Hybrid System of Fenton Process and Sequencing Batch Reactor for Coking Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wastewater Composition and Sludge Inoculum
2.2. Pretreatment of the Coking Wastewater
2.3. SBR Set up and Operation
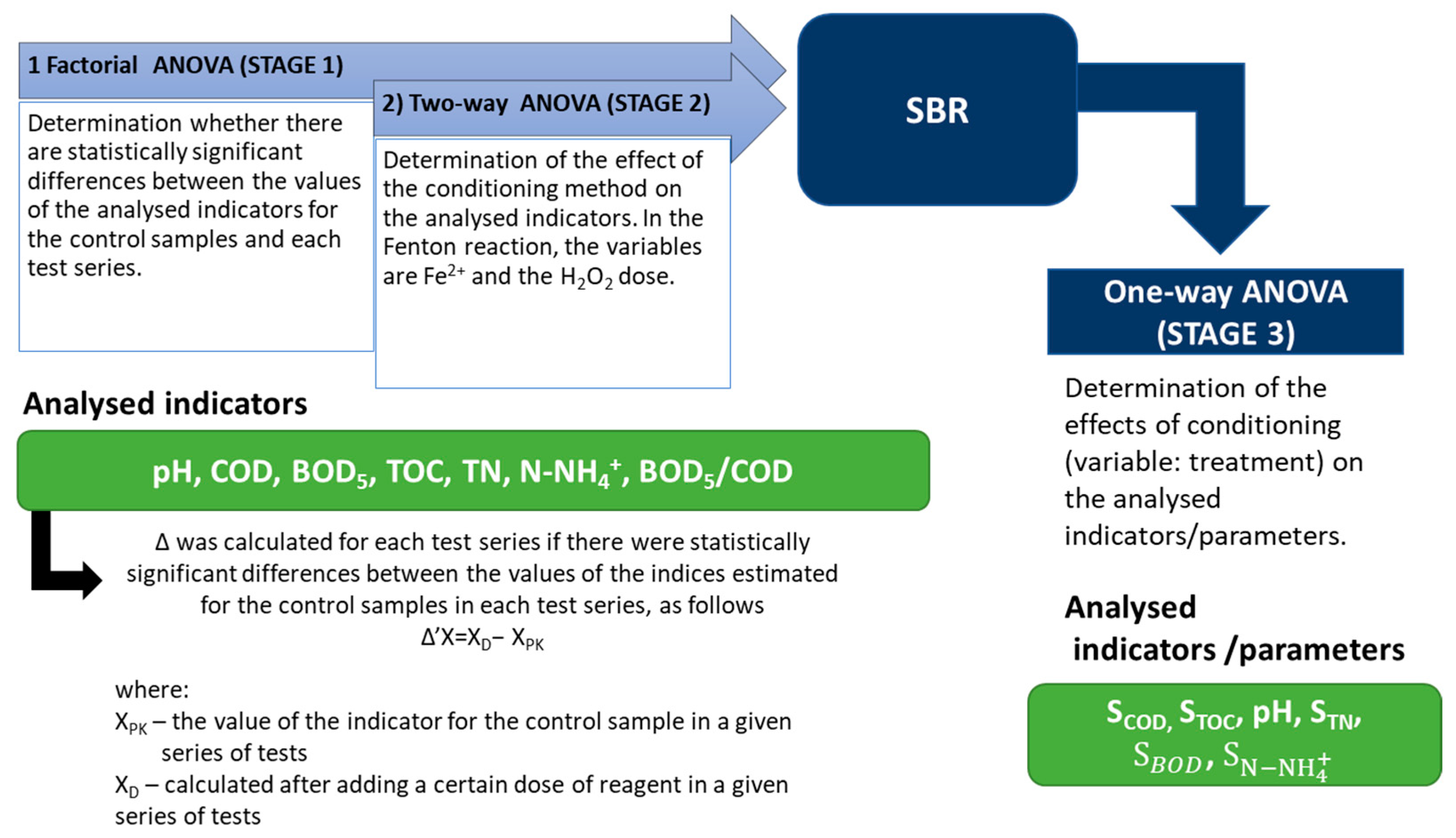
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
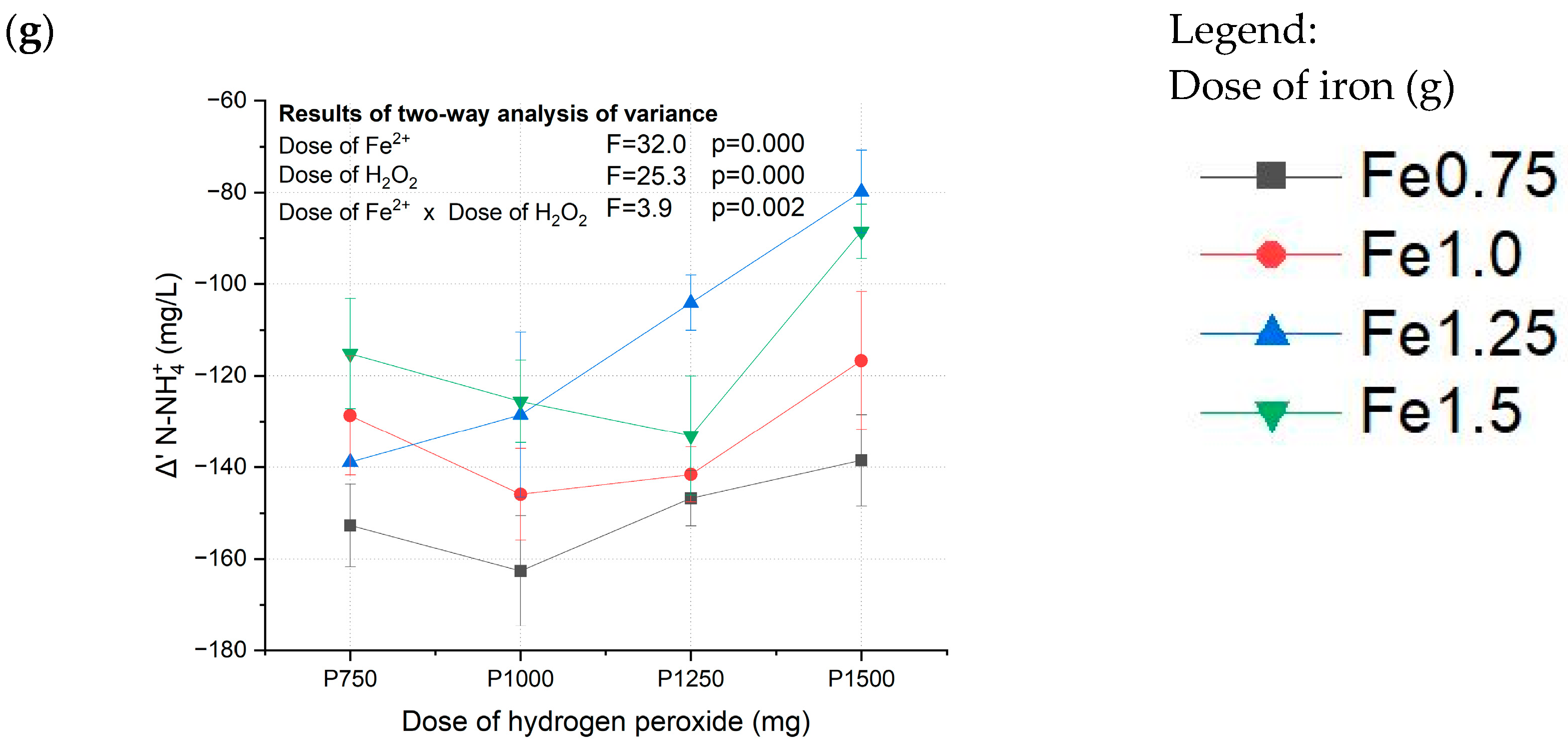
3.1. Fenton Pretreatment of Coking Wastewater
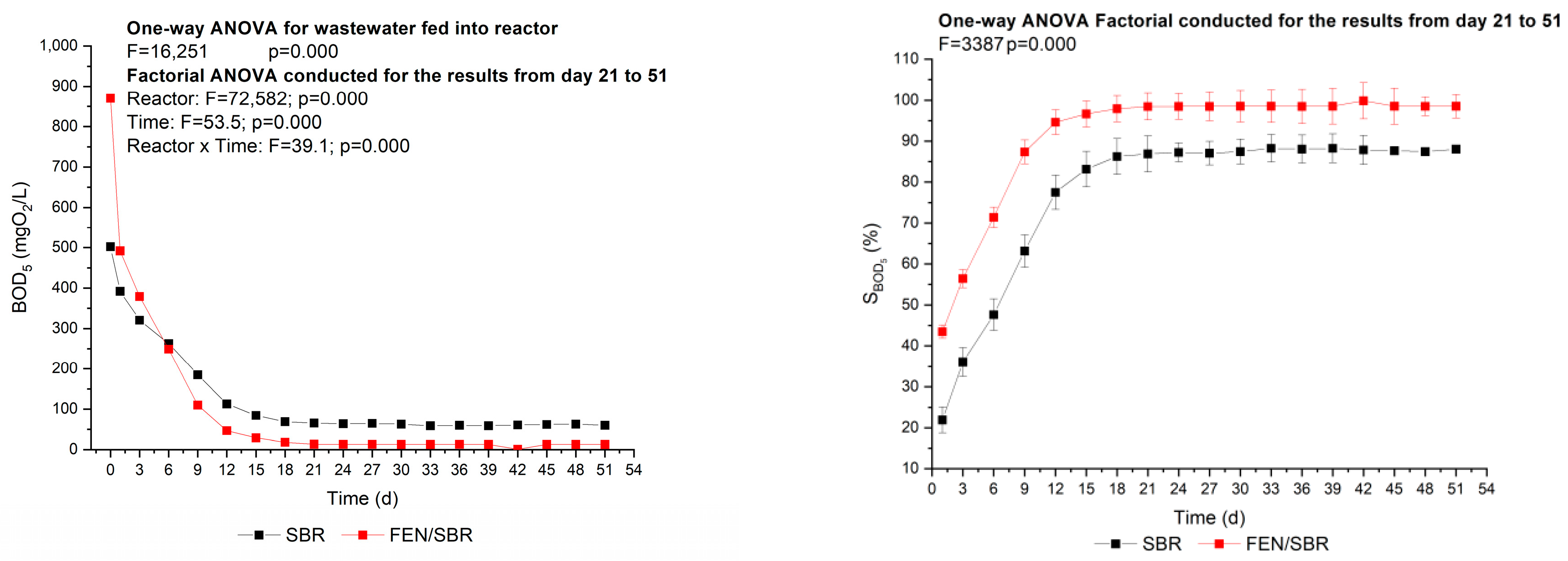
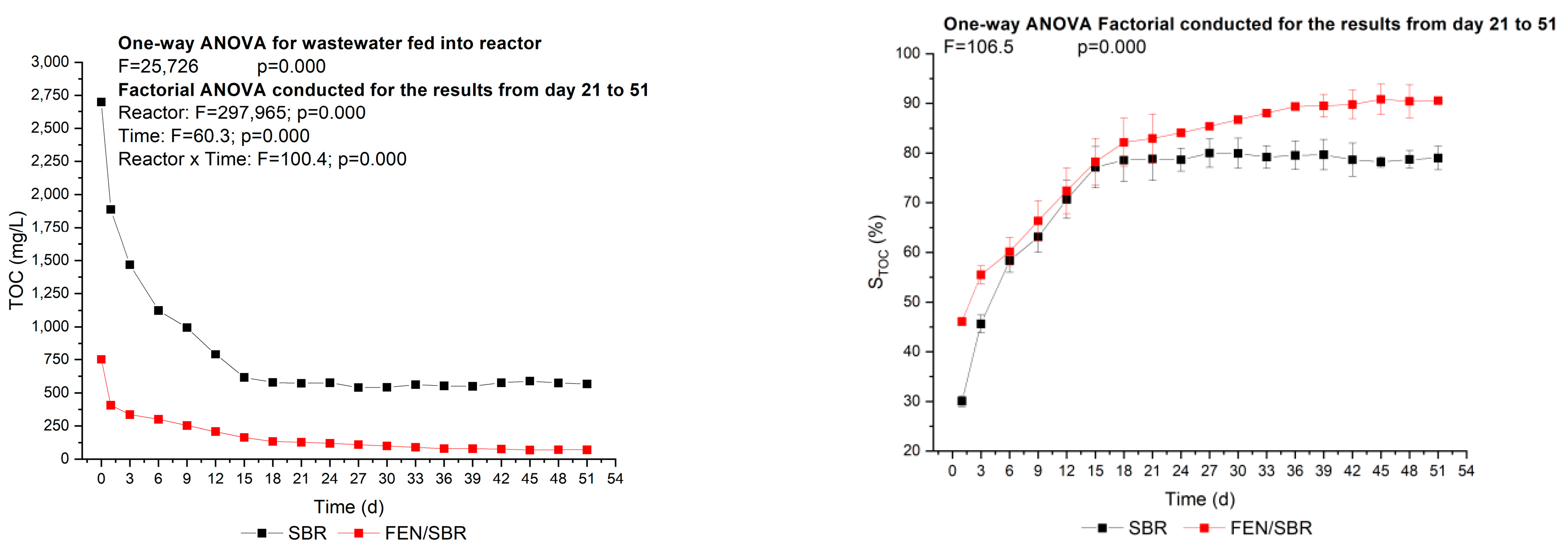
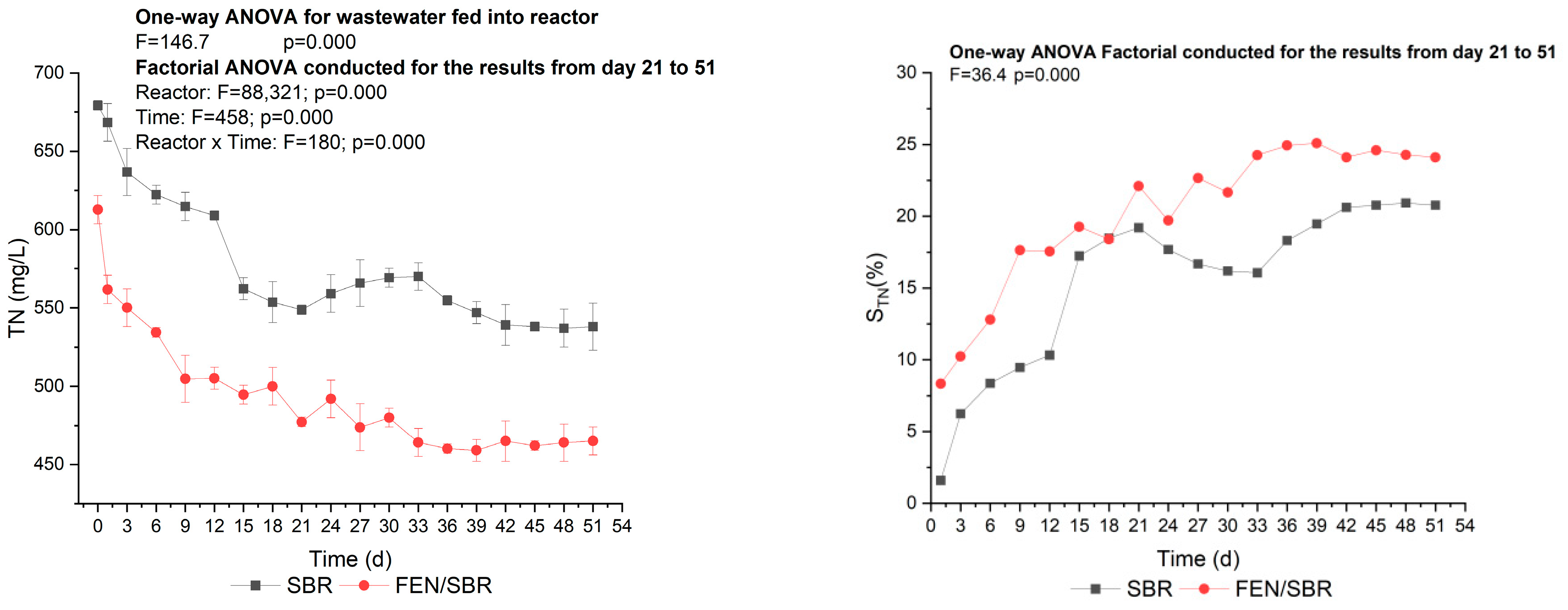
3.2. Effectiveness of the Fenton-SBR Hybrid System
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOP | advanced oxidation processes |
| BOD5 | 5-day biochemical oxygen demand |
| COD | Chemical oxygen demand |
| DO | dissolved oxygen |
| HRT | Hydraulic retention time |
| MLSS | Mixed liquor suspended solids |
| N-NO2 | nitrite |
| N-NO3 | nitrate |
| N-NH4+ | ammonium nitrogen |
| OLR | Organic loading rate |
| ROSs | reactive oxygen species |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| TOC | Total organic carbon |
| TSS | total suspended solids |
| VSS | volatile suspended solids |
References
- Smol, M.; Włóka, D.; Włodarczyk-Makuła, M. Influence of Integrated Membrane Treatment on the Phytotoxicity of Wastewater from the Coke Industry. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Watanabe, H.; Wei, C.; Wang, D.; Zhou, J.; Tatarazako, N.; Masunaga, S.; Zhang, Y. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety Reduction in Toxicity of Coking Wastewater to Aquatic Organisms by Vertical Tubular Biological Reactor. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 115, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiecińska, A.; Lajnert, R.; Bigda, R. Coke Oven Wastewater—Formation, Treatment and Utilization Methods—A Review. Proc. ECOpole 2017, 11, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machowska, H. Przemysł Koksowniczy w Aspekcie Ochrony Środowiska. Proc. ECOpole 2011, 5, 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Pillai, I.M.S.; Gupta, A.K. Anodic Oxidation of Coke Oven Wastewater: Multiparameter Optimization for Simultaneous Removal of Cyanide, COD and Phenol. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 176, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wei, C.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, R. Improvement of Biodegradability for Coking Wastewater by Selective Adsorption of Hydrophobic Organic Pollutants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 151, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felföldi, T.; Nagymáté, Z.; Székely, A.J.; Jurecska, L.; Márialigeti, K. Biological Treatment of Coke Plant Effluents: From a Microbiological Perspective. Biol. Futur. 2020, 71, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozak, J.; Włodarczyk-Makuła, M. Fotodegradacja Małocząsteczkowych WWA w Warunkach Reakcji Fentona. Zesz. Naukowe. Inżynieria Sr. 2017, 168, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Mielczarek, K.; Kwarciak-Kozłowska, A.; Bohdziewicz, J. Oczyszczanie Ścieków Koksowniczych w Układzie Zintegrowanym Łaczacym Proces Koagulacji z Ciśnieniowymi Technikami Membranowymi. Rocz. Ochr. Sr. 2011, 13, 1965–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, L.; Paul, K.K.; Jena, S. Characterization of Coke Oven Wastewater. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 167, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Wu, G.; Mao, J.; Zhou, T. Simulation and Optimization of a Coking Wastewater Biological Treatment Process by Activated Sludge Models (ASM). J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 165, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargieł, P.; Zabochnicka-Świątek, M. Technologies of Coke Wastewater Treatment in the Frame of Legislation in Force. Ochr. Sr. Zasobów Nat. 2018, 29, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, F.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Z. Highly Efficient One-Step Advanced Treatment of Biologically Pretreated Coking Wastewater by an Integration of Coagulation and Adsorption Process. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1206–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, L.; Paul, K.K.; Jena, S. Coke Wastewater Treatment Methods: Mini Review. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2021, 98, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Jin, X.; Lu, S. Microbial Communities in Biological Denitrification System Using Methanol as Carbon Source for Treatment of Reverse Osmosis Concentrate from Coking Wastewater. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2018, 8, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Wu, D.; Chen, W.; Feng, C.; Wei, C. Biocathode Denitrification of Coke Wastewater Effluent from an Industrial Aeration Tank: Effect of Long-Term Adaptation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 125, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raper, E.; Stephenson, T.; Simões, F.; Fisher, R.; Anderson, D.R.; Soares, A. Enhancing the Removal of Pollutants from Coke Wastewater by Bioaugmentation: A Scoping Study. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 2535–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, B.G.; Kim, J.; Han, J.I.; Kim, K.; Kim, D.; Seo, B.K.; Kang, C.M.; Yang, J.W. Evaluation of an Electro-Flotation-Oxidation Process for Harvesting Bio-Flocculated Algal Biomass and Simultaneous Treatment of Residual Pollutants in Coke Wastewater Following an Algal-Bacterial Process. Algal Res. 2018, 31, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, B.G.; Kim, J.; Han, J.I.; Yang, J.W. Feasibility of Using a Microalgal-Bacterial Consortium for Treatment of Toxic Coke Wastewater with Concomitant Production of Microbial Lipids. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 225, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Fu, S.; Hao, X.; Zhou, D. Synergistic Effects of Simultaneous Coupling Ozonation and Biodegradation for Coking Wastewater Treatment: Advances in COD Removal, Toxic Elimination, and Microbial Regulation. Chemosphere 2023, 318, 137956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Hou, Z.; Lv, L.; Song, J.; Yin, Z. Electro-Fenton with Peroxi-Coagulation as a Feasible Pre-Treatment for High-Strength Refractory Coke Plant Wastewater: Parameters Optimization, Removal Behavior and Kinetics Analysis. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamang, M.; Paul, K.K. Advances in Treatment of Coking Wastewater—A State of Art Review. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 449–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, L.; Wang, J.; Dong, J.; Liu, H.; Sun, X. Chemosphere Treatment of Coking Wastewater by an Advanced Fenton Oxidation Process Using Iron Powder and Hydrogen Peroxide. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Tian, J.; Liu, R.; Chen, L. Optimization of Fenton and Electro-Fenton Oxidation of Biologically Treated Coking Wastewater Using Response Surface Methodology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 81, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutić, A.; Miloloža, M.; Cvetnić, M.; Martinjak, V.; Furač, L.; Markić, M.; Ukić, Š.; Bolanča, T.; Kučić Grgić, D. An Overview of Coking Wastewater Characteristics and Treatment Technologies. Kem. Ind. 2023, 72, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Huang, M.; Xiang, W.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Zan, F.; Zhou, T. A Rational Strategy of Combining Fenton Oxidation and Biological Processes for Efficient Nitrogen Removal in Toxic Coking Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 127897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Całus-Makowska, K.; Dziubińska, J.; Grosser, A.; Grobelak, A. Application of the Fenton and Photo-Fenton Processes in Pharmaceutical Removal: New Perspectives in Environmental Protection. Desalin. Water Treat. 2025, 321, 100949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.K.; Philip, L. Combined Biological and Photocatalytic Treatment of Real Coke Oven Wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 295, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Włodarczyk-Makuła, M.; Wiśniowska, E.; Turek, A.; Obstój, A. Removal of PAHs from Coking Wastewater during Photodegradation Process. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 1262–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, X. Effect of Wastewater Particles on Catalytic Ozonation in the Advanced Treatment of Petrochemical Secondary Effluent. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, M.; Jing, G.; Piao, Y.; Liu, D.; Jin, L. Treatment of Refractory Organic Pollutants in Industrial Wastewater by Wet Air Oxidation. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S769–S776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, P. Ti–Sn–Ce/Bamboo Biochar Particle Electrodes for Enhanced Electrocatalytic Treatment of Coking Wastewater in a Three-Dimensional Electrochemical Reaction System. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, G.; Wang, P. A Review on Fenton-like Processes for Organic Wastewater Treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 762–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, F.; Teixeira, A.C.S.C.; Ruotolo, L.A.M. Critical Review of Fenton and Photo-Fenton Wastewater Treatment Processes over the Last Two Decades. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 13995–14032. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, J.P.; Sarinho, L.; Nunes, M.I. Application of Life Cycle Assessment to Fenton Processes in Wastewater Treatment–A Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 57, 104692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kwarciak-Kozłowska, A.; Worwąg, M. The Impact of an Ultrasonic Field on the Efficiency of Coke Wastewater Treatment in a Sequencing Batch Reactor. Energies 2021, 14, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dhall, P.; Kumar, R. Redefining BOD: COD Ratio of Pulp Mill Industrial Wastewaters in BOD Analysis by Formulating a Specific Microbial Seed. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2010, 64, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Chaudhari, P.K. Optimization of Multiple Parameters for Treatment of Coking Wastewater Using Fenton Oxidation. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 5084–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, C. Comparative Activity of TiO2 Microspheres and P25 Powder for Organic Degradation: Implicative Importance of Structural Defects and Organic Adsorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 319, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, A.M.F.M.; Madeira, L.M.P.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Costa, C.A.V. Fenton Oxidation of Cork Cooking Wastewater—Overall Kinetic Analysis. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3061–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamarro, E.; Marco, A.; Esplugas, S. Use of Fenton Reagent to Improve Organic Chemical Biodegradability. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Reaction | Reaction Rate Constant, L/(mol × s) | |
|---|---|---|
| Fenton system | Fe2+ + H2O2 → Fe3+ + HO• + OH− | 53–76 |
| Fe2+ + HO• → Fe 3+ + OH− | 2.6–5.8 × 108 | |
| H2O2 + HO• → HO2• + H2O | 1.7–4.5 × 107 | |
| Fe2+ + HO2• → Fe 3+ + OH2− | 0.72–1.5 × 108 | |
| Fe3+ + HO2• → Fe2+ + O2 + H+ | 0.33–2.1 × 106 | |
| HO• + HO• → H2O | 5–8 × 109 | |
| HO2• + HO2• → H2O2 + O2 | 0.8–2.2 × 106 | |
| HO• + HO2• → H2O + O2 | 1.4 × 10 10 | |
| 2 H2O2 → 2H2O + O2 | ||
| Fe3+ + H2O2 → [Fe(HO2)]2+ + H+ | 3.1 × 10−3 | |
| [Fe(HO2)]2+ → Fe2+ + HO• | ||
| Fe2+ + HO2• → Fe3+ + HO2− | 0.75–1.5 × 106 | |
| R + HO• → R• + H2O | 107–1010 | |
| R + HO• → HOR• | 107–1010 | |
| R• → RR | ||
| R• + Fe2+ → R− + Fe3+ | ||
| R• + Fe3+ → R+ + Fe2+ | ||
| R+ + OH− → R-OH | ||
| Fe2+ (g/L) | H2O2 (mg/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.75 | 750 | 1000 | 1250 | 1500 |
| 1.0 | ||||
| 1.25 | ||||
| 1.50 | ||||
| Δ’BOD | Δ’COD | Δ’BOD5/COD | ||||||
| Sample | time | results | Sample | time | results | Sample | time | results |
| Fe1.0 | P1500 | 301 | Fe1.0 | P1250 | −2335 | Fe1.25 | P1250 | 0.16 |
| Fe0.75 | P750 | 347 | Fe1.0 | P1500 | −2286 | Fe0.75 | P750 | 0.17 |
| Fe1.0 | P1000 | 372 | Fe1.25 | P1250 | −2104 | Fe1.0 | P1500 | 0.19 |
| Fe1.0 | P1250 | 394 | Fe0.75 | P750 | −2067 | Fe0.75 | P1000 | 0.22 |
| Fe0.75 | P1000 | 454 | Fe0.75 | P1000 | −2032 | Fe1.0 | P1250 | 0.23 |
| Δ’TOC | Δ’pH | |||||||
| Sample | time | results | Sample | time | results | |||
| Fe1.25 | P1250 | −0.71 | Fe1.0 | P750 | −1.49 | |||
| Fe1.0 | P1250 | −0.64 | Fe1.5 | P1000 | −1.45 | |||
| Fe1.25 | P1000 | −0.61 | Fe1.5 | P1250 | −1.44 | |||
| Fe1.0 | P1000 | −0.56 | Fe0.75 | P1500 | −1.42 | |||
| Fe1.25 | P1500 | −0.56 | Fe1.0 | P1000 | −1.33 | |||
| Δ’TN | Δ’N-NH4+ | |||||||
| Sample | time | results | Sample | time | results | |||
| Fe0.75 | P1000 | −155.2 | Fe0.75 | P1000 | −162.6 | |||
| Fe0.75 | P750 | −149.7 | Fe0.75 | P750 | −152.7 | |||
| Fe0.75 | P1250 | −139.4 | Fe0.75 | P1250 | −146.8 | |||
| Fe1.0 | P1000 | −139.3 | Fe1.0 | P1000 | −145.9 | |||
| Fe1.0 | P1250 | −138.8 | Fe1.0 | P1250 | −141.6 | |||
| Frequency of Sample Appearance in the Analysed Set | ||||||||
| Fe0.75 | P750 | 5 | Fe1.0 | P750 | 1 | Fe1.25 | P1000 | 1 |
| Fe0.75 | P1000 | 5 | Fe1.0 | P1250 | 6 | Fe1.25 | P1250 | 2 |
| Fe0.75 | P1250 | 2 | Fe1.0 | P1000 | 5 | Fe1.25 | P1500 | 1 |
| Fe0.75 | P1500 | 1 | Fe1.0 | P1500 | 3 | Fe1.5 | P1000 | 1 |
| Fe1.5 | P1250 | 1 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grosser, A.; Neczaj, E.; Krzemińska, D.; Ratman-Kłosińska, I. Hybrid System of Fenton Process and Sequencing Batch Reactor for Coking Wastewater Treatment. Water 2025, 17, 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050751
Grosser A, Neczaj E, Krzemińska D, Ratman-Kłosińska I. Hybrid System of Fenton Process and Sequencing Batch Reactor for Coking Wastewater Treatment. Water. 2025; 17(5):751. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050751
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrosser, Anna, Ewa Neczaj, Dorota Krzemińska, and Izabela Ratman-Kłosińska. 2025. "Hybrid System of Fenton Process and Sequencing Batch Reactor for Coking Wastewater Treatment" Water 17, no. 5: 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050751
APA StyleGrosser, A., Neczaj, E., Krzemińska, D., & Ratman-Kłosińska, I. (2025). Hybrid System of Fenton Process and Sequencing Batch Reactor for Coking Wastewater Treatment. Water, 17(5), 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050751







