Mercury Fraction and Transformation in Sediment Cores of the Eutrophic Estuary in Northern Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sampling and Methods
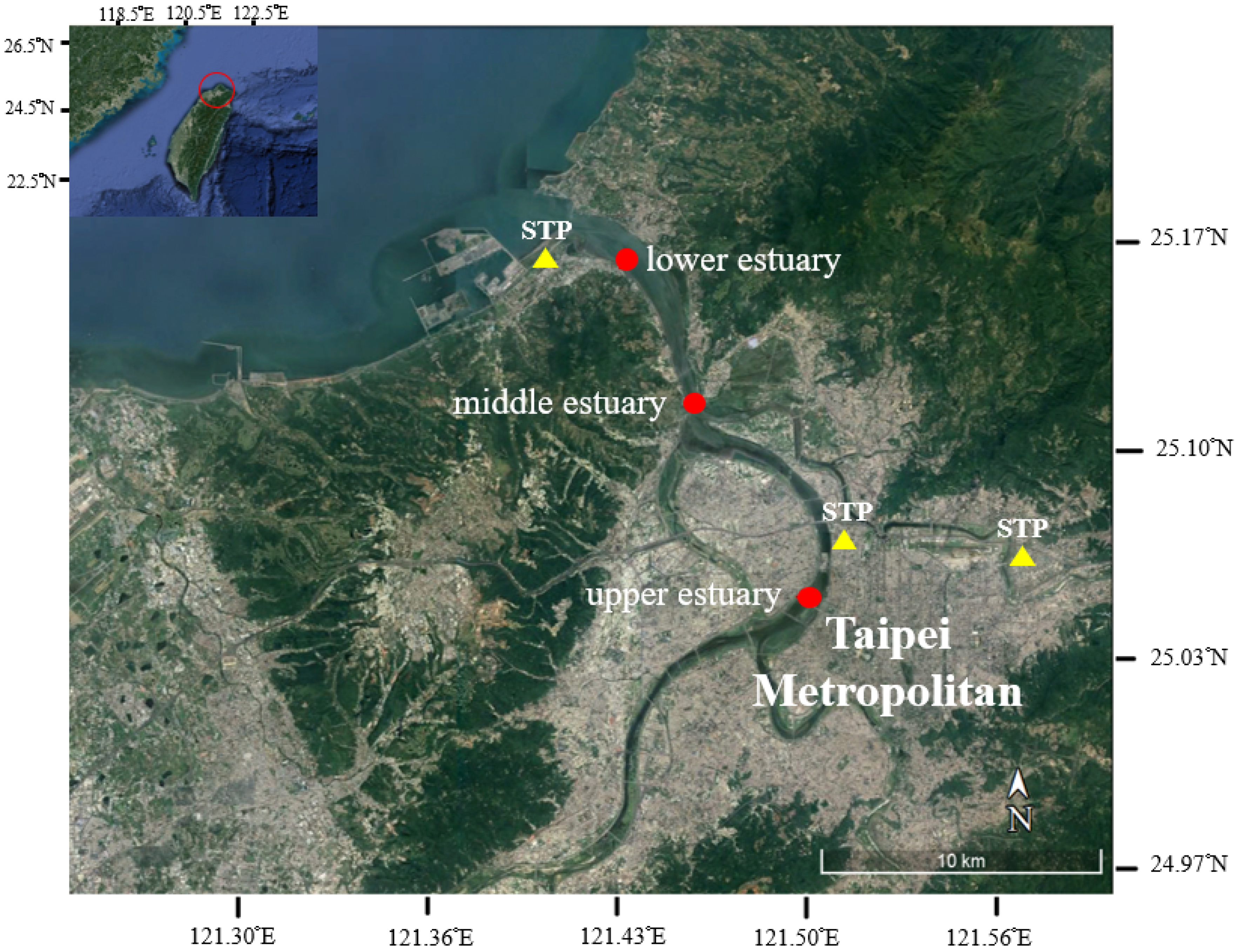
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Analysis
2.3.1. Hg Fractions with the Three SEMs
2.3.2. Sediment Core Analysis
2.3.3. Trace Metals Contamination Assessment
3. Results
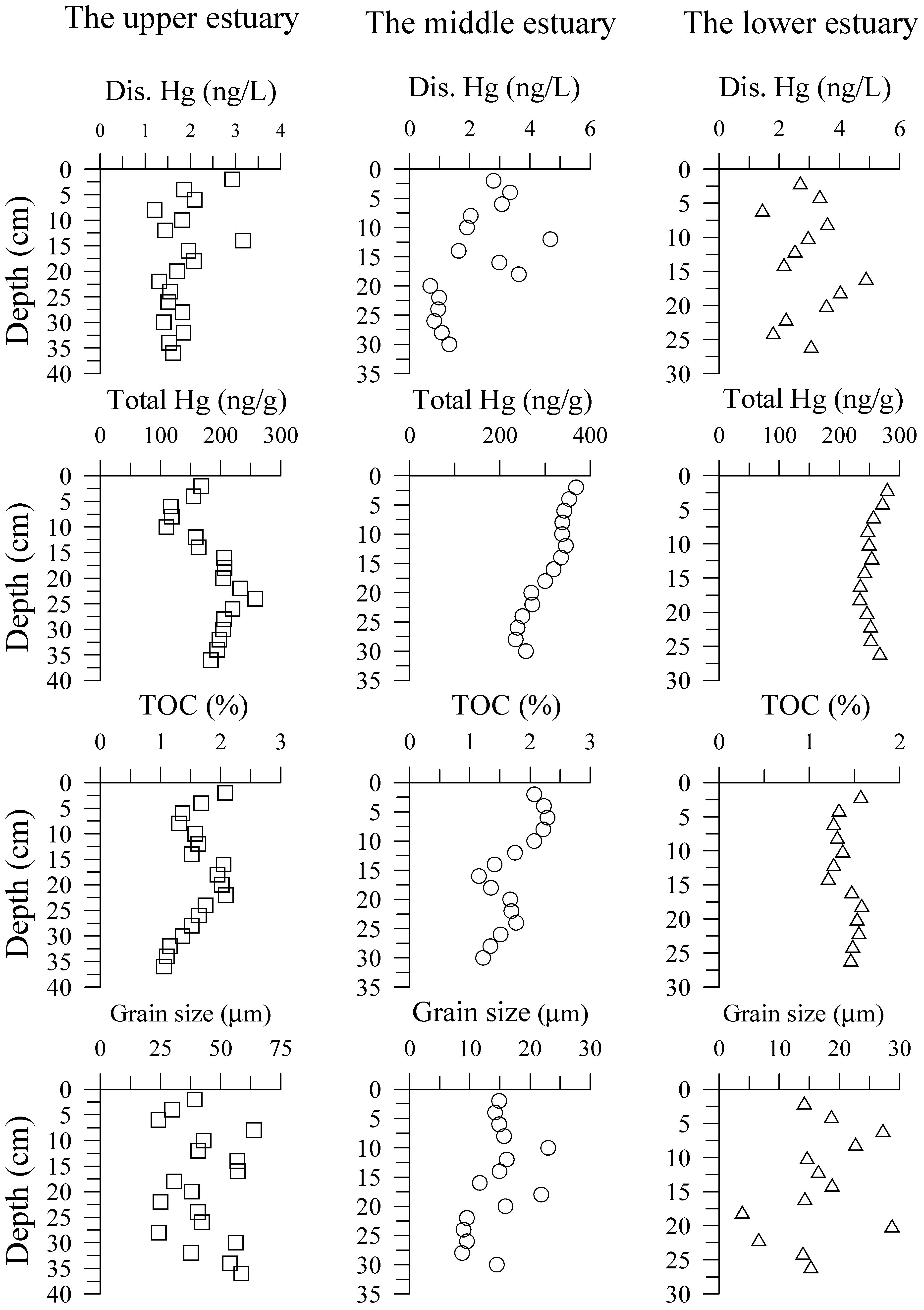
3.1. Hg in Pore Water and Sediment Cores
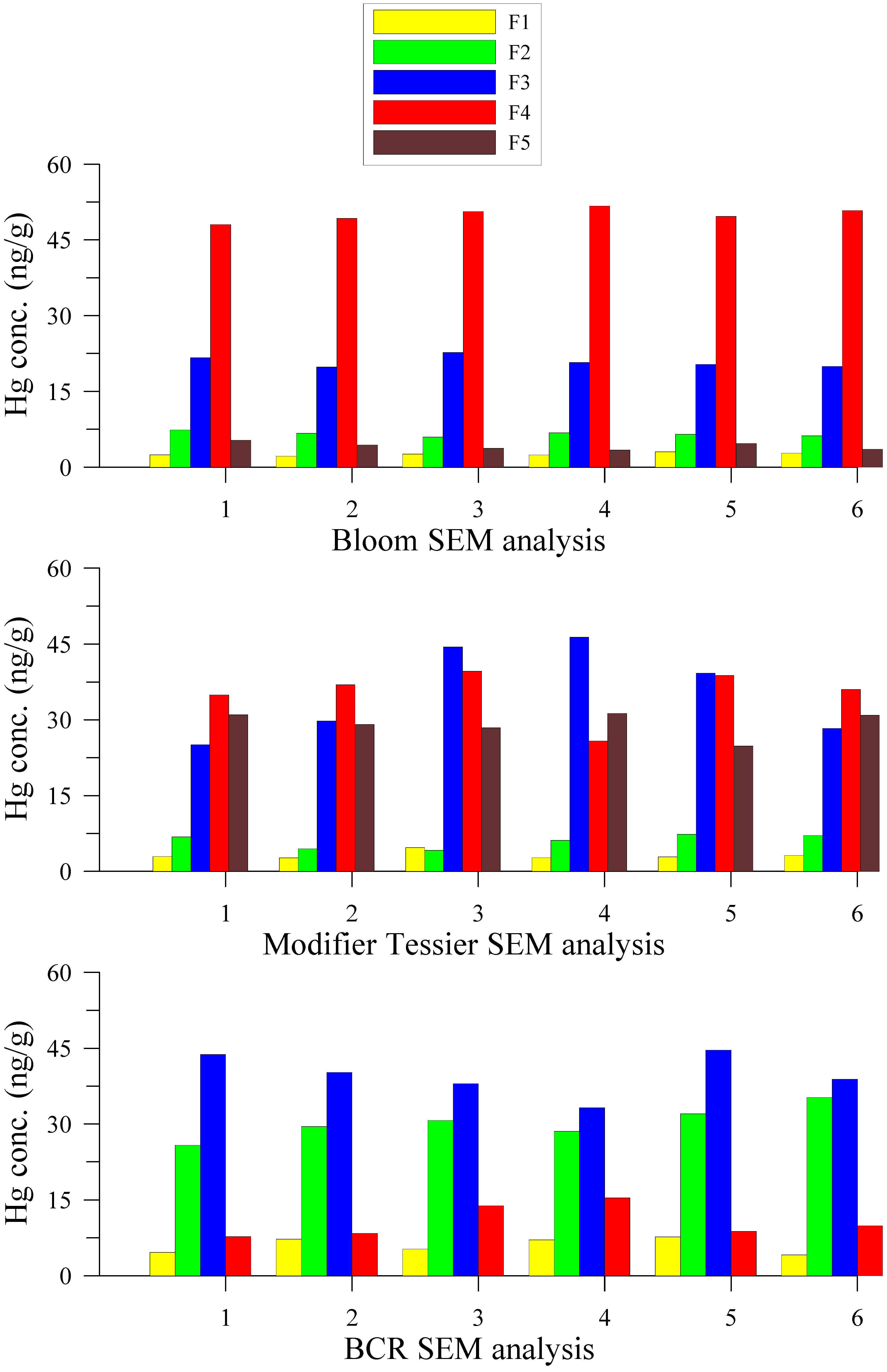
3.2. Hg Fractions in Sediment Cores
4. Discussion
4.1. DTHg in Sediment Pore Waters
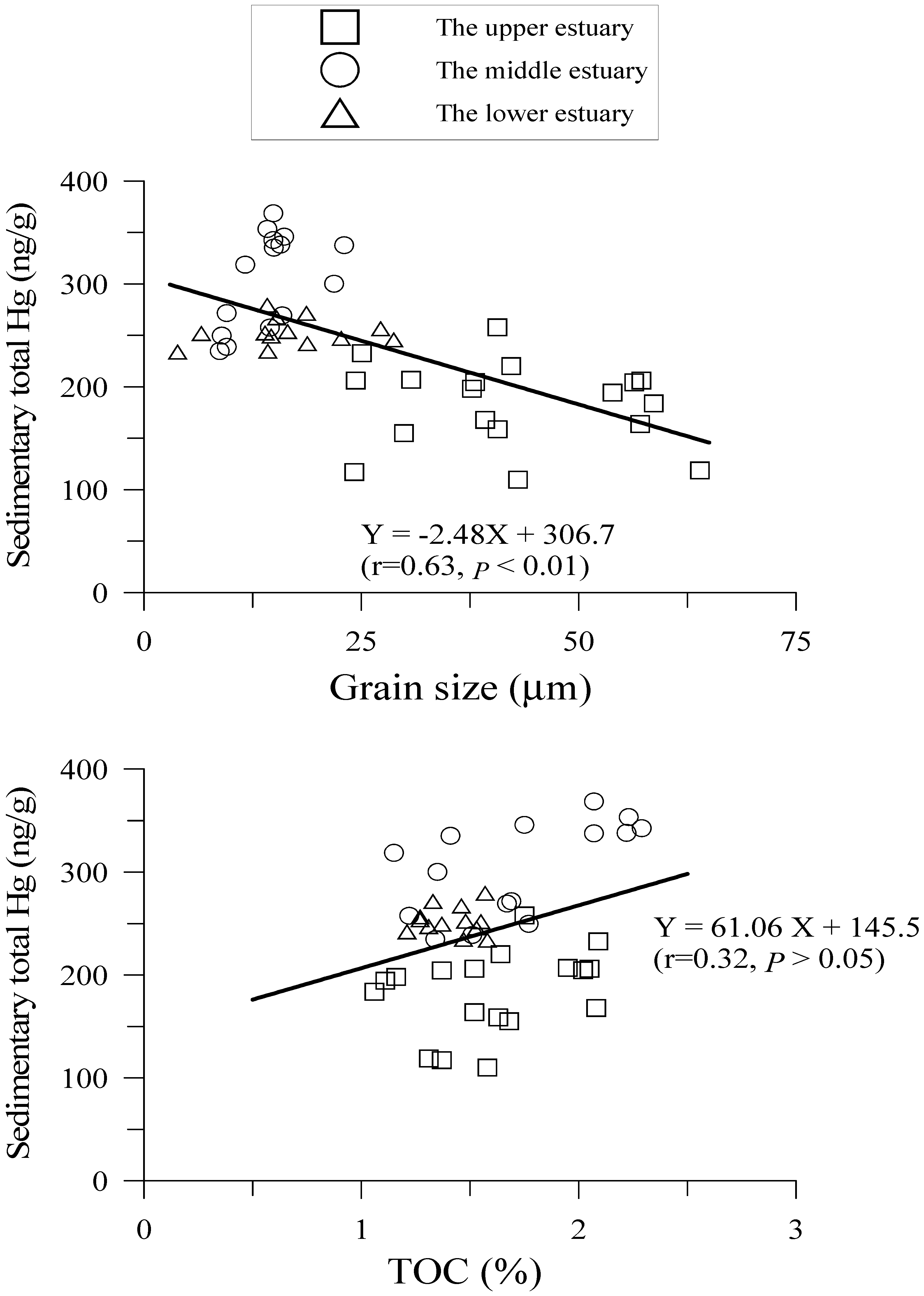
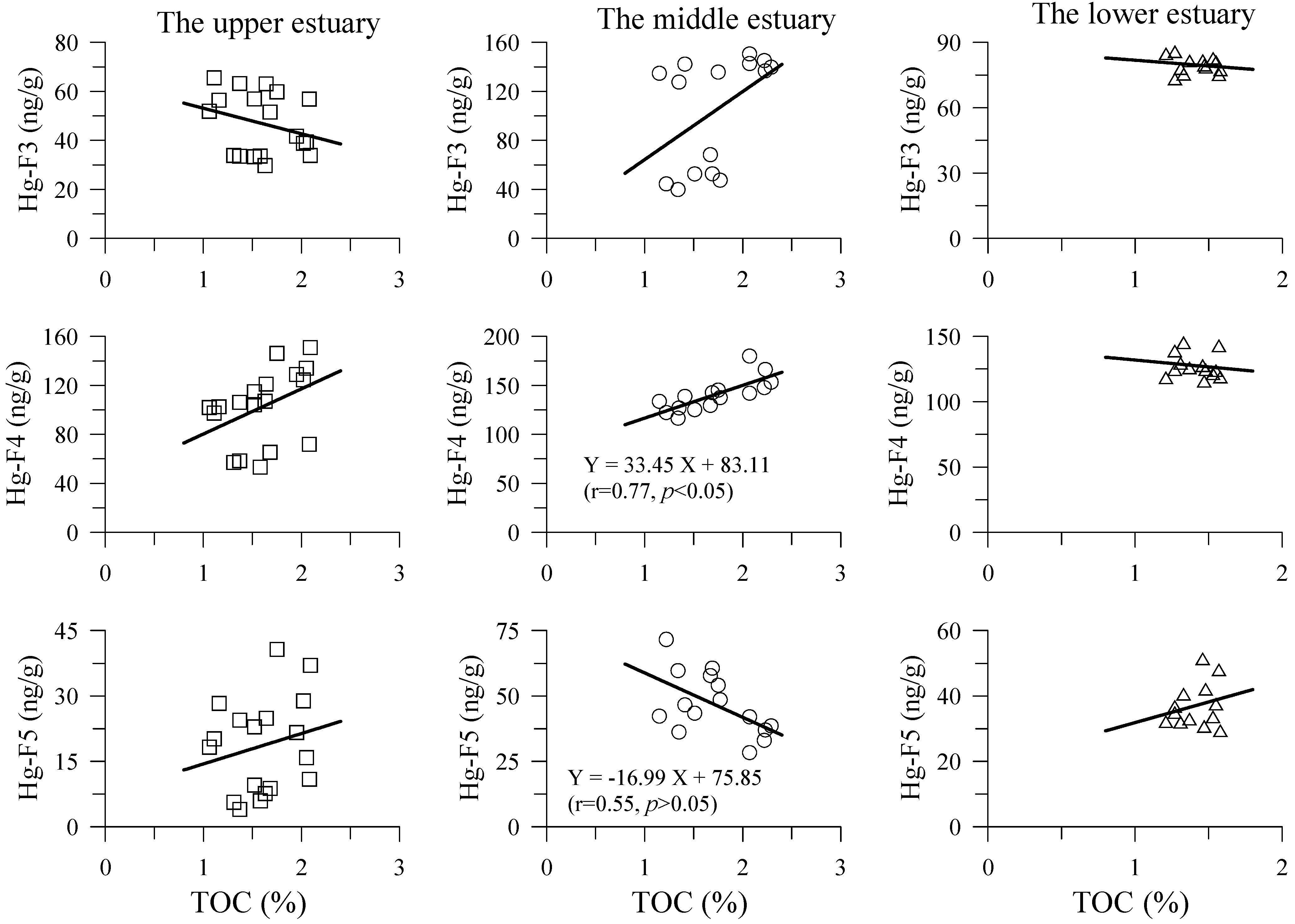
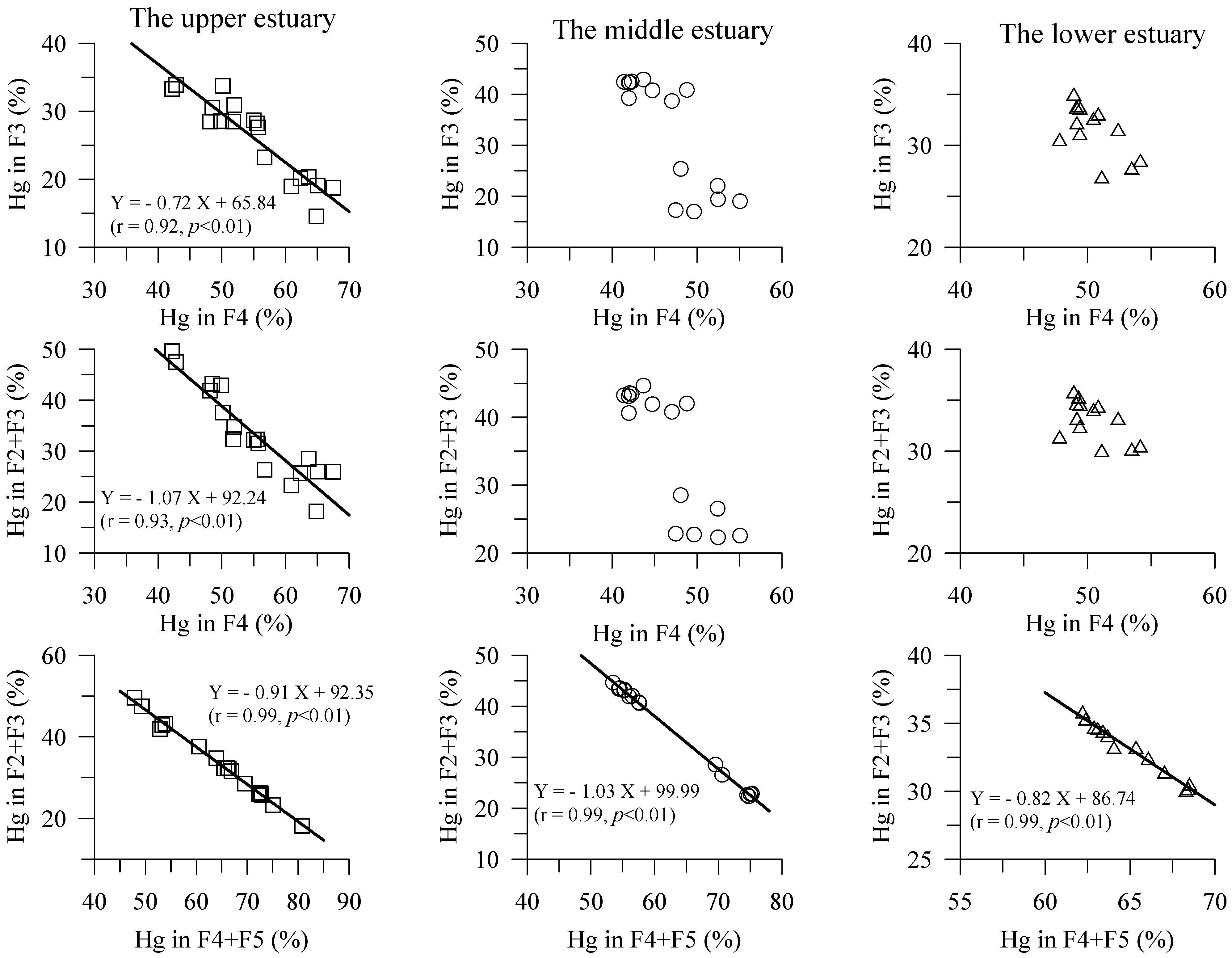
4.2. Hg Fractions in Sediment Cores
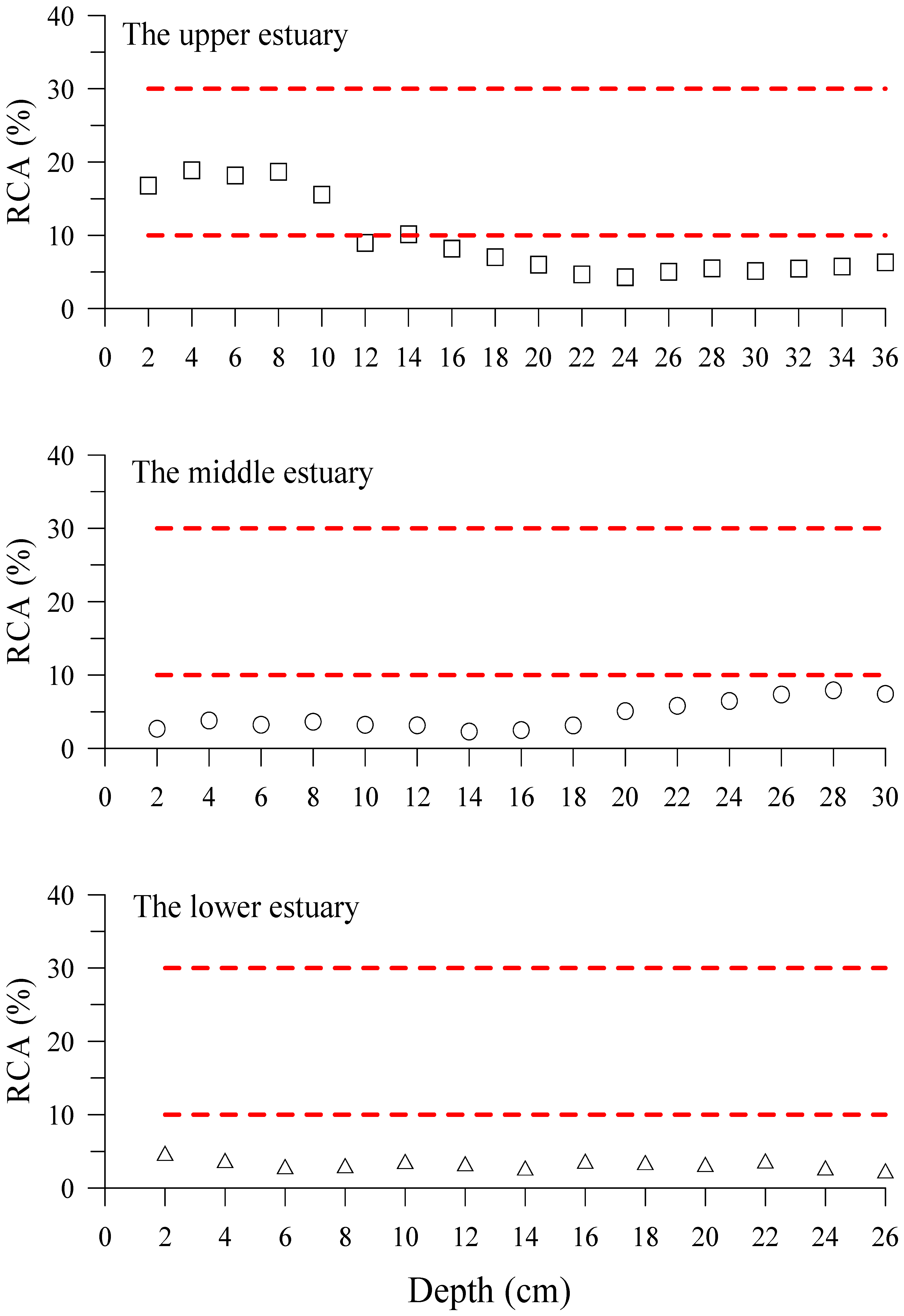
4.3. Hg Contamination Assessment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tomiyasu, T.; Matsuyama, A.; Eguchi, T.; Fuchigami, Y.; Oki, K.; Horvat, M.; Rajar, R.; Akagi, H. Spatial variations of mercury in sediment of Minamata Bay, Japan. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2006, 368, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neff, J.M. Bioaccumulation in Marine Organisms: Effect of Contaminants from Oil Well Produced Water; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gworek, B.; Bemowska-Kalabun, O.; Kijenska, M.; Wrzosek-Jakubowska, J. Mercury in marine and oceanic waters—A review. Wat. Air. Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, W.F.; Lamborg, C.H.; Hammerschmidt, C.R. Marine Biogeochemical Cycling of Mercury. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 641–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, H.C.; Bordalo, M.D.; Figueroa, A.G.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Morgado, F.; Abreu, S.N.; Osten, J.R. Mercury distribution and enrichment in coastal sediments from different geographical areas in the North Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 165, 112153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbondo-Tugbawa, S.S.; McAlear, J.A.; Driscoll, C.T.; Sharpe, C.W. Total and methyl mercury transformations and mass loadings within a wastewater treatment plant and the impact of the effluent discharge to an alkaline hypereutrophic lake. Wat. Res. 2010, 44, 2863–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streets, D.G.; Devane, M.K.; Lu, Z.; Bond, T.C.; Sunderland, E.M.; Jacob, D.J. All-time release of mercury to the atmosphere from human activities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 10485–10491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Outridge, P.M.; Mason, R.P.; Wang, F.; Guerrero, S.; Heimburger-Boavida, L.E. Updated global and oceanic mercury budgets for the United Nations global mercury assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11466–11477. [Google Scholar]
- Bloom, N.S.; Preus, E.; Katon, J.; Hiltner, M. Selective extractions to assess the biogeochemically relevant fractionation of inorganic mercury in sediments and soils. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 479, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumm, W.; Morgan, J.J. Aquatic Chemistry, 3rd ed.; A Wiley-Interscience Publication: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt, C.R.; Fitzgerald, W.F.; Lamborg, C.H.; Balcom, P.H.; Visscher, P.T. Biogeochemistry of methylmercury in sediments of Long Island Sound. Mar. Chem. 2004, 90, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderland, E.M.; Gobas, F.A.P.C.; Heyes, A.; Branfireun, B.A.; Bayer, A.K. Environmental controls on the speciation and distribution of mercury in coastal sediments. Mar. Chem. 2006, 102, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covelli, S.; Faganeli, J.; De Vittor, C.; Predonzani, S.; Acquavita, A.; Horvat, M. Benthic fluxes of mercury species in a lagoon environment (Grado Lagoon, Northern Adriatic Sea, Italy). Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 529–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covelli, S.; Acquavita, A.; Piani, R.; Predonzani, S.; De Vittor, C. Recent contamination of mercury in an estuarine environment (Marano lagoon, Northern Adriatic, Italy). Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 82, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emile, A.; Acquavita, A.; Koron, N.; Covelli, S.; Faganeli, J.; Horvat, M.; Zizek, S.; Fajon, V. Benthic flux measurements of Hg species in a northern Adriatic lagoon environment (Marano and Grado Lagoon, Italy). Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 113, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosnell, K.; Balcom, P.; Ortiz, V.; DiMento, B.; Schartup, A.; Greene, R.; Mason, R. Seasonal cycling and transport of mercury and methylmercury in the turbidity maximum of the Delaware estuary. Aquat. Geochem. 2016, 22, 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.H.; Lien, C.Y. Different mercury species partitioning and distribution in the water and sediment of a eutrophic estuary in Northern Taiwan. Water 2021, 13, 2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrit, K.A.; Amirbahman, A. Mercury methylation dynamics in estuarine and coastal marine environment—A critical review. Ear. Sci. Rev. 2009, 96, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, B.; Arsenie, I. Abiotic reduction of mercury by humic substances in aquatic system—An important process for the mercury cycle. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1991, 56, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, S.; Skyllberg, U.; Nilsson, M.; Lundberg, E.; Andersson, A.; Bjorn, E. Differentaited availability of geochemical mercury pools controls methylmercury levels in estuarine sediment and biota. Nature Commun. 2014, 5, 4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covelli, S.; Protopsalti, I.; Acquavita, A.; Sperle, M.; Bonardi, M.; Emili, A. Spatial variation, speciation and sedimentary records of mercury in the Guanabara Bay (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil). Cont. Shelf Res. 2012, 35, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoham-Frider, E.; Azran, S.; Kree, N. Mercury speciation and total carbon in marine sediments along the Mediterranean Coast of Israel. Arch. Environ. Technol. 2012, 63, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.Q.; Song, J.M.; Yu, Y.; Yuan, H.M.; Li, X.G.; Li, N. Spatial variation, fractionation and sedimentary records of mercury in the East China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issaro, N.; Abi-Ghanem, C.; Bermond, A. Fractionation studies of mercury in soils and sediments: A review of the chemical reagents used for mercury extraction. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2009, 631, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.T.; Davidson, C.M.; Vale, C.; Pereira, E. Overview and challenges of mercury fractionation and speciation in soils. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, J.R.; Davidson, C.M. Is there a future for sequential chemical extraction? Analyst 2008, 133, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BCR, European Commission. The Certification of the Extractable Contents (Mass Fractions) of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in Freshwater Sediment Following a Sequential Extraction Procedure—BCR 701; Community Res.; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2001; Volumes 1–88, Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/02c41803-8f6d-41f2-a73d-c47225ff8c6e (accessed on 11 August 2020).
- Hung, J.J.; Lu, C.C.; Huh, C.A.; Liu, J.T. Geochemical controls on distributions and speciation of As and Hg in sediments along the Gaoping (Kaoping) Estuary-Canyon system off southwestern Taiwan. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 76, 479–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumkrong, P.; Mercier, P.H.J.; Gedara, I.P.; Mihai, O.; Tyo, D.D.; Cindy, J.; Kingston, D.M.; Mester, Z. Determination of 27 metals in HISS-1, MESS-4 and PACS-3 marine sediment certified reference materials by the BCR sequential extraction. Talanta 2021, 221, 121543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orecchio, S.; Polizzotto, G. Fractionation of mercury in sediments during draining of Augusta (Italy) coastal area by modifier Tessier method. Microchem. 2013, 110, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Babu, P.V.R.; Vudamala, K.; Ramteke, D.; Chennuri, K. Mercury speciation in coastal sediments from the central east coast of Indis by modified BCR method. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 81, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, M.; Li, R.; Qiu, Z.; Niu, Z.; Shen, X. Mercury distribution and transfer in sediment-mangrove system in urban mangrove of fast-developing coastal region, Southern China. Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 240, 106770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.H. Partitioning and behavior of different forms of phosphorus in the Tanshui estuary and one of its tributaries, Northern Taiwan. Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2000, 50, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.H.; Chen, R.Y. Mercury contamination and accumulation in sediments of the East China Sea. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.H.; Wang, C.W. Dissolved and particulate phosphorus species partitioning and distribution in the Danshuei River Estuary, Northern Taiwan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.H.; Chen, W.H. Dissolved and particulate nitrogen species partitioning and distribution in the Danshuei River Estuary, Northern Taiwan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 164, 111981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.H.; Wang, C.W. Distribution of geochemical species of P, Fe and Mn in surface sediments in the eutrophic estuary, northern Taiwan. Water 2021, 13, 3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.C.; Lin, W.Y.; Fang, T.H. Spatial variability of nitrogen cycling in the sediments of the Danshuie River Estuary (Northern Taiwan). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 197, 115776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.M.; Chen, Y.S.; Ang, S.J.; Li, K.C.; Peng, H.C.; Gong, G.C. Probing the outfall-related anomalous Hg levels in the Danshuei Estuarine Coastal, Taiwan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 181, 1138940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.H.; Chang, F.W. Temporal variation of mercury and methyl mercury in water and accumulation by phytoplankton in the eutrophic estuary, northern Taiwan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 205, 116624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcom, P.H.; Schartup, A.T.; Mason, R.P.; Chen, C.Y. Sources of water column methylmercury across multiple estuaries in the Northeast U.S. Mar. Chem. 2015, 177, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, A.; Monperrus, M.; Tessier, E.; Bouchet, S.; Pinaly, H.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, P.; Maron, P.; Amouroux, D. Fate of mercury species in the coastal plume of the Adour River estuary (Bay of Biscay, SW France). Sci. Tot. Environ. 2014, 496, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.R.; Macdonald, D.D.; Smith, S.; Calder, F.D. Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ. Manag. 1995, 19, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Feng, X.; Zhang, X.; Yin, R. Spatial distribution and speciation of mercury and methyl mercury in the surface waters of East River (Dongjiang) tributry of Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Lin, H.; Sun, X. Total mercury flux and offshore transport via submarine groundwater discfharge and coal-fired power plant in the Jiulong River estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesario, R.; Hintelmann, H.; O’Driscoll, N.J.; Monteiro, C.E.; Caetano, M.; Nogueira, M.; Mota, A.M.; Canario, J. Biogeochemical cycle of mercury and methylmetcury on two highly contaminated areas of Tagus Estuary (Portugal). Wat. Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Du, P.; Yu, C.; He, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Lin, H.; Luo, Y.; Xie, H.; Guo, J.; et al. Increases of total mercury and methylmercury releases from municipal sewage into environment in China and implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.C.; Chen, W.B.; Kuo, J.T.; Wu, C. Numerical determination of residence time and age in a partially mixed estuary using three-dimensional hydrodynamic model. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1068–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Resources Bureau. Hydrological Year Book of Taiwan, Ministry of Economic Affairs, Republic of China. 2020. Available online: https://gweb.wra.gov.tw/wrhygis (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Kao, S.; Milliman, J.D. Water and sediment discharge from small mountainous rivers, Taiwan: The roles of lithology, episodic events, and human activities. J. Geol. 2008, 116, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewerage System Office of the Public Works Department of Taipei City Government. 2023. Available online: https://www.sso.gov.taipei (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Environmental Protection Agency. Method 7474. Mercury in Sediment and Tissue Samples by Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry. 2007. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/hw-sw846/sw-846-test-method-7474-mercury-sediment-and-tissue-samples-atomic-fluorescence (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Environmental Protection Agency. Method 1631. Revision E: Mercury in Water by Oxidation, Purge and Trap, and Cold Vapor Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry. 2002. Available online: https://ddei3-0-ctp.trendmicro.com:443/wis/clicktime/v1/query?url=https%3a%2f%2fwww.epa.gov%2fsites%2fdefault%2ffiles%2f2015%2d08%2fdocuments%2fmethod%5f1631e%5f2002.pdf&umid=646E13A4-2C19-9306-AA56-A84667BFC3BC&auth=c26fd05b9d068d74167cd5770ee96b266b7e88ac-17a15ef09736f94e661b89873c1d4dfa1ae43296 (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Kim, C.S.; Bloom, N.S.; Rytuba, J.J.; Brown, G.E. Mercury speciation by X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy and sequential chemical extractions: A comparison of speciation methods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5102–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Martínez, R.; Rucandio, I. Assessment of a sequential extraction method to evaluate mercury mobility and geochemistry in solid environmental samples. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 97, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleyzes, C.; Tellier, S.; Astruc, M. Fractionation studies of trace elements in contaminated soils and sediments: A review of sequential extraction procedures. Trends. Anal. Chem. 2002, 21, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R. Petrology of Sedimentary Rocks; Hamphill’s: Austin, TX, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Long, E.R.; Macdonald, D.D.; Severn, C.G.; Hong, C.B. Classifying probabilities of acute toxicity in marine sediments with emprically derived sediment quality guildlines. Environ. Toxic. Chem. 2000, 19, 2598–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, G.; Craboledda, L.; Lucchese, M.; Cirillo, R.; Dotta, L.; Zanette, M.L.; Orio, A.A. Heavy metal speciation in the sediments Northern Adriatic sea: A new approach for environmental toxicity determination. In Heavy Metals in the Environment; Lekkas, T.D., Ed.; CEP Consultants: Edinburgh, UK, 1985; Volume 2, pp. 454–456. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Zhuang, W.; Chen, C.T.A.; Zhang, Y. Sediment quality of the SW coastal Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, China: A comprehensive assessment based on the analysis of heavy metals. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pempkowiak, J.; Cossa, D.; Sikora, A.; Sanjuan, J. Mercury in water and sediments of the southern Baltic Sea. Sci. Tot. Environ. 1998, 213, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, D.; Pineda, P.; Olivero, J.; Gonzalez, H.; Campos, N. Mercury levels in muscle of two fish species and sediments from the Cartagena bay and the Cienaga Grande de Santa Marta, Colombia. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 109, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covelli, S.; Faganeli, J.; Horvat, M.; Brambati, A. Mercury contamination of coastal sediments as the result of long-term cinnabar mining activity (Gulf of Trieste, northern Adriatic sea). Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Liang, L.; Yuan, C.; He, B. Methylmercury and total mercury in sediments collected from the East China Sea. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2005, 74, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, K.Y.; Gill, G.A.; Lehman, R.D.; Han, S.; Heim, W.A.; Coale, K.H. Sediment-water exchange of total mercury and monomethyl mercury in the San Francisco Bay-Delta. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 1512–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyes, A.; Miller, C.; Mason, R. Mercury and methylmercury in Hudson River sediment: Impact of tidal resuspension on partitioning and methylation. Mar. Chem. 2004, 90, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, J.; Castelle, S.; Blanc, G.; Dabrin, A.; Masson, M.; Lanceleur, L.; Bossy, C. Mercury methylation in the sediments of a macrotidal estuary (Gironde Estuary, south-west France). Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 90, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcom, P.H.; Hammerschmidt, C.R.; Fitzgerald, W.F.; Lamborg, C.H.; O’Connor, J.S. Seasonal distributions and cycling of mercury and methylmercury in the waters of New York/New Jersey Harbor Estuary. Mar. Chem. 2008, 109, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.E.; Chen, C.Y.; Voytek, M.A.; Amirbahman, A. The effect of sediment mixing on mercury dynamics in two intertidal mudflats at great Bay Estuary, New Hampshire. Mar. Chem. 2015, 177, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, A.; Yano, S.; Taninaka, T.; Kindachi, M.; Sonoda, I.; Tada, A.; Akagi, H. Chemical characteristics of dissolved mercury in the pore water of Minamata Bay sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, G.; Rozan, T.F. The influence of size distribution on the particle concentration effect and trace metal partitioning in rivers. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schartup, A.T.; Balcom, P.H.; Mason, R.P. Sediment-Porewater Partitioning, Total Sulfur, and Methylmercury Production in Estuaries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvin-DiPasquale, M.; Lutz, M.A.; Brigham, M.E.; Krabbenhoft, D.P.; Aiken, G.R.; Orem, W.H.; Hall, B.D. Mercury Cycling in Stream Ecosystems. 2. Benthic Methylmercury Production and Bed Sediment-Pore Water Partitioning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2726–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, S.; Netti, R. Sea water intrusion and mercury pollution of some coastal aquifers in the province of Grosseto (Southern Tuscany, Italy). J. Hydrol. 2000, 237, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Millward, G.E.; Le Roux, S.M. Sediment-water partitioning of inorganic mercury in estuaries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4648–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, J.M.; Mason, R.P.; Gilmour, C.C.; Aiken, G.R. Constants for mercury binding by dissolved organic matter isolated from the Florida Everglades. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 4445–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haitzer, M.; Aiken, G.R.; Ryan, J.N. Binding of mercury (II) to dissolved organic matter: The role of the mercury-to-DOM concentration ratio. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3564–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollweg, T.A.; Gilmour, C.C.; Mason, R.P. Methylmercury production in sediments of Chespeake Bay and the mid-Atlantic continental margin. Mar. Chem. 2009, 134, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boszke, L.; Kowalski, A.; Szczucinski, W.; Rachlewicz, G.; Lorenc, S.; Siepak, J. Assessment of mercury mobility and bioavailability by fractionation method in sediments from coastal zone inundated by the 26 December 2004 tsunami in Thailand. Environ. Geol. 2006, 51, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, H.; Pan, Y.; Wang, W.X. Mercury distribution, speciation and bioavailability in sediments from the Pearl River Estuary, Southern China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1699–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daye, M.; Kadlecova, M.; Wuddane, B. Biogeochemical factors affecting the distribution, speciation, and transport of Hg species in the Deule and Lys Rivers (Northern France). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 2708–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravichandran, M. Interactions between mercury and dissolved organic matter- a review. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu-Kim, H.; Kucharzyk, K.H.; Zhang, T.; Deshusses, M.A. Mechanisms Regulating Mercury Bioavailability for Methylating Microorganisms in the Aquatic Environment: A Critical Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2441–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beldowski, J.; Miotk, M.; Beldowska, M.; Pempkowiak, J. Total, methyl and organic mercury in sediments of the Southern Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 87, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoham-Frider, E.; Shelef, G.; Kress, N. Mercury speciation in sediments at a domestic sewage sludge marine disposal site. Mar. Environ. Res. 2007, 64, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Wang, W.X. Inorganic mercury binding with different sulfur species in anoxic sediments and their gut juice extractions. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 1851–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
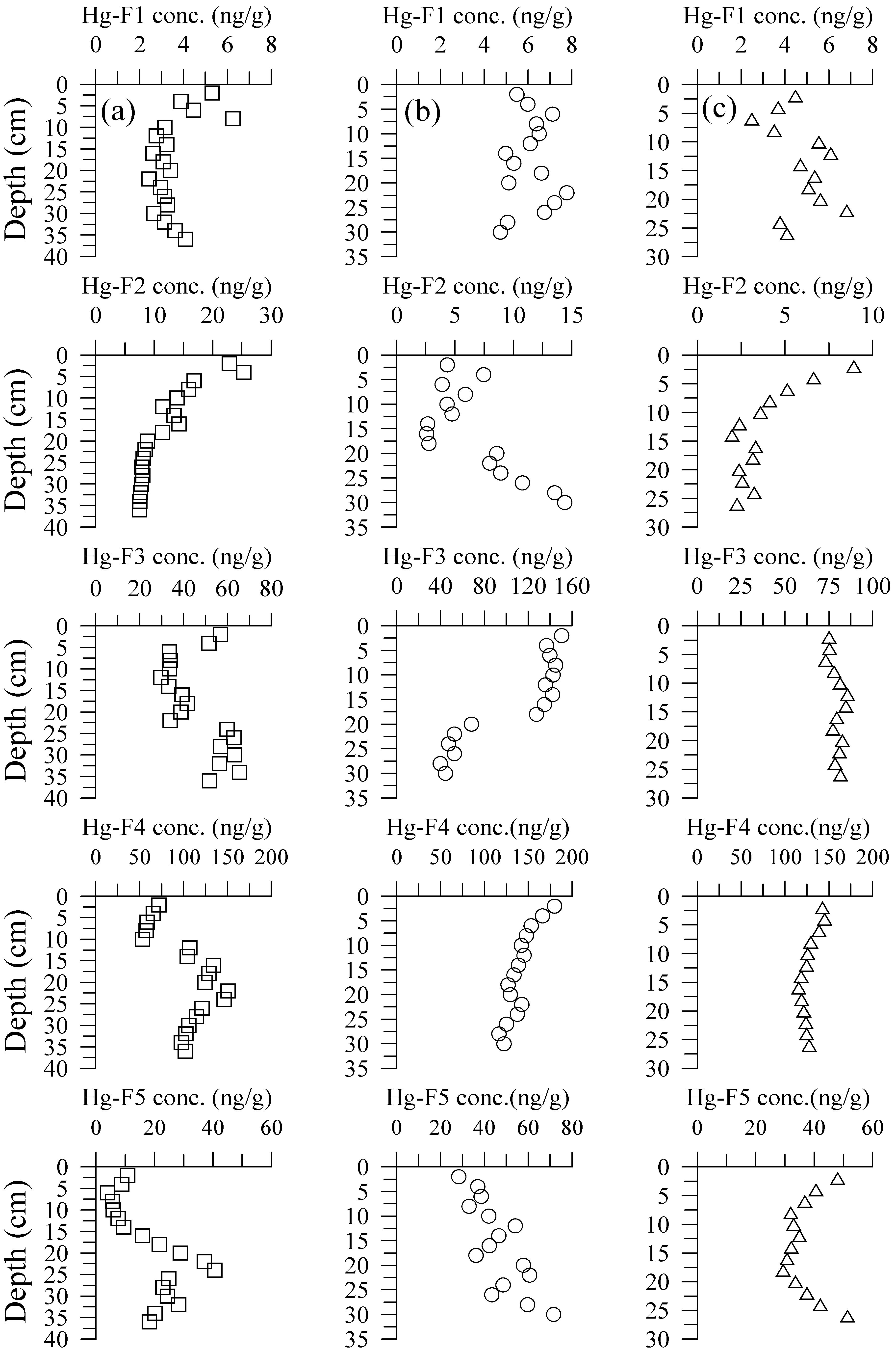
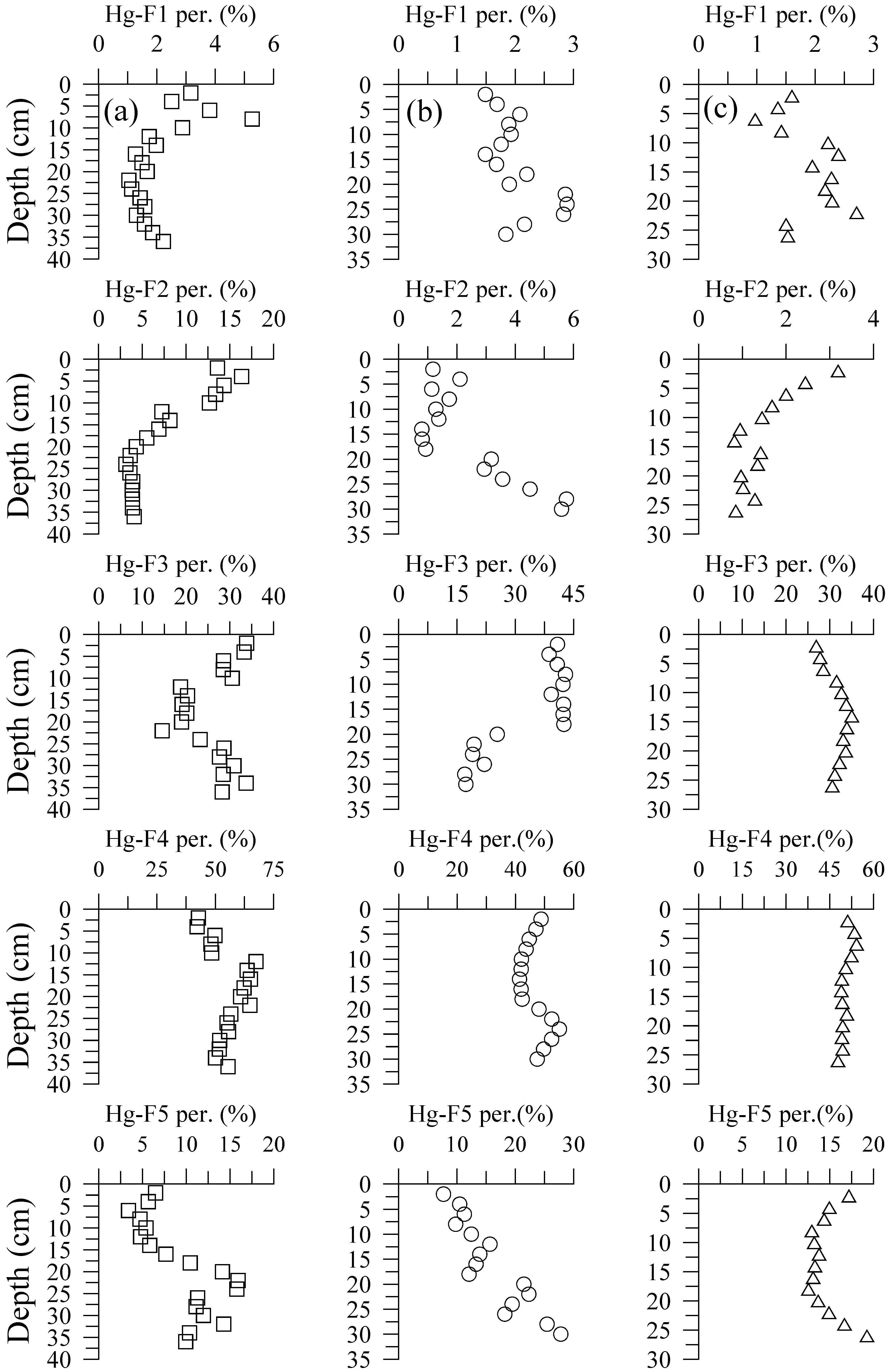
| Sequential Extraction Process | Chemical Treatment | Possible Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Bloom Method | ||
| F1 Water-soluble | Milli-Q water | Water soluble, HgCl2 |
| F2 Human Stomach Acid | 0.1 M HOAc + 0.01 M HCl | bond to high water-solubility species |
| F3 Organo-chelated | 1 M KOH | bond to humic, Hg humic, Hg2Cl2, CH3Hg |
| F4 Elemental Hg | 12 M HNO3 | crystalline in Fe-Mn oxides, organosulfur |
| F5 Residual | Aqua regia | bond to HgS, crystal lattice |
| Modified Tessier method | ||
| F1 Exchangeable | 1 M NaOAc (pH = 8.2) | bond to ion exchange |
| F2 Carbonates | 1 M NaOAc (pH = 5.0) | bond to carbonate |
| F3 Fe-Mn Oxides | 0.04 M NH2OH·HCl in 25% (v/v) HOAc | bond to Fe-Mn oxides |
| F4 Organic Matter | 0.02 M HNO3 in 30% H2O2 (pH = 2.0) | bond to organic matter |
| and 3.2 M NH4OAc in 20% (v/v) HNO3 | ||
| F5 Residual | Aqua regia | bond to HgS, crystal lattice |
| BCR method | ||
| F1 Exchangeable | 0.11 M HOAc | bond to ion exchangeable |
| F2 Reducible | 0.5 M NH2OH·HCl and 0.4 M HNO3 | bond to Fe-Mn oxides |
| F3 Oxidizable | 8.8 M H2O2 (pH = 2~3) | bond to organic matter |
| and 1 M NH4OAc (pH = 2.0) | ||
| F4 Residual | Aqua regia | bond to HgS, crystal lattice |
| Concentration (ng/g) | Total Conc. | Anal. Accur. | Fraction Percentage (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | (ng/g) | (%) | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | |
| Bloom SEM | ||||||||||||
| Min | 2.19 | 5.97 | 19.84 | 48.07 | 3.37 | 82.39 | 91.54 | 2.66 | 6.97 | 23.95 | 56.64 | 3.96 |
| Max | 3.06 | 7.36 | 22.70 | 51.73 | 5.34 | 85.62 | 95.13 | 3.63 | 8.67 | 26.51 | 60.99 | 6.29 |
| Mean± | 2.58 | 6.60 | 20.87 | 50.03 | 4.18 | 84.26 | 93.62 | 3.06 | 7.83 | 24.76 | 59.38 | 4.96 |
| 1 std | 0.31 | 0.49 | 1.11 | 1.30 | 0.76 | 1.20 | 1.33 | 0.36 | 0.59 | 1.03 | 1.59 | 0.91 |
| Modified Tessier SEM | ||||||||||||
| Min | 2.70 | 4.16 | 25.09 | 25.83 | 24.81 | 100.82 | 112.00 | 2.42 | 3.43 | 24.89 | 22.99 | 21.94 |
| Max | 4.72 | 7.35 | 46.38 | 39.64 | 31.29 | 121.44 | 134.93 | 3.89 | 6.77 | 41.27 | 35.88 | 30.76 |
| Mean± | 3.18 | 6.02 | 35.55 | 35.37 | 29.26 | 109.38 | 121.53 | 2.89 | 5.55 | 32.21 | 32.44 | 26.92 |
| 1 std | 0.77 | 1.37 | 9.00 | 4.98 | 2.46 | 7.70 | 8.55 | 0.53 | 1.40 | 6.34 | 4.74 | 3.46 |
| modified BCR SEM | ||||||||||||
| Min | 4.13 | 25.80 | 33.20 | 7.76 | 81.97 | 91.08 | 4.68 | 31.47 | 39.40 | 9.44 | ||
| Max | 7.70 | 35.27 | 44.64 | 15.41 | 93.18 | 103.53 | 8.49 | 40.00 | 53.41 | 18.29 | ||
| Mean± | 6.02 | 30.31 | 39.79 | 10.69 | 86.81 | 96.46 | 6.92 | 34.87 | 45.86 | 12.34 | ||
| 1 std | 1.52 | 3.22 | 4.17 | 3.17 | 3.89 | 4.32 | 1.67 | 2.80 | 4.78 | 3.77 | ||
| Pore Water | Sediment Core | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DTHg (ng/L) | Total Hg (ng/g) | TOC (%) | Grain Size (µm) | Medium Sand (%) | Fine Sand (%) | Very Fine Sand (%) | Mud (%) | |
| The upper estuary | ||||||||
| Min | 1.21 | 109.9 | 1.06 | 24.19 | 1.31 | 5.35 | 10.41 | 25.04 |
| Max | 3.17 | 257.7 | 2.09 | 63.94 | 12.99 | 25.75 | 60.22 | 74.48 |
| Mean | 1.83 | 183.6 | 1.61 | 42.39 | 5.15 | 14.56 | 33.15 | 47.14 |
| The middle estuary | ||||||||
| Min | 0.69 | 234.8 | 1.15 | 8.71 | 0.37 | 0.46 | 1.91 | 85.44 |
| Max | 4.68 | 368.7 | 2.29 | 23.02 | 4.61 | 3.09 | 7.41 | 97.26 |
| Mean | 2.13 | 304.2 | 1.72 | 14.28 | 1.67 | 1.35 | 4.16 | 92.82 |
| The lower estuary | ||||||||
| Min | 1.44 | 234.0 | 1.21 | 3.86 | 1.08 | 1.22 | 5.35 | 67.93 |
| Max | 4.89 | 279.5 | 1.58 | 28.73 | 5.53 | 12.35 | 18.62 | 91.86 |
| Mean | 2.95 | 252.8 | 1.42 | 16.56 | 2.24 | 4.01 | 10.67 | 83.08 |
| Sampled Time | Concentration (ng/g) | Percentage (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | Total | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | |
| The upper estuary | |||||||||||
| Min | 2.43 | 7.52 | 29.72 | 53.27 | 3.98 | 109.9 | 1.04 | 3.15 | 14.55 | 42.20 | 3.40 |
| Max | 6.26 | 25.35 | 65.53 | 150.85 | 40.69 | 257.7 | 5.27 | 16.36 | 33.87 | 67.51 | 15.93 |
| Mean | 3.53 | 12.08 | 46.82 | 102.6 | 18.6 | 183.6 | 2.11 | 7.36 | 25.97 | 55.15 | 9.41 |
| The middle estuary | |||||||||||
| Min | 4.74 | 2.58 | 39.88 | 116.57 | 28.35 | 234.77 | 1.49 | 0.80 | 16.99 | 41.39 | 7.69 |
| Max | 7.77 | 14.39 | 150.58 | 179.90 | 71.61 | 368.67 | 2.89 | 5.76 | 42.91 | 55.07 | 27.80 |
| Mean | 6.08 | 6.88 | 104.06 | 140.51 | 46.68 | 304.19 | 2.05 | 2.46 | 32.80 | 46.61 | 16.08 |
| The lower estuary | |||||||||||
| Min | 2.49 | 1.99 | 73.20 | 115.74 | 29.38 | 233.97 | 0.97 | 0.82 | 26.90 | 47.80 | 12.56 |
| Max | 6.82 | 8.93 | 85.71 | 145.24 | 51.42 | 279.50 | 2.71 | 3.19 | 35.02 | 54.15 | 19.24 |
| Mean | 4.71 | 3.83 | 79.61 | 127.55 | 37.11 | 252.81 | 1.88 | 1.49 | 31.60 | 50.43 | 14.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, T.-H.; Wu, X.L. Mercury Fraction and Transformation in Sediment Cores of the Eutrophic Estuary in Northern Taiwan. Water 2025, 17, 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030290
Fang T-H, Wu XL. Mercury Fraction and Transformation in Sediment Cores of the Eutrophic Estuary in Northern Taiwan. Water. 2025; 17(3):290. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030290
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Tien-Hsi, and Xiang Lu Wu. 2025. "Mercury Fraction and Transformation in Sediment Cores of the Eutrophic Estuary in Northern Taiwan" Water 17, no. 3: 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030290
APA StyleFang, T.-H., & Wu, X. L. (2025). Mercury Fraction and Transformation in Sediment Cores of the Eutrophic Estuary in Northern Taiwan. Water, 17(3), 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030290








