Research Status and Emerging Trends in the Comprehensive Impact of Inter-Basin Water Transfer Projects (IBWTs)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Approach
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Analysis Methods
3. Results and Discussion
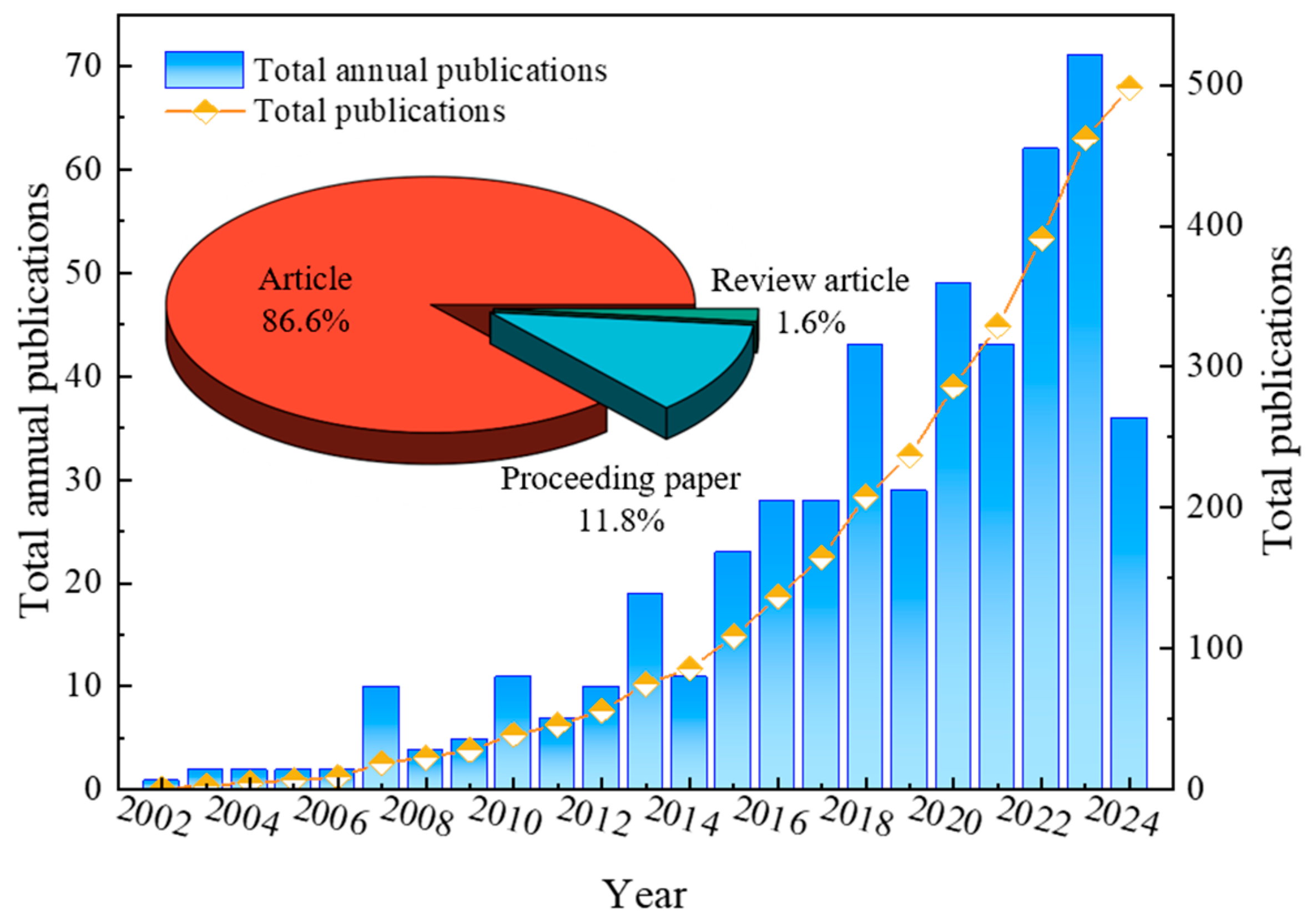
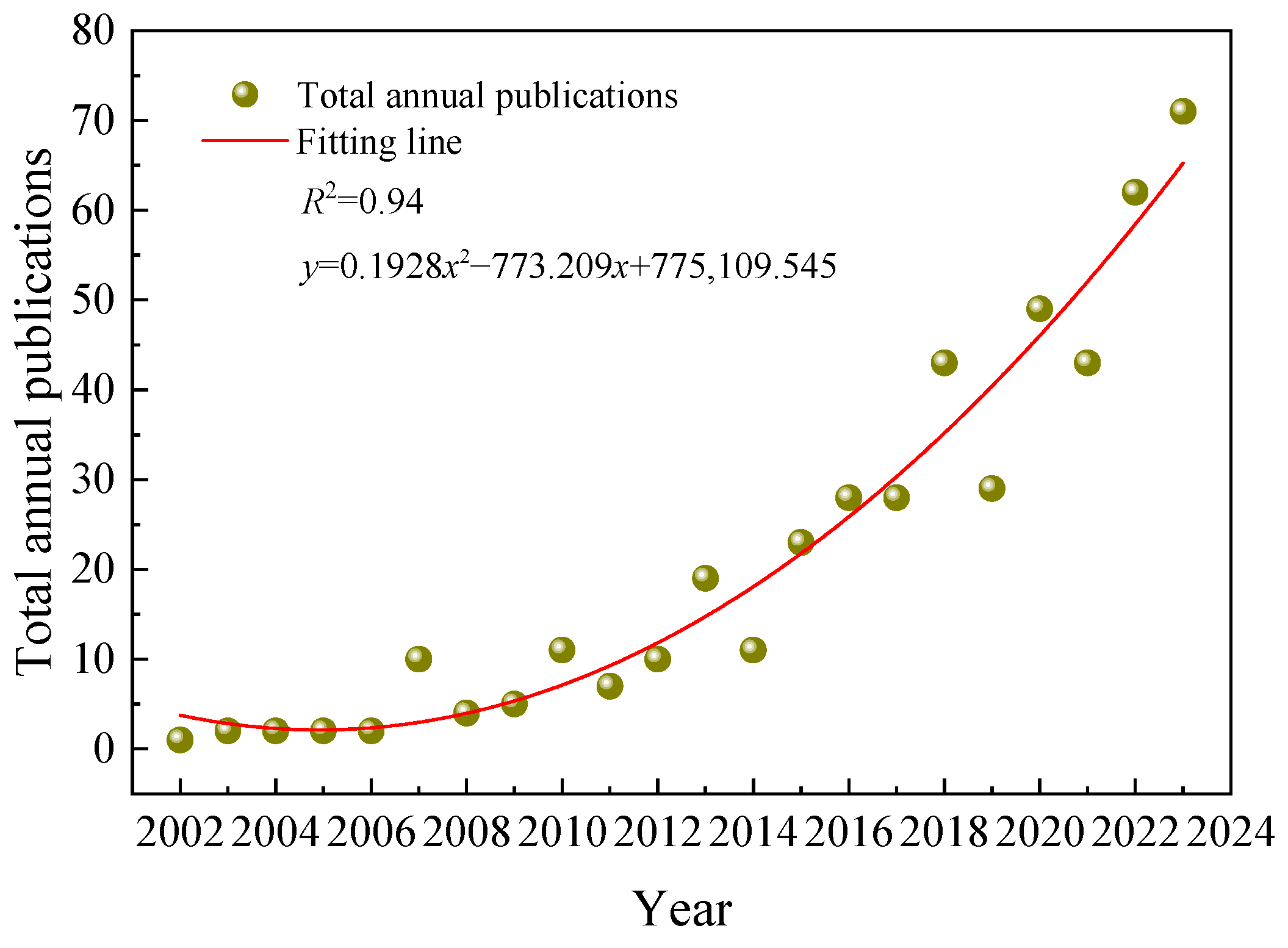
3.1. Characteristics of Publication Outputs
3.2. Performance of Published Journals
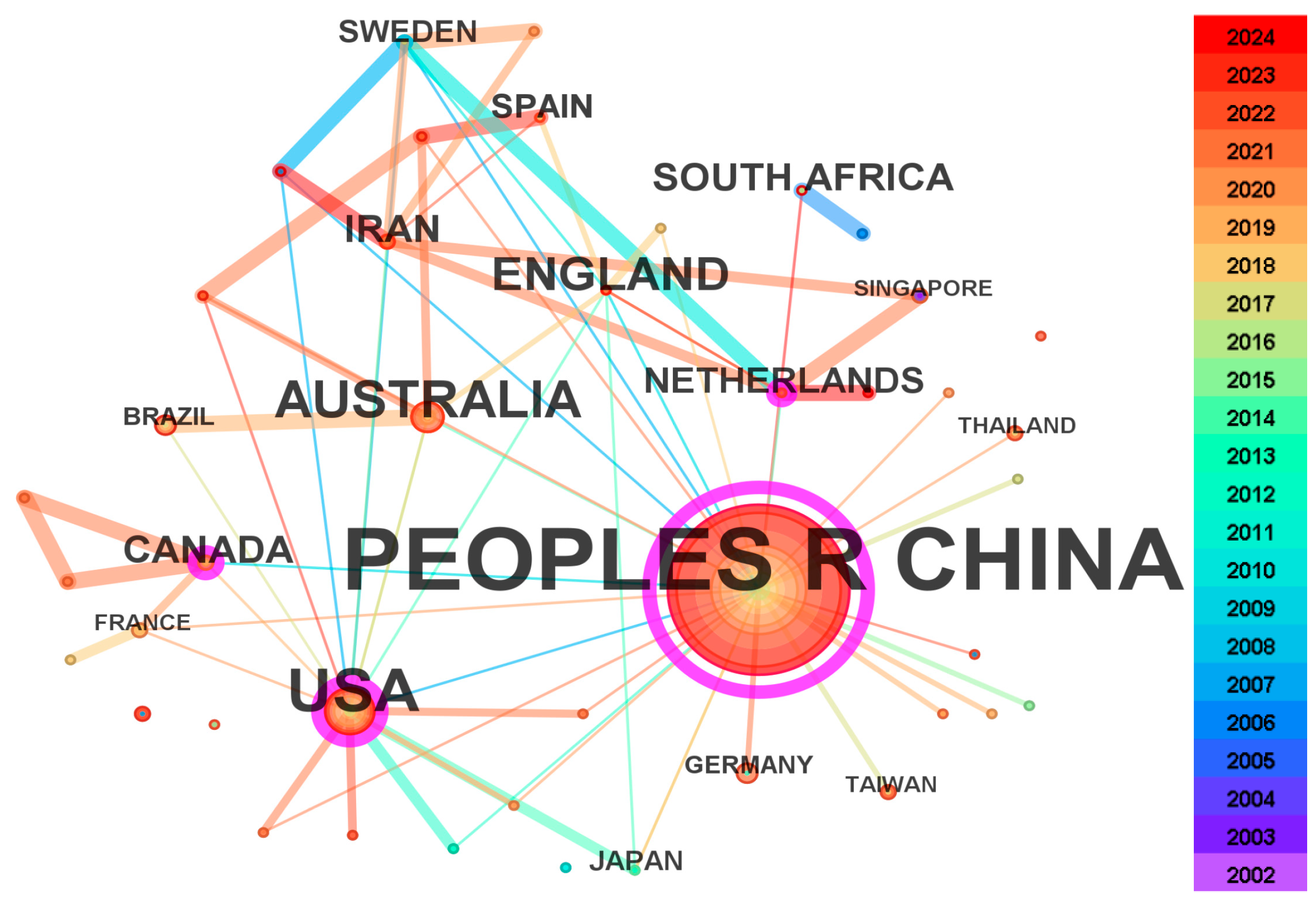
3.3. Cooperation Between Countries
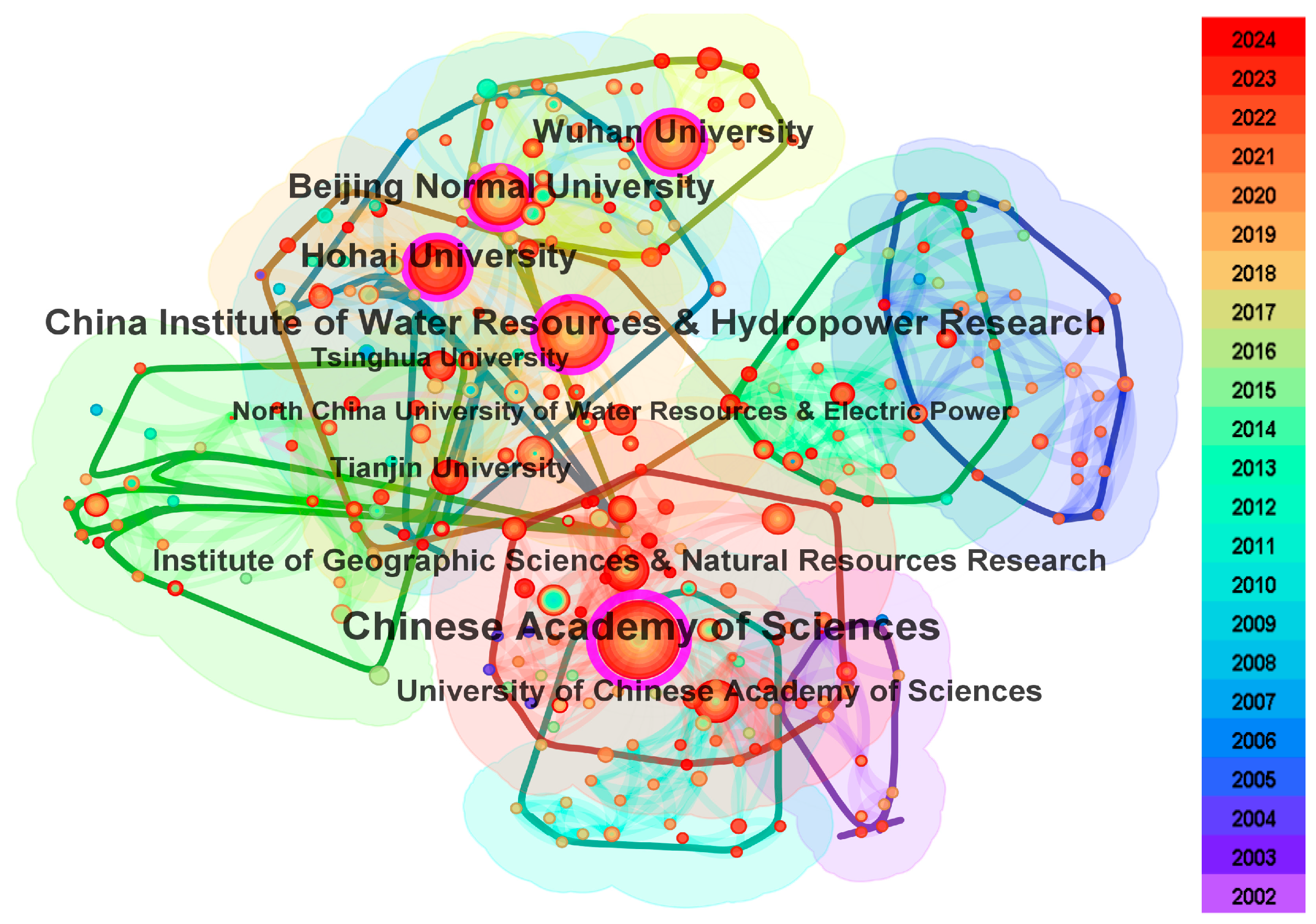
3.4. Cooperation Between Institutions
3.5. Subject Category Co-Occurrence Analysis
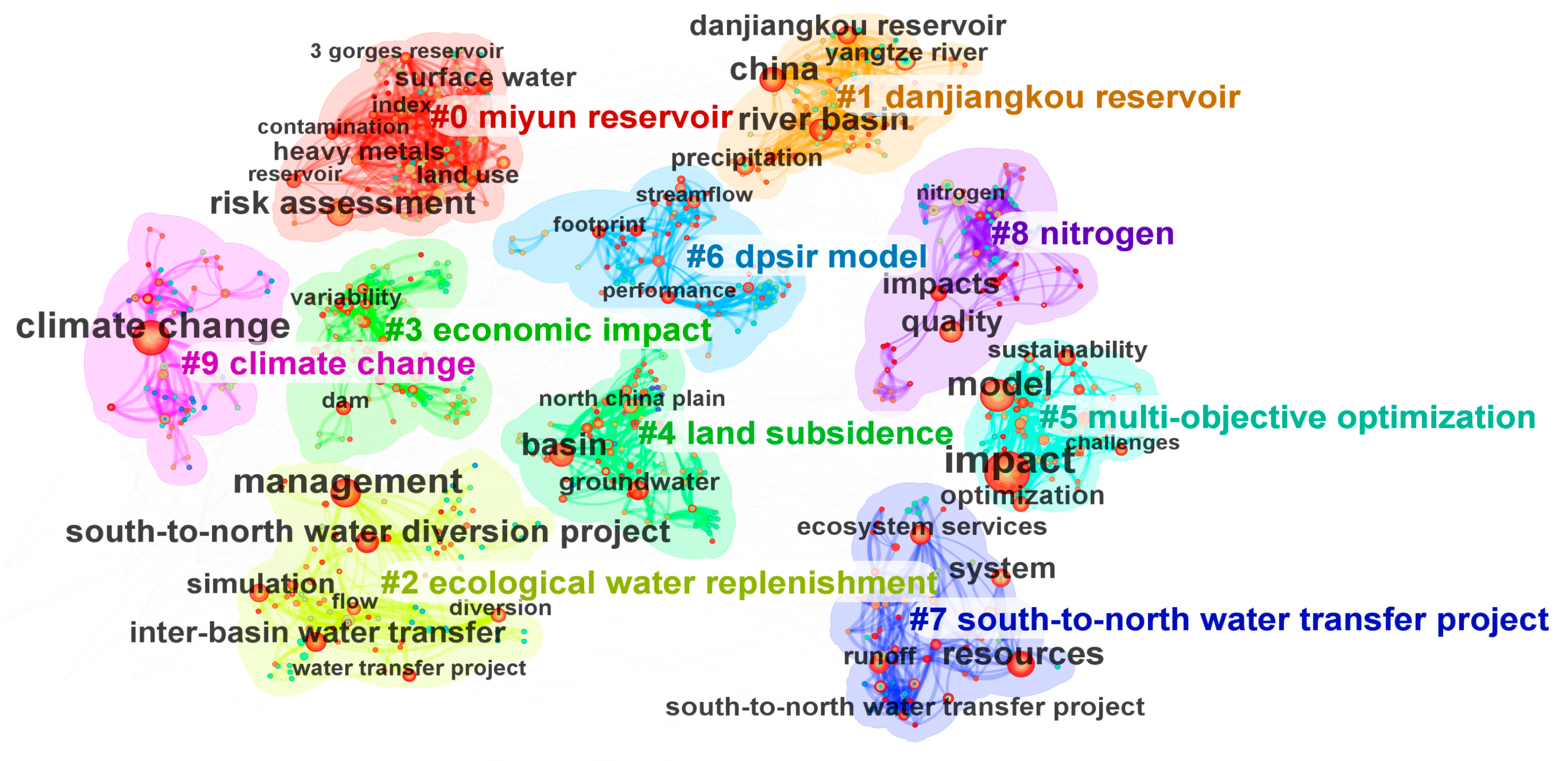
3.6. Keyword Cluster Analysis
3.6.1. Related Projects for Studying the Impact of IBWTs
3.6.2. The Impact of IBWTs on the Region
3.6.3. Strategies and Methodologies for Mitigating the Impacts of IBWTs
3.7. Research Emphasis and Development Tendency of IBWT Impacts
3.7.1. The Impact Mechanism of IBWTs
3.7.2. Assessment of and Response to the Impact of IBWTs
3.7.3. The Development Tendency of Research on the Impact of IBWTs
- (1)
- Long-term hydro-eco–economic linkages between donor and recipient basins remain poorly understood. In particular, how to ensure water supply safety and ecological integrity under extreme conditions is an urgent problem to be solved. IBWTs urgently necessitate an integration of the actual engineering plan for both the water source and water-receiving areas, as well as consideration of local climate characteristics, in order to conduct a systematic identification and analysis of the project’s influencing factors.
- (2)
- Internationally accepted standards are lacking in the design, performance, and ecological-impact assessment of IBWTs. A unified interdisciplinary framework should be established, integrating environmental science, water resources, and related fields, and then establish internationally recognized standards on both human and ecosystem health. And large-scale IBWTs should be integral to the national water resources management plan.
- (3)
- Real-time risk-warning models for IBWTs (e.g., heavy-metal pollution, land subsidence) should be incorporated with AI and remote-sensing technologies to support life-cycle adaptive management of projects. The incorporation of advanced technologies, such as machine learning algorithms, is essential for establishing correlations between the influencing factors of IBWTs. For instance, there is a significant correlation to be determined between indices like the fish community index and water quality indicators in lakes. This approach aids in gaining a comprehensive understanding and successfully managing the impacts of IBWTs on the environment and society.
4. Conclusions
4.1. Summary
- (1)
- It has been observed that the total number of publications on the impact of IBWTs is positively correlated with time, indicating a potential for continued rapid growth in the coming years. Notably, the academic journals that have published research on the impact of IBWTs include Water, Science of the Total Environment, Journal of Hydrology, and Journal of Cleaner Production. Within the domain of IBWT impact research, China, the USA, Australia, the UK, and Canada have been prominent, engaging in high-level cooperation with other countries and regions. Institutions in China have been particularly active, with the Chinese Academy of Sciences being notably prominent. The SNWDP in China is expected to maintain a significant position in the study of IBWT impacts, both currently and in the future.
- (2)
- The study of IBWTs’ impacts encompasses a multitude of disciplinary fields, characterizing it as a quintessential interdisciplinary research area. These subject categories span 80 distinct groups, with notable representation in “Environmental Sciences”, “Water Resources”, “Engineering, Environmental”, “Geosciences, Multidisciplinary”, “Engineering, Civil” and “Green and Sustainable Science and Technology”, “Environmental Studies”, “Biodiversity Conservation”, and “Ecology”. In recent years, there has been a significant expansion in topics such as “Geosciences, Multidisciplinary”, “Green and Sustainable Science and Technology”, and “Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence”, which have emerged as pivotal areas for the study and assessment of water diversion impacts.
- (3)
- Research hotspots in the field of the impact of IBWTs are primarily concentrated on scientifically assessing the effects on water source areas, water-receiving areas, and areas along the transmission routes of such projects, as well as proposing viable response strategies and methods. The focus is predominantly on aspects such as “heavy metals”, “water quality”, “nitrogen”, “land subsidence”, “economy”, “climate change”, “modeling”, “control”, “ecological water replenishment”, and “evaluation”. A systematic study of the IBWTs’ impacts from hydrological and water resources, ecological environment, and economic and social perspectives remains a critical priority for future research. The models for studying the impacts of IBWTs mainly include DPSIR and multi-objective optimization, which aid in formulating response strategies.
4.2. Outlook
- (1)
- Probe the long-term hydro-ecological–economic nexus between donor and recipient basins, with an emphasis on safeguarding both water-supply security and ecological integrity under extreme events. It is recommended to enhance water conservation measures and develop adaptive and flexible water transfer strategies that align with environmental shifts.
- (2)
- Forge an international consensus on design, performance and eco-impact benchmarks for IBWTs and embed these standards in national water resource governance.
- (3)
- Couple AI with remote-sensing technologies to create a real-time risk-warning platform that enables adaptive, life-cycle management of IBWTs.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dou, X.S. China’s inter-basin water management in the context of regional water shortage. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 4, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Wang, C.R.; Liu, Y.; Olsson, G.; Wang, C.Y. Sustainability of mega water diversion projects: Experience and lessons from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.A.; Zhou, X.; Liu, H.X.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Zhou, H.C.; Zhang, C.; Fu, G.T. Unraveling the effect of inter-basin water transfer on reducing water scarcity and its inequality in China. Water Res. 2021, 194, 116931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Q.; Ouyang, Q.; Zhang, Y.D.; Wei, J.H.; Ren, Z.Y. World Water Diversion Project; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, J.C.; Zhang, R.Z.; Yang, H.Q. Inter-basin water transfers and water rebound effects: The South-North water transfer Project in China. J. Hydrol. 2024, 638, 131516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Y.; Xu, Z.K.; Yao, J.W.; Yin, X.L. Water transfer projects and the regional distribution characteristics analysis of China. South North Water Divers. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 14, 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Wang, Q. Do water transfer projects promote water use efficiency? Case study of South-to-North Water Transfer Project in Yellow River Basin of China. Water 2024, 16, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.H. Research on allocation and effects of water diversion by Stage Ⅰ Project of the West Route of South-to-North Water Transfer. Yellow River 2016, 38, 122–125. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.L.; He, W. Calculation of urban water resources utilization efficiency and analysis of its influencing fators in water affected areas of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Acta Sci. Circ. 2023, 44, 438–450. [Google Scholar]
- Long, D.; Yang, W.T.; Scanlon, B.R.; Zhao, J.S.; Liu, D.G.; Burek, P.; Pan, Y.; You, L.Z.; Wada, Y. South-to-North Water Diversion stabilizing Beijing’s groundwater levels. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Ma, C.M.; Zhang, D.; Ma, Y.H.; Huang, P. Integrating the impact of large-scale hydraulic engineering with a sustainable groundwater development strategy: A case study of Zhengzhou City, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faúndez, M.; Alcayaga, H.; Walters, J.; Pizarro, A.; Soto-Alvarez, M. Sustainability of water transfer projects: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, X.Z.; Shao, D.G.; Zhong, H.; Liang, J.K. Evaluation of water quality in the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China using the water quality index (WQI) method. Water Res. 2020, 178, 115781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, D.K.; Liu, C.M.; Xu, Y.X. Preliminary study of the impacts of water transfer from South to North on natural environment. Geogr. Res. 1982, 1, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.H.; Bing, J.P.; Li, X.C.; Guo, L.Q.; Deng, Z.M.; Wang, D.W.; Liu, L.S. Inter-basin water transfer enhances the human health risk of heavy metals in the middle and lower Han River, China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 613, 128423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.J.; Lin, D.C.; Zou, C.W. Impact of inter-basin water diversion on ecological environment of middle and lower reaches of Hanjiang River and countermeasure suggestion. Yangtze River 2010, 41, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.L.; Lin, Y.Q.; Chen, Q.W.; Zhang, J.Y.; He, S.F.; Feng, T.; Wang, Z.Y.; Chen, C.; Ding, J. A review of the eco-environmental impacts of the South-to-North Water Diversion: Implications for interbasin water transfers. Engineering 2023, 30, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masero, A.J.; Pérez-González, M.; Basadre, M.; Otero-Saavedra, M. Food supply for waders (Aves: Charadrii) in an estuarine area in the Bay of Cádiz (SW Iberian Peninsula). Acta Oecol. 1999, 20, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.Q.; Zhang, W.X.; Wang, P.; Wang, S.Q. Impacts of water transfer from the Yellow River on water environment in the receiving area of the Fenhe River. J. Nat. Resour. 2018, 33, 1416–1426. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.L. Snow Mountain Water Diversion Project in Australian. World Agric. 2001, 271, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.B.; Chen, Y.S.; Liu, H.; Lu, Y.; Qu, X.; Yuan, H.; Lek, S.; Xie, S.G. Modelling fish communities in relation to water quality in the impounded lakes of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Ecol. Model. 2019, 397, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zhou, X.X. Analysis on ecological impact identification and evaluation index system of inter basin water diversion project. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2017, 42, 190–194. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Li, M.J.; Lei, X.H.; Ni, Q.W.; Liu, Z.W. Spatiotemporal characteristics and potential pollution factors of water quality in the eastern route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project in China. J. Hydrol. 2024, 638, 131523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, C.Y.; Hu, W.Y.; Li, M.Y.; Ding, L. Spatial distribution and driving force analysis of soil heavy metals in the water source area of the middle route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 112126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Zeng, S.D.; Du, H.; Ren, Y.X.; Xia, J. Projected flow regimes and biodiversity changes under climate change in the planning western route source areas of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.S.; Zhang, J.P. Evaluation on coordinated development between economic society and ecological environment of water resources district of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. South North Water Divers. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 12, 113–116, 141. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, W. Eco-environmental impact of inter-basin water transfer projects: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 12867–12879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boros, A.; Gordos, B.; Tőzsér, D. A bibliometric analysis-based literature review of the relationship between sustainable water management and green innovations in the agricultural sector. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.W.; Dong, X.Q.; Li, X.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Lu, Y.S.; Yang, F. Research status and emerging trends in remediation of contaminated sites: A bibliometric network analysis. Environ. Rev. 2023, 31, 542–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.X.; Zeng, W.H.; Chen, J.J. Study on the carrying capacity of “ecology, environment and resources” based on visualization analysis. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 5031–5040. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, F.L.; Zhu, Y.; Ao, T.Q.; Chen, T. The development trend and research frontiers of distributed hydrological models--visual bibliometric analysis based on Citespace. Water 2021, 13, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Chen, Y.; Horowitz, M.; Hou, H.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Pellegrino, D. Towards an explanatory and computational theory of scientific discovery. J. Informetr. 2009, 3, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Liu, X.H.; Hussain, K.M.; Suraya, M.; Cabrera, J.; Zhang, P.P. The global research trend on cadmium in freshwater: A bibliometric review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 71585–71598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Ji, X.H.; Yun, C.L.; Wang, M.L.; Luo, X.G. The knowledge domain and emerging trends in phytoremediation: A scientometric analysis with CiteSpace. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 15515–15536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.M. Searching for intellectual turning points: Progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5303–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.M.; Shen, J.L.; Sun, Z.Q.; Ma, F.J.; Jones, K.C.; Gu, Q.B. A bibliometric analysis and assessment of priorities for heavy metal bioavailability research and risk management in contaminated land. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 2691–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Ilan, J. Which h-index? - A comparison of WoS, Scopus and Google Scholar. Scientometrics 2008, 74, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, P.; Rollason, E.; Bracken, L.J.; Wainwright, J.; Reaney, S.M. A new framework for integrated, holistic, and transparent evaluation of inter-basin water transfer schemes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.L.; Xiong, Z.Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, G.H.; Liu, W.Z. Distribution, source identification, and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in wetland soils of a river–reservoir system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 24, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Fan, W.W.; Yi, Y.J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.H. Evaluation method for regional water cycle health based on nature-society water cycle theory. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. The United Nations adopts “the Water Action Agenda”. Ecol. Econ. 2023, 39, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.J.; Liu, G.H.; Zhao, F.Z.; Fu, B.J. Eco-environmental benefit assessment of the western route in China’s South-North Water Transfer Project. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2005, 12, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.M.; Zhao, J.Z.; Liu, G.H.; Ke, B.; Xiao, H.; Wu, G.; Deng, H.B. Eco-environmental benefit assessment of China’s South-North Water Transfer Scheme--the middle route project. J. Environ. Sci. 2004, 16, 308–315. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.B.; Han, B.L.; Lu, F.; Gong, C.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Jiang, C.Q.; Zhang, X.L. Improving water efficiency is more effective in mitigating water stress than water transfer in Chinese cities. iScience 2024, 27, 109195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.H.; Guo, L.Q.; Huang, T.; Zhang, D.D.; Deng, Z.M.; Liu, L.S.; Yan, T. Hydro-environmental response to the inter-basin water resource development in the middle and lower Han River, China. Hydrol. Res. 2022, 53, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.M.; Niu, J.L.; Ling, M.H.; Wu, Z.N.; Yan, D.H. Quantitative study on eco-economic compensation for water rights trading along the South-to-North Water Diversion Project in China. Water Supply 2022, 22, 8893–8906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, J.F.; Yu, C.; Wang, Q.; Ding, T.H. Emergency risk assessment of sudden water pollution in South-to-North Water Diversion Project in China based on driving force–pressure–state–impact–response (DPSIR) model and variable fuzzy set. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 26, 20233–20253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.Y. Water Transfer Energy Efficiency Index for inter-basin water transfer projects. Water Environ. J. 2024, 38, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorg-Haddad, O.; Abutalebi, M.; Chu, X.F.; Loáiciga, H.A. Assessment of potential of intraregional conflicts by developing a transferability index for inter-basin water transfers, and their impacts on the water resources. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 192, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.; Li, X.Y.; Ma, Y.J.; Smith, A.; Wu, J.G. A review of the economic, social, and environmental impacts of China’s South–North Water Transfer Project: A sustainability perspective. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, X.P.; Fu, G.T.; Zhou, H.C.; Wang, H. The impacts of climate change on water diversion strategies for a water deficit reservoir. J. Hydroinform. 2014, 16, 872–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.L.; Liang, Z.M.; Li, B.Q.; Hu, Y.M.; Wang, J. Integrated impact assessment method for the water transfer project on regional development. J. Hydroinform. 2019, 21, 638–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.F.; Gao, B.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, D.Y.; Gao, L.; Sun, K. Pollution characteristics and source identification of trace metals in riparian soils of Miyun Reservoir, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 144, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Gao, B.; Yin, S.H.; Xu, D.Y.; Gao, J.J. Predicting Ni dynamic mobilization in reservoir riparian soils prior to water submergence using DGT and DIFS. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, N.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Liao, Y.; Cao, G.; Li, C.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Z. Eutrophication risk assessment considering joint effects of water quality and water quantity for a receiving reservoir in the South-to-North Water Transfer Project, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 331, 129966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.M.; Liang, Z.M.; Xiong, L.H.; Sun, L.; Wang, K.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Li, B.Q. Assessment on annual precipitation change in the headwater source of the middle route of China’s South to North Water Diversion Project. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 137, 2529–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Di, H.; Huang, Y.F.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Y. A comprehensive study of the impact of large-scale landscape pattern changes on the watershed ecosystem. Water 2021, 13, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.J.; Wu, C.G.; Ding, F.X.; Zhou, Z.X. Predicting basin water quality using source-sink landscape distribution metrics in the Danjiangkou Reservoir of China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.X.; Hou, K.; Tang, H.J.; Liu, J.W.; Wu, S.Q.; Li, X.X.; Sun, P.C. A new perspective on the whole process of ecological vulnerability analysis based on the EFP framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 139160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, L.F.; Liu, R.M.; Cao, L.P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Evaluating the impacts of inter-basin water transfer projects on ecosystem services in the Fenhe River Basin using the SWAT model. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.B.; Chen, Y.S.; Gozlan, R.E.; Liu, H.; Lu, Y.; Qu, X.; Xia, W.T.; Xiong, F.Y.; Xie, S.G.; Wang, L.Z. Patterns of fish communities and water quality in impounded lakes of China’s south-to-north water diversion project. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Zhang, W.S.; Zhao, Y.X.; Peng, H.; Shi, Y.Y. Modelling water quality and quantity with the influence of inter-basin water diversion projects and cascade reservoirs in the Middle-lower Hanjiang River. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 1348–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, B.H.; Liu, C.M.; Xia, J.; Liu, S.X. Runoff and its impacting factors in the water-exporting rivers of the First Stage Project of the South-to-North Water Transfer Scheme via the Western Route: A case study in Daqu. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2006, 26, 674–681. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.S.; Yang, X.H.; Wang, K.W.; Di, C.L.; Xiang, W.Q.; Zhang, J. Exploring China’s water scarcity incorporating surface water quality and multiple existing solutions. Environ. Res. 2024, 246, 118191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Yang, R. The economic impact of water diversion: Evidence from China. Water Supply 2024, 24, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Che, L.; Wang, Z.Z. Where are the critical points of water transfer impact on grain production from the middle route of the south-to-north water diversion project? J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 436, 140465. [Google Scholar]
- Matete, M.; Hassan, R. Integrated ecological economics accounting approach to evaluation of inter-basin water transfers: An application to the Lesotho Highlands Water Project. Ecol. Econ. 2006, 60, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumilova, O.; Tockner, K.; Thieme, M.; Koska, A.; Zarfl, C. Global water transfer megaprojects: A potential solution for the water-food-energy nexus? Front. Env. Sci. 2018, 6, 150. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.R.; Zhu, L.; Guo, L.; Luo, Y.; Du, D.; Sun, Y. Understanding the different responses from the similarity between displacement and groundwater level time series in Beijing, China. Nat. Hazards 2021, 111, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.Y.; Ge, L.; Ng, A.H.M.; Lian, X.G.; Zhu, Q.G.Z.; Horgan, F.G.; Zhang, Q. Analysis of the impact of the South-to-North water diversion project on water balance and land subsidence in Beijing, China between 2007 and 2020. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.C.; Wang, Y.P.; Balz, T. Beijing land subsidence revealed using PS-InSAR with long time series TerraSAR-X SAR data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.B.; Zhou, J.; Xu, S.Y.; Chen, Z.L.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.Q.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.F.; Meng, W.Q. Assessment of hazards and economic losses induced by land subsidence in Tianjin Binhai new area from 2011 to 2020 based on scenario analysis. Nat. Hazards 2013, 66, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.J.; Liu, R.M.; Wang, L.F.; Li, L.; Cao, L.P. Evaluating Spatiotemporal Variations in the Impact of Inter-basin Water Transfer Projects in Water-receiving Basin. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 5409–5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.Y.; Yang, L.W.; Wang, L.Y.; Yang, R.; Chen, S.Y. Water environment quality of Dongyu River and estuary area of Nansi lake (Shandong Province, China) based on the characteristics of diatom community. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2023, 38, 2274349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Wang, C.L.; Zhang, C.M.; Liang, J.K.; Mi, W.J.; Song, G.F.; Zhu, Y.X.; Wang, S.L.; Shang, Y.M.; Bi, Y.H. Water quality variation in the middle route of South-to-North Water Diversion Project, China. Front. Env. Sci. 2023, 11, 945884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Chen, Y.S.; Liu, H.; Xia, W.T.; Lu, Y.; Gang, D.D.; Lin, L.S. A holistic assessment of water quality condition and spatiotemporal patterns in impounded lakes along the eastern route of China’s South-to-North water diversion project. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; She, D.X. Assessing the influence of climate change and inter-basin water diversion on Haihe River basin, eastern China: A coupled model approach. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1455–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.R.; Zhang, J.Y.; Yuan, S.S.; Wang, G.Q. Impact of Climate Change on Water Resources in the Western Route Areas of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadem, M.; Dawson, R.J.; Walsh, C.L. The feasibility of inter-basin water transfers to manage climate risk in England. Clim. Risk Manag. 2021, 33, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Caldwell, P.V.; Sun, G.; McNulty, S.G.; Qin, Y.; Chen, X.H.; Liu, N. Climate change challenges efficiency of inter-basin water transfers in alleviating water stress. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 044050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.D.; Guo, S.L.; Shao, Q.X.; Liu, P.; Xiong, L.H.; Wang, L.; Hong, X.J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Assessing the effects of adaptation measures on optimal water resources allocation under varied water availability conditions. J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 759–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Fakhreddine, S.; Rateb, A.; Graaf, I.D.; Famiglietti, J.; Gleeson, T.; Grafton, R.Q.; Jobbagy, E.; Kebede, S.; Kolusu, S.R.; et al. Global water resources and the role of groundwater in a resilient water future. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 351. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; He, W.B.; Shen, Y.F.; Yan, T.S.; Liu, C.; Yang, Z.Z.; Han, J.M.; Xie, W.S. Ecological security evaluation and early warning in the water source area of the Middle Route of South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 868, 161561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.W.; Liu, W.D.; Zhu, M.Y.; Ma, Y.F.; Li, Z.M. A priority-based multi-objective framework for water resources diversion and allocation in the middle route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Socio. Econ. Plan. Sci. 2021, 78, 101085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Gao, M.L.; Chen, Z.; Lyu, M.Y.; Gong, H.L.; Zhai, Y.Z.; Pan, Y. Land subsidence in Beijing: Response to the joint influence of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project and ecological water replenishment, observed by satellite radar interferometry. GISci. Remote Sens. 2024, 61, 2315708. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Duan, B.S.; He, S.Y.; Lu, Y.H. Simulation study on the impact of ecological water replenishment on reservoir water environment based on Mike21-Taking Baiguishan reservoir as an example. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108802. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, H.F.; Yang, W.; Xing, L.M.; Tu, G.Q.; Ru, Z.M.; Xu, Z.H. The assessment of ecological water replenishment scheme based on the two-dimensional lattice-Boltzmann water age theory. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2022, 25, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, J.P.; Cohen Liechti, T.; Boillat, J.L.; Schleiss, A.; Portela, M.M. Analysis of flow regime changes due to operation of large reservoirs on the Zambezi River. In Environmental Hydraulics: Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Environmental Hydraulic; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, S.J.; Zhou, Y.R.; Ma, G.W.; Huang, W.B.; Zhu, Y.M. Method for quantitatively assessing the impact of an inter-basin water transfer project on ecological environment-power generation in a water supply region. J. Hydrol. 2023, 618, 129250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.Z.; Bai, T.; Huang, Q. Tradeoff analysis between economic and ecological benefits of the inter basin water transfer project under changing environment and its operation rules. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.Q.; Li, X.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Croke, B.F.W.; Jakeman, A.J. Water-energy-ecosystem nexus modeling using multi-objective, non-linear programming in a regulated river: Exploring tradeoffs among environmental flows, cascaded small hydropower, and inter-basin water diversion projects. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 308, 114582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkara, S.V.; Singh, R. Assessing the impact of the temporal resolution of performance indicators on optimal decisions of a water resources system. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Lei, X.H.; Long, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Yao, Y.; Hou, X.S.; Shi, M.S.; Wang, P.W.; Zhang, C.L.; et al. A novel comprehensive risk assessment method for sudden water accidents in the Middle Route of the South–North Water Transfer Project (China). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.G.; Guo, B.T.; Duan, G.Y.; Yang, L.B. Analysis on the effect of the first phase water transfer of the West Route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project on cascade power generation of Yellow River. Water Power 2020, 46, 90–92, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, M.J.; Huang, Q.; Chang, J.X.; Huang, S.Z.; Guo, A.J. Connotation, process and dimensionality of generalized ecological water conservancy. Adv. Water Sci. 2020, 31, 775–792. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.N.; Gao, J.F. Comprehensive assessment of eco-environment impact of the South-to-North Water Transfer Middle Route Project on the middle-lower Hanjiang River Basin. Prog. Geogr. 2010, 29, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Karamouz, M.; Mojahedi, S.A.; Ahmadi, A. Interbasin water transfer: Economic water quality-based model. J. Irrig. Drain. Div. 2010, 136, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.S.; Ma, J.X.; Zuo, Q.T.; Han, S.Y. Quantitative analysis on harmony degree of water resources-economic society-ecological environment coupling system in the Tarim River Basin. Water Resour. Prot. 2021, 37, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, J.H.; Mei, C.; Wang, H.; Shao, W.W. Water security evaluation based on comprehensive index in Jing-Jin-Ji district, China. Water Supply 2020, 20, 2698–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ranking | Journal Title | Category | IF | H-Index | TLCS | TGCS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | WATER | WATER RESOURCES | 3.3 | 33 | 0 | 173 |
| 2 | SCIENCE OF THE TOTAL ENVIRONMENT | ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES | 8.7 | 205 | 41 | 957 |
| 3 | JOURNAL OF HYDROLOGY | GEOSCIENCE—MULTIPLE EARTH SCIENCE | 6.9 | 192 | 38 | 854 |
| 4 | JOURNAL OF CLEANER PRODUCTION | ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES | 10.7 | 150 | 8 | 505 |
| 5 | SUSTAINABILITY | ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES | 3.6 | 53 | 0 | 196 |
| 6 | ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE AND POLLUTION RESEARCH | ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES | 5.8 | 82 | 69 | 474 |
| 7 | ECOLOGICAL INDICATORS | ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES | 7.2 | 97 | 11 | 273 |
| 8 | JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT | ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES | 8.6 | 146 | 3 | 345 |
| 9 | REMOTE SENSING | REMOTE SENSING | 4.8 | 81 | 1 | 129 |
| 10 | WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT | ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE—ENGINEERING/CIVIL ENGINEERING | 4.2 | 82 | 29 | 191 |
| Ranking | Countries/Regions | Count | Centrality | Countries/Regions | Centrality | Count |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CHINA | 424 | 1.11 | CHINA | 1.11 | 424 |
| 2 | USA | 57 | 0.34 | USA | 0.34 | 57 |
| 3 | AUSTRALIA | 29 | 0.03 | CANADA | 0.17 | 12 |
| 4 | ENGLAND | 19 | 0.07 | THE NETHERLANDS | 0.15 | 9 |
| 5 | CANADA | 12 | 0.17 | SOUTH AFRICA | 0.09 | 11 |
| 6 | SOUTH AFRICA | 11 | 0.09 | FRANCE | 0.09 | 3 |
| 7 | IRAN | 10 | 0.07 | SWEDEN | 0.08 | 6 |
| 8 | THE NETHERLANDS | 9 | 0.15 | ENGLAND | 0.07 | 19 |
| 9 | SPAIN | 7 | 0.01 | IRAN | 0.07 | 10 |
| 10 | SWEDEN | 6 | 0.08 | AUSTRALIA | 0.03 | 29 |
| Ranking | Institutions | Count | Centrality | Institutions | Centrality | Count |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chinese Academy of Sciences | 93 | 0.46 | Chinese Academy of Sciences | 0.46 | 93 |
| 2 | China Institute of Water Resources & Hydropower Research | 62 | 0.16 | China Institute of Water Resources & Hydropower Research | 0.16 | 62 |
| 3 | Hohai University | 53 | 0.11 | Wuhan University | 0.14 | 36 |
| 4 | Beijing Normal University | 46 | 0.13 | Beijing Normal University | 0.13 | 46 |
| 5 | Wuhan University | 36 | 0.14 | Hohai University | 0.11 | 53 |
| 6 | Institute of Geographic Sciences & Natural Resources Research | 28 | 0.05 | University of California System | 0.10 | 12 |
| 7 | University of Chinese Academy of Sciences | 27 | 0.03 | Institute of Geographic Sciences & Natural Resources Research | 0.05 | 28 |
| 8 | Tianjin University | 21 | 0.03 | Peking University | 0.05 | 15 |
| 9 | Tsinghua University | 18 | 0.04 | China Agricultural University | 0.05 | 11 |
| 10 | North China University of Water Resources & Electric Power | 16 | 0.03 | Texas A&M University System | 0.05 | 4 |
| Ranking | Subject Categories | Count | Centrality | Subject Categories | Centrality | Count |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES | 282 | 0.45 | ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES | 0.45 | 282 |
| 2 | WATER RESOURCES | 181 | 0.23 | WATER RESOURCES | 0.23 | 181 |
| 3 | ENGINEERING, ENVIRONMENTAL | 67 | 0.04 | COMPUTER SCIENCE, INTERDISCIPLINARY APPLICATIONS | 0.21 | 10 |
| 4 | GEOSCIENCES, MULTIDISCIPLINARY | 62 | 0.02 | ENGINEERING, CIVIL | 0.20 | 59 |
| 5 | ENGINEERING, CIVIL | 59 | 0.20 | ECONOMICS | 0.17 | 7 |
| 6 | GREEN AND SUSTAINABLE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY | 52 | 0.01 | ENGINEERING, MULTIDISCIPLINARY | 0.15 | 10 |
| 7 | ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES | 36 | 0.07 | ENGINEERING, ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC | 0.15 | 8 |
| 8 | BIODIVERSITY CONSERVATION | 22 | 0.00 | COMPUTER SCIENCE, ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE | 0.11 | 5 |
| 9 | ECOLOGY | 19 | 0.05 | OPERATION RESEARCH AND MANAGEMENT SCIENCE | 0.10 | 5 |
| 10 | REMOTE SENSING | 18 | 0.00 | PUBLIC, ENVIRONMENTAL AND OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH | 0.08 | 13 |
| Subject Categories | Strength | Begin | End | 2002–2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENGINEERING, MULTIDISCIPLINARY | 4.16 | 2010 | 2017 |  |
| GEOSCIENCES, MULTIDISCIPLINARY | 3.09 | 2021 | 2022 |  |
| MATERIALS SCIENCE, MULTIDISCIPLINARY | 2.97 | 2010 | 2013 |  |
| ECOLOGY | 2.84 | 2012 | 2016 |  |
| COMPUTER SCIENCE, INTERDISCIPLINARY APPLICATIONS | 2.00 | 2007 | 2011 |  |
| GREEN AND SUSTAINABLE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY | 1.87 | 2017 | 2019 |  |
| ENGINEERING, MECHANICAL | 1.85 | 2011 | 2013 |  |
| ENGINEERING, ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC | 1.82 | 2009 | 2010 |  |
| MANAGEMENT | 1.67 | 2010 | 2016 |  |
| TOXICOLOGY | 1.65 | 2017 | 2018 |  |
| GEOGRAPHY | 1.6 | 2017 | 2020 |  |
| ENERGY AND FUELS | 1.6 | 2010 | 2015 |  |
| BUSINESS, FINANCE | 1.57 | 2010 | 2015 |  |
| GEOCHEMISTRY AND GEOPHYSICS | 1.51 | 2022 | 2024 |  |
| ENGINEERING, CIVIL | 1.33 | 2012 | 2014 |  |
| ENGINEERING, BIOMEDICAL | 1.32 | 2009 | 2010 |  |
| MATHEMATICS, APPLIED | 1.29 | 2009 | 2011 |  |
| MINING AND MINERAL PROCESSING | 1.26 | 2012 | 2013 |  |
| COMPUTER SCIENCE, ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE | 1.19 | 2014 | 2017 |  |
| ECONOMICS | 1.18 | 2006 | 2007 |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, T.; Jing, L.; Yan, D.; Lu, Y.; Fan, X. Research Status and Emerging Trends in the Comprehensive Impact of Inter-Basin Water Transfer Projects (IBWTs). Water 2025, 17, 2981. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202981
Han T, Jing L, Yan D, Lu Y, Fan X. Research Status and Emerging Trends in the Comprehensive Impact of Inter-Basin Water Transfer Projects (IBWTs). Water. 2025; 17(20):2981. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202981
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Tao, Laihong Jing, Dengming Yan, Yisi Lu, and Xinying Fan. 2025. "Research Status and Emerging Trends in the Comprehensive Impact of Inter-Basin Water Transfer Projects (IBWTs)" Water 17, no. 20: 2981. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202981
APA StyleHan, T., Jing, L., Yan, D., Lu, Y., & Fan, X. (2025). Research Status and Emerging Trends in the Comprehensive Impact of Inter-Basin Water Transfer Projects (IBWTs). Water, 17(20), 2981. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202981





