Distribution and Source Appointment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Rivers via Self-Organizing Map and Positive Matrix Factorization (Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection and Analysis
3.2. Assessment Methods
3.2.1. Evaluation of Surface Water Quality
3.2.2. Potential Ecological Risk Index (PERI) Assessment
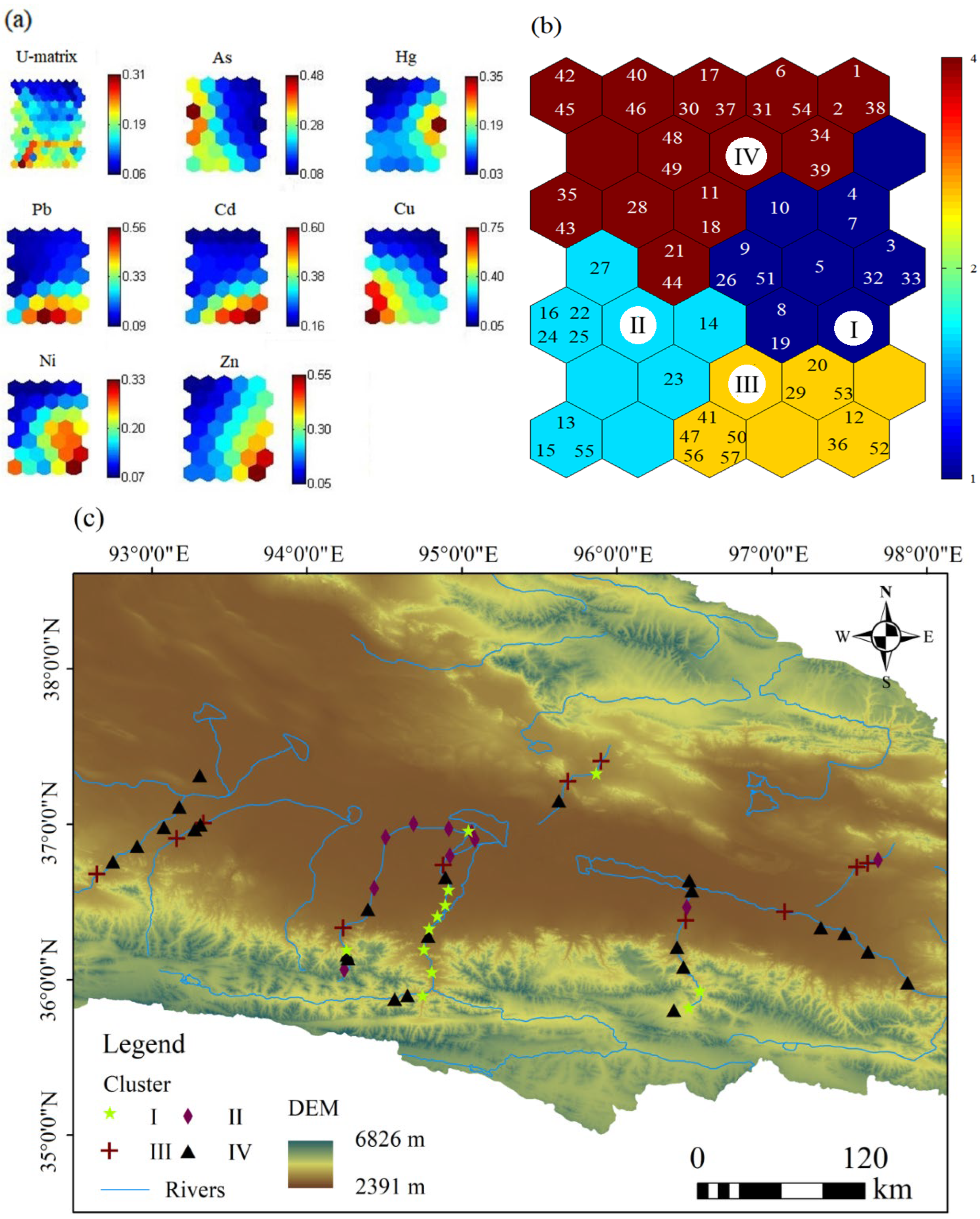
3.2.3. Self-Organizing Map (SOM)
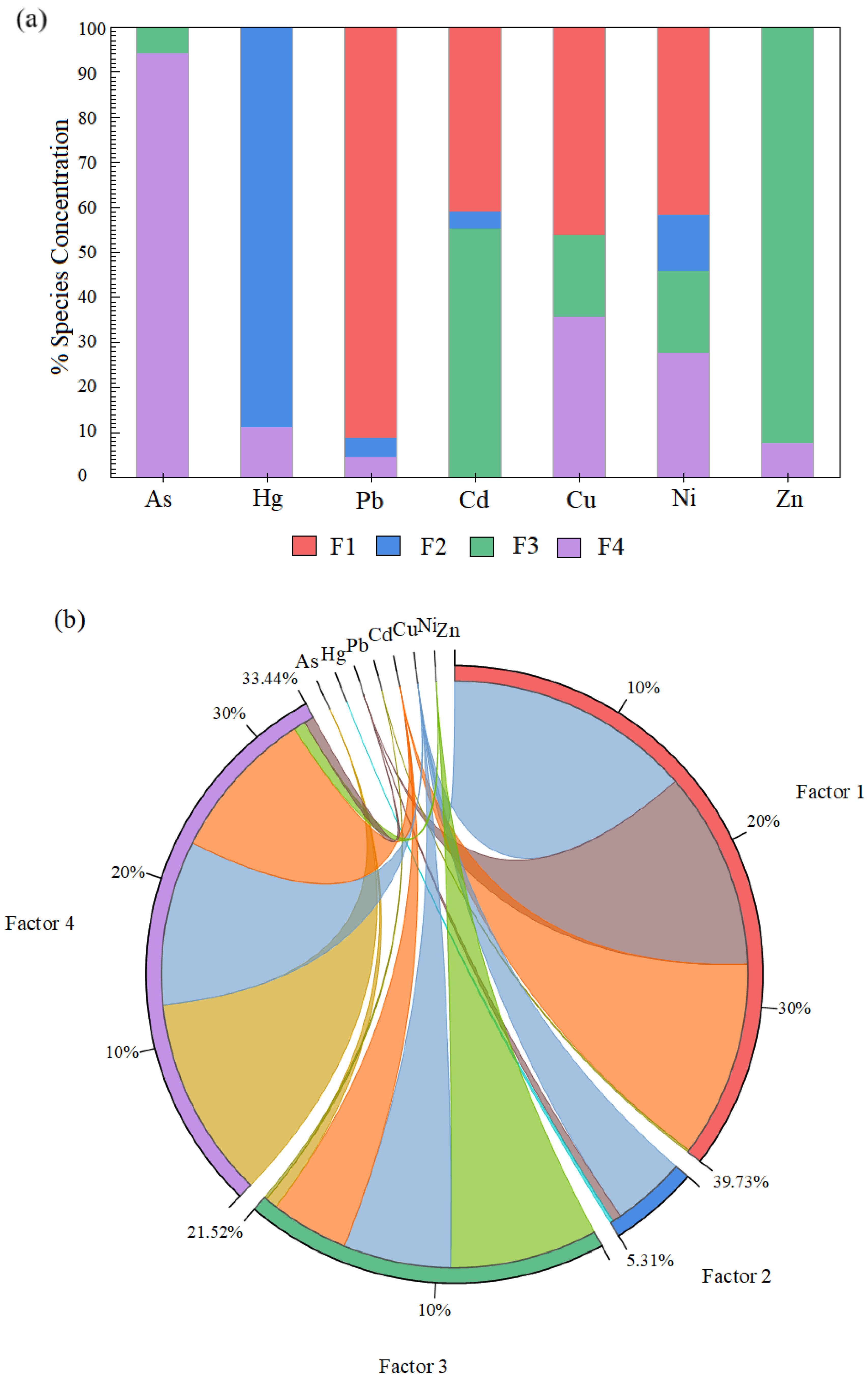
3.2.4. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) Models
4. Results and Discussion
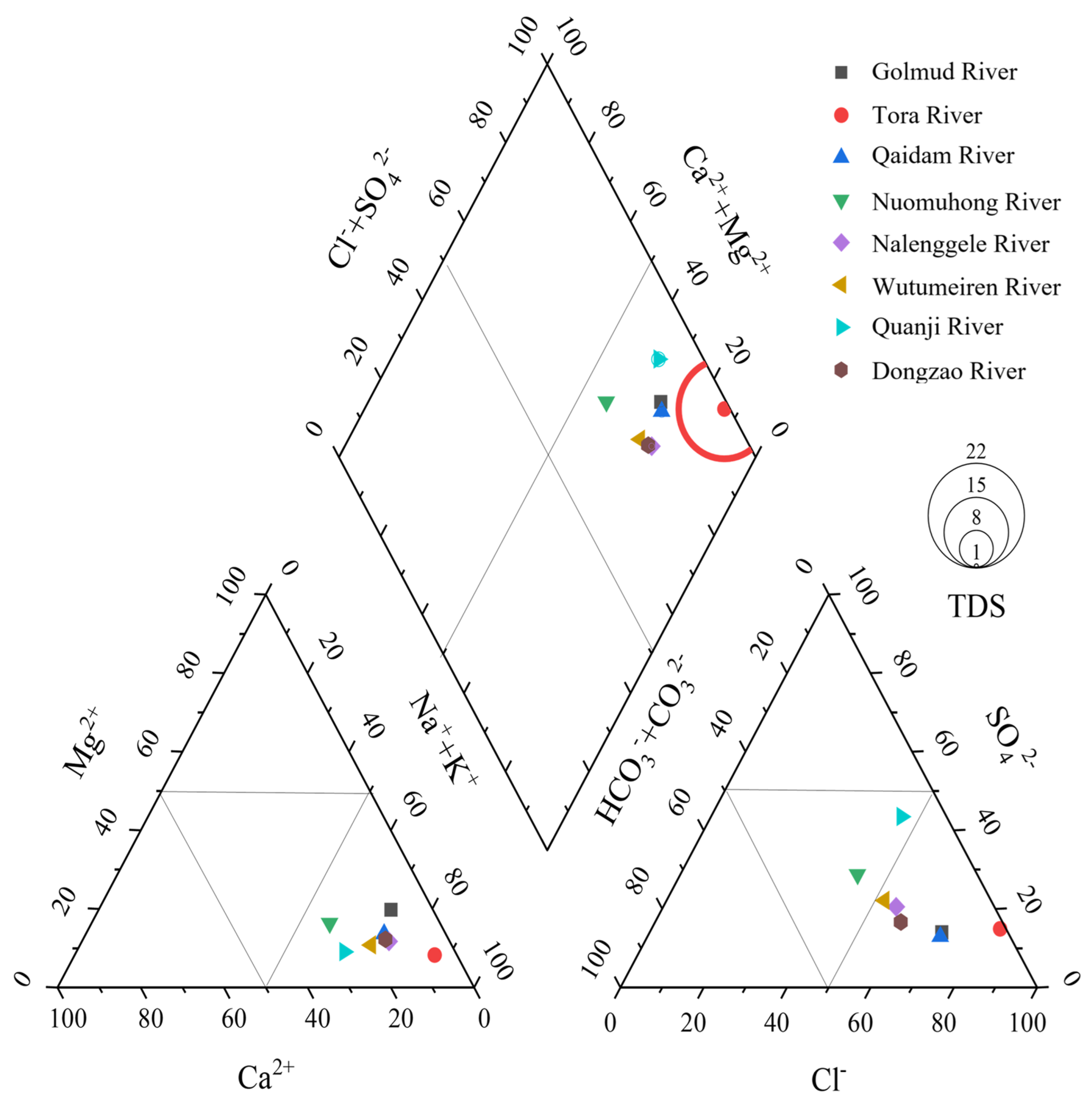
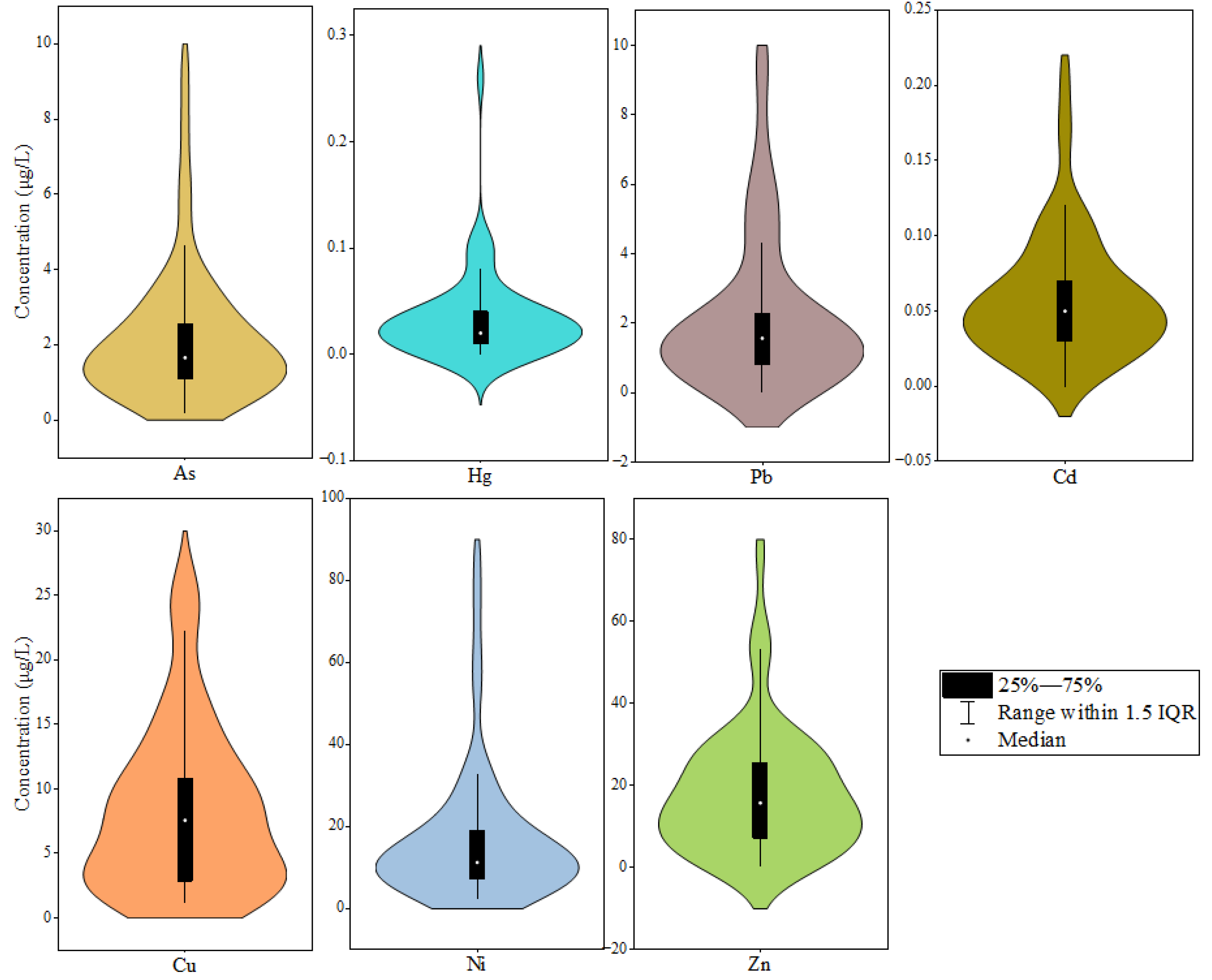
4.1. Hydrochemistry Values and PTE Distribution in Surface Water
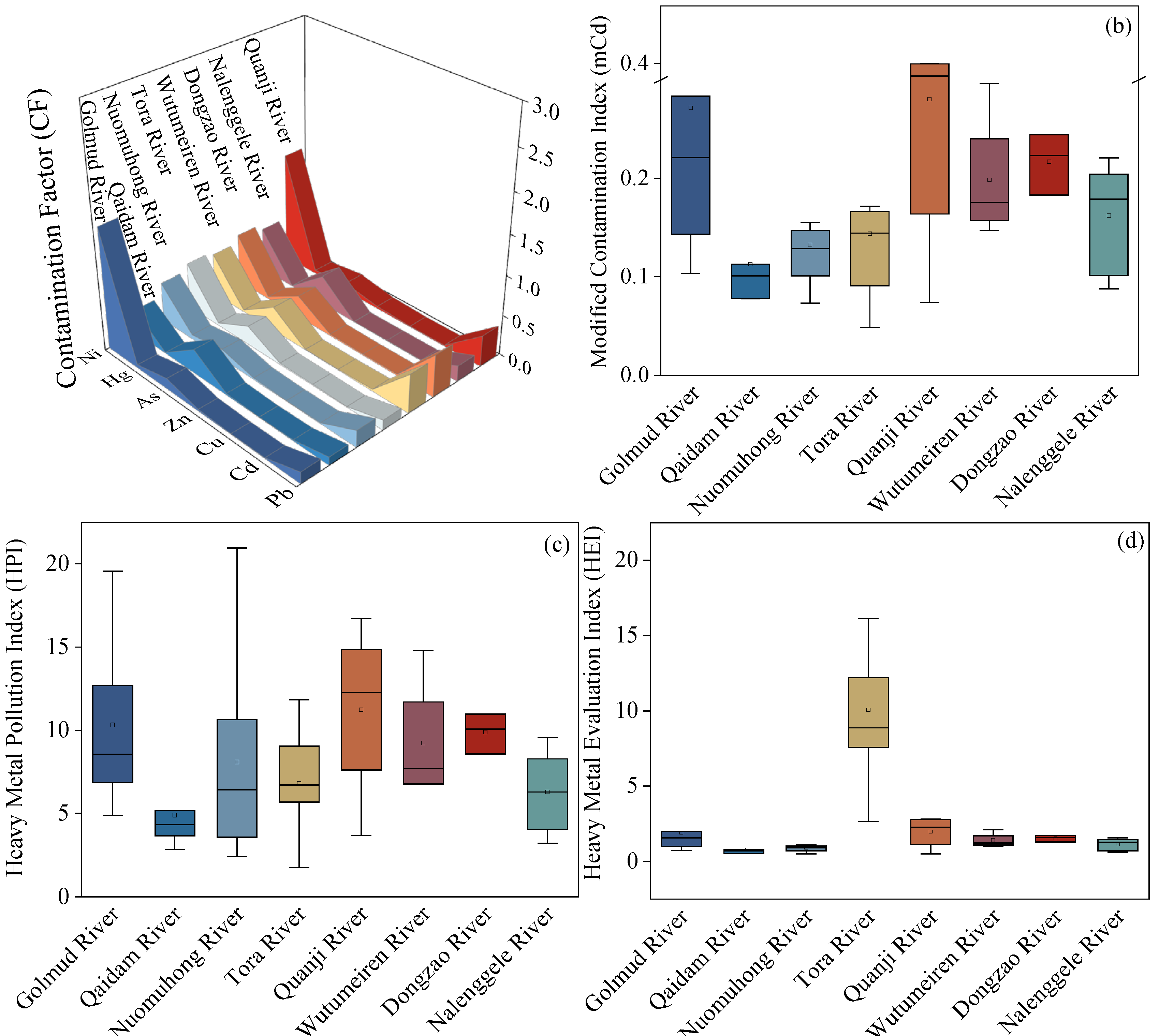
4.2. Water Quality Assessment
4.3. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment
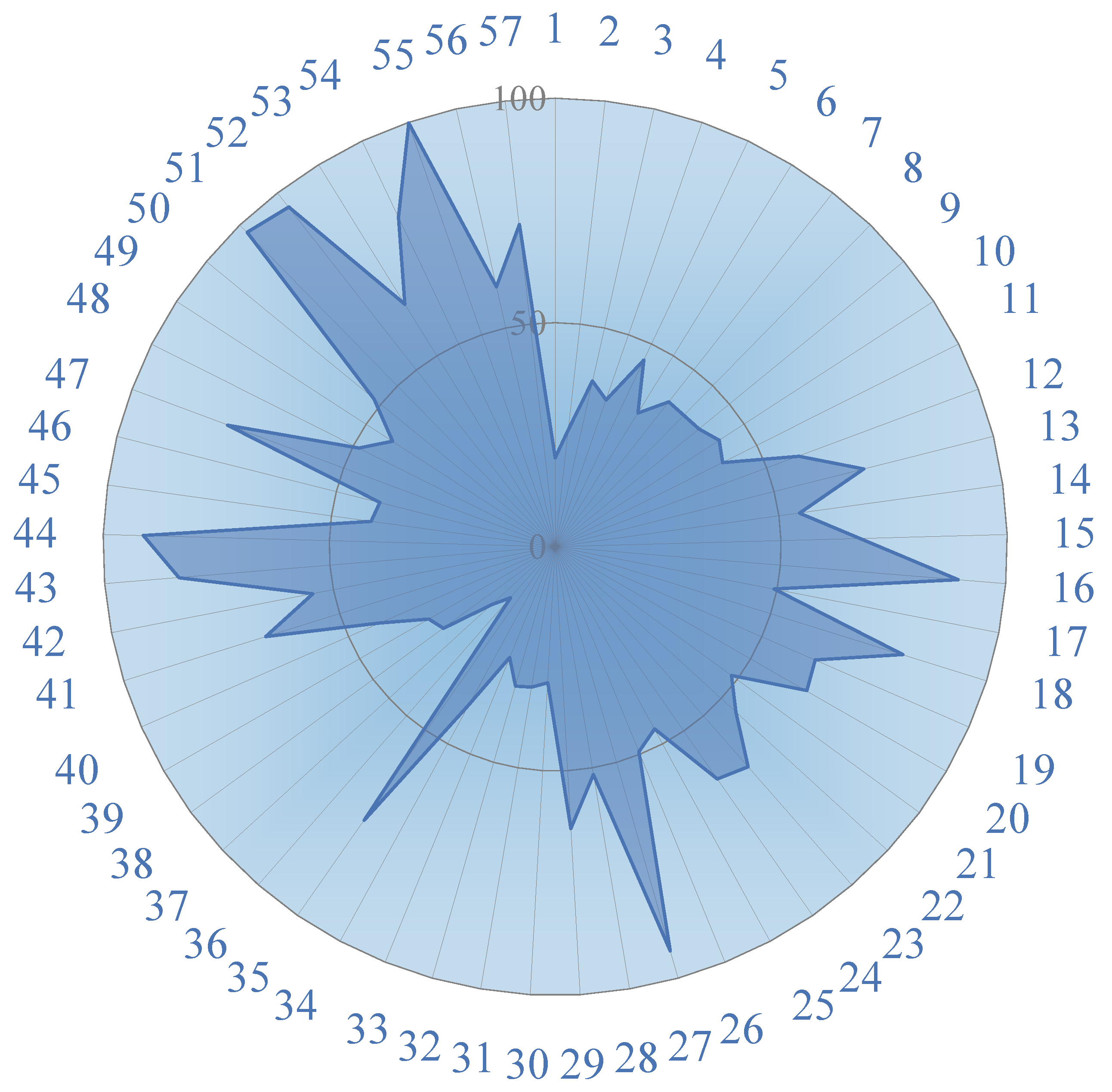
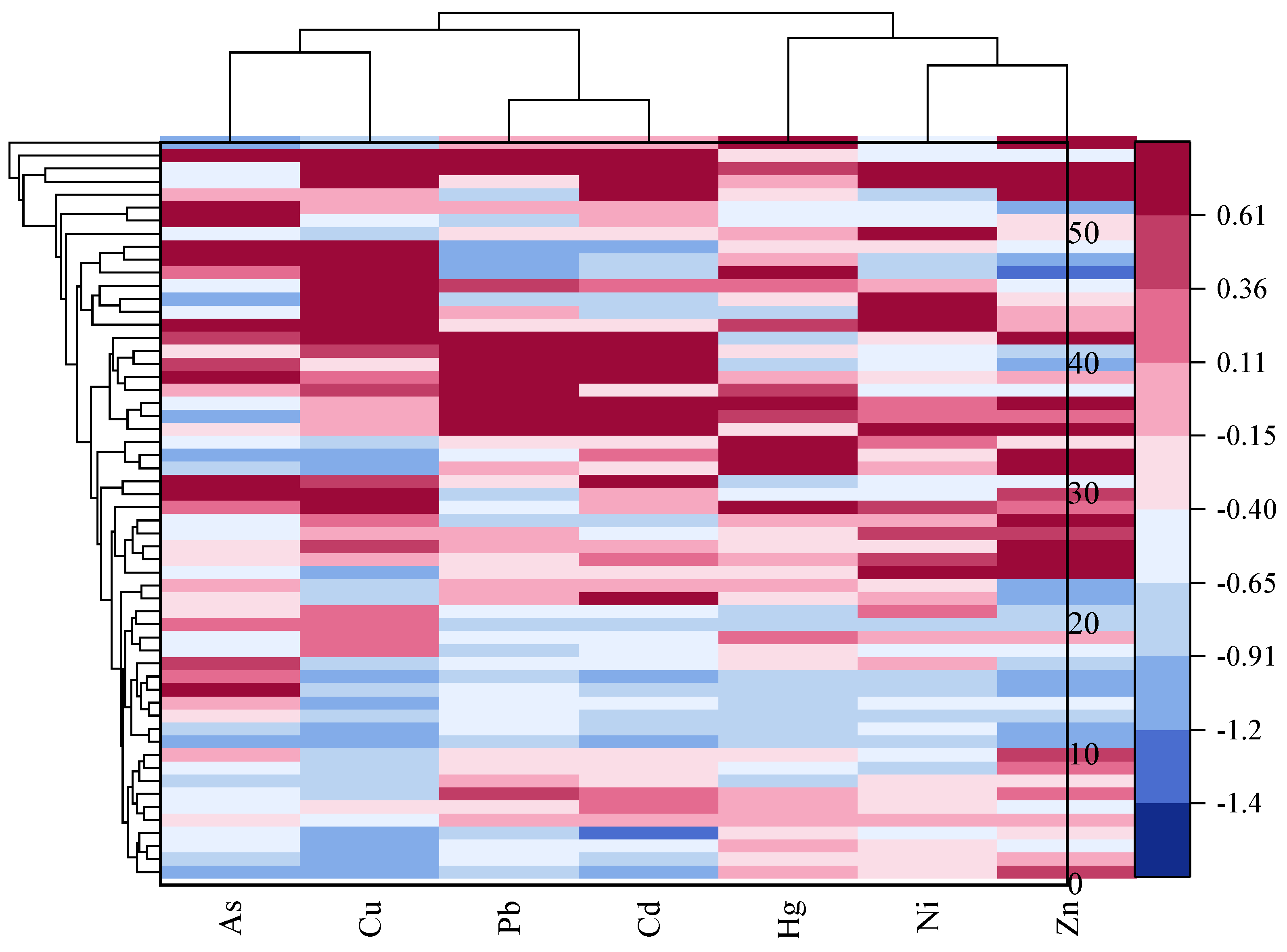
4.4. SOM Cluster Analysis
4.5. PMF-Based Source Contribution Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, H.B.; Deane, D.C.; Zhang, Y.L.; Li, S.C.; Miao, S.Y.; Xie, G.W.; Yin, X.; Favre, A. Integrating multiple indices of geobiodiversity reveals a series of regional species-rich areas worthy of conservation in the region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Biol. Conserv. 2021, 261, 109238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.H.; Ke, C.Q.; Fan, Y.B.; Wang, Z.F. Accelerated glacier mass loss in the southeastern Tibetan Plateau since the 1970s. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2023, 14, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, T.; Kong, Y.L.; Kang, S.C.; Wang, S.J.; Guo, J.M.; Jia, J.; Wu, K.P.; Shi, X.Y.; Wang, K.; Sun, S.W.; et al. Mercury export from a glacier-fed river of Mt. Meili, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Y.; Liu, S.D.; Liu, Y.X.; Liu, W.; Peter, A.R.; Xia, X.H. Permafrost rivers emit mostly pre-aged carbon on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau under climate warming. Cell Rep. Sustain. 2025, 2, 100368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffine, L.; Tang, A.M.; O’Neill, N.; Toffin, L.; Paris, J.D.; Yang, J.H.; Georgiev, V.; Fietzek, P.; Giustiniani, M.; Tinivella, U. Environmental challenges related to methane hydrate decomposition from climate change scenario and anthropic activities: State of the art, potential consequences and monitoring solutions. Earth Sci. Rev. 2023, 246, 104578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, A.H.; Duan, H.C.; Wang, X.F.; You, Q.G.; Peng, F.; Du, H.Q.; Zhao, G.H.; Liu, F.Y.; Li, C.Y.; Lai, C.M. Different response of alpine meadow and alpine steppe to climatic and anthropogenic disturbance on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 27, e01512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.M.; Wu, J.; Lu, J.; Li, K.X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Min, X.Y.; Gao, C.L.; Xu, J. Water quality evaluation and ecological-health risk assessment on trace elements in surface water of the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 241, 113775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.Z.; Gao, S.L.; Wu, Q.X.; Xia, H.; Wu, P.; Zeng, J.; Wang, W.F. Dissolved trace elements in the upper reaches of Lancang River, southeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Current status and distribution, risk and source. Environ. Res. 2024, 260, 119749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Rukumesh, P.; Ramesh, R.P.; Faizan, U.R.Q. Chapter Four—Inorganic components in river waters in the Third Pole. In Water Quality in the Third Pole; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 137–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Miao, W.L.; He, M.Y.; Li, C.Z.; Gu, H.E.; Zhang, X.Y. Origin of lithium-rich salt lakes on the western Kunlun Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from hydrogeochemistry and lithium isotopes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 155, 105356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.; Fatima, F.; Waheed, I.; Akash, M.S.H. Prevalence of exposure of heavy metals and their impact on health consequences. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 157–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alengebawy, A.; Abdelkhalek, S.T.; Qureshi, S.R.; Wang, M.Q. Heavy metals and pesticides toxicity in agricultural soil and plants: Ecological risks and human health implications. Toxics 2021, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.S.; Ding, S.M.; Zhang, L.P.; Li, Y.Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, C.S. An investigation of the effects of elevated phosphorus in water on the release of heavy metals in sediments at a high resolution. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, H.I.; Yap, P.S. A review on three-dimensional cellulose-based aerogels for the removal of heavy metals from water. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807 Pt 1, 150606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angon, P.B.; Islam, M.S.; Shreejana, K.C.; Das, A.; Anjum, N.; Poudel, A.; Suchi, S.A. Sources, effects and present perspectives of heavy metals contamination: Soil, plants and human food chain. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Kant, R.; Sharma, A.K. Exploring the impact of heavy metals toxicity in the aquatic ecosystem. Int. J. Energy Water Res. 2025, 9, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.W.; Liu, Y.X.; Ren, L.; Huo, J.X.; Zhao, J.; Lu, R.J.; Huang, Y.M.; Duan, L. Assessment of atmospheric heavy metal pollution in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Using mosses as biomonitor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.Y.; Zuo, Y.P.; Gao, C.L.; Li, H.Y.; Wei, H.C.; Wu, X.S.; Wen, J.X. Potentially toxic elements of lake and wetland in Northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Distribution, potential sources and risk assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.W.; Lou, S.; Zhang, Z.R.; Liu, S.G.; Zhou, X.S.; Zhou, F.; Radnaeva, L.D.; Nikitina, E.; Fedorova, I.V. Predictions of heavy metal concentrations by physiochemical water quality parameters in coastal areas of Yangtze river estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 199, 115951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yuan, Y.; Xi, B.; Lu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Hui, K.; Tan, W.; Wang, H.; Meng, F. Hydrochemistry characteristics and genesis of shallow groundwater in diverse industrial agglomeration areas in typical alluvial plain of the Yellow River. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 177764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, A.; Khan, M.U.; Rai, N.; Kumar, S.; Dar, T.A. Geochemical characterization, its controlling factors, and comparison between the upstream and downstream segments of the Himalayan Satluj River basin, India. Geochemistry 2023, 83, 125974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, N.; Wang, X.P.; Wang, W.L.; Wang, L.Q.; Tian, S.H.; Zhu, H.X.; Zhang, X.Y. Accumulation, ecological health risks, and source identification of potentially toxic elements in river sediments of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 182, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Xue, S.L.; Jian, H.M.; Yang, F.X.; Yao, Q.Z. Artificial water regulation and natural flood processes control heavy metal concentrations and transport in the Yellow River, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 209 Pt A, 117092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, A.P.; Das, S.; Kalamdhad, A.S. Assessment of possible pollution risk using spatial distribution and temporal variation of heavy metals in river sediments. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, R.; Hopke, P.K.; Van Impe, J.; Sannigrahi, S.; Salauddin, M.; Cummins, E.; Nag, R. Source identification of heavy metals and metalloids in soil using open-source Tellus database and their impact on ecology and human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 175987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fartas, F.F.; Remini, B.; Sekiou, F.; Marouf, N. The use of PCA and ANN to improve evaluation of the WQI classic, development of a new index, and prediction of WQI, coastel constantinois, northern coast of eastern Algeria. Water Supply 2022, 22, 8727–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Li, S.Y.; Xu, J.Z.; Yang, Z.H.; Liu, Z.Y.; Chen, P.; Liu, Y.Z.; Ding, Y.M.; Tan, J.Y.; Li, J.Y. Evaluation of surface water quality in Heilongjiang Province, China: Based on different quantities of water quality indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.H.; Xu, C.J.; Zuo, Y.P.; Luo, X.; Wang, L.Q.; Chen, H.; Xie, X.J.; Yan, D.; Liang, T. Analysis of water quality indexes and their relationships with vegetation using self-organizing map and geographically and temporally weighted regression. Environ. Res. 2023, 216 Pt 2, 114587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjana, K.R.; Suresh, A.; Soman, V.; Rahman, K.H. Metal contamination in the Ashtamudi Wetland ecosystem: Source identification, toxicological risk assessment of Ni, Cd, Cr, and Pb and remediation strategies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 212, 117534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Huang, L.; Gan, J.; Yang, M.; Zhu, G.; Li, Y. Hydrochemical Characteristics, Mechanisms of Formation, and Sources of Different Water Bodies in the Northwest Coal-Electricity Agglomeration Area. Water 2024, 16, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, A.; Motamed-Jahromi, M.; Abbasi, F.; Hesaruiyeh, F.A.; Shahsavani, E.; Khaneghah, A.M. Evaluation of the concentration and human health risk of nitrate and potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in melons from a southern region of Iran: Identification of pollution sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Shao, M.; Wang, T.; Pei, Y.; Chen, B. Geochemistry of lacustrine carbonate rocks in southwestern Qaidam: Implications of silicate weathering and carbon burial triggered by the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2022, 265, 104167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jian, X.; Fu, H.J.; Zhang, W.; Shang, F.; Fu, L. Decoupled local climate and chemical weathering intensity of fine-grained siliciclastic sediments from a paleo-megalake: An example from the Qaidam basin, northern Tibetan Plateau. Sediment. Geol. 2023, 454, 106462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.L.; Li, X.Y. The impact of climate changes on water level of Qinghai Lake in China over the past 50 years. Nord. Hydrol. 2016, 47, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.G.; Li, X.Y.; Deng, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, X. Stable isotope evidence confirms lakes are more sensitive than rivers to extreme drought on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2023, 627 Pt B, 130466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Wang, G.C.; Hou, E.K.; Guo, L.; Xiong, L.Y.; Song, X.M. Triple isotopes (δD, δ18O, δ17O) characteristic of river water and groundwater in an arid watershed from Qaidam Basin, Northwestern China: Implications for hydrological cycle. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 172229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.L.C.; da Silva, J.B.; dos Santos, I.F.; de Oliveira, O.M.C.; Cerda, V.; Queiroz, A.F.S. Use of pollution indices and ecological risk in the assessment of contamination from chemical elements in soils and sediments- Practical aspects. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 35, e00169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayakumar, A.; Aju, C.D.; Rajesh, R.; Reji, S.; Krishnan, K.A.; Arya, S. Exploring hydrochemical drivers of drinking water quality in a tropical river basin using self-organizing maps and explainable AI. Water Res. 2025, 284, 123884. Available online: https://wgmktpgxscrjl-s.p.lib.tju.edu.cn/10.1016/j.watres.2025.123884 (accessed on 3 April 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.T.M.S.; Kono, Y.; Hosono, T. Self-organizing map improves understanding on the hydrochemical processes in aquifer systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.Y.; Li, M.H.; Qu, S.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Duan, L.M.; Yang, X.; Li, D.Y.; Liao, Z.L.; Yu, R.H. Spatio-seasonal variability of source contributions to water quality in a large irrigation drainage lake basin based on the entropy weighted quality index, positive matrix factorization, and isotopic tracers. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 382, 126670. Available online: https://wgmktpgxscrjl-s.p.lib.tju.edu.cn/10.1016/j.envpol.2025.126670 (accessed on 3 April 2025). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Li, F.; Liu, S.; You, Y.; Liu, C. Enhanced Assessment of Water Quality and Pollutant Source Apportionment Using APCS-MLR and PMF Models in the Upper Reaches of the Tarim River. Water 2024, 16, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.M.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, W.; Niu, F.J.; Gao, Z.Y. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and processes of thermokarst lake and groundwater during the melting of the active layer in a permafrost region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851 Pt 2, 158183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Ma, J.X.; Wu, S.Q.; Shekhar, N.V.R.; Biswas, S.; Sahu, A.K. Determination of Physicochemical Parameters and Levels of Heavy Metals in Food Waste Water with Environmental Effects. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2020, 2020, 8886093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, A.; Das, S.; Mandal, A.; Mondal, N.S.; Kole, D.; Dutta, P.; Ghosh, A.R. Seasonal variation of physicochemical parameters and heavy metal concentration in water and bottom sediment at harboring areas of Digha coast, West Bengal, India. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 62, 102945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Liu, S.X.; Li, K.; Jiang, H.B.; Jiang, T.; Tang, G.P. Modeling Spatial Patterns of Dissolved Oxygen and the Impact Mechanisms in a Cascade River. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 9, 781646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, D.; Wang, L.Q.; Dai, L.J.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, T. Evaluation of water environment quality in a typical wetland on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau using positive matrix factorization and self-organizing map. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 479, 144069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, M.; Rehana, S. Impact of climate change on river water temperature and dissolved oxygen: Indian riverine thermal regimes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, W.; Ouyang, W.; Shen, C.; Li, L. Temperature Outweighs Light and Flow as the Predominant Driver of Dissolved Oxygen in US Rivers. Nat. Water 2023, 1, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Q.; Rong, N.; Jin, X.; Meng, X.; Han, S.J.; Zhang, D.W.; Shan, B.Q. Dissolved oxygen variation in the North China Plain river network region over 2011–2020 and the influencing factors. Chemosphere 2021, 287, 132354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Azhari, A.; Ait Brahim, Y.; Barbecot, F.; Hssaisoune, M.; Berrouch, H.; Laamrani, A.; Hadri, A.; Brouziyne, Y.; Bouchaou, L. Evaluating groundwater salinity patterns and spatiotemporal dynamics in complex endorheic aquifer systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 994, 180055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.H.; Gao, B.; He, L.; Hu, X.H.; Dong, L.; Sanjay, D.; Dong, A.; Sun, Z.X.; Wan, W. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Controlling Factors of the Lhasa River under the Influence of Anthropogenic Activities. Water 2019, 11, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Zhou, J.J.; Yang, J.C.; Huang, M.H.; Feng, W.; Li, Q.Q.; Xue, D.X.; Zhao, Y.R.; Zhu, G.F. Applying multivariate statistics for identification of groundwater chemistry and qualities in the Sugan Lake Basin, Northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 448–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Li, W.X.; Yuan, X.L.; Li, C.Z. Lithium and strontium isotopic systematics in the Nalenggele River catchment of Qaidam basin, China: Quantifying contributions to lithium brines and deciphering lithium behavior in hydrological processes. J. Hydrol. 2022, 614 Pt B, 128630. Available online: https://wgmktpgxscrjl-s.p.lib.tju.edu.cn/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128630 (accessed on 18 April 2025). [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.H. Hydrochemistry of inland rivers in the north Tibetan Plateau: Constraints and weathering rate estimation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Hu, B.X.; Wang, P.; Chen, J.B.; Yang, L.; Xiao, K.; Zhang, X.W. Hydrogeochemical evolution and heavy metal contamination in groundwater of a reclaimed land on Zhoushan Island. Water 2018, 10, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.R.; Fan, Q.S.; Li, Q.K.; Du, Y.S.; Qin, Z.J.; Wei, H.C.; Shan, F.S. The Source, Distribution, and Sedimentary Pattern of K-Rich Brines in the Qaidam Basin, Western China. Minerals 2019, 9, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.T.; Wang, W.K.; Cui, X.D.; Wang, D.; Liu, W.H.; Liu, X.M.; Wang, S.B. Environmental risk-based hydroeconomic evaluation for alluvial aquifer management in arid river basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.H.; Wu, Q.X.; An, Y.L.; Lv, J.M. Major ion compositions, sources and risk assessment of karst stream under the influence of anthropogenic activities, Guizhou Province, Southwest China. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.K.; Fan, Q.S.; Wei, H.C.; Qin, Z.J.; Zhang, X.R.; Du, Y.S.; Shan, F.S. Sulfur isotope constraints on the formation of MgSO4-deficient evaporites in the Qarhan Salt Lake, western China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 189, 104160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.Y.; Chen, T.Y.; Li, X.Z.; Liu, X.J.; Wang, Y.X.; Chen, Z.Y.; Chong, Y.E. Formation, mechanism and significance of alluvial-dammed lakes in Golmud River catchment, north-eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2021, 46, 2421–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Yang, Q.C.; Xie, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.L. Spatiotemporal characteristics of groundwater quality and health risk assessment in Jinghe River Basin, Chinese Loess Plateau. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 248, 114278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Cheng, P.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Chen, S.H.; Wang, C.X.; Wang, J.C.; Zhang, J.C.; Fan, B.G.; Jin, Y. Study on the co-combustion process and mercury emission characteristics of sewage sludge-coal slime coupled fuel. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2023, 25, 1369–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigham, M.E.; VanderMeulen, D.D.; Eagles-Smith, C.A.; Krabbenhoft, D.P.; Maki, R.P.; DeWild, J.F. Long-Term Trends in Regional Wet Mercury Deposition and Lacustrine Mercury Concentrations in Four Lakes in Voyageurs National Park. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.J.; Rong, Y.M.; Chen, D.; Sun, R.Y.; Huang, J.; Ding, H.W.; Olid, C.; Yan, H.Y. Anthropogenic activity and millennial climate variability affect Holocene mercury deposition of an alpine wetland near the largest mercury mine in China. Chemosphere 2023, 316, 137855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.M.; Tripathee, L.; Kang, S.C.; Zhang, Q.G.; Huang, J.; Sharma, C.M.; Chen, P.F.; Paudyal, R.; Rupakheti, D. Atmospheric particle-bound mercury in the northern Indo-Gangetic Plain region: Insights into sources from mercury isotope analysis and influencing factors. Geosci. Front. 2021, 13, 101274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.G.; Chen, X.F.; Liu, W.L.; Li, T.S.; Qiu, G.L.; Yan, H.Y.; Wang, M.M.; Chen, J.; Sun, G.Y.; Wang, Q.F.; et al. Soil and ambient air mercury as an indicator of coal-fired power plant emissions: A case study in North China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 33146–33157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lu, J.; Li, L.M.; Min, X.Y.; Luo, Y.M. Pollution, ecological-health risks, and sources of heavy metals in soil of the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Chang, Q.R.; Liu, J.; Clevers, J.G.P.W.; Kooistra, L. Identification of soil heavy metal sources and improvement in spatial mapping based on soil spectral information: A case study in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, S.T.; Gao, Z.J.; Zhang, H.R.; Zhu, Z.H.; Jiang, B.; Liu, J.T.; Dong, H.Z. Contamination characteristics, source analysis and health risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil in Shi River Basin in China based on high density sampling. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 227, 112926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, L.Q.; Deng, L.; Jin, Z.D. Characteristics, sources, water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in river water and well water in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2004–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.Y.; Wang, Z.C.; Zhao, H.Y.; Bu, Z.J.; Peros, M.; Liu, S.S.; Li, H.K.; Wang, S.Z. Characteristics and Assessment of Trace Elements (Hg, As, Sb, Se, and Bi) in Mire Surface Water from the Changbai Mountains, Northeastern China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R.H.; Shao, L.; Liu, X.Y.; Han, K.; Song, P. Variation of mercury fractionation and speciation in municipal sewage treatment plant: Effects of mercury on the atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 36475–36485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.P.; Liu, X.J.; Wang, L.Q.; Yang, J.; Wan, X.M.; Liang, T. A holistic assessment of spatiotemporal variation, driving factors, and risks influencing river water quality in the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 157942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yan, Y.L.; Hu, D.M.; Peng, L.; Wang, C. PM 2.5-bound heavy metals in a typical industrial city of Changzhi in North China: Pollution sources and health risk assessment. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 321, 120344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, M.I.; Rehman, A.; Mehmood, M.S.; Mahmood, S.; Zafar, Z.; Lu, H.L.; Feng, W.F.; Lu, S.Q. Spatial distribution, ecological and human health risks of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in river Ravi, Pakistan: A comprehensive study. Environ. Res. 2024, 263 Pt 3, 120205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezouki, S.; Moubchir, T.; El Hanafi, L.; Flouchi, R.; Zahir, I.; Alzain, M.N.; El Guerrouj, B.; Noman, O.; Shahat, A.A.; Allali, A. Assessment of Ecological Hazards in the Inaouen Wadi and Its Tributaries Using the Presence of Potentially Toxic Elements in Its Sediments. Water 2024, 16, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Men, C.; Liu, Y.; Yu, W.; Xu, F.; Shen, Z. Spatial distribution and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in Yangtze estuary sediment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, L.; Wang, J.P.; Xie, M.Y.; Yang, B.K. Ecological risk and health risk analysis of soil potentially toxic elements from oil production plants in central China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.W.; Liu, K.; Liu, X.; Tang, Z.E.; Wang, X.J.; Fu, R.C.; Lin, X.J.; Liu, N.; Qiu, J.R. Driving factor, source identification, and health risk of PFAS contamination in groundwater based on the self-organizing map. Water Res. 2024, 267, 122458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robledo Ardila, P.A.; Álvarez, A.R.; Árcega, C.F.; Durán, V.J.J.; Morales, G.R.; Lamas, C.E.; Oceguera-Vargas, I.; DelValls, A. Assessment and Review of Heavy Metals Pollution in Sediments of the Mediterranean Sea. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.L.; Yang, X.; Liang, T.; Liu, S.Y.; Yan, X.L.; Li, J.C.; Liu, Z.S. Source apportionment of soil PTE in a northern industrial county using PMF model: Partitioning strategies and uncertainty analysis. Environ. Res. 2024, 252 Pt 2, 118855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazapoe, R.W.; Kwayisi, D.; Alidu, S.; Sagoe, S.D.; Umaru, A.O.; Amuah, E.E.Y.; Addai, M.O.; Fynn, O.F. Advanced analysis of soil pollution in southwestern Ghana using Variational Autoencoders (VAE) and positive matrix factorization (PMF). Environ. Sustain. Ind. 2025, 26, 100627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, S.; Huang, W.; Xu, J.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Q.; Ning, X. Response of Trace Elements in Urban Deposition to Emissions in a Northwestern River Valley Type City: 2010–2021. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McComb, J.Q.; Han, F.X.; Rogers, C.; Thomas, C.; Arslan, Z.; Ardeshir, A.; Tchounwou, P.B. Trace elements and heavy metals in the Grand Bay National Estuarine Reserve in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 99, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.Y.; Li, R.L.; Wang, C.; Yang, S.C.; Shao, M.Y.; Zhang, L.M.; Li, P.; Feng, X.B. Transport and transformation of colloidal and particulate mercury in contaminated watershed. Water Res. 2025, 278, 123428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.W.; Feng, X.; Liang, P.; Deliger, H.; Zhang, J.J.; Liu, P. Temporal trend and sources of speciated atmospheric mercury at Waliguan GAW station, northwestern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 1951–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.T.; Cai, X.Y.; Jia, L.Y.; Wang, X.; Yuan, W.; Lin, C.J.; Wang, D.Y.; Feng, X.B. Quantifying Mercury Distribution and Source Contribution in Surface Soil of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Using Mercury Isotopes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 5903–5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, X.D. Impacts of the uplift of four mountain ranges on the arid climate and dust cycle of inland Asia. Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl. 2018, 505, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.K.; Li, C.X.; Ai, C.; Zhang, B.; Huang, H.Y.; Xiao, J. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of snow cover in the northeastern Tibet plateau. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Min | Max | Mean | Median | SD | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.24 | 10.11 | 9.43 | 9.43 | 0.33 | 0.04 |
| DO (mg/L) | 4.15 | 13.33 | 8.55 | 8.63 | 1.37 | 0.16 |
| EC (mS/cm) | 0.33 | 56.63 | 3.88 | 0.80 | 10.10 | 2.60 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 4.12 | 81,420.73 | 5002.94 | 940.79 | 13,933.13 | 2.78 |
| SAL (ppt) | 0.30 | 86.49 | 4.74 | 0.72 | 14.35 | 3.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, N.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Deng, L. Distribution and Source Appointment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Rivers via Self-Organizing Map and Positive Matrix Factorization (Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China). Water 2025, 17, 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17172547
Cai N, Wang X, Liu X, Deng L. Distribution and Source Appointment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Rivers via Self-Organizing Map and Positive Matrix Factorization (Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China). Water. 2025; 17(17):2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17172547
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Na, Xueping Wang, Xiaoyang Liu, and Li Deng. 2025. "Distribution and Source Appointment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Rivers via Self-Organizing Map and Positive Matrix Factorization (Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China)" Water 17, no. 17: 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17172547
APA StyleCai, N., Wang, X., Liu, X., & Deng, L. (2025). Distribution and Source Appointment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Rivers via Self-Organizing Map and Positive Matrix Factorization (Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China). Water, 17(17), 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17172547






