The Synthesis of Functionalized W5O14 Nanorods for the Adsorption of Bismarck Brown R from Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of P. granatum Peel Extract
2.2.2. Green (Biogenic) Synthesis of W5O14 Nanorods
2.3. Characterization
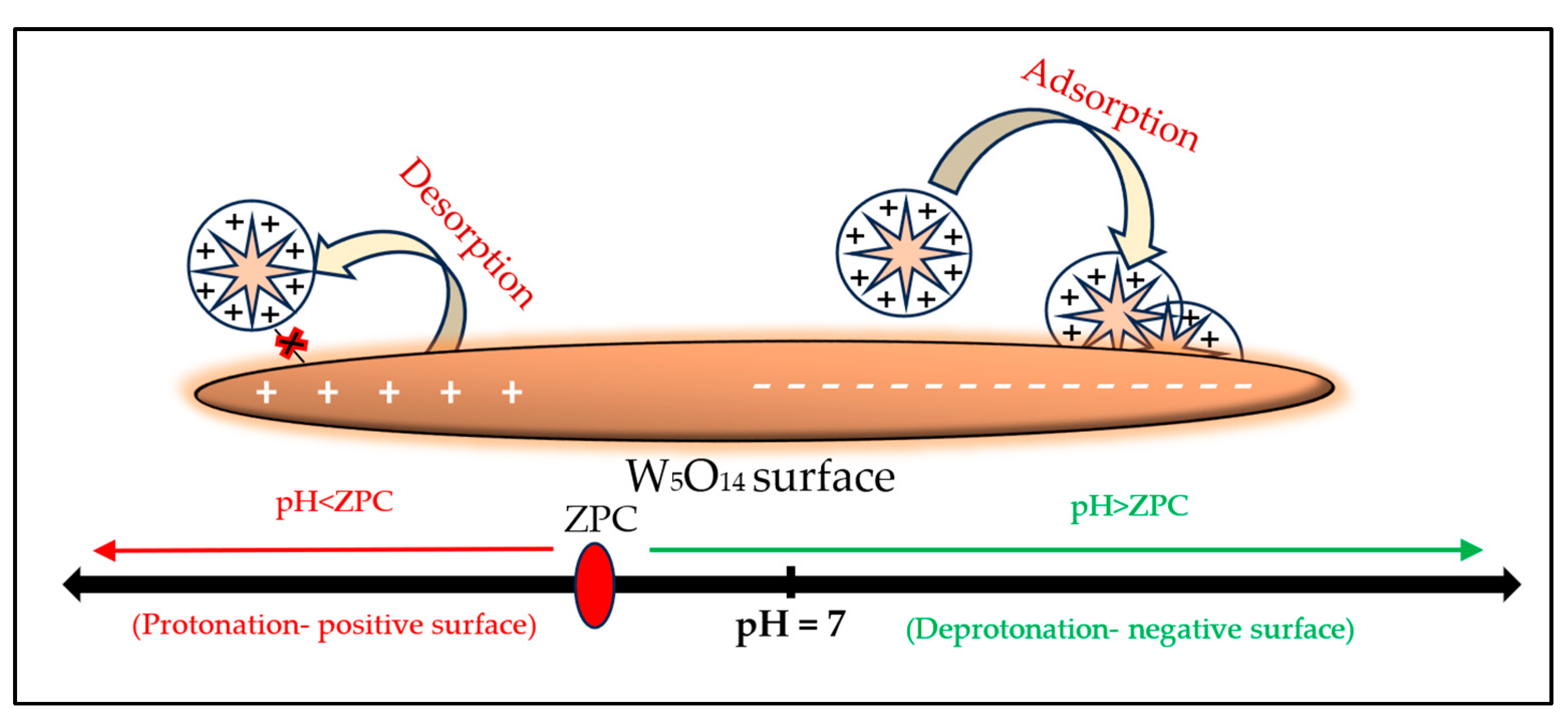
Point of Zero Charge Determination with Temperature Variation
2.4. Adsorption Study
2.5. Thermodynamics
2.6. Isotherms
2.7. Kinetics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of W5O14 Nanorods
3.1.1. FTIR Analysis
3.1.2. XRD Analysis
3.1.3. SEM Analysis
3.1.4. TEM Analysis
3.1.5. ZPC Analysis
3.2. Adsorption Studies
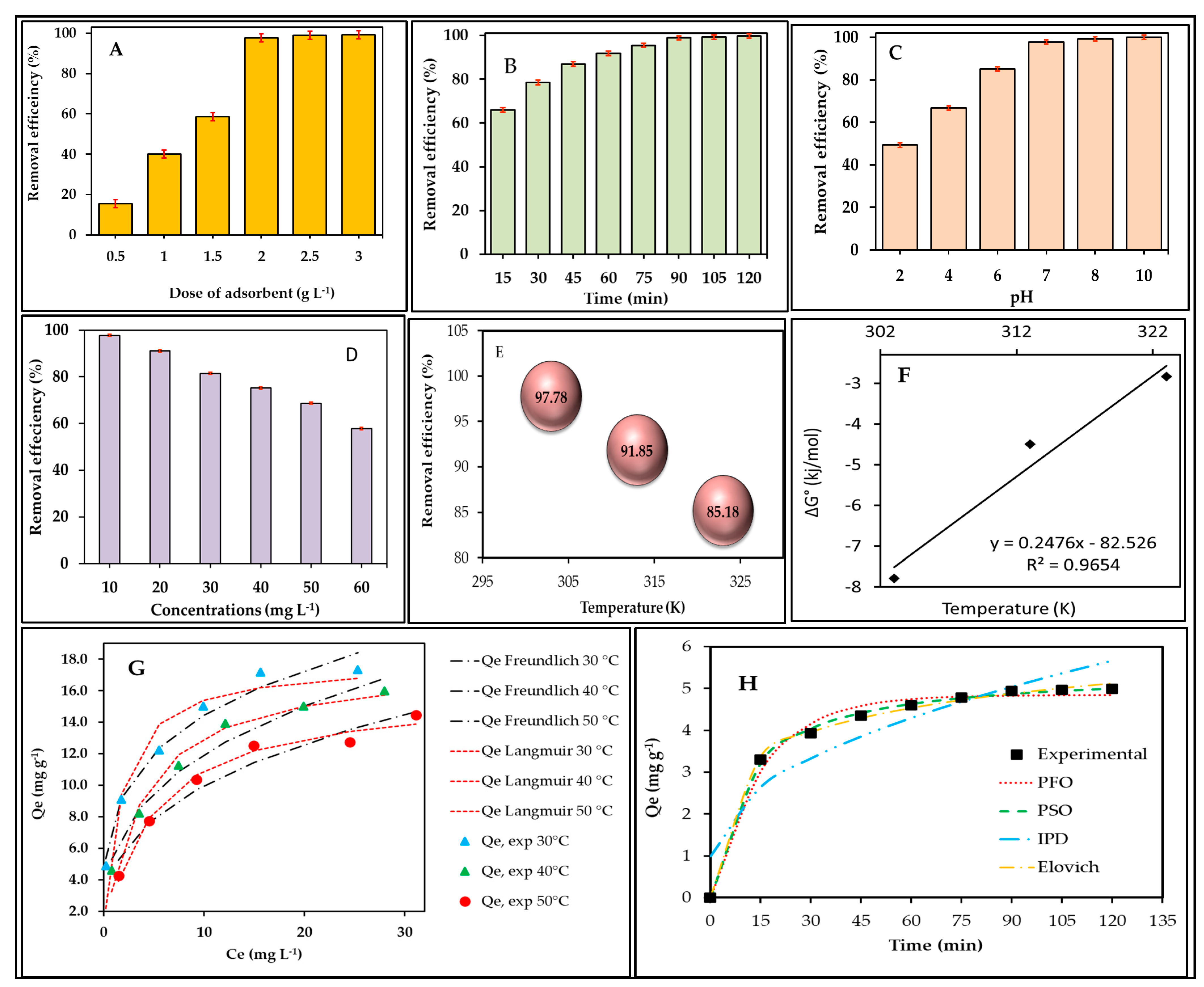
3.2.1. Effect of W5O14 Dose
3.2.2. Effect of Contact Time
3.2.3. Effect of pH
3.2.4. Effect of Concentration
3.2.5. Temperature Effect
3.2.6. Thermodynamic Result
3.2.7. Isotherm Results
3.2.8. Kinetic Results
3.2.9. Mechanism of BBR Adsorption onto the W5O14 Nanorods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alsukaibi, A.K. Various approaches for the detoxification of toxic dyes in wastewater. Processes 2022, 10, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.U.; Ahmed, S.; Dhoble, Y.; Madhav, S. A critical review of hazardous waste generation from textile industries and associated ecological impacts. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2023, 100, 100829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viktoryová, N.; Szarka, A.; Hrouzková, S. Recent developments and emerging trends in paint industry wastewater treatment methods. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivalingam, S.; Sowmiya, A. Industrial biomass waste as an economical, potential adsorbent for removing the Bismarck Brown R dye and zinc metal ions from effluents. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2024, 3, 732–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, S.; Sinha, S.; Seth, C.S.; Tyagi, S.; Goyal, A.; Singh, R. Enhanced adsorption of Bismark Brown R dye by chitosan conjugated magnetic pectin loaded filter mud: A comprehensive study on modeling and mechanisms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 131987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawhari, A.H.; Malik, M.A.; Hasan, N.; Fatima, B. MgO-CdWO4: A visible-light-active heterojunction photocatalyst for Bismark brown dye degradation. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1305, 137594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrano-Rodríguez, F.; Picos-Benítez, A.; Brillas, E.; Bandala, E.R.; Pérez, T.; Peralta-Hernández, J.M. Electrochemical advanced oxidation discoloration and removal of three brown diazo dyes used in the tannery industry. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 873, 114360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Gupta, B.; Srivastava, S.K.; Gupta, A.K. Recent advances on the removal of dyes from wastewater using various adsorbents: A critical review. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 4497–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, S.; Hassani, A.; Merrikhpour, H. Aqueous phosphorous adsorption onto SnO2 and WO3 nanoparticles in batch mode: Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic study. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2020, 15, 242–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighalo, J.O.; Sagboye, P.A.; Umenweke, G.; Ajala, O.J.; Omoarukhe, F.O.; Adeyanju, C.A.; Ogunniyi, S.; Adeniyi, A.G. CuO nanoparticles (CuO NPs) for water treatment: A review of recent advances. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 15, 100443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayalath, S.; Wu, H.; Larsen, S.C.; Grassian, V.H. Surface adsorption of Suwannee River humic acid on TiO2 nanoparticles: A study of pH and particle size. Langmuir 2018, 34, 3136–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbar, K.Q.; Barzinjy, A.A.; Hamad, S.M. Iron oxide nanoparticles: Preparation methods, functions, adsorption and coagulation/flocculation in wastewater treatment. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Arjan, W.S. Zinc oxide nanoparticles and their application in adsorption of toxic dye from aqueous solution. Polymers 2022, 14, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Chelike, D.K.; Rathore, R.K. Adsorption-Based Approaches for Exploring Nanoparticle Effectiveness in Wastewater Treatment. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202400959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hkiri, K.; Mohamed HE, A.; Abodouh, M.M.; Maaza, M. Experimental and theoretical insights into the adsorption mechanism of methylene blue on the (002) WO3 surface. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Lin, Q.; Chen, T.; Wei, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z. Oxygen vacancy regulation on tungsten oxides with specific exposed facets for enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic oxidation. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 2908–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Sun, M.; Chen, S.; Sun, M. Progress in Functionalized WO3-based Gas Sensors for Selective H2S and NH3: A Review. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 40631–40665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fu, L.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Chen, F.; Zhao, S. Innovations in WO3 gas sensors: Nanostructure engineering, functionalization, and future perspectives. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsini, A.; Naciri, Y.; Laabd, M.; Bouziani, A.; Navío, J.; Puga, F.; Boukherroub, R.; Lakhmiri, R.; Albourine, A. Development of a novel PANI@ WO3 hybrid composite and its application as a promising adsorbent for Cr (VI) ions removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khawaga, A.M.; Zidan, A.; Abd El-Mageed, A.I. Preparation methods of different nanomaterials for various potential applications: A review. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1281, 135148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altammar, K.A. A review on nanoparticles: Characteristics, synthesis, applications, and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1155622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Fuh, J.Y.H.; Dheen, S.T.; Senthil Kumar, A. Synthesis methods of functionalized nanoparticles: A review. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2021, 4, 379–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, J.; Kumar, S.; Pal, M.; Kaur, H.; Batoo, K.M.; Momoh, J.O. Current trends: Zinc oxide nanoparticles preparation via chemical and green method for the photocatalytic degradation of various organic dyes. Hybrid Adv. 2024, 5, 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, H.; Khalaj, G.; Soleymani, F.; Moalem, M.; Pourabdollah, M.; Mahmoudan, M. Electrochemical synthesis and characterization of Cu2O nanoparticles: Effect of electrolyte composition. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2024, 28, 2269–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Blas, M.; Maldonado-Luna, N.M.; Rivera-Quiñones, C.M.; Vega-Avila, A.L.; Roman-Velázquez, F.R.; Perales-Perez, O.J. Single step microwave assisted synthesis and antimicrobial activity of silver, copper and silver-copper nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.H.; Su, Y.H.; Teoh, L.G.; Tsai, Y.T.; Hon, M.H. Synthesis of tungsten oxide particles by chemical deposition method. Mater. Trans. 2007, 48, 1575–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, N.L.; Luu, T.L.A.; Nguyen, H.L.; Nguyen, C.T. Effects of acidity on the formation and adsorption activity of tungsten oxide nanostructures prepared via the acid precipitation method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 272, 125014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juelsholt, M.; Lindahl Christiansen, T.; Jensen, K.M. Mechanisms for tungsten oxide nanoparticle formation in solvothermal synthesis: From polyoxometalates to crystalline materials. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 5110–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirtaheri, B.; Shokouhimehr, M.; Beitollahi, A. Synthesis of mesoporous tungsten oxide by template-assisted sol–gel method and its photocatalytic degradation activity. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, G.; Wang, D.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, M.; Xi, G. Crystallographic phase and morphology dependent hydrothermal synthesis of tungsten oxide for robust hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 875, 160054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, S.; Preetam, S.; Pandey, C.; Bera, S.P. Exploring synthesis and applications of green nanoparticles and the role of nanotechnology in wastewater treatment. Biotechnol. Rep. 2024, 41, e00830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, S.; Guan, Z.; Ofoegbu, P.C.; Clubb, P.; Rico, C.; He, F.; Hong, J. Green synthesis of nanoparticles: Current developments and limitations. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 26, 102336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banjara, R.A.; Kumar, A.; Aneshwari, R.; Satnami, M.L.; Sinha, S.K. A comparative analysis of chemical vs green synthesis of nanoparticles and their various applications. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2024, 22, 100988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Tiwari, H.; Verma, A.; Gupta, P.; Chattopadhaya, A.; Singh, A.; Singh, S.; Kumar, B.; Mandal, A.; Kumar, R.; et al. Sustainable synthesis of novel green-based nanoparticles for therapeutic interventions and environmental remediation. ACS Synth. Biol. 2024, 13, 1994–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villagrán, Z.; Anaya-Esparza, L.M.; Velázquez-Carriles, C.A.; Silva-Jara, J.M.; Ruvalcaba-Gómez, J.M.; Aurora-Vigo, E.F.; Rodríguez-Lafitte, E.; Rodríguez-Barajas, N.; Balderas-León, I.; Martínez-Esquivias, F. Plant-Based Extracts as Reducing, Capping, and Stabilizing Agents for the Green Synthesis of Inorganic Nanoparticles. Resources 2024, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaram, S.; Razafindralambo, H.; Sun, Y.Z.; Vasantharaj, S.; Ghafarifarsani, H.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Raeeszadeh, M. Applications of green synthesized metal nanoparticles—A review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024, 202, 360–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Chaudhry, S.A.; Ikram, S. A review on biogenic synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using plant extracts and microbes: A prospect towards green chemistry. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 166, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelghany, T.M.; Al-Rajhi, A.M.; Al Abboud, M.A.; Alawlaqi, M.M.; Ganash Magdah, A.; Helmy, E.A.; Mabrouk, A.S. Recent advances in green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their applications: About future directions. A review. BioNanoScience 2018, 8, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, T.L.; Olisah, C.; Acho, M.A.; Oyetunde-Joshua, F.; Amoo, S.O. Global Research Trends and Recent Advances in Medicinal Plant-Synthesized Nanoparticles for Cancer Treatment. Plants 2024, 13, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monika, P.; Chandraprabha, M.N.; Hari Krishna, R.; Vittal, M.; Likhitha, C.; Pooja, N.; Chaudhary, V. Recent advances in pomegranate peel extract mediated nanoparticles for clinical and biomedical applications. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2024, 40, 3379–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthasarathy, P.R.; Varshan, E.I.; Shanmugam, R. In Vitro Anti-diabetic Activity of Pomegranate Peel Extract-Mediated Strontium Nanoparticles. Cureus 2023, 15, e51356. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, S.; Duo, L.; Wang, J.; Zhula, G.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Tu, Y. A unique understanding of traditional medicine of pomegranate, Punica granatum L. and its current research status. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 271, 113877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadivi, A.; Rezagholi, M.; Shams, M. Phytochemical properties and bioactive compounds of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.). J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 99, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, S.; Aslam, A.; Parveen, A.; Dilshad, M.; Hussain, S. Phytochemistry of Punica granatum Fruit: Its Nutritional and Biological Potential. Bioactivities 2024, 2, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Maity, A. Pomgerenate Phytochemicals: Neutraceutical and Therapeutic values. Fruit Veg. Cereal Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 4, 56–76. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Guo, C.; Yang, J.; Wei, J.; Xu, J.; Cheng, S. Evaluation of antioxidant properties of pomegranate peel extract in comparison with pomegranate pulp extract. Food Chem. 2006, 96, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moneim, A.E.A. Antioxidant activities of Punica granatum (pomegranate) peel extract on brain of rats. J. Med. Plants Res. 2012, 6, 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Moghaddam, A.; Yasini Ardakani, S.A. Antimicrobial activity of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) peel extract, physical, mechanical, barrier and antimicrobial properties of pomegranate peel extract-incorporated sodium caseinate film and application in packaging for ground beef. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2015, 28, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleci, K. In Vitro Anticarcinogenic, Antiparasitic and Antimicrobial Effects of P. granatum Extract. Biol. Bull. Rev. 2023, 13 (Suppl. S3), S264–S269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, T.P.; Veeraragavan, G.R.; Narayanan, M.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Subramani, B.; Brindhadevi, K.; Pimpimon, T.; Pikulkaew, S. Green synthesis of Zirconium nanoparticles using Punica granatum (pomegranate) peel extract and their antimicrobial and antioxidant potency. Environ. Res. 2022, 209, 112771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusefi, M.; Shameli, K.; Ali, R.R.; Pang, S.W.; Teow, S.Y. Evaluating anticancer activity of plant-mediated synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles using Punica granatum fruit peel extract. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1204, 127539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, A.S.; Owda, M.E.; Basuoni, M.M.; Mousa, M.A.; Radwan, A.A.; Saleh, A.K. Punica granatum peel extract mediated green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles: Structure and evaluation of their biological applications. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 12265–12281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
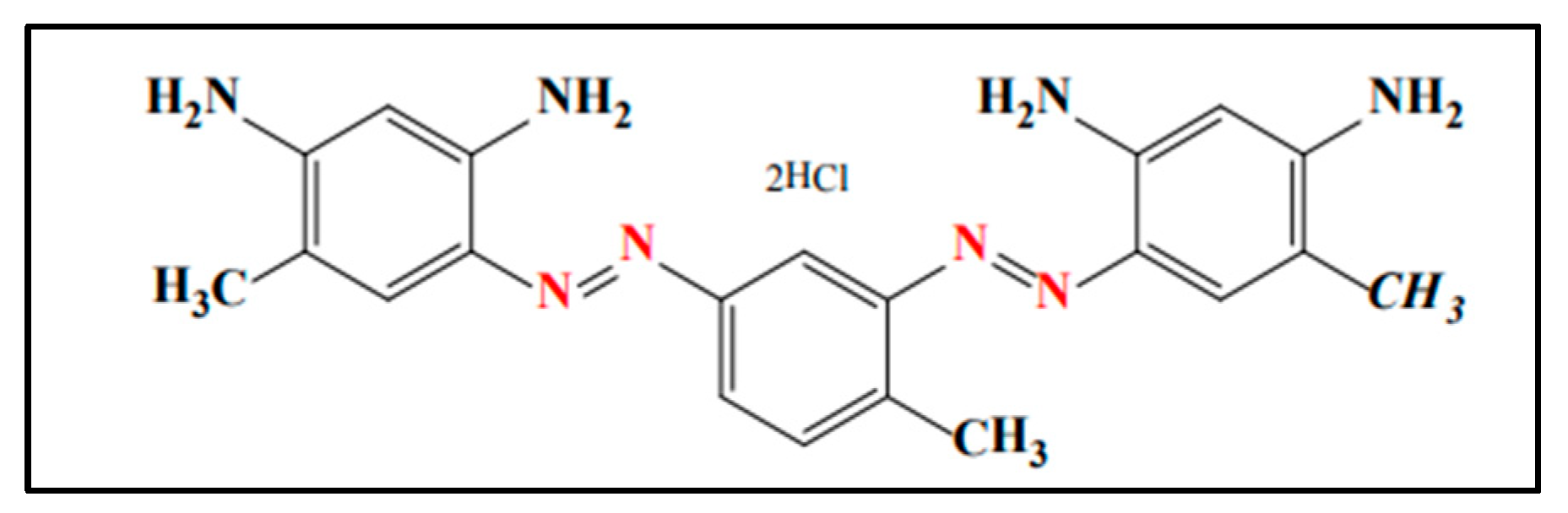
- Kamil, A.M.; Abdalrazak, F.H.; Halbus, A.F.; Hussein, F.H. Adsorption of Bismarck Brown R Dye onto Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2014, 1, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanakkasaranee, S.; Kasi, G.; Kadhiravan, S.; Arumugam, A.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Riaz, M.N.; Govindarajan, M. Synthesis of Tungsten Oxide Nanoflakes and Their Antibacterial and Photocatalytic Properties. Fermentation 2023, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.T.H.S.; Hussain, S.T.; Waseem, M.; Naeem, A.; Hussain, J.; Tariq Jan, M. Surface charge properties of zirconium dioxide. Iran. J. Sci. 2012, 36, 481–486. [Google Scholar]
- Fatima, B.; Siddiqui, S.; Ahmed, R.; Chaudhry, S.A. Preparation of functionalized CuO nanoparticles using Brassica rapa leave extract for water purification. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 164, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, B.; Alwan, B.A.; Siddiqui, S.I.; Ahmad, R.; Almesfer, M.; Khanna, M.K.; Mishra, R.; Ravi, R.; Oh, S. Facile synthesis of cu-zn binary oxide coupled cadmium tungstate (Cu-znbo-cp-ct) with enhanced performance of dye adsorption. Water 2021, 13, 3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Chowdhury, S. Insight into adsorption thermodynamics. In Thermodynamics; Tadashi, M., Ed.; Intech Open: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.J.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Chao, H.P. Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Water Res. 2017, 120, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasper, E.E.; Ajibola, V.O.; Onwuka, J.C. Nonlinear regression analysis of the sorption of crystal violet and methylene blue from aqueous solutions onto an agro-waste derived activated carbon. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Alzahrani, E.A.; Dwivedi, P.; Hafeez, S.; Deswal, J.; Fatima, B.; Siddiqui, S.I.; Oh, S. Biodegradable Acid-Based Fe2MnO4 Nanoparticles for Water Remediation. Molecules 2024, 29, 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falahian, Z.; Torki, F.; Faghihian, H. Synthesis and application of polypyrrole/Fe3O4 nanosize magnetic adsorbent for efficient separation of Hg2+ from aqueous solution. Glob. Chall. 2018, 2, 1700078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, J. Interpretation of infrared spectra, a practical approach. Encycl. Anal. Chem. 2000, 12, 10815–10837. [Google Scholar]
- Narasimharao, K.; Al-Thabaiti, S.; Rajor, H.K.; Mokhtar, M.; Alsheshri, A.; Alfaifi, S.Y.; Siddiqui, S.I.; Abdulla, N.K. Fe3O4@ date seeds powder: A sustainable nanocomposite material for wastewater treatment. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 3581–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.S. Microwave-assisted synthesis of CdWO4 by solid-state metathetic reaction. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 131, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, B.; Paul, B.; Dhar, S.S.; Vadivel, S. Facile hydrothermal synthesis of ultrasmall W18O49 nanorods and studies of their photocatalytic activity towards degradation of methylene blue. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 188, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.B.; Mohant, D.B. Formation of nanoscale tungsten oxide structures and colouration characteristics. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2011, 34, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColm, I.J.; Steadman, R.; Wilson, S.J. Iron-promoted phases in the tungsten-oxygen system. J. Solid State Chem. 1978, 23, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqib, M.; Jelenc, J.; Pirker, L.; Škapin, S.D.; De Pietro, L.; Ramsperger, U.; Knápek, A.; Müllerová, I.; Remškar, M. Field emission properties of single crystalline W5O14 and W18O49 nanowires. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2020, 241, 146837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinila, V.S.; Isac, J. Synthesis and structural studies of superconducting perovskite GdBa2Ca3Cu4O10.5+δ nanosystems. In Design, Fabrication, and Characterization of Multifunctional Nanomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 319–341. [Google Scholar]
- Akratopulu, K.C.; Vordonis, L.; Lycourghiotis, A. Effect of temperature on the point of zero charge and surface dissociation constants of aqueous suspensions of γ-Al2O3. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1986, 82, 3697–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Siddiqui, S.I.; Al Alwan, B.; Almesfer, M.; Khanna, M.K.; Fatima, B.; Mishra, R.; Ansari, M.A.; Oh, S. Biodegradable acid based nanocomposite-CuO-ZnO-Ni (OH) 2/PA: A novel material for water cleansing. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 341, 130860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, H.; Kannan, A. Sustainable and Circular Adsorption of Anionic Dye from Textile Wastewater Using Economical Adsorbent. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litefti, K.; Freire, M.S.; Stitou, M.; González-Álvarez, J. Adsorption of an anionic dye (Congo red) from aqueous solutions by pine bark. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Agarwal, A.; Singh, M.K.; Singh, N.B. Kail sawdust charcoal: A low-cost adsorbent for removal of textile dyes from aqueous solution. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Order | Temperature (K) | ∆G (KJ mol−1) | ∆H (KJ mol−1) | ∆S (KJ K−1 mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 303 | −7.787 | −82.252 | −0.247 |
| 2. | 313 | −4.500 | ||
| 3. | 323 | −2.836 |
| Order | Temp. (°C) | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qo (mg g−1) | b (L mg−1) | RL | SSR | χ2 | KF [(mg g−1)(L mg−1)1/n] | 1/n | SSR | χ2 | ||
| 1. | 30 | 17.840 | 0.629 | 0.137 | 11.506 | 0.155 | 7.905 | 0.261 | 2.704 | 0.036 |
| 2. | 40 | 17.786 | 0.272 | 0.268 | 2.734 | 0.040 | 5.627 | 0.328 | 2.648 | 0.038 |
| 3. | 50 | 15.929 | 0.217 | 0.314 | 1.126 | 0.018 | 4.579 | 0.339 | 3.188 | 0.051 |
| Order | Model | Parameters | BBR |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | PFO | K1 (minutes−1) | 0.065 |
| 2. | Qe,Cal (mg g−1) | 4.840 | |
| 3. | SSR | 0.261 | |
| 4. | χ2 | 0.007 | |
| 5. | PSO | K2 (g mg−1 min−1) | 0.018 |
| 6. | Qe,Cal (mg g−1) | 5.425 | |
| 7. | SSR | 0.031 | |
| 8. | χ2 | 0.0008 | |
| 9. | Elovich | α (mg g−1 min−1) | 2.905 |
| 10. | β (g mg−1) | 1.175 | |
| 11. | SSR | 0.039 | |
| 12. | χ2 | 0.001 | |
| 13. | IPD | Kipd (mg g−1 min−1/2) | 0.426 |
| 14. | C (mg g−1) | 0.991 | |
| 15. | SSR | 2.753 | |
| 16. | χ2 | 0.077 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fatima, B.; Ahmad, R.; Alsebaii, N.M.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Aldahiri, R.H.; Alzahrani, E.A.; Kumar Khanna, M.; Oh, S.; Siddiqui, S.I. The Synthesis of Functionalized W5O14 Nanorods for the Adsorption of Bismarck Brown R from Wastewater. Water 2025, 17, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020196
Fatima B, Ahmad R, Alsebaii NM, Al-Ghamdi AA, Aldahiri RH, Alzahrani EA, Kumar Khanna M, Oh S, Siddiqui SI. The Synthesis of Functionalized W5O14 Nanorods for the Adsorption of Bismarck Brown R from Wastewater. Water. 2025; 17(2):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020196
Chicago/Turabian StyleFatima, Bushra, Rabia Ahmad, Naha Meslet Alsebaii, Azza A. Al-Ghamdi, Reema H. Aldahiri, Elham A. Alzahrani, Manoj Kumar Khanna, Seungdae Oh, and Sharf Ilahi Siddiqui. 2025. "The Synthesis of Functionalized W5O14 Nanorods for the Adsorption of Bismarck Brown R from Wastewater" Water 17, no. 2: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020196
APA StyleFatima, B., Ahmad, R., Alsebaii, N. M., Al-Ghamdi, A. A., Aldahiri, R. H., Alzahrani, E. A., Kumar Khanna, M., Oh, S., & Siddiqui, S. I. (2025). The Synthesis of Functionalized W5O14 Nanorods for the Adsorption of Bismarck Brown R from Wastewater. Water, 17(2), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020196






