Research Progress on the Application of Electrodialysis Technology for Clean Discharge Water Treatment from Power Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Materials for the Electrodialysis System
2.2. Optimization of Pretreatment Process
2.3. Optimization of the Electrodialysis System
3. Principles of Electrodialysis Technology
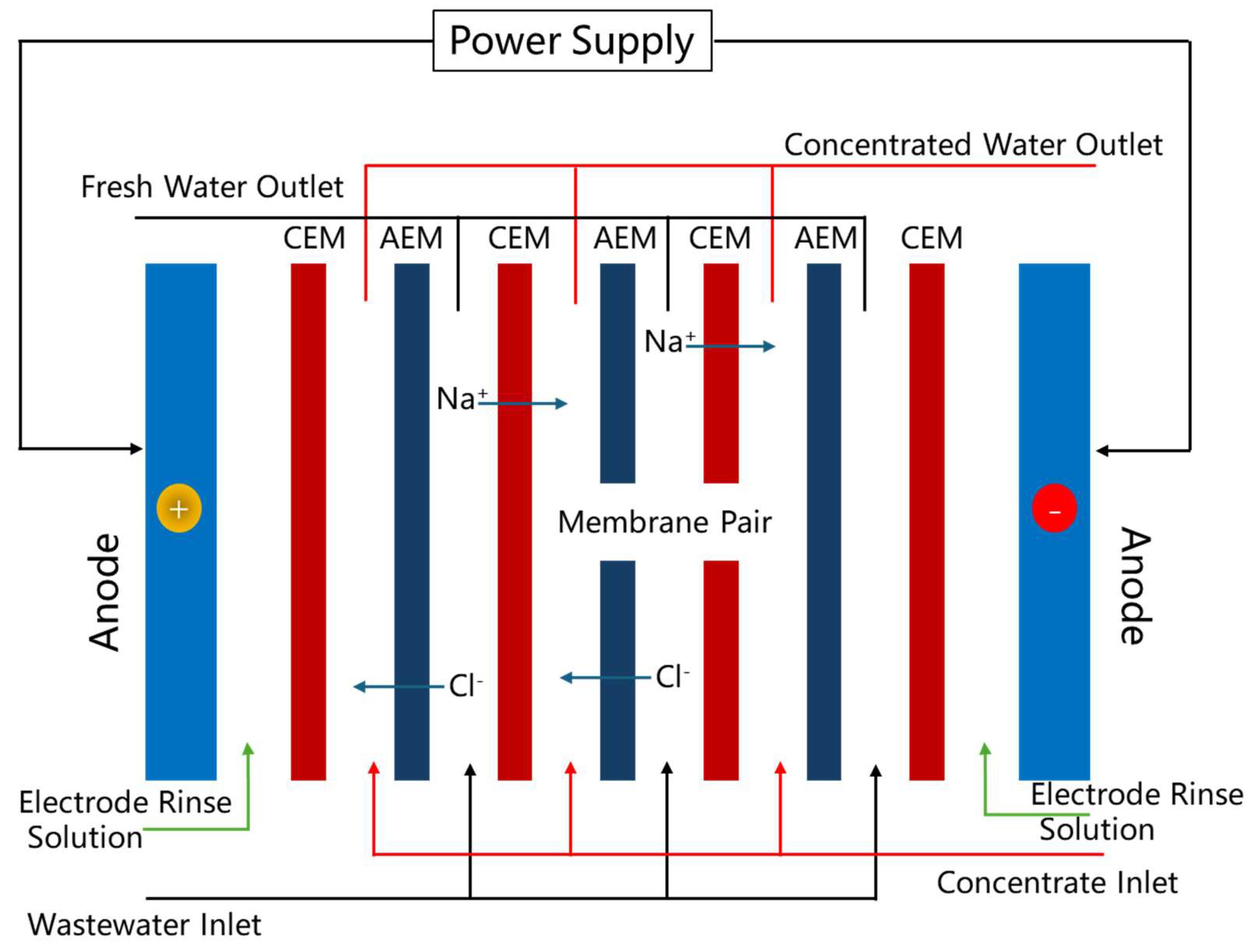
3.1. Fundamental Components of Electrodialysis Systems
3.2. Selective Permeability of Ion-Exchange Membranes
3.3. Ion Migration in the Electrodialysis Process
4. Application of Electrodialysis Technology in Power Plant Clean Discharge Water Treatment
4.1. Pretreatment Process Optimization
4.2. Optimization of Electrodialysis Reaction Systems
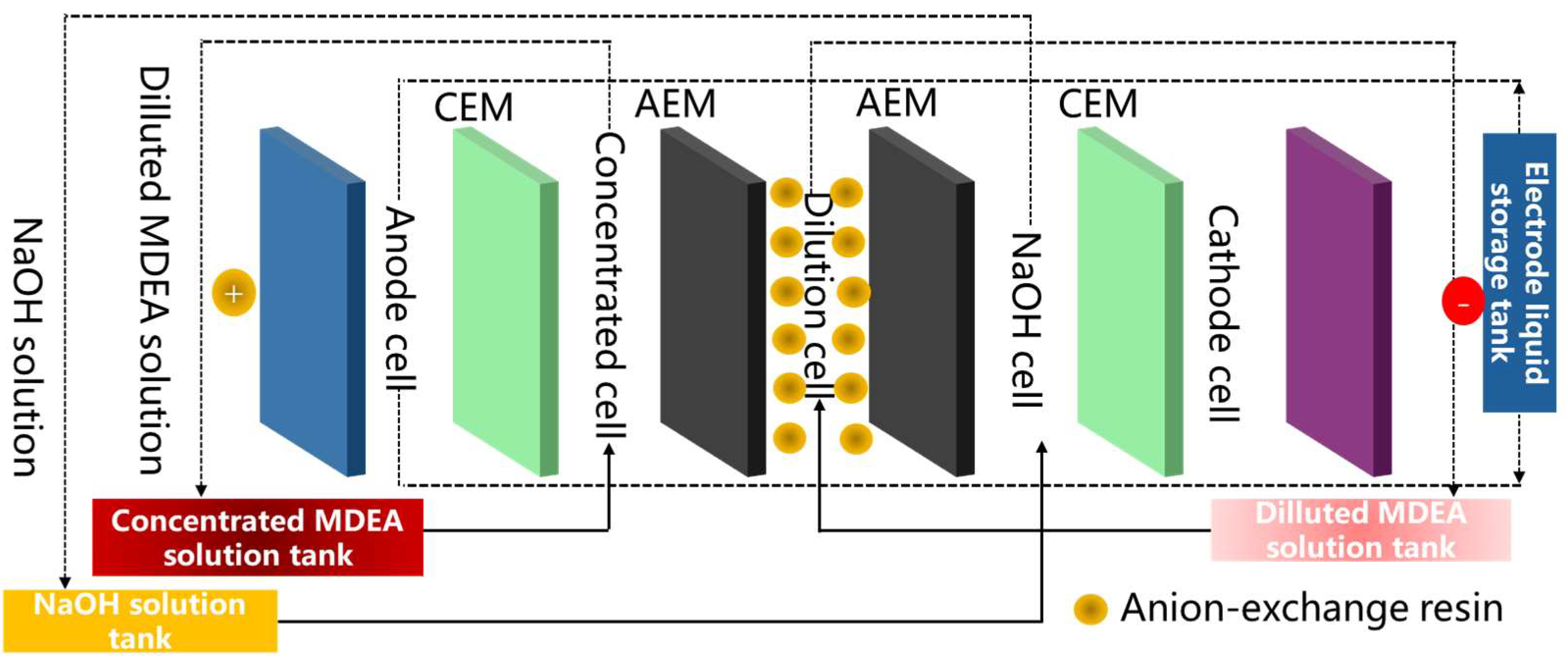
4.2.1. Construction of Multifunctional Electrodialysis Membrane Stacks
4.2.2. Coupling of Electrodialysis with Nanofiltration
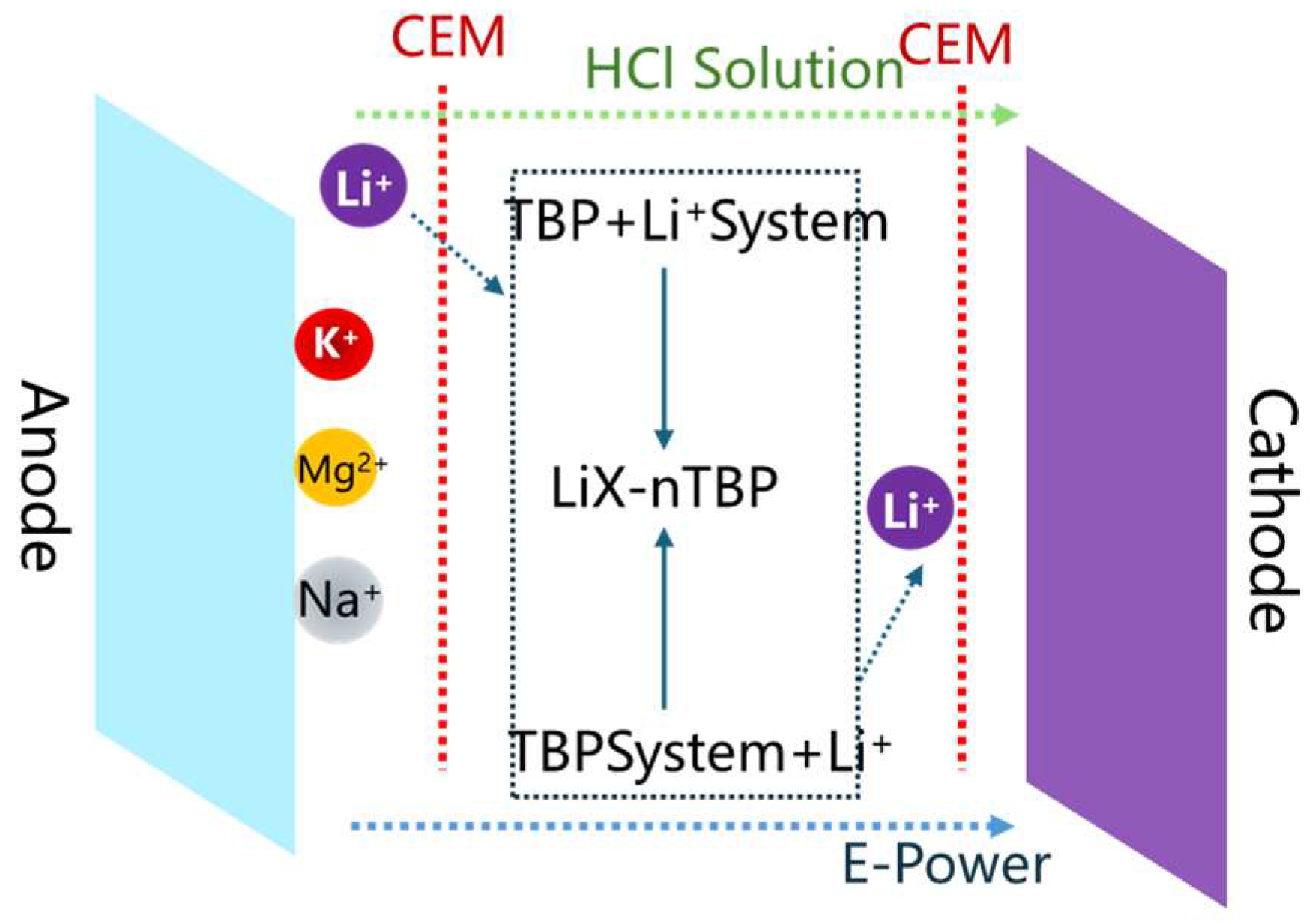
4.2.3. Integration of Electrodialysis with Extraction
4.3. System Design and Operational Optimization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohsen, M.S. Treatment and reuse of industrial effluents: Case study of a thermal power plant. Desalination 2004, 167, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Zeng, X.; Ling, Z.; Zhao, S.; Li, B.; Han, X. Recent Advances in Zero Discharge Treatment Technologies for Desulfurization Wastewater in Coal-Fired Power Plants: A Mini-Review. Processes 2025, 13, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grauberger, B.M.; Cole, G.M.; Tong, T.; Lin, S.; Quinn, J.C.; Bandhauer, T. Targeting sustainable desalination solutions: A techno-economic and life cycle approach to guiding zero liquid discharge desalination. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 504, 145445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.F.; Park, A.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, P.; Cho, Y.; Park, H.; Nam, S.; Park, Y. Harnessing clean water from power plant emissions using membrane condenser technology. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6425–6433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingerich, D.B.; Grol, E.; Mauter, M.S. Fundamental challenges and engineering opportunities in flue gas desulfurization wastewater treatment at coal fired power plants. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 909–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, M.; Patyal, V.; Jaspal, D.; Malviya, A.; Khare, K. Zero liquid discharge technology for recovery, reuse, and reclamation of wastewater: A critical review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Aleid, S.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, R.; Wu, M.; Zhuo, S.; Wang, P. Integrated solar-driven PV cooling and seawater desalination with zero liquid discharge. Joule 2021, 5, 1873–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Hao, S.; Liao, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Liu, T.; Chen, B.; Xie, H. Efficient hydrogen production and optional power generation through coal-assisted water electrolysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 503, 158668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ-BAT-001; Guidelines for Best Available Techniques of Pollution Prevention and Control for Thermal Power Plants. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2010.
- Guo Fa [2015] No. 17. Water Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan. State Council of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Zhang, B.; Guo, X.; Sun, H.; Mao, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. Zero discharge advanced treatment control system for wet desulfurization wastewater in power plant adapted to water quality fluctuation. Desalination Water Treat. 2025, 321, 100985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, D.; Mao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Li, J. Coordinated disposal of FGD gypsum and power plant concentrated brine via preparation of α-hemihydrate gypsum. Mater. Today Sustain. 2024, 25, 100644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F. Interpretation of “Guidelines on Available Techniques of Pollution Prevention and Control for Thermal Power Plants” (HJ 2301-2017). Environ. Impact Assess. 2018, 40, 1–4+16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K. Sustainable water management through integrated technologies and circular resource recovery. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2025, 11, 1822–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazigil, L.; Er, E.; Kestioğlu, O.E.; Yonar, T. Pilot-scale test results of electrodialysis bipolar membrane for reverse-osmosis concentrate recovery. Membranes 2022, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.K.; Lee, B.; Westerhoff, P.; Elimelech, M. The potential of electrodialysis as a cost-effective alternative to reverse osmosis for brackish water desalination. Water Res. 2024, 250, 121009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Li, H.; Xu, M.; Ruan, H. Sustainable reverse osmosis, electrodialysis and bipolar membrane electrodialysis application for cold-rolling wastewater treatment in the steel industry. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubita, T.M.; Porada, S.; Biesheuvel, P.M.; Van Der Wal, A.; Dykstra, J.E. Strategies to increase ion selectivity in electrodialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 292, 120944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Miedema, H.; de Smet, L.C.; Sudhölter, E.J. Permeation selectivity in the electro-dialysis of mono-and divalent cations using supported liquid membranes. Desalination 2022, 521, 115398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lin, S. Membrane design principles for ion-selective electrodialysis: An analysis for Li/Mg separation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 3552–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.P.; Wang, H.L.; Tian, C.C.; Chang, Y.L.; Yuan, W.; Qi, Y.H.; Chao, Z.L.; Chen, W.Y.; Lv, W.J. An optimized design for zero liquid discharge from coal chemical industry: A case study in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 319, 128572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, R.; Tang, W.; Sillanpää, M. A systematic review and statistical analysis of nutrient recovery from municipal wastewater by electrodialysis. Desalination 2021, 498, 114626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.; Jeong, H.; Ko, S.; Moon, S.H.; Chang, I.S. Recycling of minerals with acetate separation in biological syngas fermentation with an electrodialysis system. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 459, 141555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 19923–2005; Design Code for Industrial Circulating Cooling Water Treatment. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Sharma, P.; Agrawal, S.; Rathore, M.S.; Shahi, V.K. Cross-linked anion-exchange membrane with side-chain grafted multi-cationic spacer for electrodialysis: Imparting dual anti-fouling and anti-bacterial characteristics. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 660, 120871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, I.; Wu, J.; Shocron, A.N.; Suss, M.E. Spatial variations of pH in electrodialysis stacks: Theory. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 413, 140151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, M.; Hong, S.P.; Lee, K.M.; Lee, C. Optimization of redox-mediated electrodialysis systems for efficient water softening: Enhanced removal of calcium and magnesium ions. Environ. Eng. Res. 2025, 30, 240692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kırmızı, S.; Karabacakoğlu, B. Performance of electrodialysis for Ni (II) and Cr (VI) removal from effluents: Effect of process parameters on removal efficiency, energy consumption and current efficiency. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2023, 53, 2039–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Yao, Y.; Xu, J.; Ang, E.H.; Xu, G.; Liao, J.; Sotto, A.; Shen, J. Strategies for lithium extraction from salt lakes by nanofiltration and selective-electrodialysis and analysis of differences between the two methods. Desalination 2024, 586, 117749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Jiao, L.; Su, M.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, J. A critical review of amyloid fibrils composites as emerging materials for the removal of metal ions from water: Synthesis, characteristics, removal performance and mechanism. Desalination 2025, 615, 119243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, G.; Li, H.; Wang, D. Research on the Process for Removing Heat-Stable Salts from Organic Amine Absorbents via Electrodialysis. Processes 2025, 13, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, M.; Kim, K.; Oh, K.; Choi, H.J.; Ha, C.; Chang, S. Sodium Cholate-Based Active Delipidation for Rapid and Efficient Clearing and Immunostaining of Deep Biological Samples. Small Methods 2022, 6, 2100943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomin, E.; Salah, Z.; Osintsev, K.; Aliukov, S.; Kuskarbekova, S.; Konchakov, V.; Olinichenko, A.; Karelin, A.; Tarasova, T. Ecological Hydrogen Production and Water Sterilization: An Innovative Approach to the Trigeneration of Renewable Energy Sources for Water Desalination: A Review. Energies 2023, 16, 6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Jin, D.; Xu, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, P.; Wu, D.; Xi, R. Three-dimensional multi-physical simulation of a reverse electrodialysis stack with profiled membranes. Desalination 2022, 537, 115894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; She, Q. Scaling-enhanced scaling during electrodialysis desalination. ACS EST Eng. 2024, 4, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Foo, Z.H.; She, Q. The potential of electrodialysis with mediating solution (EDM) for eliminating alkaline scaling: Experimental validation and mechanistic elucidation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 6307–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z. Current status and challenges of ion imprinting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 13598–13627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Li, S.; Xu, M.; Xu, C.; Feng, L.; Du, K. The effect of lithium bromide on the performance of ammonia-water absorption-resorption heat pump system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 181, 115888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, G.; Ren, S.; Pooley, S.; Sun, W.; Kowalczuk, P.B.; Gao, Z. Electrocoagulation for industrial wastewater treatment: An updated review. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 1177–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, G.; Fernández, B.; Bonmatí, A. Significance of anaerobic digestion as a source of clean energy in wastewater treatment plants. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 101, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Qi, Y.; Li, F.; Shu, J.; Sun, Z.; Sun, S.; Chen, M.; Pu, S. Effect of electrolyte reuse on metal recovery from waste CPU slots by slurry electrolysis. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Yang, Z.; Lin, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Pu, S. Two-dimensional Na-Bentonite@ MXene composite membrane with switchable wettability for selective oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 306, 122677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhumal, P.S.; Khose, R.V.; Wadekar, P.H.; Lokhande, K.D.; Some, S. Graphene-bentonite supported free-standing, flexible membrane with switchable wettability for selective oil–water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 266, 118569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Guo, Z.; Tian, D.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, L. Electric field induced switchable wettability to water on the polyaniline membrane and oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3, 1600461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Avalos, S.; Soliz, A.; Cáceres, L.; Conejeros, S.; Brito, I.; Galvez, E.; Galleguillos Madrid, F.M. Metal Recovery from Natural Saline Brines with an Electrochemical Ion Pumping Method Using Hexacyanoferrate Materials as Electrodes. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Liu, R.; Chen, X.; Chen, Q.; Lin, J.; Lin, X.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Zhao, S. Loose nanofiltration-based electrodialysis for highly efficient textile wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 608, 118182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Liu, L.; Du, J.; Fu, R.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Zhang, Y. Fracsis: Ion fractionation and metathesis by a NF-ED integrated system to improve water recovery. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Fei, X.; Yang, K.; Fu, C. Removal of heat stable salts from N-methyldiethanolamine wastewater by anion exchange resin coupled three-compartment electrodialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 242, 116777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchbender, F.; Wiese, M. Efficient concentration of an amino acid using reactive extraction coupled with bipolar electrodialysis. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2018, 41, 2298–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, G.; Jia, H.; He, L. Sandwiched liquid-membrane electrodialysis: Lithium selective recovery from salt lake brines with high Mg/Li ratio. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 596, 117685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Zhao, K.; Li, S.; Lian, Y.; Yang, M.; Liu, H.; Chen, C.; Fang, C. Degradation of typical tetracycline antibiotics in landfill leachate by three-dimensional aerated electrocatalytic reactor (3D-AER): Electrode properties, influencing factors and degradation mechanism. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 386, 125787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhandauletova, F.; Abikenova, A.; Sanatova, T. Analysis of Wastewater Treatment and Recycling in Textile Enterprises. Water Conserv. Manag. 2024, 8, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Feng, J.; He, X.; Xu, R.; Yang, Z.; Chen, R.; Sheng, K.; Zhang, Y. Assessing the dynamics of endotoxin release and removal in water supply systems: A study of four disinfection methods. Energy Environ. Sustain. 2025, 1, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.B.; Park, K.K.; Eum, H.M.; Lee, C.W. Desalination of a thermal power plant wastewater by membrane capacitive deionization. Desalination 2006, 196, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liao, P.; Chen, Q. Improving commercial-scale alkaline water electrolysis systems for fluctuating renewable energy: Unsteady-state thermodynamic analysis and optimization. Appl. Energy 2025, 395, 126183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, X.; Xia, L.; Qiu, Y.; Zheng, S.; Lu, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. Enabling an ultraefficient lithium-selective construction through electric field–assisted ion control. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eadv6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasappa, S.; Subbukrishna, D.N.; Suresh, K.C.; Paul, P.J.; Prabhu, G.S. Operational experience on a grid connected 100ákWe biomass gasification power plant in Karnataka, India. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2011, 15, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleman, M.; Al-Rudainy, B.; Lipnizki, F. Overcoming the Limitations of Forward Osmosis and Membrane Distillation in Sustainable Hybrid Processes Managing the Water–Energy Nexus. Membranes 2025, 15, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Ni, Z.; Liu, J.; Shen, J.; Zhu, L.; Pan, M.; Yang, W. Effects of the co-existence of humic acid on the defluorination/desalination treatment of brackish groundwater in a hybrid capacitive deionizing membrane distillation (CDIMD) system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 364, 132403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Peng, C. Efficient high-rate brackish water desalination via solid-electrolyte-assisted flow-electrode capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 361, 131523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Song, Y.; Sun, Y.; Luo, L.; Wang, J.; He, J. Research on the desalination kinetics of carbon tableting electrodes for capacitive deionization water purification. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soshinskaya, M.; Crijns-Graus, W.H.; van der Meer, J.; Guerrero, J.M. Application of a microgrid with renewables for a water treatment plant. Appl. Energy 2014, 134, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvito, D.T.; Allen, H.E.; Parkhurst, B.R.; Warren-Hicks, W.J. Comparison of trace metals in the intake and discharge water of power plants using “clean” techniques. Water Environ. Res. 2001, 73, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, K.D.; VanBriesen, J.M. Power plant bromide discharges and downstream drinking water systems in Pennsylvania. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11829–11838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Desalination Technology | Energy Consumption (kWh/m3) | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Electrodialysis | 0.4~8.7 | Low energy consumption, minimal chemical usage, adaptable to varying salinity levels | Membrane fouling, poor ion selectivity |
| Multi-stage Flash (MSF) | 14~25 | Rapid evaporation, less prone to scaling | High energy consumption |
| Multi-effect Distillation (MED) | 7~25 | Mature technology | Scaling issues, high energy consumption |
| Membrane Distillation (MD) | 22~67 | Capable of treating high-salinity wastewater with low fouling potential | Low recovery rate, high energy consumption |
| Mechanical Vapor Compression (MVC) | 20~25 | Technologically mature | Scaling problems, high energy consumption |
| Process Unit | Function |
|---|---|
| Equalization Tank | Serves as the preliminary storage and regulation unit for raw water, ensuring stable flow and quality for subsequent treatment systems. |
| High-Density Tank | Adds coagulants or flocculants to promote aggregation and sedimentation of suspended solids/colloids, improving water clarity. |
| Sedimentation | Utilizes gravity to settle flocs formed in the high-density tank, producing sludge at the bottom and supernatant for the next stage. |
| Multi-Media Filter | Further removes suspended solids, colloids, and organic matter to protect downstream membrane components from fouling. |
| Ultrafiltration (UF) | Uses UF membranes to retain macromolecules, bacteria, and viruses, providing pretreatment for NF and RO. |
| Nanofiltration (NF) | Softens UF-treated water by removing partial hardness ions (e.g., Ca2+, Mg2+), reducing the load on the RO system. |
| SWRO (Seawater RO) | Treats 1% NaCl solution (from ED desalination) for further desalination, producing high-quality freshwater. |
| Electrodialysis (ED) | Core process: Separates pretreated 4% NaCl solution into dilute (1% for RO) and concentrate (15% brine) streams. |
| Parameter | Design Value | Optimization Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Membrane stack configuration | 3-stage, 6-section | Electrode reversal design (EDR) |
| Effective area per membrane pair | 0.5 m2 | Wave-shaped spacer design |
| Operating voltage | 1.2 V/cell pair | Pulsed power supply (duty cycle 0.7) |
| Recovery rate | 75–85% | Concentrate recirculation ratio at 30% |
| Desalination rate | ≥90% | Automatic current density adjustment |
| Technology | Desalination Rate | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional ED | Moderate (~50–90% salt removal) | Low energy use, minimal chemicals, adaptable to salinity | Membrane fouling, poor ion selectivity |
| Reverse ED (RED) | Low (~30–60% salt removal) | Energy recovery, low fouling | Low driving force, limited scalability |
| Nanofiltration-ED (NF-ED) | High (~70–95% salt removal) | High selectivity, reduced fouling | Higher cost, complex operation |
| Selective-Layer MED (SLMED) | Moderate-High (~60–85% salt removal) | Improved ion selectivity, stable operation | Moderate scaling risk |
| Bipolar Membrane ED (BMED) | High (~80–98% salt removal) | Acid/base production, high efficiency | High voltage required, membrane degradation |
| Capacitive Deionization (CDI) + ED | Moderate (~50–80% salt removal) | Low fouling, energy-efficient regeneration | Limited to high salinity, electrode degradation |
| Membrane Distillation-ED (MD-ED) | Very High (~90–99% salt removal) | Handles hypersaline brine, high purity | High energy demand, thermal management needed |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, K.; Su, P. Research Progress on the Application of Electrodialysis Technology for Clean Discharge Water Treatment from Power Plants. Water 2025, 17, 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182701
Kang Z, Zhao G, Xiong H, Zhang K, Su P. Research Progress on the Application of Electrodialysis Technology for Clean Discharge Water Treatment from Power Plants. Water. 2025; 17(18):2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182701
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Zhiwei, Guifeng Zhao, Haoyang Xiong, Kai Zhang, and Peidong Su. 2025. "Research Progress on the Application of Electrodialysis Technology for Clean Discharge Water Treatment from Power Plants" Water 17, no. 18: 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182701
APA StyleKang, Z., Zhao, G., Xiong, H., Zhang, K., & Su, P. (2025). Research Progress on the Application of Electrodialysis Technology for Clean Discharge Water Treatment from Power Plants. Water, 17(18), 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182701







