Efficiency of Graphene Quantum Dots in Water Contaminant Removal: Trends and Future Research Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Questions for the Review
2.2. Search Strategies
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis Methods of GQDs
Applications of GQDs
3.2. Efficiency of GQDs in Water Contaminant Removal
3.3. Adsorption of Heavy Metals with GQDs
3.4. Trends and Knowledge Gaps in GQDs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, S.N.; Baker, G.A. Luminescent carbon nanodots: Emergent nanolights. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6726–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trauzettel, B.; Bulaev, D.V.; Loss, D.; Burkard, G. Spin qubits in graphene quantum dots. Nat. Phys. 2007, 3, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnez, S.; Molitor, F.; Stampfer, C.; Güttinger, J.; Shorubalko, I.; Ihn, T.; Ensslin, K. Observation of excited states in a graphene quantum dot. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zeng, H.; Sun, L. Graphene quantum dots: Versatile photoluminescence for energy, biomedical, and environmental applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, F.; Luo, Y.; Li, M.; Hu, G.; Pu, X.; Tang, T.; Wen, J.; Li, X.; Li, W. Size effect of graphene quantum dots on photoluminescence. Molecules 2021, 26, 3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.T.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Luo, K.Q.; Chen, P. Glowing graphene quantum dots and carbon dots: Properties, syntheses, and biological applications. Small 2015, 11, 1620–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Tang, L.; Teng, K.S.; Lau, S.P. Graphene quantum dots from chemistry to applications. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 10, 221–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, M.; Shadjou, N. What are the reasons for low use of graphene quantum dots in immunosensing of cancer biomarkers? Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, C.; Tang, S.; Li, Y.; Yuan, W.; Li, B.; Tian, L.; Liu, F.; Hu, R.; et al. Strongly green-photoluminescent graphene quantum dots for bioimaging applications. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6858–6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervez, M.; Wei, Y.; Sun, P.; Qu, G.; Naddeo, V.; Zhao, Y. α-FeOOH quantum dots impregnated graphene oxide hybrids enhanced arsenic adsorption: The mediation role of environmental organic ligands. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Shah, S.A.; Huang, D.; Parviz, D.; Yu, Y.-H.; Wang, X.; Green, M.J.; Cheng, Z. Aqueous Exfoliation of Graphite into Graphene Assisted by Sulfonyl Graphene Quantum Dots for Photonic Crystal Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 30797–30804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponomarenko, L.A.; Schedin, F.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Yang, R.; Hill, E.W.; Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K. Chaotic dirac billiard in graphene quantum dots. Science 2008, 320, 356–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tshangana, C.; Muleja, A.; Kuvarega, A.; Malefetse, T.; Mamba, B. The applications of graphene oxide quantum dots in the removal of emerging pollutants in water: An overview. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 43, 102249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare Pirhaji, J.; Moeinpour, F.; Mirhoseini Dehabadi, A.; Yasini Ardakani, S.A. Synthesis and characterization of halloysite/graphene quantum dots magnetic nanocomposite as a new adsorbent for Pb(II) removal from water. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 300, 112345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarenezhad, M.; Zarei, M.; Ebratkhahan, M.; Hosseinzadeh, M. Synthesis and study of functionalized magnetic graphene oxide for Pb2+ removal from wastewater. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakibuddin, M.; Kim, H. Sol-gel derived Fe3O4 quantum dot decorated silica composites for effective removal of arsenic (III) from water. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 240, 122245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Jun, G.H.; Hong, S.H.; Jeon, S. Tuning the photoluminescence of graphene quantum dots through the charge transfer effect of functional groups. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, A.; Godoy-Gallardo, M.; Ashley, J.; Feng, X.; Zhou, T.; Hosta-Rigau, L.; Sun, Y. One-pot green synthesis of biocompatible graphene quantum dots and their cell uptake studies. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.T.; Pham, H.P.; Tran, Q.T. A Facile Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of Graphene Quantum Dots for Organic Solar Cell Efficiency Improvement. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; He, H.; Huang, G.; Xing, B.; Jia, J.; Zhang, C. Green preparation of high yield fluorescent graphene quantum dots from coal-tar-pitch by mild oxidation. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaro, M.; Carraro, F.; Cattelan, M.; Colazzo, L.; Durante, C.; Sambi, M.; Gennaro, A.; Agnoli, S.; Granozzi, G. Multiple doping of graphene oxide foams and quantum dots: New switchable systems for oxygen reduction and water remediation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 14334–14347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Pan, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, M. Three Minute Ultrarapid Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Bright Fluorescent Graphene Quantum Dots for Live Cell Staining and White LEDs. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 1623–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Peng, Q. Amino-Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots as Cathode Interlayer for Efficient Organic Solar Cells: Quantum Dot Size on Interfacial Modification Ability and Photovoltaic Performance. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1801480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Gao, W.; Gupta, B.K.; Liu, Z.; Romero-Aburto, R.; Ge, L.; Song, L.; Alemany, L.B.; Zhan, X.; Gao, G.; et al. Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, C. Graphene quantum dots: Emergent nanolights for bioimaging, sensors, catalysis and photovoltaic devices. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3686–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Jeong, Y.K.; Jung, K.H.; Son, Y.; Choi, S.-C.; An, G.S.; Han, H.; Kim, K.M. Simple preparation of graphene quantum dots with controllable surface states from graphite. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 38447–38453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y.-H.; Zhang, L.; Shafi, W.; Huang, X.; Cheng, Z. The Synthesis of Amphiphilic Luminescent Graphene Quantum Dot and Its Application in Miniemulsion Polymerization. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 6490383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, H.; Niu, J.; Liu, B. Facile synthesis and photoluminescence of graphene oxide quantum dots and their reduction products. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 4970–4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Yang, C.; Hou, J.; Wang, F.; Min, S.; Ma, X.; Jin, Z.; Xu, J.; Lu, G.; Huang, K.-W. Strongly coupled CdS/graphene quantum dots nanohybrids for highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution: Unraveling the essential roles of graphene quantum dots. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 216, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J.; Morales, A.; Duque, C. Estados electrónicos de puntos cuánticos piramidales y cónicos. Rev. EIA 2018, 15, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Portacio Lamadrid, A.A.; Arias Hernández, J.D.; Rasero Causil, D.A. Respuesta óptica lineal de un punto cuántico cónico en el régimen de Born-Markov. Orinoquia 2021, 25, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Green synthesis, biomedical and biotechnological applications of carbon and graphene quantum dots. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 703–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, H.; Goh, P.S.; Saud, A.; Khan, M.A.W.; Munira, N.; Ismail, A.F.; Zaidi, S.J. Graphene Quantum Dot-Added Thin-Film Composite Membrane with Advanced Nanofibrous Support for Forward Osmosis. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohal, N.; Singla, S.; Malode, S.J.; Basu, S.; Maity, B.; Shetti, N.P. Bioresource-Based Graphene Quantum Dots and Their Applications: A Review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 10925–10943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, C.K.; Sofer, Z.; Šimek, P.; Jankovský, O.; Klímová, K.; Bakardjieva, S.; Kučková, H.; Pumera, M. Synthesis of strongly fluorescent graphene quantum dots by cage-opening buckminsterfullerene. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 2548–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, A.; Sasi, S.; Arya, J.; Arjun, K. Synthesis of Graphene Quantum dots from the fresh leaves extract of Cynodon Dactylon and its Photoluminescence studies. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1219, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, S. Creating high yield water soluble luminescent graphene quantum dots via exfoliating and disintegrating carbon nanotubes and graphite flakes. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10177–10179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Valencia, C.A.; Reyes-Valderrama, M.I.; Salado-Lesa, D.E.; Rodriguez-Lugo, V. Síntesis hidrotermal de puntos cuánticos de carbono PEGilados. Pädi Bol. Científico Cienc. Básicas Ing. ICBI 2023, 11, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarin-Guio, P.; Cano-Calle, H.D.J.; Castillo-León, J.J. Detección electroquímica de peróxido de hidrógeno usando peroxidasa de pasto Guinea (Panicum maximum) inmovilizada sobre electrodos serigrafiados de puntos cuánticos. Rev. ION 2019, 32, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arredondo-Martínez, B.; Juárez-Gómez, J.; Guzmán-Hernández, D.S.; Ramírez-Silva, M.T.; Rojas-Hernández, A. Cuantificación de cafeína, utilizando como fluorosensor puntos cuánticos de carbono. Pädi Bol. Científico Cienc. Básicas Ing. ICBI 2023, 11, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estudillo-Diaz, E.B.; Gutiérrez-Miceli, F.A.; González-Mendoza, D.; Valdez-Salas, B.; Abud-Archila, M. Desarrollo y caracterización de películas activas con nanopartículas de plata obtenidas mediante síntesis verde. Biotecnia 2022, 25, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, T.; Mukherjee, S.; Ghorai, A.; Das, S.; Ray, S.K. Effects of Size and Localized States in Charge Carrier Dynamics and Performance of Solution-Processed Graphene Quantum Dots/Silicon Heterojunction Near-UV Photodetectors. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 12161–12167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, A.; Razzaq, A.; Zafar, M.; Idrees, I.; Rehman, F.; Kim, W.Y. Copper tungstate (CuWO4)/graphene quantum dots (GQDs) composite photocatalyst for enhanced degradation of phenol under visible light irradiation. Results Phys. 2023, 45, 106253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, E.; Kim, J.; Malgras, V.; Reddy, K.R.; Ward, A.C.; You, J.; Bando, Y.; Hossain, S.A.; Yamauchi, Y. Recent advances in graphene quantum dots: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Small Methods 2018, 2, 1800050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantatos, G.; Badioli, M.; Gaudreau, L.; Osmond, J.; Bernechea, M.; de Arquer, F.P.G.; Gatti, F.; Koppens, F.H.L. Hybrid grapheneĝquantum dot phototransistors with ultrahigh gain. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, M. Hydrothermal route for cutting graphene sheets into blue-luminescent graphene quantum dots. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Ma, H.; Gao, X.; Sun, H.; Wang, L.; An, M. Study on Long-Term Tracing of Fibroblasts on Three-Dimensional Tissue Engineering Scaffolds Based on Graphene Quantum Dots. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucko, J.; Schäfer, F.; Herman, F.; Garreis, R.; Tong, C.; Kurzmann, A.; Ihn, T.; Greplova, E. Automated Reconstruction of Bound States in Bilayer Graphene Quantum Dots. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2023, 19, 024015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Lavie, J.; Rondin, L.; Orcin-Chaix, L.; Diederichs, C.; Roussignol, P.; Chassagneux, Y.; Voisin, C.; Müllen, K.; Narita, A.; et al. Single photon emission from graphene quantum dots at room temperature. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Guo, S. Chemically doped fluorescent carbon and graphene quantum dots for bioimaging, sensor, catalytic and photoelectronic applications. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 2532–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Pan, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Fu, L.; Zhang, K.; Tang, N.; Du, Y. Magnetism of graphene quantum dots. npj Quantum Mater. 2017, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phophayu, S.; Pimpang, P.; Wongrerkdee, S.; Sujinnapram, S.; Wongrerkdee, S. Modified graphene quantum dots-zinc oxide nanocomposites for photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes and commercial herbicide. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2020, 39, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, G.H.; Huang, Y.Y.; Zhao, X. Water-Oil Interface Directed Self-Assembly of Graphene- g-PGMA/CdTe Nanocomposites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 16565–16570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Shen, J.; Chen, S.; Yan, J.; Zhang, N.; Zheng, K.; Liu, X. Synthesis of graphene quantum dot-stabilized gold nanoparticles and their application. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 21215–21219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozali Balkanloo, P.; Mohammad Sharifi, K.; Poursattar Marjani, A. Graphene quantum dots: Synthesis, characterization, and application in wastewater treatment: A review. Mater. Adv. 2023, 4, 4272–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh Mohd Ghazali, S.A.I.; Fatimah, I.; Zamil, Z.N.; Zulkifli, N.N.; Adam, N. Graphene quantum dots: A comprehensive overview. Open Chem. 2023, 21, 20220285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, V.; Ferlazzo, A.; Iannazzo, D.; Espro, C. Graphene quantum dots by eco-friendly green synthesis for electrochemical sensing: Recent advances and future perspectives. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, L.; Shi, M.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Q.; Liu, C. A Review of Advances in Graphene Quantum Dots: From Preparation and Modification Methods to Application. J. Carbon. Res. 2024, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Mariana, L.T.; Phan, A.N. Biomass-waste derived graphene quantum dots and their applications. Carbon. 2018, 140, 77–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, R.; Yang, B. Carbon Dots: A New Type of Carbon-Based Nanomaterial with Wide Applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 2179–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Zi, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zeng, W.; Luo, W.; Zeng, H.; Xia, M.; Luo, Z. Recent Advances in the Synthesis, Characterization, and Application of Carbon Nanomaterials for the Removal of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad-Rezaei, R.; Jaymand, M. Graphene quantum dots coated on quartz sand as efficient and low-cost adsorbent for removal of Hg2+ and Pb2+ from aqueous solutions. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2019, 38, S24–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Jiao, J.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Feng, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, M. Efficient separation of electron-hole pairs in graphene quantum dots by TiO2 heterojunctions for dye degradation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2405–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, A.; Lei, H.; Xi, F.; Liu, J.; Qin, L.; Chen, Z.; Dong, X. Graphene quantum dots decorated graphitic carbon nitride nanorods for photocatalytic removal of antibiotics. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2019, 548, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.U.; Jo, W.K. g-C3N4/oxygen-deficient BiOCl nanocomposite assisted by distinguished properties of graphene quantum dots for the efficient photocatalytic removal of organic vapors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 493, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.U.; Jo, W.K. FeWO4/g-C3N4 heterostructures decorated with N-doped graphene quantum dots prepared under various sonication conditions for efficient removal of noxious vapors. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 11346–11356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, N.; Sahoo, G.; Swain, S.K. Graphene quantum dot decorated magnetic graphene oxide filled polyvinyl alcohol hybrid hydrogel for removal of dye pollutants. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 302, 112591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.; Fekry, N.; Abdelfattah, A. Novel supramolecular network of graphene quantum dots-vitamin B9-iron (III)-tannic acid complex for removal of chromium (VI) and malachite green. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 341, 117312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Fekry, N.A.; Abdelfattah, A.M. Engineering nanocomposite of graphene quantum dots/carbon foam/alginate/zinc oxide beads for efficacious removal of lead and methylene. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 115, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Li, G.; Zhou, N.; Wang, R.; Chi, Y.; Chen, G. Graphene quantum dot as a green and facile sensor for free chlorine in drinking water. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8378–8382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulska, E.; Breczko, J.; Basa, A. Pristine and graphene-quantum-dots-decorated spinel nickel aluminate for water remediation from dyes and toxic pollutants. Water 2019, 11, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Du, P.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, L.; Cao, K.; Li, S.; Sheng, P. Architecting Bi2S3/graphene quantum dots/TiO2 photoelectrodes for aqueous Cr(VI)/methyl orange removal. Mater. Lett. 2018, 214, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.; Fekry, N.; Abdelfattah, A. A novel nanobiosorbent of functionalized graphene quantum dots from rice husk with barium hydroxide for microwave enhanced removal of lead (II) and lanthanum (III). Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafai, N.M.; Abdelfatah, M.M.; El-Khouly, M.E.; El-Mehasseb, I.M.; El-Shaer, A.; Ramadan, M.S.; Masoud, M.S.; El-Kemary, M.A. Magnetite nano-spherical quantum dots decorated graphene oxide nano sheet (GO@Fe3O4): Electrochemical properties and applications for removal heavy metals, pesticide and solar cell. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 506, 144896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshangana, C.; Muleja, A. Graphene oxide quantum dots membrane: A hybrid filtration-advanced technology system to enhance process of wastewater reclamation. Chem. Pap. 2024, 78, 1317–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc Anh, N.T.; Chang, P.Y.; Doong, R.A. Sulfur-doped graphene quantum dot-based paper sensor for highly sensitive and selective detection of 4-nitrophenol in contaminated water and wastewater. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 26588–26597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Du, X.; Hua, F.; Wen, J.; Li, M.; Tang, T. Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dot-Passivated δ-Phase CsPbI3, A Water-Stable Photocatalytic Adjuvant to Degrade Rhodamine B. Molecules 2023, 28, 7310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachi, S.; Morita, H.; Takahashi, M.; Okabayashi, Y.; Hosokai, T.; Sugai, T.; Kuwahara, S. Quantum Yield Enhancement in Graphene Quantum Dots via Esterification with Benzyl Alcohol. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvand, M.; Shemirani, F. A Fe3O4@SiO2@graphene quantum dot core-shell structured nanomaterial as a fluorescent probe and for magnetic removal of mercury(II) ion. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1621–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, A.; Munusamy, M.; Al-Arfaj, A.; Rajan, M. Functional Ionic Liquid-Capped Graphene Quantum Dots for Chromium Removal from Chromium Contaminated Water. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 651–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuengmatcha, P. Mercapto-Functionalized Magnetic Graphene Quantum Dots as Adsorbent for Cd2+ Removal from Wastewater. Environ. Process 2021, 8, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, D.; Weng, R.J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Rahardja, M.R.; Nanaricka, Z.C.; Chiang, W.H. Recent advances in the graphene quantum dot-based biological and environmental sensors. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2022, 4, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.; Cheung, P.L.; Yu, J.C. A visible-light-driven composite photocatalyst of TiO2 nanotube arrays and graphene quantum dots. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozfidan, I.; Korkusinski, M.; Hawrylak, P. Electronic properties and electron-electron interactions in graphene quantum dots. Phys. Status Solidi—Rapid Res. Lett. 2016, 10, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtepliuk, I.; Yakimova, R. Interband absorption in few-layer graphene quantum dots: Effect of heavy metals. Materials 2018, 11, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Pan, D.; Li, Z.; Jiao, Z.; Hu, P.; Shek, C.-H.; Wu, C.M.L.; et al. Assembling tin dioxide quantum dots to graphene nanosheets by a facile ultrasonic route. Langmuir 2013, 29, 4111–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweetman, M.J.; May, S.; Mebberson, N.; Pendleton, P.; Vasilev, K.; Plush, S.E.; Hayball, J.D. Activated Carbon, Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene: Materials and Composites for Advanced Water Purification. C 2017, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.X.; Zhang, M.; Fu, Q.Q.; Liu, R.; Shi, G.Y. Highly sensitive and selective fluorescent detection of cerebral lead(II) based on graphene quantum dot conjugates. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 10599–10601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, S.; Roy, A.; Sundaram, S.; Kumar Mallick, T. A Review on Heavy Metal Ions and Containing Dyes Removal Through Graphene Oxide-Based Adsorption Strategies for Textile Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Rec. 2021, 21, 1570–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zor, E.; Morales-Narváez, E.; Zamora-Gálvez, A.; Bingol, H.; Ersoz, M.; Merkoçi, A. Graphene quantum dots-based photoluminescent sensor: A multifunctional composite for pesticide detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 20272–20279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Peng, X.; Sun, F.; Kong, Z.; Shen, J.W. A review on the cytotoxicity of graphene quantum dots: From experiment to simulation. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaoli, F.; Qiyue, C.; Weihong, G.; Yaqing, Z.; Chen, H.; Junrong, W.; Longquan, S. Toxicology data of graphene-family nanomaterials: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 1915–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Han, J.W.; Eppakayala, V.; Kim, J.H. Biocompatibility of microbially reduced graphene oxide in primary mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 105, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, K.; Take, S.; Tani, R.; Maru, J.; Obara, S.; Endoh, S. Assessment of cytotoxicity and mutagenicity of exfoliated graphene. Toxicol. Vitr. 2018, 52, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Torres, F.F.; Rodríguez-Galván, A.; Guerrero-Beltrán, C.E.; Martínez-Lorán, E.; Vázquez-Garza, E.; Ornelas-Soto, N.; García-Rivas, G. Differential cytotoxicity and internalization of graphene family nanomaterials in myocardial cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, K.; Mukherjee, S.P.; Gallud, A.; Burkert, S.C.; Bistarelli, S.; Bellucci, S.; Bottini, M.; Star, A.; Fadeel, B. Biological interactions of carbon-based nanomaterials: From coronation to degradation. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtson, S.; Knudsen, K.B.; Kyjovska, Z.O.; Berthing, T.; Skaug, V.; Levin, M.; Koponen, I.K.; Shivayogimath, A.; Booth, T.J.; Alonso, B.; et al. Differences in inflammation and acute phase response but similar genotoxicity in mice following pulmonary exposure to graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrighi, M.; Trusel, M.; Tonini, R.; Giordani, S. Carbon nanomaterials interfacing with neurons: An in vivo perspective. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrollahi-Sharifabadi, M.; Koohi, M.K.; Zayerzadeh, E.; Hablolvarid, M.H.; Hassan, J.; Seifalian, A.M. In vivo toxicological evaluation of graphene oxide nanoplatelets for clinical application. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 4757–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babadaei, M.M.N.; Moghaddam, M.F.; Solhvand, S.; Alizadehmollayaghoob, E.; Attar, F.; Rajabbeigi, E.; Akhtari, K.; Sari, S.; Falahati, M. Biophysical, bioinformatical, cellular, and molecular investigations on the effects of graphene oxide nanosheets on the hemoglobin structure and lymphocyte cell cytotoxicity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 6871–6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


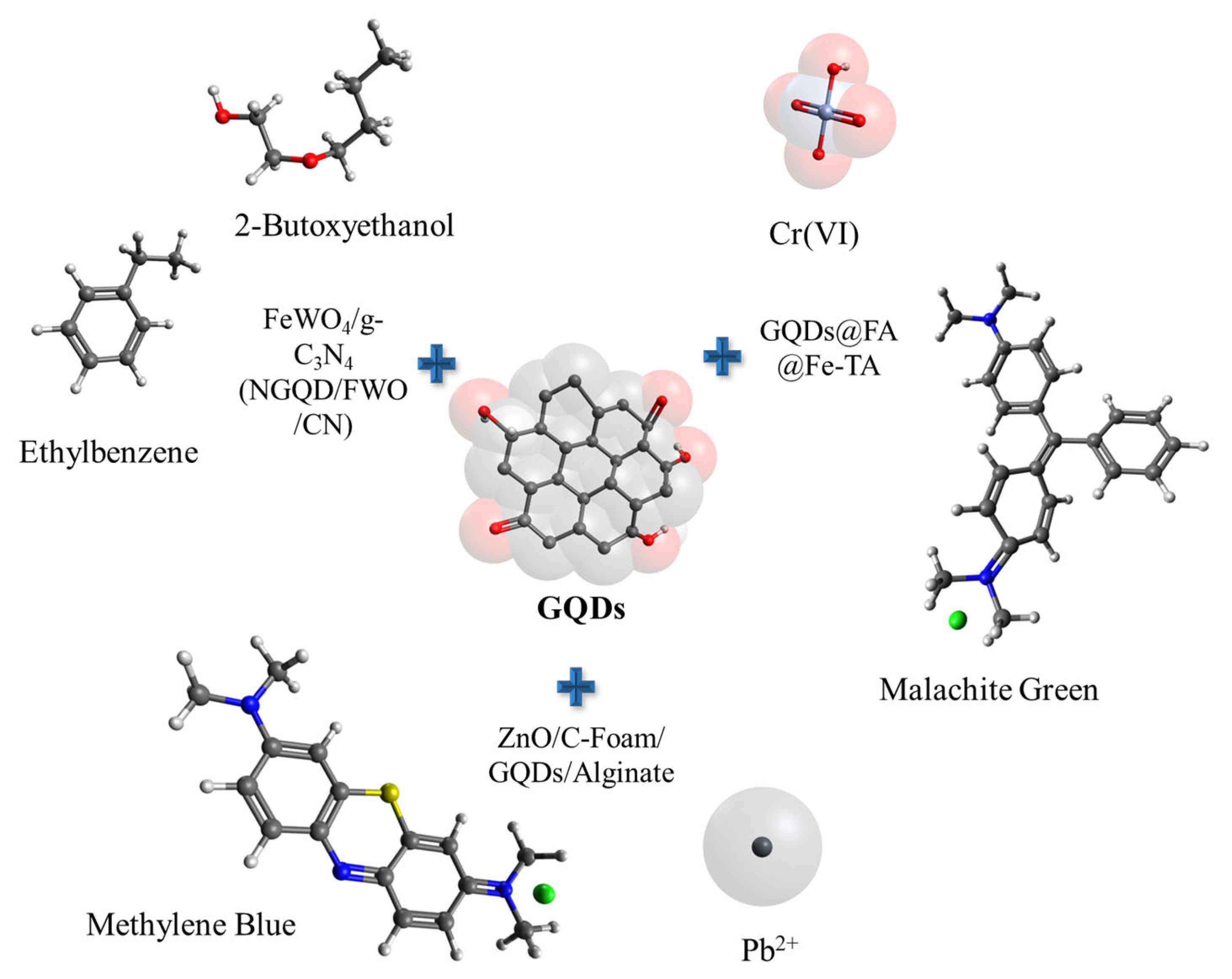
| Material | Contaminant | pH | Efficiency % | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GQDs/g-CNNR | Antibiotic OTC | - | 80 | [64] |
| GQDs/gCN/ODBOC | Vapores orgánicos | - | 95 | [65] |
| FeWO4/g-C3N4 (NGQD/FWO/CN) | Vapores 2-butoxietanol etilbenceno | - | 97.3 | [66] |
| 55.1 | ||||
| PVA/CMC-B@GO/Fe3O4/GQD | Dye pollutants | 8 | 86.7 | [67] |
| GQDs@FA@Fe-TA | Cr(VI) MG | 3 | 99.5 | [68] |
| 94.8 | ||||
| ZnO/C-Foam/GQDs/Alginate | Pb (II) Azul metileno MB | 6 7 | 100 | [69] |
| 92.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Caicedo, J.P.; Joya-Cárdenas, D.R.; Corona-Rivera, M.A.; Saldaña-Robles, N.; Damian-Ascencio, C.E.; Saldaña-Robles, A. Efficiency of Graphene Quantum Dots in Water Contaminant Removal: Trends and Future Research Directions. Water 2025, 17, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020166
Rodríguez-Caicedo JP, Joya-Cárdenas DR, Corona-Rivera MA, Saldaña-Robles N, Damian-Ascencio CE, Saldaña-Robles A. Efficiency of Graphene Quantum Dots in Water Contaminant Removal: Trends and Future Research Directions. Water. 2025; 17(2):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020166
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Caicedo, Juliana P., Diego R. Joya-Cárdenas, Miguel A. Corona-Rivera, Noé Saldaña-Robles, Cesar E. Damian-Ascencio, and Adriana Saldaña-Robles. 2025. "Efficiency of Graphene Quantum Dots in Water Contaminant Removal: Trends and Future Research Directions" Water 17, no. 2: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020166
APA StyleRodríguez-Caicedo, J. P., Joya-Cárdenas, D. R., Corona-Rivera, M. A., Saldaña-Robles, N., Damian-Ascencio, C. E., & Saldaña-Robles, A. (2025). Efficiency of Graphene Quantum Dots in Water Contaminant Removal: Trends and Future Research Directions. Water, 17(2), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17020166






