Evolution of the Hydrological Regime at the Outlet of West Dongting Lake Since 1955
Abstract
1. Introduction
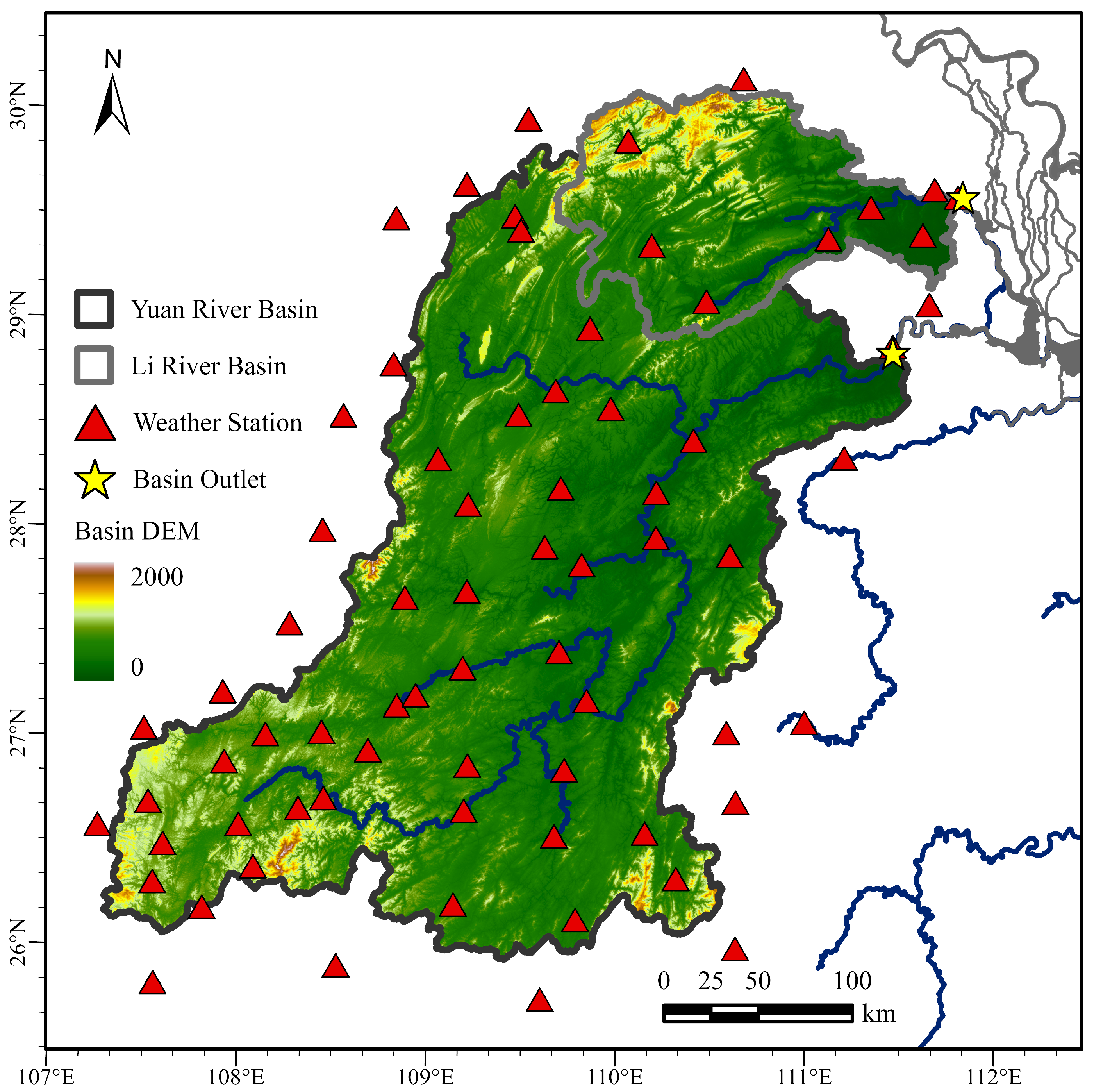
2. Study Area and Data
3. Methodology
3.1. Trend Analysis and Change Point Detection Methods
3.2. IHA–RVA Framework
3.3. SCRAQ Method
4. Results
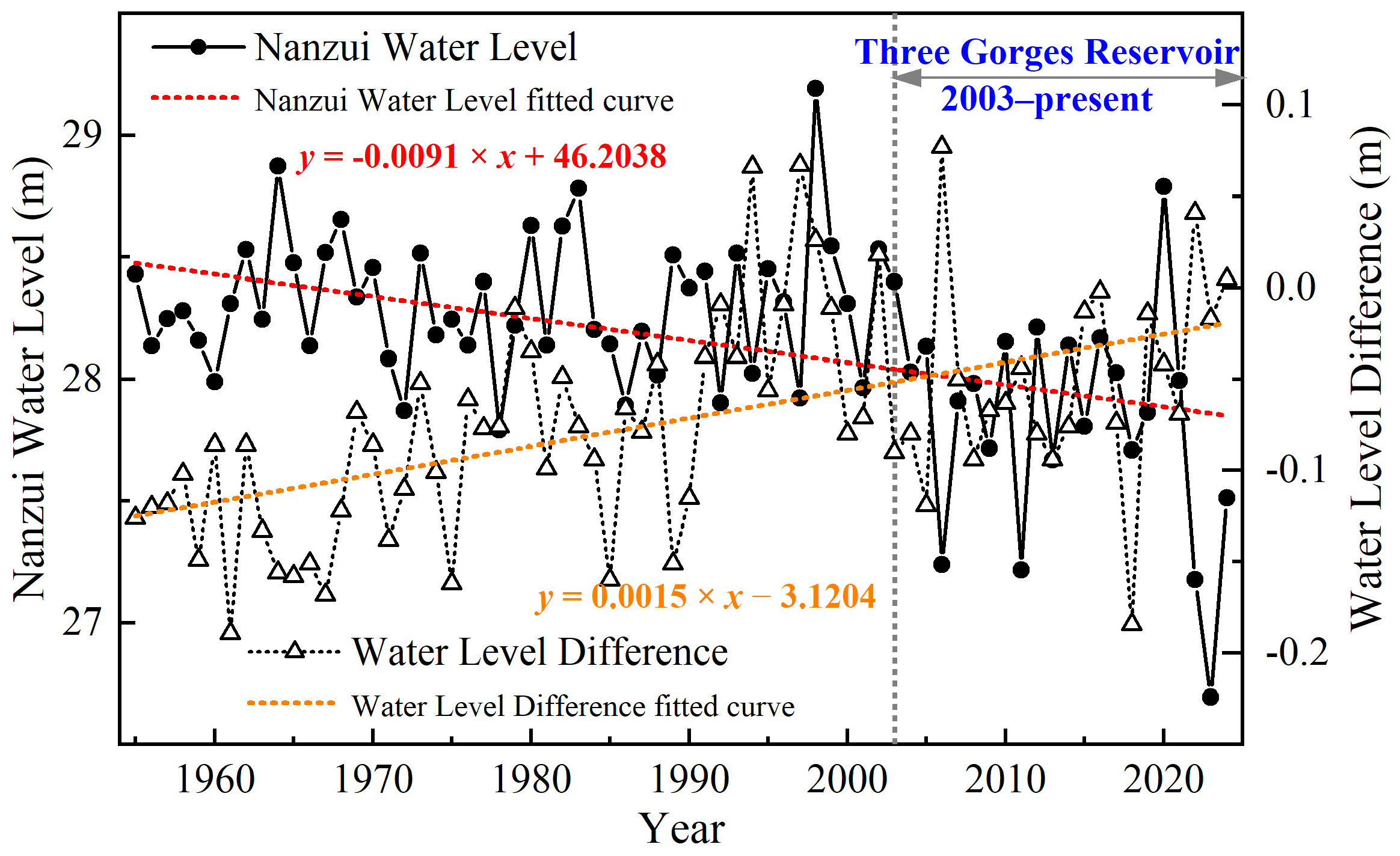
4.1. Trend and Changepoint Analysis
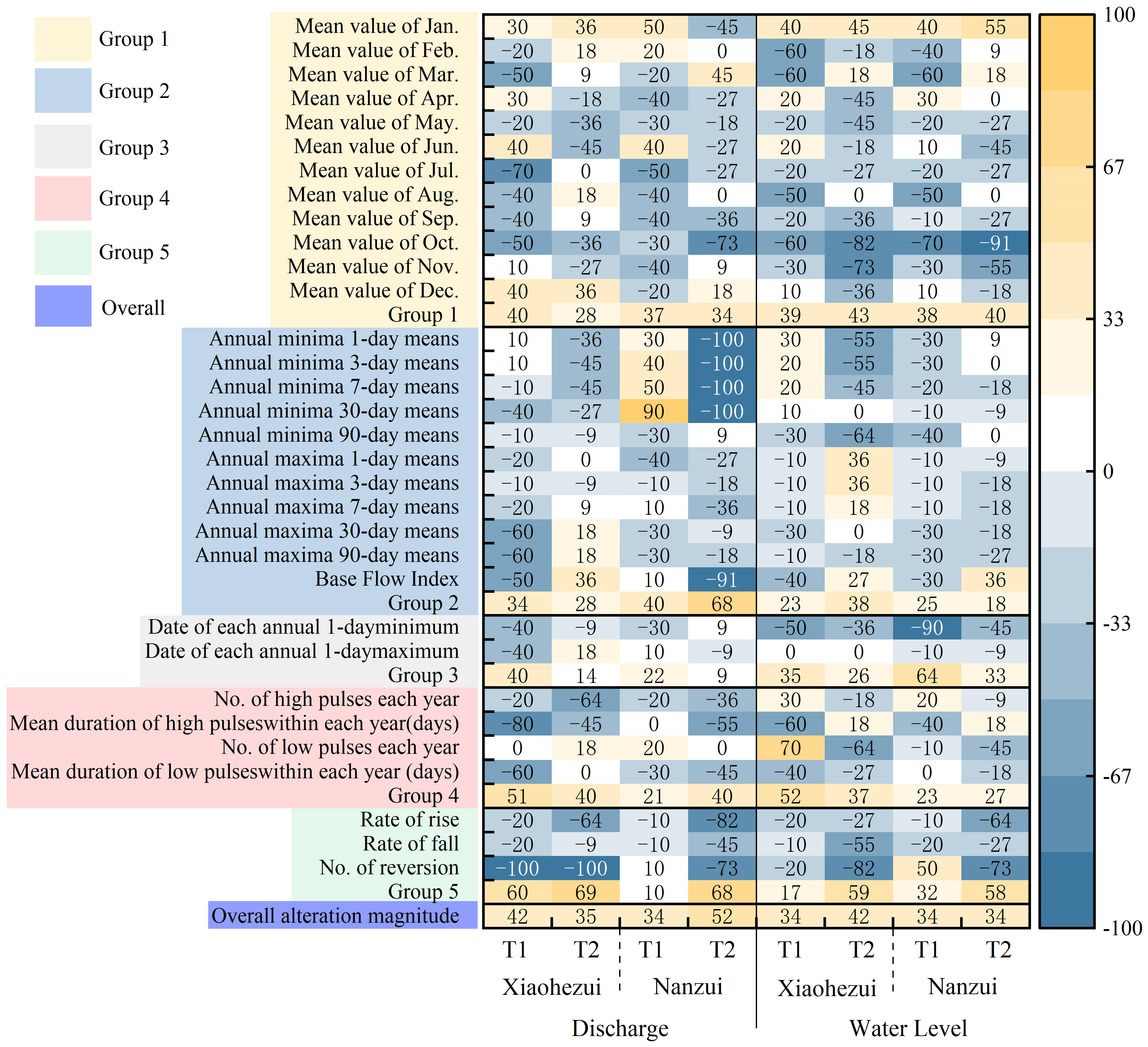
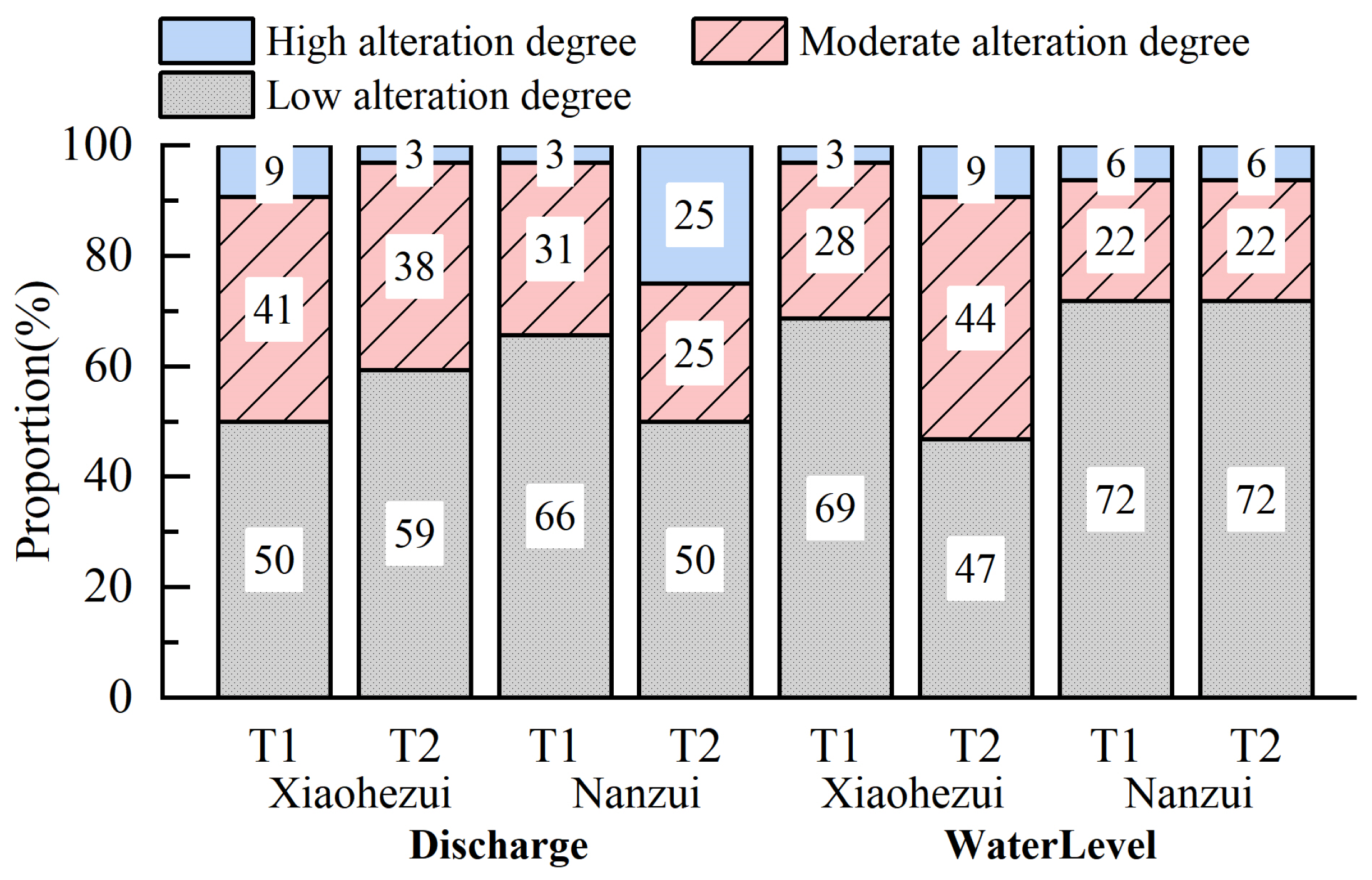
4.2. Hydrological Alteration Degree at West Dongting Lake Outlets
4.3. Alteration Degree of Water Level Difference (ΔH)
5. Discussion
5.1. Inflow Dynamics to Dongting Lake
5.2. Impacts of Precipitation Changes and Human Activities
5.3. Discharge Variation Driven by Water-Level Gradients
5.4. Negative Impacts on Ecosystems
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cooley, S.W.; Ryan, J.C.; Smith, L.C. Human alteration of global surface water storage variability. Nature 2021, 591, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Mo, S.; Wu, H.; Qu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L. Influence of human activities and climate change on wetland landscape pattern—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 163112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyoum, W.M.; Milewski, A.M.; Durham, M.C. Understanding the relative impacts of natural processes and human activities on the hydrology of the Central Rift Valley lakes, East Africa. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 4312–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huziy, O.; Sushama, L. Lake–river and lake–atmosphere interactions in a changing climate over Northeast Canada. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 48, 3227–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, J.S.; Lacombe, G.; Arias, M.E.; Dang, T.D.; Piman, T. Hydropower dams of the Mekong River basin: A review of their hydrological impacts. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Chen, Y.; Guan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Mao, W. Recent climate and hydrological changes in a mountain–basin system in Xinjiang, China. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 226, 103957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Livneh, B.; Rajagopalan, B.; Wang, J.; Crétaux, J.-F.; Wada, Y.; Berge-Nguyen, M. Satellites reveal widespread decline in global lake water storage. Science 2023, 380, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Brucet, S.; Naselli-Flores, L.; Papastergiadou, E.; Stefanidis, K.; Noges, T.; Noges, P.; Attayde, J.L.; Zohary, T.; Coppens, J. Ecological impacts of global warming and water abstraction on lakes and reservoirs due to changes in water level and related changes in salinity. Hydrobiologia 2015, 750, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.L.; Charles, D.; Horwitz, R.J.; Pizzuto, J.E.; Skalak, K.; Velinsky, D.J.; Hart, D.D. Size-dependent effects of dams on river ecosystems and implications for dam removal outcomes. Ecol. Appl. 2024, 34, e3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdian, M.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Siadatmousavi, S.M.; Chalipa, Z.; Delavar, M.; Guo, M.; Abolfathi, S.; Noori, R. Modelling impacts of climate change and anthropogenic activities on inflows and sediment loads of wetlands: Case study of the Anzali wetland. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulik, M.; Urban, D.; Grzywaczewski, G.; Bochniak, A.; Grzywna, A.; Sender, J. Half a century of wetland degradation: The present state and trends of changes in Western Polesie—Long-term wetland degradation. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 56, e03324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczera, G.A. Three Decades of Inundation Dynamics in an Australian Dryland Wetland: An Eco-Hydrological Perspective. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3310. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Zang, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhao, Z. Spatiotemporal dynamics of wetlands and their future multi-scenario simulation in the Yellow River Delta, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 353, 120193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, M.; Guo, H.; Chen, E. Spatiotemporal distribution and historical evolution of polders in the Dongting Lake area, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1561–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, C.; Peng, P.; Deng, C.; Li, J. Impacts of Three Gorges Reservoir’s water storage on flow-sediment characteristics of Dongting Lake. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Electric Technology and Civil Engineering (ICETCE), Lushan, China, 22–24 April 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 6012–6015. [Google Scholar]
- Olden, J.D.; Poff, N. Redundancy and the choice of hydrologic indices for characterizing streamflow regimes. River Res. Appl. 2003, 19, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.D.; Baumgartner, J.V.; Powell, J.; Braun, D.P. A method for assessing hydrologic alteration within ecosystems. Conserv. Biol. 1996, 10, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.; Baumgartner, J.; Wigington, R.; Braun, D. How much water does a river need? Freshw. Biol. 1997, 37, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habel, M.; Nowak, B.; Szadek, P. Evaluating indicators of hydrologic alteration to demonstrate the impact of open-pit lignite mining on the flow regimes of small and medium-sized rivers. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 157, 111295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Sun, C. Quantitative assessment of hydrological alteration caused by irrigation projects in the Tarim River basin, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Tripathi, V.K.; Kumar, P.; Rakshit, A. Assessment of hydrologic impact on flow regime due to dam inception using IHA framework. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 37821–37844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Long, D.; Zhao, J.; Lu, H.; Hong, Y. Observed changes in flow regimes in the Mekong River basin. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, M.; Liu, C.-L.; Singh, V.P. Reservoir-induced hydrological alterations and environmental flow variation in the East River, the Pearl River basin, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 28, 2119–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Jiao, X.; Huang, L.; Chen, H.; Guo, W. Runoff change in the Yellow River Basin of China from 1960 to 2020 and its driving factors. J. Arid Land 2024, 16, 168–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Deng, H.; Pan, Y. Detecting changes in extreme streamflow in the Tarim River, Northwest China. Quat. Int. 2015, 380, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, Y.; Yang, H.; Hong, F.; Guo, W. Quantitative evaluation of the impact of climate change and human activities on Jialing river runoff changes in the past 60 years, China. J. Water Clim. Change 2023, 14, 590–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ye, H.; Yuan, W.; Cheng, S.; Bai, X.; Lan, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, G.; Guo, W. Quantitative evaluation of the evolution of the ecohydrological regime and its drivers in the Han River Basin. J. Water Clim. Change 2024, 15, 4613–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Xu, L.; Feng, W.; Fan, H.; Jiang, J. Changes in water level regimes in China’s two largest freshwater lakes: Characterization and implication. Water 2019, 11, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q. Variation Mechanism of the Relation Between Jingjiang River and Dongting Lake. J. Chang. River Sci. Res. Inst. 2014, 31, 104–112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Q.; Shen, D.; Xu, J. The history and future of the relationship between the Yangtze River and connected lakes. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2021, 52, 1183–1192. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Li, B.; Wan, R.; Duan, W.; He, Z. Quantifying the effects of channel change on the discharge diversion of Jingjiang Three Outlets after the operation of the Three Gorges Dam. Hydrol. Res. 2016, 47, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Mei, X.; Dai, Z.; Gao, J.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Lou, Y. Hydromorphological processes of Dongting Lake in China between 1951 and 2014. J. Hydrol. 2018, 562, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Guo, W. Quantitative assessment of hydrological alteration over multiple periods caused by human activities at the Jingjiang Three Outlets, China. Water Supply 2022, 22, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, S.-h.; Xu, W.; Wang, B.-d.; Wang, H. Flow regime of the three outlets on the south bank of Jingjiang River, China: An impact assessment of the Three Gorges Reservoir for 2003–2010. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 2047–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Xie, Y.; Zou, D. Changes of Runoff and Sediment Discharge into Dongting Lake from the Four Rivers in Hunan Province. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 32, 609–615. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Feng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Brookes, J.D.; Jeppesen, E. Influence of the three Gorges Reservoir on the shrinkage of China’s two largest freshwater lakes. Glob. Planet. Change 2019, 177, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zha, H.; Guo, W. Quantitative assessment of water level regime alterations during 1959–2016 caused by Three Gorges Reservoir in the Dongting Lake, China. Water Supply 2021, 21, 1188–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Yu, G.; Liao, X. Effects of the dispatch modes of the Three Gorges Reservoir on the water regimes in the Dongting Lake area in typical years. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zeng, G.; Liang, J.; Huang, L.; Hua, S.; Li, F.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; He, X. Variation of water level in Dongting Lake over a 50-year period: Implications for the impacts of anthropogenic and climatic factors. J. Hydrol. 2015, 525, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Chen, H.; Hou, Y.; Finlayson, B.; Li, M.; Chen, J. Lowering water level of Dongting lake of the Mid-Yangtze River in response to large-scale dam construction: A 60-year analysis. Geomorphology 2021, 391, 107894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, C.; Li, J.; Yu, G.; Yang, Y.; Deng, C.; Zhang, L. Response of Dongting Lake’s System Function Under Changed Water and Silt Process. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 31, 654–660. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Xie, S. Modified Hydrological Regime on Irrigation and Water Supply in Lake Areas: A Case Study of the Yangtze River–Dongting Lake. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 888729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Wu, Y. Maintaining the connected river-lake relationship in the middle Yangtze River reaches after completion of the Three Gorges Project. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2017, 32, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Ding, W.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H. Mitigating adverse impacts of reservoir impoundment on lake ecology: A case study of the Three Gorges Reservoir and Dongting Lake. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 451, 141835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, K.P.; Mukherjee, S.; Mishra, A.; Mann, M.; Williams, A.P. Climate change will accelerate the high-end risk of compound drought and heatwave events. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2219825120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, R.; Noy, I. The global costs of extreme weather that are attributable to climate change. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, S.H.; Rahman, M.T.U.; Hoque, M.A.; Hussain, M.M. Analysis of seasonal and annual rainfall trends in the northern region of Bangladesh. Atmos. Res. 2016, 176–177, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.-H.; Palmer, R.N. Trend and Variability in Observed Hydrological Extremes in the United States. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2016, 21, 04015061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajani, E.; Rahman, A. Characterizing changes in rainfall: A case study for New South Wales, Australia. Int. J. Climatol. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 38, 1452–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suen, J.-P. Potential impacts to freshwater ecosystems caused by flow regime alteration under changing climate conditions in Taiwan. Hydrobiologia 2010, 649, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Yang, T.; Cui, T.; Xu, C.; Qin, Y. A revised range of variability approach considering the morphological alteration of hydrological indicators. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2020, 35, 1783–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Peng, W.; Huang, W.; Qu, X.; Singh, S.K. Quantitative Assessment of Flow Regime Alteration Using a Revised Range of Variability Methods. Water 2018, 10, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yin, X.a.; Yang, Z. A revised range of variability approach for the comprehensive assessment of the alteration of flow regime. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 96, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yan, Y.; Yan, M.; Zhao, X. Quantitative estimation of the impact of precipitation and human activities on runoff change of the Huangfuchuan River Basin. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 906–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Zou, H.; Jiang, J.; Jia, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, W. Hydrological dynamics of the Yangtze river-Dongting lake system after the construction of the three Gorges dam. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S. Reflections on the Three Gorges Project since Its Operation. Engineering 2016, 2, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayou, L.A.; Alamdari, N.; Ahmadisharaf, E.; Kamali, M. Impacts of future climate and land use/land cover change on urban runoff using fine-scale hydrologic modeling. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 362, 121284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cai, X.; Tang, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y. Climate feedbacks associated with land-use and land-cover change on hydrological extremes over the Yangtze River Delta Region, China. J. Hydrol. 2023, 623, 129855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Marnn, P.; Jiang, H.; Wen, Y.; Yan, H.; Li, D.; He, C.; Li, L. A study on the response of waterbird diversity to habitat changes caused by ecological engineering construction. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 208, 107358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Xia, H.; Shi, Q.; Chen, H.; Chu, N.; Liang, J.; Gao, Z. Monitoring spatial and temporal dynamics of wetland vegetation and their response to hydrological conditions in a large seasonal lake with time series Landsat data. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-x.; Huang, J.-l.; Du, Y.; Han, P.-p.; Wang, J.-l.; Huang, W. Monitoring wetland vegetation pattern response to water-level change resulting from the Three Gorges Project in the two largest freshwater lakes of China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 74, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xie, Y.-h.; Zou, D.-s. Hydrological regime change and its ecological responses in East Dongting Lake, China. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2020, 20, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hu, X.; Sun, S.; Dai, J.; Ye, S.; Du, C.; Chen, H.; Yu, G.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J. Effect of increasing of water level during the middle of dry season on landscape pattern of the two largest freshwater lakes of China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.-Y.; Xie, Y.-H.; Tang, Y.; Li, F.; Zou, Y.-A. Changes of vegetation distribution in the east Dongting Lake after the operation of the Three Gorges Dam, China. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, X.-S.; Li, F.; Hou, Z.-Y.; Li, X.; Zeng, J.; Deng, Z.-M.; Zou, Y.-A.; Xie, Y.-H. Community trait responses of three dominant macrophytes to variations in flooding during 2011–2019 in a Yangtze river-connected floodplain wetland (Dongting lake, China). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 604677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, D.; Chen, L.; Li, M.; Luan, Z. Typical vegetation dynamics and hydrological changes of Dongting Lake wetland from 1985 to 2020. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2024, 24, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, X.; Tian, L.; Cui, G.; Liu, Y. Vegetation and carbon sink response to water level changes in a seasonal lake wetland. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1445906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Liu, X.; Peng, W.; Dong, F.; Han, Z.; Du, F.; Ma, B.; Wang, W. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of inundation pattern of floodplain lake wetlands and impact on wetland vegetation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wei, Z.; Zhou, L.; Cheng, B. Effects of constant high water levels in winter on waterbird diversity in Caizi Lakes: A functional perspective. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 52, e02934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, J.; Zeng, G.; Xu, J.; Sang, L.; Liu, Q.; Dai, J.; Xiong, W.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, Y. Effects of Early Dry Season on Habitat Suitability for Migratory Birds in China’s Two Largest Freshwater Lake Wetlands after the Impoundment of Three Gorges Dam. J. Environ. Inform. 2020, 36, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Dai, J.; Sun, S.; Du, C.; Long, Y.; Chen, H.; Yu, G.; Ye, S.; Chen, J. Responses of habitat suitability for migratory birds to increased water level during middle of dry season in the two largest freshwater lake wetlands of China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, W. The impacts of water level fluctuations of East Dongting Lake on habitat suitability of migratory birds. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, B.; Qi, S.; Luo, J. The Influence of Short-Term Water Level Fluctuations on the Habitat Response and Ecological Fragility of Siberian Cranes in Poyang Lake, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Xie, C.; Chen, S.; Song, Z. Taxonomic and functional response of fish assemblages to flood-triggered water level fluctuations in a large floodplain lake along the Yangtze River. Ichthyol. Res. 2025, 72, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Chen, S.; Hua, Q.; Wang, L.; Yang, Q.; Hu, M. Fish community and its relationships with environmental variables in the channel connecting Poyang Lake and the Yangtze River. Aquat. Sci. 2024, 86, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Gong, Z.; Liu, H. Lateral migration of fish between China’s second largest freshwater lake (Dongting Lake) and the mainstem of the Yangtze River. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2019, 102, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Mao, J.; Wang, K.; Chen, Y.; Gao, H.; Wang, T. Significant expansion of small water bodies in the Dongting Lake region following the impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 376, 124443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Bai, X.; Huang, L.; Hong, F.; Yuan, W.; Guo, W. The spatial variation of hydrological conditions and their impact on wetland vegetation in connected floodplain wetlands: Dongting Lake Basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 8483–8498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huang, L.; Guo, W.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, H.; Jiao, X.; Zhou, H. Evaluation of ecohydrological regime and its driving forces in the Dongting Lake, China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 41, 101067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yuan, Y.; Zeng, G.; Liang, J.; Guo, S.; Huang, L.; Hua, S.; Wu, H.; Zhu, Y.; An, H. Influence of hydrological regime and climatic factor on waterbird abundance in Dongting Lake Wetland, China: Implications for biological conservation. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 90, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J. Influence of Seasonal Water Level Fluctuations on Food Web Structure of a Large Floodplain Lake in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, L.; Yu, D.; Yao, R.; Li, C.; He, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. Four decades of wetland changes in Dongting Lake using Landsat observations during 1978–2018. J. Hydrol. 2020, 587, 124954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


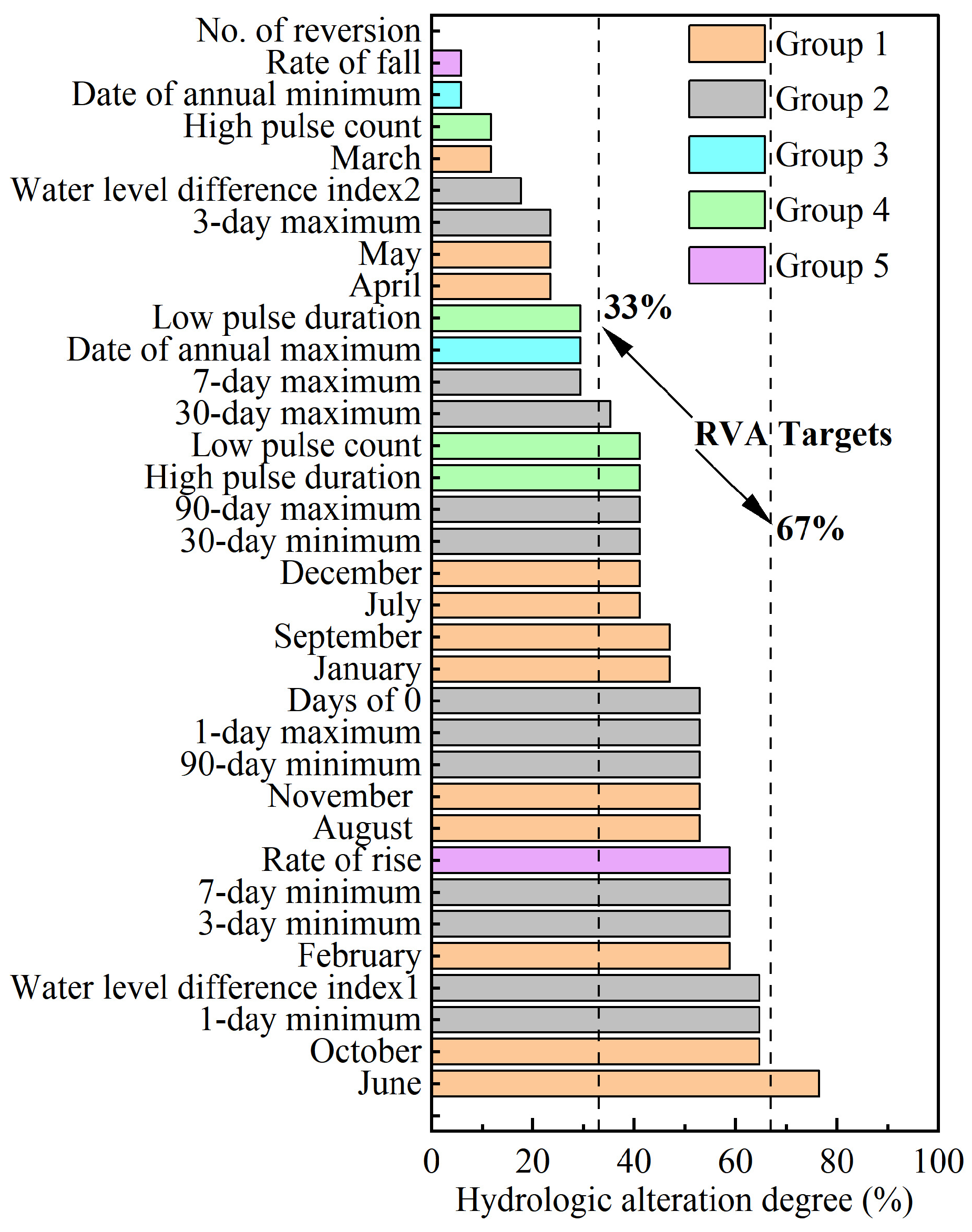


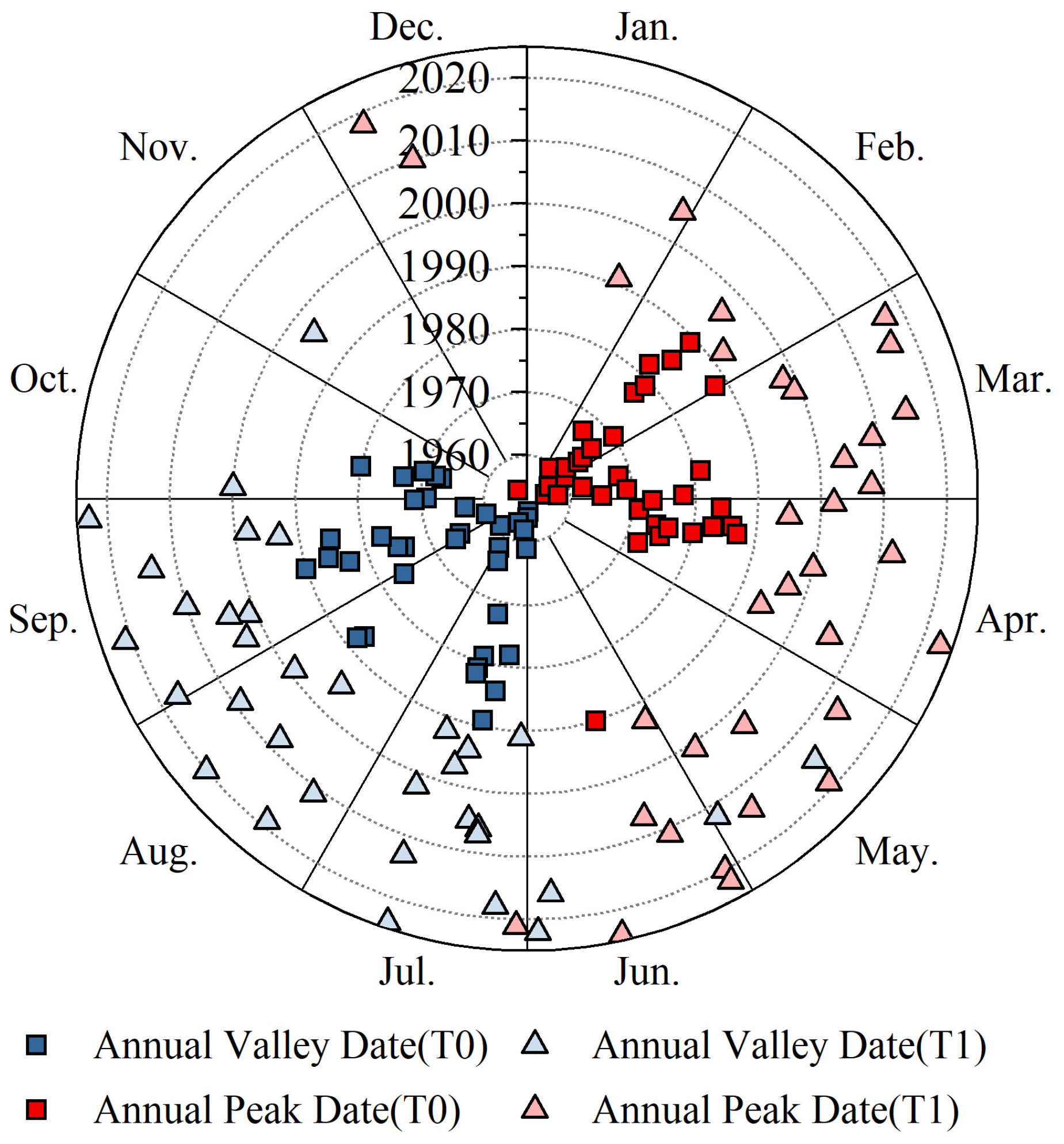
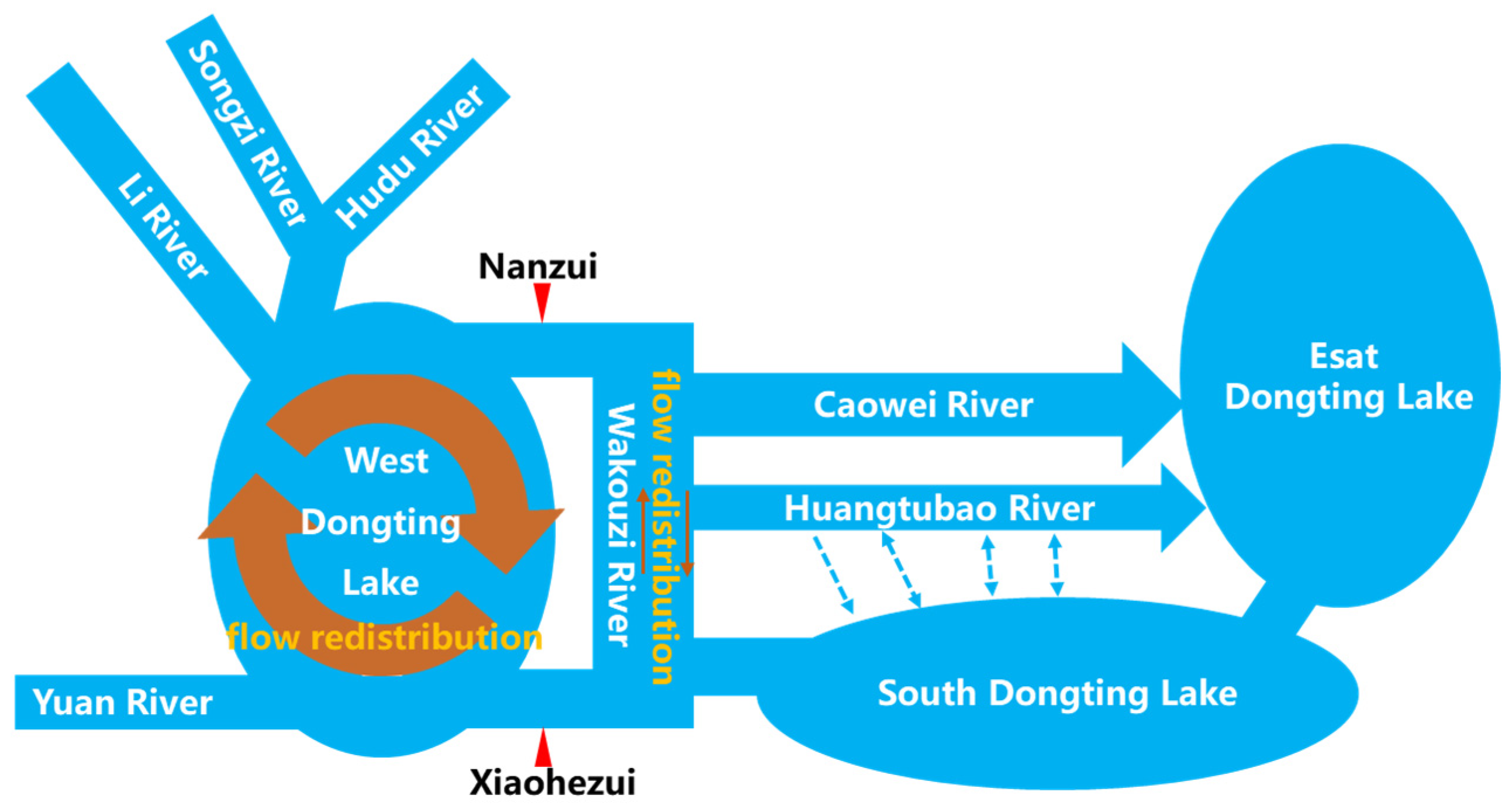
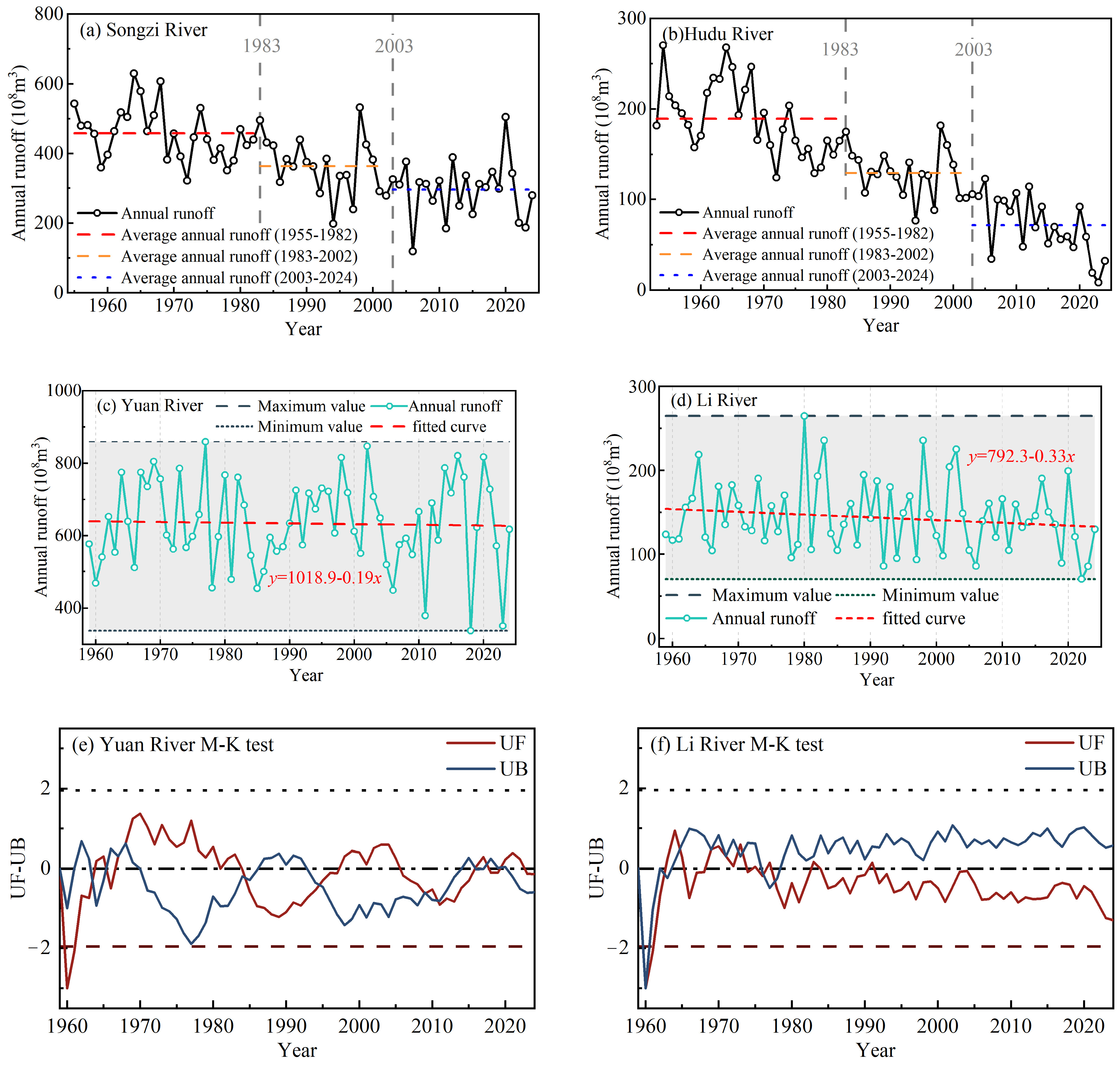
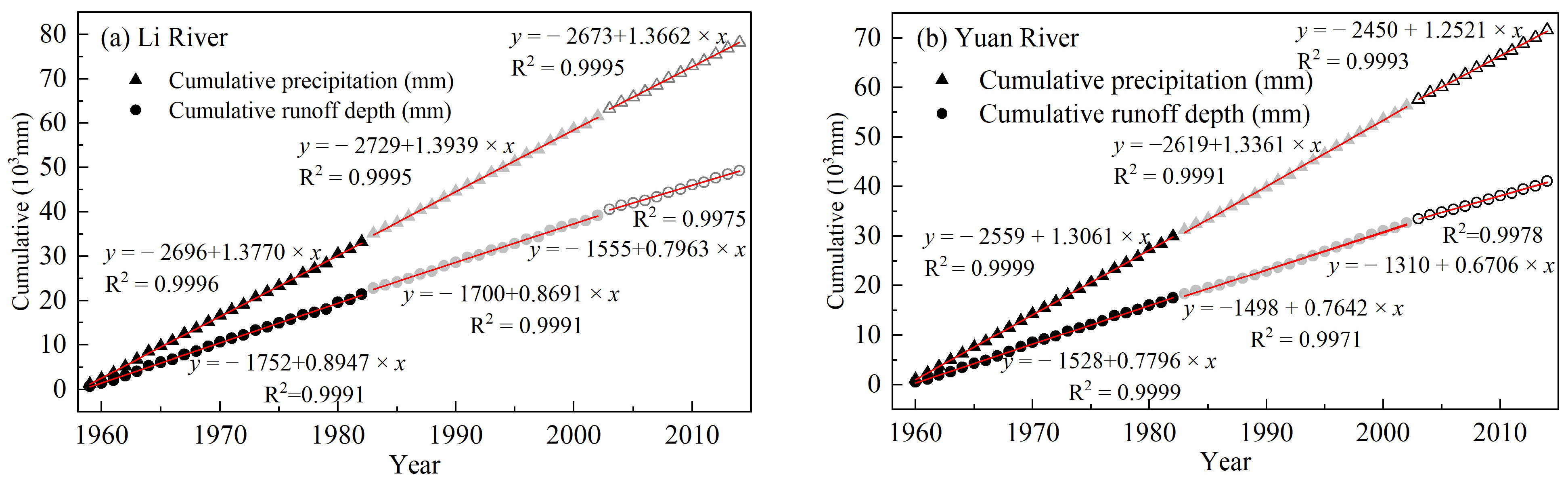
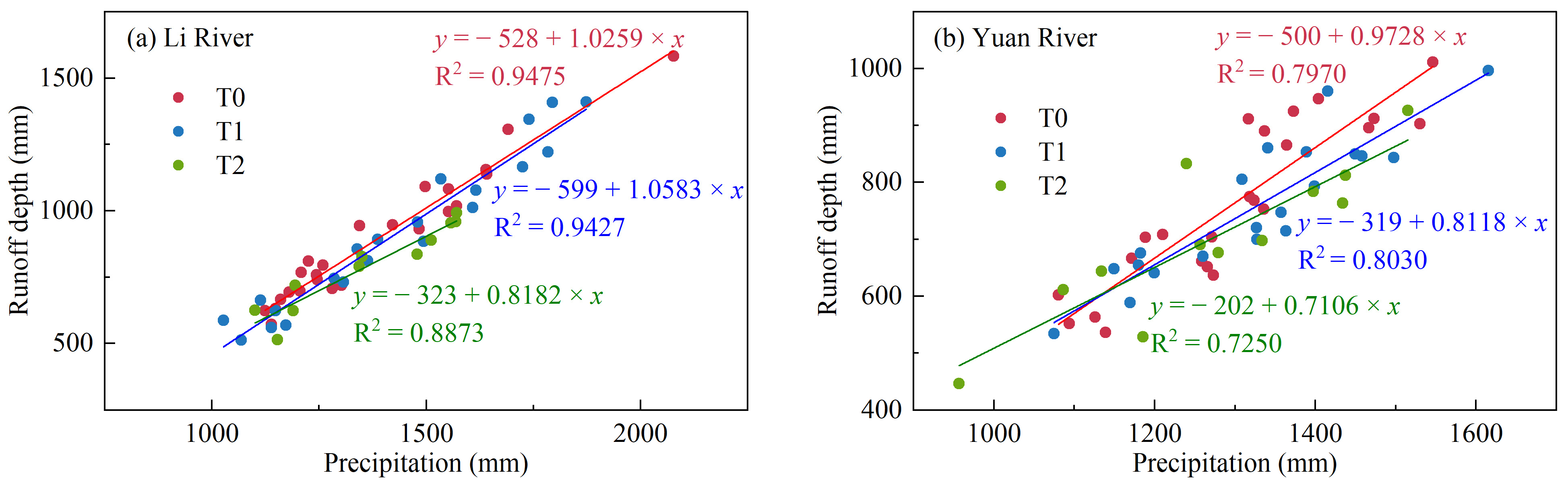
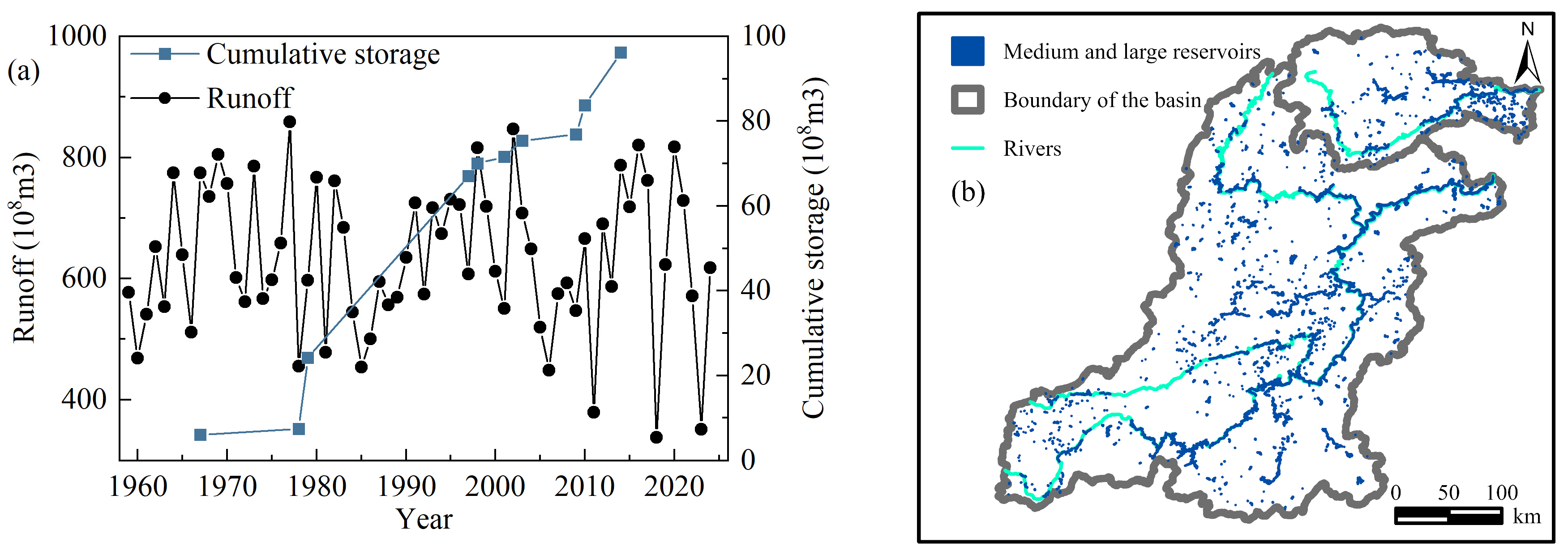
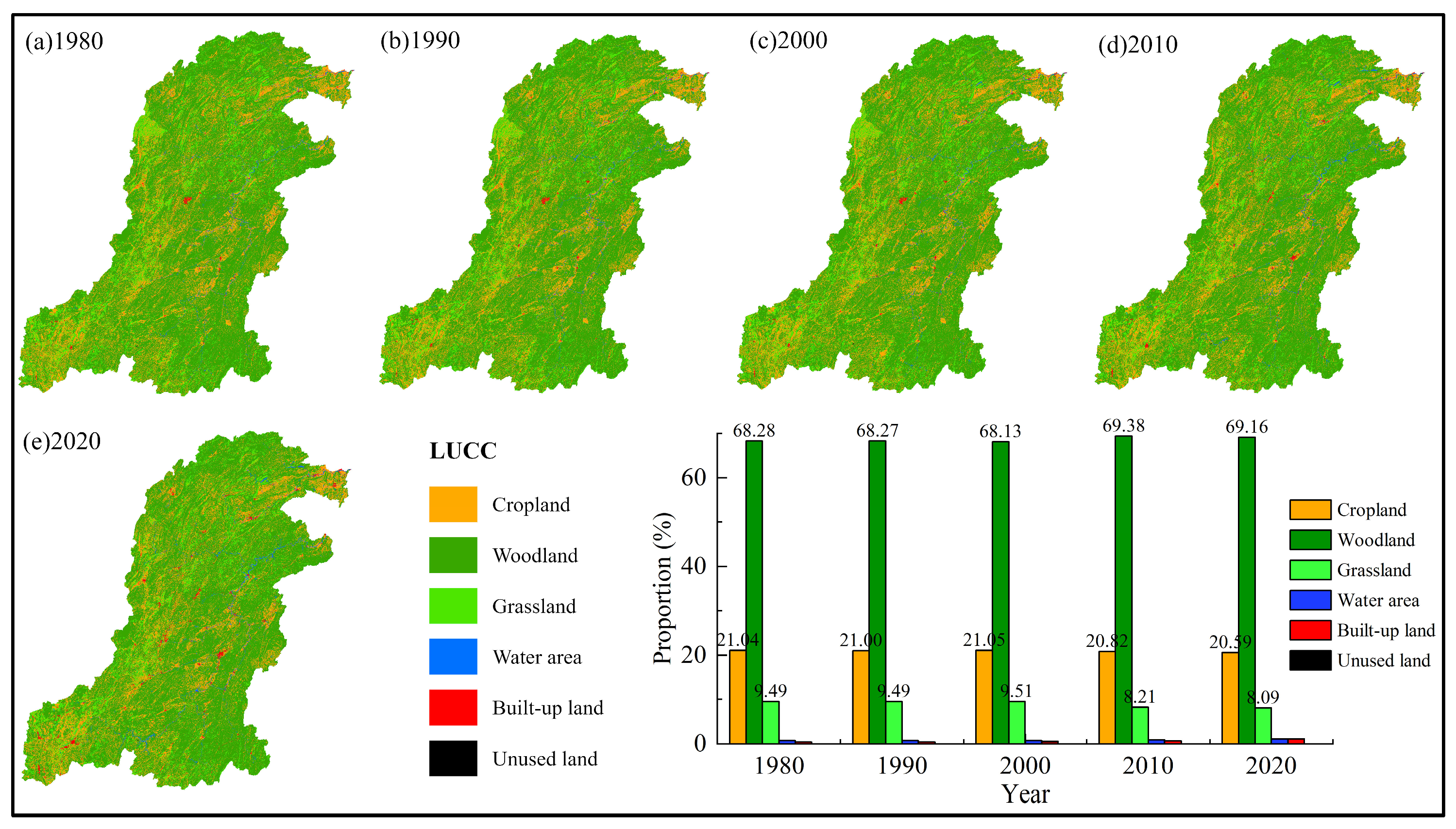
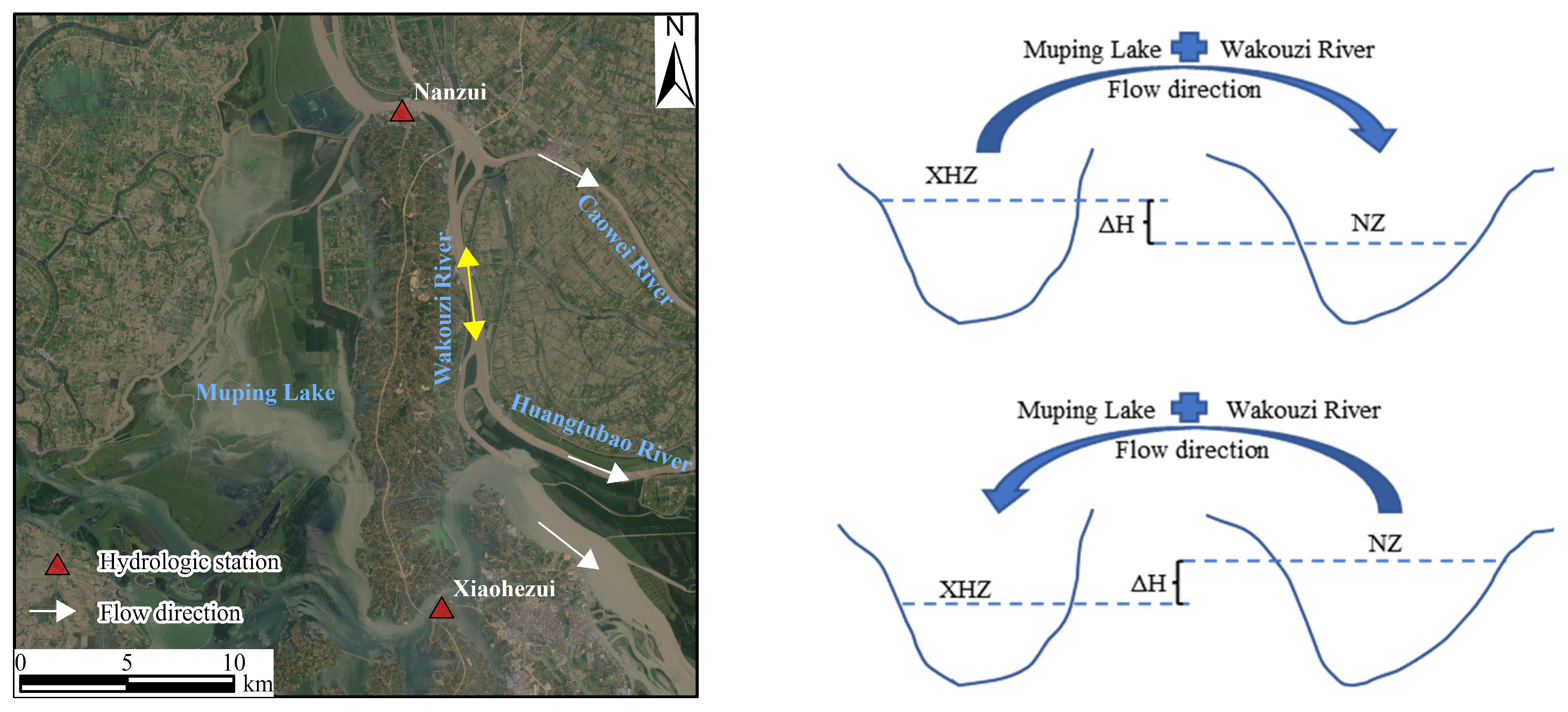
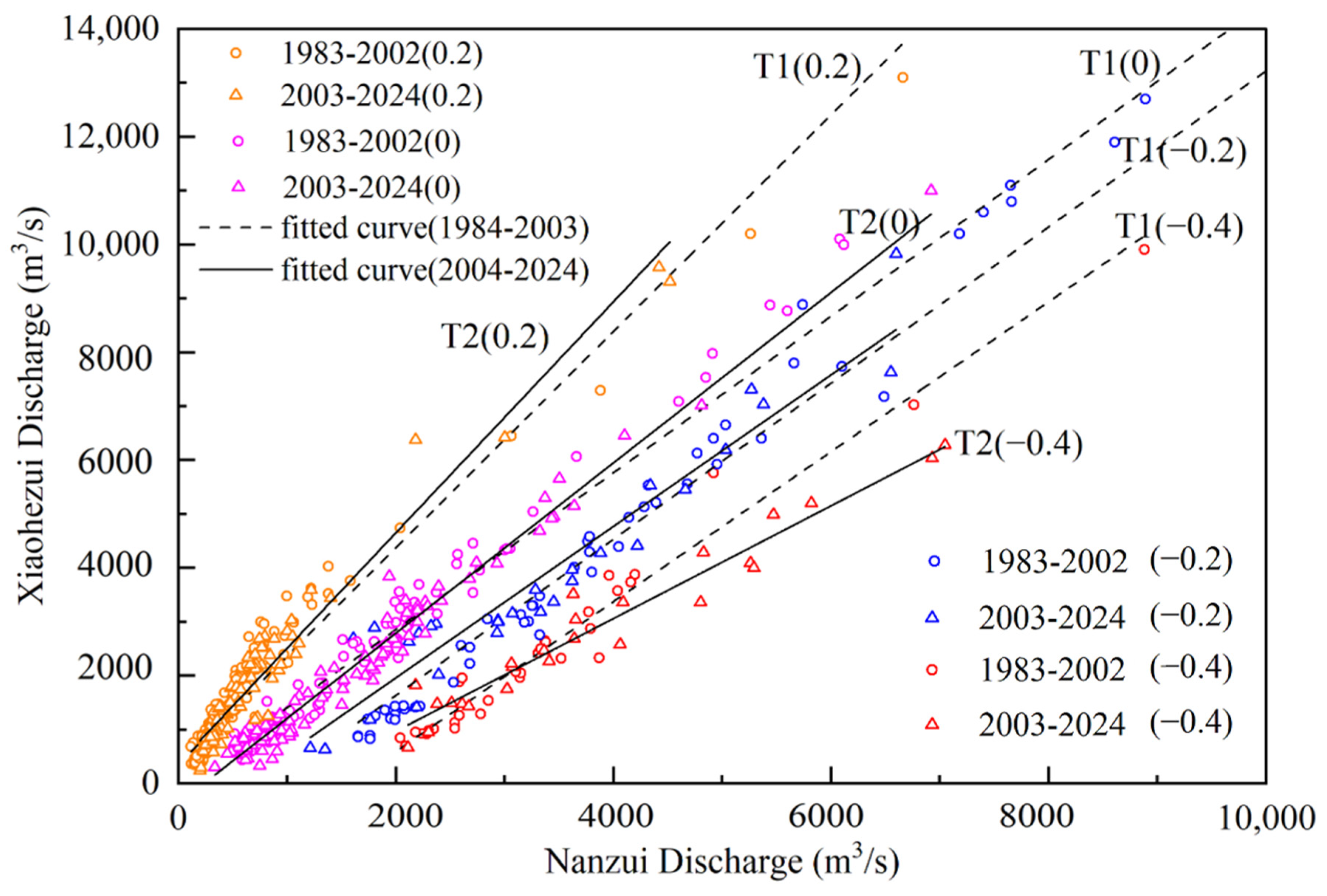
| Parameter | XHZ Discharge | NZ Discharge | XHZ Water Level | NZ Water Level | Water Level Difference (ΔH) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z statistic | −2.98 | −3.09 | −3.17 | −3.66 | 4.39 |
| Critical Z | ±1.96 | ±1.96 | ±1.96 | ±1.96 | ±1.96 |
| p-value | 2.87 × 10−3 | 1.98 × 10−3 | 1.51 × 10−3 | 2.52 × 10−4 | 2.81 × 10−6 |
| α Threshold | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Trend | decreasing | decreasing | decreasing | decreasing | increasing |
| Parameter | Methods | Changepoint Year (s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-K Test | CUSUM | Moving t-Test | Pettitt’s Test | ||
| XHZ Discharge | 1983 | 1983 | 1983, 2003 | 1983 | 1983, 2003 |
| NZ Discharge | 1985, 1990 | 1993 | 1983, 2003 | - | 1983, 2003 |
| XHZ Water Level | 2003 | 2003 | 1983, 2004 | 2003 | 1983, 2003 |
| NZ Water Level | 2003 | 2003 | 1983, 2003 | 2003 | 1983, 2003 |
| Water Level Difference (ΔH) | 1976 | 1991 | 1978, 1991 | 1975 | 1991 |
| Indicator | Mean (m) | ΔH (m) | Mean Relative Deviation (%) | Alteration Degree (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | ||||
| January ΔH | 0.223 | 0.146 | −0.077 | −35 | −47 (M) |
| February ΔH | 0.277 | 0.172 | −0.105 | −38 | −59 (M) |
| March ΔH | 0.218 | 0.184 | −0.034 | −16 | 12 (L) |
| April ΔH | 0.120 | 0.140 | 0.020 | 17 | 24 (L) |
| May ΔH | −0.065 | 0.036 | 0.101 | −155 | −24 (L) |
| June ΔH | −0.197 | −0.062 | 0.135 | −69 | −76 (H) |
| July ΔH | −0.416 | −0.335 | 0.081 | −19 | −41 (M) |
| August ΔH | −0.471 | −0.364 | 0.107 | −23 | −53 (M) |
| September ΔH | −0.493 | −0.322 | 0.171 | −35 | −47 (M) |
| October ΔH | −0.402 | −0.162 | 0.240 | −60 | −65 (M) |
| November ΔH | −0.117 | 0.014 | 0.131 | −112 | −53 (M) |
| December ΔH | 0.091 | 0.105 | 0.014 | 15 | 41 (M) |
| Indicator | Mean (m) | Mean Relative Deviation (%) | Cv | Cv Relative Deviation (%) | Alteration Degree (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | P1 | P2 | ||||
| Annualminima1-daymeans | −1.470 | −1.600 | 9 | −24.01 | 46.35 | 93 | −65 |
| Annualminima3-daymeans | −1.380 | −1.367 | −1 | −23.66 | 50.21 | 112 | −59 |
| Annualminima7-daymeans | −1.150 | −1.147 | 0 | −21.16 | 39.39 | 86 | −59 |
| Annualminima30-daymeans | −0.918 | −0.986 | 7 | −20.28 | 27.56 | 36 | −41 |
| Annualminima90-daymeans | −0.734 | −0.697 | −5 | −17.38 | 31.91 | 84 | −53 |
| Annualmaxima1-daymeans | 0.280 | 0.180 | −36 | 21.86 | −33.52 | 53 | −53 |
| Annualmaxima3-daymeans | 0.267 | 0.167 | −37 | 21.65 | −33.37 | 54 | −24 |
| Annualmaxima7-daymeans | 0.254 | 0.144 | −43 | 21.24 | −32.21 | 52 | −29 |
| Annualmaxima30-daymeans | 0.167 | 0.108 | −35 | 23.29 | −39.74 | 71 | −35 |
| Annualmaxima90-daymeans | 0.090 | 0.031 | −66 | 29.54 | −45.30 | 53 | −41 |
| Water level difference index1 | 10.233 | 13.504 | 32 | 100.50 | 226.47 | 125 | −65 |
| Water level difference index2 | −5.279 | −6.123 | 16 | −123.67 | −274.61 | 122 | −18 |
| Indicator | Mean (m) | Mean Relative Deviation (%) | Cv | Cv Relative Deviation (%) | Alteration Degree (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | P1 | P2 | ||||
| Number of high ΔH events | 5.64 | 9.32 | 65 | 62.04 | 37.50 | −40 | −12 |
| Mean duration of high ΔH events | 23.54 | 9.17 | −61 | 77.75 | 55.07 | −29 | −41 |
| Number of low ΔH events | 6.67 | 5.35 | −20 | 39.61 | 40.85 | 3 | 41 |
| Mean duration of low ΔH events | 21.23 | 16.59 | −22 | 56.33 | 115.87 | 106 | −29 |
| Mean rising rate of ΔH | 0.040 | 0.038 | −5 | 12.36 | 19.73 | 60 | −59 |
| Mean falling rate of ΔH | −0.046 | −0.044 | −4 | −15.21 | −20.04 | 32 | 6 |
| Number of reversals | 89.89 | 88.09 | −2 | 10.57 | 9.99 | −5 | 0 |
| River Basin | No. | Reservoir | Gross Reservoir Capacity (108 m3) | Flood Storage Capacity (108 m3) | Year Completed | Catchment Area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li River | 1 | Yutan | 1.24 | 0.47 | 1997 | 3478 |
| 2 | Jiangya | 17.41 | 7.4 | 1999 | 3711 | |
| 3 | Zaoshi | 14.4 | 7.83 | 2008 | 3000 | |
| Yuan River | 1 | Huangshi | 6 | 1.42 | 1967 | 552 |
| 2 | Zhuyuan | 1.4 | 0.53 | 1978 | 701.5 | |
| 3 | Fengtan | 16.757 | 2.8 | 1979 | 17,500 | |
| 4 | Wuqiangxi | 42.9 | 13.6 | 1997 | 83,800 | |
| 5 | Baiyun | 2.98 | 0.17 | 1998 | 556 | |
| 6 | Mangtangxi | 1.53 | 0.22 | 2001 | 8182 | |
| 7 | Wanmipo | 3.78 | 1 | 2003 | 10,415 | |
| 8 | Youchou | 1.52 | 0.54 | 2009 | 4775 | |
| 9 | Baishi | 6.87 | 1.202 | 2010 | 16,530 | |
| 10 | Tuokou | 12.49 | 1.98 | 2014 | 24,450 |
| Water Level Difference (m) | 1984–2003 (T1) | 2004–2022 (T2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Regression Equation | R2 | Linear Regression Equation | R2 | |
| −0.4 | y = 1.39 × x − 2186 | 0.97 | y = 1.05 × x − 1122 | 0.95 |
| −0.2 | y = 1.41 × x − 849 | 0.91 | y = 1.45 × x − 1261 | 0.97 |
| 0 | y = 1.45 × x − 46 | 0.97 | y = 1.58 × x − 370 | 0.97 |
| 0.2 | y = 2.01 × x + 360 | 0.95 | y = 2.14 × x + 367 | 0.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, S.; Jiang, C.; Ma, Y.; Li, S. Evolution of the Hydrological Regime at the Outlet of West Dongting Lake Since 1955. Water 2025, 17, 2487. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162487
Yuan S, Jiang C, Ma Y, Li S. Evolution of the Hydrological Regime at the Outlet of West Dongting Lake Since 1955. Water. 2025; 17(16):2487. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162487
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Shuai, Changbo Jiang, Yuan Ma, and Shanshan Li. 2025. "Evolution of the Hydrological Regime at the Outlet of West Dongting Lake Since 1955" Water 17, no. 16: 2487. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162487
APA StyleYuan, S., Jiang, C., Ma, Y., & Li, S. (2025). Evolution of the Hydrological Regime at the Outlet of West Dongting Lake Since 1955. Water, 17(16), 2487. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162487









