| G2 | 0.1260492 | 0.0154428 |
| G3 | −0.296539 | −0.108407 |
| G4 | 0.2244371 | 0.1015928 |
| G5 | −13.53145 | −0.02954 |
| G6 | −26.52959 | −0.147242 |
| G7 | −1.592181 | −0.012404 |
| G8 | −0.124738 | −0.398618 |
| Method | Equation | No. | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Larson Index (LI) | LI = ([Cl−] + [SO42−])/[ALK] | 1 | [42,43] |
| Ryzner Index (RI) | RI = 2pHs − pHa | 2 | [42,43] |
| pHs = log[Ca2+] − log[ALK] + Kc | 3 | ||
| pHs = log[Ca2+] − log[ALK] + Ke | 4 | ||
| T(°F) = 32 + 9/5 × T | 5 | ||
| Relative saturation of gypsum (R.S.) | R.S. = 10^(logppmCa2+ + logppmSO42− −logKgypsum) | 6 | [44] |
| Relative saturation of silica (R.S.) | R.S. = SiO2/(2.446 × 10,000 × e^( −1553/Tk)) | 7 |
| Number | LI | Trend of Scaling Up | RI1 | Trend of Scaling Up | RI2 | Trend of Scaling Up | Cl− (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | – | – | 5.67 | Medium | 7.08 | No scaling or deposition | 0.26 |
| G2 | – | – | 2.91 | Very serious | 4.10 | Serious | 10.91 |
| G3 | 14.31 | No scaling or deposition | 3.04 | – | 4.23 | – | 26.77 |
| G4 | 18.26 | No scaling or deposition | 4.30 | – | 4.94 | – | 31.16 |
| G5 | – | – | 5.35 | Medium | 6.97 | Slight | 0.22 |
| G6 | – | – | 4.65 | Serious | 5.87 | Medium | 0.55 |
| G7 | – | – | 3.45 | Very serious | 4.60 | Serious | 0.77 |
| G8 | 63.65 | No scaling or deposition | 1.69 | – | 4.21 | – | 76.17 |
| Parameter | pH | TDS | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | NH4+ | Cl− | SO42− | F− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 0.112 | 0.095 | 0.201 | 0.044 | 0.048 | 0.219 | 0.197 | 0.033 | 0.051 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Pu, W.; Chen, P.; Li, Q.; Jiang, Z.; He, H.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Hydrochemical Processes, Mineral Scaling and Water Quality of Geothermal Waters in Sichuan Basin, Southwestern China. Water 2025, 17, 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060827
Zhang J, Pu W, Chen P, Li Q, Jiang Z, He H, Yuan X, Zhang Y, Li X. Hydrochemical Processes, Mineral Scaling and Water Quality of Geothermal Waters in Sichuan Basin, Southwestern China. Water. 2025; 17(6):827. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060827
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ji, Wenbin Pu, Peng Chen, Qiang Li, Zheng Jiang, Haiyang He, Xingcheng Yuan, Yunhui Zhang, and Xingze Li. 2025. "Hydrochemical Processes, Mineral Scaling and Water Quality of Geothermal Waters in Sichuan Basin, Southwestern China" Water 17, no. 6: 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060827
APA StyleZhang, J., Pu, W., Chen, P., Li, Q., Jiang, Z., He, H., Yuan, X., Zhang, Y., & Li, X. (2025). Hydrochemical Processes, Mineral Scaling and Water Quality of Geothermal Waters in Sichuan Basin, Southwestern China. Water, 17(6), 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060827







