Impact of Stepwise Salinity Elevation on Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Properties of Morphologically Distinct Anammox Sludge
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Characteristics of Inoculating Sludge
2.2. The Protocol and Synthetic Wastewater
2.3. Conventional Water Quality Analysis
2.4. Methods for Analyzing Sludge Properties
3. Results and Discussion
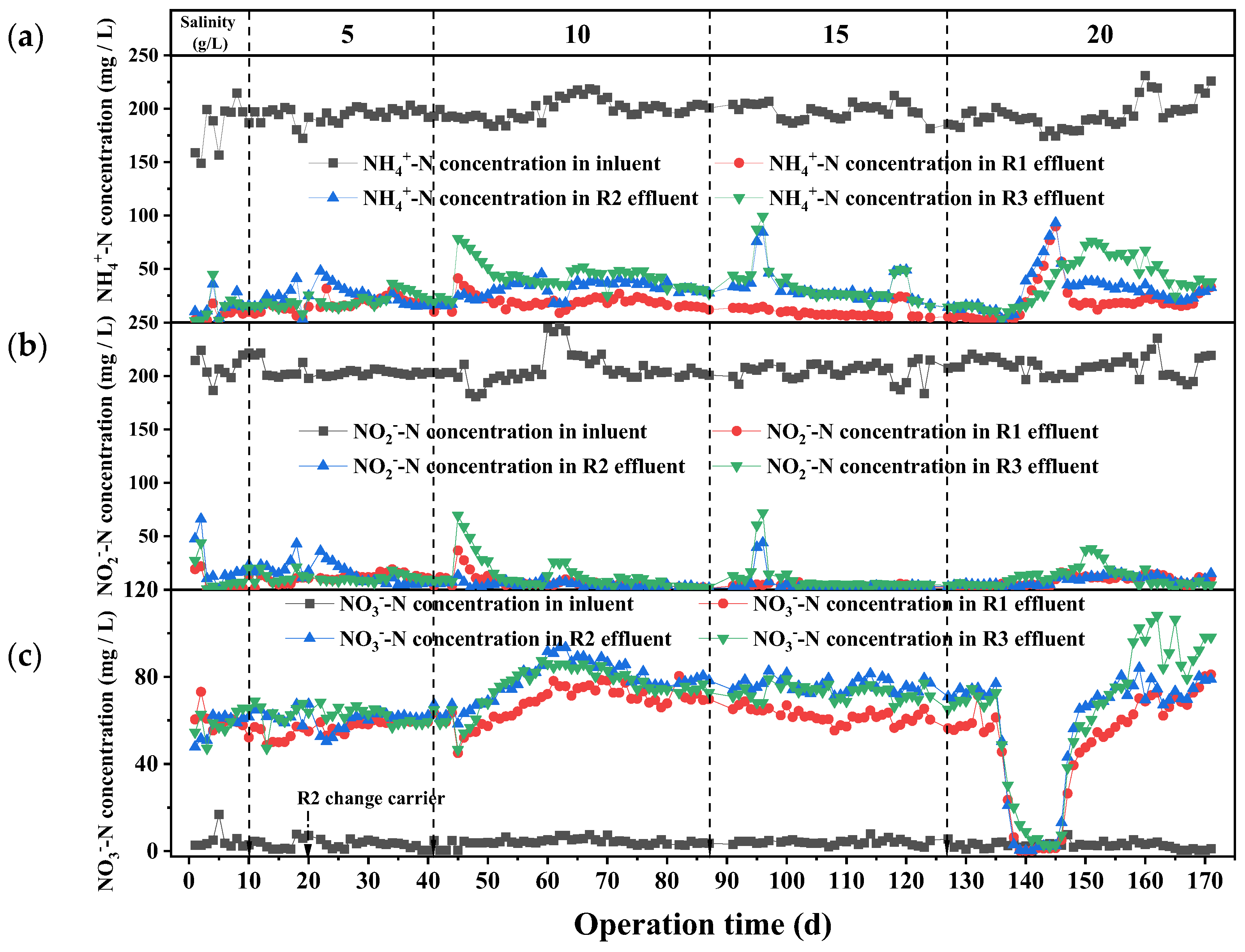
3.1. Effects of Salinity on Nitrogen Removal Effect of Three Different Forms of Sludge Systems
3.1.1. Variations in Nitrogen Removal by Different Sludge Morphologies Under Identical Salinity Levels
3.1.2. Variations in NRR and NRE of Different Sludge Morphologies Under Varying Salinity Levels
3.1.3. Variations in Anammox Stoichiometric Ratios of Different Sludge Morphologies Under Varying Salinity Levels
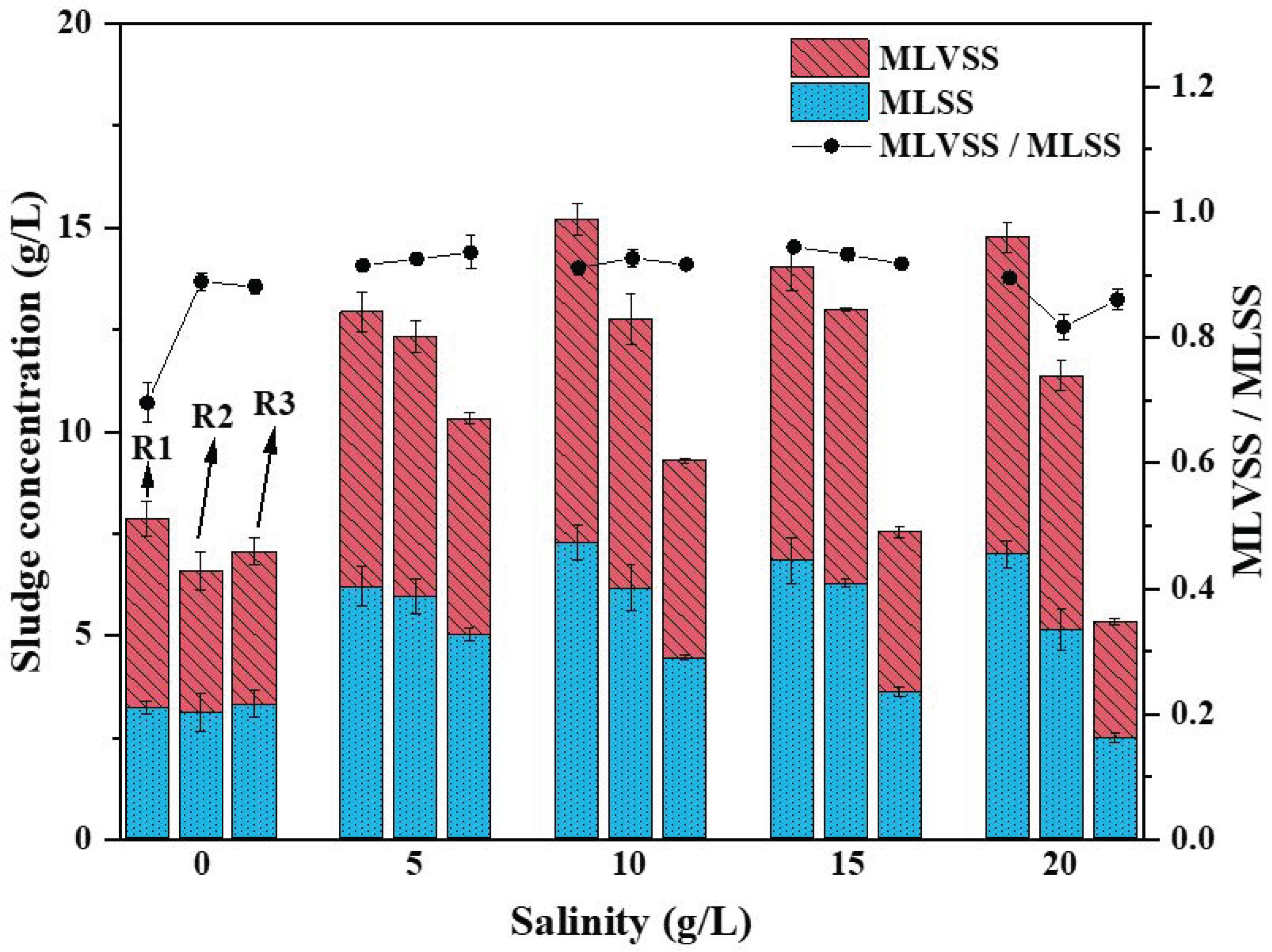
3.2. Effects of Salinity on Physical Characteristics of Three Sludge Morphologies
3.2.1. Influence of Salinity on Sludge Concentration
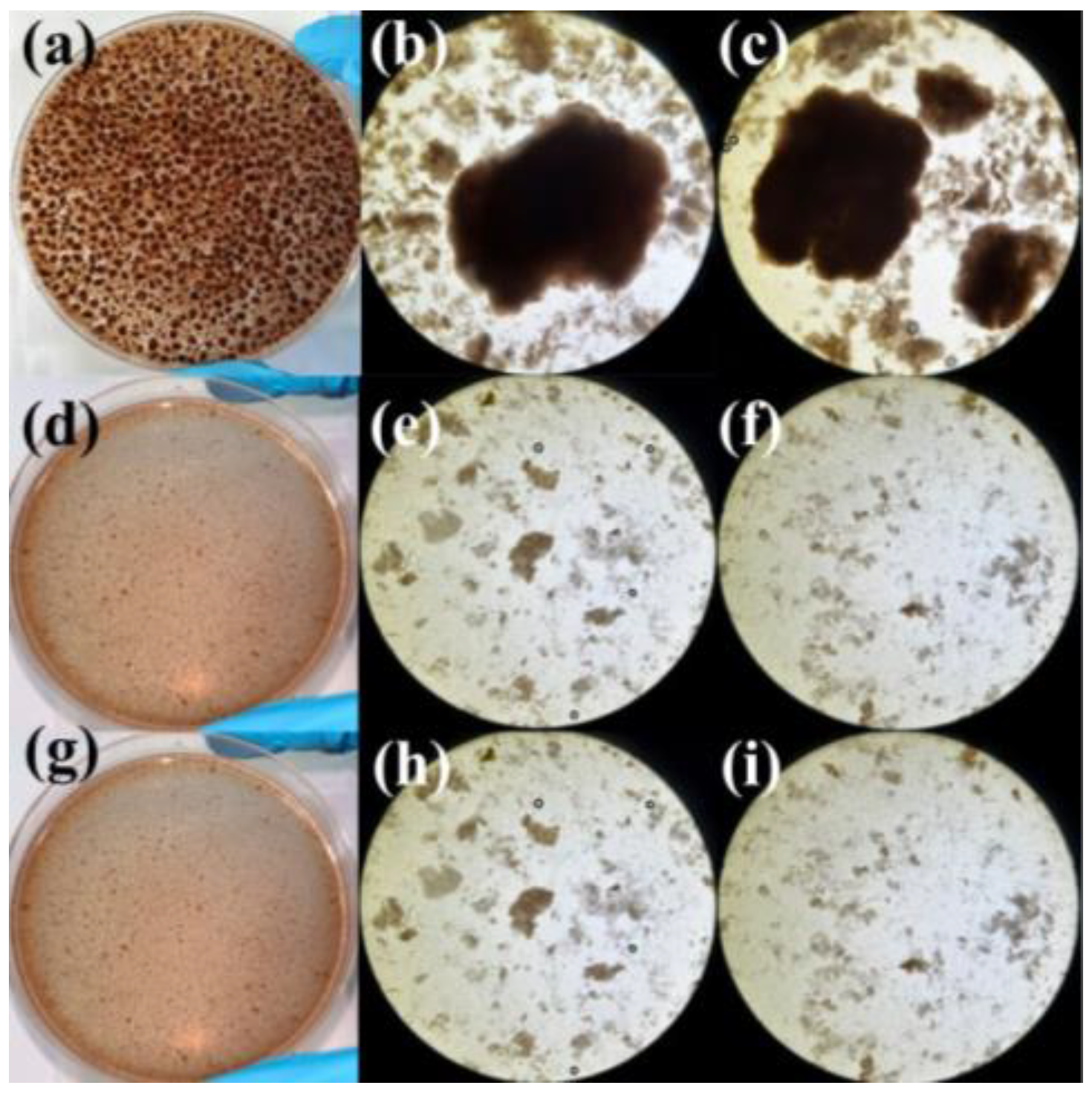
3.2.2. Effects of Salinity on Macroscopic Sludge Morphology
3.2.3. Effects of Salinity on Micromorphology of Sludge
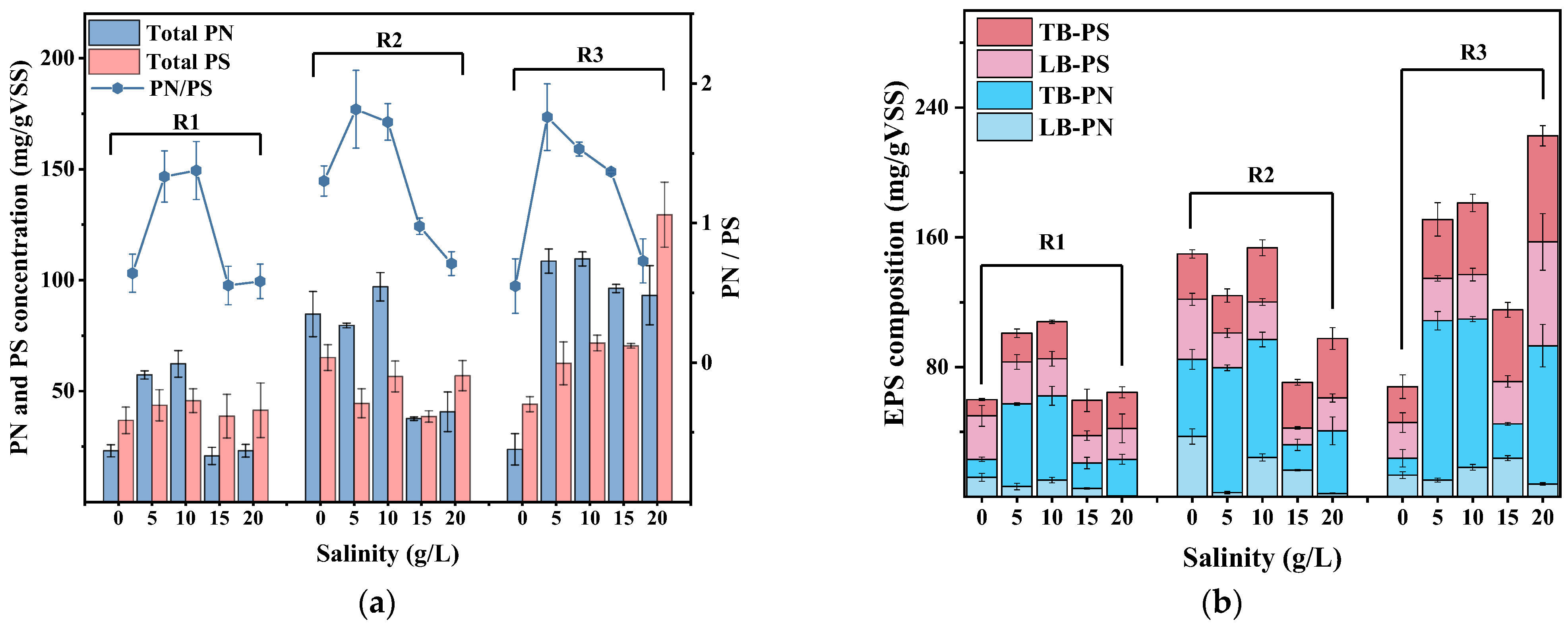
3.3. Effects of Salinity on Chemical Characteristics of Three Sludge Morphologies
3.3.1. Regulation Mechanism of Salinity on Formation and Function of EPS
3.3.2. 3D-EEM and FTIR Characterization Analysis
3.3.3. Response of DHA, SAA, and Heme C to Salinity Stress
3.4. Response Characteristics of Microbial Community Structure to Salinity Stress
3.4.1. Phylum-Level Microbial Community Evolution
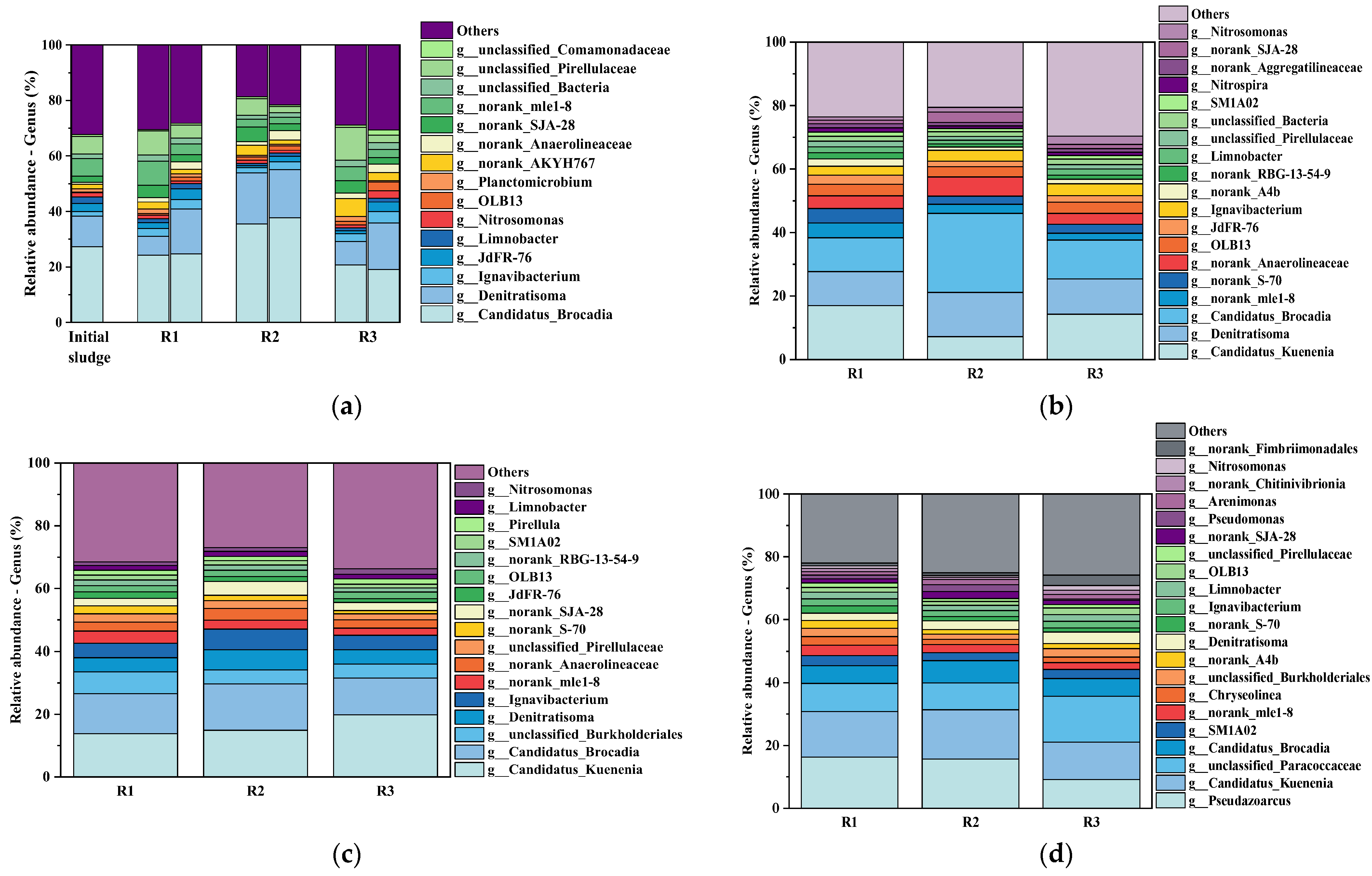
3.4.2. Genus-Level Functional Community Restructuring
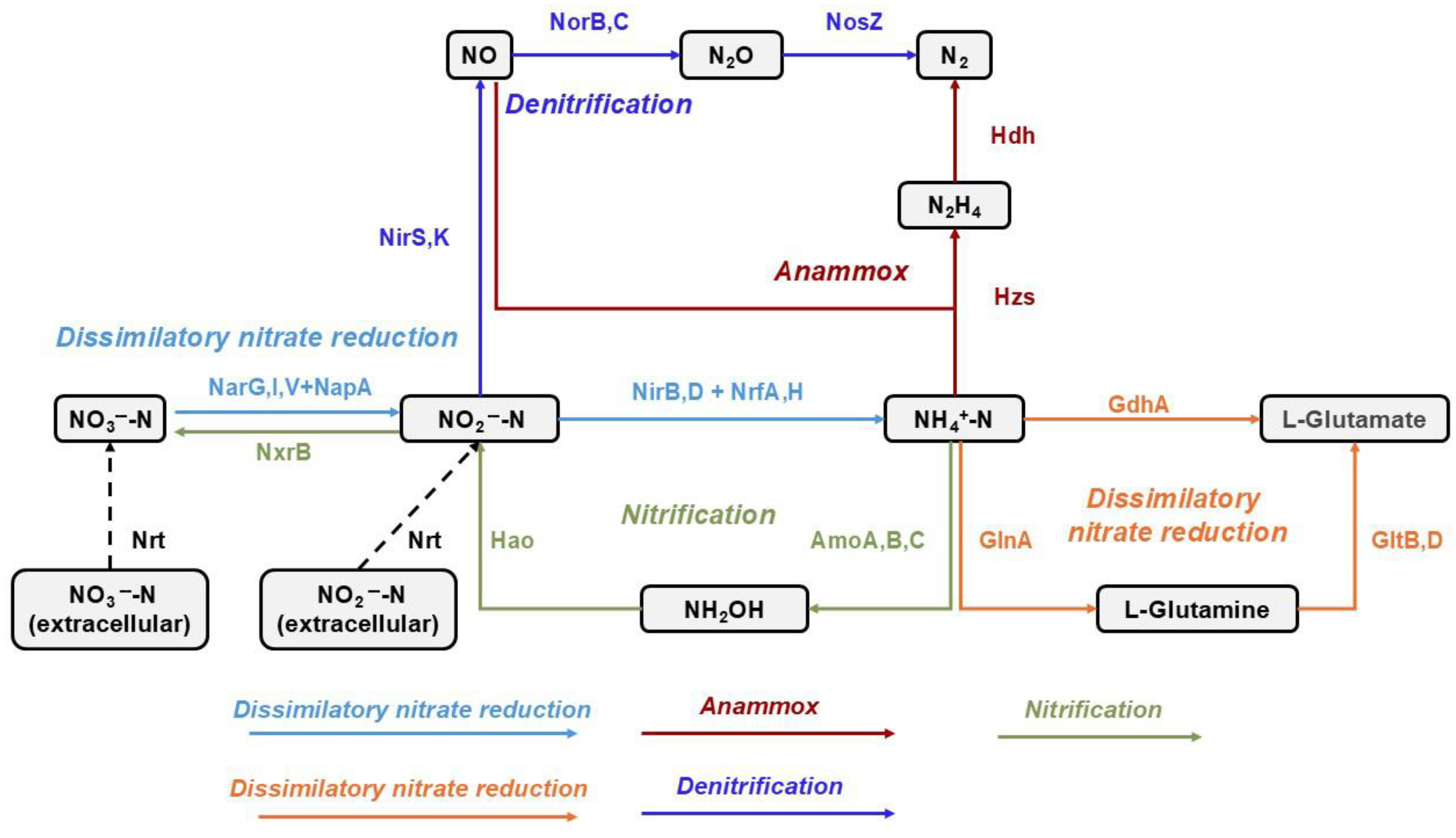
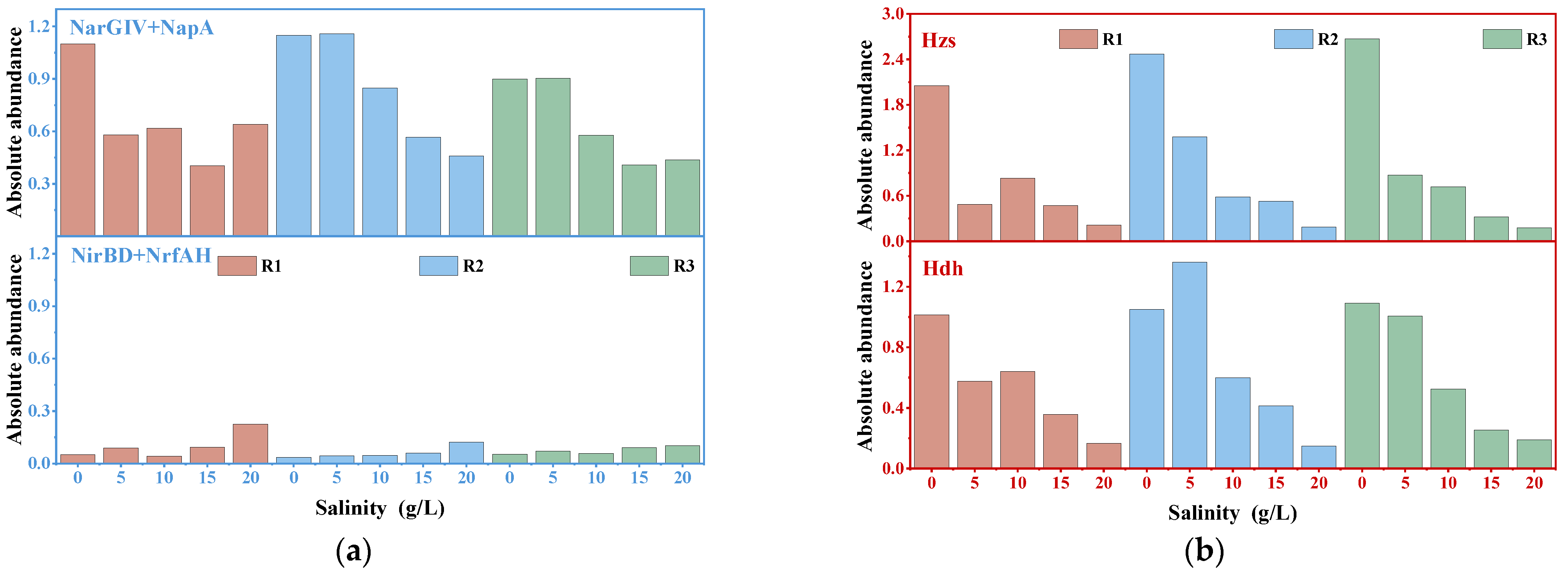
3.5. Effects of Salinity on Nitrogen Metabolism-Related Genes in Different Anammox Sludge Morphologies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOB | ammonia oxidizing bacteria |
| AnAOB | anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria |
| Anammox | anaerobic ammonium oxidation |
| COD | chemical oxygen demand |
| DHA | dehydrogenase activity |
| DO | dissolved oxygen |
| EPS | extracellular polymeric substances |
| Em | emission wavelength |
| Ex | excitation wavelength |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| HRT | hydraulic retention time |
| LB-EPS | loosely bound-eps |
| MLSS | mixed liquor suspended solids |
| MLVSS | mixed liquor volatile suspended solids |
| -N | ammonia nitrogen |
| -N | nitrite nitrogen |
| -N | nitrate nitrogen |
| NOB | nitrite-oxidizing bacteria |
| NLR | volumetric nitrogen loading rate |
| NRR | volumetric nitrogen removal rate |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| PN | proteins |
| PS | polysaccharides |
| SAA | specific anammox activity |
| SAGs | single-amplified genomes |
| SBR | sequencing batch reactor |
| TB-EPS | tightly bound eps |
| TDS | total dissolved solids |
| TP | total nitrogen |
| UASB | up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket |
| 3D-EEM | three-dimensional excitation–emission matrix |
References
- Tsipa, A.; Papalli, M.; Christou, A.; Pissaridou, P.; Vasquez, M.I. Ex-Situ Biological Treatment of Industrial Saline Seafood Wastewater by Salt-Tolerant Mixed Cultures and Phytotoxicity Evaluation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.; Zhou, Z.; Tu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, F.; Tian, S.; Ren, Z. Calcium-Based Catalyst for Ozone Catalytic Oxidation for Advanced Treatment of High Salt Organic Wastewater. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 654, 130149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, J.; Ding, X.; Xia, R.; Hu, M.; Tian, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, A. Acclimatization of Salt-Tolerant Bacteria in a Pilot-Scale Biological Treatment System for Actual High-Salinity Wastewater from a Chemical Industrial Park. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 117397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.-T.; Yan, Z.-L.; He, J.-H.; Liu, S.-Y.; Chen, Y.-P.; Guo, J.-S.; Fang, F.; Yan, P. Adaptation of Anammox Bacteria in Granular Sludge under the Different Temperature Rhythms. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 521, 166721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, B.; He, B.; Zhang, S.; Wu, H. Endophytic Bacteria Enhance Macrophyte Resilience but Reduce Microbial Network Stability under Eutrophication. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 177, 113804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, N.; Baeyens, J.; Wang, S.; Su, H. Fe3O4-Mediated Regulation of Aerobic Granular Sludge under High Salinity and Fluctuating C/N Ratio: Mechanisms and Implications for Seafood Processing Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Res. 2025, 284, 122257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Yu, D.; Wang, X.; Du, S.; Wang, J.; Gong, X.; Du, Y.; Zhao, J. Performance and Microbial Structure of Partial Denitrification in Response to Salt Stress: Achieving Stable Nitrite Accumulation with Municipal Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 311, 123559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Pratt, S.; Crick, O.; Xia, J.; Duan, H.; Ye, L. Salinity Effect on Freshwater Anammox Bacteria: Ionic Stress and Ion Composition. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Cui, L.; Lin, H.; Zhu, W.; Shao, Z.; Wang, Y. Comparison of Nitrification Performance in SBR and SBBR with Response to NaCl Salinity Shock: Microbial Structure and Functional Genes. Environ. Res 2024, 252, 118917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Ma, B.; Song, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Y. Can Anammox Process Be Adopted for Treating Wastewater with High Salinity Exposure Risk? Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Yang, H. Response of ANAMMOX Bacteria to Salinity under Different Environments and the Role of Biomass. Ind. Water Treat. 2022, 42, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Guowei, G. The Treatment of Saline Wastewater Using a Two-Stage Contact Oxidation Method. Water Sci. Technol. 1993, 28, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gong, B.; Zhou, J.; Qing, X. Start-up and Microbial Communities of a Simultaneous Nitrogen Removal System for High Salinity and High Nitrogen Organic Wastewater via Heterotrophic Nitrification. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudayah, N.; Krainara, S.; Kongduan, V.; Chaiprasert, P.; Suraraksa, B. Efficiencies of Anaerobic Hybrid and UASB Reactors to Alleviate the Adverse Effect of Elevated Salinity in Wastewater. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 3426–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal Khan, S.; Ilyas, S.; Javid, S.; Visvanathan, C.; Jegatheesan, V. Performance of Suspended and Attached Growth MBR Systems in Treating High Strength Synthetic Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5331–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Yang, S.F. Influence of Loosely Bound Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) on the Flocculation, Sedimentation and Dewaterability of Activated Sludge. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, K.; Yuan, X.; Ma, J.; Qian, Y. Effect of the Rapid Increase of Salinity on Anoxic-Oxic Biofilm Reactor for Treatment of High-Salt and High-Ammonia–Nitrogen Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; He, H.; Liu, H.; Li, H.; Zeng, G.; Xia, X.; Yang, C. Effect of Salinity on Removal Performance and Activated Sludge Characteristics in Sequencing Batch Reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Li, K.; Tong, S. A Linear Regression Method for the Study of the Coomassie Brilliant Blue Protein Assay. Talanta 1997, 44, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyva, A.; Quintana, A.; Sánchez, M.; Rodríguez, E.N.; Cremata, J.; Sánchez, J.C. Rapid and Sensitive Anthrone–Sulfuric Acid Assay in Microplate Format to Quantify Carbohydrate in Biopharmaceutical Products: Method Development and Validation. Biologicals 2008, 36, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Tan, X.J.; Ren, N.Q.; Cui, Y.B.; Tang, L. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Inhibition of Activated Sludge by TTC and INT-Electron Transport System Activity Tests. Water. Sci. Technol. 2005, 52, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Li, G.-F.; Shi, Z.-J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, B.-C.; Fan, N.-S.; Jin, R.-C. Co-Inhibition of Salinity and Ni(II) in the Anammox-UASB Reactor. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.F.; Jin, R.C. Reactivation of Effluent Granular Sludge from a High-Rate Anammox Reactor after Storage. Biodegradation 2013, 24, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Z.; Zhang, Q.-Q.; Xu, J.-J.; Deng, R.; Ji, Z.-Q.; Wu, Y.-H.; Jin, R.-C. Evaluation of the Inhibitory Effects of Heavy Metals on Anammox Activity: A Batch Test Study. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, E.A.; Trumpower, B.L. Simultaneous Determination of Hemes a, b, and c from Pyridine Hemochrome Spectra. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 161, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burian, A.; Pinn, D.; Peralta-Maraver, I.; Sweet, M.; Mauvisseau, Q.; Eyice, O.; Bulling, M.; Roethig, T.; Kratina, P. Predation Increases Multiple Components of Microbial Diversity in Activated Sludge Communities. ISME J. Emultidisciplinary J. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 16, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Dong, Y.; Hu, F.; Wu, G.; Bai, Z.; Chai, F.; Liu, L.; et al. Response of the Partial Denitrification Coupled with Anaerobic Ammonia Oxidation System to Disinfectant Residues Stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 489, 137723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapena-Mora, A.; Vázquez-Padín, J.R.; Campos, J.L.; Mosquera-Corral, A.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Méndez, R. Monitoring the Stability of an Anammox Reactor under High Salinity Conditions. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 51, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Ning, F.; Zhang, S.; Hou, Y.; Gao, M.; Wang, J.; Aining, Z.; Liu, Y. Resistance and Adaptation of Mature Algal-Bacterial Granular Sludge under Salinity Stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 861, 160558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Fang, F.; Yan, P.; Liu, Z. Effect of Different Forms and Components of EPS on Sludge Aggregation during Granulation Process of Aerobic Granular Sludge. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavi, N.; Kazemi, A.S.; Bonakdarpour, B. The Development of Aerobic Granules from Conventional Activated Sludge under Anaerobic-Aerobic Cycles and Their Adaptation for Treatment of Dyeing Wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 312, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaff, D.R.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Pronk, M. Stable Granulation of Seawater-Adapted Aerobic Granular Sludge with Filamentous Thiothrix Bacteria. Water Res. 2020, 175, 115683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, R.; Chen, R.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, A.; Deng, Y.; Ma, J.; Chen, M. Formation of Filamentous Fungal Pellets in Aerobic Granular Sludge via Reducing Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen: Characteristics of Filamentous Fungi and Denitrification Performance. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 332, 125056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strotmann, U.J.; Windecker, G. Kinetics of Ammonium Removal with Suspended and Immobilized Nitrifying Bacteria in Different Reactor Systems. Chemosphere 1997, 35, 2939–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, X.; Yang, Z.; Song, W.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Tu, C.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, X.; Bai, X. Ammonium Salt Stress-Dependent Compositional Alteration in EPS from Desulfovibrio desulfuricans Subsp. desulfuricans and Its Mediating Role in PbS QDs Biosynthesis. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 512, 162360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, Z.; Ding, Y.; Lu, Y. Identification of the Change in Fouling Potential of Soluble Microbial Products (SMP) in Membrane Bioreactor Coupled with Worm Reactor. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2015–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Sun, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, S.; Chen, F.; Yao, F.; An, H.; Zhong, Y.; Xie, T.; Wang, Y.; et al. Effect of Nickel on the Flocculability, Settleability, and Dewaterability of Activated Sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Fang, F.; Yan, P.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Ma, T.; Shen, Y. The Branched Chains and Branching Degree of Exopolysaccharides Affecting the Stability of Anammox Granular Sludge. Water Res. 2020, 178, 115818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, P.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Ma, J.; Li, S. Effects of Salinity on the Simultaneous Anammox and Denitrification Process: Performance, Sludge Morphology and Shifts in Microbial Communities. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 202099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, W.; Li, D.; He, Y.; Zhan, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.; Singh, R.P. Sludge Reduction and Pollutants Removal in Anaerobic-Anoxic-Oxic Reactor with 2450 MHz Electromagnetic Wave Loading on Returned Sludge: Performance and Mechanism. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 147, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yan, J.; Wu, L.; Bao, Y.; Yu, D.; Li, J. Insight into Halotolerance of a Robust Heterotrophic Nitrifying and Aerobic Denitrifying Bacterium Halomonas Salifodinae. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 351, 126925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, K.; Gong, H.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, M.; He, C.; Shi, C.; San, E. Integrating Floc, Aggregate and Carrier to Reap High-Quality Anammox Biofilm. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 309, 123325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Kim, W.; Lim, H.; Bae, H. Shift in Bacterial Community Structure in Response to Salinity in a Continuous Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidation (Anammox) Reactor. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2020, 147, 104873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Kim, J.; Direstiyani, L.C.; Kim, Y.; Yu, J.; Lee, T. Long-Term Adaptation of Two Anammox Granules with Different Ratios of Candidatus Brocadia and Candidatus Jettenia under Increasing Salinity and Their Application to Treat Saline Wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Fu, J.-J.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Chen, J.-Y.; Fan, N.-S.; Huang, B.-C.; Jin, R.-C. Build the Expressway for the Salt-Tolerant Anammox Process: Acclimation Strategy Tells the Story. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deore, R.; Kumar, R.; Waqqas Mirza, M.; Ali Khan, A. Selecting Suitable Seed Sludge for Anammox Enrichment: Role of Influent Characteristics and Reactor Operational Conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.S.; Loganathachetti, D.S.; Khan, M.A.; Sadaiappan, B.; Mundra, S. Bacterial Resistome in Different Stages of Wastewater Treatment Plant Is Highly Impacted by the Abundance of the Pseudomonadota Community. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2024, 26, 101814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovio-Winkler, P.; Guerrero, L.D.; Erijman, L.; Oyarzúa, P.; Suárez-Ojeda, M.E.; Cabezas, A.; Etchebehere, C. Genome-Centric Metagenomic Insights into the Role of Chloroflexi in Anammox, Activated Sludge and Methanogenic Reactors. BMC Microbiol 2023, 23, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, K.; Xue, G.; Gao, P.; Wu, F. Impacts of Filamentous Bulking on Treatment Effect and Fouling Characteristics of Nonwoven Bioreactor. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 2241–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Shen, G.; Zhao, L.; Liu, W.; Zhao, W.; Wang, F.; Ai, S.; Bian, D.; Zou, D. Sewage Treatment Effect of MPSRs under Different Influent NH4+-N Concentrations and Its Mechanism of Nitrogen Removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, X.; Jin, W.; Liu, L.; Meng, F.; Yang, F. Deciphering the Partial Denitrification Function of Companion Bacteria in Mixotrophic Anammox Systems under Different Carbon/Nitrogen Ratios. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Nnorom, M.-A.; Avignone-Rossa, C.; Yang, K.; Guo, B. Multi-Faceted Effects and Mechanisms of Granular Activated Carbon to Enhance Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidation (Anammox) for Nitrogen Removal from Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 418, 132001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Yu, M.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Xue, C.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Yao, P.; Chen, L.; Fu, L.; Yang, Z.; et al. Microbial Communities Related to the Sulfur Cycle in the Sansha Yongle Blue Hole. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e01149-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Umana, V.M.; Coates, J.D. A Description of the Genus Denitromonas Nom. Rev.: Denitromonas Iodatirespirans Sp. Nov., a Novel Iodate-Reducing Bacterium, and Two Novel Perchlorate-Reducing Bacteria, Denitromonas halophila and Denitromonas ohlonensis, Isolated from San Francisco Bay Intertidal Mudflats. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0091523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, J.; Xu, L.; Wu, Q.L.; Zeng, J. Dissimilatory Nitrate Reduction Pathways Drive High Nitrous Oxide Emissions and Nitrogen Retention under the Flash Drought in the Largest Freshwater Lake in China. Water Res. 2025, 274, 123075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, L.; Wu, C.; Chen, S.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Xu, X. Operation Performance of Aerobic Granular Sludge Process Treating Saline Wastewater: Granular Structure, Microbial Activity, and Effluent Quality. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 118894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohilla, P.; Yadav, J.P. Acute Salt Stress Differentially Modulates Nitrate Reductase Expression in Contrasting Salt Responsive Rice Cultivars. Protoplasma 2019, 256, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nuland, A.; Vandormael, P.; Donaton, M.; Alenquer, M.; Lourenço, A.; Quintino, E.; Versele, M.; Thevelein, J.M. Ammonium Permease-Based Sensing Mechanism for Rapid Ammonium Activation of the Protein Kinase A Pathway in Yeast. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 1485–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, C.V.M.; Nascimento, R.B.; Oliveira, C.A.; Strotmann, U.J.; da Silva, E.M. The use of Microtox® to assess toxicity removal of industrial effluents from the industrial district of Camaçari (BA, Brazil). Chemosphere 2005, 58, 1277–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, S.; Kamizono, A.; Zhang, L.; Kawasaki, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Oshiki, M. Salinity Tolerance and Osmoadaptation Strategies in Four Genera of Anammox Bacteria: Brocadia, Jettenia, Kuenenia, and Scalindua. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 5357–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.-Y.; Sedlacek, C.J.; Kits, K.D.; Mueller, A.J.; Rhee, S.-K.; Hink, L.; Nicol, G.W.; Bayer, B.; Lehtovirta-Morley, L.; Wright, C.; et al. Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea Possess a Wide Range of Cellular Ammonia Affinities. ISME J. 2022, 16, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Bai, M.; Qin, Y. Research Progress on Ammonia Oxidizing Microorganisms: The Discovery, Nitrogen Metabolic Pathways, Influencing Factors and Contribution Rate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 117477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, G.; Wilkinson, M.L.; Gow, A.J. Nitric Oxide Regulation of Cellular Metabolism: Adaptive Tuning of Cellular Energy. Nitric Oxide 2023, 131, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, X.; Wu, Z.-D.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Xue, Y.; Zheng, Y.-G. Nitrogen Removal Characteristics and Salt Tolerance Mechanisms of the Novel Bacterium Halomonas Sp. W07 in Saline Wastewater Treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 426, 132338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derkaoui, K.M.; Sahnoune, M.; Belkohodja, M. The Effect of Salinity on Accumulation Proline, Glycine Betaine and Mineral Elements in Four Varieties of Tomatoes. Ukr. J. Ecol. 2022, 12, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Cao, X.; Zhang, M.; Wei, X.; Zhang, J.; Wan, X. Plant Nitrogen Availability and Crosstalk with Phytohormones Signallings and Their Biotechnology Breeding Application in Crops. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 1320–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.Y.A.; Gill, L.; Monleon, A.; Pronk, M.; Loosdrecht, M.V.; Saikaly, P.E.; Ali, M. Genome-Resolved Metatranscriptomics Unveils Distinct Microbial Functionalities Across Aggregate Sizes in Aerobic Granular Sludge. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnology 2025, 25, 100560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



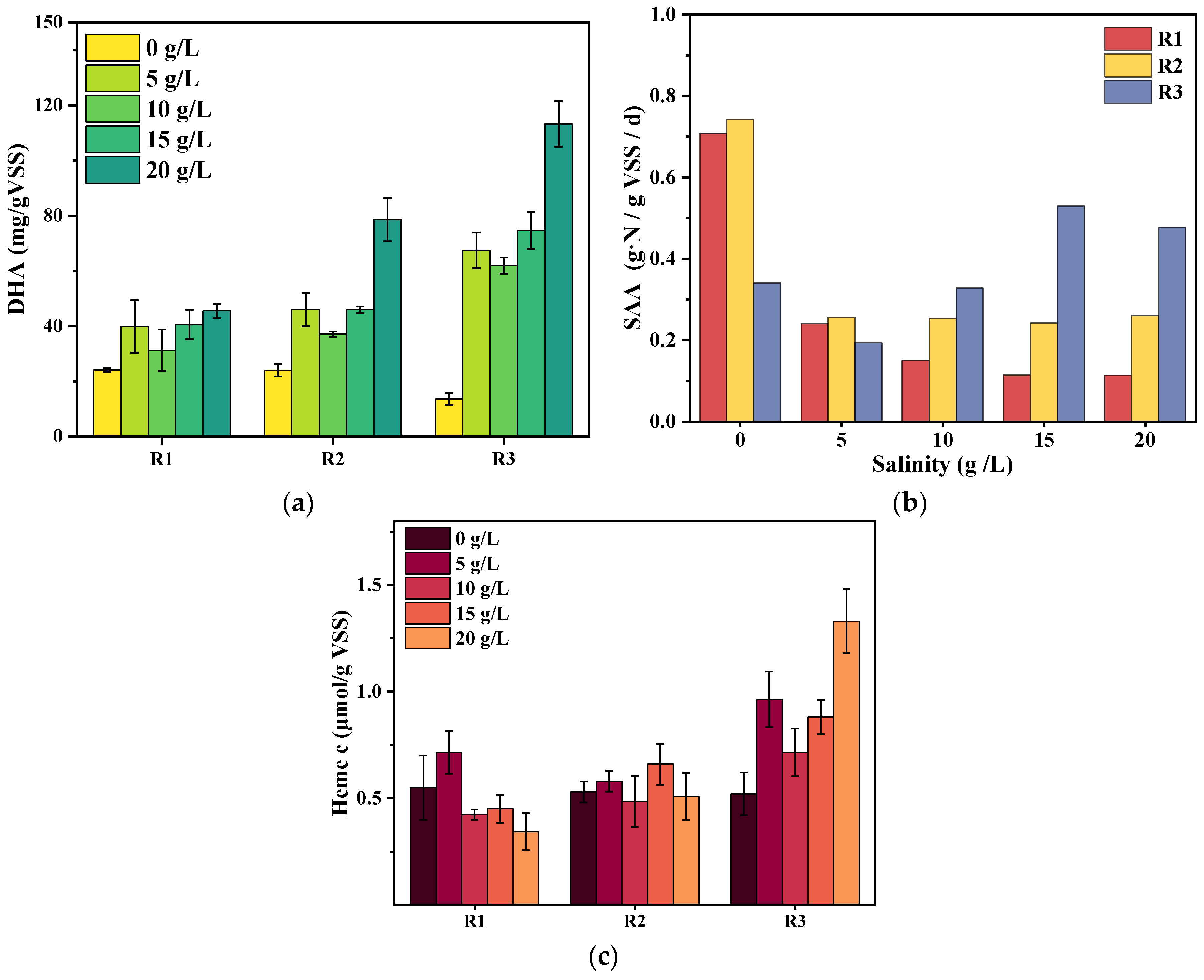


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, K.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, K.; Ma, J.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, S. Impact of Stepwise Salinity Elevation on Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Properties of Morphologically Distinct Anammox Sludge. Water 2025, 17, 2611. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17172611
Sun K, Zhang H, Zhang K, Ma J, Pan Z, Zhang S. Impact of Stepwise Salinity Elevation on Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Properties of Morphologically Distinct Anammox Sludge. Water. 2025; 17(17):2611. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17172611
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Keying, Huining Zhang, Kefeng Zhang, Jianqing Ma, Zhengmin Pan, and Shuting Zhang. 2025. "Impact of Stepwise Salinity Elevation on Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Properties of Morphologically Distinct Anammox Sludge" Water 17, no. 17: 2611. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17172611
APA StyleSun, K., Zhang, H., Zhang, K., Ma, J., Pan, Z., & Zhang, S. (2025). Impact of Stepwise Salinity Elevation on Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Properties of Morphologically Distinct Anammox Sludge. Water, 17(17), 2611. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17172611






