Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Phthalates Deposition in Sediments of Reservoirs: Impact of Some Environmental Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Analytical Procedures
2.3.1. Analysis of POC and δ13C-POC
2.3.2. Analysis of EC, pH, TOC, and Chla
2.3.3. Analysis of PAHs and PAEs
2.4. Methodology of the Results Elaboration
2.4.1. Determination of the Accumulation Rates
2.4.2. Origin of Organic Matter in Entrapped Sediments
2.5. Ecotoxicological Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
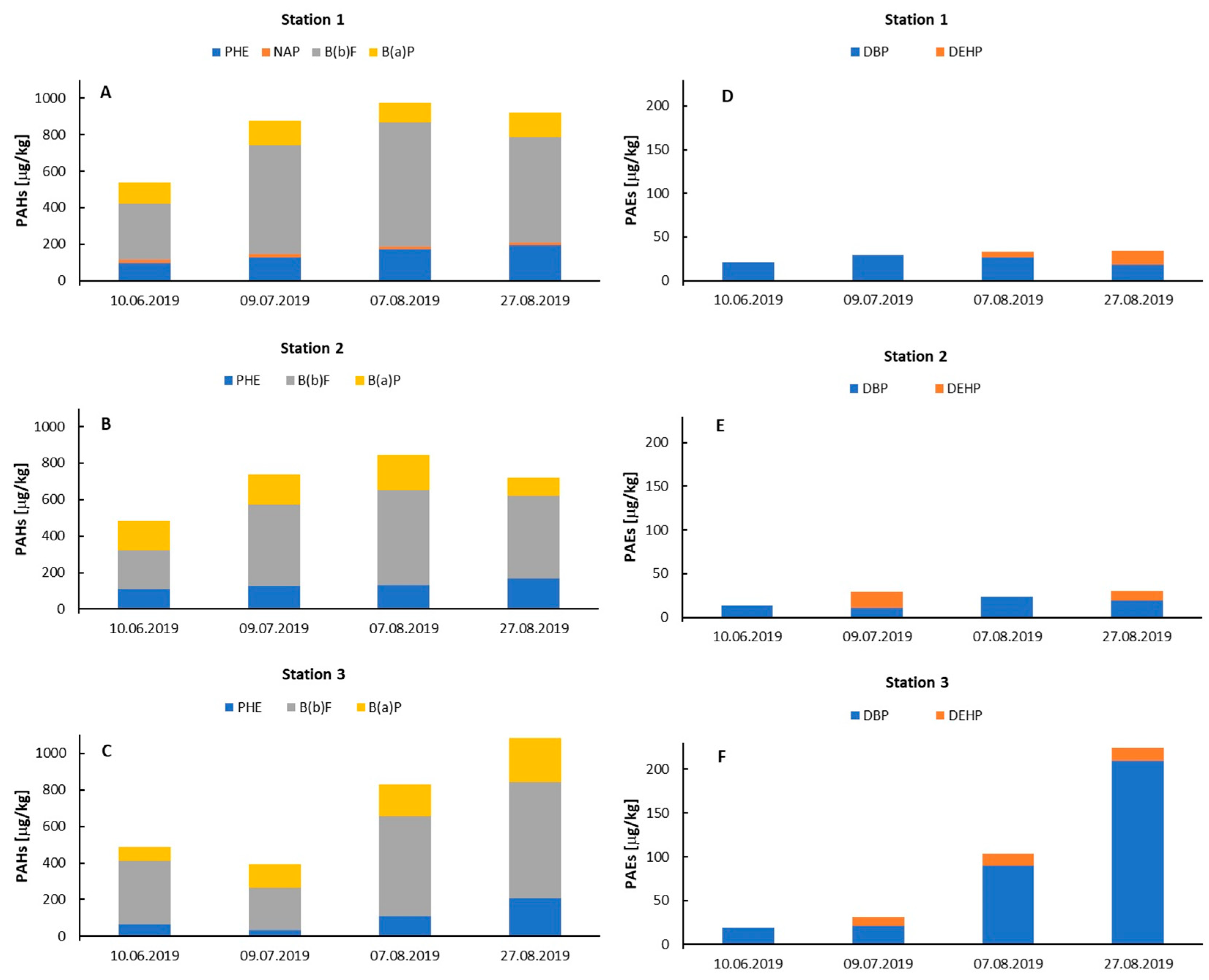
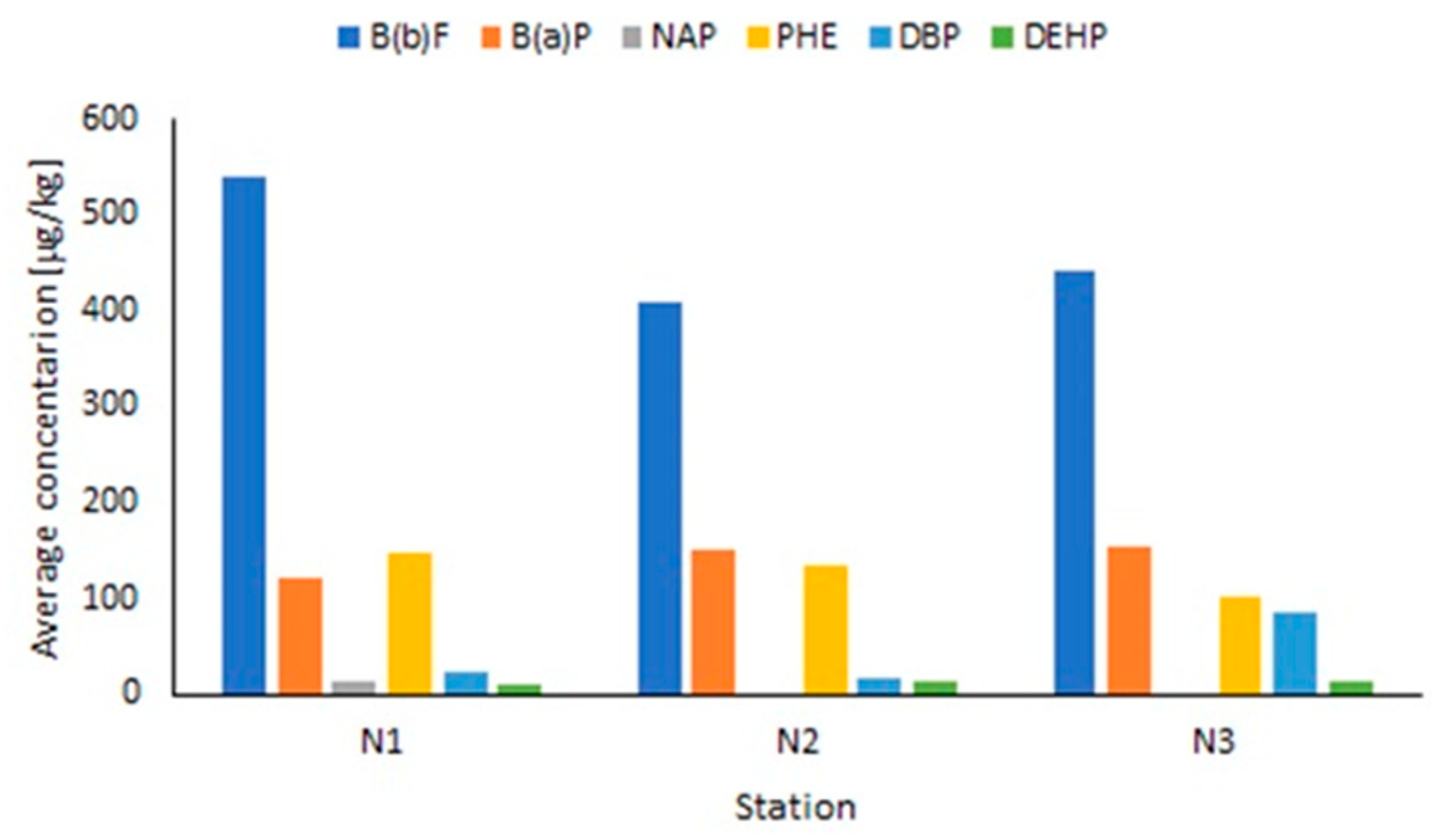
3.1. Concentrations and Distributions of PAHs and PAEs in Entrapped Sediments
3.2. Findings of the Ecotoxicological Assessment
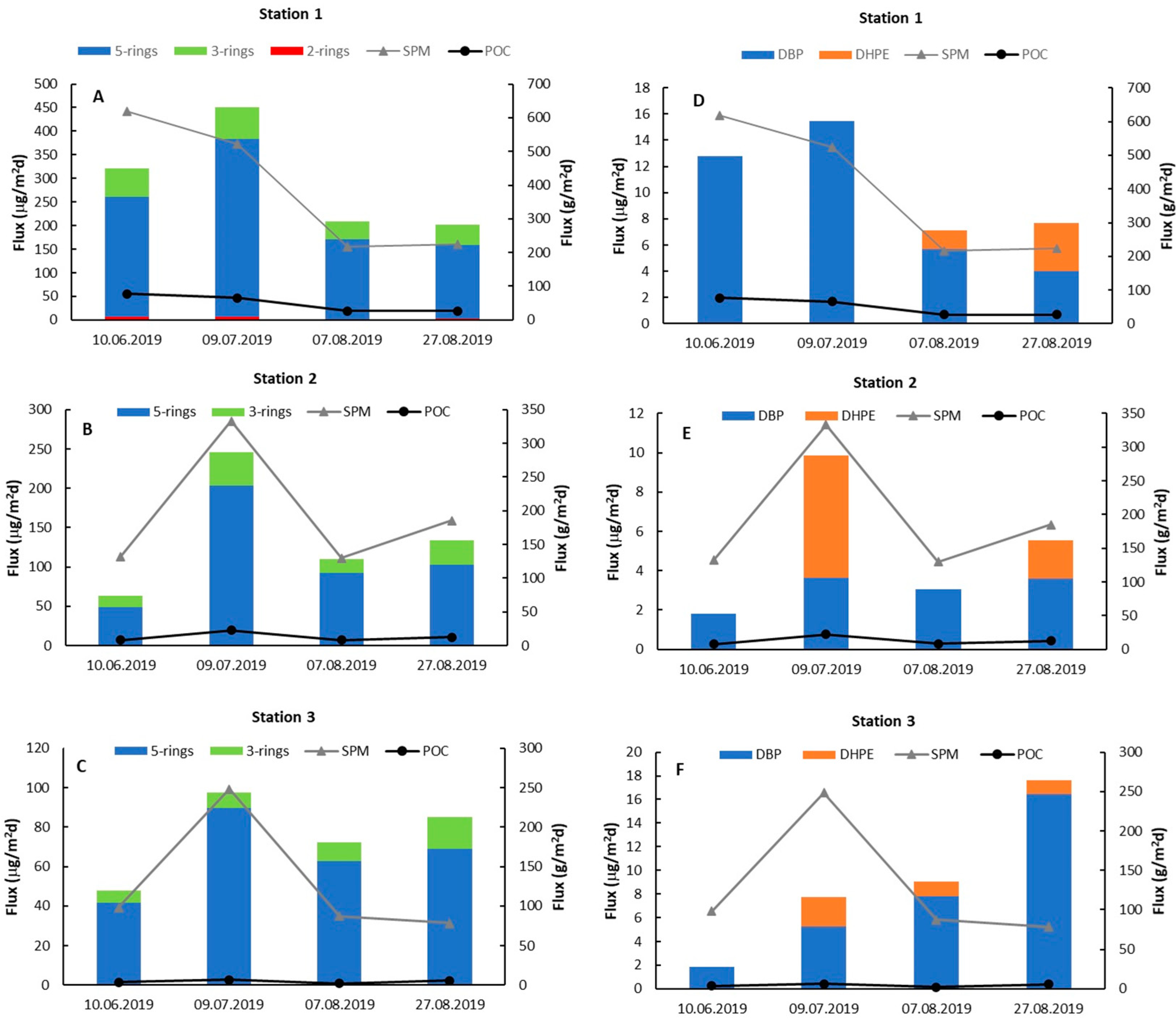
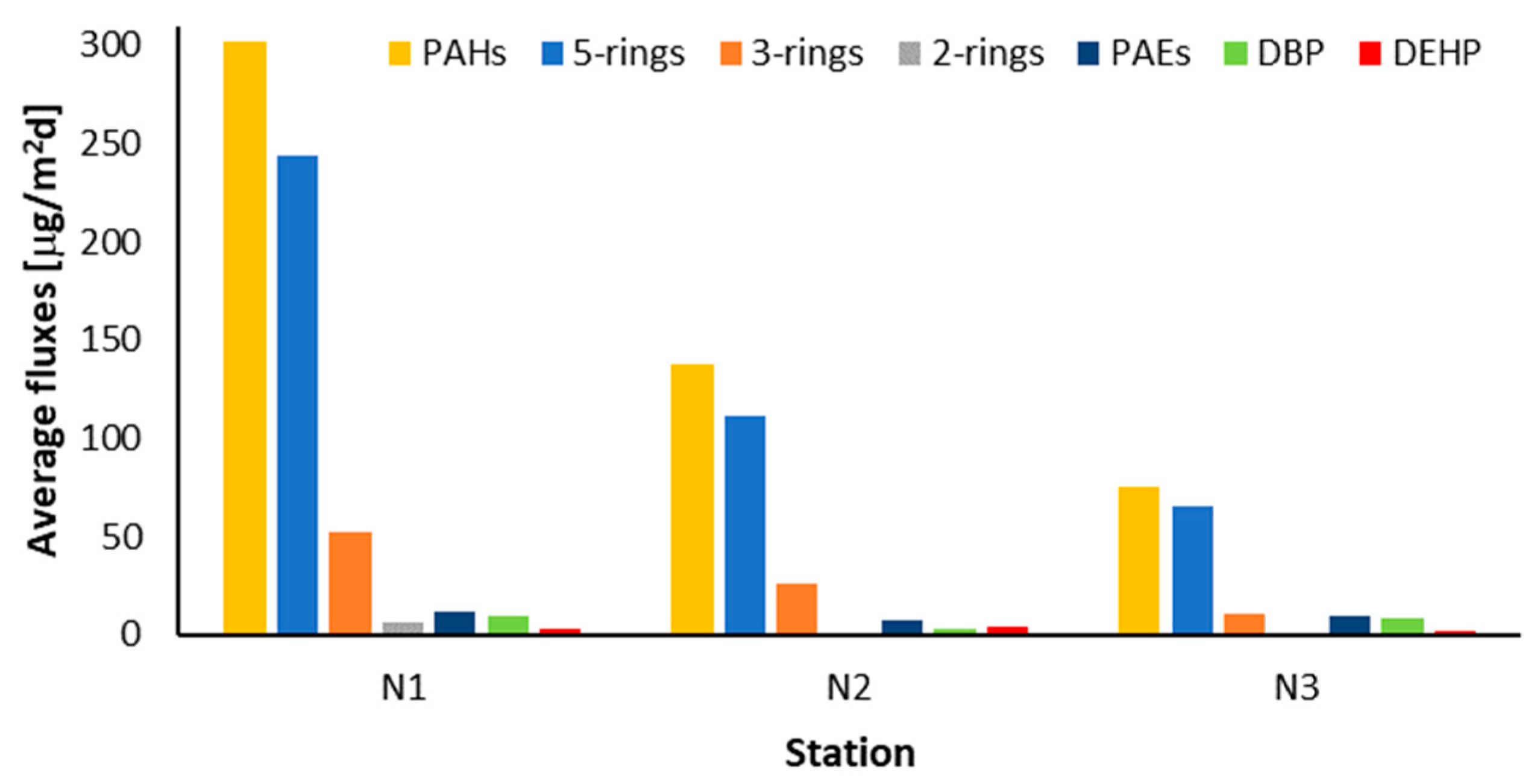
3.3. Deposition Fluxes of SPM, POC, PAHs, and PAEs
3.4. Factors Controlling the Deposition of PAHs and PAEs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- López-Tarazón, J.A.; López, P.; Lobera, G.; Batalla, R.J. Suspended sediment, carbon and nitrogen transport in a regulated Pyrenean river. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 540, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.J.; Kim, J.; Hur, J.; Choi, I.H.; Toorman, E.A.; Fettweis, M.; Choi, J.W. Seasonal Dynamics of organic matter composition and its effects on suspended sediment flocculation in river water. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 6323–7438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maselli, V.; Pellegrini, C.; Del Bianco, F.; Mercorella, A.; Nones, M.; Crose, L.; Nittrouer, J.A. River morphodynamic evolution under dam-induced backwater: An example from the Po River (Italy). J. Sediment. Res. 2018, 88, 1190–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieśla, M.; Gruca-Rokosz, R.; Bartoszek, L. Significance of organic matter in the process of aggregation of suspended sediments in retention reservoirs. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, C.; Saliu, F.; Bosman, A.; Sammartino, I.; Raguso, C.; Mercorella, A.; Rovere, M. Hotspots of microplastic accumulation at the land-sea transition and their spatial heterogeneity: The Po River prodelta (Adriatic Sea). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 895, 164908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trincardi, F.; Francocci, F.; Pellegrini, C.; d’Alcalà, M.R.; Sprovieri, M. The Mediterranean Sea in the Anthropocene. In Oceanography of the Mediterranean Sea; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 501–553. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Song, K.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; He, W.; Xu, F. Suspended particulate matter (SPM)-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in lakes and reservoirs across a large geographical scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 15, 142863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Mao, W.; Shen, Y.; Feng, W.; Mao, G.; Zhao, T.; Yang, L.; Yang, L.; Meng, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Distribution, source, and environmental risk assessment of phthalate esters (PAEs) in water, suspended particulate matter, and sediment of a typical Yangtze River Delta City, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 24609–24619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, K.; Sokhi, R.; Grieken, R.V. Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source attribution, emission factors and regulation. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2895–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobiszewski, M.; Namieśnik, J. PAH diagnostic ratios for the identification of pollution emission sources. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 162, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Yin, C.; Chen, M.; Wang, W. Runoff pollution impacts of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in street dusts from a stream network town. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 2069–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uno, S.; Kokushi, E.; Añasco, N.C.; Iwai, T.; Ito, K.; Koyama, J. Oil spill off the coast of Guimaras Island, Philippines: Distributions and changes of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in shellfish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 962–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaurav, G.K.; Mehmood, T.; Kumar, M.; Cheng, L.; Sathishkumar, K.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, D. Review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) migration from wastewater. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 236, 103715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.B.; Shaikh, S.; Jain, K.R.; Desai, C.; Madamwar, D. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Sources, Toxicity, and Remediation Approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 562813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciejczyk, M.; Tyrpień-Golder, K.; Janoszka, B.; Gierat, B.; Muzyka, R. Mutagenic and carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in food-occurrence, human health effects, and assessment methods of exposure. Environ. Med. 2023, 26, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source, environmental impact, effect on human health and remediation. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhang, K.; Xu, S.; Yan, M.; Leung, K.M.; Lam, P.K. Microplastics: A major source of phthalate esters in aquatic environments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrank, I.; Trotter, B.; Dummert, J.; Scholz Böttcher, B.M.; Löder, M.G.J.; Laforsch, C. Effects of microplastic particles and leaching additive on the life history and morphology of Daphnia magna. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzellitti, S.; Canesi, L.; Auguste, M.; Wathsala, R.H.G.R.; Fabbri, E. Microplastic exposure and effects in aquatic organisms: A physiological perspective. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 68, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, J.; Herat, S. Ecotoxicity of microplastic pollutants to marine organisms: A systematic review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA, Environmental Protection Agency. Integrated Risk Information System. Phthalates, The Action Plan. 2012. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/iris (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Wang, W.L.; Wu, Q.Y.; Wang, C.; He, T.; Hu, H.Y. Health risk assessment of phthalate esters (PAEs) in drinking water sources of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 3620–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenkel, R.; Carl, M.P. European Union Risk Assessment Report: Bis (2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP); Institute of Health and Consumer Protection (IHCP): Ispra, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Some Chemicals Present in Industrial and Consumer Products, Food and Drinking-Water. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC Publications: Lyon, France, 2013; Volume 101, p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Testa, C.; Nuti, F.; Hayek, J.; De Felice, C.; Chelli, M.; Rovero, P.; Latini, G.; Papini, A.M. Di–(2–ethylhexyl) phthalate and autism spectrum disorders. ASN Neuro 2012, 4, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, M.A.; Gómara, B.; González, M.J. Occurrence of phthalates and their metabolites in the environment and human health implications. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Emerging Organic Contaminants and Human Health; Barceló, D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 20. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin, S.; Masai, E.; Kamimura, N.; Takahashi, K.; Anderson, R.C.; Faisal, P.A. Phthalates impact human health: Epidemiological evidences and plausible mechanism of action. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 340, 360–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jancewicz, A.; Dmitruk, U.; Sośnicki, Ł.; Tomczuk, U.; Bartczak, A. Wpływ zagospodarowania zlewni na jakość osadów dennych w wybranych zbiornikach zaporowych. Ochr. Sr. 2012, 34, 29–34. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Cieśla, M.; Bartoszek, L.; Gruca-Rokosz, R. Effectiveness assessment of a new system of sediment trap in the investigation of matter sedimentation in a reservoir—A case study. Hydrology 2019, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieśla, M.; Gruca-Rokosz, R. Implications of suspended sediment in the migration of nutrients at the water-sediment interface in retention reservoirs. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murase, J.; Sakamoto, M. Horizontal distribution of the carbon and nitrogen and their isotopic composition in the surface sediment of Lake Biwa. Limnology 2000, 1, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes, N.; Güde, H.; Wessels, M.; Straile, D. Allochthonous contribution to seasonal and spatial variability of organic matter sedimentation in a deep oligotrophic lake (Lake Constance). Limnologica 2013, 43, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.D.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Berger, T.A. Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 39, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingsley, O.; Witthayawirasak, B. Deterministic Assessment of the Risk of Phthalate Esters in Sediments of U-Tapao Canal, Southern Thailand. Toxics 2020, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perra, G.; Pozo, K.; Guerranti, C.; Lazzeri, D.; Volpi, V.; Corsolini, S.; Focardi, S. Levels and spatial distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in coastal marine sediments of Ross Sea, Antarctica. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2961–2968. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Liu, B.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J. Spatial distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from Dachan Bay, Shenzhen City. Water 2023, 15, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Meng, W.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, C. Spatial distribution and potential toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from Liaohe River Basin, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolska, L.; Mechlińska, A.; Rogowska, J.; Namieśnik, J. Sources and fate of PAHs and PCBs in the marine environment. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 1172–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasher, E.; Heng, L.Y.; Zakaria, Z.; Surif, S. Assessing the ecological risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments at Langkawi Island, Malaysia. Sci. World J. 2013, 17, 858309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Książek, S.; Kida, M.; Koszelnik, P. The occurrence and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in bottom sediments of the Wisłok River. Pol. J. Natur. Sci. 2016, 31, 373–386. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, D.; Wen, Z. Phthalate esters in the environment: A critical review of their occurrence, biodegradation, and removal during wastewater treatment processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 986–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Lin, L.; Pan, X.; Zhang, S.; Lv, Z.; Mi, C. Distribution dynamics of phthalate esters in surface water and sediment of the middle-lower Hanjiang River, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Lee, J.-E.; Choe, W.; Kim, T.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kho, Y.; Choi, K.; Zoh, K.-D. Distribution of phthalate esters in air, water, sediments, and fish in the Asan Lake of Korea. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Xu, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, W.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. Occurrence, spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of phthalate esters in water, soil and sediment from Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-F.; Ju, Y.-R.; Lim, Y.C.; Chang, J.-H.; Chen, C.-W.; Dong, C.-D. Spatial and temporal distribution of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in urban river sediments. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weizhen, Z.; Xiaowei, Z.; Peng, G.; Ning, W.; Zini, L.; Jian, H.; Zheng, Z. Distribution and risk assessment of phthalates in water and sediment of the Pearl River Delta. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12550–12565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohl, A.; Tytła, M.; Kernert, J.; Bodzek, M. Plastics-derived and heavy metals contaminants in the granulometric fractions of bottom sediments of anthropogenic water reservoir—Comprehensive analysis. Desalination Water Treat. 2022, 258, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, Q.; He, W.; Xu, F. The occurrence, composition and partitioning of phthalate esters (PAEs) in the water-suspended particulate matter (SPM) system of Lake Chaohu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohl, A.; Kostecki, M. Spatial distribution, ecological risk and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water and bottom sediments of the anthropogenic lymnic ecosystems under conditions of diversified anthropopressure. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2020, 46, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, A.; Tarnawski, M.; Urbański, K.; Klimkowicz-Pawlas, A.; Spałek, I. Concentration, sources and risk assessment of PAHs in bottom sediments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 23180–23195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoszek, L.; Koszelnik, P.; Gruca-Rokosz, R.; Kida, M. Ocena rolniczego wykorzystania osadów dennych form eutroficznego Zbiornika Rzeszowskiego. Annu. Set Environ. Prot. 2015, 17, 394–409. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.Q.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.D.; Li, J.; Peng, X.Z.; Qi, S.H. Sedimentary record of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a sediment core from the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, N.; Gao, J.; Duan, D.; Yang, Y.; Ran, Y. Sedimentation and Resuspension Fluxes of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Lake and Reservoir, South China. 2022. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4231087 (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Terasmaa, J.; Punning, J.M. Sedimentation dynamics in a small dimictic lake in northern Estonia. Proc. Estonian Acad. Sci. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 55, 228–242. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, Y.M.; Ramirez, J.J. Seston fluxes in the dam of a Colombian tropical reservoir. Acta Limnol. Brasil. 2010, 22, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieśla, M.; Bartoszek, L.; Gruca-Rokosz, R. Characteristics and origin of suspended matter in a small reservoir in Poland. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2020, 20, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieśla, M.; Gruca-Rokosz, R.; Bartoszek, L. The connection between a suspended sediments and reservoir siltation: Empirical analysis in the Maziarnia Reservoir, Poland. Resources 2020, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodosi, C.; Stavrakakis, S.; Koulaki, F.; Stavrakaki, I.; Moncheva, S.; Papathanasiou, E.; Sanchez-Vidal, A.; Koҫak, M.; Mihalopoulos, N. The significance of atmospheric inputs of major and trace metals to the Black Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 109, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieśla, M.; Gruca-Rokosz, R.; Bartoszek, L. A new concept to forecast the process of suspended sediment accumulation in the bottom sediment of small reservoirs. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2023, 38, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamura, S.; Sato, T.; Ota, Y.; Aota, Y.; Kashiwaya, K.; Kumagai, M. Seasonal deposition fluxes of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Lake Biwa, Japan. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 198, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cranwell, P.A.; Koul, V.K. Sedimentary record of polycyclic aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons in the Windermere catchment. Water Res. 1989, 23, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikenaka, Y.; Eun, H.; Watanabe, E.; Kumon, F.; Miyabara, Y. Estimation of sources and inflow of dioxins and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from the sediment core of Lake Suwa, Japan. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 138, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.R.; Eadie, B.J.; Baker, J.E. Episodic particle transport events controlling PAH and PCB cycling in Grand Traverse Bay, Lake Michigan. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Huang, Q.; Ding, F.; He, X. Adsorption of PAHs on the sediments from the Yellow River Delta as a function of particle size and salinity. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2015, 24, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirivithayapakorn, S.; Limtrakul, S. Distribution coefficient and adsorption–desorption rates of di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) onto and from the surface of suspended particles in fresh water. Water Air. Soil. Pollut. 2008, 190, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfaeinia, H.; Fazlzadeh, M.; Taghizadeh, F.; Saeedi, R.; Spitz, J.; Dobaradaran, S. Phthalate acid esters (PAEs) accumulation in coastal sediments from regions with different land use configuration along the Persian Gulf. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Zhang, J.M.; Zhang, H.H.; Shi, X.Z.; Zou, Y.W.; Yang, G.P. Pollution characteristics, spatial variation, and potential risks of phthalate esters in the water-sediment system of the Yangtze River estuary and its adjacent East China Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265 Pt A, 114913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapok, K.J.; Karim, A.T.A.; Hashim, N.H.; Muhammad, A. Adsorption isotherms of dimethyl phthalate (DMP), diethyl phthalate (DEP), dibutyl phthlate (DBP) and benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP) compounds in synthetic and Sembrong River sediment. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1022, 012056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Omran, L.A.; Preston, M.R. The interactions of phthalate esters with suspended particulate material in fresh and marine waters. Environ. Pollut. 1987, 46, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, L.; Kohl, S.D.; Rice, J.A.; Gagné, J.-P. Effects of temperature, salinity, and dissolved humic substances on the sorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to estuarine particles. Mar. Chem. 2005, 96, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.; Gopalani, M.; Ramteke, D.S.; Wate, S.R. Influence of salinity on PAH uptake from water soluble fraction of crude oil in Tilapia mossambica. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 79, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.R.; Li, X.Y. Adsorption behaviour of dibutyl phthalate on marine sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 57, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.; Rawling, M.C. The behaviour of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in estuaries. Mar. Chem. 2000, 68, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuwatini, E.; Hata, N.; Kuramitz, H.; Taguchi, S. Effect of salting-out on distribution behavior of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and its analogues between water and sediment. SpringerPlus 2013, 2, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Gong, X.; Lv, M.; Song, W.; Ma, X.; Qi, Y.; Wang, L. Effect of temperature and pH on the sorption of dibutyl phthalate on humic acid. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.; Gupta, B. Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on banana peel activated carbon. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 57, 9498–9509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| PAHs | PAEs | |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature program | 40 °C hold 3 min, 40 to 300 °C rate 8 °C/min, 300 °C hold 4 min | 40 °C hold 1 min, 40 to 300 °C rate 9 °C/min, 300 °C hold 5 min |
| Dosing system | Split–Splitless injector with automatic sample feeder | |
| Operating mode | Splitless | |
| Sample volume (µL) | 1.0 | |
| Temperature injector (°C) | 300 | 300 |
| Carrier gas | Helium | |
| Carrier gas flow rate (mL/min) | 1.1 | 1.0 |
| PAEs | Retention Time RT (min) | Linearity R2 | CV (%) | Recovery (%) n = 3 | LOQ (μg/kg) | LOD (μg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether | 6.92 | 0.9482 | 2.55 | 91 | 25 | 8.33 |
| Bis(2-chloroisopropyl)ether | 8.13 | 0.995 | 1.86 | 96 | 10 | 3.33 |
| Bis(2-chloroethoxy)methane | 9.94 | 0.9919 | 2.25 | 105 | 15 | 5 |
| Dimethyl phthalate | 14.41 | 0.9939 | 1.58 | 98 | 12 | 4 |
| Diethyl phthalate | 16.31 | 0.995 | 0.94 | 105 | 15 | 5 |
| 4-Chlorodiphenyl ether | 16.50 | 0.9775 | 2.33 | 89 | 18 | 6 |
| 4-Bromodiphenyl ether | 17.79 | 0.9872 | 1.57 | 69 | 22 | 7.33 |
| Di-n-butyl phthalate | 20.71 | 0.9885 | 0.87 | 109 | 8 | 2.67 |
| Butylbenzyl phthalate | 24.68 | 0.9776 | 0.92 | 111 | 13 | 4.33 |
| Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate | 26.31 | 0.9747 | 1.11 | 95 | 6 | 2 |
| Di-n-octyl phthalate | 27.96 | 0.9446 | 1.23 | 95 | 10 | 3.33 |
| PAHs | Retention Time RT (min) | Linearity R2 | CV (%) | Recovery (%) n = 3 | LOQ (μg/kg) | LOD (μg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naphthalene | 12.93 | 0.9708 | 3.25 | 95 | 10 | 3.33 |
| Acenaphthylene | 17.57 | 0.9659 | 3.10 | 104 | 35 | 11.67 |
| Acenephthene | 18.09 | 0.9952 | 2.42 | 97 | 21 | 7 |
| Fluorene | 19.63 | 0.974 | 3.34 | 94 | 25 | 8.33 |
| Phenenthrene | 22.45 | 0.9633 | 4.12 | 89 | 30 | 10 |
| Anthracene | 22.60 | 0.9905 | 2.50 | 94 | 18 | 6 |
| Fluoranthene | 25.98 | 0.9567 | 3.88 | 110 | 45 | 15 |
| Pyrene | 26.62 | 0.9624 | 3.98 | 89 | 51 | 17 |
| Benz(a)anthracene | 30.23 | 0.9588 | 3.51 | 91 | 40 | 13.33 |
| Chrysene | 30.32 | 0.9685 | 3.22 | 90 | 45 | 15 |
| Benzo(b)fluoranthene | 33.21 | 0.9619 | 3.60 | 92 | 55 | 18.33 |
| Benzo(k)fluoranthene | 33.28 | 0.9516 | 3.79 | 89 | 35 | 11.67 |
| Benzo(a)pyrene | 34.02 | 0.9774 | 3.15 | 92 | 40 | 13.33 |
| Indeno(1,2,3-c,d)pyrene | 36.74 | 0.9891 | 2.86 | 96 | 24 | 8 |
| Dibenz(a,h)anthracene | 36.84 | 0.9625 | 3.55 | 91 | 42 | 14 |
| Benzo(g,h,i)perylene | 37.42 | 0.9674 | 3.74 | 90 | 50 | 16.67 |
| Min | Max | Mean | Median | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B(b)F | 213 | 679 | 464 | 488 | 150 |
| B(a)P | 74.3 | 242 | 143 | 133 | 43.0 |
| NAP | <LOD | 15.8 | 15.3 | 15.5 | 0.6 |
| PHE | 31.5 | 208 | 129 | 128 | 49.2 |
| LMW-PAHs | 31.5 | 208 | 134 | 129 | 51.6 |
| HMW-PAHs | 361 | 876 | 606 | 661 | 169 |
| Σ4PAHs | 393 | 1084 | 740 | 783 | 212 |
| DBP | 10.9 | 210 | 41.8 | 21.0 | 54.4 |
| DEHP | <LOD | 18.7 | 13.0 | 14.5 | 3.9 |
| Σ2PAEs | 13.7 | 225 | 49.4 | 29.8 | 57.3 |
| TEC (μg/kg) | PEC (μg/kg) | Station N1 | Station N2 | Station N3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SI | SII | SIII | SIV | SI | SII | SIII | SIV | SI | SII | SIII | SIV | |||
| NAP | 176 | 561 | I | I | I | I | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PHE | 204 | 1170 | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | II |
| B(b)F | 240 | 13,400 | II | II | II | II | I | II | II | II | I | II | II | II |
| B(a)P | 150 | 1450 | I | I | I | I | I | II | II | I | I | I | II | II |
| DBP | 2200 | 17,000 | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I |
| DEHP | 610 | 1100 | - | - | I | I | - | I | - | I | - | I | I | I |
| Final assessment | II | II | II | II | I | II | II | II | I | II | II | II | ||
| Lake/Reservoir | ∑PAHs Flux (μg/m2d) | References |
|---|---|---|
| Nielisz Reservoir | 172 | This study |
| Lake Biwa (Japan) | 2.06 | [60] |
| Lake Windermere (UK) | 109.59 | [61] |
| Lake Suwa (Japan) | 2.41 | [62] |
| Lian’an Reservoir (China) | 2.85 | [53] |
| Liuhuahu Lake (China) | 34.1 | [53] |
| Lake Michigan (USA) | 1.17 | [63] |
| Min | Max | Mean | Median | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | |||||
| pH (-) | 8.00 | 8.86 | - | - | - |
| EC (μS/cm) | 384 | 481 | 418 | 417 | 26 |
| TOC (mg/dm3) | 9.18 | 18.9 | 14.3 | 14.8 | 2.96 |
| Chla (μg/dm3) | 42.6 | 185 | 90.9 | 71.3 | 43.5 |
| Entrapped sediments | |||||
| POC (%) | 2.26 | 12.6 | 7.65 | 6.81 | 3.70 |
| δ13C-POC (‰) | −24.1 | −17.2 | −21.5 | −21.9 | 2.19 |
| ua (-) | 0.24 | 0.73 | 0.55 | 0.58 | 0.16 |
| SPM Flux (g/m2d) | POC Flux (μg/m2d) | Water | Entrapped Sediments | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH (-) | EC (μS/cm) | TOC (mg/dm3) | Chla (μg/dm3) | POC (%) | δ13C-POC (‰) | ua (-) | |||
| Σ4PAHs flux (μg/m2d) | 0.900 * | 0.922 * | −0.754 * | 0.648 * | 0.613 * | 0.442 | 0.779 * | −0.497 | 0.488 |
| 2-rings PAHs flux (μg/m2d) | 0.889 * | 0.976 * | −0.728 * | 0.833 * | 0.613 * | 0.258 | 0.791 * | −0.591 * | 0.585 * |
| 3-rings PAHs flux (μg/m2d) | 0.869 * | 0.923 * | −0.783 * | 0.747 * | 0.634 * | 0.425 | 0.868 * | −0.581 * | 0.574 |
| 5-rings PAHs flux (μg/m2d) | 0.894 * | 0.907 * | −0.738 * | 0.612 * | 0.600 * | 0.446 | 0.749 * | −0.469 | 0.460 |
| Σ2PAEs flux (μg/m2d) | 0.480 | 0.511 | −0.294 | 0.119 | 0.036 | 0.154 | 0.412 | −0.316 | 0.300 |
| DBP flux (μg/m2d) | 0.462 | 0.548 | −0.294 | 0.181 | −0.035 | −0.081 | 0.415 | −0.375 | 0.363 |
| DEHP flux (μg/m2d) | 0.831 * | 0.513 | −0.202 | 0.153 | 0.775 * | 0.717 | 0.103 | 0.351 | −0.356 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gruca-Rokosz, R.; Cieśla, M.; Kida, M.; Ignatowicz, K. Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Phthalates Deposition in Sediments of Reservoirs: Impact of Some Environmental Factors. Water 2025, 17, 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050641
Gruca-Rokosz R, Cieśla M, Kida M, Ignatowicz K. Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Phthalates Deposition in Sediments of Reservoirs: Impact of Some Environmental Factors. Water. 2025; 17(5):641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050641
Chicago/Turabian StyleGruca-Rokosz, Renata, Maksymilian Cieśla, Małgorzata Kida, and Katarzyna Ignatowicz. 2025. "Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Phthalates Deposition in Sediments of Reservoirs: Impact of Some Environmental Factors" Water 17, no. 5: 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050641
APA StyleGruca-Rokosz, R., Cieśla, M., Kida, M., & Ignatowicz, K. (2025). Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Phthalates Deposition in Sediments of Reservoirs: Impact of Some Environmental Factors. Water, 17(5), 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17050641







