Modelling Arsenic-Removal Efficiency from Water Through Adsorption Using Modified Saxaul Ash as Adsorbent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussions
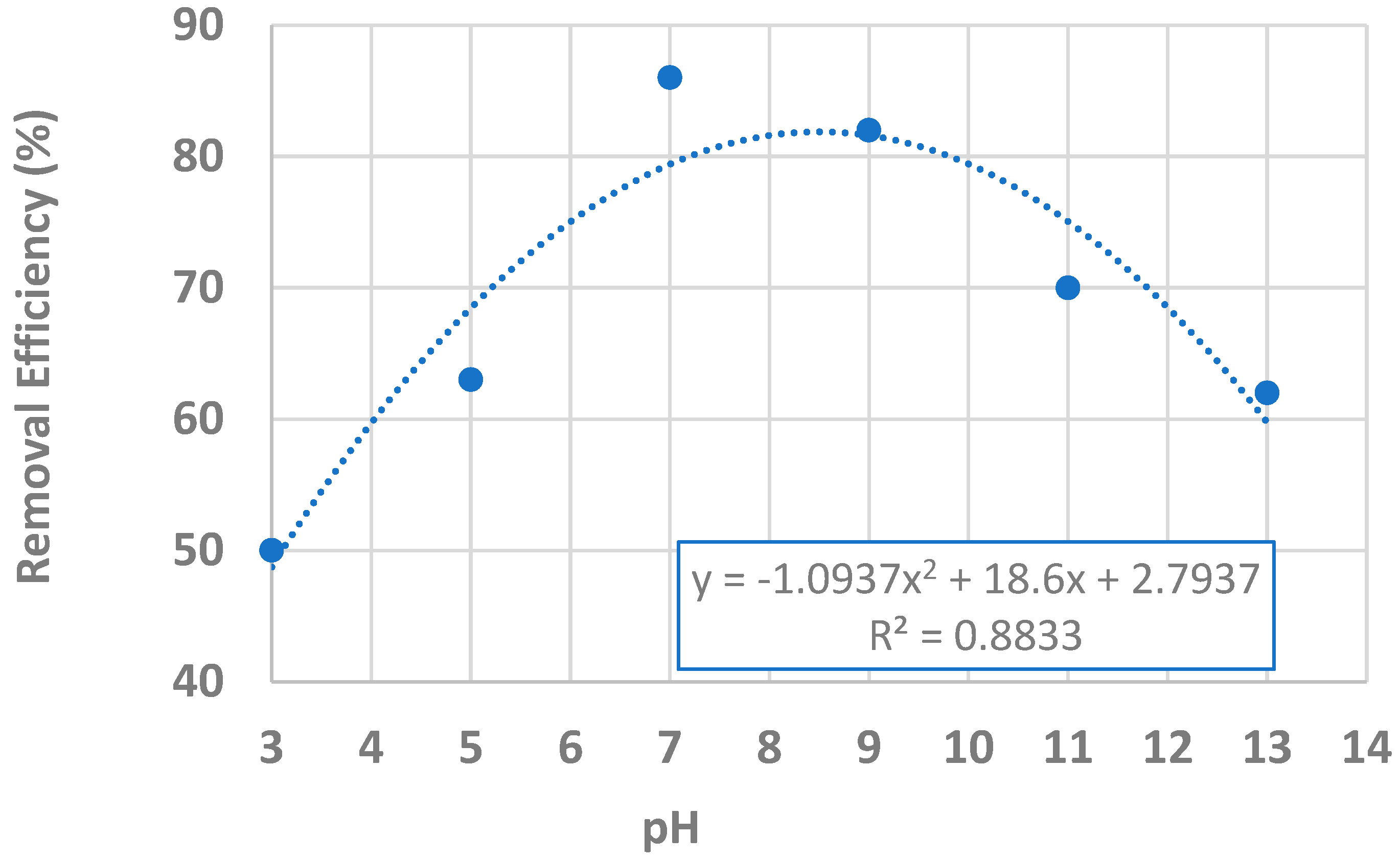
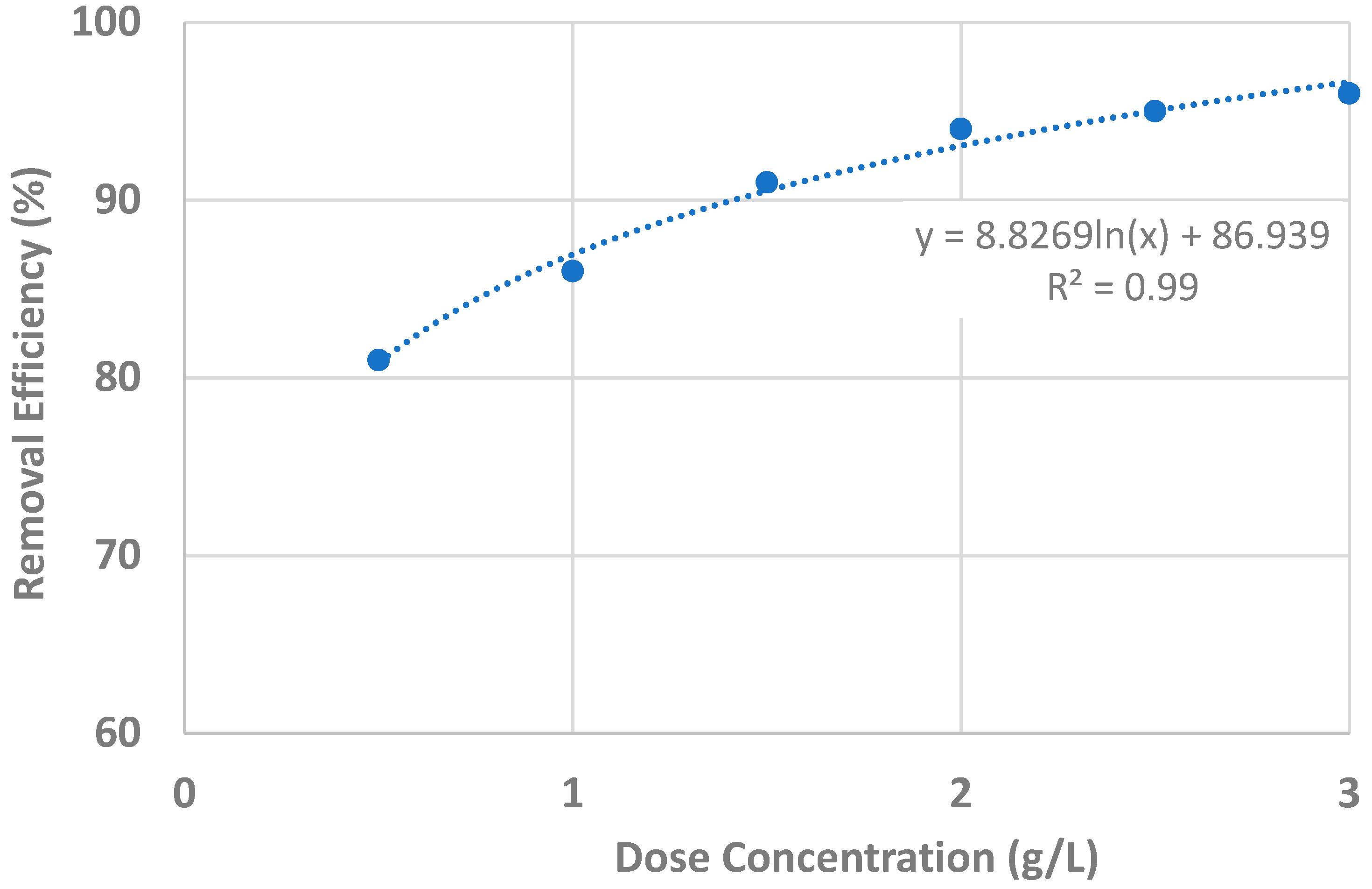
3.1. Derivation of Factors
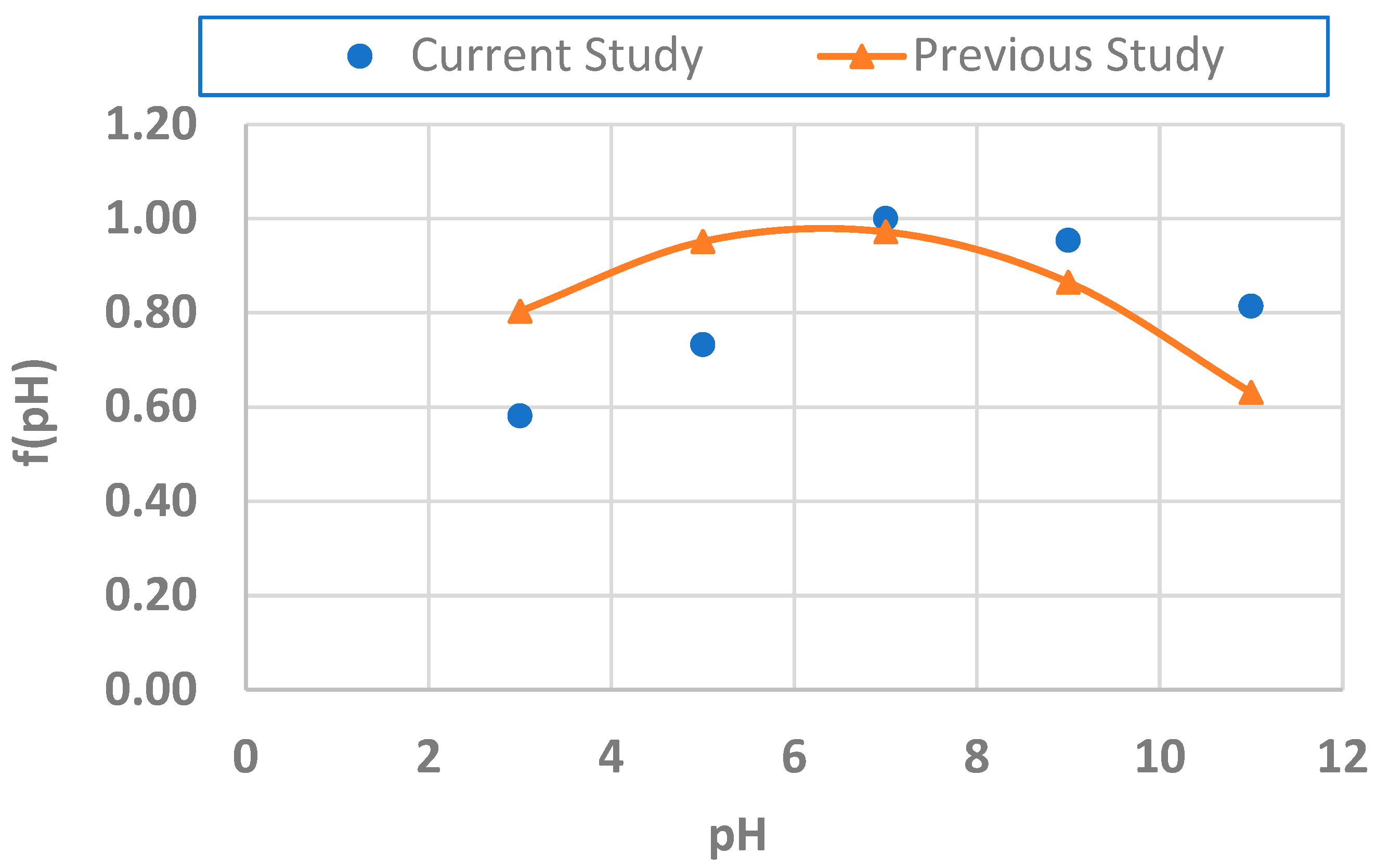
3.2. Assessment of Developed Factors
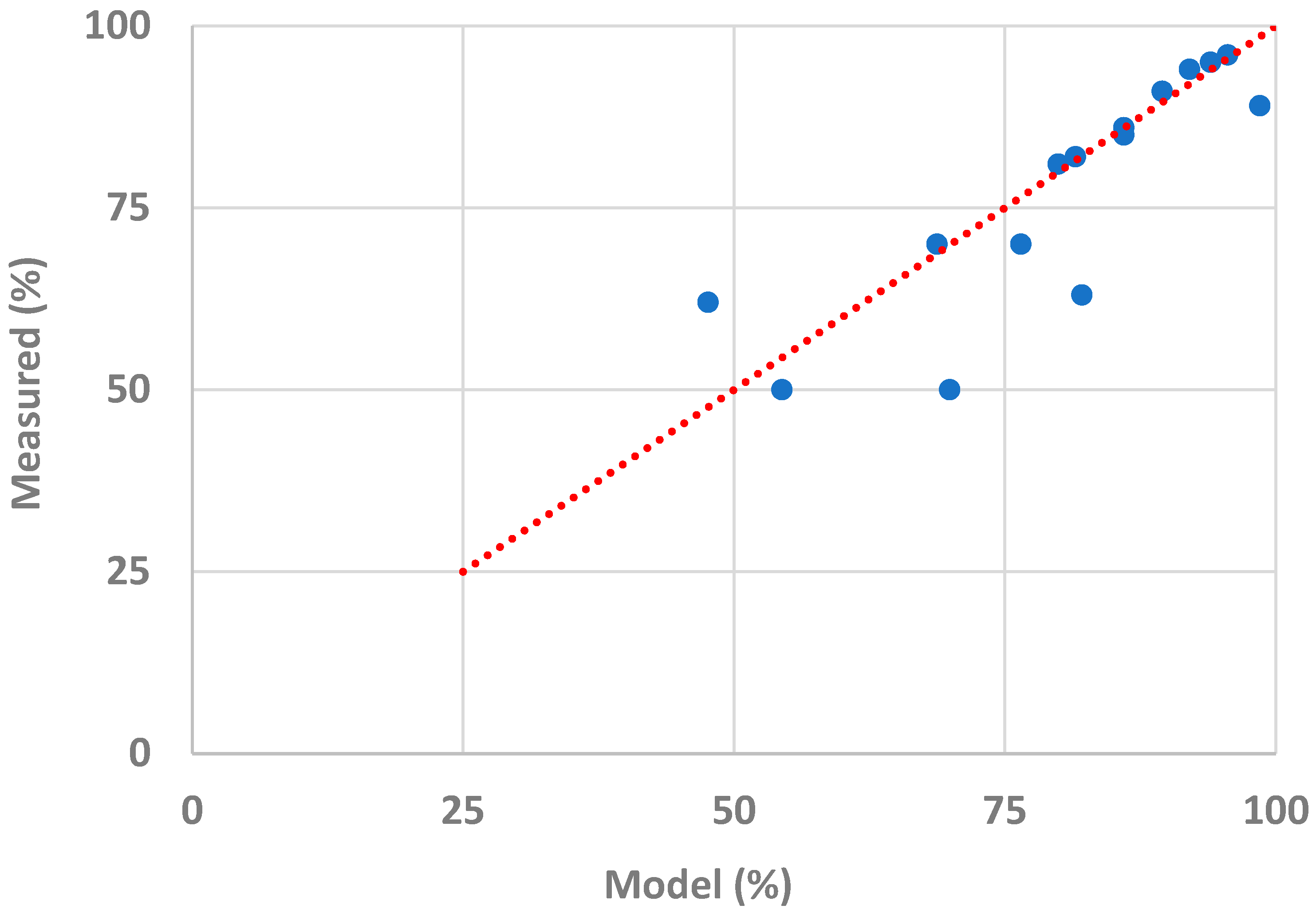
3.3. Final Model's Accuracy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jain, R. Recent advances of magnetite nanomaterials to remove arsenic from water. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 32197–32209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah SM, A.; Islam, M.T.; Islam SZ Hossain, I.; Samsuzzoha, M.; Hossain, M.D.; Latif, S.A.; Islam, F.M.A. Analysis of Arsenic Concentrations and Correlation in Water, Soil and Aurum by Neutron Activation Analysis Technique: A Case Study in Bagerhat, Bangladesh. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 85, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Imteaz, M.A. Prototype experiments assessing arsenic and iron removal efficiencies through adsorption using natural Skye sand. Water 2023, 15, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lata, S.; Samadder, S.R. Removal of arsenic from water using nano adsorbents and challenges: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 387–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, D.L.; Pérez, R.; Okio, C.K.Y.A.; Castillo, E. Assessment of mining activity on arsenic contamination in surface water and sediments in southwestern area of Santurbán paramo, Colombia. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 264, 110478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asante, K.A.; Agusa, T.; Subramanian, A.; Ansa-Asare, O.D.; Biney, C.A.; Tanabe, S. Contamination status of arsenic and other trace elements in drinking water and residents from Tarkwa, a historic mining township in Ghana. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandio, T.A.; Khan, M.N.; Muhammad, M.T.; Yalcinkaya, O.; Wasim, A.A.; Kayis, A.F. Fluoride and arsenic contamination in drinking water due to mining activities and its impact on local area population. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 2355–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, B.S.; Kumar, P.S. A review on sources, identification and treatment strategies for the removal of toxic Arsenic from water system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.; Mondal, N.K.; Das, K. Modeling of the adsorptive removal of arsenic: A statistical approach. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, M.A.; Fernandez, D.P.; Hering, J.G. Lowering the detection limit for arsenic: Implications for a future practical quantitation limit. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2007, 99, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahdar, S.; Taghavi, M.; Khaksefidi, R.; Ahmadi, S. Adsorption of arsenic (V) from aqueous solution using modified saxaul ash: Isotherm and thermodynamic study. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, M.-C. An overview of arsenic removal by pressure-driven membrane processes. Desalination 2005, 172, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.H.; Khan, Z.M.; Mahmood, Q.; Nasreen, S.; Bhatti, Z.A. Perspectives of low cost arsenic remediation of drinking water in Pakistan and other countries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, B.; Vinka, C.; Pawan, L.; David, S. Sustainable groundwater treatment technologies for underserved rural communities in emerging economies. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rott, U.; Meyer, C.; Friedle, M. Residue-free removal of arsenic, iron, manganese and ammonia from groundwater. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2002, 2, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, P. In Bangladesh, funds dry up for arsenic mitigation research. Lancet 2013, 382, 1693–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, B.S.; Kumar, P.S.; Ponprasath, R.; Rohan, K.; Jahnavi, N. An effective separation of toxic arsenic from aquatic environment using electrochemical ion exchange process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.P.; Galinha, C.F.; Crespo, J.G.; Velizarov, S. Optimisation of arsenate removal from water by an integrated ion-exchange membrane process coupled with Fe co-precipitation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 246, 116894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elcik, H.; Celik, S.O.; Cakmakci, M.; Özkaya, B. Performance of nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes for arsenic removal from drinking water. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 20422–20429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Wang, N.; Wang, C.; Li, G. Arsenic removal from water and river water by the combined adsorption-UF membrane process. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.V.; Singh, T.S.A. Arsenic removal by electrocoagulation process: Recent trends and removal mechanism. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 418–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.; Moon, S.-H. Investigation of the performance determinants in the treatment of arsenic-contaminated water by continuous electrodeionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 179, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y. A review on arsenic removal from coal combustion: Advances, challenges and opportunities. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 414, 128785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, T.; Loganathan, P.; Ahmed, M.B.; Johir, M.a.H.; Nguyen, T.V.; Vigneswaran, S. Removing arsenic from water by coprecipitation with iron: Effect of arsenic and iron concentrations and adsorbent incorporation. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gahrouei, A.E.; Rezapour, A.; Pirooz, M.; Pourebrahimi, S. From classic to cutting-edge solutions: A comprehensive review of materials and methods for heavy metal removal from water environments. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 319, 100446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, D. Conventional as well as emerging arsenic removal technologies—A critical review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Kim, K.-H.; Kumar, V.; Kim, S. A review of functional sorbents for adsorptive removal of arsenic ions in aqueous systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Imteaz, M.A. Treatment and Operational Efficiencies of Several Natural and Synthetic Sands on Treating Arsenic Through Adsorption. In Arsenic Toxicity Remediation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; Chapter 11; ISBN 978-3-031-52613-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, A.; Das, S.; Debnath, A. Fabrication and characterization of organometallic nanocomposite for efficient abatement of dye laden wastewater: CCD optimization, adsorption mechanism, co-existing ions, and cost analysis. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2023, 830, 140820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ccamerccoa, M.H.; Falcon, N.T.; Félix, L.L.; Pacheco-Salazar, D.G.; Aragón, F.F.H.; Coaquira, J.A.H.; Garnier, J.; Vera-Gonzales, C. High efficiency of magnetite nanoparticles for the arsenic removal from an aqueous solution and natural water taken from Tambo River in Peru. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2022, 20, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, M.; Deb, K.; Debnath, A.; Saha, B. Mixed phase Fe2O3/Mn3O4 magnetic nanocomposite for enhanced adsorption of methyl orange dye: Neural network modeling and response surface methodology optimization. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Paul, S.R.; Debnath, A. Fabrication of biochar from jarul (Lagerstroemia speciosa) seed hull for ultrasound aided sequestration of ofloxacin from water: Phytotoxic assessments and cost analysis. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 387, 122610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.; Siddiqa, A.; Shahida, S.; Qaisar, S. Titanium-based nanocomposite materials for arsenic removal from water: A review. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litter, M.I.; Ingallinella, A.M.; Olmos, V.; Savio, M.; Difeo, G.; Botto, L.; Torres EM, F.; Taylor, S.; Frangie, S.; Herkovits, J. Arsenic in Argentina: Technologies for arsenic removal from groundwater sources, investment costs and waste management practices. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Ligaray, M.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, K.H.; Sthiannopkao, S. Development of enhanced groundwater arsenic prediction model using machine learning approaches in Southeast Asian countries. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 12227–12236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junyapoon, S. Use of zero-valent iron for wastewater treatment. Curr. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2005, 5, 587–595. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Chen, A.S.C.; Sorg, T.J.; Fields, K.A. Field evaluation of As removal by IX and AA. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2002, 94, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizian, S.; Eris, S.; Wilson, L.D. Re-evaluation of the century-old Langmuir isotherm for modeling adsorption phenomena in solution. Chem. Phys. 2018, 513, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Romero, J.A.; Mendoza-Castillo, D.I.; Reynel-Ávila, H.E.; De Haro-Del Rio, D.A.; González-Rodríguez, L.M.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Duran-Valle, C.J.; Camacho-Aguilar, K.I. Preparation of a new adsorbent for the removal of arsenic and its simulation with artificial neural network-based adsorption models. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakat, P.B.; Gupta, A.K.; Ayoob, S. Feasibility analysis of As (III) removal in a continuous flow fixed bed system by modified calcined bauxite (MCB). J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 139, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Sankararamakrishnan, N. Column studies on the evaluation of novel spacer granules for the removal of arsenite and arsenate from contaminated water. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2173–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, P.; Anuradha, K.; Lahari, S.B.; Kumar, Y.P.; Prasad, V. Biosorption of zinc from aqueous solution using Azadirachta indica bark: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellaoui, L.; Depci, T.; Kul, A.R.; Knani, S.; Lamine, A.B. A new statistical physics model to interpret the binary adsorption isotherms of lead and zinc on activated carbon. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 214, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imteaz, M.A.; Bayatvarkeshi, M.; Kaur, P. Mathematical modelling for predicting Methylene Blue removal efficiency through adsorption using activated carbon of Parthenium Hysterophorus. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imteaz, M.A.; Ahsan, A.; Kaur, P. Mathematical modelling for predicting pollutant removal efficiencies of an electrolysis system. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastkhoon, M.; Ghaedi, M.; Asfaram, A.; Azqhandi, M.H.A.; Purkait, M.K. Simultaneous removal of dyes onto nanowires adsorbent use of ultrasound assisted adsorption to clean waste water: Chemometrics for modeling and optimization, multicomponent adsorption and kinetic study. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 124, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imteaz, M.A.; Khan, S.A.; Kaur, P. Generalised equation for the effect of pH on Arsenic removal efficiency using natural adsorbents. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dose (g/L) | Initial Conc. (μg/L) | pH | Estimated Removal Efficiency (%) | Measured Removal Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 100 | 7 | 79.9 | 80.5 |
| 1.0 | 100 | 7 | 86.0 | 86.0 |
| 1.5 | 100 | 7 | 89.5 | 90.5 |
| 2.0 | 100 | 7 | 92.0 | 93.5 |
| 2.5 | 100 | 7 | 94.0 | 94.5 |
| 3.0 | 100 | 7 | 96.0 | 96.0 |
| 1.0 | 10 | 7 | 54.4 | 50.5 |
| 1.0 | 50 | 7 | 76.5 | 70.5 |
| 1.0 | 100 | 7 | 86.0 | 85.0 |
| 1.0 | 250 | 7 | 98.5 | 90.5 |
| 1.0 | 100 | 3 | 69.9 | 50.5 |
| 1.0 | 100 | 5 | 82.1 | 63.0 |
| 1.0 | 100 | 7 | 86.0 | 86.0 |
| 1.0 | 100 | 9 | 81.5 | 81.5 |
| 1.0 | 100 | 11 | 68.7 | 69.5 |
| 1.0 | 100 | 13 | 47.6 | 61.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Imteaz, M.A.; Hossain, I.; Ahsan, A.; Karim, M.R. Modelling Arsenic-Removal Efficiency from Water Through Adsorption Using Modified Saxaul Ash as Adsorbent. Water 2025, 17, 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060811
Imteaz MA, Hossain I, Ahsan A, Karim MR. Modelling Arsenic-Removal Efficiency from Water Through Adsorption Using Modified Saxaul Ash as Adsorbent. Water. 2025; 17(6):811. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060811
Chicago/Turabian StyleImteaz, Monzur A., Iqbal Hossain, Amimul Ahsan, and Md Rezaul Karim. 2025. "Modelling Arsenic-Removal Efficiency from Water Through Adsorption Using Modified Saxaul Ash as Adsorbent" Water 17, no. 6: 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060811
APA StyleImteaz, M. A., Hossain, I., Ahsan, A., & Karim, M. R. (2025). Modelling Arsenic-Removal Efficiency from Water Through Adsorption Using Modified Saxaul Ash as Adsorbent. Water, 17(6), 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060811









