Integrated Assessment of Anthropogenic Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Inputs: A Panjin City Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Developed Framework Model for Net Anthropogenic C, N, and P Inputs
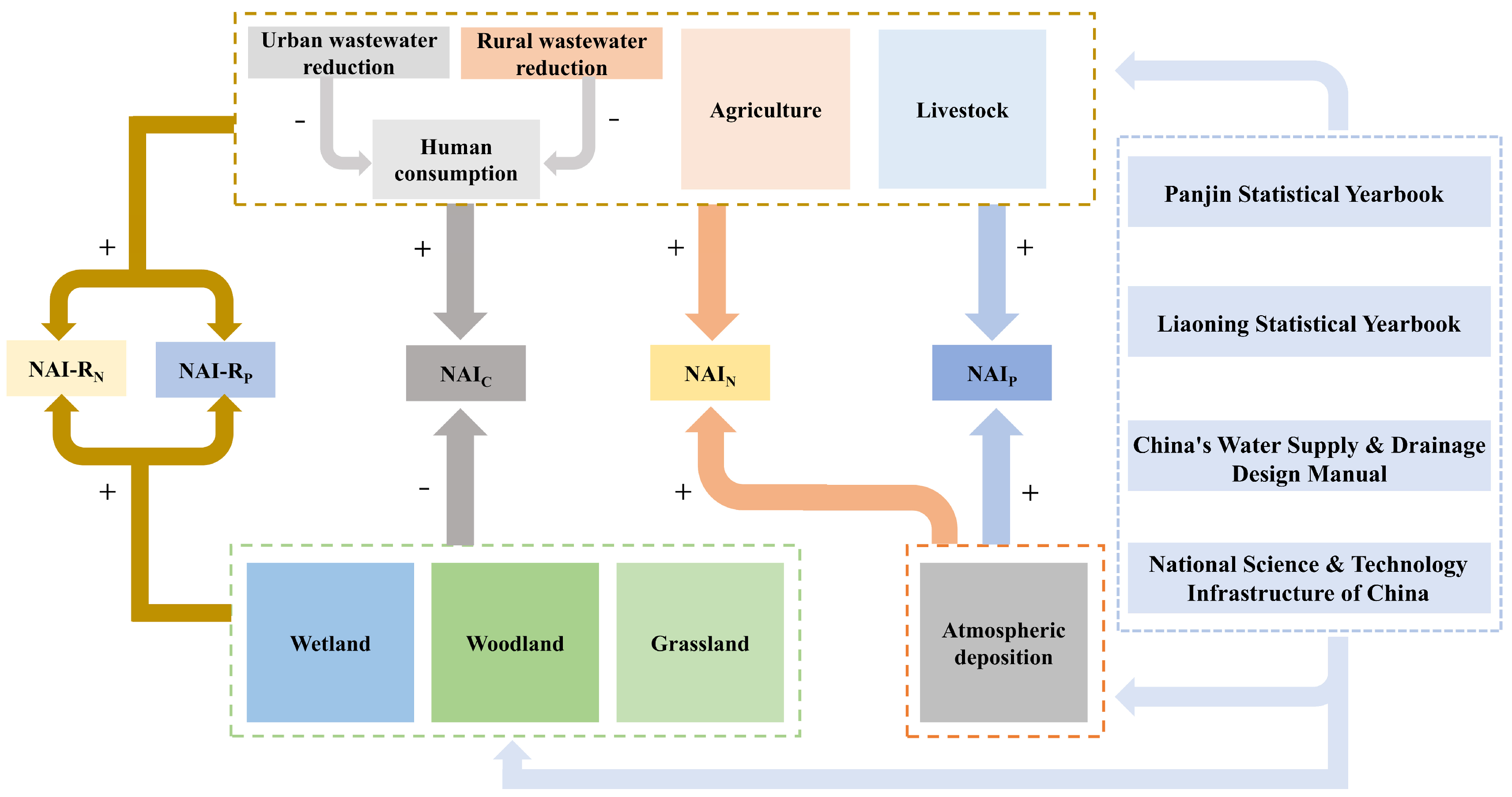
2.2.1. Framework Model
2.2.2. Human Consumption (HI)
2.2.3. Agricultural Production (AI)
2.2.4. Livestock (LI)
2.2.5. Atmospheric Deposition
2.2.6. Forests, Grasslands, and Wetlands
2.3. Comprehensive Environmental Impact Assessment Model for Anthropogenic C, N, and P Inputs
- 1.
- When a = 1 and p = 1, the relative membership degree of sample j is represented by the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model.
- 2.
- When a = 1 and p = 2, the relative membership degree of sample j is determined by the TOPSIS ideal point model.
- 3.
- When a = 2 and p = 1, the relative membership degree of sample j is represented by the incentive function model.
- 4.
- When a = 2 and p = 2, the relative membership degree of sample j is defined by the fuzzy optimization model.
2.4. Log-Mean Divisia Index Model
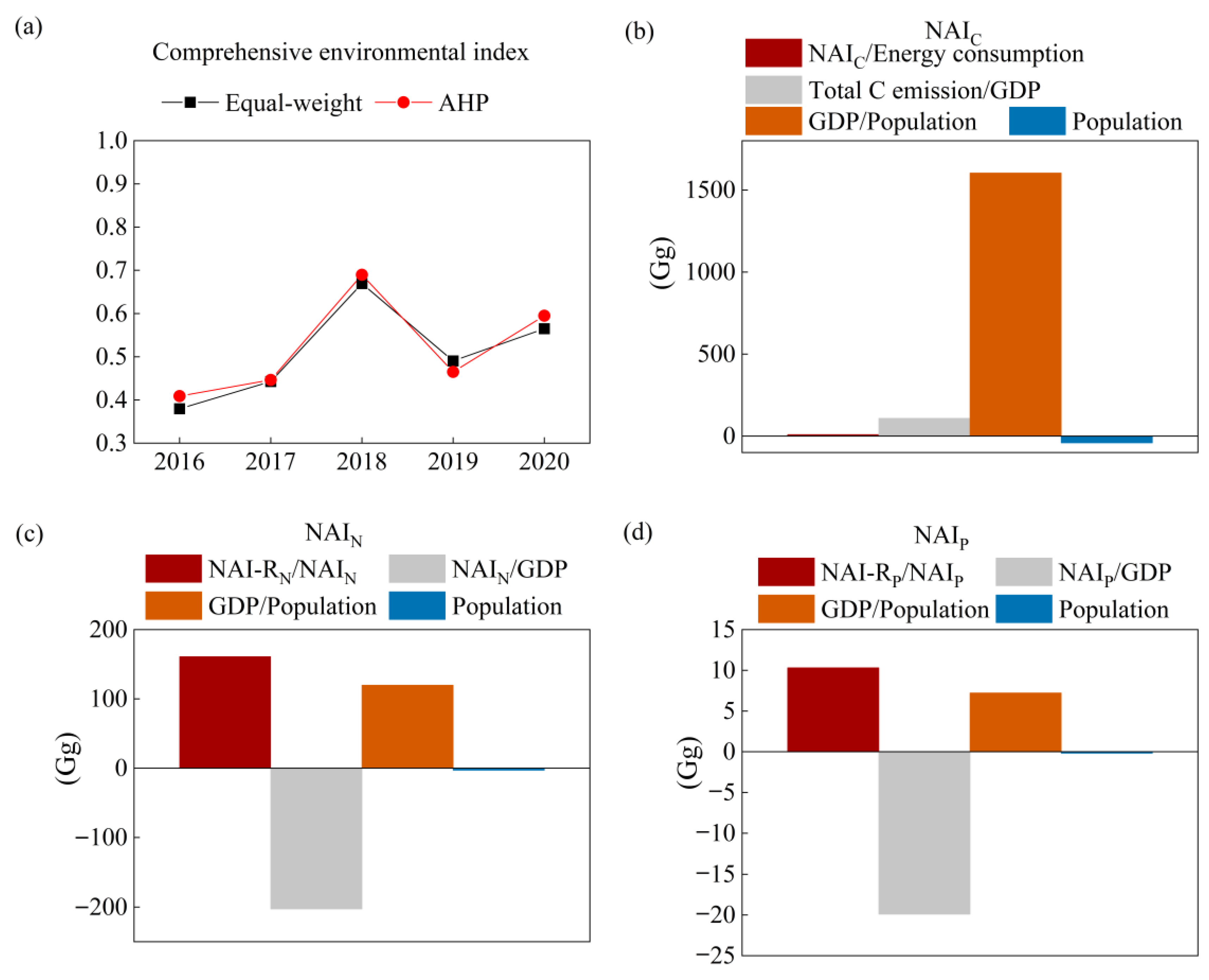
3. Results
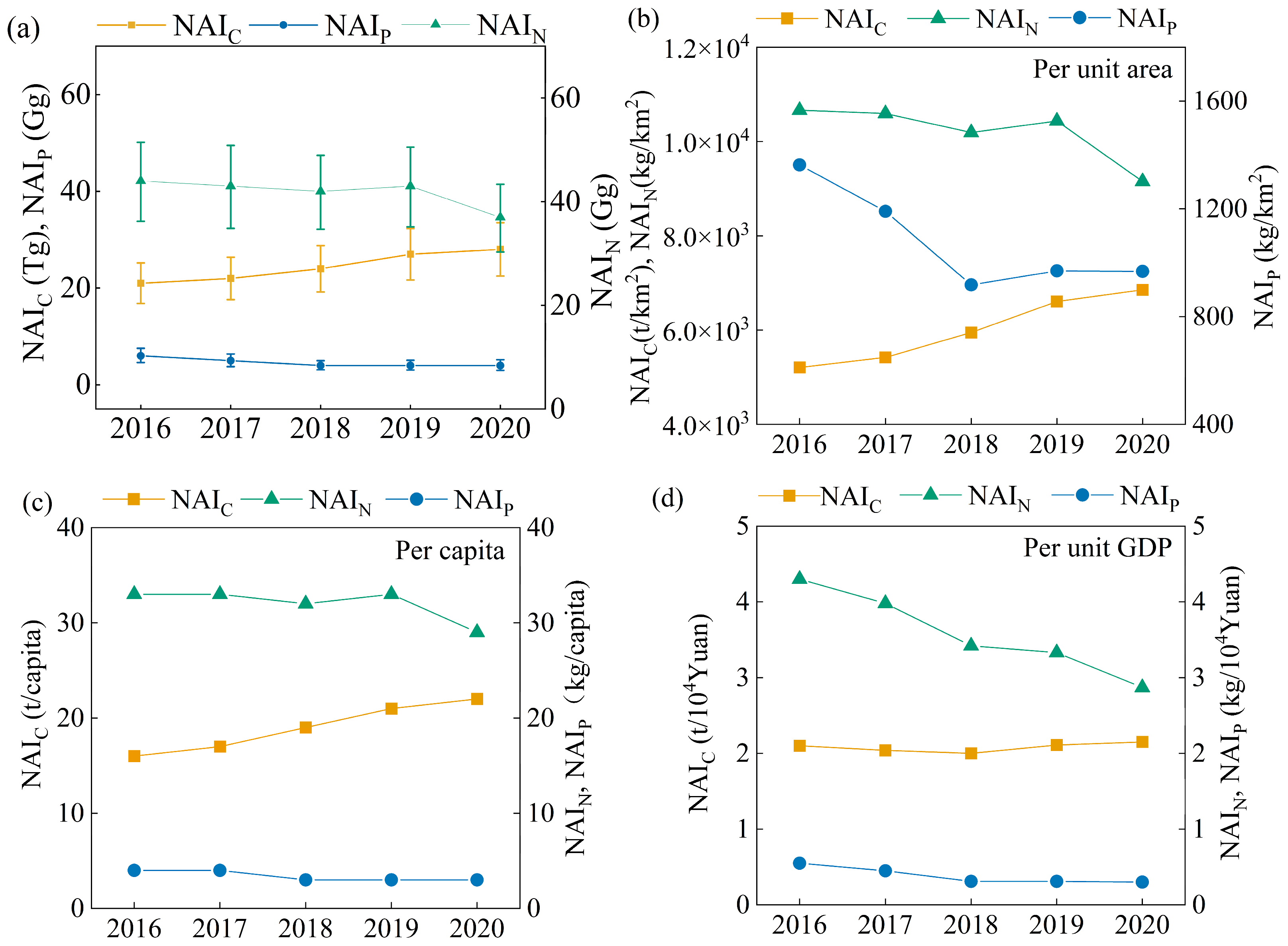
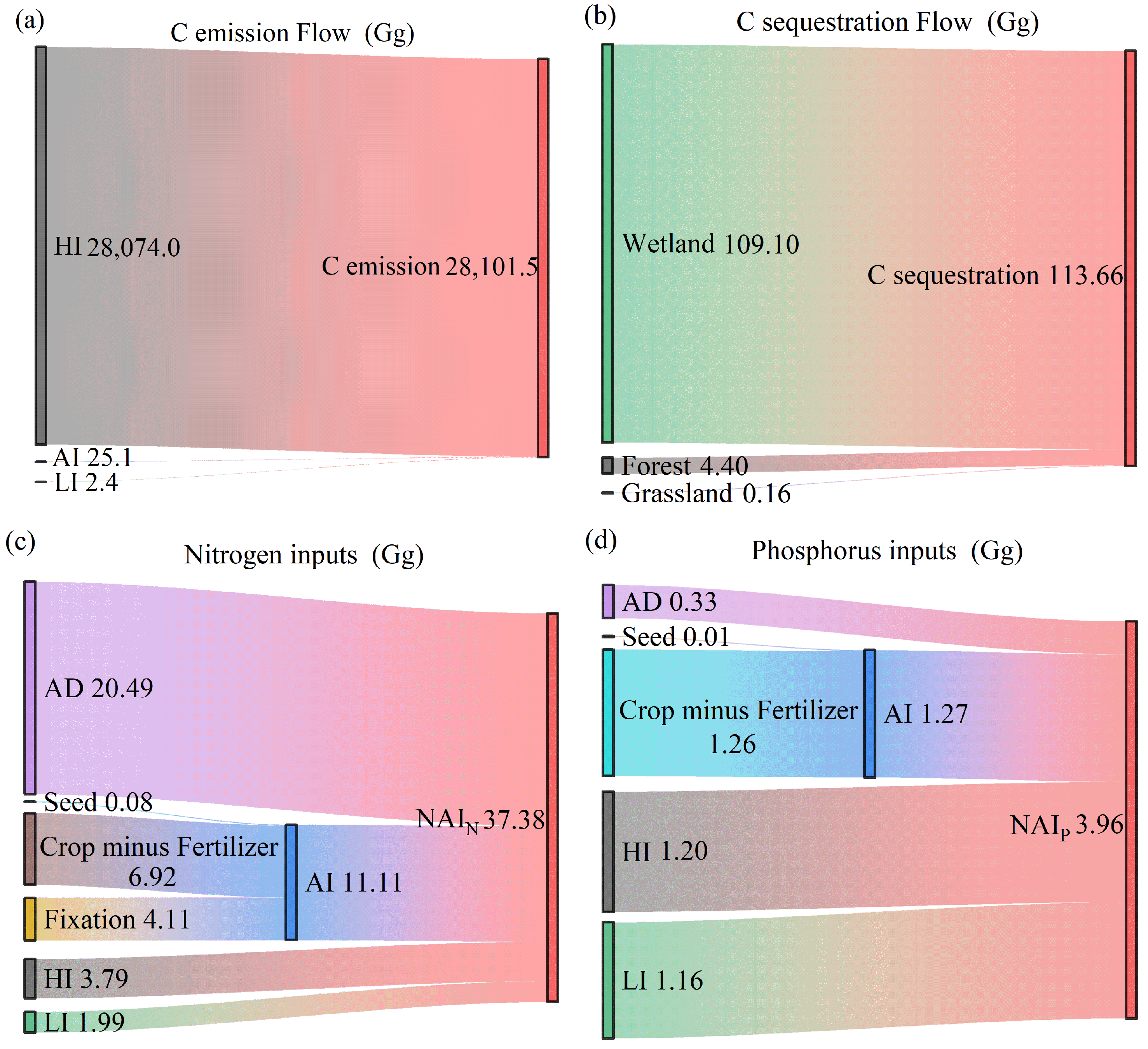
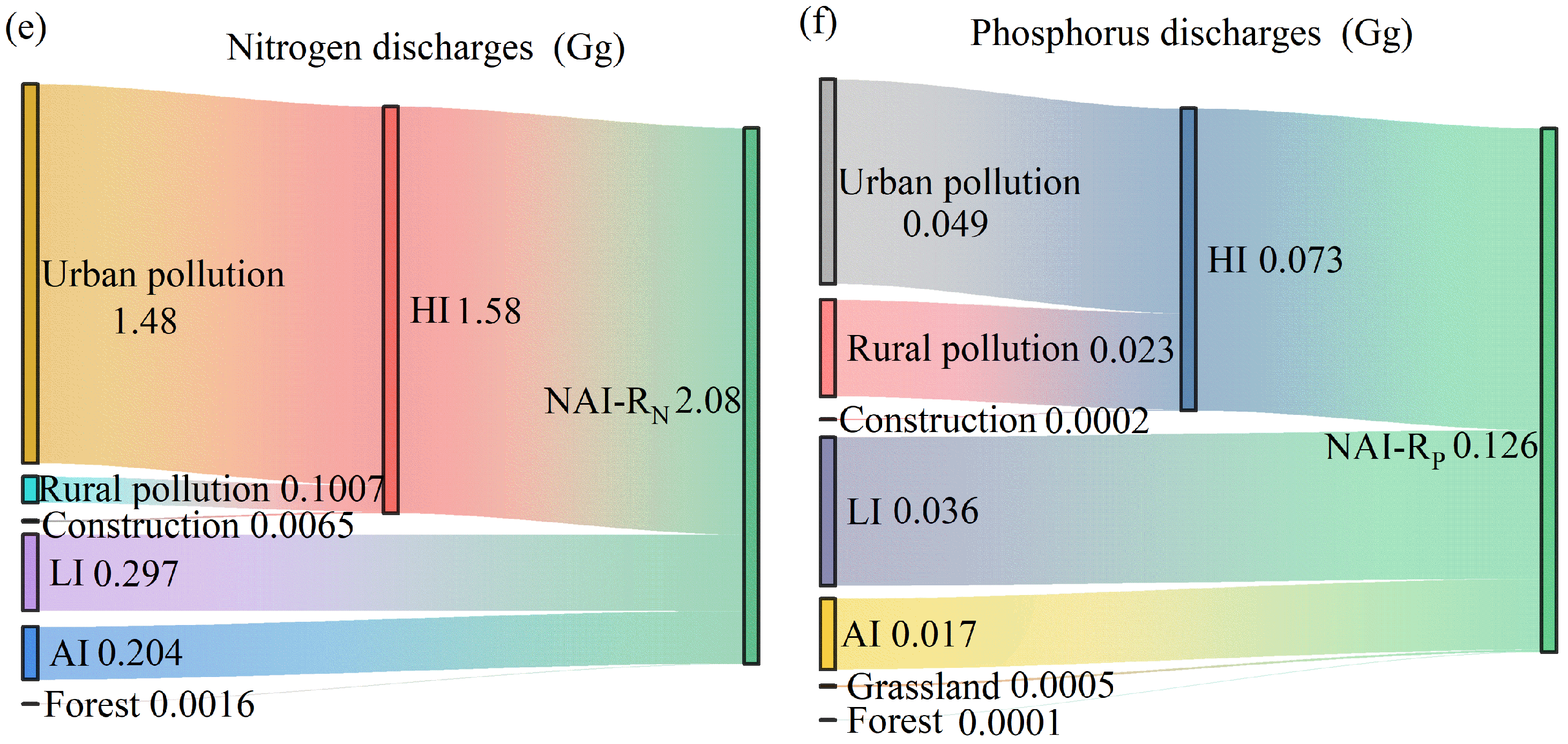
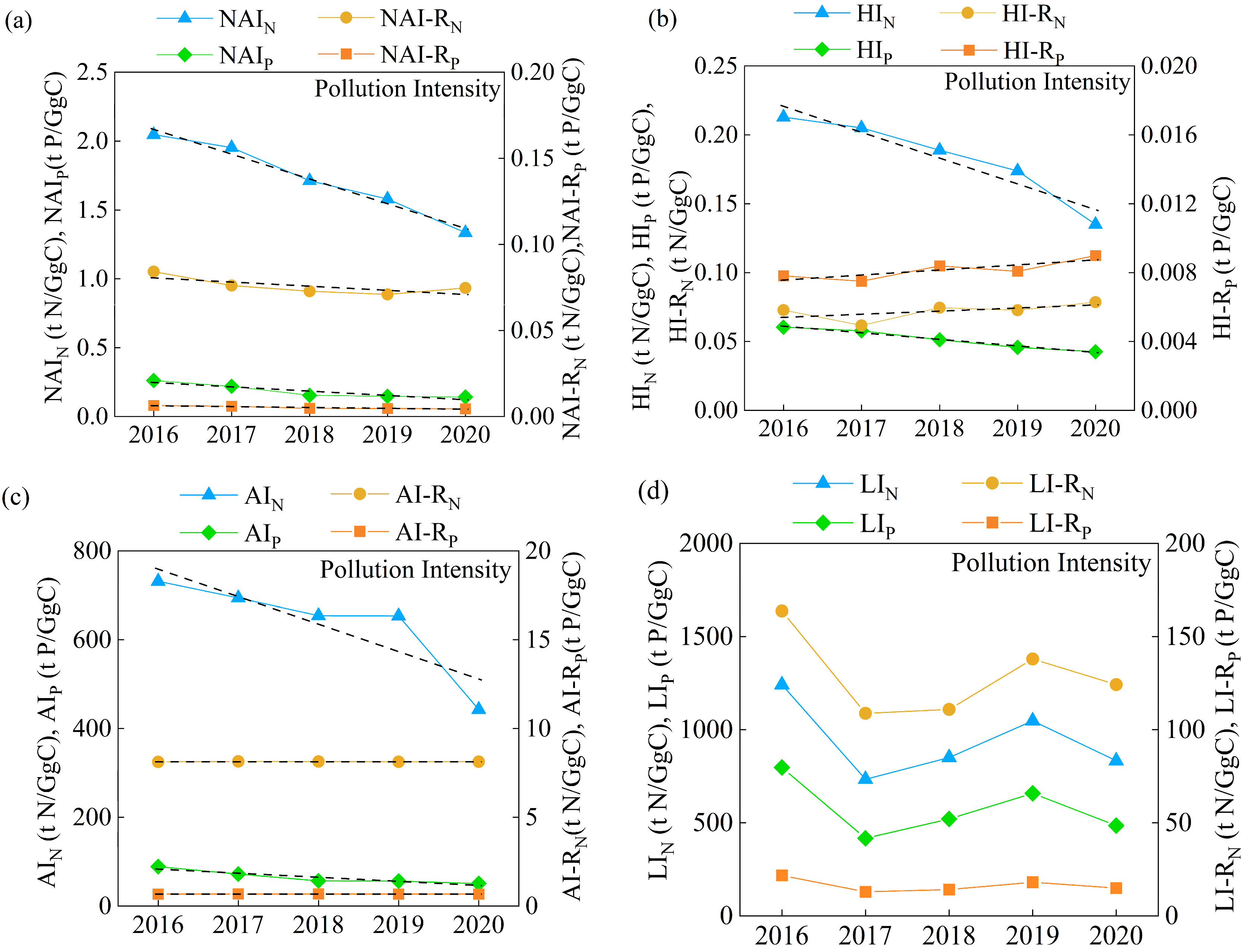
3.1. Dynamic Changes in Net Anthropogenic C, N, and P Inputs
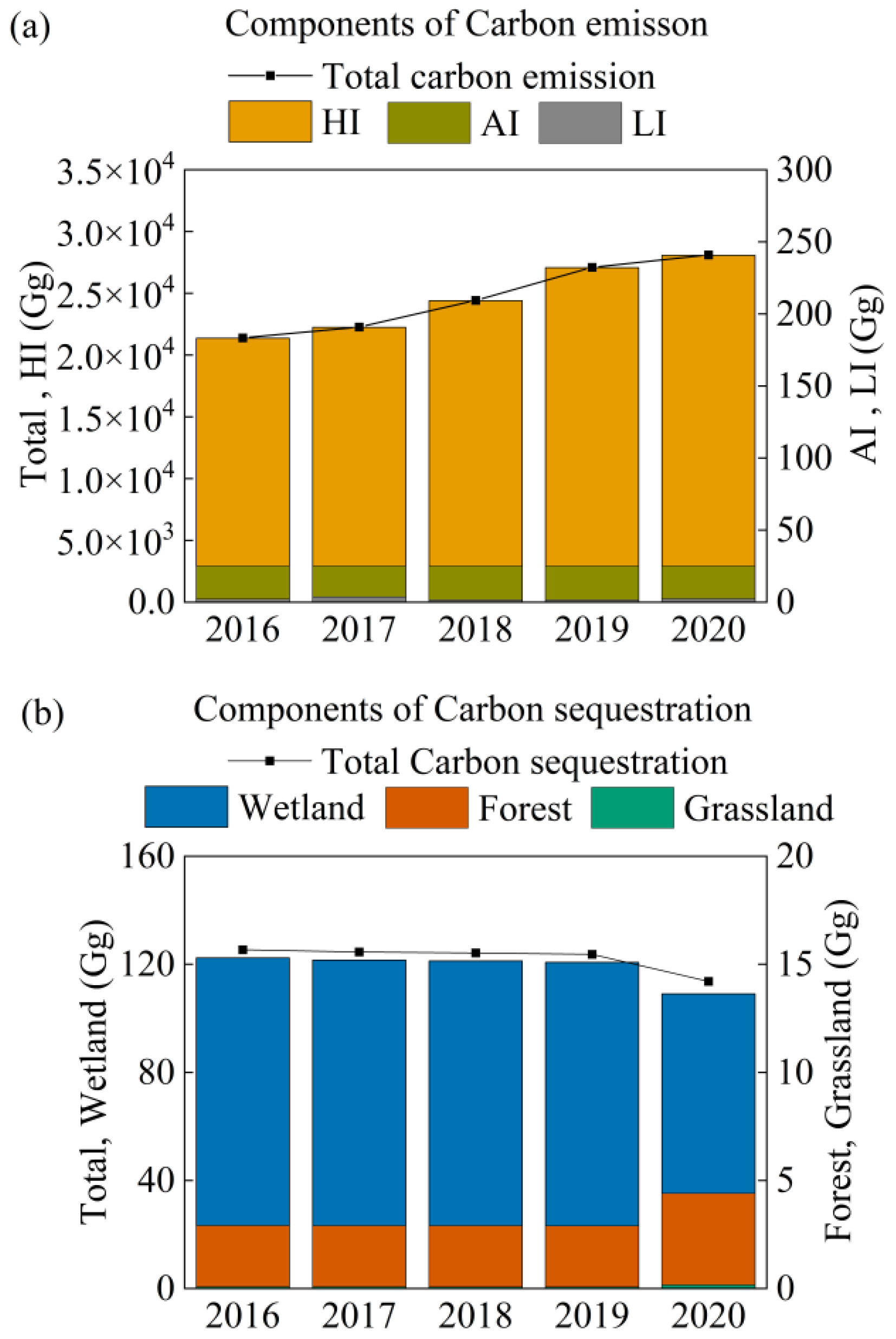
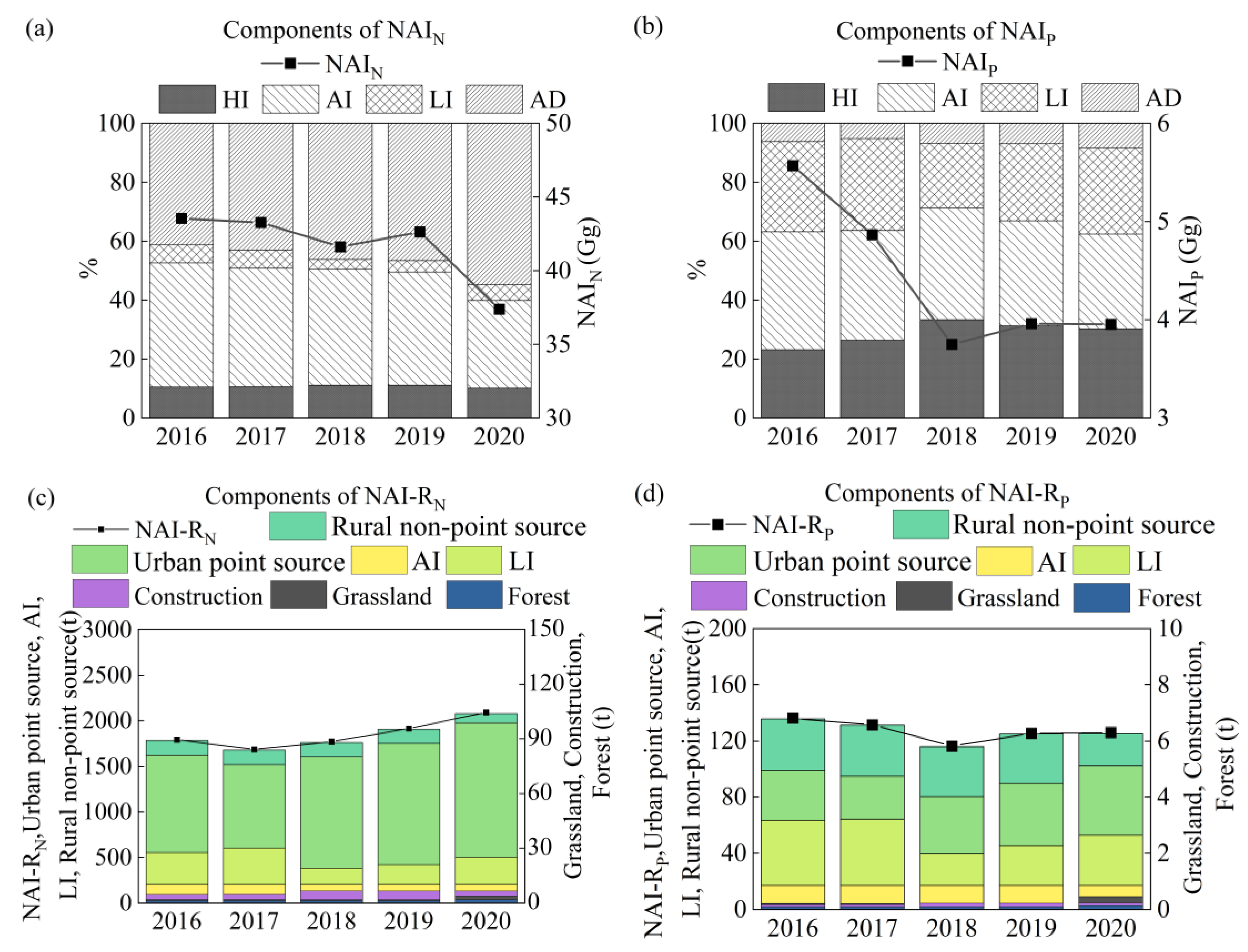
3.2. Components and Environmental Impacts of Net Anthropogenic Pollutant Inputs
4. Discussion
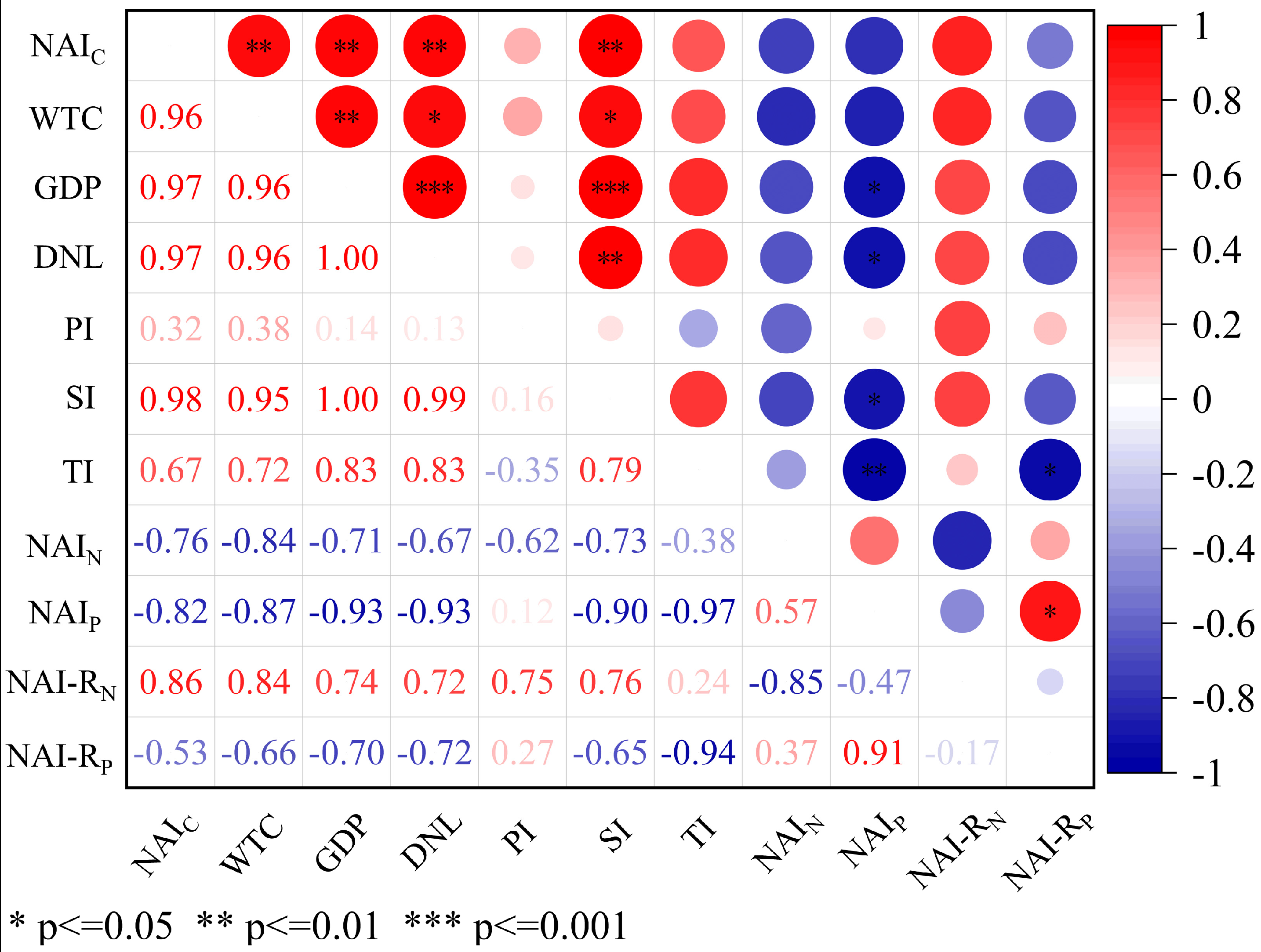
4.1. Associations of Net Anthropogenic C, N, and P Inputs
4.2. Comprehensive Assessment and Identification of Driving Forces
4.3. Management Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kanter, D.R.; Brownlie, W.J. Joint nitrogen and phosphorus management for sustainable development and climate goals. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 92, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonchyk, M.; Peterson, M.P.; Zhang, L.; Hurynovich, V.; He, Y. Greenhouse gases emissions and global climate change: Examining the influence of CO2, CH4, and N2O. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 935, 173359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, C.; Brutschin, E.; Drouet, L.; Luderer, G.; van Ruijven, B.; Reis, L.A.; Baptista, L.B.; de Boer, H.-S.; Cui, R.; Daioglou, V.; et al. Author Correction: Feasibility of peak temperature targets in light of institutional constraints. Nat. Clim. Change 2025, 15, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Zhang, Z.; Song, X.; Peng, D.; Zhao, C.; Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Shen, P.; Xie, M. Nitrogen-derived environmental behavior, economic performance, and regulation potential by human production and consumption in a mega river basin. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penuelas, J.; Sardans, J. Human-driven global nutrient imbalances increase risks to health. Eco-Environ. Health 2023, 2, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Guan, Y.; Oldfield, J.; Guan, D.; Shan, Y. China carbon emission accounts 2020–2021. Appl. Energy 2024, 360, 122837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Qi, L. Empirical decomposition and peaking path of carbon emissions in resource-based areas. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 395, 136372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Xie, T.; Zhang, W.; Wu, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, X.; Ma, X.; Wu, M.; Luo, P. Rasterizing CO2 emissions and characterizing their trends via an enhanced population-light index at multiple scales in China during 2013–2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liang, H.; Wu, Z.; Xie, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, B.; Wan, W. Comprehensive assessment of refined greenhouse gas emissions from China’s livestock sector. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluko, O.O.; Liu, Z.; Sun, X. The interplay of carbon and nitrogen distribution: Prospects for improved crop yields. Mod. Agric. 2023, 1, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, W.; Jiang, H.; Cao, D. Agricultural Methane Emissions in China: Inventories, Driving Forces and Mitigation Strategies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 13292–13303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Guo, Y.; Wang, M.; Brachhold, K.; Chu, C.; Hanson, A.; Kumar, S.; Lin, R.; Long, W.; et al. 100 essential questions for the future of agriculture. Mod. Agric. 2023, 1, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Ying, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, K. A review of mitigation technologies and management strategies for greenhouse gas and air pollutant emissions in livestock production. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 352, 120028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, C. Atmospheric remote sensing for anthropogenic methane emissions: Applications and research opportunities. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Duan, X.; Li, P.; Wang, L. Spatiotemporal intensification of net anthropogenic nitrogen input driven by human activities in China from 1990 to 2020. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Liu, X.; Lei, Q.; Luo, J.; Di, H.; Du, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Net Anthropogenic Phosphorus Inputs (NAPIs) and Their Impacts in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Using Monte Carlo Simulations and Sensitivity Analysis. Water 2024, 16, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.; Bi, Y.; Song, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, G.; Ma, G.; Abbaspour, K.C.; Yang, H. The response of non-point source pollution to land use change and risk assessment based on model simulation and grey water footprint theory in an agricultural river basin of Yangtze River, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Zhonghua, Y.; Wei, Y.; Minghui, Y.; Fengpeng, B.; Yao, Y.; Yufeng, R. Tracing the sources and transport of the total phosphorus in the upper Yangtze River. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 77, 102230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Hu, S.; Gao, S. Dynamic spatiotemporal change of net anthropogenic phosphorus inputs and its response of water quality in the Liao river basin. Chemosphere 2023, 331, 138757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Maqsood, A.; Li, M. Rapid urbanization decelerates regional net anthropogenic phosphorus input: Evidence from the Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 374, 124171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Zhao, H.; Luo, W.; Guo, Y.; Ji, X.; Hu, W. Dynamic characteristics of net anthropogenic phosphorus input to the upper Yangtze River Basin from 1989 to 2019: Focus on the phosphate ore rich area in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gu, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Shao, D. Influence of anthropogenic nitrogen inputs and legacy nitrogen change on riverine nitrogen export in areas with high agricultural activity. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 338, 117833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qi, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Yin, Q. Assessing the response of non-point source nitrogen pollution to land use change based on SWAT model. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Liu, L.; Peng, D.; Li, H.; Zhao, Z.; Lyu, C.; Zhang, Z. Net anthropogenic nitrogen and phosphorus inputs in the Yangtze River economic belt: Spatiotemporal dynamics, attribution analysis, and diversity management. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, P.; Dai, S.; Han, Y. Analysis of non-point source nitrogen pollution in watersheds based on SWAT model. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kaluskar, S.; Mugalingam, S.; Blukacz-Richards, A.; Long, T.; Morley, A.; Arhonditsis, G.B. A Bayesian approach for estimating phosphorus export and delivery rates with the SPAtially Referenced Regression On Watershed attributes (SPARROW) model. Ecol. Inform. 2017, 37, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, J.; Yin, L.; Song, B. Spatio-temporal variation and influencing factors of industrial carbon emission effect in China based on water-land-energy-carbon nexus. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 152, 110307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, C.; Cheng, Z. Attribution of climate change and human activities to vegetation NDVI in Jilin Province, China during 1998–2020. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. Ministry of Ecology and Environment, People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T.; Shumin, M.; Hu, S.; Gao, S.; Ye, L.; Runfa, C.; Arhonditsis, G. Evaluation of the role of urban domestic wastewater treatment systems for greenhouse gases emissions in China. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 81, 102571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Matsumoto, K. Drivers of the change in carbon dioxide emissions under the progress of urbanization in 30 provinces in China: A decomposition analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 322, 129000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Xue, M.; Peng, M.; Wang, C. Impact of spatial structure of urban agglomeration on carbon emissions: An analysis of the Shandong Peninsula, China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 161, 120313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yi, Y.; Yang, Z. Nitrogen and phosphorus retention budgets of a semiarid plain basin under different human activity intensity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Deng, C. Changes in net anthropogenic nitrogen and phosphorus inputs in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China (1999–2018). Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, F.; Du, S. Assessment and analysis of non-point source nitrogen and phosphorus loads in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area of Hubei Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 412–413, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, D.; Hu, Z.; Yang, Y.; He, S. Research on the Relationship between Agricultural Carbon Emission Intensity, Agricultural Economic Development and Agricultural Trade in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Cui, B.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Yao, L. Source apportionment of nitrogen and phosphorus from non-point source pollution in Nansi Lake Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 19101–19113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Pei, X.; Zhou, L. Trend and inequality in livestock CO2 emission intensity: Evidence from 341 prefecture-level cities from 2006 to 2022 in China. Environ. Res. 2025, 284, 122209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J. A Leading Role of Water Resources and Animal Husbandry in Environmental Sustainability: A Case Study of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 72146–72159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.; Wang, S.; Wang, A.; Yang, D.; Tang, L. Spatiotemporal characteristics of nonpoint source nutrient loads and their impact on river water quality in Yancheng city, China, simulated by an improved export coefficient model coupled with grid-based runoff calculations. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Qin, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Q. Evaluation of crop residues and manure production and their geographical distribution in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, P.; Liu, Q.; Zhan, S. Forest carbon storage in China from 2003 to 2021: Estimation based on the volume-derived carbon storage model with scale-compatible and tree species-merged. Forest. Ecol. Manag. 2025, 578, 122483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xu, M. Assessing the Sustainability Impact of Land-Use Changes and Carbon Emission Intensity in the Loess Plateau. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Chen, L.; Sun, R.; Jing, Y. An improved export coefficient model to estimate non-point source phosphorus pollution risks under complex precipitation and terrain conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 20946–20955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huishu, L.; Qiuliang, L.; Xinyu, Z.; Haw, Y.; Hongyuan, W.; Limei, Z.; Hongbin, L.; Jr-Chuan, H.; Tianzhi, R.; Jiaogen, Z.; et al. Effects of anthropogenic activities on long-term changes of nitrogen budget in a plain river network region: A case study in the Taihu Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Fang, X.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, X. Carbon emissions induced by cropland expansion in Northeast China during the past 300 years. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 2259–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Deng, M.; Li, D.; Sun, Y. Characteristics and driving factors of carbon emissions in China. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2024, 67, 967–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Li, B.; Yu, W.; Han, J.-C.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, Z.; Wu, X.; Young, B.; Huang, Y. Revisiting China’s domestic greenhouse gas emission from wastewater treatment: A quantitative process life-cycle assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Boiarkina, I.; Young, B.; Yu, W. Substance flow analysis of phosphorus within New Zealand and comparison with other countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527–528, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Guan, Y.; Hang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Li, Y.; Guan, D.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Hubacek, K. City-level emission peak and drivers in China. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 1910–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Fan, Y.; Yang, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Tian, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, C. Net anthropogenic nitrogen inputs (NANI) index application in Mainland China. Geoderma 2014, 213, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Pang, J.; Li, Y. Spatial-Temporal Dynamics of Anthropogenic Nitrogen Inputs in the Rapid Developing Chaohu Lake Basin. Water 2023, 15, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, W.; Yan, T.; Lei, Q.; Zhang, T.; Fan, B.; Du, X.; Luo, J.; Lindsey, S.; Liu, H. Spatio-temporal variation of net anthropogenic nitrogen inputs (NANI) from 1991 to 2019 and its impacts analysis from parameters in Northwest China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Howarth, R.W.; Swaney, D.P.; Hong, B.; Guo, H.C. Enhanced N input to Lake Dianchi Basin from 1980 to 2010: Drivers and consequences. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Tian, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, C. Net anthropogenic phosphorus inputs (NAPI) index application in Mainland China. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, M. Variation of net anthropogenic phosphorus inputs (NAPI) and riverine phosphorus fluxes in seven major river basins in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Shi, K. What Are the Driving Forces of Urban CO2 Emissions in China? A Refined Scale Analysis between National and Urban Agglomeration Levels. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, R. The Relationship between the Low-Carbon Industrial Model and Human Well-Being: A Case Study of the Electric Power Industry. Energies 2023, 16, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayagam, V.; Sikarwar, D.; Das, S.; Pugazhendhi, A. Envisioning the innovative approaches to achieve circular economy in the water and wastewater sector. Environ. Res. 2024, 241, 117663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Wang, S.; Ye, L.; Su, G.; Wang, T.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Z. Integrated Assessment of Anthropogenic Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Inputs: A Panjin City Case Study. Water 2025, 17, 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202962
Wang T, Wang S, Ye L, Su G, Wang T, Ma R, Zhang Z. Integrated Assessment of Anthropogenic Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Inputs: A Panjin City Case Study. Water. 2025; 17(20):2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202962
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Tianxiang, Simiao Wang, Li Ye, Guangyu Su, Tianzi Wang, Rongyue Ma, and Zipeng Zhang. 2025. "Integrated Assessment of Anthropogenic Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Inputs: A Panjin City Case Study" Water 17, no. 20: 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202962
APA StyleWang, T., Wang, S., Ye, L., Su, G., Wang, T., Ma, R., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Integrated Assessment of Anthropogenic Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Inputs: A Panjin City Case Study. Water, 17(20), 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202962






