Surface Water–Groundwater Interactions in a Sahelian Catchment: Exploring Hydrochemistry and Isotopes and Implications for Water Quality Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
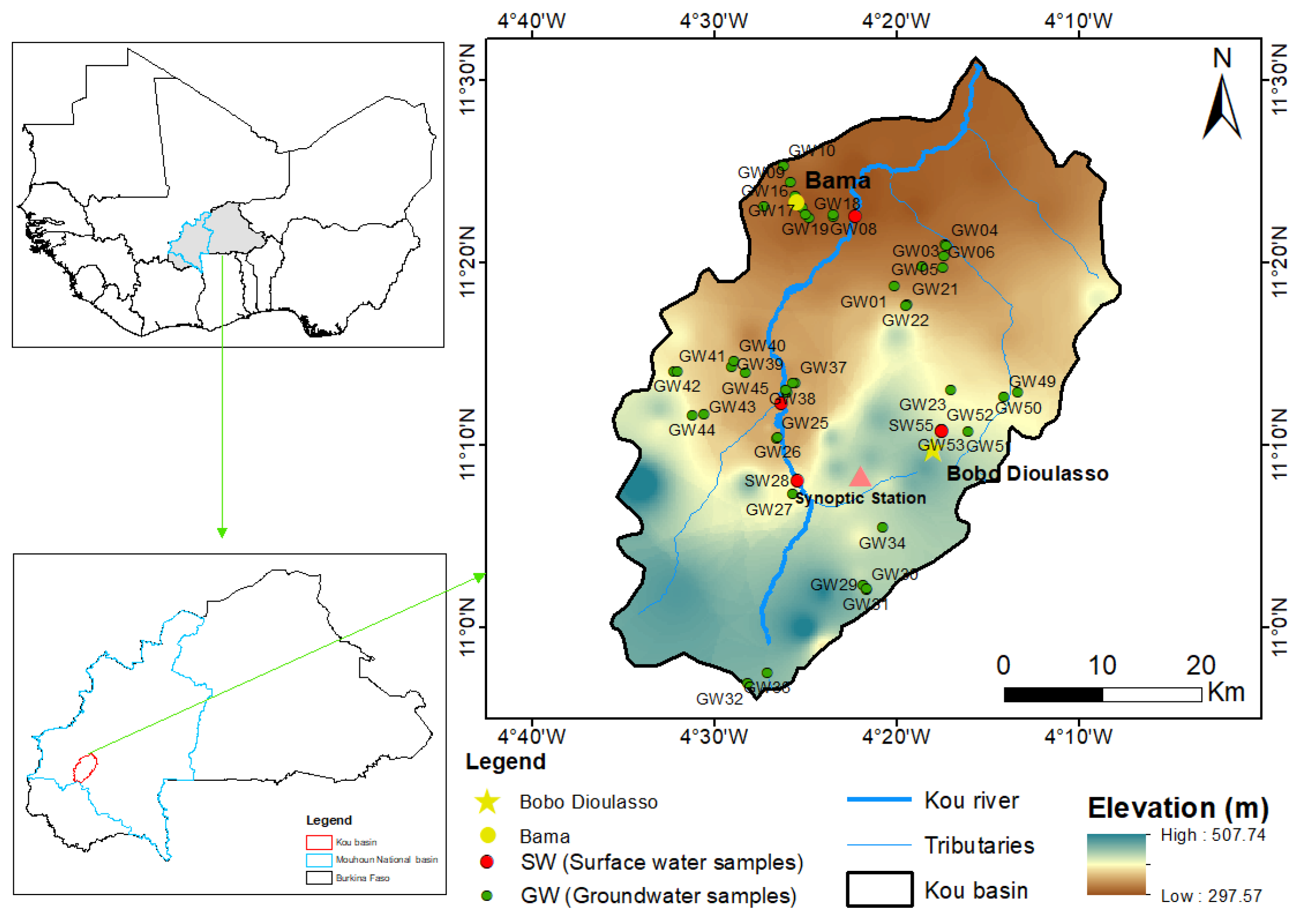
2.1. Study Area
2.1.1. General Information
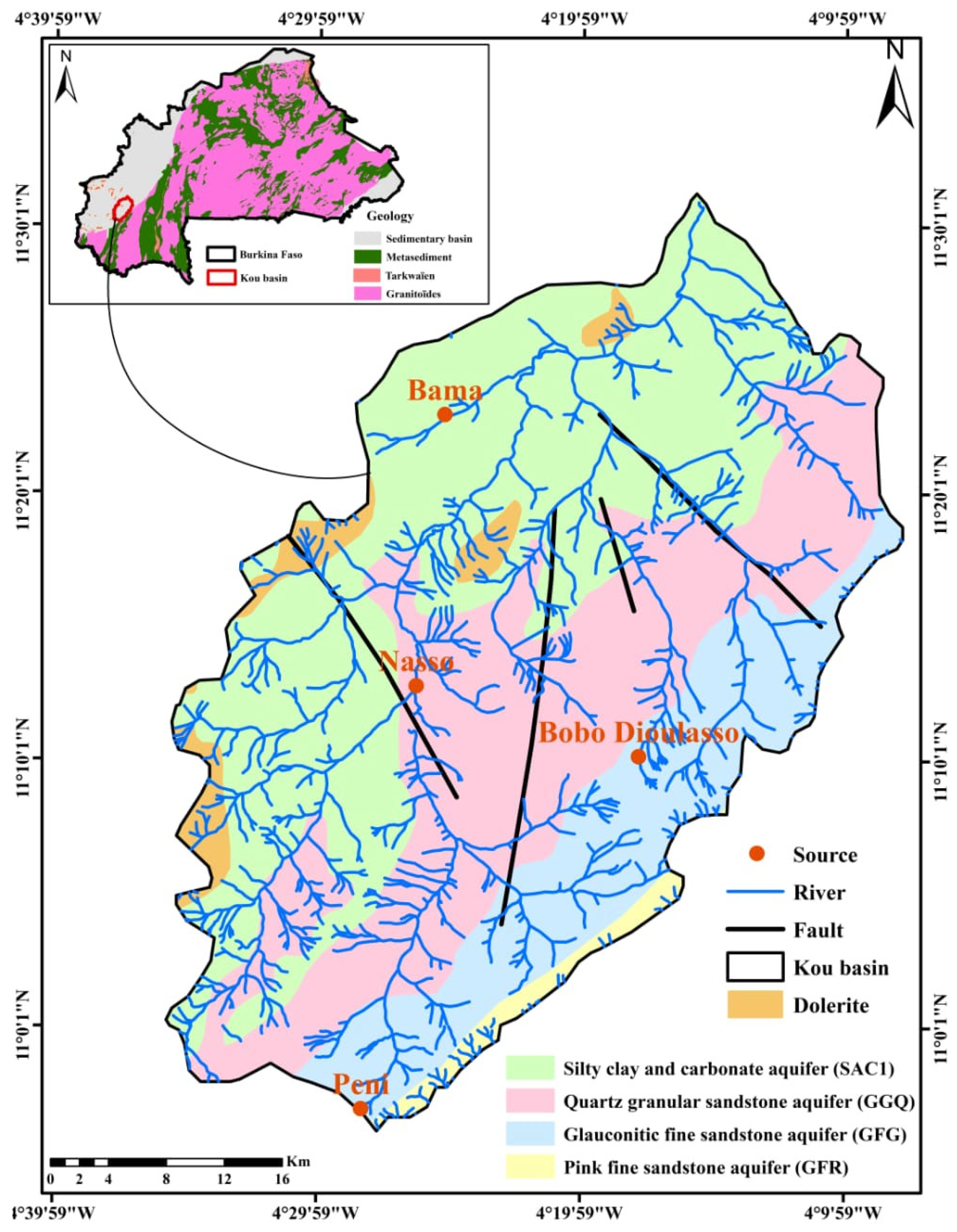
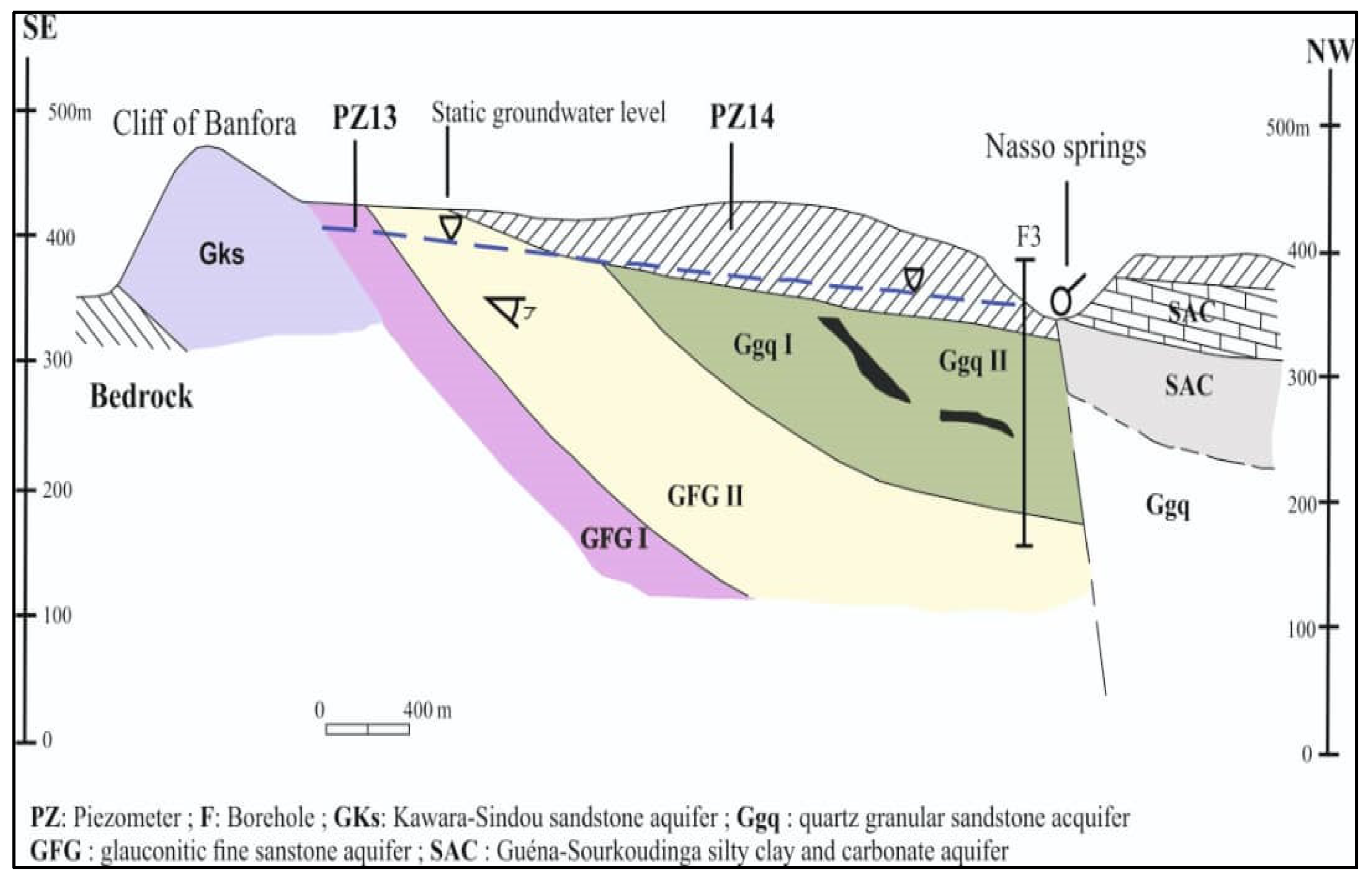
2.1.2. Geological and Hydrogeological Setting
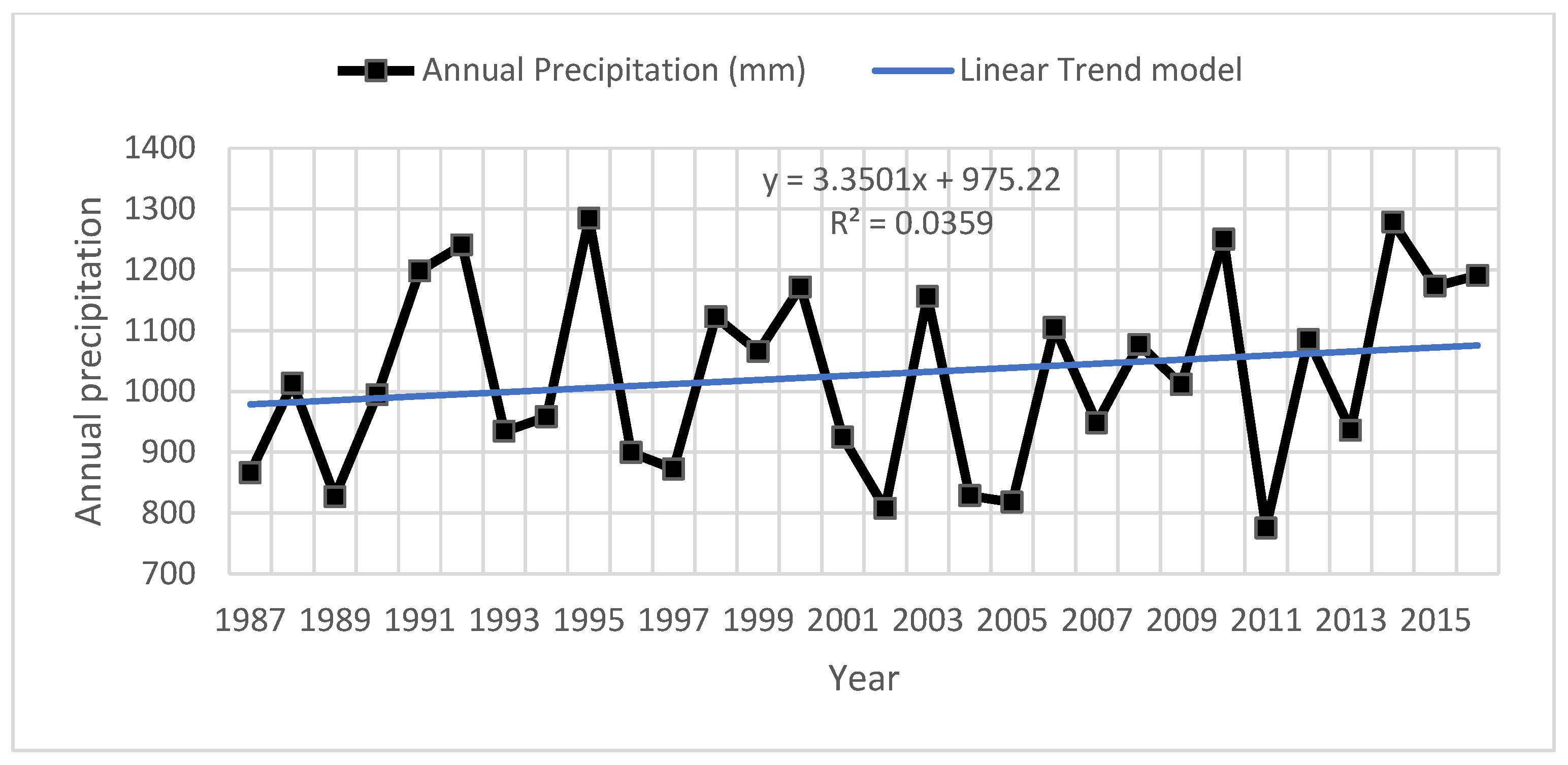
2.1.3. Hydrology and Anthropogenic Pressure
2.2. Sampling Method and Isotope Analysis
2.2.1. Sampling Procedures
2.2.2. Analytical Techniques
2.2.3. Spatial Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
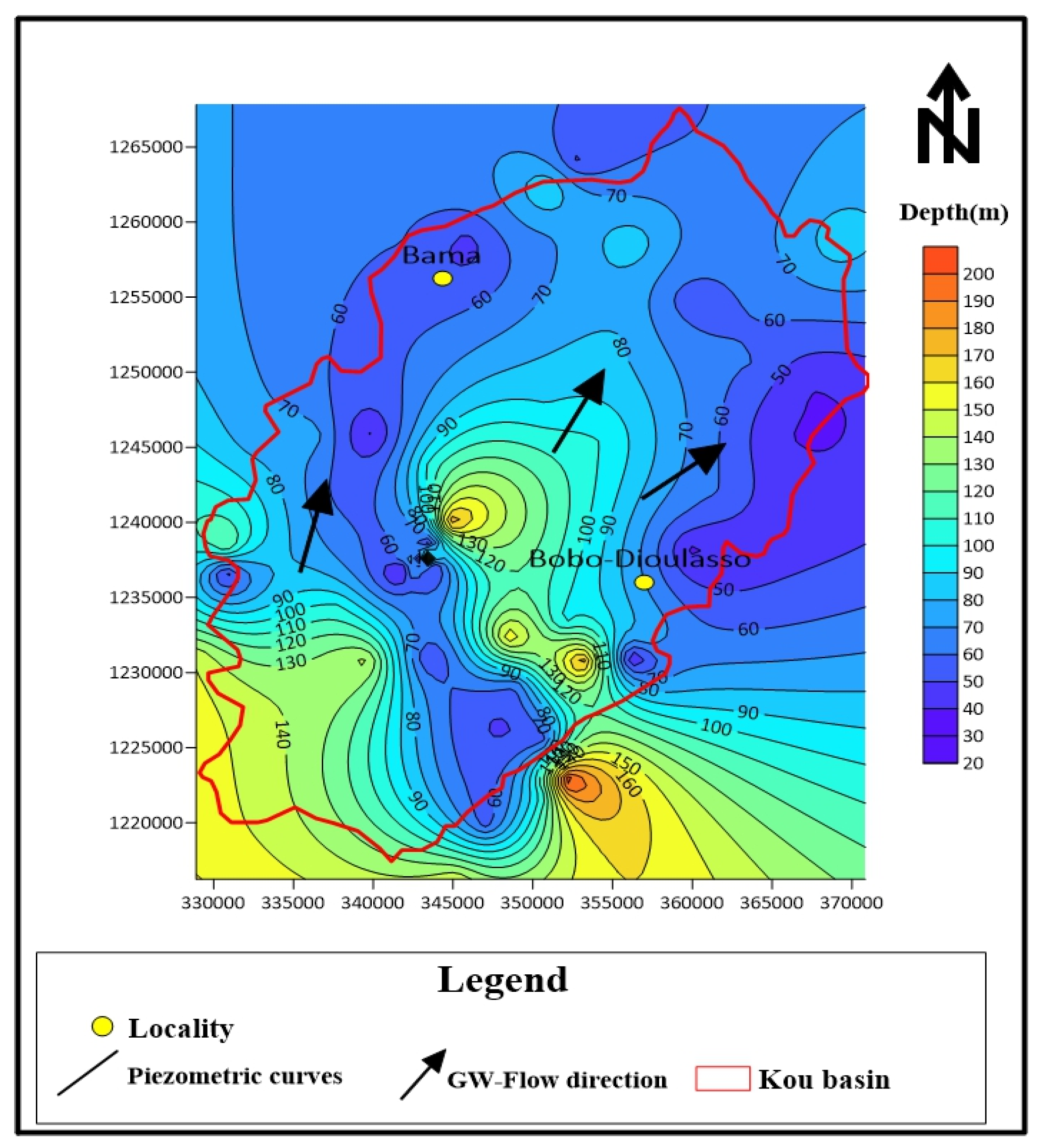
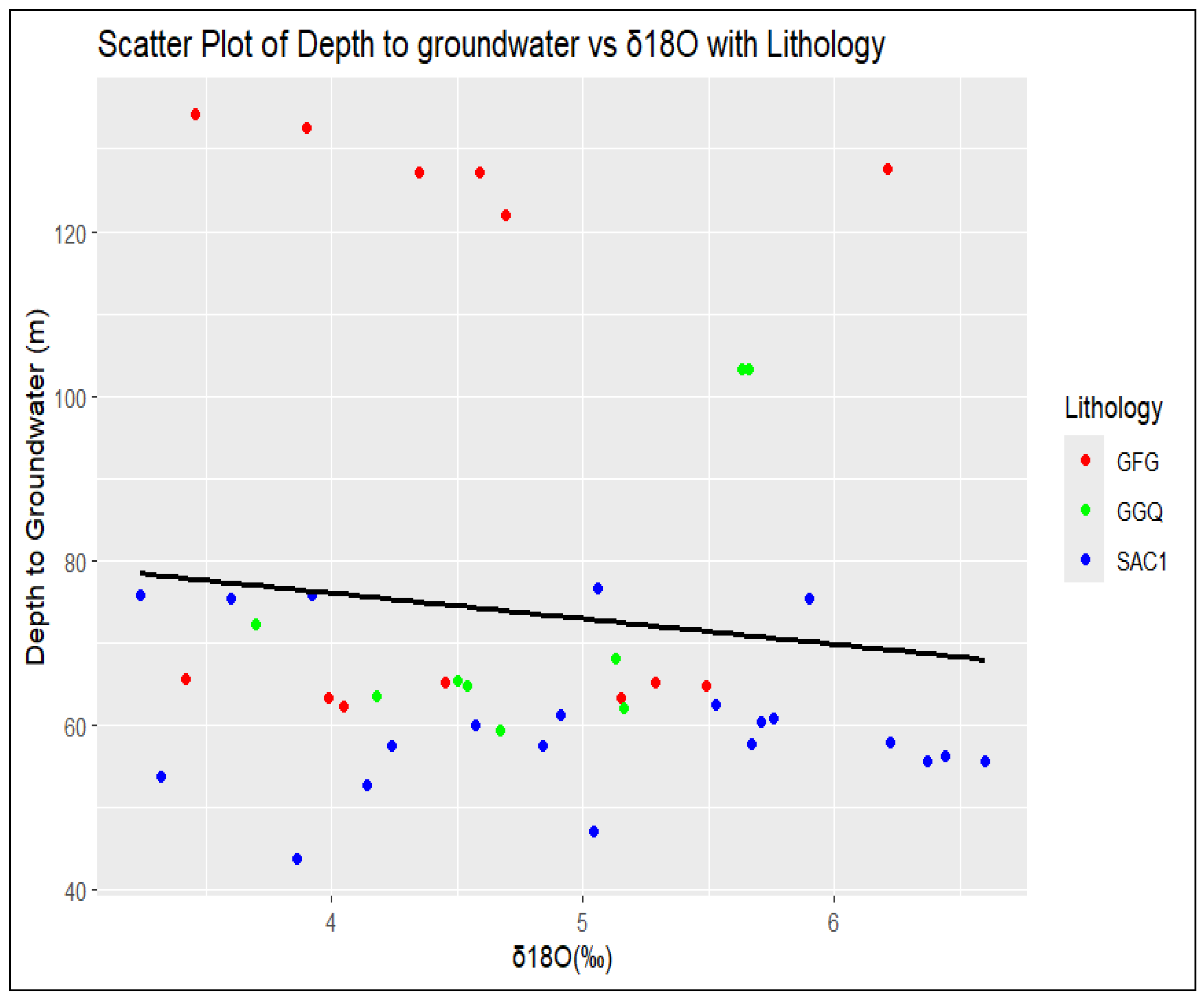
3.1. Groundwater Depth and Direction of Flows
3.2. Hydrochemical Characteristics
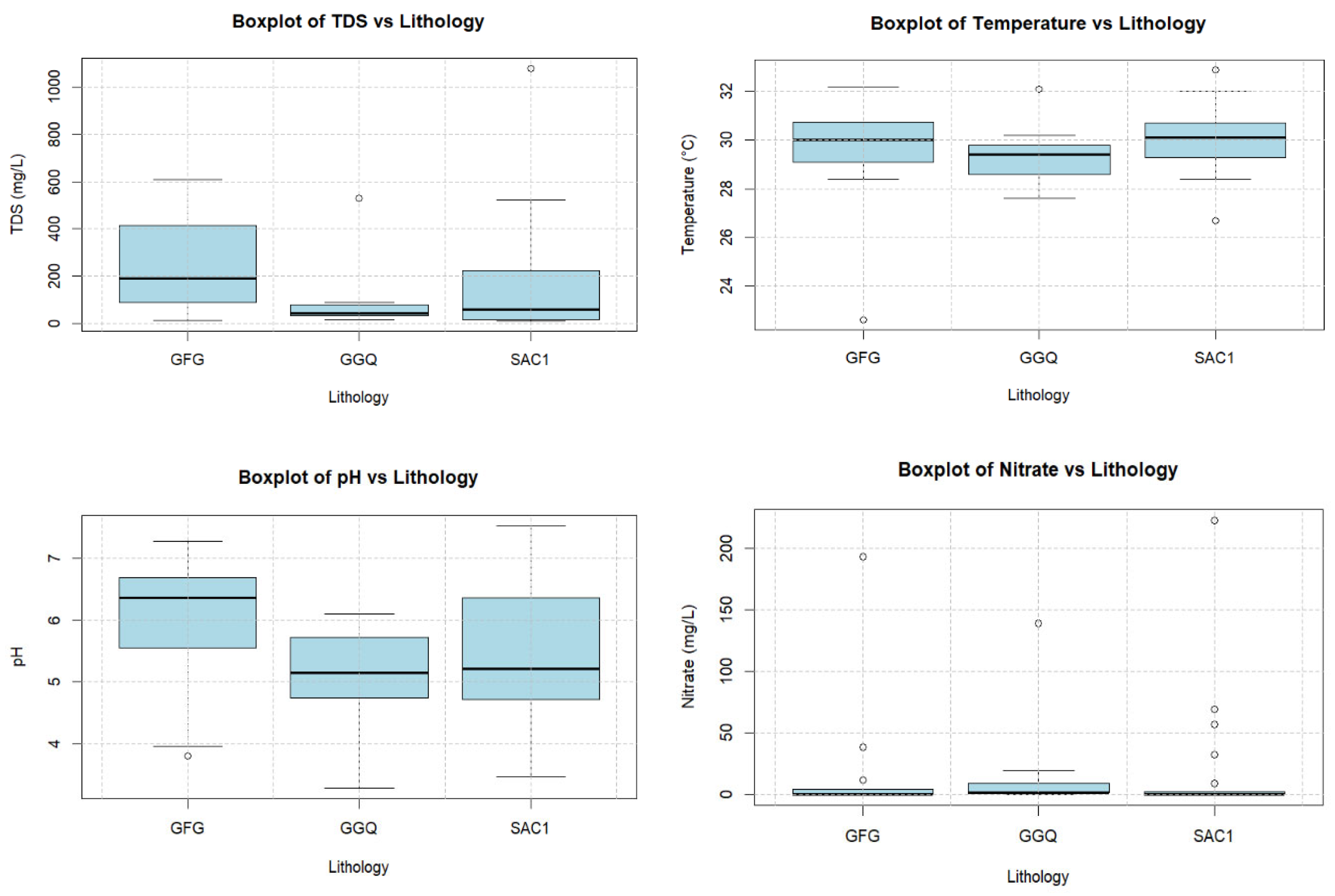
3.2.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2.2. Correlation Matrix Analysis
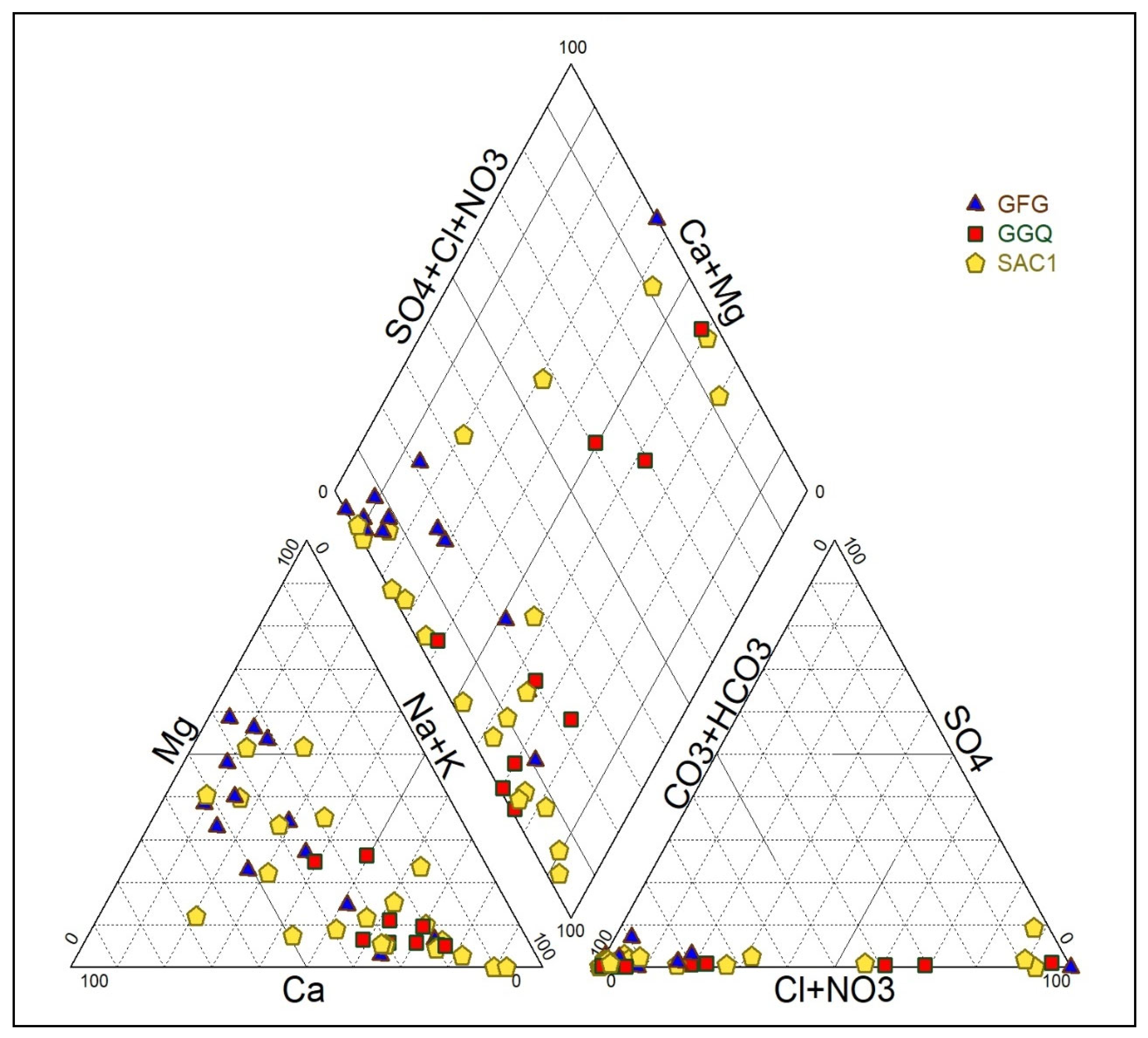
3.2.3. Groundwater Types Classification Based on the Lithology
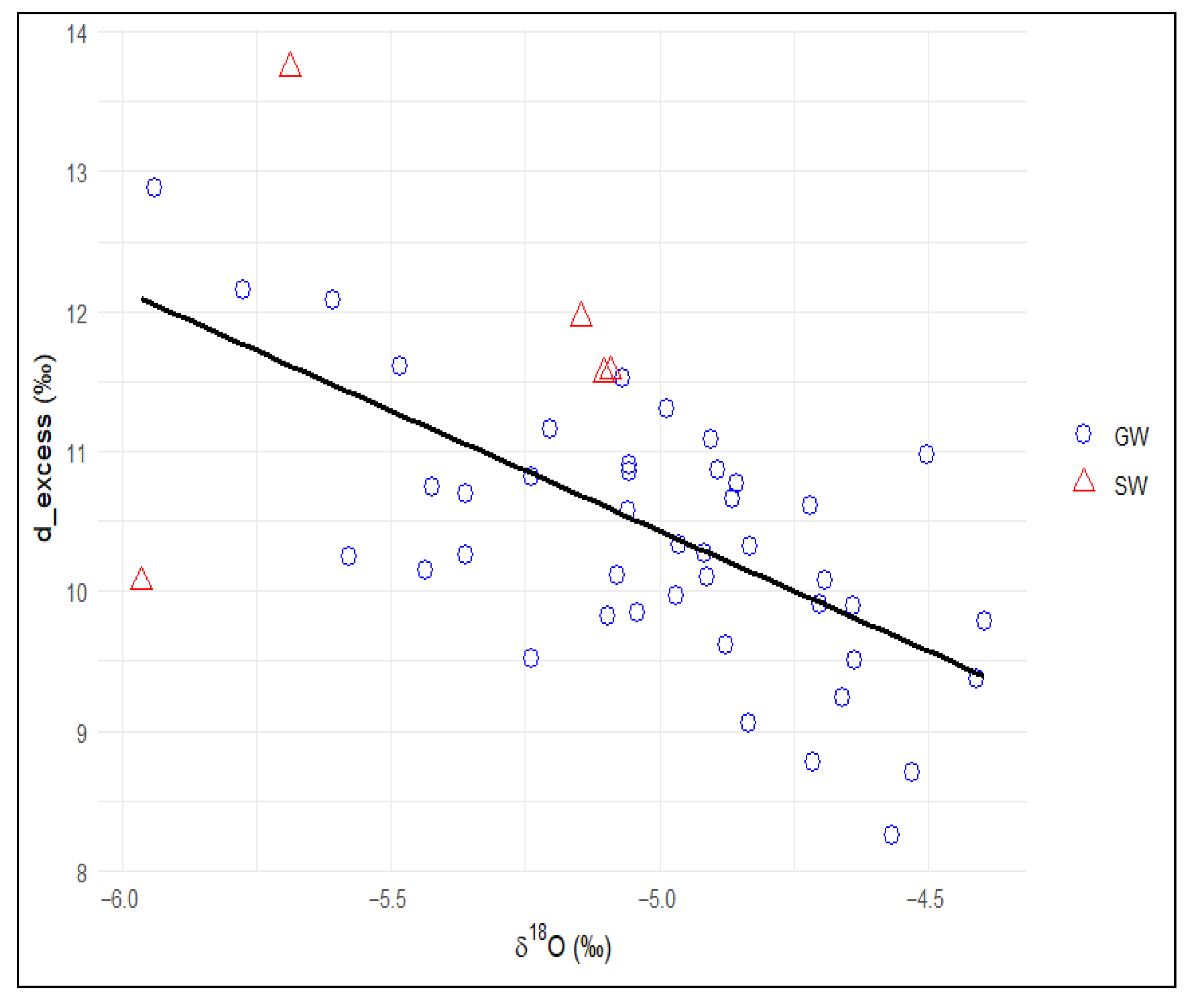
3.3. Isotopic Characterization of Surface Water and Groundwater
3.3.1. Isotope Signature
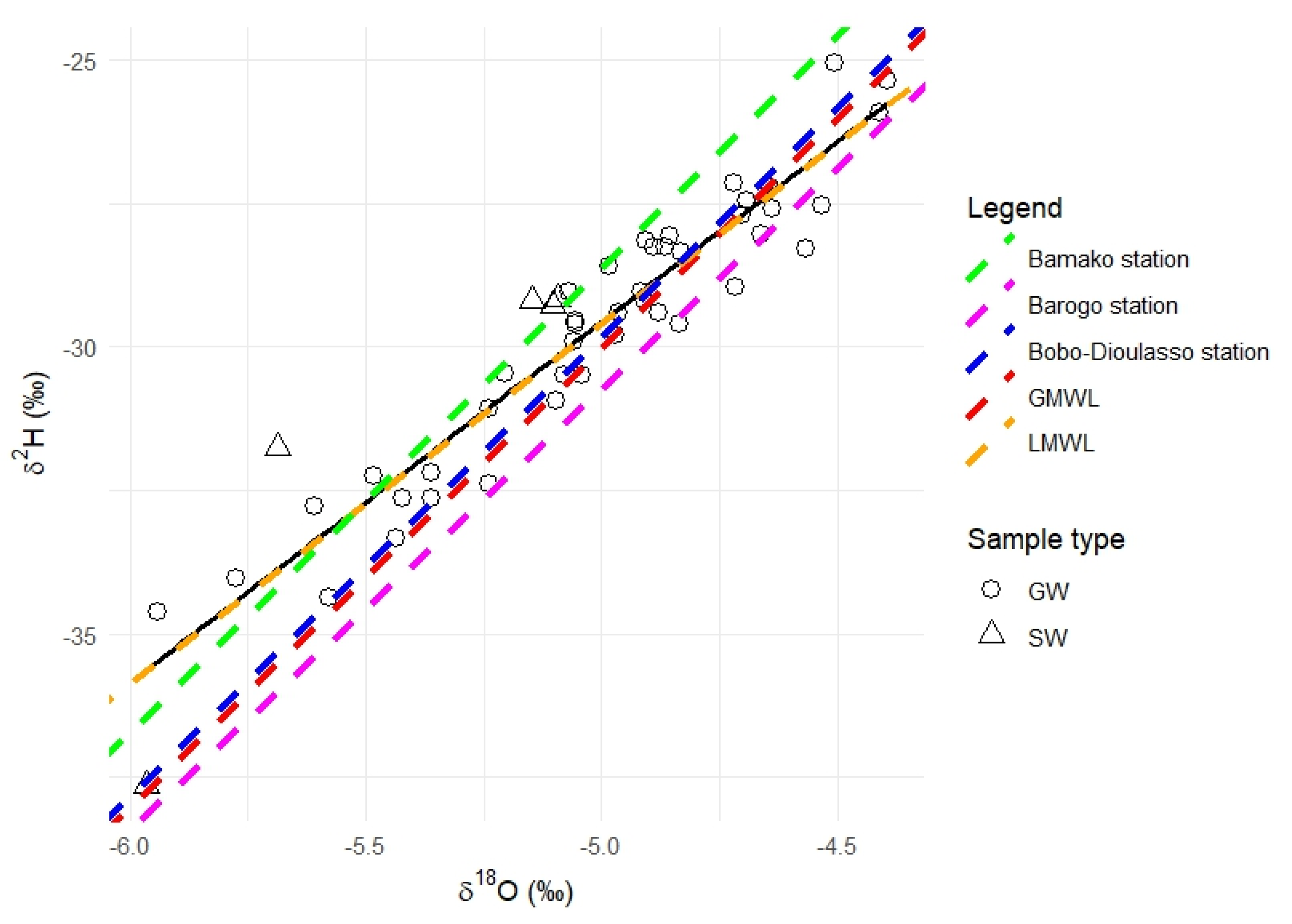
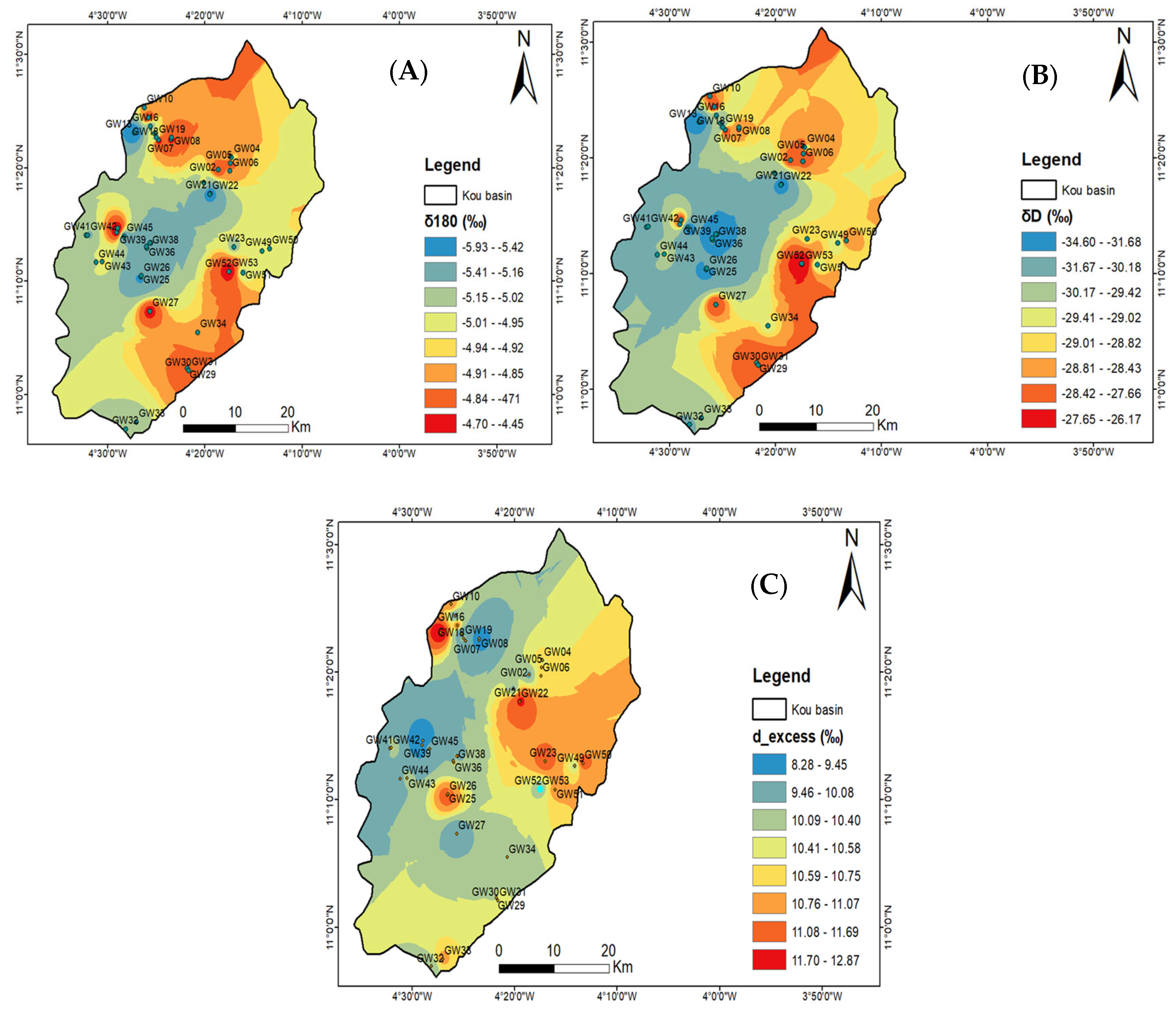
3.3.2. Spatial Pattern of δ2H and δ18O in Groundwater
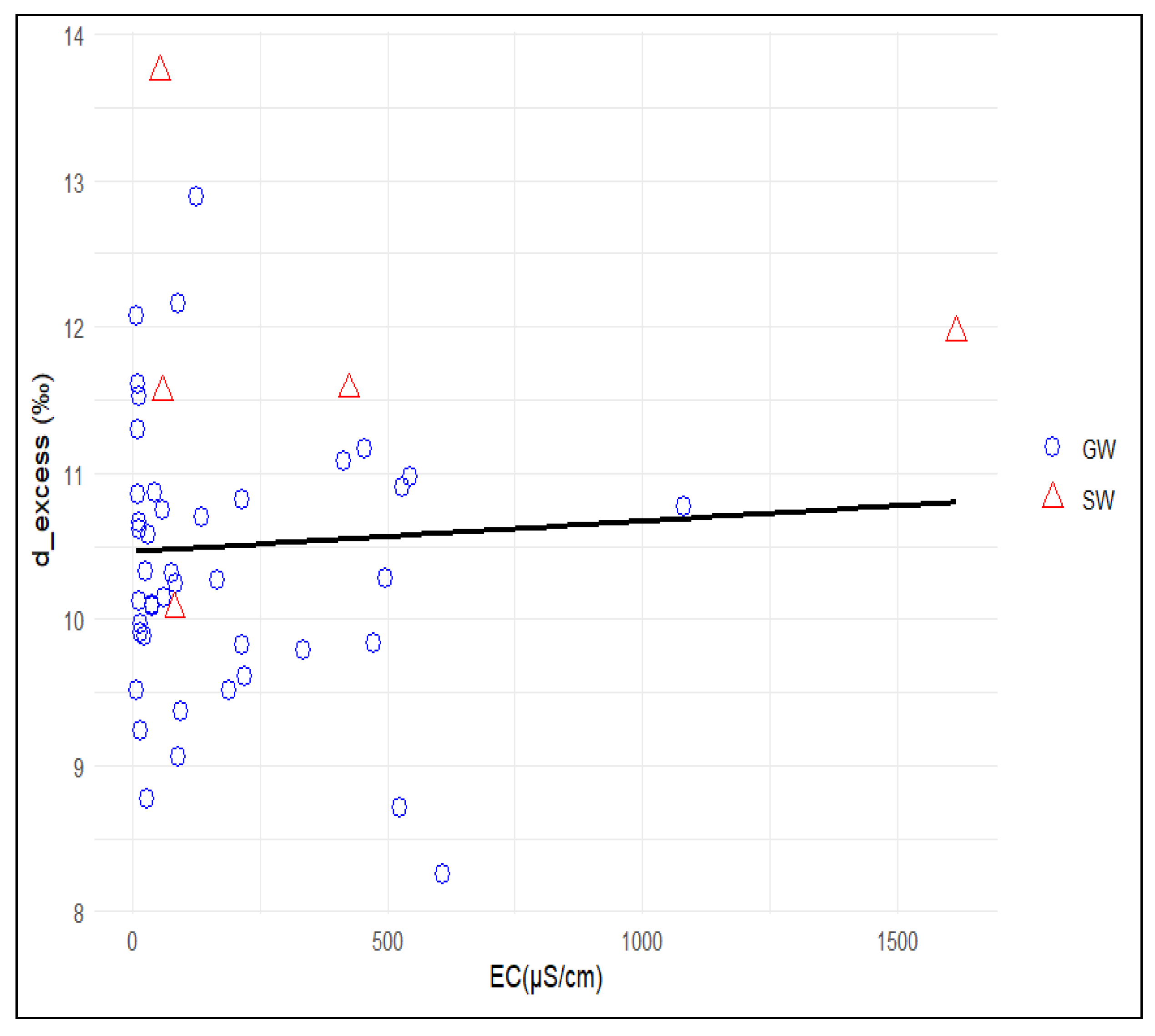
3.3.3. Identification of Groundwater Mineralisation
3.4. Implication of SW-GW Interactions and Prospects of Water Management
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change). Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. In Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Pörtner, H.-O., Roberts, D.C., Tignor, M., Poloczanska, E.S., Mintenbeck, K., Alegría, A., Craig, M., Langsdorf, S., Löschke, S., Möller, V., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022; p. 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (BGR); United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization—International Hydrological Programme (UNESCO-IHP). River and Groundwater Basins of the World. 2012. Available online: www.whymap.org (accessed on 28 January 2024).
- Guo, X.; Zuo, R.; Wang, J.; Meng, L.; Teng, Y.; Shi, R.; Gao, X.; Ding, F. Hydrogeochemical Evolution of Interaction between Surface Water and Groundwater Affected by Exploitation. Groundwater 2018, 57, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tang, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.L. The interaction between surface water and groundwater and its effect on water quality in the Second Songhua River basin, northeast China. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 125, 1495–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Du, Y.; Sun, X.; Tian, H.; Zhu, S.; Gan, Y.; Wang, Y. Spatial variability of nutrient fluxes associated with lacustrine groundwater discharge in a typical oxbow lake, Central China. Water Res. 2025, 281, 123701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paturel, J.E.; Servat, E.; Kouame, B.; Boyer, J.F. Manifestation de la sécheresse en Afrique de l’Ouest non sahélienne. Cas de la Côte d’Ivoire, du Togo et du Bénin. Sécheresse 1995, 6, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Amoussou, E.; Camberlin, P.; Mahé, G. Impact de la variabilité climatique et du barrage Nangbéto sur l’hydrologie du système Mono-Couffo (Ouest Afrique). Hydrol. Sci. J. 2012, 57, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouanda, B. Modélisation Intégrée du Complexe Mouhoun Supérieur-Sourou Dans le Contexte des Changements Climatiques. Thèse en Sciences et Technologies de l’Eau, de l’Energie et de l’Environnement. 2019. 2iE, p. 250. Available online: http://documentation.2ie-edu.org/cdi2ie/opac_css/index.php?lvl=notice_display&id=30165 (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Mahe, G.; Paturel, J.-E.; Servat, E.; Conway, D.; Dezetter, A. The impact of land use change on soil water holding capacity and river flow modelling in the Nakambe River, Burkina-Faso. J. Hydrol. 2005, 300, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahe, G.; Lienou, G.; Descroix, L.; Bamba, F.; Paturel, J.E.; Laraque, A.; Meddi, M.; Habaieb, H.; Adeaga, O.; Dieulin, C.; et al. The rivers of Africa: Witness of climate change and human impact on the environment. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakouré, D. Etude Hydrogéologique et Géochimique de la Bordure Sud-Est du Bassin Sédimentaire de Taoudéni (Burkina Faso-Mali)—Essai de Modélisation. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paris VI, Paris, France, 2003; p. 266. [Google Scholar]
- Derouane, J. Modélisation Hydrogéologique du Bassin Sédimentaire; Programme de Valorisation des Ressources en Eau de l’Ouest (VREO); Direction Générale des Ressources en Eau. Ministère de l’Agriculture, de l’Hydraulique et des Ressources Halieutiques: Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso, 2008; p. 101. [Google Scholar]
- Koussoube, Y. Hydrogéologie des Séries Sédimentaires de la Dépression Piézométrique du Gondo (Bassin du Sourou): Burkina Faso/Mali. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Pierre et Marie Curie—Paris VI, Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Huneau, F.; Dakoure, D.; Celle-Jeanton, H.; Vitvar, T.; Ito, M.; Traore, S.; Compaore, N.F.; Jirakova, H.; Le Coustumer, P. Flow pattern and residence time of groundwater within the south-eastern Taoudeni sedimentary basin (Burkina Faso, Mali). J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauret, E. Etude des Potentialités Hydrogéologiques d’une Plaine Alluviale en Relation Avec Les Eaux Souterraines et de Surface Dans Un Contexte d’agriculture Irriguée (Burkina Faso). 2013. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/openview/b301b26b22e695d0e2c6678bace0a611/1.pdf?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=2026366&diss=y (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- Tirogo, J.; Jost, A.; Biaou, A.; Valdes-Lao, D.; Koussoubé, Y.; Ribstein, P. Climate variability and groundwater response: A case study in Burkina Faso (West Africa). Water 2016, 8, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derouane, J.; Dakouré, D. Etude Hydrogéologique et Modélisation Mathématique du Système Aquifère du Bassin Sédimentaire de Taoudeni au Burkina Faso; Colloque International—Gestion des Grands Aquifères: Dijon, France, 2006; p. 21. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228467900_Etude_hydrogeologique_et_modelisation_mathematique_du_systeme_aquifere_du_bassin_sedimentaire_de_Taoudeni_au_Burkina_Faso (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- Wang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, W.; Qi, Z.; You, X.; Gu, X.; Chen, H.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Hydrogeochemical sources and enrichment mechanisms of trace elements in river water of a typical endorheic headwater region on Tibetan Plateau. Appl. Water Sci. 2025, 15, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, M.; Zabik, M.; Cady, C.; Cousens, B.; Chiarenzelli, J. Multi-Element Analysis and Geochemical Spatial Trends of Groundwater in Rural Northern New York. Water 2010, 2, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doveri, M.; Mussi, M. Water Isotopes as Environmental Tracers for Conceptual Understanding of Groundwater Flow: An Application for Fractured Aquifer Systems in the “Scansano-Magliano in Toscana” Area (Southern Tuscany, Italy). Water 2014, 6, 2255–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Li, X.; Qi, J.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, R. Hydrochemical characteristics and multivariate statistical analysis of natural water system: A case study in Kangding County, Southwestern China. Water 2018, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhang, W.; Cui, H.; Zhang, W. Estimation of groundwater recharge using tracers and numerical modeling in the North China Plain. Water 2016, 8, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Xu, F.; Deng, G.; Tang, Y.; Li, P. Hydrogeochemistry of shallow groundwater in a karst aquifer system of Bijie City, Guizhou Province. Water 2017, 9, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, E.; Visser, A.; Esser, B.K.; Moran, J.E. Tracers Reveal Recharge Elevations, Groundwater Flow Paths and Travel Times on Mount Shasta, California. Water 2018, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sako, A.; Yaro, J.M.; Bamba, O. Impacts of hydrogeochemical processes and anthropogenic activities on groundwater quality in the Upper Precambrian sedimentary aquifer of northwestern Burkina Faso. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Kumar, S.; Rao, M.S.; Mukherjee, S.; Sen, R. Isotopic Signature in Integration with Hydrochemistry to Infer the Groundwater Quality in Alluvial Aquifer, Jhajjar District, Haryana, NCR, India. 2021. Available online: https://assets-eu.researchsquare.com/files/rs-599293/v1/4633c7a3-6023-4072-bf23-60a821dbb046.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2024). [CrossRef]
- Coplen, T.B.; Herczeg, A.L.; Barnes, C. Isotope engineering—Using stable isotopes of the water molecule to solve practical problems. In Environmental Tracers in Subsurface Hydrology; Cook, P.G., Herczeg, A.L., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 79–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, P.S.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Tyagi, S.K. 18O studies on recharge of phreatic aquifers and groundwater flowpaths of mixing in Delhi area. J. Hydrol. 1996, 176, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Deshpande, R.D. Groundwater isotopic investigations in India: What has been learned? Curr. Sci. 2005, 89, 825–835. [Google Scholar]
- Jeelani, G.H.; Bhat, N.A.; Shivanna, K. Use of δ18O tracer to identify stream and spring origins of a mountainous catchment: A case study from Liddar watershed, Western Himalaya, India. J. Hydrol. 2010, 393, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, A.S.; Shah, M.; Deshpande, R.D.; Bhardwaj, R.M.; Prasad, A.; Gupta, S.K. Hydrograph separation and precipitation source identification using stable water isotopes and conductivity: River Ganga at Himalayan foothills. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rina, K.; Singh, C.K.; Datta, P.S.; Singh, N.; Mukherjee, S. Geochemical modelling, ionic ratio and GIS based mapping of groundwater salinity and assessment of governing processes in Northern Gujarat, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 2377–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, P.; Kumari, R.; Mukherjee, S. Hydrochemistry in integration with stable isotopes (δ18O and δD) to assess seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers of Kachchh district, Gujarat, India. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 196, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breme, M. Caractérisation Physique du Bassin du Kou. Mémoire Master II, 2IE. 70 pp + Annexes. 2014. Available online: http://documentation.2ie-edu.org/cdi2ie/opac_css/doc_num.php?explnum_id=4066 (accessed on 23 January 2024).
- Qu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Fan, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Gomes, H.I.; Gomes, R.L.; Duan, L.; et al. Fate and Risks of Potentially Toxic Elements Associated with Lacustrine Groundwater Discharge: Quantification, Modeling, and Biogeochemistry. Environ. Int. 2025, 202, 109707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traoré, F.; Cornet, Y.; Denis, A.; Wellens, J.; Tychon, B. Monitoring the evolution of irrigated areas with Landsat images using backward and forward change detection analysis in the Kou watershed, Burkina Faso. Geocarto Int. 2013, 28, 733–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourcy, L.; Aranyossy, J.F.; Olivry, J.C.; Zuppi, G.M. Space and time variations in the isotopic composition (d2H–d18O) of Niger inland delta water (Mali). C. R. L’acad. Sci. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 331, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frappart, F.; Hiernaux, P.; Guichard, F.; Mougin, E.; Kergoat, L.; Arjounin, M.; Lavenu, F.; Koité, M.; Paturel, J.E.; Lebel, T. Rainfall regime across the Sahel band in the Gourma region, Mali. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taupin, J.D.; Gaultier, G.; Favreau, G.; Leduc, C.; Marlin, C. Isotopic variability of Sahelian rainfall at different time steps in Niamey (Niger, 1992–1999): Climatic implications. C. R. Geosci. 2002, 334, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellens, J.; Compaoré, N.F. Renforcement de la Capacité de Gestion des Ressources en eau dans l’Agriculture Moyennant des Outils de Suivi-Évaluation–GEeau; Rapport Annuel N1 (Décembre 2001–Novembre 2002); Direction Régionale de l’Agriculture, de l’Hydraulique et des Ressources Halieutiques des Hauts Bassins: Bobo-Dioulasso, Burkina Faso, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ogou, C. Etude des Potentialités Aquifères de la Plaine Alluviale du Kou Entre Nasso et Diaradougou; Institut International D’ingénierie de L’eau et de L’environnement: Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ouedraogo, C. Synthèse Géologique de la Région Ouest du Burkina Faso; Programme VREO, SOFRECO-SAWES: Bobo-Dioulasso, Burkina Faso, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bronner, G.; Roussel, J.; Trompette, R.A.; Clauer, N. Genesis and geodynamic evolution of the Taoudeni cratonic basin (Upper Precambrian and Paleozoic), Western Africa. Dyn. Plate Inter. 1980, 1, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogreah Ingénierie. Notice Explicative de la Carte Hydrogéologique 1:50000 de la Région de Bobo-Dioulasso; Etude des Ressources de la Zone Sédimentaire de la Région de Bobo-Dioulasso; Ministère de l’Agriculture de l’Hydraulique et des Ressources Halieutiques—Direction des Etudes et de la Planification—Direction Régionale de l’Eau des Hauts-Bassins: Bobo-Dioulasso, Burkina Faso, 1993; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Sogreah Ingenierie. Etude des Ressources en Eaux Souterraines de la Zone Sédimentaire de la Région de Bobo-Dioulasso; Ministère de l’Agriculture de l’Hydraulique et des Ressources Halieutiques—Direction des Etudes et de la Planification—Direction Régionale de l’Eau des Hauts-Bassins: Bobo-Dioulasso, Burkina Faso, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzini, G. Etude du Bassin D’alimentation des Sources de Nasso—Etat des Lieux des Ressources en Eaux Souterraines du Bassin du Kou, Département ArGEnCo; Université de Liège: Liège, Belgique, 2007; p. 119. [Google Scholar]
- Gombert, P. Synthèse sur la Géologie et l’Hydrogéologie de la Série Sédimentaire du Sud-Ouest du Burkina Faso; Programme RESO, IWACO-BURGEAP: Bobo-Dioulasso, Burkina Faso, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sauret, E. Contribution à la Compréhension du Fonctionnement Hydrogeologique du Système Aquifère dans le Bassin du Kou (Burkina Faso) [Specialised Master, ULiège—Université de Liège]. ORBi-University of Liège. 2008. Available online: https://orbi.uliege.be/handle/2268/153604 (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- Wellens, J.; Traoré, F.; Diallo, M.; Tychon, B. A framework for the use of decision-support tools at various spatial scales for the management of irrigated agriculture in West-Africa. Agric. Sci. 2013, 4, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traoré, F. Optimisation de L’utilisation des Ressources en Eau du Bassin du Kou pour des Usages Agricoles. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Liège, Liège, Belgium, 2012. p. 195. Available online: https://orbi.uliege.be/handle/2268/132698 (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- RGPH. Cinquième Recensement Général de la Population et de l’Habitation du Burkina Faso. 2022. p. 136. Available online: https://www.insd.bf/sites/default/files/2023-08/INSD_Rapport_SYNTHESE%20DES%20RESULTATS%20DEFINITIFS_1.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2024).
- Wellens, J. A framework for Using Decision-Support Tools at Various Spatial Scales for the Management of Irrigated Agriculture in Semi-Arid West-Africa. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Liège, Liège, Belgium, 2014. Available online: https://orbi.uliege.be/handle/2268/163546 (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- Wellens, J.; Sawadogo, I.; Diallo, M.; Dakouré, D.; Compaoré, N.F.; Traoré, F.; Tychon, B. Recensement Exhaustif des Activités Hydro-Agricoles du Bassin du Kou; GEeau: Bobo-Dioulasso, Burkina Faso, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Traoré, S.; Gombert, P. Variations des Débits Interannuels de la Source de la Guinguette; Rapport Interne; Direction Régionale de l’Hydraulique des Hauts-Bassins: Bobo-Dioulasso, Burkina Faso, 1997; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Palm, P.M. Hydrological Investigation for Climate Change Investigation in the Kou Basin Burkina Faso: A Minor Field Study. TRITA LWR Degree Project 11:2. ISSN 1651-064X.. 2011. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2%3A529737 (accessed on 23 January 2024).
- Dione, M. Gestion Intégrée des Ressources en Eau de la Vallée du Kou: Profil de Pollution des Eaux de Surface en Rapport Avec les Usages. Master’s Thesis, 2iE-Institut International d’Ingénierie de l’Eau et de l’Environnemen, Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso, 2005. p. 118. Available online: http://documentation.2ie-edu.org/cdi2ie/opac_css/doc_num.php?explnum_id=1008 (accessed on 23 January 2024).
- Bieupoude, G.P. Mapping Groundwater Intrinsic Vulnerability Using a New Physically Based Modeling in Kou Basin Bobo-Dioulasso/Burkina Faso; Mémoire de Master en Hydraulique-Environnement et Infrastructure: Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, A. Influence des Rejets Industriels sur la Pollution des Eaux à Bobo Dioulasso (Burkina Faso). Master’s Thesis, Université Polytechnique de Bobo-Dioulasso, Dindéresso, Burkina Faso, 2008. p. 78. Available online: https://beep.ird.fr/collect/upb/index/assoc/IDR-2008-KOH-INF/IDR-2008-KOH-INF.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2024).
- Ben Moussa, A. Etude Hydrogéologique, Hydrochimique et Isotopique du Système Aquifère de Hammamet Nabeul, Cap Bon, Tunisie Nord Orientale. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Sfax École Nationale d’Ingénieurs de Sfax, Sfax, Tunisia, 2011. p. 147. Available online: https://gnssn.iaea.org/main/NCP/Tunisia/LRAE/Documents/Student%20Programmes/Th%C3%A8se%20Ben%20Moussa%20Amor.pdf (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- IAEA (International Atomic Energy Agency). Introduction to Water Sampling and Analysis for Isotope Hydrology; Non-Serial Publications; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Freeze, R.A.; Cherry, J.A. Groundwater; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1979; p. 604. [Google Scholar]
- Favreau, G. Caractérisation et Modélisation d’une Nappe Phréatique en Hausse au Sahel: Dynamique et Géochimie de la Dépression Piézométrique Naturelle du Kori de Dantiandou (Sud-Ouest du Niger); Université Paris-Sud 11: Orsay, France; IRD: Montpellier, France, 2000; 348p. [Google Scholar]
- Penna, D.; Stenni, B.; Šanda, M.; Wrede, S.; Bogaard, T.A.; Gobbi, A.; Borga, M.; Fischer, B.M.C.; Bonazza, M.; Cháróvá, Z. On the reproducibility and repeatability of laser absorption spectroscopy measurements for δ2H and δ18O isotopic analysis. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 1551–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable Isotope in Precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simler, R. DIAGRAMMES Software (Version 31-10-2014). Université d’Avignon. Available online: https://terre-et-eau.univ-avignon.fr/equipements-de-terrain-et-de-laboratoire/logiciels (accessed on 31 October 2024).
- WHO(World Health Organization). WHO—Guidelines on Drinking Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- IAEA (International Atomic Energy Agency). (RAF/7/011) Gestion Intégrée et Durable des Systèmes Aquifères et des Bassins Partagés de la Région du Sahel, Bassin de Taoudéni; l’AIEA: Vienna, Austria, 2017; p. 136. Available online: https://www.iaea.org/sites/default/files/18/02/raf7011_taoudeni_basin_fr.pdf (accessed on 19 January 2024).
- Serge Gaëtan, S.É.; Marie Michelle, C.H.; Ouindinboudé Jacques, K.; Poulouma Louis, Y.; Idriss, S. Hydrogeochemistry of Shallow Groundwater and Suitability to Irrigation: The Case of the Karfiguéla Paddy Field in Burkina Faso. Water 2022, 14, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheick, S. Water Nutrient Use Efficiency the Vertical Leaching Losses in Urban Vegetable Cropping Systems in Bobo–Dioulasso (Burkina Faso). Ph.D. Thesis, Université Catholique de Louvain, Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 2012. p. 193. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2078.1/110879 (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- Ouédraogo, R.A.; Kambiré, F.C.; Kestemont, M.P.; Bielders, C.L. Caractériser la diversité des exploitations maraîchères de la région de Bobo-Dioulasso au Burkina Faso pour faciliter leur transition agroécologique. Cah. Agric. 2019, 28, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, R.; Zouari, K.; Araguás Araguás, L.J.; Moulla, A.S.; Sidibe, A.M.; Bacar, T. Assessment of geochemical processes in the shared groundwater resources of the Taoudeni aquifer system (Sahel region, Africa). Hydrogeol. J. 2024, 32, 167–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huneau, F.; Travi, Y. The Miocene Aquifer of Valreas, France. In Natural Groundwater Quality; Edmunds, W.M., Shand, P., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing: London, UK, 2008; pp. 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Han, G.; Song, C.; Zhang, P. Stable HO isotopic composition and water quality assessment of surface water and groundwater: A case study in the Dabie Mountains, central China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sako, A.; Sawadogo, S.; Nimi, M.; Ouédraogo, M. Hydrogeochemical and Pollution Characterization of a Shallow Glauconitic Sandstone Aquifer in a Peri-Urban Setting of Bobo-Dioulasso, Southwestern Burkina Faso. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Feng, W.; Qian, H.; Zhang, Q. Hydrogeochemical Characterization and Irrigation Quality Assessment of Shallow Groundwater in the Central-Western Guanzhong Basin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, J.; Qian, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, N.; Jing, L.; Yu, P. Hydrogeochemical Characterization of Groundwater in and around a Wastewater Irrigated Forest in the Southeastern Edge of the Tengger Desert, Northwest China. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, T.; Rajmohan, N.; Elango, L. Groundwater Geochemistry and Identification of Hydrogeochemical Processes in a Hard Rock Region, Southern India. Environ. Monit. Assess 2010, 162, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahlangu, S.; Lorentz, S.; Diamond, R.; Dippenaar, M. Surface water-groundwater interaction using tritium and stable water isotopes: A case study of Middelburg, South Africa. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2020, 171, 103886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, R.; Bariac, T.; Fouillac, C.; Guillot, B.; Mariotti, A. Variations en isotopes stables dans les précipitations en 1988 et 1989 au Burkina Faso: Apports de la météorologie régionale. Veill. Clim. Satellitaire 1993, 45, 47–64. [Google Scholar]
- Taupin, J.D.; Gallaire, R.; Arnaud, Y. Analyses isotopiques et chimiques des précipitations sahéliennes de la région de Niamey au Niger: Implications climatologiques. IAHS Publ.-Ser. Proc. Rep.-Intern. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 1997, 244, 151–164. [Google Scholar]
- Song, F.; Nlend, B.; Boum-Nkot, S.N.; Huneau, F.; Ndondo, G.N.; Garel, E.; Leydier, T.; Celle, H.; Djieugoue, B.; Ntamak-Nida, M.-J.; et al. Groundwater Resources of the Transboundary Quaternary Aquifer of the Lake Chad Basin: Towards a Better Management via Isotope Hydrology. Resources 2023, 12, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goni, I.B.; Taylor, R.G.; Favreau, G.; Shamsudduha, M.; Nazoumou, Y.; Nhatcha, B.N. Groundwater recharge from heavy rainfall in the southwestern Lake Chad Basin: Evidence from isotopic observations. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2021, 66, 1359–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamand, B.S.; Mawlood, D.K. Identifying sources of groundwater and recharge zone using stable environmental isotopes in the Erbil basin-northern Iraq. Kuwait J. Sci. 2024, 51, 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamat Nour, A.; Vallet-Coulomb, C.; Gonçalves, J.; Sylvestre, F.; Deschamps, P. Rainfall-Discharge Relationship and Water Balance over the Past 60 Years within the Chari-Logone Sub-Basins, Lake Chad Basin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 35, 100824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamat-Nour, A.; Huneau, F.; Mahamat, A.; Mahamat Saleh, H.; Ngo Boum-Nkot, S.; Nlend, B.; Djebebe-Ndjiguim, C.-L.; Foto, E.; Sanoussi, R.; Araguas-Araguas, L.; et al. Shallow Quaternary groundwater in the Lake Chad basin is resilient to climate change but requires sustainable management strategy: Results of isotopic investigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyerle, U.; Rueedi, J.; Leuenberger, M.; Aeschbach-Hertig, W.; Peeters, F.; Kipfer, R.; Dodo, A. Evidence for periods of wetter and cooler climate in the Sahel between 6 and 40 kyr BP derived from groundwater. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Song, X.; Yeh, T.C.J.; Zhen, P. Coupling hydrochemistry and stable isotopes to identify the major factors affecting groundwater geochemical evolution in the Heilongdong Spring Basin, North China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 205, 106352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhlke, J.K. Groundwater recharge and agricultural contamination. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 153–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, M.; Sen, R.; Onyekwelu, I.; Wiederstein, T.; Sharda, V. Modeling of Groundwater Nitrate Contamination Due to Agricultural Activities—A Systematic Review. Water 2022, 14, 4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawniczak, A.E.; Sokołowska, K.; Dębska, B. Impact of Agriculture and Land Use on Nitrate Contamination of Groundwater and Surface Water in a Protected Area. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.R.M.T.; Pal, S.C.; Chowdhuri, I.; Salam, R.; Islam, M.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Zahid, A.; Idris, A.M. Application of novel framework approach for prediction of nitrate concentration susceptibility in coastal multi-aquifers, Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosillon, F.; Savadogo, B.; Kabore, A.; Bado-Sama, H.; Dianou, D. Attempts to Answer on the Origin of the High Nitrates Concentrations in Groundwaters of the Sourou Valley in Burkina Faso. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2012, 4, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
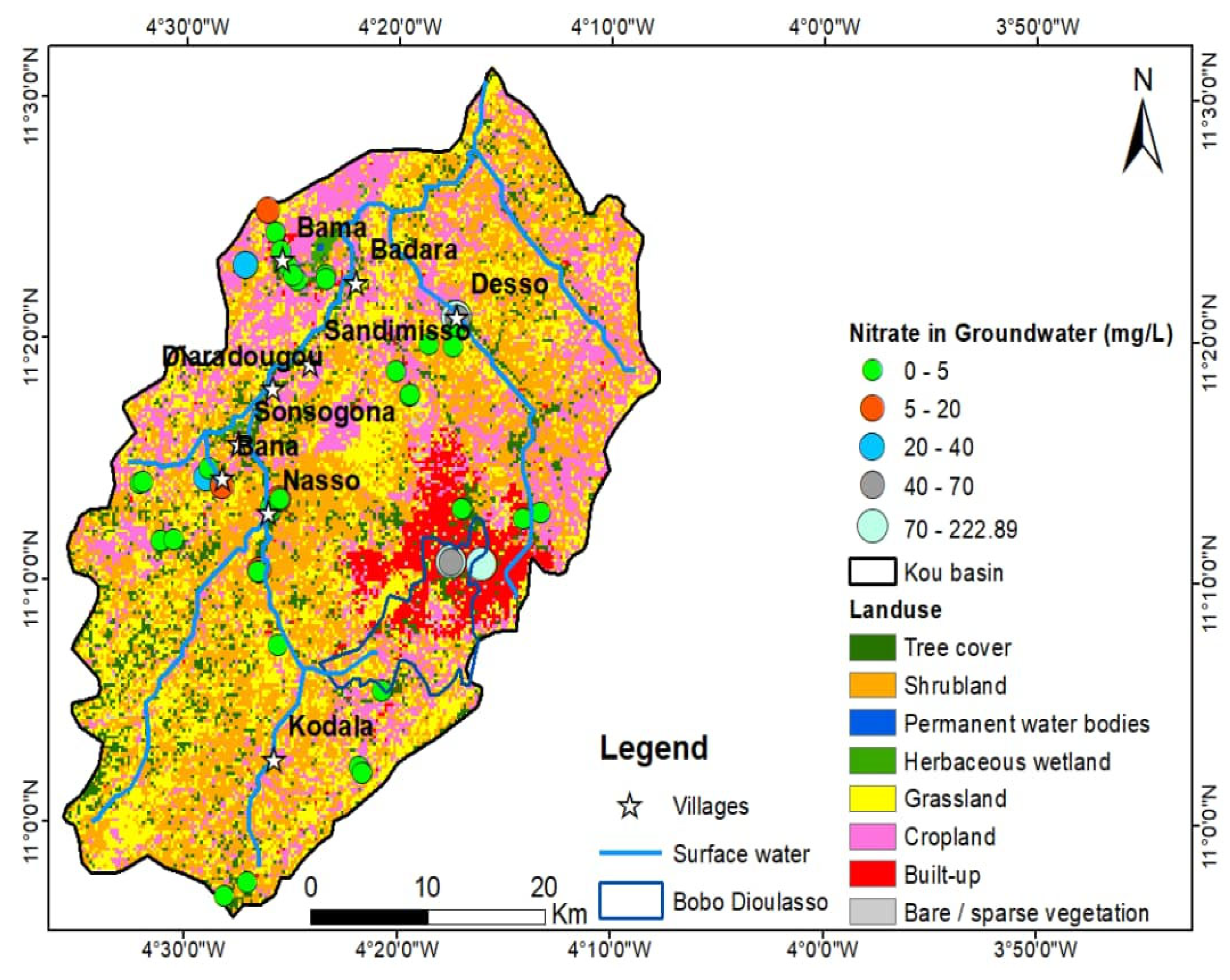
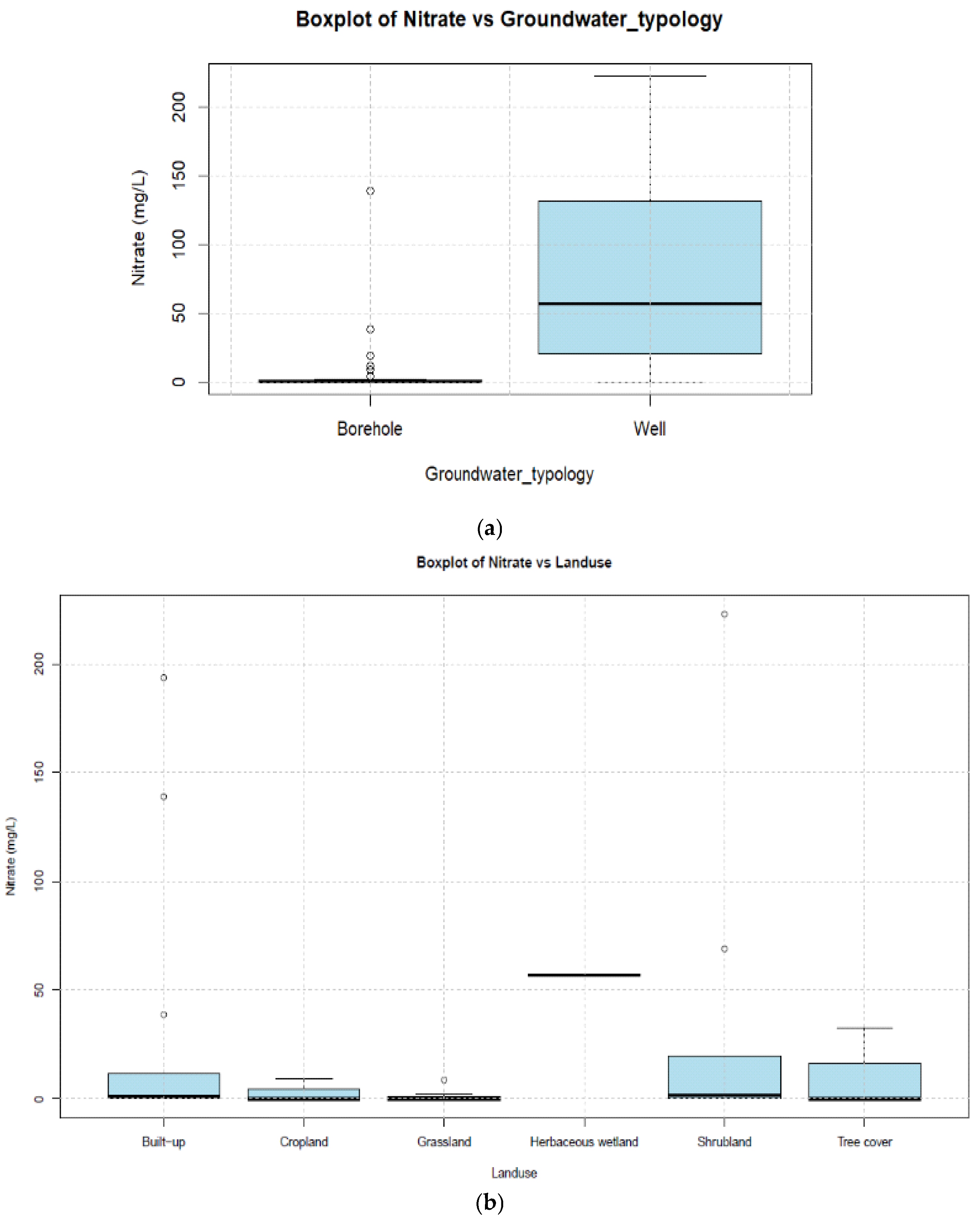
| Unit | a Number of Borehole | b Depth (m) | Mean Yield (m3/h) | Mean Specific Yield (m3/h/m) | T (10−4 m2/s) | K (10−6 m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GI | 21 | 75 | 5.1 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.2 |
| GKS | 69 | 48 | 5.1 | 0.4 | 2.7 | 1.2 |
| GFG | 166 | 80 | 9.1 | 0.5 | 2.8 | 0.5 |
| GGQ | 271 | 62 | 13.0 | 1.0 | 8.5 | 3.0 |
| SAC1 | 179 | 66 | 13.4 | 1.4 | 4.9 | 2.2 |
| GFR | 58 | 62 | 6.8 | 1.3 | 1.7 | 1.7 |
| Temp (°C) | pH (-) | EC (μS/cm) | Turb (NTU) | DO | TDS | HCO3 | F− | Cl− | NO2− | Br− | NO3− | SO42− | Li+ | Na+ | NH4+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | δ18O (‰) | δ2H (‰) | d-Excess (‰) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groundwater (n = 43) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean | 29.8 | 5.6 | 178.3 | 6.7 | 4.8 | 178.3 | 66.8 | 0.1 | 6.8 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 19.1 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 8.5 | 0.5 | 3.9 | 6.0 | 12.8 | −29.7 | −5.0 | 10.4 |
| CV×100 | 5.7 | 20.6 | 130.5 | 299.6 | 19.1 | 130.5 | 147.1 | 75.5 | 283.5 | 16.2 | 17.4 | 258.3 | 208.4 | 69.4 | 192.2 | 309.0 | 112.5 | 148.2 | 140.3 | −8.0 | −7.2 | 9.0 |
| SD | 1.7 | 1.1 | 232.8 | 19.9 | 0.9 | 232.8 | 98.3 | 0.1 | 19.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 49.3 | 2.4 | 0.0 | 16.4 | 1.4 | 4.4 | 8.9 | 17.9 | 2.4 | 0.4 | 0.9 |
| Minimum | 22.6 | 3.28 | 8.0 | 0.01 | 3.24 | 8.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | −34.6 | −5.9 | 8.3 |
| Maximum | 32.9 | 7.53 | 1080.0 | 126.1 | 6.6 | 1080.0 | 309.4 | 0.3 | 113.0 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 222.9 | 11.0 | 0.0 | 81.7 | 6.7 | 18.3 | 33.4 | 65.5 | −25.1 | −4.4 | 12.9 |
| Surface water (n = 5) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean | 30.2 | 6.4 | 447.8 | 217.4 | 5.3 | 447.8 | 83.3 | 0.1 | 37.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 15.5 | 16.0 | 0.0 | 35.2 | 0.2 | 9.2 | 3.8 | 14.9 | −31.4 | −5.4 | 11.8 |
| CV×100 | 10.9 | 10.6 | 149.9 | 164.7 | 38.9 | 149.9 | 77.1 | 39.5 | 158.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 165.3 | 173.5 | 0.0 | 175.6 | 107.8 | 86.0 | 48.5 | 108.2 | −11.7 | −7.5 | 11.2 |
| SD | 3.3 | 0.7 | 671.2 | 358.1 | 2.0 | 671.2 | 64.2 | 0.0 | 59.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 25.7 | 27.8 | 0.0 | 61.8 | 0.2 | 7.9 | 1.9 | 16.1 | 3.7 | 0.4 | 1.3 |
| Minimum | 28 | 5.5 | 55.2 | 2.1 | 2.6 | 55.0 | 28.4 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 2.6 | 1.6 | 5.2 | −37.7 | −6.0 | 10.1 |
| Maximum | 36 | 7.1 | 1616.0 | 843.9 | 6.9 | 1616.0 | 162.1 | 0.1 | 137.6 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 59.2 | 64.7 | 0.0 | 144.1 | 0.5 | 18.9 | 5.8 | 43.1 | −29.2 | −5.1 | 13.7 |
| WHO Standards | - | 6.5–8.5 | 1000 | 5 | 5–7 | 1000 | 350 | 0.7–1.7 | 250 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 50 | 200 | 1 | 200 | 4 | 12 | 150 | 200 | - | - | - |
| Temp | pH | EC | Turb | DO | TDS | HCO3− | F− | Cl− | NO2− | Br− | NO3− | SO42− | Li+ | Na+ | NH4+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| pH | −0.16 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||||
| EC | 0.06 | 0.35 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| Turb | 0.09 | 0.06 | −0.08 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||
| DO | 0.10 | −0.39 | −0.54 | 0.17 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||
| TDS | 0.06 | 0.35 | 1.00 | −0.08 | −0.54 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||
| HCO3− | 0.04 | 0.70 | 0.57 | −0.06 | −0.37 | 0.57 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| F− | 0.24 | 0.05 | 0.28 | −0.04 | −0.09 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| Cl− | −0.01 | −0.01 | 0.75 | −0.05 | −0.38 | 0.75 | −0.05 | −0.02 | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| NO2− | 0.29 | −0.12 | −0.12 | −0.03 | 0.14 | −0.12 | −0.11 | −0.07 | −0.06 | 1 | |||||||||
| Br− | −0.11 | −0.07 | 0.10 | −0.03 | −0.15 | 0.10 | −0.10 | −0.07 | 0.24 | −0.03 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| NO3− | 0.09 | −0.20 | 0.71 | −0.04 | −0.33 | 0.71 | −0.15 | 0.25 | 0.86 | −0.06 | 0.16 | 1.00 | |||||||
| SO42− | −0.16 | 0.25 | 0.59 | −0.12 | −0.46 | 0.59 | 0.29 | −0.06 | 0.58 | −0.08 | 0.64 | 0.38 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Li+ | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.20 | 0.29 | 0.71 | −0.05 | −0.04 | −0.04 | 0.08 | −0.09 | 1.00 | |||||
| Na+ | 0.11 | 0.19 | 0.70 | −0.08 | −0.36 | 0.70 | 0.27 | 0.12 | 0.69 | −0.08 | 0.11 | 0.59 | 0.58 | −0.05 | 1.00 | ||||
| NH4+ | −0.12 | −0.01 | 0.51 | −0.05 | −0.31 | 0.51 | −0.09 | −0.07 | 0.78 | −0.05 | 0.68 | 0.56 | 0.70 | −0.02 | 0.38 | 1.00 | |||
| K+ | −0.15 | 0.14 | 0.53 | −0.10 | −0.34 | 0.53 | 0.03 | 0.23 | 0.53 | −0.13 | 0.26 | 0.61 | 0.31 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.57 | 1.00 | ||
| Mg2+ | 0.06 | 0.57 | 0.62 | −0.04 | −0.36 | 0.62 | 0.89 | 0.39 | 0.01 | −0.10 | −0.05 | 0.04 | 0.21 | 0.43 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.21 | 1.00 | |
| Ca2+ | 0.08 | 0.47 | 0.92 | −0.08 | −0.54 | 0.92 | 0.75 | 0.23 | 0.54 | −0.12 | −0.04 | 0.47 | 0.54 | 0.18 | 0.57 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.74 | 1 |
| Sample Name | δ2H (‰) | δ18O (‰) | d-Excess (‰) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SW20 | −37.65 | −5.96 | 10.06 |
| GW13 | −34.62 | −5.93 | 12.88 |
| GW25 | −34.04 | −5.77 | 12.15 |
| SW28 | −31.75 | −5.68 | 13.74 |
| GW21 | −32.78 | −5.60 | 12.07 |
| GW38 | −34.37 | −5.57 | 10.24 |
| GW22 | −32.24 | −5.48 | 11.61 |
| GW45 | −33.34 | −5.43 | 10.14 |
| GW19 | −32.63 | −5.42 | 10.74 |
| GW04 | −32.62 | −5.36 | 10.26 |
| GW42 | −32.19 | −5.36 | 10.69 |
| GW35 | −31.09 | −5.23 | 10.82 |
| GW36 | −32.39 | −5.23 | 9.51 |
| GW16 | −30.46 | −5.20 | 11.16 |
| SW54 | −29.20 | −5.14 | 11.96 |
| SW24 | −29.27 | −5.10 | 11.55 |
| GW37 | −30.94 | −5.09 | 9.82 |
| SW55 | −29.15 | −5.09 | 11.57 |
| GW32 | −30.50 | −5.07 | 10.11 |
| GW23 | −29.03 | −5.06 | 11.52 |
| GW26 | −29.90 | −5.05 | 10.57 |
| GW51 | −29.54 | −5.05 | 10.90 |
| GW33 | −29.59 | −5.05 | 10.84 |
| GW44 | −30.48 | −5.04 | 9.84 |
| GW50 | −28.58 | −4.98 | 11.30 |
| GW01 | −29.79 | −4.97 | 9.96 |
| GW49 | −29.39 | −4.96 | 10.32 |
| GW43 | −29.05 | −4.91 | 10.27 |
| GW34 | −29.18 | −4.91 | 10.10 |
| GW10 | −28.15 | −4.90 | 11.08 |
| GW31 | −28.25 | −4.89 | 10.86 |
| GW41 | −29.40 | −4.87 | 9.61 |
| GW06 | −28.26 | −4.86 | 10.66 |
| GW52 | −28.07 | −4.85 | 10.76 |
| GW17 | −29.60 | −4.83 | 9.06 |
| GW29 | −28.34 | −4.83 | 10.31 |
| GW05 | −27.15 | −4.72 | 10.60 |
| GW08 | −28.95 | −4.71 | 8.77 |
| GW02 | −27.70 | −4.70 | 9.91 |
| GW30 | −27.44 | −4.69 | 10.08 |
| GW07 | −28.05 | −4.66 | 9.23 |
| GW09 | −27.23 | −4.64 | 9.88 |
| GW27 | −27.58 | −4.63 | 9.50 |
| GW39 | −28.28 | −4.56 | 8.25 |
| GW40 | −27.54 | −4.53 | 8.70 |
| GW03 | −25.05 | −4.50 | 10.97 |
| GW18 | −25.92 | −4.41 | 9.37 |
| GW53 | −25.36 | −4.39 | 9.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouedraogo, I.; Vanclooster, M.; Huneau, F.; Vystavna, Y.; Kebede, S.; Koussoubé, Y. Surface Water–Groundwater Interactions in a Sahelian Catchment: Exploring Hydrochemistry and Isotopes and Implications for Water Quality Management. Water 2025, 17, 2756. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182756
Ouedraogo I, Vanclooster M, Huneau F, Vystavna Y, Kebede S, Koussoubé Y. Surface Water–Groundwater Interactions in a Sahelian Catchment: Exploring Hydrochemistry and Isotopes and Implications for Water Quality Management. Water. 2025; 17(18):2756. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182756
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuedraogo, Issoufou, Marnik Vanclooster, Frederic Huneau, Yuliya Vystavna, Seifu Kebede, and Youssouf Koussoubé. 2025. "Surface Water–Groundwater Interactions in a Sahelian Catchment: Exploring Hydrochemistry and Isotopes and Implications for Water Quality Management" Water 17, no. 18: 2756. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182756
APA StyleOuedraogo, I., Vanclooster, M., Huneau, F., Vystavna, Y., Kebede, S., & Koussoubé, Y. (2025). Surface Water–Groundwater Interactions in a Sahelian Catchment: Exploring Hydrochemistry and Isotopes and Implications for Water Quality Management. Water, 17(18), 2756. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182756








