Abstract
The rapid expansion of the electrode foil industry has led to the generation of large volumes of acidic wastewater containing strong acids (sulfuric and hydrochloric) and metal ions (such as aluminum and copper). The generated wastewater poses serious environmental challenges, including infrastructure corrosion, soil acidification, and toxicity to aquatic life. This review evaluates three primary treatment approaches: neutralization (adjusting pH and removing metals), ion adsorption (selective recovery of metals and acid recycling), and membrane separation (precision resource recovery). Neutralization is cost-effective for pH adjustment and metal removal but is limited by secondary pollution and low resource recovery. Ion adsorption allows for the targeted recovery of metals and recycling of acid, although it faces challenges related to high costs and scalability. Membrane separation offers accurate separation and resource recovery but is affected by fouling and high energy requirements. Future research should focus on integrated treatment strategies, AI-driven process optimization, and the development of advanced materials to enhance sustainable wastewater management. These efforts aim to provide a scientific basis and technical reference for wastewater treatment in the electrode foil industry.
1. Introduction
The electrode foil industry has experienced substantial growth in recent decades, driven by the increasing demand for aluminum electrolytic capacitors and associated electronic components, leading to a significant increase in wastewater production (Figure 1) [1]. During critical manufacturing stages, notably etching and pickling, considerable quantities of sulfuric and hydrochloric acids are employed to eliminate impurities and enhance the foil’s surface characteristics. These acids are indispensable for dissolving unwanted residues, ensuring the foil adheres to stringent quality standards. However, their utilization results in the generation of highly acidic wastewater, with pH levels typically ranging from 1 to 3, characterized by elevated concentrations of metal ions, primarily aluminum (500–2000 mg/L) and copper, alongside high sulfate concentrations (10–30 g/L).
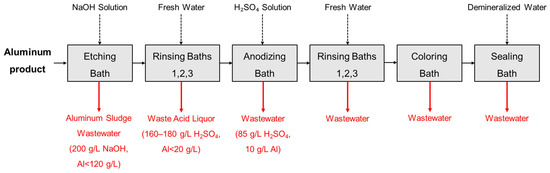
Figure 1.
Schematic visual diagram of waste liquor and wastewater generation in the aluminum industry.
Although the exact composition of this wastewater may vary depending on specific production techniques and capacitor types, the prevalent presence of high acid and metal content underscores a significant environmental challenge [2,3,4,5,6]. One immediate concern is the accelerated deterioration of infrastructure. The extremely low pH of the wastewater can quickly corrode drainage systems, leading to costly repairs and significant disruption to municipal services [7]. Furthermore, when this wastewater reaches natural water bodies, it disrupts aquatic ecosystems by altering pH levels. Even minor changes in pH can lead to a decline in biodiversity and the loss of sensitive aquatic species, thus undermining the ecological balance [8]. In addition to the direct effects on water bodies, acidic wastewater poses serious risks to terrestrial environments. When the wastewater infiltrates the soil, it leads to soil acidification—a process that diminishes the soil’s fertility by altering its chemical composition and hindering microbial activity. This acidification not only reduces crop productivity but also undermines the soil’s long-term health. Moreover, the infiltration of acidic water into groundwater systems can contaminate drinking water sources, posing significant public health risks [9,10].
Regulatory agencies worldwide have recognized these threats and established strict guidelines to manage industrial wastewater discharge. These regulations typically set limits on parameters such as pH, chemical oxygen demand (COD), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), and heavy metal concentrations. For example, the European Union’s Water Framework Directive (WFD) and the United States’ Clean Water Act (CWA) both emphasize the protection of water bodies and the sustainable management of water resources. China’s Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard (GB 8978-1996) [11] mandates that effluent must be neutralized to achieve a pH between 6 and 9. The standard also limits aluminum concentrations to below 0.5 mg/L and sulfate levels to less than 200 mg/L.
Chemical neutralization, membrane-based processes, and other physicochemical techniques have been developed to manage acidic wastewater [12,13]. The benefits and limitations of each acidic wastewater treatment technology are summarized in Figure 2. Recent reviews have addressed broad aspects of acidic, metal-rich wastewaters; for instance, Juve et al. [14] reviewed electrodialysis for metal removal, and Du et al. [15] and Nguegang et al. [16] summarized sustainable treatment strategies for acid mine drainage. However, there remains a conspicuous gap, where few studies focus specifically on the acidic wastewater generated by electrode foil manufacturing, which combines ultra-low pH (pH < 3), high dissolved metal burdens (Al, Cu, Zn), elevated chloride/sulfate loads, and the dual challenge of both pollutant treatment and resource recovery. In this context, this review makes three novel contributions. Firstly, it defines this challenging industrial stream as a discrete treatment target. Secondly, it maps major technology families (neutralization/precipitation, ion adsorption/ion exchange, membrane separation, and coagulation/flocculation) into a single process train tailored to that stream. Thirdly, it adopts a resource recovery and circular economy framework, emphasizing acid/metal recovery, low-carbon design, digital process control, and techno-economic/environmental metrics. Furthermore, this review hopes to provide engineers and researchers with a sector-specific, system-level roadmap rather than technology-by-technology summaries alone.
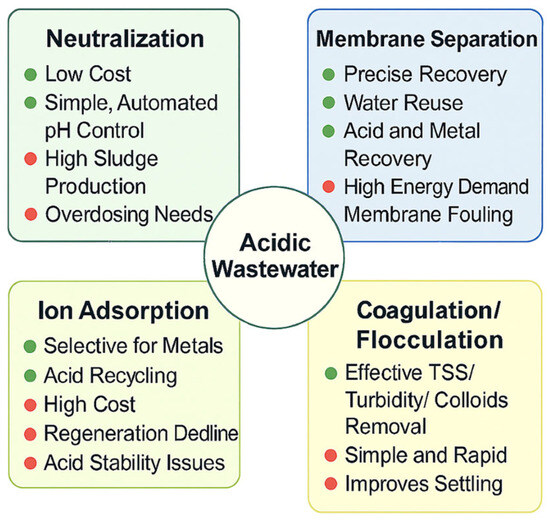
Figure 2.
Summary of acidic wastewater treatment technologies.
2. Advances and Applications of Neutralization Technology
The neutralization method, a fundamental technique for treating acidic wastewater from electrode foil production, functions by adjusting the wastewater’s pH through acid–base reactions while simultaneously removing pollutants [17,18]. In the electrode foil manufacturing process, stages such as etching and pickling generate wastewater that is rich in sulfuric and hydrochloric acids, as well as metal ions, such as aluminum and copper. Alkaline substances (e.g., sodium hydroxide, lime milk, or carbide slag) are added to the wastewater, causing hydrogen ions (H+) to combine with hydroxide ions (OH−) to form water. Concurrently, metal ions (e.g., Al3+, Cu2+) interact with hydroxide ions to precipitate as metal hydroxides (e.g., Al(OH)3, Cu(OH)2) [19]. This dual process effectively neutralizes the pH and removes metal pollutants from the wastewater. The reaction can be represented as follows:
H2SO4 + Ca(OH)2→CaSO4 + 2H2O
HCl + NaOH→NaCl + H2O
Al3+ + 3OH−→Al(OH)3 ↓
Cu2+ + 2OH−→Cu(OH)2 ↓
The neutralization–precipitation process for acidic wastewaters is fundamentally governed by pH-driven hydrolysis of dissolved metal ions and precipitation of hydroxides, as well as concomitant acid–base neutralization. In practice, the target pH range depends on the predominant metal species and their hydrolysis behavior. For example, in the treatment of acid mine drainage (AMD) with dominant Fe3+ and Mn2+ species, the pH must typically be raised to about 7–9 for complete precipitation of Fe hydroxides and Mn hydroxides [20]. Similarly, for Al3+-rich systems, the precipitation pH of Al(OH)3 is effective above 6.5–7 [21]. In high-acid, multi-metal systems similar to electrode foil wastewater, operational pH setpoints are often in the range of 5–9, frequently with a two-stage approach (e.g., pH 4.5 first, then pH 7.0), to optimize sulfate removal and metal hydroxide precipitation. Regarding alkaline reagents, conventional neutralizers include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), lime milk (Ca(OH)2 suspension), and quicklime (CaO), which reacts to form Ca(OH)2 in situ. Industrial by-products such as steel slag and carbide slag (CaC2 residual) have also been evaluated as low-cost alternatives [22,23]. For instance, NaOH exhibited a rapid pH rise (from 2.16 to 8.53) and high metal removal rates (86.7–99.9%) in an AMD study [20]. However, while NaOH provides high reactivity, it is more costly and may increase effluent alkalinity/hardness. And lime-based reagents are cheaper but produce more sludge and require longer reaction times [23]. After chemical precipitation, solid–liquid separation is a critical step to remove the generated hydroxide or sulfate precipitates and ensure effluent clarity. Common separation methods include gravity clarification and sedimentation, followed by sludge thickening and dewatering (e.g., plate-frame filtering, belt filtering, centrifugation). In more demanding streams (colloids with high ionic strength), flocculation aids (e.g., polymers) are often applied to enhance settling. It should be noted that in the context of electrode foil acidic wastewater, the high ionic strength and fine colloidal precipitates impede the settling rate and increase sludge volume. Therefore, a combination of coagulation–flocculation prior to neutralization or the use of enhanced separation (e.g., lamella clarifier, dissolved air flotation) may be advisable [24].
To summarize, the neutralization method should be described and designed by clearly specifying the following parameters: The first parameters are the initial and target pH values. The second parameters are the selected alkaline reagent (with cost, reactivity, by-product and sludge implications). The third parameter is a solid–liquid separation strategy suited to the precipitates and wastewater matrix. For instance, an electronic materials factory implemented a “two-stage neutralization + flocculation precipitation” approach to treat sulfuric acid-containing wastewater (initial pH was 2.5, Al3+ concentration was 500 mg/L). In the first stage, lime milk was added to raise the pH to 4.5, facilitating the precipitation of CaSO4. In the second stage, sodium hydroxide was introduced to elevate the pH to 7.0, promoting complete precipitation of Al3+. This treatment resulted in a final effluent pH of 6.8, an Al3+ concentration reduced to 0.8 mg/L, a sulfate removal rate exceeding 90%, and sludge production of 0.15 kg/m3 wastewater, which meets the requirements of the “Comprehensive Wastewater Discharge Standard” (GB 8978-1996) [11].
The neutralization method offers significant economic and operational advantages in wastewater treatment, making it a highly valuable solution. Economically, neutralizing agents, including lime and carbide slag, reduce treatment expenses to approximately 0.29–0.73 USD per ton, making this method economically viable for large-scale applications. Technically, neutralization processes benefit from automated pH control systems, which enhance precision and reliability. These systems employ real-time sensors and adaptive dosing algorithms to dynamically adjust reagent inputs in response to variations in wastewater flow and contaminant levels, optimizing treatment stability and efficiency. This method is highly suitable for treating high-concentration acidic wastewater (sulfuric acid concentration ≤ 5%) and complex systems containing multiple metal ions. Despite its advantages, the inherent limitations of the neutralization method constrain its large-scale implementation. First, the process produces substantial sludge yields (5–10% of the treated wastewater volume), which is primarily composed of metal hydroxides, escalating both dewatering expenses and disposal complexities. Second, in the treatment of highly acidic wastewater, the consumption of alkaline reagents often exceeds 1.2 to 1.5 times the theoretical stoichiometric requirement. Such overdosing results in both unnecessary chemical consumption and elevated effluent hardness, which collectively increase operational costs while significantly hindering water recycling.
To overcome current limitations, the advancements of neutralization technology focus on optimized process control, innovative material development, and strategic technology integration. Regarding process optimization, machine learning-based dynamic dosing models enable precise neutralizer demand prediction through real-time monitoring of critical parameters such as pH and conductivity, achieving intelligent dosing control. When combined with a ‘neutralization–precipitation–recycling’ system, such as the thermal conversion of Al(OH)3 sludge into valuable α-Al2O3, this approach reduces reagent consumption by 15–20% and promotes the valorization of solid waste, thereby significantly improving the economic viability of the process. The development of advanced neutralization materials presents a promising approach for cost reduction and waste minimization in wastewater treatment. Li et al. proposed an Improved Model-Free Adaptive Predictive Control (IMFAPC) algorithm. By integrating a mechanistic model with generalized predictive control, this method provides more accurate input constraints, thereby improving the control performance for delayed systems without accumulating errors (Figure 3) [25]. While conventional lime-based neutralizers remain costly and generate excessive sludge, industrial by-products such as steel slag and red mud offer viable alternatives due to their high alkaline content [26]. Furthermore, engineered slow-release materials (e.g., CaCO3-coated microspheres) demonstrate enhanced performance by extending reaction duration and improving neutralization efficiency, thereby offering additional economic benefits. Technological innovation is crucial for enhancing wastewater treatment efficiency. Integrated neutralization–ion exchange systems demonstrate dual efficacy in concurrent acidity neutralization and heavy metal removal, significantly reducing pollutant loads for subsequent treatment stages. The hybrid neutralization–electrochemical process offers additional advantages through electrolytically enhanced metal recovery and acid regeneration [27]. For instance, during electrolytic treatment of aluminum-containing waste acid, aluminum ions are reduced cathodically to metallic aluminum, thus enabling efficient resource recovery. The combined approach not only elevates resource utilization compared to conventional methods but also establishes a closed-loop recycling pathway for acidic wastes. Industry implementation has also validated these benefits, as evidenced by an electrode foil manufacturer that integrated ‘salting-out + membrane separation’ techniques to recover sulfuric acid and separate metal salts, achieving a 30% reduction in treatment costs.
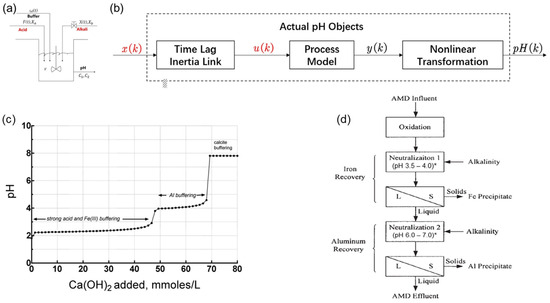
Figure 3.
(a) pH neutralization reaction schematic. (b) Object structure diagram. u(k)—output of time lag inertia link. [25]. (c) pH curve for lime precipitation removal of Fe and Al ions in acidic wastewater [28]. (d) Flow sheet of precipitation removal of Fe and Al ions in acidic wastewater [29], * pH range determined by Fe and Al precipitation processes presented in subsequent section.
The key operating conditions and other information regarding neutralization technology are summarized in Table 1. In summary, neutralization remains an essential method for treating electrode foil wastewater, but challenges such as sludge management and reagent efficiency persist. Future efforts should focus on optimizing intelligent control systems, resource recovery, and multi-technology synergies. Research should consider the development of low-carbon processes and comprehensive lifecycle cost analyses to promote sustainable wastewater treatment in the electronic materials industry and support green manufacturing initiatives.

Table 1.
Neutralization technology—operating conditions and performance for acidic electrode foil wastewater.
3. Recent Progress in Ionic Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
Ion adsorption technology effectively separates contaminants in acidic wastewater from electrode foil production through the physical and chemical interactions between the surface active sites of adsorbents and target ions (e.g., Al3+ and H+). The interaction mechanisms include ion exchange, coordination complexation, and electrostatic attraction [30,31,32,33]. Typical adsorbents contain sulfonic cation exchange resins, modified activated carbon, and metal–organic frameworks (MOFs). A general schematic of the ion exchange reaction with a strong acid cation exchange resin can be expressed as [34,35]
where R represents the resin structure. Equally, coordination binding may proceed as
where L is a functional ligand (e.g., amine, phosphonate). The adsorption equilibrium may be described by the Langmuir isotherm:
Or by the Freundlich isotherm:
Taking the 001 × 7-type strongly acidic cation exchange resin as an example, it demonstrates remarkable selectivity for H+ ions at pH = 1.5, facilitating an 85% recovery rate of sulfuric acid while achieving a removal efficiency of over 99% for Al3+ with an initial concentration of 1500 mg/L [36]. This application translates into substantial annual cost savings of up to USD 0.45 million for enterprises. The modified activated carbon (Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2) is used in combination with magnetic separation and electrolytic regeneration, enabling the concurrent recovery of Al3+ (95 mg/g) and Cu2+ (28 mg/g). This process ensures that recovered metals exhibit purity exceeding 99% while achieving a 90% reduction in hazardous waste generation. Furthermore, phospho-functionalized MIL-101(Al), MOFs, characterized by a 3.4 nm pore size and unsaturated metal sites, maintain an adsorption capacity of 195 mg/g for Al3+ even in the presence of 50 g/L Cl−. These MOFs achieve a selectivity coefficient of 16.3 (Al3+/Fe3+) and exhibit a regeneration efficiency exceeding 93%, significantly outperforming conventional neutralization methods [37].
However, the technology confronts several bottlenecks, including the high cost of adsorbents (MOF synthesis at USD 200/kg), the decline in regeneration performance (a 12% decrease in activated carbon capacity after 10 cycles), and insufficient tolerance to strong acidity (resin swelling rates exceeding 30%). To overcome these challenges, future research should concentrate on developing low-cost, acid-resistant materials such as covalent triazine frameworks (CTFs) and ion-imprinted polymers [38,39,40,41,42,43,44]. Gonsalves et al. synthesized low-cost, high-performance CTFs exhibiting an outstanding capacity for the adsorption of Cr (VI) at acidic pH. The adsorbent exhibits excellent reusability, and the adsorption mechanism is dominated by electrostatic attraction, ion exchange, and reduction mediated by nitrogen-rich sites (Figure 4a) [45]. Cheng et al. reported a cylindrical NaY zeolite adsorbent that demonstrated an effective ability to remove metal ions and water-soluble proteins from wastewater (Figure 4b) [46]. Furthermore, the integration of intelligent process control, leveraging Internet of Things (IoT) for the real-time adjustment of adsorption parameters, and the adoption of environmentally friendly regeneration technologies like supercritical CO2 desorption are essential [47,48,49]. The synergistic application of adsorption with electrochemical processes, such as electrolytic recovery of metals and acid, and zero-discharge protocols, such as evaporative crystallization of concentrates, can also enhance resource utilization and economic benefits, thereby promoting the large-scale implementation of ion adsorption technology in wastewater treatment for the electrode foil industry.
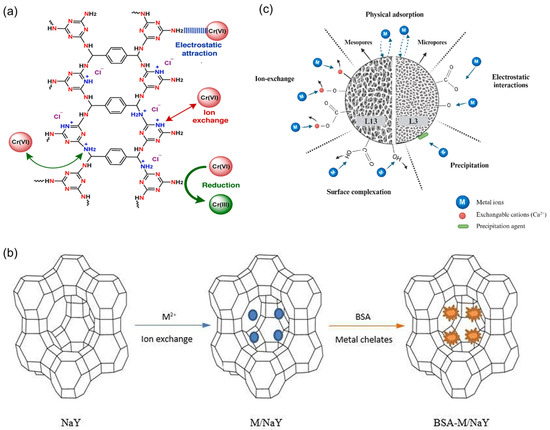
Figure 4.
(a) Schematic diagram of CTF and adsorption capacity [45]. (b) Schematic diagram of the removal of heavy metal ions and BSA by NaY zeolite [46]. (c) Schematic representation of the possible adsorption mechanisms [50].
Table 2 summarizes typical ion adsorption techniques. Moreover, Table 3 summarizes the key operating conditions and other information regarding ion adsorption techniques. The long-term performance of ion adsorption systems depends critically on the ability to regenerate the adsorbent and maintain stable capacity over many cycles. For instance, Raji et al. [34] noted that repeated acid–base regeneration or electrochemical desorption may lead to framework collapse or ligand leaching in MOFs, reducing capacity retention. Ion exchange resins in highly acidic media (e.g., pH ≤ 2) must resist H+-induced swelling or matrix degradation [21]. A recent review by Alsehli et al. [51] emphasizes that while many MOFs exhibit high initial capacities, their practical application is limited by aqueous hydrolytic instability and high costs. Table 2 includes regeneration cycle performance and residual capacity for each adsorbent type. In the design and operation of adsorption units for acid/metal wastewaters, key parameters include initial metal and acid concentration, the pH of the influent, ionic strength/competing ions (e.g., Cl−, SO42−), solid–liquid ratio, contact/retention time, flow regime (batch vs. column), and temperature. For example, Liu et al. [52] report the removal of Cu2+ by ion exchange resins at pH = 2 with 99% removal after 60 min in batch mode. High ionic strength (e.g., 50 g L−1 Cl−) may reduce adsorption capacity by ~20–30% owing to competition for active sites [53]. In the context of electrode foil acidic wastewater, the very low pH and presence of large concentrations of competing ions (e.g., Fe3+, Zn2+, Ni2+, and high SO42−) present additional challenges. These include the rapid saturation of adsorbent, increased regeneration frequency, and the need for higher adsorbent mass or multi-stage adsorption. Therefore, the cost analysis must consider adsorbent replacement, regeneration chemistry/energy, and the disposal of the spent adsorbent.

Table 2.
Comparison of representative adsorbents for ion adsorption in acidic/high-metal-load wastewaters.

Table 3.
Operating conditions of ionic adsorption technologies.
4. Membrane Separation Technology
4.1. Principles and Classification of Membrane Separation Technology
Membrane separation technology undergoes a physical process that leverages the selective permeability of semi-permeable membranes to separate specific components from wastewater. Driven by external forces such as pressure, concentration, or potential differences, membrane separation technology allows certain components to permeate the membrane while retaining others, thus facilitating effective separation and resource recovery [56,57,58]. Membrane separation technologies are classified into five types based on pore size, material properties, and separation objectives, with each type tailored to specific tasks and offering distinct advantages for various industrial applications [59,60].
Microfiltration (MF): MF primarily relies on physical sieving to remove suspended particles, colloids, and microorganisms (e.g., bacteria) from wastewater, with a typical pore size range of 0.1–10 μm [61]. MF typically functions under low pressures of 0.1 to 0.5 MPa, making it particularly effective as a pretreatment for large-molecular-weight pollutants, such as aluminum powder and aluminum oxide particles, in electrode foil wastewater. Through the pretreatment process, MF significantly reduces the risk of fouling in downstream membrane systems. For instance, MF membranes made from polypropylene (PP) or polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibit stable performance, maintaining a consistent flux of 50–100 L/(m2·h), even under highly acidic conditions (pH 1–3), while achieving >95% removal of suspended solids.
Ultrafiltration (UF): UF operates through a synergy of screening and adsorption mechanisms, efficiently removing colloids, macromolecular organics, and certain viruses, with a pore size range of 0.001–0.1 μm [62]. UF is commonly employed to remove colloidal Al(OH)3 and aluminum–organic acid complexes in the treatment of electrode foil wastewater. Ceramic UF membranes, particularly those composed of α-Al2O3 or ZrO2, maintain full functionality in highly acidic environments (pH = 1–14) and high temperatures up to 80 °C. Such metrics enable long-term operational stability in wastewater containing sulfuric acid concentrations of up to 15% while sustaining a consistent permeate flux of 60–80 L·m−2·h−1 and achieving aluminum ion rejection rates exceeding 85%, showcasing their superior treatment performance.
Nanofiltration (NF): NF membranes have a pore size range of 1–10 nm, exhibit charge characteristics, and selectively retain divalent and multivalent ions (e.g., SO42−, Al3+) while allowing monovalent ions (e.g., Cl−, Na+) to permeate [63,64]. The separation mechanism relies on a combination of the sieving effect and Donnan repulsion. For example, acid-resistant NF membranes, such as sulfonated polyether sulfone membranes, achieve rejection rates exceeding 95% for SO42− and 98% for Al3+ at pH = 2.5 and an operating pressure of 1.5 MPa, demonstrating dual functionality in concentrating sulfuric acid and removing metal ions.
Reverse osmosis (RO): RO membranes possess an ultra-dense structure featuring pores smaller than 0.1 nm and demonstrate nearly complete rejection of dissolved salts and organic compounds from wastewater [65,66]. The separation process operates under pressures of 2–8 MPa, forcing water molecules through the dense membrane while retaining solutes. In the deep desalination treatment of electrode foil wastewater, polyamide composite membranes (e.g., SW30HR model) exhibit exceptional performance. The conductivity of the treated effluent can be reduced to below 100 μS/cm, while sulfate ion removal exceeds 99.5%. This high-efficiency treatment makes RO membranes particularly well-suited for freshwater recovery from high-salinity wastewater and for concentrating acidic solutions.
Electrodialysis (ED): On the basis of the selective permeation characteristics of ion exchange membranes, ED separates charged ions under the action of a direct-current electric field. Cation exchange membranes (CEMs) allow the passage of cations (e.g., H+, Al3+), while anion exchange membranes (AEM) permit the migration of anions (e.g., Cl−, SO42−) [67,68]. Homogeneous ion exchange membranes, such as AMV/CMV series, demonstrate high selectivity for HCl recovery, achieving a H+ migration efficiency greater than 90% and Cl− recovery rates exceeding 75%, while simultaneously reducing the concentration of residual aluminum ions to below 50 mg/L.
4.2. Typical Application Cases
The wastewater generated during electrode foil production exhibits significant physicochemical complexity, characterized by strong acidity (pH 1–3), high salinity (SO42−: 10–30 g/L; Al3+: 500–2000 mg/L), and suspended particulate matter. A multi-stage membrane separation integrated process has been developed, enabling the effective separation and recovery of hydrogen ions, metal cations, and water resources through precise control of molecular weight cutoff gradients. Three representative engineering application cases are listed based on the author’s investigation.
- Case Study 1: NF-RO Combined Process
The electronic material factory produces 50,000 tons of electrode foil annually, generating wastewater with 15% sulfuric acid (H2SO4), 1200 mg/L aluminum ions (Al3+), and 25 g/L sulfate ions (SO42−). The conventional lime neutralization method has notable drawbacks, such as generating sludge that accounts for up to 15% of the wastewater volume and failing to recover sulfuric acid. An integrated process combining pretreatment with NF and RO, advancing both wastewater treatment and resource recovery, was used to overcome this. During pretreatment, a PVDF MF membrane with a 0.2 μm pore size, operating at 0.3 MPa and a stable flux of 80 L/(m2·h), effectively reduced suspended solids from 500 mg/L to below 10 mg/L and extended the membrane fouling cycle to 30 days. Then, NaOH was added to adjust the pH from 1.8 to 2.5, preventing colloid formation due to Al3+ hydrolysis, which could clog the NF membrane, and optimizing the solution for subsequent ion separation. In the NF concentration phase, a DL-2540 acid-resistant NF membrane (200 Da molecular weight cutoff) was selected for concentration. Under the conditions 1.5 MPa, 25 °C, and pH = 2.5, the membrane demonstrated exceptional rejection performance, achieving a sulfate (SO42−) retention rate exceeding 95% and concentrating the solution to 45 g/L. Meanwhile, the aluminum ion (Al3+) rejection rate reached 98%, resulting in a produced water Al3+ concentration of less than 20 mg/L. The concentrated solution accounted for 30% of the raw water volume, with sulfuric acid concentration rising to 18%, enabling direct reuse in the pickling process and forming an internal resource cycle. In the RO stage, an SW30HR polyamide composite membrane was utilized for deep desalination at an operating pressure of 4.0 MPa. The system produces a water conductivity below 100 μS/cm, meeting the industrial circulating cooling water quality standard (GB/T 50050-2017 [69]). At last, RO concentrate, containing 5 g/L SO42− and 50 mg/L Al3+, was recycled into the NF system for secondary treatment, forming a closed-loop process [70,71].
This process, through a combination of techniques, has yielded substantial environmental and economic benefits. Sulfuric acid recovery reaches 85%, with an annual recovery of 3600 tons, saving USD 0.8 million in costs. The total removal rate of Al3+ exceeds 99.5%, with effluent concentrations below 0.5 mg/L, surpassing the Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard (GB 8978-1996 [11]). Water treatment costs per ton decreased from 1.6 USD to 1 USD, reducing annual operational costs by USD 0.3 million. Sludge production decreased by 70% (from 15% to 4.5%), and hazardous waste disposal costs were cut by 80%. This process offers a resource recovery solution for high-salinity industrial wastewater treatment, demonstrating significant engineering application potential.
- Case Study 2: ED-UF Process for Synergistic Recovery of Hydrochloric Acid and Aluminum Resources
Industrial wastewater from electrode foil enterprises contains 8% hydrochloric acid (HCl), 800 mg/L Al3+, and trace organic matter (chemical oxygen demand, COD, of 200 mg/L). Conventional distillation methods require substantial energy input (2.5 tons steam per ton wastewater) while failing to recover valuable metal resources, leading to metal resource waste and an increased sludge disposal burden. An integrated process route involving UF pretreatment, ED for acid regeneration, and aluminum resource recovery has been proposed to achieve effective treatment and resource utilization. UF pretreatment was conducted using Al2O3-ZrO2 composite ceramic UF membranes with a pore size of 50 nm. Operating at 0.4 MPa and a pH of 1.5, gel-like Al(OH)3 demonstrated 90% retention efficiency. This process reduced the Al3+ concentration from 800 mg/L to 80 mg/L and maintained a stable flux of 60 L/(m2 h). In the ED unit, a 200-pair homogeneous ion exchange membrane stack (AMV/CMV composite structure) was operated at 50 mA/cm2 and 120 V across an effective membrane area of 0.8 m2. By selectively permeating H+ through the cation membrane and directing Cl− migration through the anion membrane, a 12% HCl solution was regenerated in the concentration chamber with a recovery efficiency of 75%. And the Al3+ concentration in the dilution chamber decreased to below 50 mg/L with the pH elevated to 2.0. Aluminum resource recovery was achieved through precise pH control (adding NaOH to reach pH = 6.0), triggering the precipitation of Al3+ into Al(OH)3 crystals with a purity exceeding 98%. The dewatered sludge obtained through centrifugal separation (60% moisture content) was thermally converted to γ-alumina (γ-Al2O3) nanomaterials via calcination at 800 °C for 2 h. The resulting γ-Al2O3 exhibited specific surface areas exceeding 200 m2/g, making it suitable for use as a high-performance catalyst support [72,73].
The integrated process demonstrates exceptional recycling performance, achieving a 75% recovery rate for hydrochloric acid (1500 tons annually) and 92% aluminum recovery efficiency (420 tons of γ-Al2O3 annually). A significant reduction in energy demand has been realized compared to conventional distillation methods, with energy consumption per ton of water treatment decreased from 30 kWh to 12 kWh, yielding annual energy savings of 5.4 million kWh. Economic assessments reveal an annual resource recovery revenue of CNY 8.6 million and an investment payback period of under three years. This method achieves deep pollutant removal and efficient aluminum resource recycling, offering a new perspective for chemical wastewater treatment.
- Case Study 3: Membrane Distillation–Crystallization (MDCr) Treatment of Concentrated Sulfanilic Acid Wastewater
Industrial wastewater containing 20% sulfuric acid (H2SO4), 200 mg/L ferric ions (Fe3+), and trace heavy metals such as 50 mg/L cupric ions (Cu2+) poses significant treatment challenges. Traditional neutralization methods are inefficient and generate hazardous sludge. Combining vacuum membrane distillation (VMD) with aluminum sulfate crystallization has proven to be an effective solution for wastewater treatment and resource recovery. The VMD step employs a hydrophobic PTFE membrane (0.22 μm pore size) operated at 60 °C and a vacuum of −90 kPa on the permeate side. Water vapor passes through the membrane and condenses, achieving 80% moisture recovery while concentrating sulfuric acid to 40% with a 90% recovery rate. The concentrated solution is then diluted to 15% H2SO4, and Al(OH)3 powder is added at a molar ratio of 1:1.2 (Al(OH)3:H2SO4). After stirring at 60 °C for 2 h, Al2(SO4)3 crystals with >98% purity are obtained through centrifugation These high-purity crystals then serve as raw materials for water purification agents, producing 1800 tons annually and generating a revenue of USD 0.8 million. Following neutralization of the residual solution to pH 8.0, Fe3+ and Cu2+ form hydroxide precipitates, and pressure filtration reduces the sludge moisture content to 55% with heavy metal leaching concentrations <0.1%, which meets the classification of hazardous waste [74,75].
Compared to traditional neutralization, this process reduces sludge production by 95%, cutting hazardous waste disposal costs by USD 0.2 million annually. It efficiently recycles sulfuric acid and aluminum while safely handling heavy metals, offering a sustainable solution for wastewater treatment.
4.3. Advantages and Limitations of Membrane Separation Technology
Membrane separation technology has revolutionized wastewater treatment by achieving high-precision separation of acid, metal, and water phases, and excellent resource recovery efficiency is achieved, with sulfuric acid retention consistently exceeding 75% and metal recovery rates surpassing 90%. Additionally, resource utilization is improved by more than 50% compared to conventional chemical precipitation methods. Through elimination of lime neutralization and flocculation sedimentation processes, this technology reduces sludge production by 60–80% and lowers the cost of hazardous waste treatment from 29 to 6 USD per ton (case study 1), significantly cutting both environmental risks and operating expenses. Acid-resistant membranes such as PTFE and ceramic membranes demonstrate robust performance in extreme conditions, maintaining stable operation in highly acidic (pH = 1–3) and high-temperature (80 °C) environments for 2–3 years. Wu et al. proposed a novel strategy for simultaneous desalination and selective recovery of molecular resources, integrating a supported liquid membrane (SLM) with molecular selectivity into asymmetric flow-electrode capacitive deionization. The electrochemical membrane system exhibited stable separation performance and long-term stability, effectively removing salts and recovering phenol (sodium phenol) from wastewater (Figure 5a) [76]. Its modular design provides the system with high flexibility, enabling the flexible configuration of combination processes such as NF–RO and ED–UF (Figure 5b) [77,78,79,80,81,82]. Chen et al. developed an undivided electrolytic cell coupled with MF for P recovery with high-flux and low energy consumption (Figure 5c) [83]. Through PLC-controlled automation, real-time monitoring of critical parameters (pH, pressure, conductivity) reduces manual intervention by 70% while significantly enhancing operational efficiency [84].
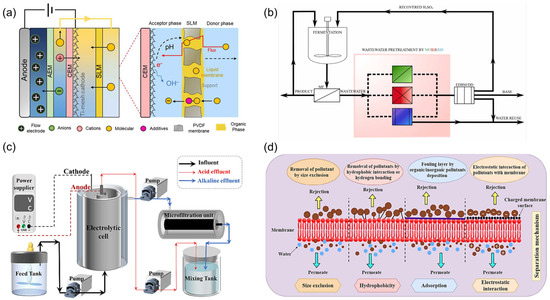
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of (a) improved FCDI system integrated with SLM [76]. (b) Process design and the experimental set-up for three technologies tested in this research (in the pink box). MF—microfiltration; NF—nanofiltration; IER—ion exchange resin; ED—electrodialysis with standard AEM and mCEM [82]. (c) Combined electrolytic cell–microfiltration system for P recovery [83]. (d) Membrane filtration and its separation mechanism [85].
However, membrane fouling remains a critical barrier to large-scale technological implementation. Colloidal particles, metal hydroxide precipitates, and dissolved organic matter in wastewater are prone to adsorption and deposition within membrane pores, causing a 5–10% weekly flux decline. Therefore, chemical cleaning cycles are necessary once or twice a week using citric acid or sodium hydroxide solutions, and membrane replacement costs account for 30–50% of operational expenses. Energy consumption is also a concern, as high-pressure processes such as RO and ED consume 3–8 kWh per ton of water, which is 30–50% higher than traditional treatment methods. Additionally, the high concentration of sulfuric acid (15–40%) and salts (TDS > 100 g/L) in the membrane concentrate necessitate a matching evaporation crystallization or neutralization treatment unit, thereby increasing process complexity. Wastewater compositional fluctuations, such as changes in aluminum ion concentration, can rapidly attenuate the flux of NF membranes. Addressing these multidimensional challenges requires integrated solutions combining advanced membrane materials with smart process control systems capable of real-time monitoring and adaptive response. The operation conditions for membrane separation and comparisons with the aforementioned neutralization and ion adsorption technologies are summarized in Table 4 and Table 5, respectively.

Table 4.
Operating conditions of membrane separation technology.

Table 5.
Comparison of neutralization, ionic adsorption/ion exchange, and membrane separation technologies.
5. Coagulation/Flocculation
In addition to the treatment technologies discussed above, conventional coagulation/flocculation remains a widely applied physicochemical unit process in industrial wastewater treatment. Coagulation/flocculation typically involves the addition of coagulants (e.g., aluminum- or iron-based salts) to neutralize colloidal charges and promote the formation of flocs, which then settle or float out of the liquid phase [87,88].
Mechanistically, the coagulant induces destabilization of suspended and colloidal particles. The flocculants (often polymers) then bridge the destabilized particles into larger aggregates, which can be removed by sedimentation or flotation. The process is effective for turbidity, total suspended solids (TSS), and some metal-colloid removal [21]. However, when applied to the highly challenging wastewater generated in electrode foil manufacturing, which is characterized by very low pH (often <3), high dissolved metal (Ni, Cu, Zn, Fe) concentrations, and elevated ionic strength, several limitations of coagulation/flocculation become evident.
Firstly, the extreme acidity is detrimental to conventional coagulant hydrolysis and floc formation. The pH properties of the solution itself will limit the efficient realization of the coagulation/flocculation process. Secondly, high metal loads and precipitation dynamics may cause rapid consumption of coagulants and produce large volumes of sludge. This may lead to the extensive use of flocculants and the generation of large amounts of sludge, which will increase the subsequent treatment load and economic costs. The residual soluble metal fraction (including complexed or colloidal forms) may not be fully captured by coagulation/flocculation, thereby limiting removal of dissolved-phase contaminants. Moreover, sludge disposal and downstream treatment (e.g., residual dissolved salts) remain challenging. For these reasons, coagulation/flocculation is most suited as a front-end or pretreatment step rather than a standalone deep-treatment route in this context.
6. Integrated and Multi-Stage Treatment Processes
Industrial wastewaters, such as those from electrode foil manufacturing, are always highly challenging to treat, which are characterized by very low pH, elevated dissolved heavy metal loads, high ionic strength, and complex speciation. It is increasingly recognized that a single treatment unit’s operation rarely suffices to meet the combined goals of effluent quality, resource recovery, and operational sustainability. Hybrid or multi-stage treatment processes are therefore adopted to harness the complementary strengths of different processes while mitigating their individual limitations [89].
A generic example of a treatment process for an acid-/metal-rich effluent might comprise the following sequence: The first process is the pretreatment/neutralization stage, in which the pH is raised and major metal hydroxides/salts are precipitated. Then the ionic strength is adjusted to remove bulk suspended solids and colloids. The second process is the intermediate removal/polishing stage, where adsorption, ion exchange, or selective sorption are applied to remove residual dissolved heavy metals and anions. Then, the deep separation/polishing stage is conducted and membrane processes (NF/RO/ED) are applied to remove dissolved salts/metals and enable water reuse or zero-liquid discharge. Lastly the concentration/resource recovery stage is processed, in which crystallization, MDCr, or electrochemical recovery are conducted to valorize metals and salts while minimizing waste.
Recent reviews on heavy metal/acid mine drainage treatment highlight that such processes enable higher removal efficiencies and resource recovery potential than conventional single-unit schemes [21,90]. For instance, Wang et al. [91] conducted a review of acid mine wastewater treatment and underscored hybrid systems as a major research trend. Similarly, Nguegang et al. [16] discussed sustainable AMD treatment via combined approaches, including neutralization, membrane, and crystallization units. It is worth noting that in the context of electrode foil wastewaters, the challenges to designing an effective scheme include (i) the extremely low initial pH requiring large neutralization dosing and producing high sludge volumes; (ii) high ionic strength/competing ions diminishing adsorption/ion exchange selectivity; (iii) membrane fouling and high energy demand in separation stages; and (iv) concentrate management and sludge or crystallized salt disposal or valorization. Addressing these challenges requires not only optimizing the operating conditions of each treatment stage but also coordinating their interfaces to ensure hydraulic, chemical, and material compatibility. Effective process integration should incorporate intermediate conditioning (e.g., pH and ionic strength adjustment), recovery and reuse of valuable by-products such as acids or metals, and minimization of sludge and concentrate volumes. Moreover, system-level optimization of energy use and operating costs is essential to achieve both treatment efficiency and economic sustainability.
7. Future Outlook
For neutralization technology, future development should focus on intelligent dosing, resource recovery, and sludge minimization. In particular, the adoption of real-time pH monitoring and model-predictive control helps to avoid reagent overdosing and optimize precipitation kinetics, thereby reducing sludge volume and chemical consumption. The valorization of the resulting metal hydroxide sludges (such as converting Al(OH)3 into α-Al2O3) can turn waste into value and support circular economy goals. Moreover, in highly acidic and high-salt environments (such as electrode foil wastewater), the cotreatment of sulfate-/chloride-rich streams demands hybridization of neutralization with ion exchange and membrane polishing in series. Recent reviews on acidic mine drainage treatment emphasize that neutralization alone may be insufficient for the deep removal of dissolved metals and high-salinity systems [88,92]. Therefore, future work should target low-cost alkaline reagents (industrial by-products, slag) with high alkalinity and minimal secondary pollution, improved solid–liquid separation (lamella clarifiers, DAF, automated dewatering), and an integrated process design that links front-end neutralization with downstream adsorption and membrane reuse loops.
For ionic adsorption technology, the future research path involves the development of acid-resistant, high-selectivity sorbents, scalable regeneration, and lifecycle cost modeling. As discussed in the main text, while many adsorbents achieve high capacities under mild conditions, performance tends to degrade under very low pH, high ionic strength, and competing ion loads (common in electrode foil waste). According to a comprehensive review of heavy metal removal methods, greater attention should be placed on real-world wastewaters and multiple-ion systems [21]. To address this, novel materials such as CTFs, ion-imprinted polymers (IIPs), and functionalized MOFs with tailored binding sites and structural stability under extreme conditions are promising. Parallel to material development, regeneration strategies (electro-desorption, supercritical CO2, low-pH/low-energy desorption) must be optimized for cyclic durability and metal recovery. Moreover, combining adsorption with downstream membrane separation or electrochemical recovery enables a comprehensive resource recovery methodology rather than mere waste removal. Finally, techno-economic and environmental lifecycle assessments (including carbon footprint, adsorbent replacement rate, regeneration energy) must become standard practice. Adsorption remains highly promising but research must shift from lab-scale, single-ion tests to realistic mixed-ion, high-ionic-strength industrial streams.
The development of membrane separation technology is focusing on several critical advancements. In materials science, new anti-fouling membrane materials such as covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are being developed to enhance membrane durability and lifespan [93,94,95]. At the process-coupling level, integrated processes like bipolar membrane electrodialysis (BMED) and membrane distillation (MD) create synergistic systems capable of concentrate solution treatment and resource recovery [86,96,97,98]. In intelligent control, IoT technology and machine learning algorithms enable real-time performance monitoring and adaptive process optimization, reducing energy consumption and boosting system efficiency [99]. Additionally, promoting high-value sludge utilization and low-carbon processes, such as converting sludge into building materials or soil amendments and integrating photovoltaic power generation, is crucial for achieving “zero emissions” and “resource recycling” [100,101,102,103,104]. Driven by the dual forces of stringent environmental standards and the deepening circular economy policies in the electrode foil industry, membrane separation technology, with its triple advantages of efficient separation, resource recovery, and environmental sustainability, is poised to become the dominant solution for treating high-acid and high-salt wastewater [105,106]. In future, breakthroughs in materials, process coupling, and intelligent control will accelerate the transition of the electrode foil industry toward greener and more sustainable practices [107,108,109,110,111,112].
8. Conclusions
This review analyzes the technological landscape of acidic wastewater treatment in the electrode foil industry, focusing on neutralization, ion adsorption, and membrane separation. Neutralization is cost-effective but generates significant sludge and recovers limited resources. Ion adsorption offers high recovery but is hindered by high material costs and regeneration limitations. Membrane separation excels in resource recovery and precision separation but faces challenges from fouling and energy intensity. This review evaluates the principles, applications, and limitations of these technologies, proposing directions for future optimization. Advancements should focus on material innovation, process improvements, and smart monitoring systems to achieve efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable wastewater treatment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.W. and Y.W.; methodology, L.W. and B.Q.; software, F.M. and Y.H.; validation, B.Q., F.M. and X.W.; formal analysis, L.W. and J.B.; investigation, G.W., B.Q. and F.M.; resources, Y.H. and X.W.; data curation, J.B. and J.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, G.W. and L.W.; writing—review and editing, J.Z. and Y.W.; visualization, F.M. and X.W.; supervision, J.Z. and Y.W.; project administration, Y.H. and Y.W.; funding acquisition, J.Z. and Y.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the financial support from the Xinjiang Key Research and Development Project [No. 2022B01022-1].
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Bing Qin, Fanbin Meng were employed by the company Sinopec Research Institute of Petroleum Processing Co., Ltd. Authors Yonghu He, Xin Wang, Jing Bai were employed by the company Shihezi Joinchin Electrode Foil Co., Ltd. Author Jingpeng Zhang were employed by the company Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Yuzer, B.; Aydin, M.I.; Yildiz, H.; Hasançebi, B.; Selcuk, H.; Kadmi, Y. Optimal performance of electrodialysis process for the recovery of acid wastes in wastewater: Practicing circular economy in aluminum finishing industry. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 434, 134755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.O.R.e.; Carpanez, T.G.; Dos Santos, C.R.; Casella, G.S.; Moreira, V.R.; de Paula, E.C.; Amaral, M.C.S. Biohydrogen production from wastewater: Production technologies, environmental and economic aspects. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos, A.S.; Landázuri, A.C. Impact of Water Circularity on Climate Change: Removal of Fats, Oils and Grease (FOG) from Water Using Green and Simple Extraction Methods. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnnok, B.; Laosiripojana, N. Integrative process for rubberwood waste digestibility improvement and levulinic acid production by hydrothermal pretreatment with acid wastewater conversion process. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.; Liu, T.-J.; Kang, L.-L.; Wang, Y.-T.; Li, J.-G.; Wang, F.-P.; Yu, Q.; Wang, X.-M.; Liu, H.; Guo, H.-W.; et al. A review of metallurgical slag for efficient wastewater treatment: Pretreatment, performance and mechanism. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 380, 135076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh, H.; Saththasivam, J.; McKay, G.; Parthasarathy, P. Adsorbent Minimization for Removal of Ibuprofen from Water in a Two-Stage Batch Process. Processes 2022, 10, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, H.; Motiee, H.; McBean, E. Forecasting impacts of climate change on changes of municipal wastewater production in wastewater reuse projects. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 329, 129790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodaglio, A.G. Biorefinery of Sewage Sludge: Overview of Possible Value-Added Products and Applicable Process Technologies. Water 2023, 15, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba-Lobo, A.; García-González, B.; Guerrero, J.L.; Bolívar, J.P. Sedimentary environmental quality of a biosphere reserve estuary in southwestern Iberian Peninsula. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 201, 116225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Su, P.; Tang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Ma, T. A review of acid mine drainage: Formation mechanism, treatment technology, typical engineering cases and resource utilization. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 170, 1240–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 8978-1996; Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard. State Environmental Protection Administration: Beijing, China, 1996.
- Ouadah, M.; Chemlal, R.; Mameri, N. Improvement of ultrafiltration of olive mill wastewater via ultrasound coupling. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 21, 3103–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, V.; Chauhan, M.S.; Pal, S.L. Potential of sugarcane bagasse in remediation of heavy metals: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juve, J.-M.A.; Christensen, F.M.S.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Z. Electrodialysis for metal removal and recovery: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Ho, H.-J.; Iizuka, A. A critical review of current treatment methods of acid mine drainage with an assessment of associated CO2 emissions toward carbon neutrality. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 77, 108347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguegang, B.; Ambushe, A.A. Sustainable acid mine drainage treatment: A comprehensive review of passive, combined, and emerging technologies. Environ. Eng. Res. 2025, 30, 156–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Xu, J.; Fu, J.; Zheng, G.; Zhou, L. Modified chemical mineralization-alkali neutralization technology: Mineralization behavior at high iron concentrations and its application in sulfur acid spent pickling solution. Water Res. 2022, 218, 118513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amudha, V.; Judes, J. Persuade of solar driven photo-Fenton process for the effective sludge reduction through chemical deflocculation. Desalination Water Treat. 2022, 246, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Qiu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Yang, W.; Chen, B.; Jiang, J.; Lin, Y. Chemical leaching−Flexible precipitation for sustainable recovery of fluoride from aluminum electrolysis multisource hazardous waste. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 500, 157138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhang, R.; Hu, M. Alkaline chemical neutralization to treat acid mine drainage with high concentrations of iron and manganese. Water 2024, 16, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, N.A.; Mohammed, R.H.; Lawal, D.U. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. Npj Clean Water 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Lu, C.; Quan, X.; Cao, D. Mechanism of acid mine drainage remediation with steel slag: A review. Acs Omega 2021, 6, 30205–30213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Tang, Y.; Cao, D.; Yang, M. Remediation of acid mine drainage (AMD) using steel slag: Mechanism of the alkalinity decayed process. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladimeji, T.; Oyedemi, M.; Emetere, M.; Agboola, O.; Adeoye, J.; Odunlami, O. Review on the impact of heavy metals from industrial wastewater effluent and removal technologies. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Tang, Z.; Luan, H.; Liu, Z.; Xu, B.; Wang, Z.; He, W. An Improved Method of Model-Free Adaptive Predictive Control: A Case of pH Neutralization in WWTP. Processes 2023, 11, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, A.; Parbhakar-Fox, A.; Meffre, S.; Cooke, D.R. Alkaline industrial wastes–Characteristics, environmental risks, and potential for mine waste management. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Wang, H.; Zhu, X.; Sun, Z. Review on electrochemical processes for the treatment of heavy metal complexes in wastewater: Performance, mechanism, application and improvement. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2025, 20, 100971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk Nordstrom, D. Geochemical Modeling of Iron and Aluminum Precipitation during Mixing and Neutralization of Acid Mine Drainage. Minerals 2020, 10, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Viadero, R.C., Jr.; Buzby, K.M. Recovery of iron and aluminum from acid mine drainage by selective precipitation. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2005, 22, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Mei, Y.; Yang, W.; Jiang, C.; Guo, H.; Feng, S.-P.; Tang, C.Y. Energy harvesting from acid mine drainage using a highly proton/ion-selective thin polyamide film. Water Res. 2024, 255, 121530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xue, C.; Lin, Y.; Lee, J.-F.; Yi, X.; Dang, Z. Efficient removal of heavy metals from acid mine drainage by ε-MnO2 adsorption. J. Clean Prod. 2024, 452, 141936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.M.; Yeo, Y.H.; Park, W.H. Facile preparation of tannin-coated waste silk fabric as an effective heavy metal adsorbent. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.-D.; Zhang, W.-Q.; Lv, H.-B.; Chen, Y.-T.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S.-H.; Du, L.; Zhao, Q.-H. Sulfate-functionalized Fe-based MOF for removal of Pb(Ⅱ) and NO3- in industrial wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, Z.; Karim, A.; Karam, A.; Khalloufi, S. Adsorption of heavy metals: Mechanisms, kinetics, and applications of various adsorbents in wastewater remediation—A review. Waste 2023, 1, 775–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, K.; Kumar, V.; Choudhary, S.; Mankotia, P.; Kumar, B.; Mishra, H.; Moulick, A.; Ekielski, A. A review of adsorbents for heavy metal decontamination: Growing approach to wastewater treatment. Materials 2021, 14, 4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xue, M.; Lv, R.; Fan, C.; Li, A. Adsorption mechanism of Ca2+, Mg2+, Fe3+, and Al3+ ions in phosphoric acid–nitric acid solution on 001× 7 and S957 resins. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 7234–7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fu, T.; Mao, Y. Metal–organic framework-based materials for adsorption and detection of uranium (VI) from aqueous solution. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 14430–14456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-H.; Wu, R.-M.; Chang, J.-S.; Juang, S.-Y.; Lee, D.-J. Manganese ferrite modified agricultural waste-derived biochars for copper ions adsorption. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 367, 128303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, U.; Sreedhar, I.; Singh, S.A.; Patel, C.M.; Anitha, K.L. Recent advances in heavy metal removal by chitosan based adsorbents. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, T.K. Agricultural Solid Wastes Based Adsorbent Materials in the Remediation of Heavy Metal Ions from Water and Wastewater by Adsorption: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtado, L.M.; Fuentes, D.P.; Ando, R.A.; Oliveira, P.V.; Siqueira Petri, D.F. Carboxymethyl cellulose/sugarcane bagasse/polydopamine adsorbents for efficient removal of Pb2+ ions from synthetic and undergraduate laboratory wastes. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 380, 134969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, M.; Liu, W.; Liu, L.; Huang, S.; He, Z.; Yin, Y.; Xiang, J. Effective fixation of Cu(II) and Cr(III) in solution by food waste biochar–Innovative and valuable treatment method for municipal solid waste. Fuel 2024, 361, 130679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Wang, X.-L.; An, Q.-D.; Xiao, Z.-Y.; Zhai, S.-R. Synergistic preparation of modified alginate aerogel with melamine/chitosan for efficiently selective adsorption of lead ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 256, 117564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.-D.; Wei, W.-M.; Li, H.; Shen, T.-Z.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S.-H.; Zhang, W.-Q.; Du, L.; Zhao, Q.-H. Metal-Organic framework derived vulcanized functional materials for ultra-efficient treatment of Hg(Ⅱ) ions in water. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 401, 124609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsalves, O.S.; Nemade, P.R. Ultrafast adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous effluents using covalent triazine frameworks. Chemosphere 2024, 351, 141246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.-H.; Sankaran, R.; Show, P.L.; Ooi, C.W.; Liu, B.-L.; Chai, W.S.; Chang, Y.-K. Removal of protein wastes by cylinder-shaped NaY zeolite adsorbents decorated with heavy metal wastes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, S.; Priya, A.K.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Hoang, T.K.A.; Sekar, K.; Chong, K.Y.; Khoo, K.S.; Ng, H.S.; Show, P.L. A critical and recent developments on adsorption technique for removal of heavy metals from wastewater-A review. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, Z.; Ebtehaj, I.; Bonakdari, H.; Khalloufi, S. Artificial intelligence-driven assessment of critical inputs for lead adsorption by agro-food wastes in wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2024, 368, 143801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Liu, X.; Xiang, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, D.; Peng, Z.; Fu, L. The design of high-efficient MOFs for selective Ag(I) capture: DFT calculations and practical applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro-Alves, L.; Yánez-Vilar, S.; González-Goméz, M.A.; Garcia-Acevedo, P.; Arnosa-Prieto, Á.; Pineiro-Redondo, Y.; Rivas, J. Understanding adsorption mechanisms and metal ion selectivity of superparamagnetic beads with mesoporous CMK-3 carbon and commercial activated carbon. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2024, 374, 113159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsehli, B.R. Toward sustainable environmental cleanup: Metal–organic frameworks in adsorption-A review. Desalination Water Treat. 2023, 316, 44–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Cui, Y.; Chen, N. Removal of copper ions from wastewater: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, H.; Devi, N.; Siwal, S.S.; Alsanie, W.F.; Thakur, M.K.; Thakur, V.K. Metal–organic framework-based materials for wastewater treatment: Superior adsorbent materials for the removal of hazardous pollutants. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 9004–9030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadehahmadi, F.; Eden, N.T.; Mahdavi, H.; Konstas, K.; Mardel, J.I.; Shaibani, M.; Banerjee, P.C.; Hill, M.R. Removal of metals from water using MOF-based composite adsorbents. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2023, 9, 1305–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Xie, J.; Quan, W.; Chen, Q.; Long, X.; Wang, A. Advances in the adsorption of heavy metal ions in water by UiO-66 composites. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1211989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebreslassie, G.; Desta, H.G.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, M.; Lin, B. Advanced membrane-based high-value metal recovery from wastewater. Water Res. 2024, 265, 122122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Qin, M. The Application of Cation Exchange Membranes in Electrochemical Systems for Ammonia Recovery from Wastewater. Membranes 2021, 11, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhantash, F.; Hegab, H.M.; Aljundi, I.H.; Hasan, S.W. Synergistic design of polylactic acid/functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes composite membrane for enhanced oil-water separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis-Perucho, P.; Aguado, D.; Ferrer, J.; Seco, A.; Robles, Á. A comprehensive review of the direct membrane filtration of municipal wastewater. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 35, 103732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterkaoui, A.; Eskikaya, O.; Keskinler, B.; Dizge, N.; Balakrishnan, D.; Hiremath, P.; Naik, N. Caustic recovery from caustic-containing polyethylene terephthalate (PET) washing wastewater generated during the recycling of plastic bottles. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tang, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, B.; Shen, Y.; Shi, W. Microfiltration pretreatment of polymer-flooding produced wastewater before desalination: Role of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in membrane fouling. Desalination 2022, 539, 115934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayegh, A.; Shylaja Prakash, N.; Pedersen, T.H.; Horn, H.; Saravia, F. Treatment of hydrothermal liquefaction wastewater with ultrafiltration and air stripping for oil and particle removal and ammonia recovery. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 44, 102427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.N.R.; Ang, W.L.; Teow, Y.H.; Mohammad, A.W.; Hilal, N. Nanofiltration membrane processes for water recycling, reuse and product recovery within various industries: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhen, H.; Jia, Y.; Xiao, W.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; Li, T.; He, G.; Jiang, X. Polyelectrolyte fabricated nanofiltration membrane with heterogeneously charged channels for high efficient cephalexin wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Sanders, K.T.; Childress, A.E. Reclaiming wastewater with increasing salinity for potable water reuse: Water recovery and energy consumption during reverse osmosis desalination. Desalination 2021, 520, 115316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, M.T.T.; Diep, B.Q.; Sano, H.; Nishimura, Y.; Boivin, S.; Kodamatani, H.; Takeuchi, H.; Sakti, S.C.W.; Fujioka, T. Membrane distillation for achieving high water recovery for potable water reuse. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, C.; Peng, S.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Z.; Lei, Z.; Wu, D. Selective ammonia recovery from wastewater by SDS-AC based microfiltration membrane flow electrode capacitor deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 359, 130555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, T.; Yan, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, L. A novel bio-flocculation combined with electrodialysis process: Efficient removal of pollutants and sustainable resource recovery from swine wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 304, 122330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50050-2017; Code for Design of Industrial Recirculating Cooling Water Treatment. China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Ricci, B.C.; Ferreira, C.D.; Aguiar, A.O.; Amaral, M.C. Integration of nanofiltration and reverse osmosis for metal separation and sulfuric acid recovery from gold mining effluent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 154, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, W.L.; Mohammad, A.W.; Ahmad, N.N.R.; Teow, Y.H. Role of Nanofiltration Process for Sustainability in Industries: Reuse, Recycle, and Resource Recovery. In Nanofiltration for Sustainability; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T. Recovery of hydrochloric acid from simulated chemosynthesis aluminum foils wastewater: An integration of diffusion dialysis and conventional electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 409, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrillo-Gonzalez, M.d.M.; Villen-Guzman, M.; Rodriguez-Maroto, J.M.; Paz-Garcia, J.M. Metal recovery from wastewater using electrodialysis separation. Metals 2023, 14, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creusen, R.; van Medevoort, J.; Roelands, M.; van Duivenbode, A.v.R.; Hanemaaijer, J.H.; van Leerdam, R. Integrated membrane distillation–crystallization: Process design and cost estimations for seawater treatment and fluxes of single salt solutions. Desalination 2013, 323, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.-Y.; Xu, Z.; Bai, A.-P.; Resina-Gallego, M.; Ji, Z.-G. Separation and recycling of concentrated heavy metal wastewater by tube membrane distillation integrated with crystallization. Membranes 2020, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Peng, S.; Wu, D. Simultaneous desalination and molecular resource recovery from wastewater using an electrical separation system integrated with a supporting liquid membrane. Water Res. 2023, 246, 120706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, G.; Liu, R.; Ji, Q.; Liu, H. Integration of concentration and electro-driven membrane system for effective water-saved acid recycling performance. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 191, 106885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Ren, L.-F.; Xia, L.; Zhong, C.; Shao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Van der Bruggen, B. Recovery of Fluoride-Rich and Silica-Rich Wastewaters as Valuable Resources: A Resource Capture Ultrafiltration–Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis-Based Closed-Loop Process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 16221–16229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapia-Quirós, P.; Montenegro-Landívar, M.F.; Reig, M.; Vecino, X.; Saurina, J.; Granados, M.; Cortina, J.L. Integration of Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis Technologies in Polyphenols Recovery Schemes from Winery and Olive Mill Wastes by Aqueous-Based Processing. Membranes 2022, 12, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Chen, Q.; Huang, X.; Yan, Z.; Lin, X.; Ye, W.; Arcadio, S.; Luis, P.; Bi, J.; Van der Bruggen, B.; et al. Integrated loose nanofiltration-electrodialysis process for sustainable resource extraction from high-salinity textile wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Chi, M.; Eygen, G.V.; Guan, K.; Matsuyama, H. Comprehensive review of nanofiltration membranes for efficient resource recovery from textile wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 506, 160132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knežević, K.; Saracevic, E.; Krampe, J.; Kreuzinger, N. Comparison of ion removal from waste fermentation effluent by nanofiltration, electrodialysis and ion exchange for a subsequent sulfuric acid recovery. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cheng, Z.; Yuan, W.; Song, W.; Zhou, Y.; Lei, Y.; Jiang, B. High-flux electrochemical phosphorus recovery in an undivided electrolytic cell coupled with microfiltration with low energy consumption. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Badireddy, A.R. Synergistic effect of alternating current-based electric and acoustic fields on flux recovery in crossflow microfiltration of synthetic wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 306, 122534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.I.; Chen, Z.; Elgarahy, A.M.; Farghali, M.; Mohamed, I.M.; Priya, A.; Hawash, H.B.; Yap, P.S. Membrane technology for energy saving: Principles, techniques, applications, challenges, and prospects. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2024, 5, 2400011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Bi, J.; Ji, Z.; Yuan, J.; Zhao, Y. Application of bipolar membrane electrodialysis for simultaneous recovery of high-value acid/alkali from saline wastewater: An in-depth review. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, M.S.; Teixeira, A.R.; Jorge, N.; Peres, J.A. Industrial wastewater treatment by coagulation–flocculation and advanced oxidation processes: A review. Water 2025, 17, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Kansha, Y. Comprehensive review of industrial wastewater treatment techniques. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 51064–51097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asheghmoalla, M.; Mehrvar, M. Integrated and hybrid processes for the treatment of actual wastewaters containing micropollutants: A review on recent advances. Processes 2024, 12, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, Y.G.; Safitri, H.; Khairurrijal, K.; Taher, T.; Arham, L.O.; Jasipto, A.; Danasla, M.A.; Fadhilah, R.; Army, E.K.; Hakim, H.Z. Recent advances in acid mine drainage treatment through hybrid technology: Comprehensive review of scientific literature. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2024, 21, 100945. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, J.; Biswas, A.; Fang, W.; Chen, L. Acid mine wastewater treatment: A scientometrics review. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 57, 104713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraz, U.; Li, Y.; Ahmad, I.; Iqbal, R.; Ditta, A. Remediation technologies for acid mine drainage: Recent trends and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 137089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Sun, J.; He, Y.; Wu, B.; Ge, L.; Pan, J. Ultrathin zwitterionic COF membranes from colloidal 2D-COF towards precise molecular sieving. Water Res. 2025, 274, 123073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liu, J.; Tao, H.; Meng, J.; Yang, J.; Shuai, Q.; Asakura, Y.; Huang, L.; Yamauchi, Y. Covalent Organic Framework Nanoarchitectonics: Recent Advances for Precious Metal Recovery. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2405399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Qin, Y.; Ni, C.; Liu, C.; Yan, H.; Zou, J.; Luo, S. Hydrazide-functionalized COFs exhibit ultra-high palladium adsorption capacity and excellent selectivity. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 494, 153027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Peng, K.; Yan, J.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Feng, H.; Yang, Z.; Wu, L.; Xu, T. Bipolar membrane-assisted reverse electrodialysis for high power density energy conversion via acid-base neutralization. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 647, 120288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.; Guo, L.; Ding, N.; Cui, H.; Lu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Liao, J.; Shen, J. Enhanced recovery of p-Aminophenol from high-salt wastewater via optimized bipolar membrane electrodialysis in a Water-Ethanol system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 360, 131038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Yan, H.; Ul Afsar, N.; Wang, H.; Yan, J.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T. Acid recovery from molybdenum metallurgical wastewater via selective electrodialysis and nanofiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 295, 121318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathvik, S.; Kumar, R.; Ulloa, N.; Shakor, P.; Ujwal, M.S.; Onyelowe, K.; Kumar, G.S.; Christo, M.S. Modelling the mechanical properties of concrete produced with polycarbonate waste ash by machine learning. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Jiao, F.; Liu, W.; Wang, D.; Chen, W.; Qin, W. Selective preparation of lithium carbonate from overhaul slag by high temperature sulfuric acid roasting–Water leaching. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 359, 120963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, H.; Safaeipour, N.; Othman, R.S.; Otadi, M.; Sheibani, R.; Kargaran, F.; Van Le, Q.; Khonakdar, H.A.; Li, C. Agricultural waste-derived (nano)materials for water and wastewater treatment: Current challenges and future perspectives. J. Clean Prod. 2023, 421, 138524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.I.; Dickson, R.; Mancini, E.; Malanca, A.A.; Pinelo, M.; Mansouri, S.S. An integrated sustainable biorefinery concept towards achieving zero-waste production. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 336, 130317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, T.; Zhang, M.; Sun, H.; Zhu, Z.; Li, J.; Liang, W. Excellent acid resistance and MXene enhanced photothermal conversion of bilayered porous solar evaporator fabricated by palygorskite and pectin. Desalination 2024, 591, 118053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.; Chai, J.; Wu, M.; Tang, L. Recent progress of photoelectrocatalysis systems for wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Su, Z.; Wang, G.-m. An effective integrated control with intelligent optimization for wastewater treatment process. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2021, 24, 100237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, S.; Yan, H.; Li, C.; Wang, H. Green treatment of turbid traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) wastewater: Optimization of UF-MD coupling process. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, X.; Zhu, F.; Peng, X. Reductive Removal and Recovery of As(V) and As(III) from Strongly Acidic Wastewater by a UV/Formic Acid Process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 9732–9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, A.; Xu, Q.; He, Z.; Yang, C.; Wang, A. Short-chain fatty acid production from waste activated sludge and in situ use in wastewater treatment plants with life cycle assessment. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 198, 107186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Sim, S.J. Enhancement of microalgal biomass productivity through mixotrophic culture process utilizing waste soy sauce and industrial flue gas. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 373, 128719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-León, A.G.; Castro-Jiménez, C.C.; Saldarriaga-Molina, J.C.; García A, E.F.; Correa-Ochoa, M.A. Aluminium recovered coagulant from water treatment sludge as an alternative for improving the primary treatment of domestic wastewater. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 346, 131229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, A.; Yue, B.; Lin, T.; Ding, M. Microalgae treatment of food processing wastewater for simultaneous biomass resource recycling and water reuse. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 369, 122394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y. An ultrastable cationic covalent organic framework for selective capture of silver from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1292, 136173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).