Detection of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli in the Upper Citarum River Using a β-D-Glucuronidase Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. River Water Sampling
2.2. Enumeration of Total Escherichia coli (TEc) and Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli (AREc) Using the Conventional Agar Method
2.3. Enumeration of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli (AREc) Ratio Using the Microplate Reader (MPR Method)
2.4. Stastitical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatiotemporal Concentration of Total Escherichia coli (TEc) in Upper Citarum River
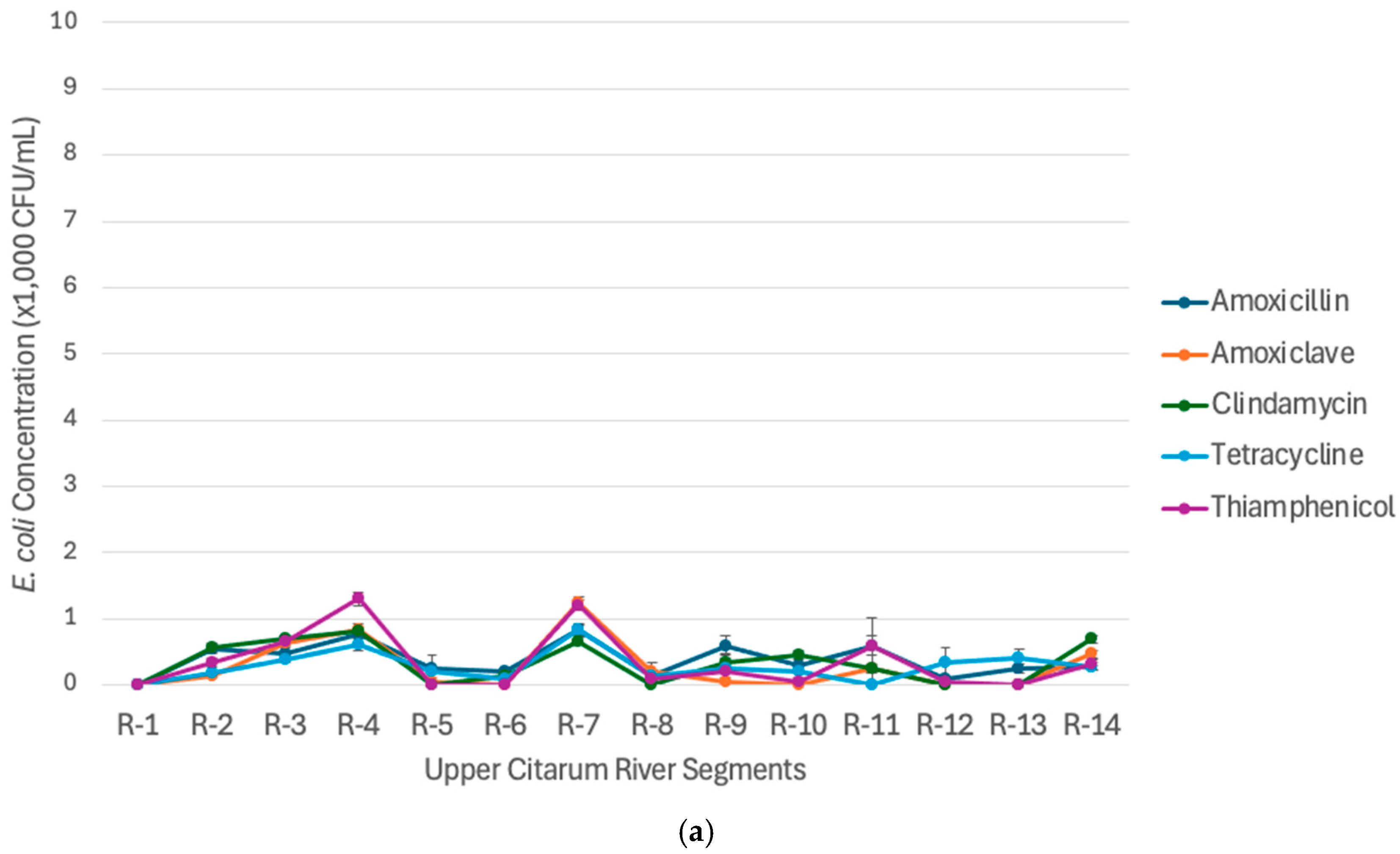
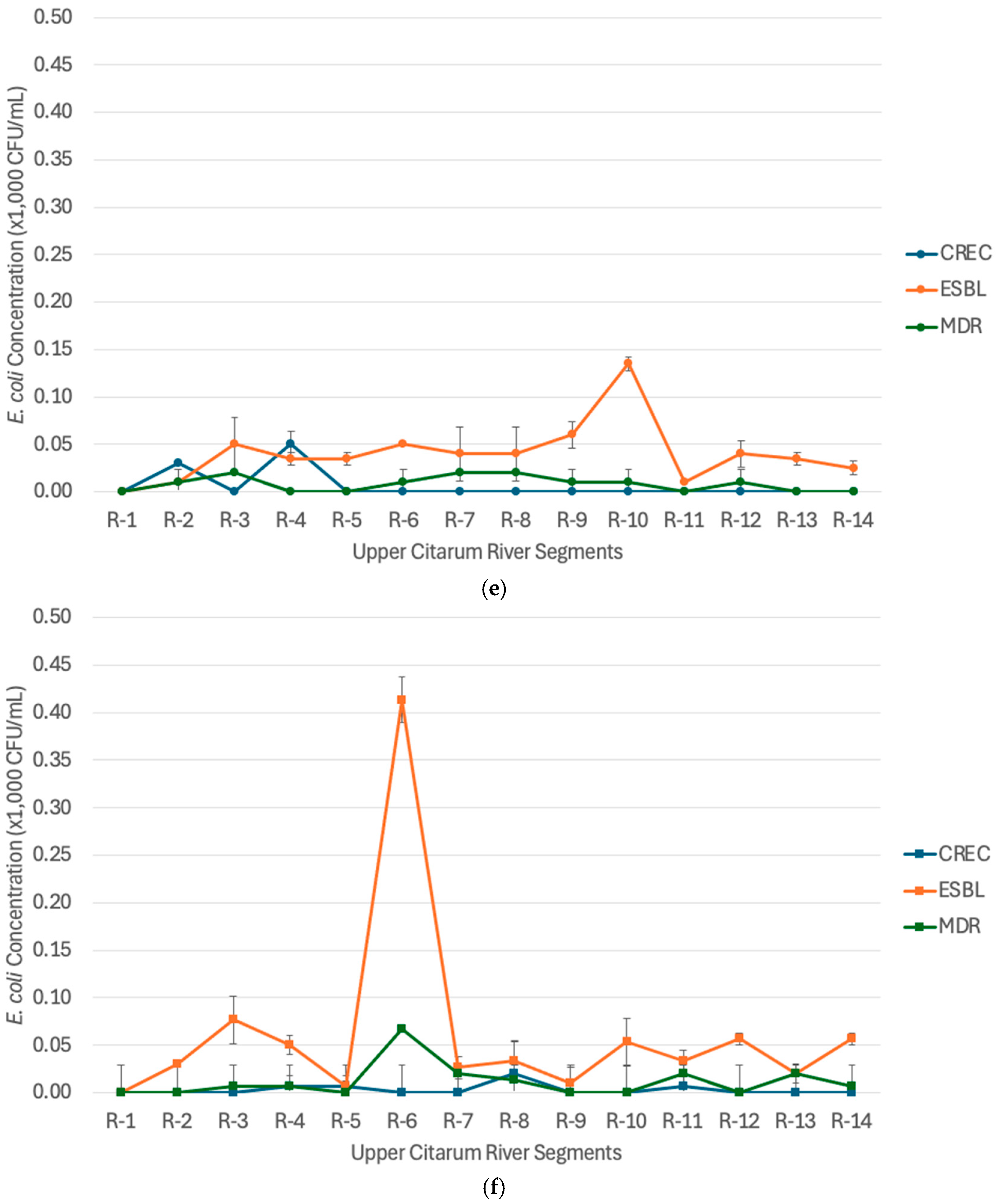
3.2. Spatiotemporal Concentration of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli (AREc) in the Upper Citarum River
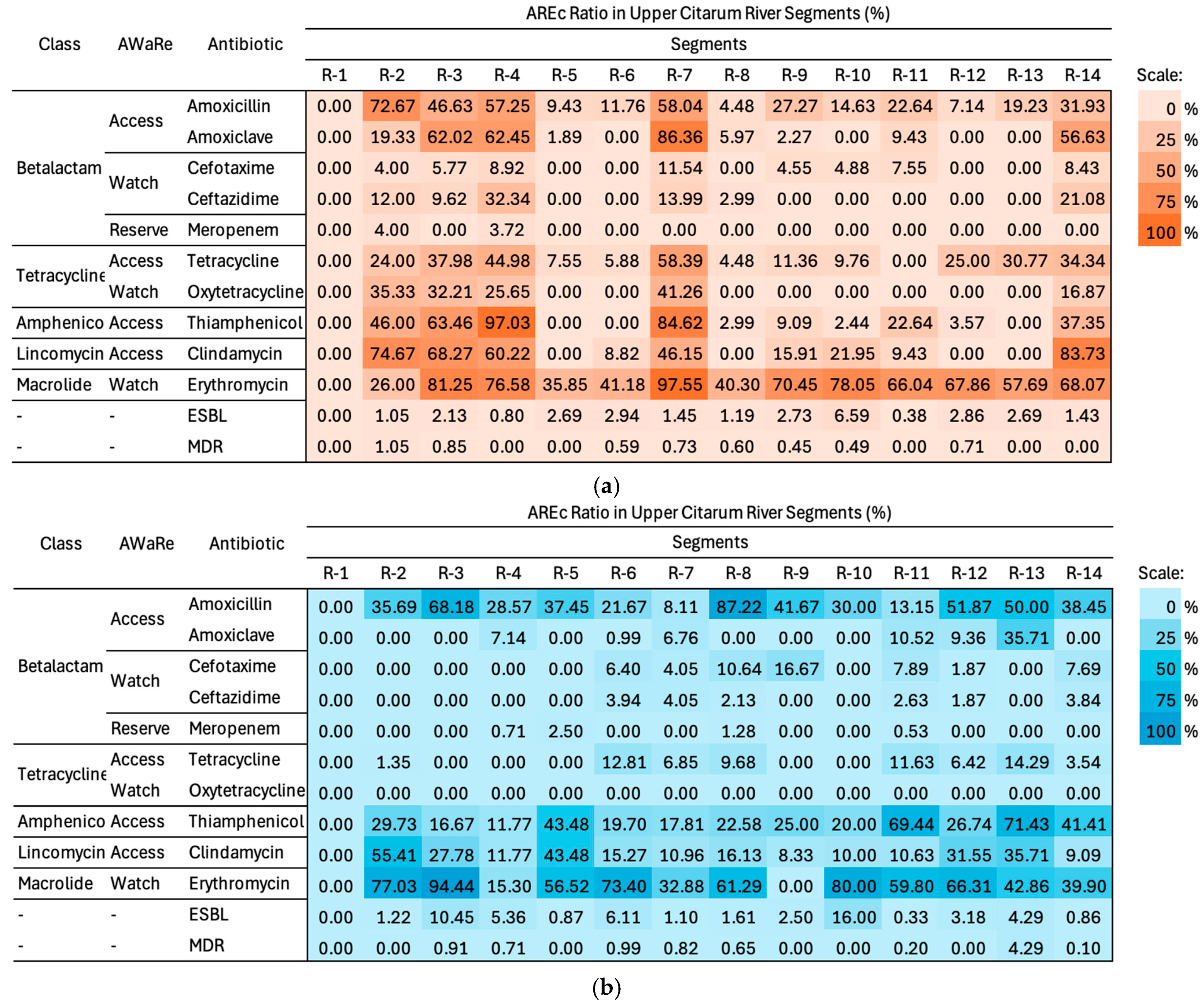
3.3. Priority Bacterial Target of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli (AREc) in the Upper Citarum River
3.4. Comparison of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli Ratio Using the Two Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hutchings, M.; Truman, A.; Wilkinson, B. Antibiotics: Past, present and future. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.Y.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Martinez, E.M.; Pant, S.; Gandra, S.; Levin, S.A.; Goossens, H.; Laxminarayan, R. Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3463–E3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camcioglu, Y.; Okur, D.S.; Aksaray, N.; Darendeliler, F.; Hasanoglu, E. Factors affecting physicians’ perception of the overuse of antibiotics. Med. Mal. Infect. 2020, 50, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Bornman, C.; Zafer, M.M. Antimicrobial Resistance Threats in the emerging COVID-19 pandemic: Where do we stand? J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, G.; Midiri, A.; Gerace, E.; Biondo, C. Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance: The Most Critical Pathogens. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastiti, A.; Utami, R.R.; Ramadhina, S.Q.; Fathonah, N.; Yoga, G.P.; Ariesyady, H.D.A.; Kusumah, S.W.D.; Hidayat. Disposal practices, risk perceptions, and quantification of potential active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) from used human medicine in Upper Citarum River Basin. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2025, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney, A.R.; Safaee, M.M.; Wuest, W.M.; Furst, A.L. The silent pandemic: Emergent antibiotic resistances following the global response to SARS-CoV-2. iScience 2021, 24, 102304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomini, E.; Perrone, V.; ALessandriani, D.; Paoli, D.; Nappi, C.; Degli, E.L. Evidence of antibiotic resistance from population-based studies: A narrative review. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. GLASS Method for Estimating Attributable Mortality of Antimicrobial Resistant Bloodstream Infections; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, D.; Flach, C.F. Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Song, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, T.; Zhu, L. Simultaneous removal of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and its resistance genes in water by plasma oxidation: Highlights the effects of inorganic ions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 278, 119672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fang, D.; Yang, B.; Li, R.; Liu, Y. Acetaminophen promotes horizontal transfer of plasmid-borne multiple antibiotic resistance genes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240093461 (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Bengstton-Palme, J.; Larsson, D.G.J. Concentrations of antibiotics predicted to select for resistant bacteria: Proposed limits for environmental regulation. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben, Y.; Fu, C.X.; Hu, M.; Liu, L.; Zheng, C.M. Human health risk assessment of antibiotic resistance associated with antibiotic residues in the environment: A review. Environ. Res. 2019, 169, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, H.; Nagahashi, N.; Kikuchi, K.; Hirano, R. Screening Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli in Wastewater and River Water Using a Novel Simple Phenotypic Antibiotic-Susceptibility Testing Method. ACS EST Water 2022, 2, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenni, P. Antimicrobial resistance in rivers: A review of the genes detected and new challenges. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 687–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gekenidis, M.T.; Qi, W.; Hummerjohann, J.; Zbinden, R.; Walsh, F.; Drissner, D. Antibiotic-resistant indicator bacteria in irrigation water: High prevalence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Truchado, P.; Cordero-García, R.; Gil, M.I.; Soler, M.A.; Rancaño, A.; García, F.; Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Allende, A. Surveillance on ESBL-Escherichia coli and indicator ARG in wastewater and reclaimed water of four regions of Spain: Impact of different disinfection treatments. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, N.H.F.; Yusoff, M.A.M.; Gunggang, R.A.T.; Razak, R.A.; Jaafar, M.Z.; Yahaya, N.K.E. Water Quality and Prevalence of Extended Spectrum Beta Lactamase Producing Escherichia coli (ESBL E. coli) in Sungai Terengganu, Malaysia. Malays. Appl. Biol. 2024, 53, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, T.R.; Islam, M.A.; Pickering, A.J.; Roy, S.; Fuhrmeister, E.R.; Ercumen, A.; Harris, A.; Bishai, J.; Schwab, K.J. Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of Escherichia coli isolates from feces, hands, and soils in rural bangladesh via the colilert quanti-tray system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genter, F.; Marks, S.J.; Clair-Caliot, G.; Mugume, D.S.; Johnston, R.B.; Bain, R.E.; Julian, T.R. Evaluation of the novel substrate rugTM for the detection of Escherichia coli in water from temperate (zurich, switzerland) and tropical (bushenyi, uganda) field sites. Environ. Sci. 2019, 5, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Chen, J.; Nugen, S. Electrochemical detection of Escherichia coli from aqueous samples using engineered phages. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hong, P.Y.; LeChevallier, M.W.; Liu, W.T. Phenotypic and phylogenetic identification of coliform bacteria obtained using 12 coliform methods approved by the US Environmental Protection Agency. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6012–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayan, M.N.; Tanaka, Y.; Hirano, R.; Nakaya, Y.; Satoh, H. A simple and rapid method for detecting fecal pollution in urban rivers by measuring the intrinsic β-D-glucuronidase activity of Escherichia coli. Water Res. 2023, 246, 120689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadhil, M.Y.; Hidayat, Y.; Murtilaksono, K.; Baskoro, D.P.T. Changes in land use and hydrological characteristics of the Upstream Citarum watershed. J. Ilmu Pertan. Indones. 2021, 26, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitriana, F.; Yudianto, D.; Sanjaya, S.; Roy, A.F.; Seo, Y.C. The assessment of Citarum river water quality in Majalaya District, Bandung regency. Rekayasa Sipil 2023, 17, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumah, S.W.D.; Kandio, N.; Maghfirah, R.; Setiyawan, A.S.; Ariesyady, H.D. The occurrence of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli in the Upper Citarum River and surrounding wastewater effluents. E3S Web Conf. 2024, 485, 07006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriani, F.; Ariesyady, H.D. Microbiological Source Tracking Bakteri Escherichia coli dengan Metode Antibiotic Resistance Analysis di Sungai Cikapundung. J. Environ. Eng. ITB 2013, 19, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badan Standardisasi Nasional. “SNI 03-7016-2004: Tata Cara Pengambilan Contoh Dalam Rangka Pemantauan Kualitas Air pada Suatu Daerah Pengaliran Sungai,” Jakarta: BSN. Available online: https://perpustakaan.ciptakarya.pu.go.id/opac/index.php?p=show_detail&id=10227 (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 34th ed.; CLSI Supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Satoh, H.; Kikuchi, K.; Katayose, Y.; Tsuda, S.; Hirano, R.; Hirakata, Y.; Kitajima, M.; Ishii, S.; Oshiki, M.; Hatamoto, M.; et al. Simple and reliable enumeration of Escherichia coli concentrations in wastewater samples by measuring β-d-glucuronidase (GUS) activities via a microplate reader. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, H.; Katayose, Y.; Hirano, R. Simple enumeration of Escherichia coli concentrations in river water samples by measuring β-D-glucuronidase activities in a microplate reader. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahayudin, Y.; Iskandar, I.; Agus, M.; Ramdhan. Hidrogeologi dan Hidrogeokimia Mata Air Danau Cisanti (Hulu Sungai Citarum). Master’s Thesis, Bandung Institute of Technology, Bandung, Indonesia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- BPS Provinsi Jawa Barat. Persentase Rumah Tangga yang Memiliki Akses Terhadap Sanitasi Layak (Persen), 2022–2024. Available online: https://jabar.bps.go.id/id/statistics-table/2/NzI4IzI=/persentase-rumah-tangga-yang-memiliki-akses-terhadap-sanitasi-layak.html (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Zahra, Z.; Indrawaty, L.; Arfines, P.P. Manajemen Pengelolaan Sampah Rumah Tangga Dan Limbah Ternak Di Kawasan Peternakan Daerah Aliran Sungai Citarum Kabupaten Bandung. J. Ekol. Kesehat. 2021, 20, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kementerian Lingkungan Hidup dan Kehutanan Republik Indonesia. “Laporan Kinerja Tahun 2023: Direktorat Pengendalian Pencemaran Air, Direktorat Jenderal Pengendalian Pencemaran dan Kerusakan Lingkungan,” Kementerian Lingkungan Hidup dan Kehutanan Republik Indonesia. Available online: https://ppkl.menlhk.go.id/website/filebox/1194/240118150657LKj%20Direktorat%20PPA%202023.pdf (accessed on 2 August 2025).
- Ram, S.; Vajpayee, P.; Shanker, R. Prevalence of multi-antimicrobial-agent resistant, shiga toxin and enterotoxin producing Escherichia coli in surface waters of river ganga. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7383–7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowes, M.J.; Read, D.S.; Joshi, H.; Sinha, R.; Ansari, A.; Hazra, M.; Simon, M.; Vishwakarma, R.; Armstrong, L.K.; Nicholls, D.J.; et al. Nutrient and microbial water quality of the upper Ganga River, India: Identification of pollution sources. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, G.; Naik, P.K.; Machell, J.; Kumar, A.; Gjyli, L.; Tiwari, A.K.; Kumar, A. Comparative study on seasonal variation in hydro-chemical parameters of Ganga River water using comprehensive pollution index (CPI) at Rishikesh (Uttarakhand) India. Desalination Water Treat. 2018, 118, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Sinha, S.K.; Rani, N.; Sinha, R.K. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in water, sediment, and fish of the river Ganga at Varanasi, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohene, A.; Srikaran, P. Modeling the Impact of Animal Farming on Water Quality of Sg. Serin. Ph.D. Thesis, Universiti Malaysia Sarawak, Kota Samarahan, Malaysia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yee, L.; Wee, L.; Bilung, L.; Lee, N. Impact of different land uses on the Escherichia coli concentrations, physical and chemical water quality parameters in a tropical stream. Borneo J. Resour. Sci. Technol. 2016, 2, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Yoshizawa, K.; Magara, Y. Non-point pollution of Ishikari river, Hokkaido, Japan. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikder, M.T.; Kihara, Y.; Yasuda, M.; Yustiawati Mihara, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Odgerel, D.; Mijiddorj, B.; Syawal, S.M.; Hosokawa, T.; Saito, T. River Water Pollution in Developed and Developing Countries: Judge and Assessment of Physicochemical Characteristics and Selected Dissolved Metal Concentration. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2013, 41, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negishi, J.N.; Izumi, H.; Wu, J.; Fukui, S.; Koizumi, I. Does winterkill explain contrasting demographics of winter. bioRxiv 2023. 2023.11.07.565987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayati, N.V.; Syakti, A.D.; Asia, L.; Lebarillier, S.; Khabouchi, I.; Widowati, I.; Sabdono, A.; Piram, A.; Doumenq, P. Emerging contaminants detected in aquaculture sites in Java, Indonesia. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, A.R.; Suryani, E.; Putra, I.M. Antibiotic utilization and its implications among ruminant farmers and stakeholders in Sumbawa Regency, Indonesia. One Health 2017, 7, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Wanniatie, S.; Furi, M.; Widiasih, D.A. Detection of antibiotic residues in chicken meat and eggs from traditional markets at Yogyakarta City using bioassay method. Vet. World 2019, 12, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar]
- Widiasih, D.A.; Pratama, R.P.; Drastini, Y.; Putri, K.; Fatimah, L.N.; Indarjulianto, S. Rapid testing of antibiotic residues to increase food safety awareness of animal origin. Vet. World 2024, 17, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassini, A.; Högberg, L.D.; Plachouras, D.; Quattrocchi, A.; Hoxha, A.; Simonsen, G.S.; Colomb-Cotinat, M.; Kretzschmar, M.E.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Cecchini, M.; et al. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: A population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomi, R.; Matsuda, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Tanaka, M.; Ichiyama, S.; Yoneda, M. Whole-Genome Analysis of Antimicrobial-Resistant and Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli in River Water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e02703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessa, L.J.; Barbosa-Vasconcelos, A.; Mendes, Â.; Vaz-Pires, P.; da Costa, P.M. High prevalence of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli and Enterococcus spp. in river water, upstream and downstream of a wastewater treatment plant. J. Water Health 2014, 12, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderpour, A.; Ho, W.S.; Chew, L.-L.; Bong, C.W.; Chong, V.C.; Thong, K.-L.; Chai, L.C. Diverse and abundant multi-drug resistant E. coli in Matang mangrove estuaries, Malaysia. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odonkor, S.T.; Addo, K.K. Prevalence of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from drinking water sources. Int. J. Microbiol. 2018, 1, 7204013. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, J.S.; Burmølle, M.; Hansen, L.H.; Sørensen, S.J. The interconnection between biofilm formation and horizontal gene transfer. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2012, 65, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felis, E.; Montesissa, C.; Gabbarini, C. Persistence and degradation of erythromycin in sediments and water under laboratory conditions. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 847–852. [Google Scholar]
- Hidayati, R.; Anggiani, S.T.; Maufikoh, I. Incidence Analysis of an Acute Respiratory Infection due to Climate Conditions and PM10 Concentration. Agromet 2017, 31, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.F.; Schmitt, H.; Börjesson, S.; Berendonk, T.U.; Donner, E.; Stehling, E.G.; Boerlin, P.; Topp, E.; Jardine, C.; Li, X.; et al. The potential of using E. coli as an indicator for the surveillance of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in the environment. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2021, 64, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerek, Á.; Román, I.; Szabó, Á.; Kovács, D.; Kardos, G.; Kovács, L.; Jerzsele, Á. Antibiotic resistance genes in Escherichia coli—Literature review. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2025, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, D.L.; Bonomo, R.A. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: A clinical update. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 657–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, S.P.; Pawar, P.P.; Patil, K.S.; Jadhav, P.V. A fluorescence-based sensor for selective and sensitive detection of amoxicillin in aqueous media. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 179, 108–115. [Google Scholar]
- Cansizoglu, M.; Tamer, Y.; Farid, M.; Koh, A.; Toprak, E. Rapid ultrasensitive detection platform for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meerwein, M.; Tarnutzer, A.; Böni, M.; Bambeke, F.; Hombach, M.; Zinkernagel, A. Increased azithromycin susceptibility of multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria on rpmi-1640 agar assessed by disk diffusion testing. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| No | Test Plates for Specific Escherichia coli Variants | Antibiotics Used in the Agar | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (μg/mL) | AwaRe Classification for the Antibiotic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Total Escherichia coli | None | - | - |
| 2 | Amoxicillin-resistant Escherichia coli | Amoxicillin | 32 | Access |
| 3 | Thiamphenicol- resistant Escherichia coli | Thiamphenicol | 32 | Access |
| 4 | Tetracycline-resistant Escherichia coli | Tetracycline | 16 | Access |
| 5 | Clindamycin-resistant Escherichia coli | Clindamycin | 32 | Access |
| 6 | Amoxiclav-resistant Escherichia coli | Amoxiclav | 16 | Access |
| 7 | Oxytetracycline-resistant Escherichia coli | Oxytetracycline | 16 | Watch |
| 8 | Erythromycin-resistant Escherichia coli | Erythromycin | 16 | Watch |
| 9 | Cefotaxime-resistant Escherichia coli | Cefotaxime | 4 | Watch |
| 10 | Ceftazidime-resistant Escherichia coli | Ceftazidime | 16 | Watch |
| 11 | Carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli | Meropenem | 4 | Reserve |
| 12 | Multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli (All antibiotics are homogenized in the test tube/plate) | Amoxicillin Cefotaxime Tetracycline Ciprofloxacin | 32 4 16 1 | Access Watch Access Watch |
| 13 | ESBL-Escherichia coli (Using two stages test plate. Viable colonies in Test plate I were tested in Test Plate II) | Test Plate I: Amoxicillin Cefotaxime | 32 4 | Access Watch |
| Test Plate II: Amoxicillin Cefotaxime Clavulanic Acid | 32 4 16 | Access Watch Watch |
| Parameters | Dissolved Oxygen | BOD | Heavy Metals | Total Escherichia coli | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citarum River, Indonesia | Dry season: 3.1–7.6 mg/L Rainy season: 2.8–6.4 mg/L | <40 mg/L | Zinc, Pb, Hg concentration exceeding the WHO standard | Dry season: 0–3350 CFU/mL Rainy season: 0–10,330 CFU/mL | This study; [27] |
| Gangga River, India | <5 mg/L | <30 mg/L | Pb, Cd, Cr concentration exceeding the WHO standard | 7.94 to 501.19 CFU/mL | [38,39,40,41] |
| Serin River, Malaysia | 3.20–7.65 mg/L | 1.86–7.99 mg/L | NA | 17.42–1898.82 CFU/mL | [42,43] |
| Ishikari River, Japan | 3.3–10.6 mg/L | 1.8–29.8 mg/L | Mn and Cd exceed WHO standard | 9–44 CFU/ml | [44,45,46] |
| Factors | Variable | Agreement Rate (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | ||
| Matrices | Period I (Average Rainfall: 155.7 mm/month) | 89.8% | 83.6% | 92.4% |
| Period II (Average Rainfall: 302.3 mm/month) | 84.5% | 45.9% | 95.4% | |
| Abundance of Bacteria (Total Escherichia coli in CFU/mL) | 0–500 CFU/mL | 58.34% | 71.87% | 56.64% |
| 500–1000 CFU/mL | 75.86% | 89.47% | 50% | |
| 1000–1500 CFU/mL | 92.3% | 100% | 50% | |
| >1500 CFU/mL | 40% | 100% | 0% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kusumah, S.W.D.; Katsuya, M.; Fahmi, R.R.; Notodarmojo, P.A.; Setiyawan, A.S.; Satoh, H.; Ariesyady, H.D. Detection of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli in the Upper Citarum River Using a β-D-Glucuronidase Method. Water 2025, 17, 2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182791
Kusumah SWD, Katsuya M, Fahmi RR, Notodarmojo PA, Setiyawan AS, Satoh H, Ariesyady HD. Detection of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli in the Upper Citarum River Using a β-D-Glucuronidase Method. Water. 2025; 17(18):2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182791
Chicago/Turabian StyleKusumah, Siska Widya Dewi, Mochinaga Katsuya, Rifky Rizkullah Fahmi, Peni Astrini Notodarmojo, Ahmad Soleh Setiyawan, Hisashi Satoh, and Herto Dwi Ariesyady. 2025. "Detection of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli in the Upper Citarum River Using a β-D-Glucuronidase Method" Water 17, no. 18: 2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182791
APA StyleKusumah, S. W. D., Katsuya, M., Fahmi, R. R., Notodarmojo, P. A., Setiyawan, A. S., Satoh, H., & Ariesyady, H. D. (2025). Detection of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli in the Upper Citarum River Using a β-D-Glucuronidase Method. Water, 17(18), 2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182791






