Analysis of the Effect of Sea Surface Temperature on Sea Ice Concentration in the Laptev Sea for the Years 2004–2023
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Data Sources and Methods
3.1. Data Sources
3.1.1. Sea Surface Temperature
3.1.2. Sea Ice Concentration
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Raster Data Resampling
3.2.2. Linear Regression Analysis
3.2.3. Correlation Analysis
4. Results and Analysis
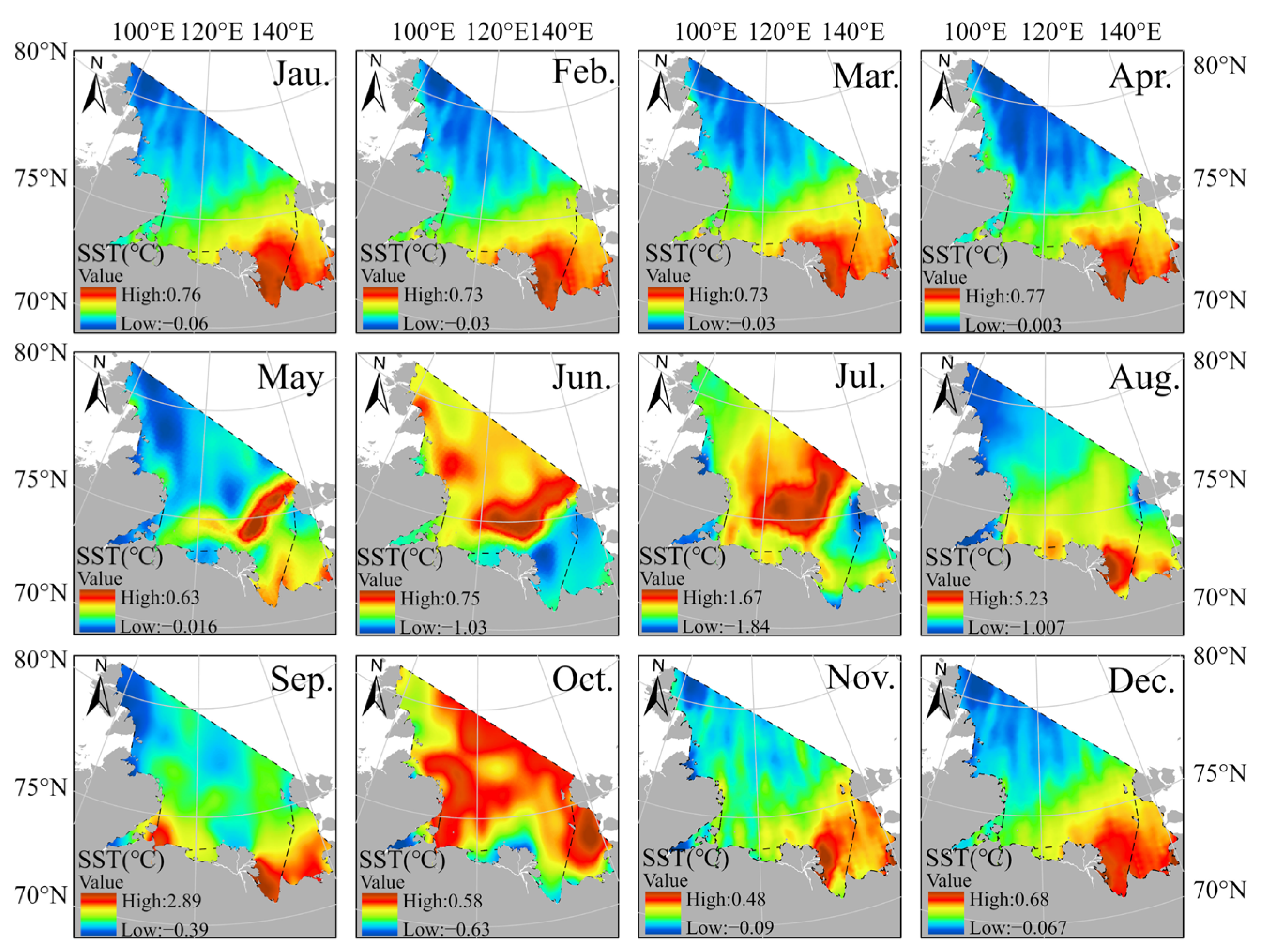
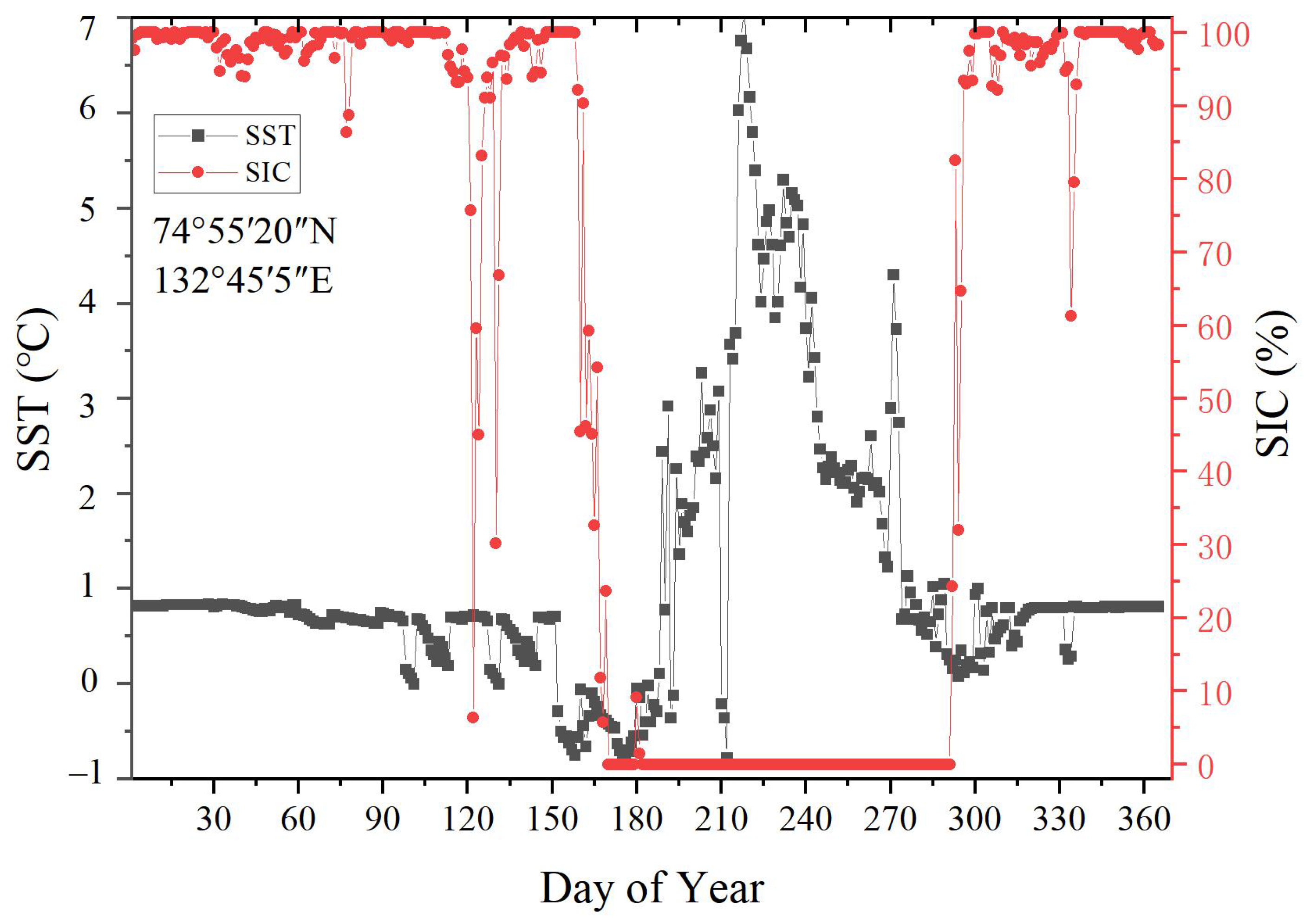
4.1. Spatiotemporal Variation in SST and Sea Ice
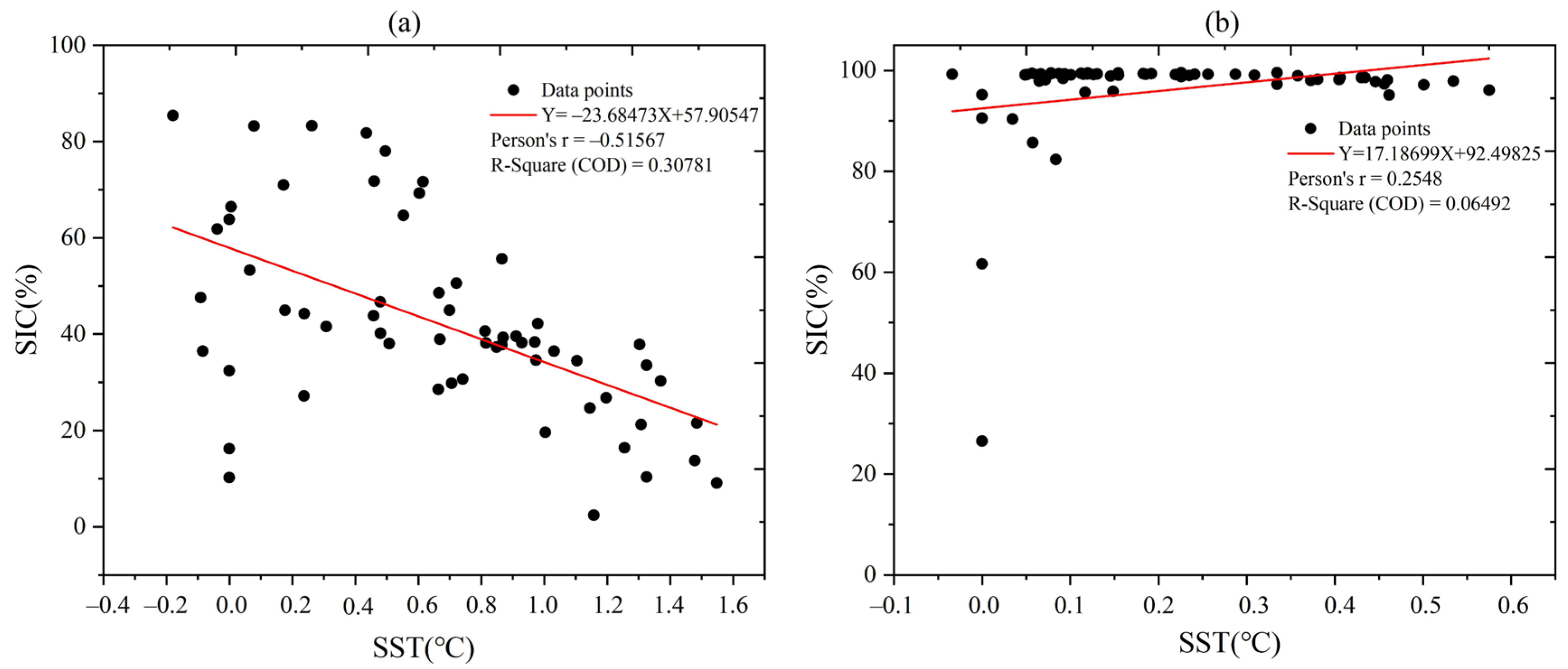
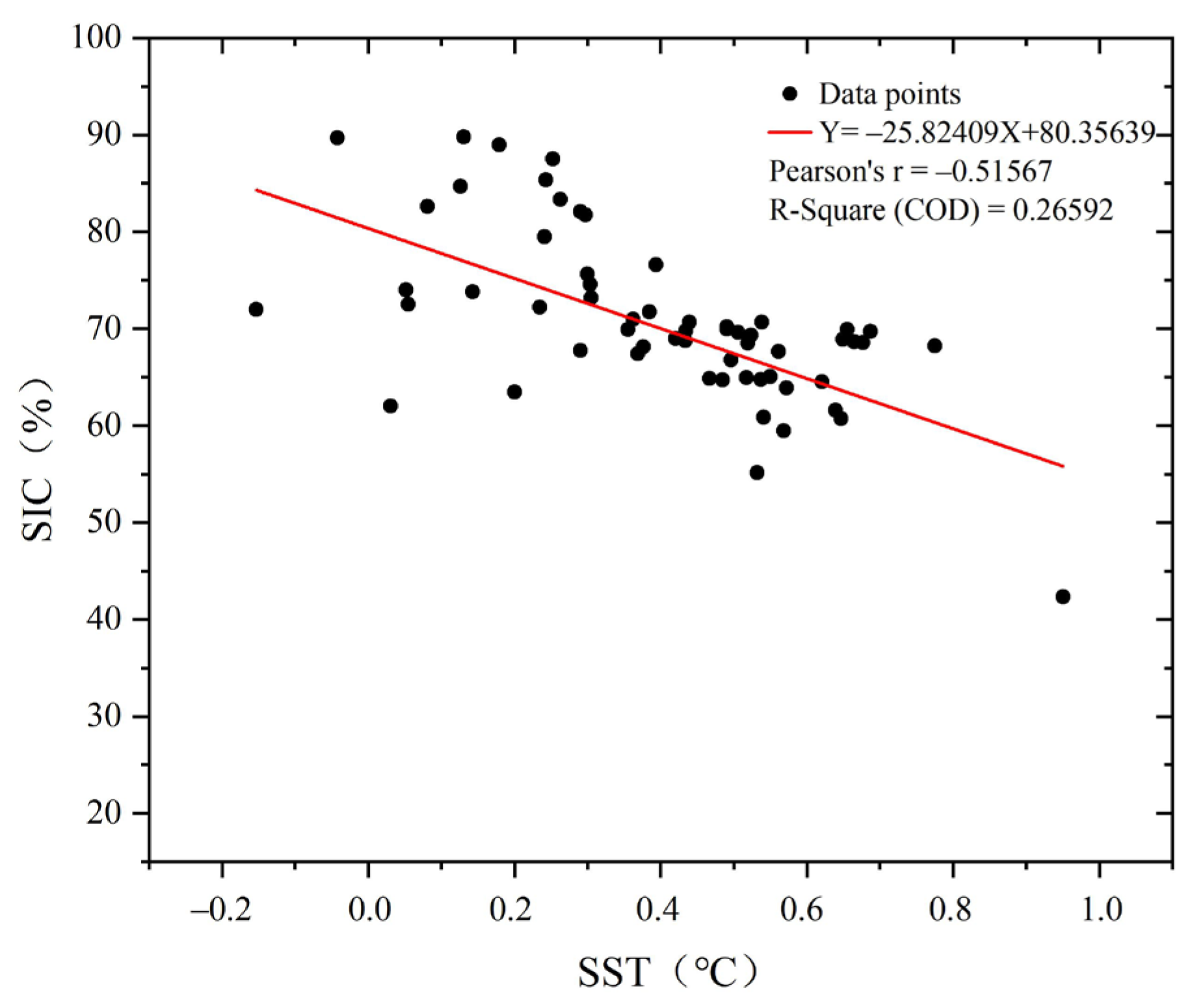
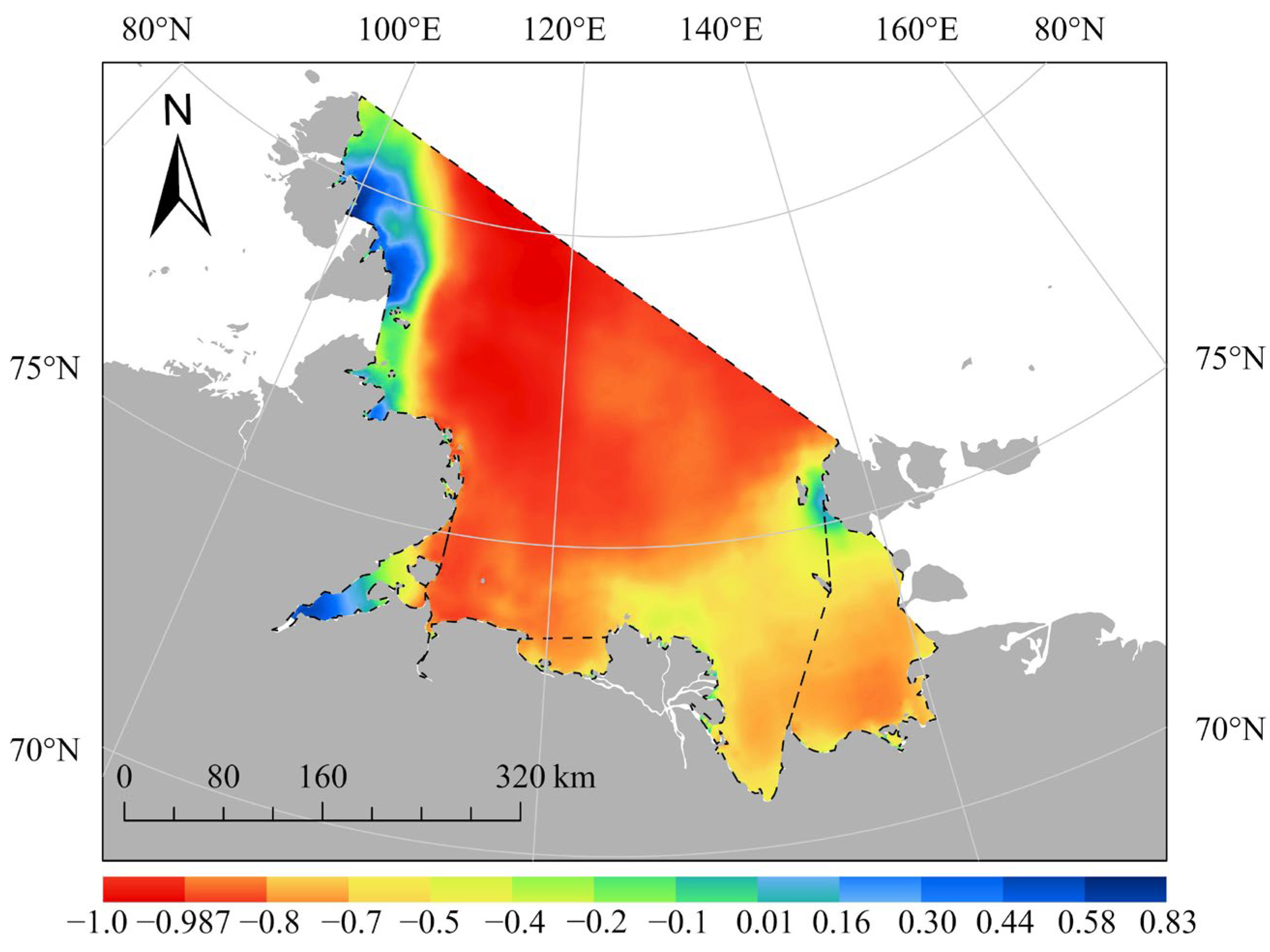
4.2. Correlation Between SST and SIC
5. Discussion
5.1. Seasonal Dynamics and Negative Correlation Between SST and SIC
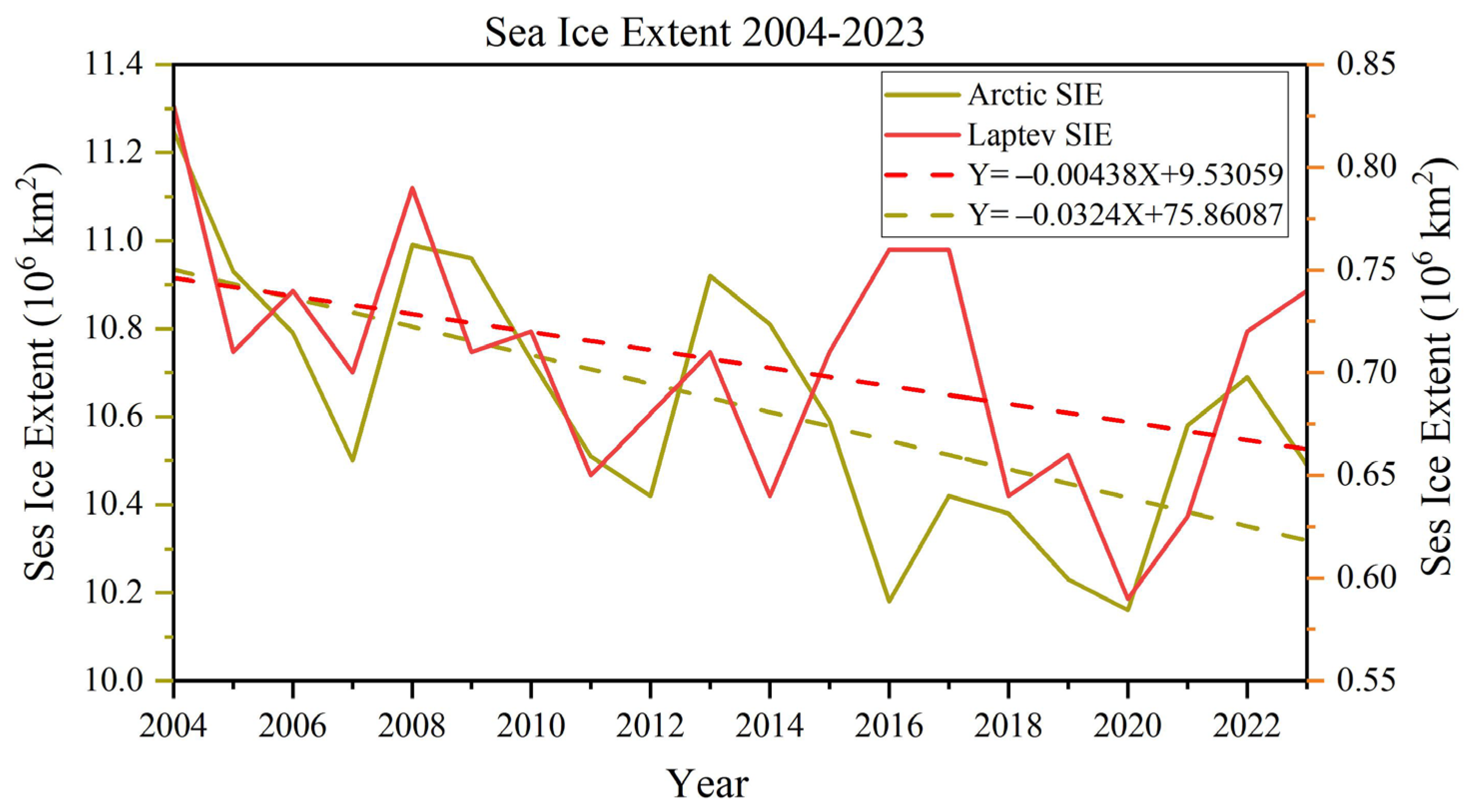
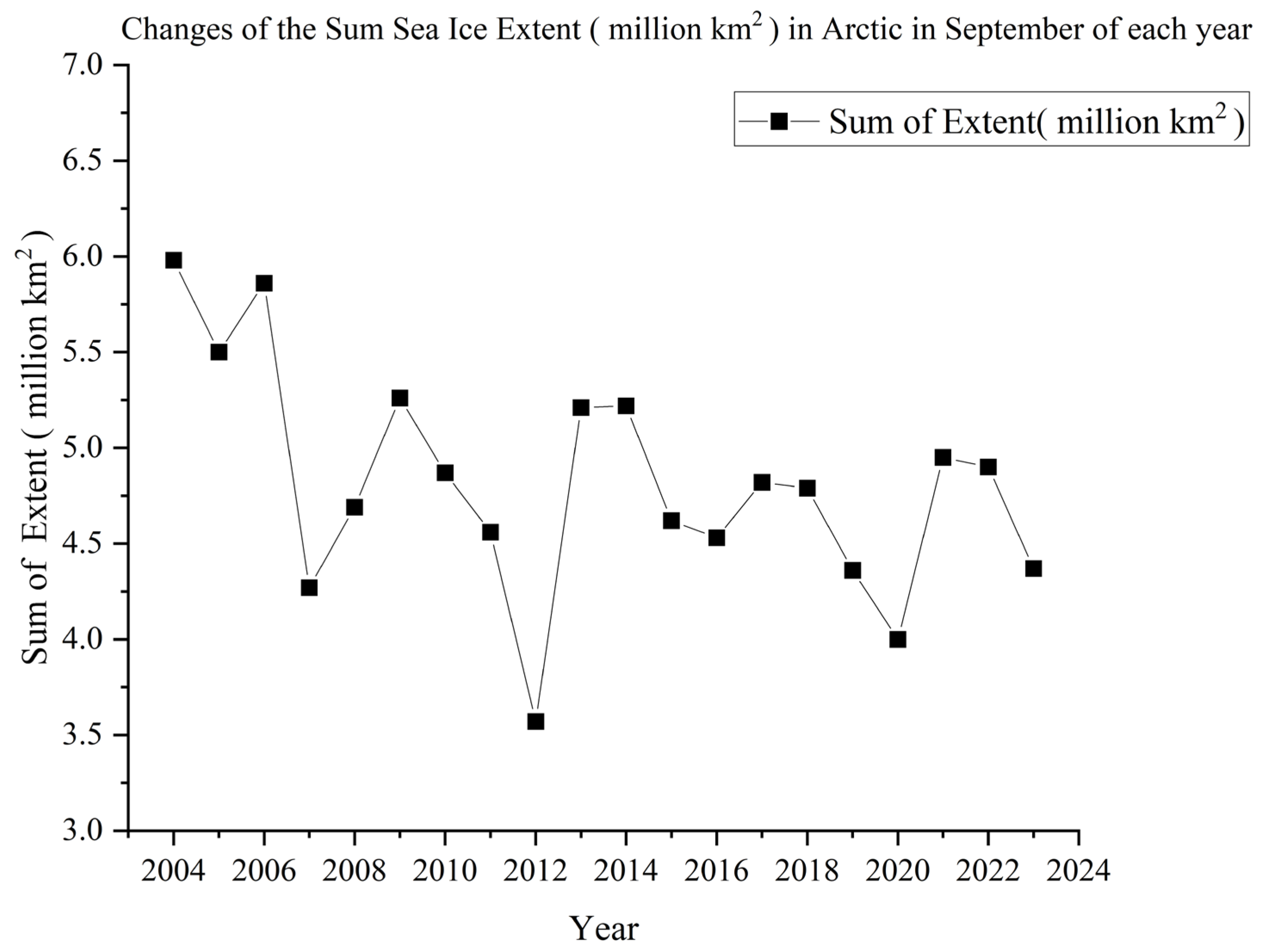
5.2. Trends of the Sea Ice Extent in Laptev Sea over the Last 20 Years
5.3. Causes of Spatiotemporal Sea Ice Changes
5.4. Internal Mechanisms Driving the Interaction Between SST and SIC
5.5. Practical Application Significance
5.6. Study Limitations
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- There is a clear spatial difference between SST and SIC. The monthly average SST in the Laptev Sea peaks at 5.23 °C in August and drops to a minimum of 0.48 °C in November. SIC reaches a maximum of 99.69% in December and a minimum of 62.58% in September, following the summer melt. The trend of interannual SST variability indicates an overall warming, though is not statistically significant (p < 0.01) at about +0.064 °C/year (Table 1), while the average annual SIC shows a statistically significant downward trend (p < 0.01), decreasing by about −1.297%/year (Table 2). The most notable trends in SST and SIC occur both in summer, with changes of +0.154 °C/year and −0.095%/year, respectively.
- (2)
- SST is the key factor influencing SIC and there was a strong negative correlation between SST and SIC in most areas of the Laptev Sea, with correlation coefficients ranging from −1 to 0.83. Sea ice melt interacts with increasing SST, particularly in summer and fall. The rise in SST can delay the fall freeze-up, resulting in thinner sea ice, which is more prone to melting in summer. This further contributes to the increase in SST.
- (3)
- Seasonal variations are observed in the influence of SST on SIC. The increase in SST in summer has a notable effect on accelerating the melting of sea ice and the decrease in SST in winter promotes the increase in SIC values. And from 2004 to 2023, the Laptev Sea’s sea ice concentration has shown a decreasing trend in summer and fall, with statistically significant interannual variability shifting from heavier to lighter ice conditions (p < 0.01).
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, W.; Zhao, J. Study on Multiyear Variations of Sea Ice in the Laptev Sea of the Arctic Ocean. Polar Stud. 2013, 25, 218–225. [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson, C.L.; Cavalieri, D.J. Antarctic sea ice variability and trends, 1979–2010. Cryosphere 2012, 6, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Lu, T.; Lin, K.-C.; Yuen, K.F.; Li, K.X. The competitiveness of Arctic shipping over Suez Canal and China-Europe railway. Transp. Policy 2020, 86, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schøyen, H.; Bråthen, S. The Northern Sea Route versus the Suez Canal: Cases from bulk shipping. J. Transp. Geogr. 2011, 19, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguíluz, V.M.; Fernández-Gracia, J.; Irigoien, X.; Duarte, C.M. A quantitative assessment of Arctic shipping in 2010–2014. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Huang, H.; Fu, M.; Fu, T.; Zhou, X.; Xu, X. Estimating sea-ice volume flux out of the Laptev Sea using multiple satellite observations. Polar Res. 2016, 35, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Muilwijk, M.; Hattermann, T.; Martin, T.; Granskog, M.A. Future sea ice weakening amplifies wind-driven trends in surface stress and Arctic Ocean spin-up. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, S.; Pant, V.; Mitra, A.K.; Kumar, A. Spatio-temporal variability of sea-ice and ocean parameters over the Arctic Ocean in response to a warming climate. Polar Sci. 2021, 30, 100721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Pang, X.; Lei, R.; Zhai, M.; Zhao, X.; Cai, Q. Arctic sea ice motion change and response to atmospheric forcing between 1979 and 2019. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 42, 1854–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhong, S.; Vihma, T.; Sun, B. Attribution of late summer early autumn Arctic sea ice decline in recent decades. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, K.; Woollings, T.; Sparrow, S.N. Dynamic and Thermodynamic Control of the Response of Winter Climate and Extreme Weather to Projected Arctic Sea-Ice Loss. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2024GL109271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliss, A.C.; Steele, M.; Peng, G.; Meier, W.N.; Dickinson, S. Regional variability of Arctic sea ice seasonal change climate indicators from a passive microwave climate data record. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 045003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Yadav, J.; Mohan, R. Global warming leading to alarming recession of the Arctic sea-ice cover: Insights from remote sensing observations and model reanalysis. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Abraham, J.; Zhu, J.; Trenberth, K.E.; Fasullo, J.; Boyer, T.; Locarnini, R.; Zhang, B.; Yu, F.; Wan, L.; et al. Record-Setting Ocean Warmth Continued in 2019. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 37, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letterly, A.; Key, J.; Liu, Y. Arctic climate: Changes in sea ice extent outweigh changes in snow cover. Cryosphere 2018, 12, 3373–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandven, S.; Spreen, G.; Heygster, G.; Girard-Ardhuin, F.; Farrell, S.L.; Dierking, W.; Allard, R.A. Sea Ice Remote Sensing—Recent Developments in Methods and Climate Data Sets. Surv. Geophys. 2023, 44, 1653–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics Ofarctic Sea Ice Concentration and Extent and Its Response to Thermal and Dynamic Factors. Ph.D. Thesis, Guangdong Ocean University, Zhanjiang, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Li, T. Physical Processes Responsible for the Interannual Variability of Sea Ice Concentration in Arctic in Boreal Autumn since 1979. J. Meteorol. Res. 2017, 31, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; BARBER, D.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Q.; Wang, X.; Xie, H. Record Low Sea-Ice Concentration in the Central Arctic during Summer 2010. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 35, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, L.; Bin, Z.; Shi, L. Polar sea ice concentration retrieval based on FY-3C microwave radiation imager data. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2020, 42, 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. An improved ARTSIST sea ice algorithm based on 19 GHz modified 91 GHz. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2019, 38, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Tian, W.; Lang, X.; Mao, W.; Zhang, J. Statistical Modeling of Arctic Sea Ice Concentrations for Northern Sea Route Shipping. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Screen, J.A.; Deser, C.; Smith, D.M.; Zhang, X.; Blackport, R.; Kushner, P.J.; Oudar, T.; McCusker, K.E.; Sun, L. Consistency and discrepancy in the atmospheric response to Arctic sea-ice loss across climate models. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, M.; Gerland, S.; Holland, M.; Hunke, E.; Kwok, R.; Lecomte, O.; Massom, R.; Perovich, D.; Sturm, M. Snow in the changing sea-ice systems. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Qiu, Y.; Huang, L.; Cheng, M.; Chen, J.; Cheng, B.; Jiang, Z. Changes in Sea Surface Temperature and Sea Ice Concentration in the Arctic Ocean over the Past Two Decades. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, D.L.; Fan, K.; He, S.; Wang, P. Sea-ice-loss slowdown modulates the sea surface salinification in the Kara–Laptev Seas since the 2008 summer. Environ. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, 084022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Liu, C.; Freeman, E.; Graham, G.; Smith, T.; Zhang, H.-M. Assessment and Intercomparison of NOAA Daily Optimum Interpolation Sea Surface Temperature (DOISST) Version 2.1. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 7421–7441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen-Englyst, P.; Hoyer, J.L.; Kolbe, W.M.; Dybkjaer, G.; Lavergne, T.; Tonboe, R.T.; Skarpalezos, S.; Karagali, I. A combined sea and sea-ice surface temperature climate dataset of the Arctic, 1982-2021. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 284, 113331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, K.S.; Wang, S. Sea surface temperature variability in the Arctic Ocean and its marginal seas in a changing climate: Patterns and mechanisms. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2020, 193, 103265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumpen, T.; Janout, M.; Hodges, K.I.; Gerdes, R.; Girard-Ardhuin, F.; Hoelemann, J.A.; Willmes, S. Variability and trends in Laptev Sea ice outflow between 1992–2011. Cryosphere 2013, 7, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, P.A.; Martin, A.C.H.; Josey, S.A.; Marzocchi, A.; Angeloudis, A. Drivers of Laptev Sea interannual variability in salinity and temperature. Ocean Sci. 2024, 20, 341–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, I.; Tyshko, K.; Kirillov, S.; Eicken, H.; Holemann, J.; Kassens, H. Impact of flaw polynyas on the hydrography of the Laptev Sea. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2005, 48, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dethleff, D.; Nürnberg, D.; Groth, E. East siberian arctic region expedition ’92: The Laptev Sea-its importance for Arctic sea ice formation and transpolar sediment flux. Berichte Zur Polarforsch. 1993, 120, 3–37. [Google Scholar]
- Torgny, V. Fram Strait ice fluxes and atmospheric circulation: 1950–2000. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 3508–3517. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, R. Annual cycles of multiyear sea ice coverage of the Arctic Ocean: 1999–2003. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2004, 109, C11004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dethleff, D.; Loewe, P.; Kleine, E. The Laptev Sea flaw lead-detailed investigation on ice formation and export during 1991/1992 winter season. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 1998, 27, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R. Recent changes in Arctic Ocean sea ice motion associated with the North Atlantic Oscillation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumpen, T.; Hölemann, J.A.; Willmes, S.; Morales Maqueda, M.A.; Busche, T.; Dmitrenko, I.A.; Gerdes, R.; Haas, C.; Heinemann, G.; Hendricks, S.; et al. Sea ice production and water mass modification in the eastern Laptev Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, C05014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfirman, S.L.; Colony, R.; Nürnberg, D.; Eicken, H.; Rigor, I. Reconstructing the origin and trajectory of drifting Arctic sea ice. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1997, 102, 12575–12586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, R.W.; Smith, T.M.; Liu, C.; Chelton, D.B.; Casey, K.S.; Schlax, M.G. Daily high-resolution-blended analyses for sea surface temperature. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5473–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banzon, V.; Smith, T.M.; Chin, T.M.; Liu, C.; Hankins, W. A long-term record of blended satellite and in situ sea-surface temperature for climate monitoring, modeling and environmental studies. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2016, 8, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banzon, V.; Smith, T.M.; Steele, M.; Huang, B.; Zhang, H.-M. Improved Estimation of Proxy Sea Surface Temperature in the Arctic. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2020, 37, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreen, G.; Kaleschke, L.; Heygster, G. Sea ice remote sensing using AMSR-E 89-GHz channels. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113, C02S03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, K.; Ohshima, K.I.; Tamura, T.; Nihashi, S. Estimation of thin ice thickness from AMSR-E data in the Chukchi Sea. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 468–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodaira, T.; Waseda, T.; Nose, T.; Inoue, J. Record high Pacific Arctic seawater temperatures and delayed sea ice advance in response to episodic atmospheric blocking. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saracoglu, F.A.; Aydogan, B.; Ayat, B.; Saracoglu, K.E. Spatial and Seasonal Variability of Long-Term Sea Surface Temperature Trends in Aegean and Levantine Basins. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2021, 178, 3769–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yang, D.; Zhong, R.; Yin, X. Interannual, Seasonal, and Monthly Variability of Sea Surface Temperature Fronts in Offshore China from 1982–2021. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comiso, J.C.; Parkinson, C.L.; Gersten, R.; Stock, L. Accelerated decline in the Arctic Sea ice cover. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L01703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Screen, J.A.; Simmonds, I. The central role of diminishing sea ice in recent Arctic temperature amplification. Nature 2010, 464, 1334–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guemas, V.; Blanchard-Wrigglesworth, E.; Chevallier, M.; Day, J.J.; Déqué, M.; Doblas-Reyes, F.J.; Fučkar, N.S.; Germe, A.; Hawkins, E.; Keeley, S.; et al. A review on Arctic sea-ice predictability and prediction on seasonal to decadal time-scales. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 142, 546–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proshutinsky, A.Y.; Johnson, M.A. Two circulation regimes of the wind-driven Arctic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1997, 102, 12493–12514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroeve, J.C.; Crawford, A.D.; Stammerjohn, S. Using timing of ice retreat to predict timing of fall freeze-up in the Arctic. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 6332–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onarheim, I.H.; Eldevik, T.; Smedsrud, L.H.; Stroeve, J.C. Seasonal and Regional Manifestation of Arctic Sea Ice Loss. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 4917–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, Y.; Hao, M.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Yao, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; et al. Recently amplified arctic warming has contributed to a continual global warming trend. Nat. Clim. Change 2017, 7, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Cui, H.; Song, L.; Gan, L.; Xu, S.; Wu, J.; Zheng, C. Influence of sea ice on ship routes and speed along the Arctic Northeast Passage. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2024, 256, 107320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Krafft, T.; Martens, P. The interaction between climate change and marine fisheries: Review, challenges, and gaps. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2024, 259, 107479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Statistics | Interannual SST Characteristics | Seasonal SST Characteristics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | Summer | Fall | Winter | ||
| Mean (°C) | 0.452 | 0.308 | 0.645 | 0.503 | 0.352 |
| Trend (°C/year) | +0.068 | +0.035 | +0.154 | +0.130 | +0.040 |
| Max SST (°C) | 1.380 | 1.112 | 3.287 | 1.777 | 0.882 |
| Min SST (°C) | −0.511 | −0.107 | −1.354 | −0.838 | −0.717 |
| Statistics | Interannual SIC Characteristics | Seasonal SIC Characteristics | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | Summer | Fall | Winter | ||
| Mean (%) | 70.01 | 99.56 | 41.34 | 50.56 | 95.59 |
| Trend (%/year) | −1.297 | −0.012 | −0.095 | −0.082 | −0.001 |
| Max SIC (%) | 95.95 | 99.22 | 88.73 | 82.62 | 99.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, C. Analysis of the Effect of Sea Surface Temperature on Sea Ice Concentration in the Laptev Sea for the Years 2004–2023. Water 2025, 17, 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050769
Zhang C, Zhang Z, Qi P, Zhang Y, Dai C. Analysis of the Effect of Sea Surface Temperature on Sea Ice Concentration in the Laptev Sea for the Years 2004–2023. Water. 2025; 17(5):769. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050769
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chenyao, Ziyu Zhang, Peng Qi, Yiding Zhang, and Changlei Dai. 2025. "Analysis of the Effect of Sea Surface Temperature on Sea Ice Concentration in the Laptev Sea for the Years 2004–2023" Water 17, no. 5: 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050769
APA StyleZhang, C., Zhang, Z., Qi, P., Zhang, Y., & Dai, C. (2025). Analysis of the Effect of Sea Surface Temperature on Sea Ice Concentration in the Laptev Sea for the Years 2004–2023. Water, 17(5), 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050769






