Application of Environmental DNA in Aquatic Ecosystem Monitoring: Opportunities, Challenges and Prospects
Abstract
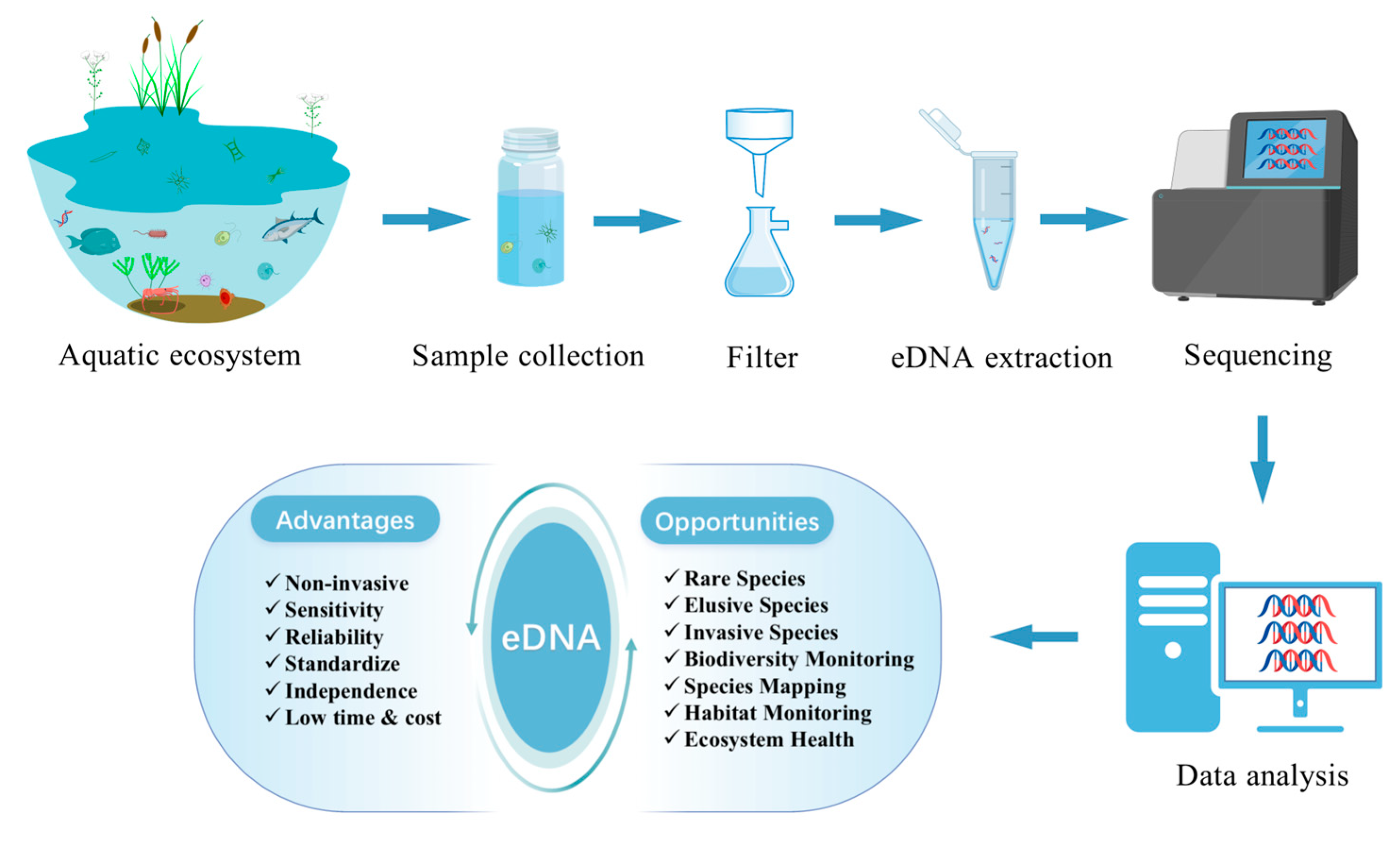
1. Introduction
2. Opportunities of eDNA in Aquatic Ecosystems
2.1. Detecting Rare and Elusive Species
2.2. Large-Scale Biodiversity Monitoring
2.3. Early Detection of Invasive Species
2.4. Species Mapping and Habitat Monitoring
2.5. Monitoring Ecosystem Health
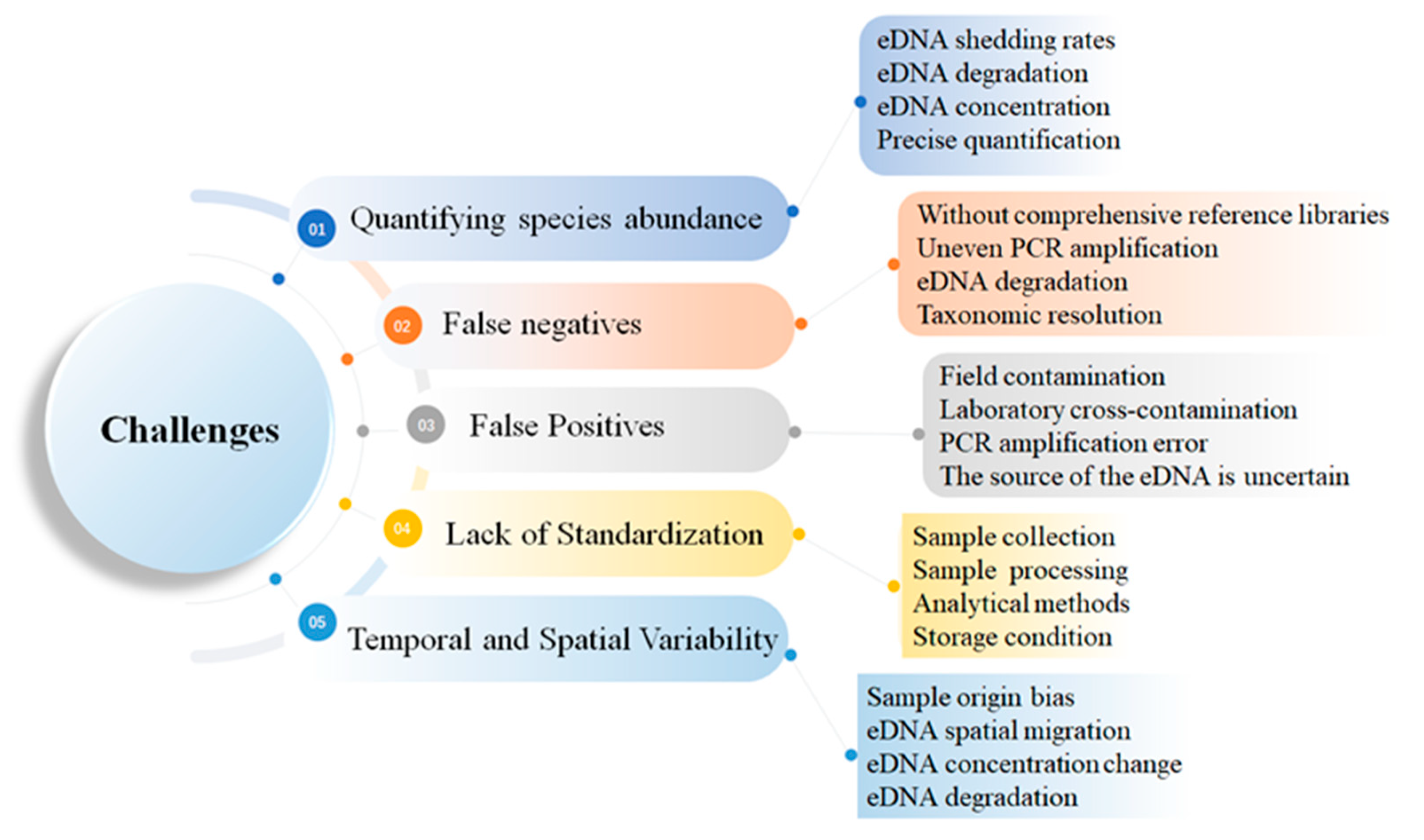
3. Challenges of Using eDNA in Aquatic Ecosystems
3.1. Difficulty in Quantifying Species Abundance
3.2. False Negatives
3.3. False Positives
3.4. Lack of Standardization in eDNA Protocols
3.5. Temporal and Spatial Variability in eDNA Dynamics
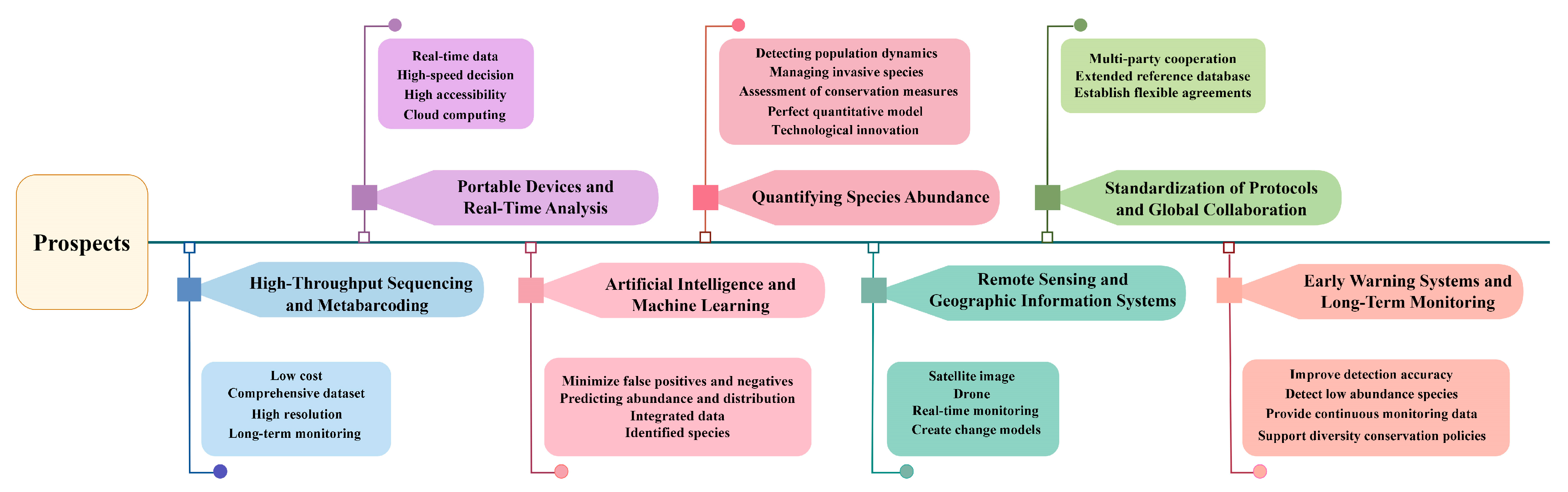
4. Prospects and Technological Advancements in eDNA
4.1. High-Throughput Sequencing and Metabarcoding
4.2. Portable Sequencing Devices and Real-Time Analysis
4.3. Integration of eDNA with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
4.4. Advancements in Quantifying Species Abundance
4.5. Combining eDNA with Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GISs)
4.6. Standardization of Protocols and Global Collaboration
4.7. eDNA for Early Warning Systems and Long-Term Monitoring
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pörtner, H.O.; Scholes, R.J.; Arneth, A.; Barnes, D.K.A.; Burrows, M.T.; Diamond, S.E.; Duarte, C.M.; Kiessling, W.; Leadley, P.; Managi, S.; et al. Overcoming the coupled climate and biodiversity crises and their societal impacts. Science 2023, 380, eabl4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogue, A.S.; Breon, K. The greatest threats to species. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2022, 4, e12670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S. Freshwater Biodiversity and Conservation Challenges: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Innov. 2021, 3, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranov, V.; Jourdan, J.; Pilotto, F.; Wagner, R.; Haase, P. Complex and nonlinear climate-driven changes in freshwater insect communities over 42 years. Conserv. Biol. 2020, 34, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Li, S.; Xiong, W.; Du, X.; Qiao, K.; Zhan, A. Monitoring bloom-forming Aphanizomenon using environmental DNA metabarcoding: Method development, validation, and field application. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 150, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, G.T.; Ozman-Sullivan, S.K. Global mite diversity is in crisis: What can we do about it? Zoosymposia 2022, 22, 089–093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, J.; Lin, H.-J.; Li, B.-Y.; Du, H.; Yan, Z.-G. Environmental DNA reveals the spatiotemporal distribution and migration characteristics of the Yangtze finless porpoise, the sole aquatic mammal in the Yangtze River. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiner, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Bernatchez, L. The future of biodiversity monitoring and conservation utilizing environmental DNA. Environ. DNA 2020, 3, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, V.G.; Davison, P.I.; Creach, V.; Stone, D.; Bass, D.; Tidbury, H.J. The Application of eDNA for Monitoring Aquatic Non-Indigenous Species: Practical and Policy Considerations. Diversity 2023, 15, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Klymus, K.E.; Marshall, N.T.; Stepien, C.A. Environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding assays to detect invasive invertebrate species in the Great Lakes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, N.K.M.; Tay, Y.C.; Srivathsan, A.; Tan, J.W.T.; Kwik, J.T.B.; Baloğlu, B.; Meier, R.; Yeo, D.C.J. Next-generation freshwater bioassessment: eDNA metabarcoding with a conserved metazoan primer reveals species-rich and reservoir-specific communities. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2016, 3, 160635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Willerslev, E. Environmental DNA—An emerging tool in conservation for monitoring past and present biodiversity. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiner, K.; Fronhofer, E.A.; Mächler, E.; Walser, J.-C.; Altermatt, F. Environmental DNA reveals that rivers are conveyer belts of biodiversity information. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djurhuus, A.; Closek, C.J.; Kelly, R.P.; Pitz, K.J.; Michisaki, R.P.; Starks, H.A.; Walz, K.R.; Andruszkiewicz, E.A.; Olesin, E.; Hubbard, K.; et al. Environmental DNA reveals seasonal shifts and potential interactions in a marine community. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carraro, L.; Mächler, E.; Wüthrich, R.; Altermatt, F. Environmental DNA allows upscaling spatial patterns of biodiversity in freshwater ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bálint, M.; Nowak, C.; Márton, O.; Pauls, S.U.; Wittwer, C.; Aramayo, J.L.; Schulze, A.; Chambert, T.; Cocchiararo, B.; Jansen, M. Accuracy, limitations and cost efficiency of eDNA-based community survey in tropical frogs. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2018, 18, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Peng, Y.; Fang, W.; Altermatt, F.; Xie, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X. Application of Environmental DNA Metabarcoding for Predicting Anthropogenic Pollution in Rivers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11708–11719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andruszkiewicz Allan, E.; Zhang, W.G.; Lavery, A.C.; Govindarajan, A.F. Environmental DNA shedding and decay rates from diverse animal forms and thermal regimes. Environ. DNA 2020, 3, 492–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, K.; Anucha, P.; Turnbull, J.; Bean, C.; Leaver, M. Searching for a signal: Environmental DNA (eDNA) for the detection of invasive signal crayfish, Pacifastacus leniusculus (Dana, 1852). Manag. Biol. Invasions 2018, 9, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klymus, K.E.; Richter, C.A.; Chapman, D.C.; Paukert, C. Quantification of eDNA shedding rates from invasive bighead carp Hypophthalmichthys nobilis and silver carp Hypophthalmichthys molitrix. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 183, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.N.; Shen, E.W.; Seemann, J.; Correa, A.M.S.; O’Donnell, J.L.; Altieri, A.H.; Knowlton, N.; Crandall, K.A.; Egan, S.P.; McMillan, W.O.; et al. Environmental DNA survey captures patterns of fish and invertebrate diversity across a tropical seascape. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlowski, J.; Apothéloz-Perret-Gentil, L.; Altermatt, F. Environmental DNA: What’s behind the term? Clarifying the terminology and recommendations for its future use in biomonitoring. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 4258–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Yan, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, S.; Zheng, X.; Fan, J.; Zhang, T. Environmental DNA: An Emerging Tool in Ecological Assessment. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 103, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, A.; Kumar, N.; Pal Singh, C.; Singh, M. Environmental DNA (eDNA): Powerful technique for biodiversity conservation. J. Nat. Conserv. 2023, 71, 126325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishan, S.T.; Kline, R.J.; Rahman, M.S. Applications of environmental DNA (eDNA) to detect subterranean and aquatic invasive species: A critical review on the challenges and limitations of eDNA metabarcoding. Environ. Adv. 2023, 12, 100370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, P.J. The use of environmental DNA in monitoring aquatic biodiversity for conservation: A review of challenges and opportunities. ARPHA Conf. Abstr. 2021, 4, e65283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truelove, N.K.; Andruszkiewicz, E.A.; Block, B.A.; Gilbert, M.T.P. A rapid environmental DNA method for detecting white sharks in the open ocean. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2019, 10, 1128–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, M.; Gotoh, R.O.; Sado, T. MiFish metabarcoding: A high-throughput approach for simultaneous detection of multiple fish species from environmental DNA and other samples. Fish. Sci. 2020, 86, 939–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeter, B.; Veríssimo, J.; Lopes-Lima, M.; Chaves, C.; Pinto, J.; Riccardi, N.; Beja, P.; Fonseca, N.A. Speeding up the detection of invasive bivalve species using environmental DNA: A Nanopore and Illumina sequencing comparison. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022, 22, 2232–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, J.; Tong, F.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Ding, S. Resource Assessment of Larimichthys crocea in the East China Sea Based on eDNA Analysis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 890756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, T.; Halfmaerten, D.; Neyrinck, S.; De Regge, N.; Jacquemyn, H.; Brys, R. Accurate detection and quantification of seasonal abundance of American bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus) using ddPCR eDNA assays. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palsson, A.; Capo, E.; Spong, G.; Norman, S.; Königsson, H.; Bartels, P.; Byström, P. Droplet digital PCR assays for the quantification of brown trout (Salmo trutta) and Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus) from environmental DNA collected in the water of mountain lakes. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, L.M.; Simmons, M.; Wegleitner, B.J.; Jerde, C.L.; Mahon, A.R. Quantifying Environmental DNA Signals for Aquatic Invasive Species Across Multiple Detection Platforms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12800–12806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uthicke, S.; Lamare, M.; Doyle, J.R. eDNA detection of corallivorous seastar (Acanthaster cf. solaris) outbreaks on the Great Barrier Reef using digital droplet PCR. Coral Reefs 2018, 37, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, F.; Li, S.; Xiong, W.; Zhan, A. Environmental DNA-Based Identification of Non-Native Fish in Beijing: Diversity, Geographical Distribution, and Interactions with Native Taxa. Animals 2024, 14, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, H.; Anglès d’Auriac, M.B.; Strand, D.A.; Mjelde, M.; Demars, B.O.L.; Thaulow, J. Detection of an invasive aquatic plant in natural water bodies using environmental DNA. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, T.S.; Sasaki, Y. Evaluating the quantitative performance of environmental DNA metabarcoding for freshwater zooplankton community: A case study in Lake Biwa, Japan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 58069–58082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, M. Environmental DNA Metabarcoding: A Novel Method for Biodiversity Monitoring of Marine Fish Communities. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2022, 14, 161–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, E.; Bylemans, J.; Goodman, S.J.; Lombardi, R.; Carr, I.; Castellano, L.; Galimberti, A.; Galli, P. Novel universal primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA surveys of marine mammals and other marine vertebrates. Environ. DNA 2020, 2, 460–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roblet, S.; Priouzeau, F.; Gambini, G.; Cottalorda, J.-M.; Gastaldi, J.M.; Pey, A.; Raybaud, V.; Suarez, G.R.; Serre, C.; Sabourault, C.; et al. From sight to sequence: Underwater visual census vs environmental DNA metabarcoding for the monitoring of taxonomic and functional fish diversity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 956, 177250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurecki, S. Application and Validation of the eDNA-Metabarcoded MiFish/MitoFish Pipeline for Assessment of Native and Non-Native Fish Communities of Lake Michigan. Master’s Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Coble, A.A.; Flinders, C.A.; Homyack, J.A.; Penaluna, B.E.; Cronn, R.C.; Weitemier, K. eDNA as a tool for identifying freshwater species in sustainable forestry: A critical review and potential future applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1157–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saenz-Agudelo, P.; Delrieu-Trottin, E.; DiBattista, J.D.; Martínez-Rincon, D.; Morales-González, S.; Pontigo, F.; Ramírez, P.; Silva, A.; Soto, M.; Correa, C. Monitoring vertebrate biodiversity of a protected coastal wetland using eDNA metabarcoding. Environ. DNA 2021, 4, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, F.N.; Brito, I.L. What Is Metagenomics Teaching Us, and What Is Missed? Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 74, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Jin, X.; Seymour, M.; Richter, C.; Logares, R.; Khim, J.S.; Klymus, K. Recent advances in environmental DNA-based biodiversity assessment and conservation. Divers. Distrib. 2021, 27, 1876–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beng, K.C.; Corlett, R.T. Applications of environmental DNA (eDNA) in ecology and conservation: Opportunities, challenges and prospects. Biodivers. Conserv. 2020, 29, 2089–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, L.; Hartikainen, H.; Jokela, J.; Bertuzzo, E.; Rinaldo, A. Estimating species distribution and abundance in river networks using environmental DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 11724–11729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.-C.; Shum, P.; Mariani, S.; Sink, K.J.; Palmer, R.; Matcher, G.F. Enhancing African coelacanth monitoring using environmental DNA. Biol. Lett. 2024, 20, 20240415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, L.R.; Buxton, A.S.; Rees, H.C.; Bruce, K.; Brys, R.; Halfmaerten, D.; Read, D.S.; Watson, H.V.; Sayer, C.D.; Jones, E.P.; et al. Prospects and challenges of environmental DNA (eDNA) monitoring in freshwater ponds. Hydrobiologia 2018, 826, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwamburi, S.M.; Uku, J.; Wambiji, N.; Kairo, J.; Oketch, F.; Oduor, K.O.; Amondi, L.; Ishmael, N. Integration of environmental DNA metabarcoding technique to reinforce fish biodiversity assessments in seagrass ecosystems: A case study of Gazi bay seagrass meadows. Environ. DNA 2023, 5, 1574–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, F.; Hürlemann, S.; Locher, N.; Stamm, C.; Deiner, K.; Altermatt, F. A triad of kicknet sampling, eDNA metabarcoding, and predictive modeling to assess richness of mayflies, stoneflies and caddisflies in rivers. Metabarcoding Metagenomics 2022, 6, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, L.J.; Suter, L.; Deagle, B.E.; Polanowski, A.M.; Terauds, A.; Johnstone, G.J.; Stark, J.S. Environmental DNA metabarcoding for monitoring metazoan biodiversity in Antarctic nearshore ecosystems. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renan, S.; Gafny, S.; Perl, R.G.B.; Roll, U.; Malka, Y.; Vences, M.; Geffen, E. Living quarters of a living fossil-Uncovering the current distribution pattern of the rediscovered Hula painted frog (Latonia nigriventer) using environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 6801–6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brys, R.; Halfmaerten, D.; Neyrinck, S.; Mauvisseau, Q.; Auwerx, J.; Sweet, M.; Mergeay, J. Reliable eDNA detection and quantification of the European weather loach (Misgurnus fossilis). J. Fish Biol. 2020, 98, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgoa Cardás, J.; Deconinck, D.; Márquez, I.; Peón Torre, P.; Garcia-Vazquez, E.; Machado-Schiaffino, G. New eDNA based tool applied to the specific detection and monitoring of the endangered European eel. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 250, 108750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, M.M.; Larson, E.R.; Renshaw, M.A.; Gantz, C.A.; Egan, S.P.; Erickson, D.M.; Lodge, D.M.; Frid, C. EnvironmentalDNA(eDNA) detects the invasive rusty crayfishOrconectes rusticusat low abundances. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 53, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, S.I.; Strand, D.A.; Rusch, J.C.; Vrålstad, T. Environmental DNA (eDNA) Monitoring of Noble Crayfish Astacus astacus in Lentic Environments Offers Reliable Presence-Absence Surveillance—But Fails to Predict Population Density. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 612253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Katano, I.; Sakata, Y.; Souma, R.; Kosuge, T.; Nagano, M.; Ikeda, K.; Yano, K.; Tojo, K. Detection of an endangered aquatic heteropteran using environmental DNA in a wetland ecosystem. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahon, A.R.; Doi, H.; Uchii, K.; Takahara, T.; Matsuhashi, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Minamoto, T. Use of Droplet Digital PCR for Estimation of Fish Abundance and Biomass in Environmental DNA Surveys. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacoursière-Roussel, A.; Rosabal, M.; Bernatchez, L. Estimating fish abundance and biomass from eDNA concentrations: Variability among capture methods and environmental conditions. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.B.; Sunday, J.M.; Rogers, S.M. Predicting the fate of eDNA in the environment and implications for studying biodiversity. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20191409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukaya, K.; Murakami, H.; Yoon, S.; Minami, K.; Osada, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Masuda, R.; Kasai, A.; Miyashita, K.; Minamoto, T.; et al. Estimating fish population abundance by integrating quantitative data on environmental DNA and hydrodynamic modelling. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 30, 3057–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Port, J.A.; O’Donnell, J.L.; Romero-Maraccini, O.C.; Leary, P.R.; Litvin, S.Y.; Nickols, K.J.; Yamahara, K.M.; Kelly, R.P. Assessing vertebrate biodiversity in a kelp forest ecosystem using environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 25, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacoursière-Roussel, A.; Howland, K.; Normandeau, E.; Grey, E.K.; Archambault, P.; Deiner, K.; Lodge, D.M.; Hernandez, C.; Leduc, N.; Bernatchez, L. eDNA metabarcoding as a new surveillance approach for coastal Arctic biodiversity. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 7763–7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales, N.G.; McKenzie, M.B.; Drake, J.; Harper, L.R.; Browett, S.S.; Coscia, I.; Wangensteen, O.S.; Baillie, C.; Bryce, E.; Dawson, D.A.; et al. Fishing for mammals: Landscape-level monitoring of terrestrial and semi-aquatic communities using eDNA from riverine systems. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 57, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, C.S.; Sepulveda, A.; Ray, A.; Baumgardt, J.; Waits, L.P. Environmental DNA as a new method for early detection of New Zealand mudsnails (Potamopyrgus antipodarum). Freshw. Sci. 2013, 32, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, H.L.A.; Noble, T.H.; Saunders, R.J.; Robson, S.K.A.; Burrows, D.W.; Jerry, D.R. Fine-tuning for the tropics: Application of eDNA technology for invasive fish detection in tropical freshwater ecosystems. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauretta, M.; Coulter, D.P.; Wang, P.; Coulter, A.A.; Van Susteren, G.E.; Eichmiller, J.J.; Garvey, J.E.; Sorensen, P.W. Nonlinear relationship between Silver Carp density and their eDNA concentration in a large river. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Nevers, M.B.; Byappanahalli, M.N.; Morris, C.C.; Shively, D.; Przybyla-Kelly, K.; Spoljaric, A.M.; Dickey, J.; Roseman, E.F. Environmental DNA (eDNA): A tool for quantifying the abundant but elusive round goby (Neogobius melanostomus). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Hervé, A.; Domaizon, I.; Baudoin, J.-M.; Dejean, T.; Gibert, P.; Jean, P.; Peroux, T.; Raymond, J.-C.; Valentini, A.; et al. Spatio-temporal variability of eDNA signal and its implication for fish monitoring in lakes. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzén, A.; Dahlgren, T.G.; Bagi, A.; Hestetun, J.T. Benthic eDNA metabarcoding provides accurate assessments of impact from oil extraction, and ecological insights. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X. eDNA metabarcoding in zooplankton improves the ecological status assessment of aquatic ecosystems. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, K.; Wang, C.; Zhuo, T.; Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Lei, X.; Li, M.; Chen, B.; Chai, B. Deciphering environmental factors influencing phytoplankton community structure in a polluted urban river. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 148, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.H.; Lee, J.; Hong, S.; Kwon, B.-O.; Xie, Y.; Giesy, J.P.; Zhang, X.; Khim, J.S. Integrated assessment of west coast of South Korea by use of benthic bacterial community structure as determined by eDNA, concentrations of contaminants, and in vitro bioassays. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, A.K.S.; Salmo Iii, S.G.; Sivakumar, K.; Then, A.Y.H.; Basyuni, M.; Fall, J.; Habib, K.A.; Isowa, Y.; Leopardas, V.; Peer, N.; et al. Prospects and challenges of environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding in mangrove restoration in Southeast Asia. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1033258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belle, C.C.; Stoeckle, B.C.; Geist, J. Taxonomic and geographical representation of freshwater environmental DNA research in aquatic conservation. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2019, 29, 1996–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, S.; Brantschen, J.; Zhang, X.; Albouy, C.; Valentini, A.; Zhang, H.; Altermatt, F.; Pellissier, L. Combining environmental DNA with remote sensing variables to map fish species distributions along a large river. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 10, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, R.S.; Ramos, M.M.; Lin, M.; Schweizer, T.M.; Gold, Z.; Ramos, D.R.; Shirazi, S.; Kandlikar, G.; Kwan, W.-Y.; Curd, E.E.; et al. The CALeDNA program: Citizen scientists and researchers inventory California’s biodiversity. Calif. Agric. 2021, 75, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Environmental DNA Shaping a New Era of Ecotoxicological Research. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5605–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, N.; Wood, S.A.; Pochon, X. Development and preliminary validation of a multi-trophic metabarcoding biotic index for monitoring benthic organic enrichment. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 1044–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Kim, S.; Hong, S.; Giesy, J.P.; Yim, U.H.; Shim, W.J.; Yu, H.; Khim, J.S. eDNA-based bioassessment of coastal sediments impacted by an oil spill. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downie, A.T.; Bennett, W.W.; Wilkinson, S.; de Bruyn, M.; DiBattista, J.D. From land to sea: Environmental DNA is correlated with long-term water quality indicators in an urbanized estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 207, 116887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.; Zhang, P.; Luo, S.; Chen, K.; Jiang, C.; Xiong, J.; Miao, W. Microbial Community Colonization Process Unveiled through eDNA-PFU Technology in Mesocosm Ecosystems. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, F.; Peng, W.; Zhang, X.; Chang, F.; Xie, P.; Zhang, H. A Review and Perspective of eDNA Application to Eutrophication and HAB Control in Freshwater and Marine Ecosystems. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Xie, Y.; Jeppe, K.; Long, S.; Pettigrove, V.; Zhang, X. Sensitive community responses of microbiota to copper in sediment toxicity test. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehnal, L.; Brammer-Robbins, E.; Wormington, A.M.; Blaha, L.; Bisesi, J.; Larkin, I.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Simonin, M.; Adamovsky, O. Microbiome Composition and Function in Aquatic Vertebrates: Small Organisms Making Big Impacts on Aquatic Animal Health. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 567408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Laender, F.; Rohr, J.R.; Ashauer, R.; Baird, D.J.; Berger, U.; Eisenhauer, N.; Grimm, V.; Hommen, U.; Maltby, L.; Meliàn, C.J.; et al. Reintroducing Environmental Change Drivers in Biodiversity–Ecosystem Functioning Research. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannar-Martin, K.H.; Kremer, C.T.; Ernest, S.K.M.; Leibold, M.A.; Auge, H.; Chase, J.; Declerck, S.A.J.; Eisenhauer, N.; Harpole, S.; Hillebrand, H.; et al. Integrating community assembly and biodiversity to better understand ecosystem function: The Community Assembly and the Functioning of Ecosystems (CAFE) approach. Ecol. Lett. 2017, 21, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Guo, F.; Gao, W.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z. Environmental DNA Biomonitoring Reveals the Interactive Effects of Dams and Nutrient Enrichment on Aquatic Multitrophic Communities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 16952–16963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, F.; Merten, V.J.; Bayer, T.; Oudejans, M.G.; de Jonge, D.S.W.; Puebla, O.; Reusch, T.B.H.; Fuss, J.; Hoving, H.J.T. Deep-sea predator niche segregation revealed by combined cetacean biologging and eDNA analysis of cephalopod prey. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Giesy, J.P.; Yu, H.; Zhang, X. Environmental DNA metabarcoding reveals primary chemical contaminants in freshwater sediments from different land-use types. Chemosphere 2017, 172, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagzi, K.; Hechler, R.M.; Fussmann, G.F.; Cristescu, M.E. Environmental RNA degrades more rapidly than environmental DNA across a broad range of pH conditions. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022, 22, 2640–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, T.; Murakami, H.; Masuda, R.; Sakata, M.K.; Yamamoto, S.; Minamoto, T. Rapid degradation of longer DNA fragments enables the improved estimation of distribution and biomass using environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, e25–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shogren, A.J.; Tank, J.L.; Egan, S.P.; August, O.; Rosi, E.J.; Hanrahan, B.R.; Renshaw, M.A.; Gantz, C.A.; Bolster, D. Water flow and biofilm cover influence environmental DNA detection in recirculating streams. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8530–8537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jane, S.F.; Wilcox, T.M.; McKelvey, K.S.; Young, M.K.; Schwartz, M.K.; Lowe, W.H.; Letcher, B.H.; Whiteley, A.R. Distance, flow and PCR inhibition: eDNA dynamics in two headwater streams. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 15, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, M.; Murakami, H.; Masuda, R.; Sado, T.; Miya, M.; Sakurai, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Minamoto, T.; Kondoh, M. Quantitative monitoring of multispecies fish environmental DNA using high-throughput sequencing. Metabarcoding Metagenom. 2018, 2, e23297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, H.; Motozawa, H.; Tsuji, S.; Miyazawa, R.C.; Takahara, T.; Minamoto, T. On-site filtration of water samples for environmental DNA analysis to avoid DNA degradation during transportation. Ecol. Res. 2016, 31, 963–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; van Bodegom, P.M.; Trimbos, K.B. Bacterial abundance and pH associate with eDNA degradation in water from various aquatic ecosystems in a laboratory setting. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1025105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartin, L.J.; Vohsen, S.A.; Ambrose, S.W.; Layden, M.; McFadden, C.S.; Cordes, E.E.; McDermott, J.M.; Herrera, S. Temperature Controls eDNA Persistence across Physicochemical Conditions in Seawater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 8629–8639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Doi, H. A Model and Simulation of the Influence of Temperature and Amplicon Length on Environmental DNA Degradation Rates: A Meta-Analysis Approach. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 623831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeHart, H.M.; Gasser, M.T.; Dixon, J.; Thielen, P. An aquatic environmental DNA filtration system to maximize recovery potential and promote filtration approach standardization. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbrecht, V.; Peinert, B.; Leese, F. Sorting things out: Assessing effects of unequal specimen biomass on DNA metabarcoding. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 6918–6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, C.I.M.; Knapp, M.; Gemmell, N.J.; Jeunen, G.-J.; Bunce, M.; Lamare, M.D.; Taylor, H.R. Beyond Biodiversity: Can Environmental DNA (eDNA) Cut It as a Population Genetics Tool? Genes 2019, 10, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassoubre, L.M.; Yamahara, K.M.; Gardner, L.D.; Block, B.A.; Boehm, A.B. Quantification of Environmental DNA (eDNA) Shedding and Decay Rates for Three Marine Fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10456–10464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillotson, M.D.; Kelly, R.P.; Duda, J.J.; Hoy, M.; Kralj, J.; Quinn, T.P. Concentrations of environmental DNA (eDNA) reflect spawning salmon abundance at fine spatial and temporal scales. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 220, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lance, R.; Klymus, K.; Richter, C.; Guan, X.; Farrington, H.; Carr, M.; Thompson, N.; Chapman, D.; Baerwaldt, K. Experimental observations on the decay of environmental DNA from bighead and silver carps. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2017, 8, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, N.G.; Wangensteen, O.S.; Carvalho, D.C.; Mariani, S. Influence of preservation methods, sample medium and sampling time on eDNA recovery in a neotropical river. Environ. DNA 2019, 1, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Doi, H. Effect of salinity and water dilution on environmental DNA degradation in freshwater environments. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bochove, K.; Bakker, F.T.; Beentjes, K.K.; Hemerik, L.; Vos, R.A.; Gravendeel, B. Organic matter reduces the amount of detectable environmental DNA in freshwater. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 3647–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, R.A.; Wangensteen, O.S.; O’Gorman, E.J.; Mariani, S.; Sims, D.W.; Genner, M.J. Persistence of environmental DNA in marine systems. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, J.M.; Benvenuto, C.; Coscia, I.; Oliveira Carvalho, C.; Ready, J.S.; Boubli, J.P.; Magnusson, W.E.; McDevitt, A.D.; Guimarães Sales, N. eDNA in a bottleneck: Obstacles to fish metabarcoding studies in megadiverse freshwater systems. Environ. DNA 2021, 3, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhang, X.; Yao, X.; Rao, J.; Dai, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, W. eDNA metabarcoding reveals differences in fish diversity and community structure in Danjiang River. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Joncour, A.; Mouchet, M.; Boussarie, G.; Lavialle, G.; Pennors, L.; Bouche, L.; Le Bourdonnec, P.; Morandeau, F.; Kopp, D. Is it worthy to use environmental DNA instead of scientific trawling or video survey to monitor taxa in soft-bottom habitats? Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 200, 106667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeter, J.C.; Maloy, A.P.; Rees, C.B.; Bartron, M.L. Fish mitochondrial genome sequencing: Expanding genetic resources to support species detection and biodiversity monitoring using environmental DNA. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2019, 12, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanco, F.A.; Richards, E.; Flück, B.; Valentini, A.; Altermatt, F.; Brosse, S.; Walser, J.C.; Eme, D.; Marques, V.; Manel, S.; et al. Comparing the performance of 12S mitochondrial primers for fish environmental DNA across ecosystems. Environ. DNA 2021, 3, 1113–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Stoeckle, B.C.; Beggel, S.; Cerwenka, A.F.; Motivans, E.; Kuehn, R.; Geist, J. A systematic approach to evaluate the influence of environmental conditions on eDNA detection success in aquatic ecosystems. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.; Schultz, M.T.; Lance, R.F. Modeling the Sensitivity of Field Surveys for Detection of Environmental DNA (eDNA). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, C.S.; Turner, C.R.; Deiner, K.; Klymus, K.E.; Thomsen, P.F.; Murphy, M.A.; Spear, S.F.; McKee, A.; Oyler-McCance, S.J.; Cornman, R.S.; et al. Critical considerations for the application of environmental DNA methods to detect aquatic species. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.C.; Wozney, K.M.; Smith, C.M.; Yu, D. Recognizing false positives: Synthetic oligonucleotide controls for environmental DNA surveillance. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 7, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, A.J.; Hutchins, P.R.; Forstchen, M.; McKeefry, M.N.; Swigris, A.M. The Elephant in the Lab (and Field): Contamination in Aquatic Environmental DNA Studies. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 609973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, P.R.; Simantel, L.N.; Sepulveda, A.J. Time to get real with qPCR controls: The frequency of sample contamination and the informative power of negative controls in environmental DNA studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 22, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willson, R.C.; Wilcox, T.M.; McKelvey, K.S.; Young, M.K.; Jane, S.F.; Lowe, W.H.; Whiteley, A.R.; Schwartz, M.K. Robust Detection of Rare Species Using Environmental DNA: The Importance of Primer Specificity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahoz-Monfort, J.J.; Guillera-Arroita, G.; Tingley, R. Statistical approaches to account for false-positive errors in environmental DNA samples. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 16, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Gao, W.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, J.; Cai, X.; Ouyang, J.; Zhao, Y. A Review of Environmental DNA Field and Laboratory Protocols Applied in Fish Ecology and Environmental Health. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 725360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Hinlo, R.; Gleeson, D.; Lintermans, M.; Furlan, E. Methods to maximise recovery of environmental DNA from water samples. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, C.; Hermans, S.M.; Lear, G.; Buckley, T.R.; Lee, K.C.; Buckley, H.L. A Systematic Review of Sources of Variability and Uncertainty in eDNA Data for Environmental Monitoring. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, S.; Ijichi, M.; Takeshima, H.; Kumagai, Y.; Yang, C.C.; Makabe-Kobayashi, Y.; Fukuda, H.; Yoshizawa, S.; Iwasaki, W.; Kogure, K.; et al. Probe Capture Enrichment Sequencing of amoA Genes Improves the Detection of Diverse Ammonia-Oxidising Archaeal and Bacterial Populations. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2024, e14042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaiko, A.; von Ammon, U.; Stuart, J.; Smith, K.; Yao, R.; Welsh, M.; Pochon, X.; Bowers, H. Performance and cost-efficiency of eDNA and eRNA capture methodologies: Experimental assessment using cultured microalgae. ARPHA Conf. Abstr. 2021, 4, e65098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, T.M.; Schreier, A.M. Optimizing an eDNA protocol for monitoring endangered Chinook Salmon in the San Francisco Estuary: Balancing sensitivity, cost and time. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteban, D.; Pedersen, J.O.P.; Nielsen, M.H. Physical oceanographic conditions and a sensitivity study on meltwater runoff in a West Greenland fjord: Kangerlussuaq. Oceanologia 2020, 62, 460–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilmin, L.; Mogollón, J.M.; Beusen, A.H.W.; van Hoek, W.J.; Liu, X.; Middelburg, J.J.; Bouwman, A.F. Modeling Process-Based Biogeochemical Dynamics in Surface Fresh Waters of Large Watersheds With the IMAGE-DGNM Framework. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2019MS001796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.; Zigic, S.; Burling, M.; Lin, H.-H. Hydrodynamic and Sediment Modelling within a Macro Tidal Estuary: Port Curtis Estuary, Australia. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2015, 3, 720–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, D.A.; Hassan, M.A.; Bird, S.; Pike, R.; Tschaplinski, P. Does variable channel morphology lead to dynamic salmon habitat? Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2020, 45, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevellec, M.; Lacoursière-Roussel, A.; Bernatchez, L.; Normandeau, E.; Solomon, E.; Arreak, A.; Fishback, L.; Howland, K. Detecting community change in Arctic marine ecosystems using the temporal dynamics of environmental DNA. Environ. DNA 2020, 3, 573–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troth, C.R.; Sweet, M.J.; Nightingale, J.; Burian, A. Seasonality, DNA degradation and spatial heterogeneity as drivers of eDNA detection dynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bylemans, J.; Gleeson, D.M.; Lintermans, M.; Hardy, C.M.; Beitzel, M.; Gilligan, D.M.; Furlan, E.M. Monitoring riverine fish communities through eDNA metabarcoding: Determining optimal sampling strategies along an altitudinal and biodiversity gradient. Metabarcoding Metagenom. 2018, 2, e30457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bista, I.; Carvalho, G.R.; Walsh, K.; Seymour, M.; Hajibabaei, M.; Lallias, D.; Christmas, M.; Creer, S. Annual time-series analysis of aqueous eDNA reveals ecologically relevant dynamics of lake ecosystem biodiversity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, K.M.; Kline, R.J.; Rahman, M.S. Past, present, and future perspectives of environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding: A systematic review in methods, monitoring, and applications of global eDNA. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 17, e00547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, P.; Peng, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, B.; Lei, K. Environmental DNA metabarcoding reveals the influence of environmental heterogeneity on microeukaryotic plankton in the offshore waters of East China Sea. Environ. Res. 2024, 262, 119921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlapati, D.; Charankumar, B.; Ramu, K.; Madeswaran, P.; Ramana Murthy, M.V. A review on the applications and recent advances in environmental DNA (eDNA) metagenomics. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2019, 18, 389–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, N.; Muniar, K.; Haris, H.; Ramli, F.F.; Sariyat, N.H.; Najmuddin, M.F.; Abdul-Latiff, M.A.B. A Review of Next-Generation Wildlife Monitoring using Environmental DNA (eDNA) Detection and Next-Generation Sequencing in Malaysia. Sains Malays. 2023, 52, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorenspleet, K.; Jansen, L.; Oosterbroek, S.; Kamermans, P.; Bos, O.; Wurz, E.; Murk, A.; Nijland, R. The long and the short of it: Nanopore based eDNA metabarcoding of marine vertebrates works; sensitivity and specificity depend on amplicon lengths. BioRxiv 2021, 11, 470087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez-Páez, A.; Sanz, Y. Multi-locus and long amplicon sequencing approach to study microbial diversity at species level using the MinION™ portable nanopore sequencer. GigaScience 2017, 6, gix043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flück, B.; Mathon, L.; Manel, S.; Valentini, A.; Dejean, T.; Albouy, C.; Mouillot, D.; Thuiller, W.; Murienne, J.; Brosse, S.; et al. Applying convolutional neural networks to speed up environmental DNA annotation in a highly diverse ecosystem. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tristan, C.; Philippe, E.; Franck, L.; Joana, V.; Amine, O.; Catarina, M.; Tomas, C.; Jan, P. Predicting the Ecological Quality Status of Marine Environments from eDNA Metabarcoding Data Using Supervised Machine Learning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9118–9126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomerantz, A.; Peñafiel, N.; Arteaga, A.; Bustamante, L.; Pichardo, F.; Coloma, L.A.; Barrio-Amorós, C.L.; Salazar-Valenzuela, D.; Prost, S. Real-time DNA barcoding in a rainforest using nanopore sequencing: Opportunities for rapid biodiversity assessments and local capacity building. GigaScience 2018, 7, giy033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; He, Y.; Chen, J.; Dong, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L. Contrasting pollution responses of native and non-native fish communities in anthropogenically disturbed estuaries unveiled by eDNA metabarcoding. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadagkar, S.R.; Menegon, M.; Cantaloni, C.; Rodriguez-Prieto, A.; Centomo, C.; Abdelfattah, A.; Rossato, M.; Bernardi, M.; Xumerle, L.; Loader, S.; et al. On site DNA barcoding by nanopore sequencing. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, L.; Holzer, A.; Baronas, J.J.; Hall, M.B.; Braeuninger-Weimer, P.; Scherm, M.J.; Kunz, D.J.; Perera, S.N.; Martin-Herranz, D.E.; Tipper, E.T.; et al. Freshwater monitoring by nanopore sequencing. eLife 2021, 10, e61504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merelli, I.; Morganti, L.; Corni, E.; Pellegrino, C.; Cesini, D.; Roverelli, L.; Zereik, G.; D’Agostino, D. Low-power portable devices for metagenomics analysis: Fog computing makes bioinformatics ready for the Internet of Things. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 88, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi-Derazmahalleh, M.; Stott, A.; Lines, R.; Peverley, G.; Nester, G.; Simpson, T.; Zawierta, M.; De La Pierre, M.; Bunce, M.; Christophersen, C.T. eDNAFlow, an automated, reproducible and scalable workflow for analysis of environmental DNA sequences exploiting Nextflow and Singularity. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burian, A.; Mauvisseau, Q.; Bulling, M.; Domisch, S.; Qian, S.; Sweet, M. Improving the reliability of eDNA data interpretation. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 1422–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathon, L.; Valentini, A.; Guérin, P.E.; Normandeau, E.; Noel, C.; Lionnet, C.; Boulanger, E.; Thuiller, W.; Bernatchez, L.; Mouillot, D.; et al. Benchmarking bioinformatic tools for fast and accurate eDNA metabarcoding species identification. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 2565–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Pansu, J.; Bonin, A.; Coissac, E.; Giguet-Covex, C.; De Barba, M.; Gielly, L.; Lopes, C.M.; Boyer, F.; Pompanon, F.; et al. Replication levels, false presences and the estimation of the presence/absence from eDNA metabarcoding data. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 15, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, S.; Davy, S.; Bunce, M.; Stat, M. Taxonomic identification of environmental DNA with informatic sequence classification trees. PeerJ 2018, 6, e26812v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, T.; Nakao, R.; Doi, H.; Minamoto, T. Simultaneous absolute quantification and sequencing of fish environmental DNA in a mesocosm by quantitative sequencing technique. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Simons, A.L.; Harrigan, R.J.; Curd, E.E.; Schneider, F.D.; Ruiz-Ramos, D.V.; Gold, Z.; Osborne, M.G.; Shirazi, S.; Schweizer, T.M.; et al. Landscape analyses using eDNA metabarcoding and Earth observation predict community biodiversity in California. Ecol. Appl. 2021, 31, e02379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, S.; Pettorelli, N.; Vihervaara, P.; Wegmann, M.; Vamosi, J. Improving biodiversity monitoring using satellite remote sensing to provide solutions towards the 2020 conservation targets. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 1784–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aucone, E.; Kirchgeorg, S.; Valentini, A.; Pellissier, L.; Deiner, K.; Mintchev, S. Drone-assisted collection of environmental DNA from tree branches for biodiversity monitoring. Sci. Robot. 2023, 8, eadd5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, K.M.; Stat, M.; Harvey, E.S.; Skepper, C.L.; DiBattista, J.D.; Richards, Z.T.; Travers, M.J.; Newman, S.J.; Bunce, M. eDNA metabarcoding survey reveals fine-scale coral reef community variation across a remote, tropical island ecosystem. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 1069–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacoeuilhe, A.; Pamerlon, S.; Archambeau, A.-S.; Denys, G.; Le Bras, Y.; Norvez, O. An Overview of the French eDNA Data Landscape: Focus on a national technical repository of reference genetic sequences. Biodivers. Inf. Sci. Stand. 2023, 7, e110103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaphu, M.F.; O’Brien, G.C.; Downs, C.T.; Willows-Munro, S. The status of COI and 12S rRNA DNA barcode reference libraries for freshwater fish in South Africa: Implications for future eDNA projects. Afr. Zool. 2023, 58, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenekar, T.; Schletterer, M.; Lecaudey, L.A.; Weiss, S.J. Reference databases, primer choice, and assay sensitivity for environmental metabarcoding: Lessons learnt from a re-evaluation of an eDNA fish assessment in the Volga headwaters. River Res. Appl. 2020, 36, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Stewart, K.A.; Dey, G.; Antognazza, C.M.; Sharma, R.K.; Maity, J.P.; Saha, S.; Doi, H.; de Vere, N.; Chan, M.W.Y.; et al. Environmental DNA analysis as an emerging non-destructive method for plant biodiversity monitoring: A review. AoB Plants 2022, 14, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bálint, M.; Tumusiime, J.; Nakintu, J.; Baranski, D.; Schardt, L.; Romahn, J.; Dusabe, M.-C.; Tolo, C.U.; Kagoro, G.R.; Ssenkuba, F.; et al. Environmental DNA barcoding reveals general biodiversity patterns in the large tropical rift Lake Albert. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curd, E.E.; Gold, Z.; Kandlikar, G.S.; Gomer, J.; Ogden, M.; O’Connell, T.; Pipes, L.; Schweizer, T.M.; Rabichow, L.; Lin, M.; et al. Anacapa Toolkit: An environmental DNA toolkit for processing multilocus metabarcode datasets. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2019, 10, 1469–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Menendez, M.; Planes, S.; Garcia-Vazquez, E.; Ardura, A. Early Alert of Biological Risk in a Coastal Lagoon Through eDNA Metabarcoding. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovero, F.; Ahumada, J. The Tropical Ecology, Assessment and Monitoring (TEAM) Network: An early warning system for tropical rain forests. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, C.; You, W.; Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Chu, L.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, C. Comparison Between Environmental DNA Metabarcoding and Traditional Survey Method to Identify Community Composition and Assembly of Stream Fish. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e70627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, E.R.; Graham, B.M.; Achury, R.; Coon, J.J.; Daniels, M.K.; Gambrell, D.K.; Jonasen, K.L.; King, G.D.; LaRacuente, N.; Perrin-Stowe, T.I.N.; et al. From eDNA to citizen science: Emerging tools for the early detection of invasive species. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 18, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, A.; Taberlet, P.; Miaud, C.; Civade, R.; Herder, J.; Thomsen, P.F.; Bellemain, E.; Besnard, A.; Coissac, E.; Boyer, F.; et al. Next-generation monitoring of aquatic biodiversity using environmental DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, H.; Ye, T.; Xie, Z.; Liu, X. Application of Environmental DNA in Aquatic Ecosystem Monitoring: Opportunities, Challenges and Prospects. Water 2025, 17, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050661
Chang H, Ye T, Xie Z, Liu X. Application of Environmental DNA in Aquatic Ecosystem Monitoring: Opportunities, Challenges and Prospects. Water. 2025; 17(5):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050661
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Huihui, Tao Ye, Zhaohui Xie, and Xinhu Liu. 2025. "Application of Environmental DNA in Aquatic Ecosystem Monitoring: Opportunities, Challenges and Prospects" Water 17, no. 5: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050661
APA StyleChang, H., Ye, T., Xie, Z., & Liu, X. (2025). Application of Environmental DNA in Aquatic Ecosystem Monitoring: Opportunities, Challenges and Prospects. Water, 17(5), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050661





