Comprehensive Review on the Distribution, Environmental Fate, and Risks of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Rivers and Lakes of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Distribution of ARGs in Lakes and Rivers
3. Environmental Fate of ARGs in Lakes and Rivers
3.1. Source of ARGs
3.2. Migration and Dissemination of ARGs
3.2.1. Horizontal Gene Transfer
3.2.2. Vertical Gene Transfer
3.2.3. Impact of Pollutants on the Migration of ARGs
3.2.4. Impact of Environmental Factors on the Migration of ARGs
3.3. Persistence of ARGs
4. Potential Risks of ARGs in Lakes and Rivers
4.1. Ecological Risks of ARGs
4.2. Human Health Risks of ARGs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARGs | Antibiotic resistance genes |
| USD | United States Dollar |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| HGT | Horizontal gene transfer |
| ARB | Antibiotic-resistant bacteria |
| ERA | Environmental risk assessments |
| iARGs | Intracellular ARGs |
| eARGs | Extracellular ARGs |
| UWTPs | Urban wastewater treatment plants |
| VGT | Vertical gene transfer |
| MGEs | Mobile genetic elements |
| ciMGEs | Chromosomally integrated mobile genetic elements |
| IMEs | Integrative mobilizable elements |
| CIMEs | Cis-mobilizable elements |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| PGRs | Plant growth regulators |
| IAA | Indole-3-acetic acid |
| ETH | Ethephon |
| SMX | Sulfamethoxazole |
| COD | Chemical oxygen demand |
| eDNA | Extracellular DNA |
| DNase I | Deoxyribonuclease I |
| EPS | Extracellular polymeric substances |
| RQ | Risk quotient |
| SSD | Species sensitivity distribution |
| PNEC | Predicted no-effect concentration |
| MEC | Measured environmental concentration |
| PERA | Probabilistic ecological risk assessment |
| QMRA | quantitative microbial risk assessment |
| RI | Risk index |
References
- Bavumiragira, J.P.; Eheneden, I.; Yin, H.L.; Mumbi, A.W.; Quoie, G.D.S., Jr.; Uyisaba, P.; Wang, R.C.; Zhao, J.F. Insight on prioritization of antibiotics in China, their occurrence, and removal by different wastewater treatment technologies. Discov. Environ. 2024, 2, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Ying, G.G.; Singer, A.C.; Zhu, Y.G. Review of antibiotic resistance in China and its environment. Environ. Int. 2018, 110, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Shi, W.Z.; Liu, W.; Li, H.M.; Zhang, W.; Hu, J.R.; Ke, Y.C.; Sun, W.L.; Ni, J.R. A duodecennial national synthesis of antibiotics in China’s major rivers and seas (2005–2016). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Pratap, S.G.; Raj, A. Occurrence and dissemination of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in aquatic environment and its ecological implications: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 47505–47529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.Q.; Lu, X.; Zhao, J.Y.; Li, H.M.; Xu, J.L.; Li, Z.P.; Wang, M.Y.; Peng, Y.; Tian, T.; Yuan, G.L.; et al. Regional antimicrobial resistance gene flow among the One Health sectors in China. Microbiome 2025, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Cao, J.J.; Zhu, Y.G.; Chen, Q.L.; Shen, F.X.; Wu, Y.; Xu, S.Y.; Fan, H.Q.; Da, G.; Huang, R.J.; et al. Global Survey of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10975–10984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, A.; Khiadani, M.; Foroughi, M.; Siuki, H.A.; Mehrfar, H. Wastewater treatment plants: The missing link in global One-Health surveillance and management of antibiotic resistance. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnadozie, C.F.; Odume, O.N. Freshwater environments as reservoirs of antibiotic resistant bacteria and their role in the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, N.; Sun, P.; Sun, Q.; Li, X.W.; Yang, X.W.; Ji, X.; Zou, H.Y.; Ottoson, J.; Nilsson, L.E.; Berglund, B.; et al. Presence of antibiotic residues in various environmental compartments of Shandong province in eastern China: Its potential for resistance development and ecological and human risk. Environ. Int. 2018, 114, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, K.J.; Liu, Y.Y.; Hua, Z.L.; Lu, Y.; Ye, F.Z. Spatio-temporal distribution and dynamics of antibiotic resistance genes in a water-diversion lake, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.X.; Jia, Y.; Huang, B.; Zhao, D.M.; Long, X.; Hu, S.Y.; Li, C.Q.; Dao, G.H.; Chen, B.; Pan, X.J. Spatial distribution, pollution characteristics, and health risks of antibiotic resistance genes in China: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 2285–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenni, P.; Ancona, V.; Caracciolo, A.B. Ecological effects of antibiotics on natural ecosystems: A review. Microchem. J. 2018, 136, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.F.; Xiao, Y.; Yan, W.D.; Ding, R.; Wang, S.H.; Zhao, F. The effect of bioelectrochemical systems on antibiotics removal and antibiotic resistance genes: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 158, 1424–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Q.; Zhang, J.H.; Wu, Y.N. Perspectives: National Action Plan in Antimicrobial Resistance Using Framework Analysis for China. China CDC Wkly. 2023, 5, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Dyar, O.J.; Yin, J.; Ma, W.W.; Sun, Q.; Lundborg, C.S. Antimicrobial resistance in China across human, animal, and environment sectors—A review of policy documents using a governance framework. Lancet Reg. Health—West. Pac. 2024, 48, 101111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.M.; Su, J.Q.; Guo, Y.Y.; Wilkinson, D.M.; Liu, Z.W.; Zhu, Y.G.; Yang, J. Large-scale biogeographical patterns of bacterial antibiotic resistome in the waterbodies of China. Environ. Int. 2018, 117, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Fang, W.K.; Zhang, Z.W.; Zhang, H.J.; Li, Y. Occurrence characteristics of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and their effects on bacterial communities and antibiotic resistance genes in Taihu Lake. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2025, 34, 1495–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Y. Pollution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Extracellular and Intracellular Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Baiyangdian Lake. Master’s Thesis, Hebei University, Baoding, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.R.; Wang, M.Y.; Shen, Y.J.; Li, B.; Zhao, D.N.; Zou, S.C.; Yang, Y. Detection of extracellular antibiotic resistance genes in river water: Application of ultrafiltration-magnetic beads method. Environ. Res. 2024, 163, 120259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, J.Y.; Li, B.L.; Xie, W.M.; Li, G.Z.; Song, H.J.; Zhai, W.Y.; Li, Y. Study on the Distribution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Antibiotics and Resistance Genes in Water Sources of Wuhan. Toxics 2024, 12, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Yang, G.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Yang, C. High-throughput profiling of antibiotic resistance genes in the Yellow River of Henan Province, China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Xi, X.Y.; Li, X.; Hu, H.J.; Chen, K.L.; Wu, C.X. Characteristics of microbial communities and antibiotic resistance genes in typical rivers of the western Qinghai Lake basin. Water Biol. Secur. 2024, 3, 100249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.C.; Song, R.R.; Lu, S.Y.; Liu, X.H.; Chen, J.M.; Wan, Z.F.; Bi, B. Multi-Media Occurrence of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in East Dongting Lake. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 866332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekar, A.; Qiu, M.R.; Wang, B.G.; Murava, R.T.; Norgbey, E. Relationship between water quality, heavy metals and antibiotic resistance genes among three freshwater lakes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, L.J.; Liu, Y.; Bian, Z.Q.; Yu, J.; Wang, D.C.; Li, H.X. Positive antibiotic and resistance genes in source water of three regions and correlation analysis. J. Environ. Occup. Med. 2023, 40, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.H.; Wang, B.; He, Y.J.; Zhu, R.T.; Tian, Y.S.; Ji, R.; Pang, W.; Qian, W.Y.; Wu, H.R. Occurrence and environmental risks of antibiotics in surface water of China. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 2120–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Mao, D.Q.; Rysz, M.; Zhou, Q.X.; Zhang, H.J.; Xu, L.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Trends in Antibiotic Resistance Genes Occurrence in the Haihe River, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7220–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.C.; Li, W.B.; Zhao, M.Z.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Shi, L.; Yang, X.Y.; Xia, H.H.; Yang, S.F.; Yang, L.P. The association between ambient temperature and antimicrobial resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae in China: A difference-in-differences analysis. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1158762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.F.; Dong, X.H.; Sun, R.; Wu, J.; Tian, L.J.; Rao, D.W.; Zhang, L.H.; Yang, K. Migratory birds-one major source of environmental antibiotic resistance around Qinghai Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okocha, R.C.; Olatoye, I.O.; Adedeji, O.B. Food safety impacts of antimicrobial use and their residues in aquaculture. Public Health Rev. 2018, 39, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, K.K.; Singh, C.K. Recent development in the sustainable remediation of antibiotics: A review. Total Environ. Res. Themes 2022, 3–4, 100008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Costa, V.M.; King, C.E.; Kalan, L.; Morar, M.; Sung, W.W.L.; Schwarz, C.; Froese, D.; Zazula, G.; Calmels, F.; Debruyne, R.; et al. Antibiotic resistance is ancient. Nature 2011, 477, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Manaia, C.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Ploy, M.C.; Michael, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalewska, M.; Błażejewska, A.; Czapko, A.; Popowska, M. Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Animal Manure—Consequences of Its Application in Agriculture. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 610656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Chu, L.M. Fate of antibiotics in soil and their uptake by edible crops. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Lv, Z.Q.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Han, Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Zhang, H.J. A Review of Antibiotics, Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria, and Resistance Genes in Aquaculture: Occurrence, Contamination, and Transmission. Toxics 2023, 11, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, D.G.J.; Flach, C.F. Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, B.J.; Huang, I.T.; Hanage, W.P. Horizontal gene transfer and adaptive evolution in bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, M.; Shintani, M. Microbial evolution through horizontal gene transfer by mobile genetic elements. Microb. Biotechnol. 2024, 17, e14408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, L.; Escobedo, S.; Gutiérrez, D.; Portilla, S.; Martínez, B.; García, P.; Rodríguez, A. Bacteriophages in the Dairy Environment: From Enemies to Allies. Antibiotics 2017, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylward, F.O.; Moniruzzaman, M. Viral Complexity. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcázar, J.L. How do bacteriophages promote antibiotic resistance in the environment? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coluzzi, C.; Garcillán-Barcia, M.P.; Cruz, F.; Rocha, E.P.C. Evolution of Plasmid Mobility: Origin and Fate of Conjugative and Nonconjugative Plasmids. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2022, 39, msac115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, J. Defense systems are pervasive across chromosomally integrated mobile genetic elements and are inversely correlated to virulence and antimicrobial resistance. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 4385–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.M.; Grossman, A.D. Integrative and Conjugative Elements (ICEs): What They Do and How They Work. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2015, 49, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guédon, G.; Libante, V.; Coluzzi, C.; Payot, S.; Leblond-Bourget, N. The Obscure World of Integrative and Mobilizable Elements, Highly Widespread Elements that Pirate Bacterial Conjugative Systems. Genes 2017, 8, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, H.; Fricker, C.; Brown, R.S.; Majury, A.; Liss, S.N. Antibiotic resistance genes as an emerging environmental contaminant. Environ. Rev. 2016, 24, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Davies, D. Origins and Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Qiu, Y.; Song, Y.Q.; Lin, H.; Yin, H.B. Dissecting horizontal and vertical gene transfer of antibiotic resistance plasmid in bacterial community using microfluidics. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 105007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Mao, L.K.; Yuan, Z.G.; Bond, P.L.; Guo, J.H. Non-antibiotic pharmaceuticals promote the transmission of multidrug resistance plasmids through intra- and intergenera conjugation. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2493–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Wang, B.J.; Ren, S.J.; Liu, X.L.; Wang, Y.K. Regulation of quorum sensing for the manipulation of conjugative transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater treatment system. Water Res. 2024, 253, 121222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.J.; Liu, W.W.; Wen, S.F.; Wang, L.J.; Zhu, L.S.; Wang, J.; Kim, Y.M.; Wang, J.H. Effect of sulfamethazine on the horizontal transfer of plasmid-mediated antibiotic resistance genes and its mechanism of action. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 127, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagón-Rojas, J.N.; Barrera, E.L.P.; Lagos, L. From environment to clinic: The role of pesticides in antimicrobial resistance. Pan Am. J. Public Health 2020, 44, e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gormez, E.; Golge, O.; Dincay, O.; Kabak, B. A potential threat to black figs intended for export from Turkey: Ethephon. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 102, 103989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanauskas, R.; Glenn, T.C.; Jagoe, C.H.; Tuckfield, R.C.; Lindell, A.H.; King, C.J.; McArthur, J.V. Coselection for microbial resistance to metals and antibiotics in freshwater microcosms. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1510–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.X.; Rensing, C.; Holm, P.E.; Virta, M.; Brandt, K.K. Comparison of Metals and Tetracycline as Selective Agents for Development of Tetracycline Resistant Bacterial Communities in Agricultural Soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3040–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.; Zhang, T.L.; Cai, T.G.; Xiang, Q.; Zhu, D. Effects of heavy metal and disinfectant on antibiotic resistance genes and virulence factor genes in the plastisphere from diverse soil ecosystems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, J.L. Bottlenecks in the transferability of antibiotic resistance from natural ecosystems to human bacterial pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.Q.; Guo, X.D.; Weller, D.L.; Pollak, S.; Buckley, D.H.; Wiedmann, M.; Cordero, O.X. Nationwide genomic atlas of soil-dwelling Listeria reveals effects of selection and population ecology on pangenome evolution. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Thomsen, L.E.; Olsen, J.E. Antimicrobial-induced horizontal transfer of antimicrobial resistance genes in bacteria: A mini-review. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, N.; Amann, M.; Arnell, P.N.; Ayeb-Karlsson, S.; Beagley, J.; Belesova, K.; Boykoff, M.; Byass, P.; Cai, W.; Campbell-Lendrum, D.; et al. The 2020 report of The Lancet Countdown on health and climate change: Responding to converging crises. Lancet 2021, 397, 129–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.Y.; Zhang, B.H.; Zheng, S.K.; Yan, W.L.; Yu, X.; Ye, C.S. High temperatures promote antibiotic resistance genes conjugative transfer under residual chlorine: Mechanisms and risks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 483, 136675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFadden, D.R.; McGough, S.F.; Fisman, D.; Santillana, M.; Brownstein, J.S. Antibiotic resistance increases with local temperature. Nat. Clim. Change 2018, 8, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.M.; Lu, P.Z. Seasonal variations in antibiotic resistance genes in estuarine sediments and the driving mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 383, 121164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakiston, M.R.; Freeman, J.T. Population-level exposures associated with MRSA and ESBL-E. coli infection across district health boards in Aotearoa New Zealand: An ecological study. N. Z. Med. J. 2020, 133, 62–69. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32078602/ (accessed on 30 September 2025). [PubMed]
- Forsberg, K.J.; Patel, S.; Gibson, M.K.; Lauber, C.L.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N.; Dantas, G. Bacterial phylogeny structures soil resistomes across habitats. Nature 2014, 509, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Chen, Y.H.; Liu, C.; Hong, J.; Deng, H.; Yu, D.J. Eutrophication and Related Antibiotic Resistance of Enterococci in the Minjiang River, China. N. Z. Med. J. 2020, 80, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkman, A.; Do, T.T.; Walsh, F.; Virta, M.P.J. Antibiotic-Resistance Genes in Waste Water. Microbiology 2018, 26, 169–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, J.P. Climate change and antibiotic resistance: A deadly combination. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, 2049936121991374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.C.; Song, L.L.; Ji, X.Y.; Huang, S.H.; Yu, Y.S.; Ye, J.; Xu, W.W.; Hou, M.F. Algal-bacterial consortium mediated system offers effective removal of nitrogen nutrients and antibiotic resistance genes. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 362, 127874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.P.; Pang, W.H.; Dou, C.L.; Yin, D.Q. Sulfamethoxazole and COD increase abundance of sulfonamide resistance genes and change bacterial community structures within sequencing batch reactors. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagler, M.; Insam, H.; Pietramellara, G.; Ascher-Jenull, J. Extracellular DNA in natural environments: Features, relevance and applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 6343–6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, S.M.; Fisher, G.; Everett, B.A.; Tran, P.; Prindle, A. Secreted nucleases reclaim extracellular DNA during biofilm development. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nihemaiti, M.; Yoon, Y.; He, H.; Dodd, M.C.; Croué, J.P.; Lee, Y. Degradation and deactivation of a plasmid-encoded extracellular antibiotic resistance gene during separate and combined exposures to UV254 and radicals. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.Q.; Luo, Y.; Mathieu, J.; Wang, Q.; Feng, L.; Mu, Q.H.; Feng, C.Y.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Persistence of Extracellular DNA in River Sediment Facilitates Antibiotic Resistance Gene Propagation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauvisseau, Q.; Harper, L.R.; Sander, M.; Hanner, R.H.; Kleyer, H.; Deiner, K. The Multiple States of Environmental DNA and What Is Known about Their Persistence in Aquatic Environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 5322–5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.R.; Mo, X.Q.; Xue, Q.; Wang, Z.Y.; Lu, X.Q.; Liu, J.; Ma, Q.Q.; Sparks, J.P.; He, M.X. Distribution, source apportionment, and ecological risk assessment of soil antibiotic resistance genes in urban green spaces. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.Y.; Li, W.M.; Cao, S.X. Driving factors for coordinating urbanization with conservation of the ecological environment in China. Ambio 2021, 50, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, J.L. Occurrence and behavior of antibiotics in water and sediments from the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.J.; Zhang, B.B.; Zhao, Y.G.; Wu, Q.L.L. Occurrence, spatiotemporal distribution, and ecological risks of steroids in a large shallow Chinese lake, Lake Taihu. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557–558, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.D.; Kong, L.Y.; Jin, M.; Yang, X.D.; Wu, Q.L.L. Trends in the occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in shallow lakes in the lower-middle reaches of the Yangtze River basin, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 183, 109511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.P.; Liu, R.M.; Wang, L.F.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Y. Reliable and Representative Estimation of Extrapolation Model Application in Deriving Water Quality Criteria for Antibiotics. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 42, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Shi, Y.J.; Lu, Y.L.; Song, S.; Wang, C.C.; Wu, Y.Q.; Liang, R.Y.; Qian, L.; Xu, Q.Y.; Shao, X.Q.; et al. Ecological risk assessment of commonly used antibiotics in aquatic ecosystems along the coast of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 935, 173263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Tu, M.C.; Li, C.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, J.; Wei, C.; Zheng, X.; Wu, Y.H. Risk Assessment of Phthalate Esters in Baiyangdian Lake and Typical Rivers in China. Toxics 2023, 11, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasiri, M.; Sano, D.; Suzuki, S. Understanding human health risks caused by antibiotic resistant bacteria (ARB) and antibiotic resistance genes (ARG) in water environments: Current knowledge and questions to be answered. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 2016–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Jing, L.J.; Teng, Y.G.; Wang, J.S. Characterization of antibiotics in a large-scale river system of China: Occurrence pattern, spatiotemporal distribution and environmental risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooban, B.; Fitzhenry, K.; Cahill, N.; Joyce, A.; O’ Connor, L.; Bray, J.E.; Brisse, S.; Passet, V.; Syed, R.A.; Cormican, M.; et al. A Point Prevalence Survey of Antibiotic Resistance in the Irish Environment, 2018–2019. Environ. Int. 2021, 152, 106466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.N.; Gaston, J.M.; Dai, C.Z.L.; Zhao, S.J.; Poyet, M.; Groussin, M.; Yin, X.L.; Li, L.G.; Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Topp, E.; et al. An omics-based framework for assessing the health risk of antimicrobial resistance genes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, T.Z.; Xu, N.H.; Lu, T.; Hong, W.J.; Penuelas, J.; Gillings, M.; Wang, M.; Gao, W.W.; et al. Assessment of global health risk of antibiotic resistance genes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.J.; Li, R.L.; Yang, K.; Xu, F.; Lin, C.S.; Chen, Q.L.; Zhu, D.; Sun, Q.; Zhu, Y.G.; Cui, L. Quantifying health risks of plastisphere antibiotic resistome and deciphering driving mechanisms in an urbanizing watershed. Water Res. 2023, 245, 120574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


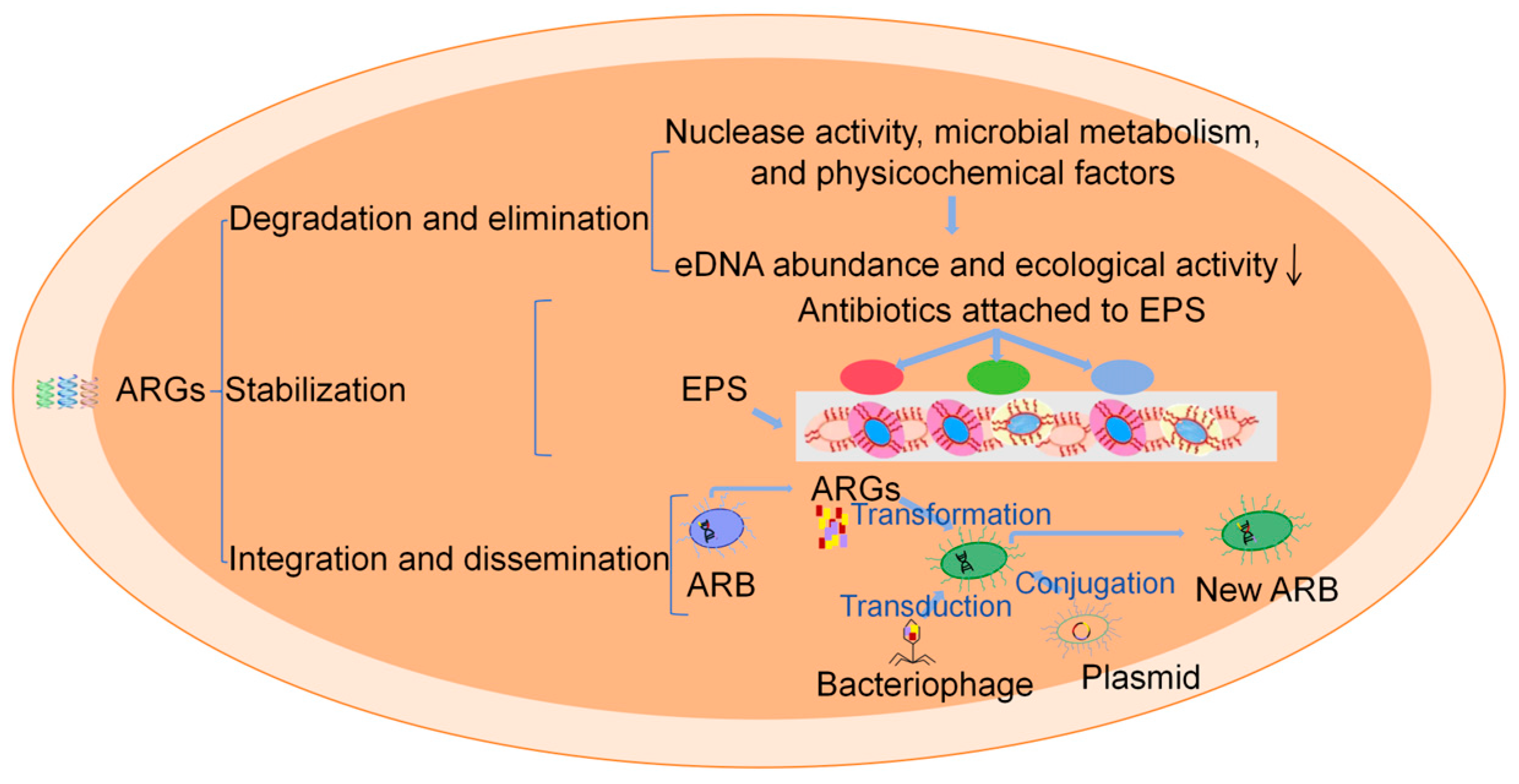
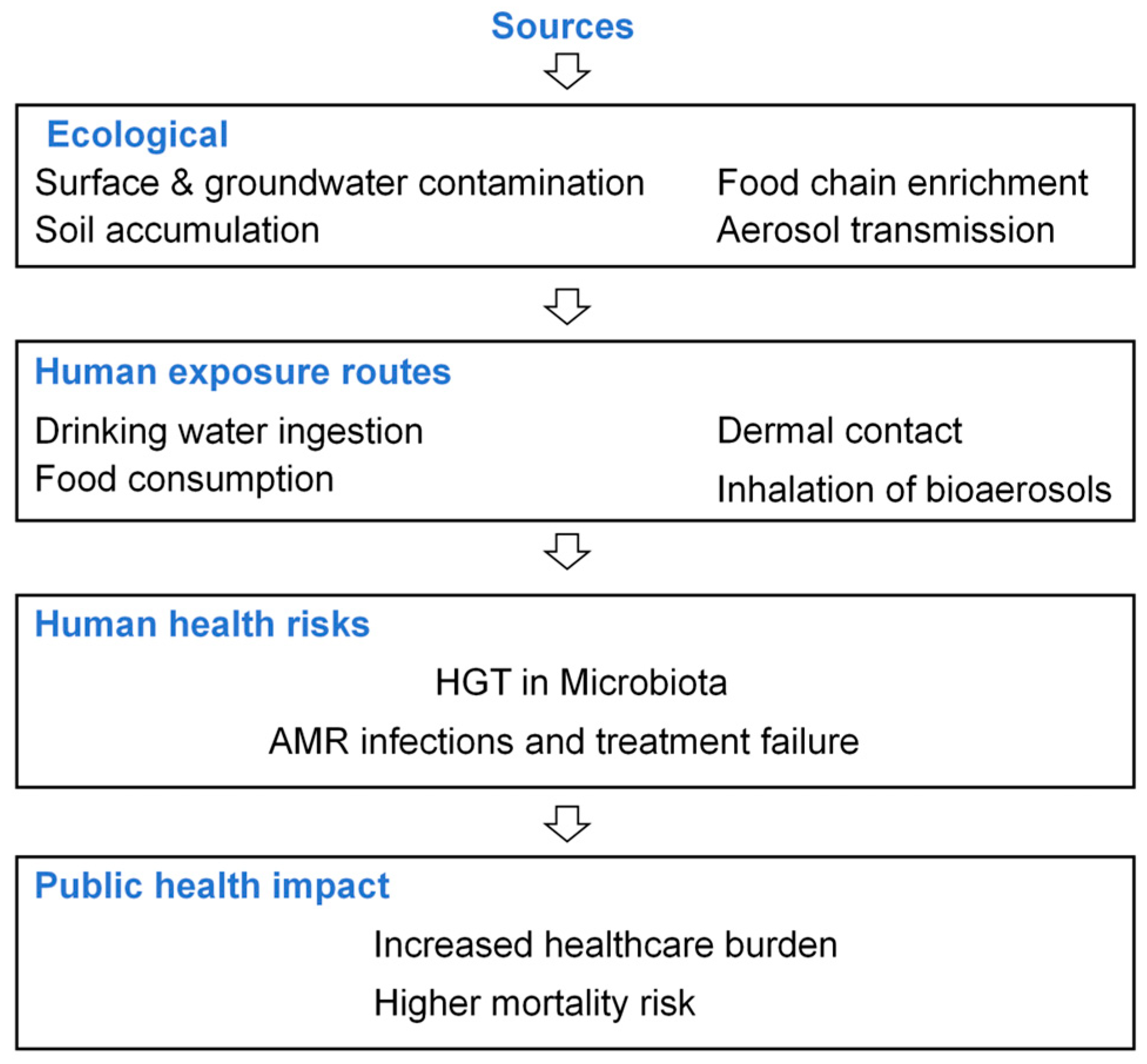
| Lake/River | Abundance |
|---|---|
| Taihu Lake [17] | 6.7 × 107–1.76 × 108 copies/mL |
| Chaohu Lake [18] | 3.5 × 103–2.63 × 105 copies/mL |
| Pearl River Basin [19] | 10−1–105 copies/mL |
| Poyang Lake [20] | 2.26 × 101–1.50 × 108 copies/mL |
| Yellow River [21] | 0–3.6 × 106 copies/mL |
| Qinghai Lake [22] | 4.93 × 102–8.10 × 103 copies/mL |
| Luoma Lake [10] | 2.87 × 103–2.94 × 104 copies/mL |
| East Dongting Lake [23] | 0–4.88 × 104 copies/mL |
| Nanhu Lake [24] | 9.4 × 107 copies/mL |
| Xuanwu Lake [24] | 2.37 × 108 copies/mL |
| Zixia Lake [24] | 4.42 × 107 copies/mL |
| Method | Principle | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| RQ [81] | Compares measured environmental concentration with a PNEC. | Simple and data-efficient, suitable for rapid large-scale screening. | Does not directly reflect human health risks; high uncertainty in the PNEC for ARGs. |
| SSD [82] | Uses dose–response data from multiple species to derive hazard thresholds. | Considers species differences; provides probabilistic risk estimates. | Lack of standardized toxicity data for ARGs limits applicability. |
| PERA [84] | Evaluates ARG mobility, host pathogenicity, and transfer potential. | Integrates biological behavior and environmental factors. | Data-intensive, model-sensitive, and computationally complex. |
| QMRA [85] | Predicts infection risk based on exposure pathways and dose–response models. | Directly linked to human exposure and disease burden. | Data-deficient, assumption-dependent, and uncertainty-prone. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, D.; Liu, D.; Chen, G.; Zhao, S.; Gao, J.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, K.; Xu, J.; et al. Comprehensive Review on the Distribution, Environmental Fate, and Risks of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Rivers and Lakes of China. Water 2025, 17, 3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223228
Sun J, Xu C, Wang D, Liu D, Chen G, Zhao S, Gao J, Shi Y, Jiang K, Xu J, et al. Comprehensive Review on the Distribution, Environmental Fate, and Risks of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Rivers and Lakes of China. Water. 2025; 17(22):3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223228
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jingjie, Cancan Xu, Dongmei Wang, Dongsheng Liu, Guomin Chen, Shiwen Zhao, Jinshan Gao, Yifan Shi, Keyang Jiang, Jiaxin Xu, and et al. 2025. "Comprehensive Review on the Distribution, Environmental Fate, and Risks of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Rivers and Lakes of China" Water 17, no. 22: 3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223228
APA StyleSun, J., Xu, C., Wang, D., Liu, D., Chen, G., Zhao, S., Gao, J., Shi, Y., Jiang, K., Xu, J., Ma, Z., Chen, Y., & Wang, Z. (2025). Comprehensive Review on the Distribution, Environmental Fate, and Risks of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Rivers and Lakes of China. Water, 17(22), 3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223228







