Abstract
Groundwater is a strategically important source of drinking water supply in the arid and rural regions of Kazakhstan. The objective of this study is to assess the quality of groundwater at 11 water intakes located in the Kordai, Shu, and Merke Districts of the Shu transboundary basin in the Zhambyl Region. A comprehensive assessment of physicochemical parameters was performed, including concentrations of nitrates, sulfates, chlorides, iron, manganese, and other constituents, with subsequent comparison against regulatory limits defined by Order No. 26 of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Kazakhstan (dated 20 February 2023), GOST standards, and ST RK ISO standards. The findings revealed that a number of water intakes exceeded the maximum allowable concentrations for specific indicators, especially in areas subject to significant anthropogenic pressure. The most vulnerable sources were identified near settlements characterized by intensive agricultural practices and inadequate wastewater treatment systems. Spatial comparison of the results enabled the identification of potentially contaminated areas as well as aquifer zones suitable for drinking water supply. The study emphasizes the importance of regular groundwater monitoring and spatial analysis techniques (GIS) to enhance the reliability and comprehensiveness of water quality assessments. The data obtained in this study can serve as a basis for informed decision-making in the area of water resource protection and contribute to the achievement of United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6)—to ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all.
1. Introduction
Groundwater serves as a critical source of drinking water, particularly in arid and rural areas where surface water resources are scarce or subject to seasonal variability [1,2,3,4,5,6]. According to United Nations estimates, approximately 50% of the global rural population depends on groundwater as their main source of drinking water. Given the growing challenges of water scarcity and contamination of aquifers, the need for systematic groundwater quality monitoring is becoming increasingly urgent to ensure public health protection and the sustainable management of water resources [7,8,9,10].
The main groundwater contaminants are considered to be nitrates, heavy metals (such as Pb, As, Cd, etc.), as well as chlorides and sulfates. According to the WHO, the primary sources of nitrates in drinking water are agricultural fertilizers, manure, and discharges of domestic and industrial wastewater [11,12,13,14]. The main groundwater contaminants are considered to be nitrates, heavy metals (such as Pb, As, Cd, etc.), as well as chlorides and sulfates. Heavy metals may enter groundwater from both natural (geogenic) sources—such as the leaching of minerals from host rocks, weathering of carbonate, sulfate, and sulfide formations, and volcanic deposits—and anthropogenic activities, including mining and ore-processing operations, landfills, and other industrial emissions. Chlorides and sulfates are commonly found in groundwater due to the leaching of geological minerals, seawater intrusion into coastal aquifers, or the application of de-icing agents and discharge of untreated or insufficiently treated wastewater [15,16,17,18].
In recent years, spatial analysis methods—in particular, the use of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and spatial interpolation techniques (such as IDW and kriging)—have significantly enhanced the informativeness of groundwater monitoring. Spatio-temporal analysis enables the visualization of contamination zones, the identification of areas exceeding maximum permissible concentrations (MPCs), and the tracking of seasonal and long-term trends in groundwater quality degradation [19,20,21,22].
In the Republic of Kazakhstan, the sanitary control system for drinking water quality is regulated by sanitary norms and standards, including Order No. 26 of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated 20 February 2023 [23]. Chemical and analytical studies of water are conducted using methodological guidelines based on international standards, which define procedures for assessing the concentrations of ions and salts in natural and drinking waters. These regulatory documents ensure a consistent approach to monitoring and evaluating water quality compliance with established sanitary requirements [23,24,25].
The issue of water security, in the context of the scarcity and vulnerability of water resources, is a critical component of the national security of the Republic of Kazakhstan. The “Kazakhstan 2050” Strategy: A New Political Course for a Mature State emphasizes, “Water is an extremely limited resource, and the struggle for access to sources is already becoming a key factor in geopolitics, serving as one of the causes of tension and conflict around the world.” [26,27,28,29,30]. The sustainable utilization of transboundary freshwater groundwater is hindered by the absence of accurate assessments of its potential capacity. A lack of sound scientific evidence and insufficient information may give rise to international disputes. These risks can be mitigated through the rational management of transboundary groundwater resources, which must be grounded in comprehensive analysis and the integration of reliable data on shared aquifers at both regional and national scales [31,32,33,34,35].
Along the border between the Zhambyl Region of the Republic of Kazakhstan and the Kyrgyz Republic, two major transboundary groundwater basins—the Shu and Talas basins—have been identified. These basins contain substantial reserves of freshwater, which play a crucial role in supplying water to numerous socioeconomically significant sites. For example, recent studies have revealed the strategic importance and vulnerability of transboundary groundwater resources in Central Asia, including the Chu-Talas basin shared by Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan [36]. The long-term trends analyzed in [37] show an increase in nitrate concentrations associated with runoff from agricultural land, indicating diffuse pollution. Similar problems have been noted in other transboundary systems in Central Asia [38], which states that the sustainable management of shared aquifers requires a reliable inventory of transboundary aquifers and deeper knowledge of shared groundwater systems. Broader regional assessments highlight the lack of coordinated monitoring and data exchange, advocating integrated joint management of shared aquifers [39]. As strategic water resources, they are vital to both regional and national water security and therefore require heightened attention to their sustainable management. Increased groundwater abstraction in the Kyrgyz Republic poses potential risks of transboundary migration of anthropogenically contaminated groundwater, partial or complete interception of renewable aquifer inflows, and depletion of groundwater storage reserves in the border region.
Currently, there is a lack of reliable assessments concerning the transboundary challenges associated with groundwater use in the Zhambyl Region. Scientific findings will enable the identification of trends in both storage and renewable groundwater resources within the Shu transboundary basin, influenced by climatic conditions and escalating anthropogenic pressure. In addition, these findings will contribute to the development of a transboundary aquifer database for evaluating resource potential.
In this context, the study undertook a comprehensive assessment of the chemical composition of groundwater from 11 water intakes located in the Kordai, Shu, and Merke Districts of the Zhambyl Region, Kazakhstan. The objectives included evaluating the suitability of groundwater for drinking purposes, identifying areas with potential exceedances of MPCs for macro- and microelements, delineating contamination zones through spatial comparison of data, and correlating the results with national standards and the UN Sustainable Development Goal 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation).
2. Materials and Methods
The hydrogeological assessment focused on the middle section of the Shu River Basin situated within the Zhambyl Region (see Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Map of Kazakhstan highlighting the Zhambyl Region (in purple).
2.1. Analysis of Empirical Data on the Patterns of Formation and Distribution of Transboundary Groundwater
In Kazakhstan, transboundary groundwater resources are found along the borders with the Russian Federation, the People’s Republic of China, the Kyrgyz Republic, and Uzbekistan. A total of 15 transboundary groundwater basins have been identified across the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan (see Table 1). These aquifers play a vital role in ensuring a sustainable water supply for border regions and require joint management at the interstate level. Within the framework of this study, particular attention is given to the Shu groundwater basin located in the southern part of Kazakhstan, which serves as one of the key water sources for rural water supply in the Zhambyl Region.

Table 1.
Overview of transboundary groundwater basins.
The Shu transboundary groundwater basin is divided by the state border with the Kyrgyz Republic. Its area within Kazakhstan is 7297 km2, and in the Kyrgyz Republic—5123 km2. The length of the shared border with the Kyrgyz Republic is 200 km.
To assess the current state, a field expedition was conducted within the territory of the Shu transboundary basin, including ecological and hydrogeological surveys and an evaluation of groundwater use at 11 water intakes located in the Kordai, Shu, and Merke Districts of the Zhambyl Region. Samples were collected for chemical laboratory analysis (see Figure 2). For all 11 wells associated with these water intakes, groundwater extraction volumes have been officially approved for a 27-year period for domestic and drinking water supply purposes.
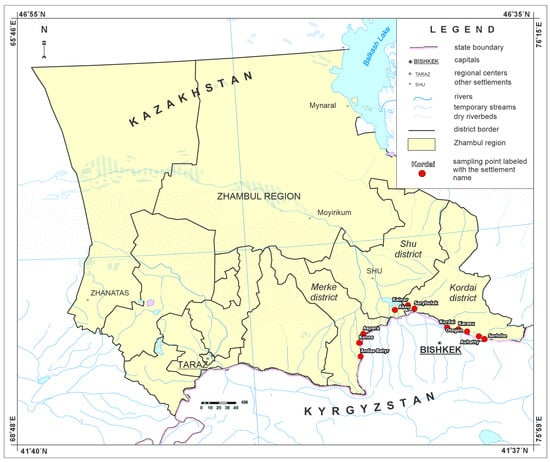
Figure 2.
Locations of 11 groundwater intakes in the Kordai, Shu, and Merke Districts of Zhambyl Region.
As part of the 2025 field investigations, a total of 11 groundwater intakes within the Shu transboundary basin were surveyed (see Table 2).

Table 2.
Results of the water intake survey.
2.2. Data Collection and Processing
A total of 11 average groundwater samples were taken, with at least three samples for each season from each of the 11 existing water intakes and a fourth control sample, the date of which is indicated in Table A1, located in the Kordai, Shu, and Merke Districts of the Zhambyl Region. The values shown in Table A1 were obtained directly from each well during the 2024 field campaign. All samples were taken from the existing production wells of these intakes. In addition, the literature sources from the archives of the National Scientific and Technical Library in Almaty and the library of the K.I. Satpayev Institute of Geological Sciences were reviewed. Data were also obtained from the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources, the Ministry of Water Resources and Land Reclamation, the Statistics Agency of the Republic of Kazakhstan, and the Kazgiprovodkhoz Institute, as well as from regional and District Akimats of the Zhambyl Region on issues related to water supply. The results of laboratory analyses of groundwater samples from the Zhambyl Region were processed using the software package AquaChem 11 (S/N: AQCHM-700-444163796-4298), developed by Waterloo Hydrogeologic (Canada), for graphical visualization in the form of Piper diagrams.
2.3. Research Methods for the Shu Basin
During the study, water samples were collected from each water intake to assess compliance with sanitary and epidemiological requirements for water sources, intake points for domestic and drinking purposes, domestic drinking water supply systems, recreational water use sites, and water body safety, in accordance with Order No. 26 of the Minister of Health of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated 20 February 2023. Laboratory chemical-analytical studies were conducted at the U.M. Akhmedsafin Institute of Hydrogeology and Geoecology, in an accredited laboratory (accreditation certificate No. KZ.T.02.0782, valid until 27 November 2025). The set of components used to characterize groundwater quality included total mineralization, pH level, major chemical constituents, as well as microcomponents (cadmium, lead, copper, and zinc) and petroleum hydrocarbons. Exceedances of the maximum allowable concentrations of these components indicate contamination. The laboratory testing procedures, methods, and equipment used to determine the chemical indicators in the collected samples are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Methodologies for conducting laboratory tests [40].
3. Results
3.1. Analysis and Assessment of Trends in the Change in Storage and Renewable Groundwater Resources of the Shu Transboundary Basin Under the Influence of Climatic Factors and Anthropogenic Pressures
At present, one of the major challenges is assessing the potential impact of climate change and anthropogenic activities on the formation of natural and projected reserves of fresh and slightly saline groundwater. Considering the diversity of natural and hydrogeological conditions in Kazakhstan, variations in natural groundwater recharge may result in both beneficial and adverse outcomes [48,49].
Groundwater flow is a key dynamic component of the hydrological cycle and is sensitive to both climatic and anthropogenic changes. Increasing exploitation of subsurface resources leads to alterations in both the quantitative and qualitative characteristics of groundwater. These anthropogenic impacts are often comparable in magnitude to natural processes, resulting in the formation of natural-anthropogenic hydrogeological systems. Such systems are characterized by significant variability in hydrogeodynamic and hydrogeochemical parameters and by the manifestation of depletion and contamination processes during groundwater exploitation [50].
In recent years, projected global warming has raised concerns about global climate change and its potential effects on regional and global surface and groundwater resources. These changes involve key climatic parameters such as the amount and distribution patterns of air temperature and precipitation, as well as evaporation and air humidity. Forecasting changes in hydrogeological conditions largely depends on the climate models adopted for different landscapes of Kazakhstan [51].
At the same time, many researchers emphasize that global warming, if it occurs, does not necessarily mean uniform or immediate warming across all regions. It is expected that climate changes will manifest unevenly across various landscapes, with some areas experiencing warming while others may undergo significant cooling. Likewise, the interpretation of temperature trends is not unambiguous; some experts argue that the currently observed warming is taking place within the context of a long-term global cooling cycle [52,53]. In addition, climate change involves not only rising air temperatures but also alterations in both the quantity and spatial-temporal distribution of precipitation.
To assess climate change in the foothill areas of the Kyrgyz Alatau, an analysis of long-term meteorological observations was carried out using data from three key meteorological stations in the Zhambyl Region: Zhambyl, Merke, and Kulan. Figure 3 presents the dynamics of average annual air temperature changes over the observation period from the early 20th century to 2020. All three stations show a consistent trend of rising temperatures, with a particularly pronounced increase observed since the 1980s, which corresponds to global warming trends [54,55,56]. The highest temperature values are recorded at the Zhambyl meteorological station, which is attributed to its location in the lowland part of the region. The trend lines confirm a statistically significant increase in the average annual temperature by 1.5–2.0 °C over the past century.
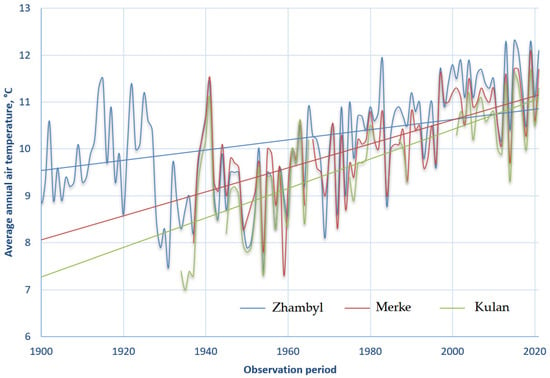
Figure 3.
Dynamics of changes in average annual air temperatures at meteorological stations in the foothills of the Kyrgyz Alatau.
Figure 4 shows the dynamics of annual precipitation levels. The data indicate high interannual variability in precipitation throughout the study period. Peak values (up to 600 mm/year) occurred during the 1950s–1970s, particularly at the Kulan station, which is located closer to the mountain range. However, since the late 20th century, a general downward trend in precipitation has been observed, most notably at the Zhambyl meteorological station. This may indicate a gradual intensification of climate aridization, which—when combined with rising temperatures—has a significant impact on water availability and the productivity of pasture ecosystems in the region.
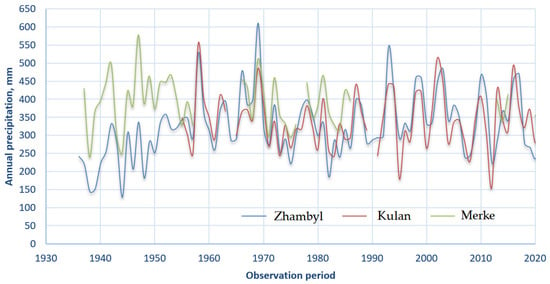
Figure 4.
Dynamics of changes in the amount of annual precipitation at meteorological stations in the foothills of the Kyrgyz Alatau.
Thus, the results of the analysis point to a deterioration of climatic conditions in the foothills of the Kyrgyz Alatau, highlighting the need for adaptation of water supply systems, pasture management practices, and hydrological resource monitoring in response to growing climate challenges.
3.2. Chemical and Analytical Studies of Groundwater Samples
The Zhambyl Region is characterized by agricultural and partially industrial use of natural water resources. Groundwater in the Merke, Shu, and Kordai Districts generally complies with Kazakhstan’s hygienic standards for drinking water; however, increasing extraction and use of these resources impose anthropogenic pressure on water quality [57]. Water from the studied intakes is used for domestic and drinking purposes by the local population, which necessitates regular updates of chemical composition assessments and comparisons with regulatory standards to ensure safety and to support the achievement of SDG 6—Clean Water and Sanitation.
The results of chemical and analytical studies of samples from 11 water intakes within the Shu transboundary groundwater basin are presented in detail in Table A1. Elevated levels of nitrates, nitrites, and phosphates (based on laboratory analyses) may indicate the influence of agricultural and domestic wastewater. The use of mineral fertilizers and manure in irrigated areas leads to soil enrichment with nitrates, which then percolate into the groundwater. Similarly, untreated or insufficiently treated domestic sewage from settlements can contribute additional nitrogen and chlorides.
Thus, the combined impact of agricultural runoff and domestic pollution exacerbates the processes of eutrophication and mineralization of groundwater, particularly in zones with scattered wells and boreholes.
To classify and compare the hydrochemical composition of water samples collected from various settlements of the Zhambyl Region, a Piper diagram was constructed (Figure 5). This diagram provides a visual representation of the ionic composition based on major cations (Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, K+) and anions (Cl−, SO42−, HCO3− + CO32−) and allows identification of hydrochemical facies. Most samples are characterized by a calcium-sodium type with dominance of Ca2+ and Na+/K+. A significant share of magnesium (Mg2+) was detected in samples from Sarybulak, Aspara, Sortobe, and Kainar, which may indicate the influence of carbonate rocks.
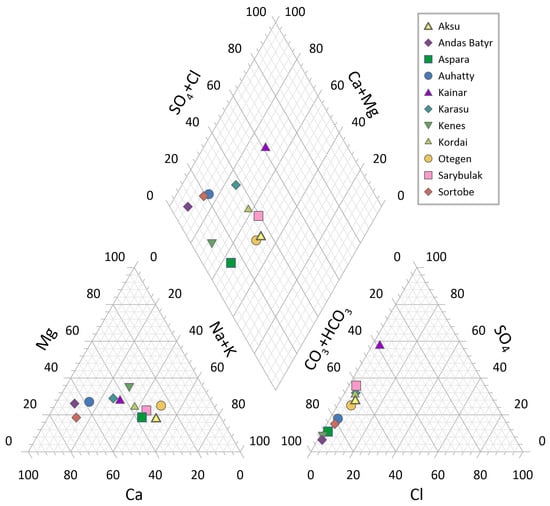
Figure 5.
Piper diagram illustrating the hydrochemical composition of groundwater in different settlements across the Zhambyl Region.
Most samples are clustered in the bicarbonate-dominant field (HCO3−), typical for natural waters not heavily affected by anthropogenic activity. However, in samples from Kainar and partially from Auhatty and Kenes, a higher proportion of sulfates (SO42−) is observed, which may result from sulfate leaching processes or anthropogenic contamination sources.
The majority of samples belong to the hydrochemical facies of bicarbonate-calcium-sodium and bicarbonate-calcium-magnesium types, confirming the natural origin of major ions. Exceptions include waters from Kainar and Auhatty, which tend toward a sulfate-magnesium type, possibly indicating a regional geochemical background feature or local contamination sources. The Piper diagram analysis showed that most groundwater samples correspond to typical natural freshwater bicarbonate types. However, in some locations, the presence of mineralized ions (sulfates and magnesium) suggests the need for further investigation into potential sources of contamination and clarification of the lithologic and hydrogeochemical setting.
For a comprehensive assessment of the hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater in the study sites across the Zhambyl Region, a modified Piper diagram scheme was used. It includes triangular diagrams for cations and anions, along with axis plots for pH, total dissolved solids (TDS), and Na+ + K+ ions. The results are presented in Figure 6. The dominant component in most samples is bicarbonate (CO32− + HCO3−), indicating a natural origin of the water formed in carbonate rock formations. However, samples from Kainar, Karasu, and Sarybulak show a high proportion of sulfates (SO42−), which may result from the presence of sulfate minerals or anthropogenic contamination sources.
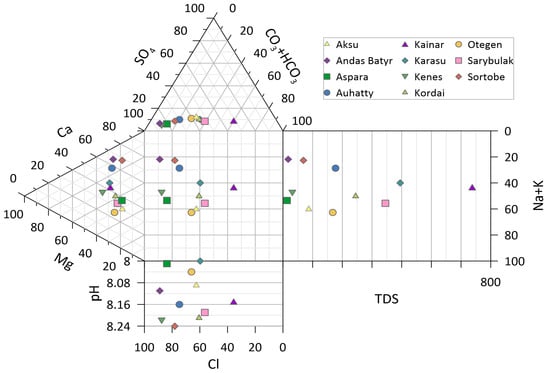
Figure 6.
Graphical interpretation of hydrochemical parameters of groundwater in various settlements of the Zhambyl Region using an extended Piper diagram.
Calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+) ions prevail in most samples, especially in those from Andas Batyr, Sortobe, and Auhatty. Elevated Mg2+ concentrations may suggest water–rock interaction with magnesite or dolomite. Some samples, such as those from Otegen and Kenes, show a trend toward increased sodium and potassium (Na+ + K+) content, potentially due to ion exchange processes or contamination.
The pH values range from 8.2 to 8.7, indicating a mildly alkaline environment typical for carbonate systems. Relatively high chloride (Cl−) concentrations were observed in samples from Sarybulak, Auhatty, and Sortobe, which may point to increased mineralization or anthropogenic influence (e.g., agriculture). TDS ranges from low to moderate levels (approximately 200–700 mg/L), which in most cases corresponds to satisfactory-quality drinking water. The highest TDS value was recorded at the Kainar site, which also showed sulfate dominance and elevated Na+ + K+ levels—potential indicators of partial degradation in water quality.
Most samples are characterized by a bicarbonate-calcium-magnesium hydrochemical type and moderate mineralization, suggesting a natural origin of groundwater. At the same time, several locations (e.g., Kainar, Otegen, Sarybulak) exhibit signs of anthropogenic influence and increased mineralization, which require further environmental monitoring and clarification of potential contamination sources.
For all macrocomponents, the concentrations in the 11 groundwater samples from the water intakes were within the MPCs. In all 11 samples, mineralization did not exceed the MPC of 1000 mg/dm3.
At the Sarybulak water intake, fluoride exceeded the MPC, reaching 2.3 mg/dm3 (with an MPC of 1.5 mg/dm3). The fluoride content in the Sarybulak intake is 2.3 mg/dm3 due to the fact that the foothills of the Kyrgyz Alatau contain intrusive minerals with fluoride content. At borehole No. 1 of the Andas Batyr water intake, arsenic concentration was significantly elevated at 0.240 mg/dm3 (MPC = 0.05 mg/dm3), and the odor rating was 4 points (MPC = 2 points). The arsenic content in the Andas Batyr intake is 0.24 mg/dm3 due to the fact that in this territory the foothills of the Kyrgyz Alatau at depths of 150–200 m are waters of the sporadic distribution of Miocene-Pliocene deposits represented by sands and sandstones among clays. The exceedances observed in the three boreholes from three water intakes were generally minor, except for the arsenic level in the Andas Batyr sample, which was substantially above the permissible limit.
This exceedance was examined in more detail. Given that the depth of the borehole at the Andas Batyr water intake is 350 m and reaches bedrock formations, it can be concluded that the elevated arsenic concentration is likely related to water–rock interaction with the underlying geological strata.
3.3. Categorization of Risks Related to Transboundary Groundwater Issues
Risk categorization of transboundary groundwater-related problems is carried out according to the following principle shown in Figure 7.
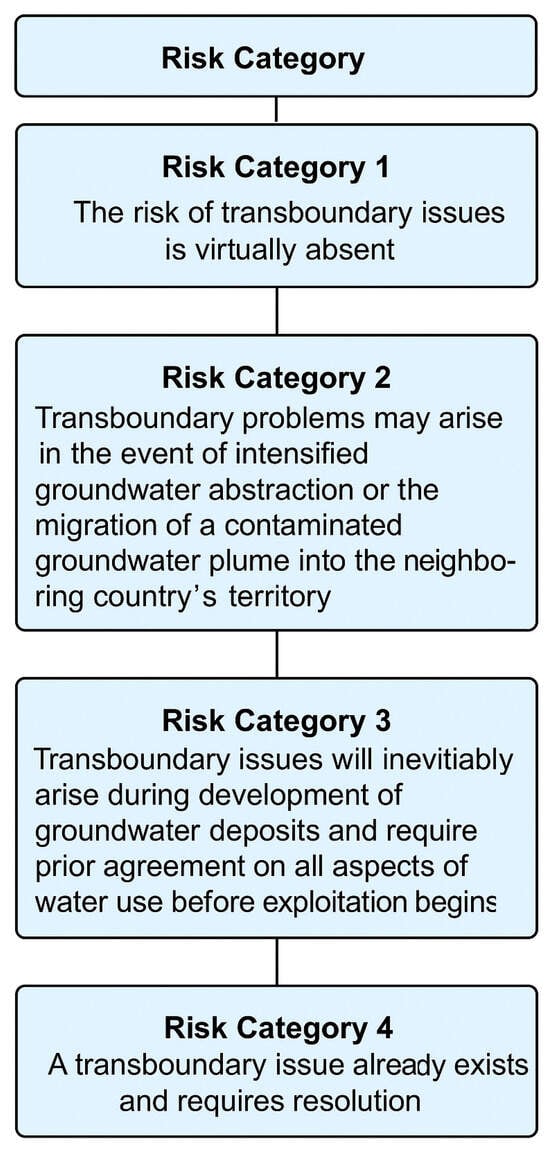
Figure 7.
Risk categorization of transboundary groundwater-related problems.
As an example, we examine the risk associated with the Shu transboundary hydrogeological aquifer, which is classified as Risk Category 3: transboundary problems are likely to occur during the economic development of groundwater deposits or due to the migration of contaminated groundwater from the neighboring country—the Kyrgyz Republic—into the territory of the Zhambyl Region. The general characteristics of the identified transboundary hydrogeological aquifer are summarized in Table 4.

Table 4.
Characteristics of transboundary aquifers of Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan.
The Shu transboundary aquifer is associated with the Shu artesian basin, which belongs to the foredeep of the Kyrgyz Alatau and, according to hydrogeological zoning, is classified as a second-order confined groundwater basin within the North Tien Shan hydrogeological province. Its area within Kazakhstan is 6.3 thousand km2, and within the Kyrgyz Republic—5.1 thousand km2. The length of the border with the Kyrgyz Republic is approximately 232 km.
The piedmont plain borders the mountain structures of the Kyrgyz Range in the south and geostructurally represents the southeastern marginal part of the Shu-Sarysu depression, filled with loose terrigenous material. The hydrogeological system consists of several subdivisions, among which aquifers and complexes significant for recharge, transit, and discharge of transboundary flows are identified:
The Upper Quaternary–Holocene alluvial aquifer underlies riverbeds.
The Middle–Upper Quaternary alluvial-proluvial complex, widespread in the piedmont area of the Kyrgyz Range, is the most promising for use. It represents a multilayered formation with alternating water-bearing and poorly permeable layers, ranging in thickness from 2 to 10 m in the piedmont apron zone to 15–20 m or more in the northern part of the area. This complex is of high practical importance and is currently widely used in the agro-industrial sector for water supply and irrigation. The Middle Quaternary alluvial aquifer is distributed in the northwestern part of the area, on the left bank of the Kuragayty River.
The Neogene aquifer complex is widespread and lies beneath the Middle–Upper Quaternary complex at depths of 150 to 300 m. It surfaces on the terraces in the foothills of the Kyrgyz Range and then rapidly dips to depths greater than 300 m. The upper section of this complex is considered the most promising for practical use. For the Shu transboundary hydrogeological aquifer, four types of transboundary groundwater flows have been identified, illustrated in Figure 8.
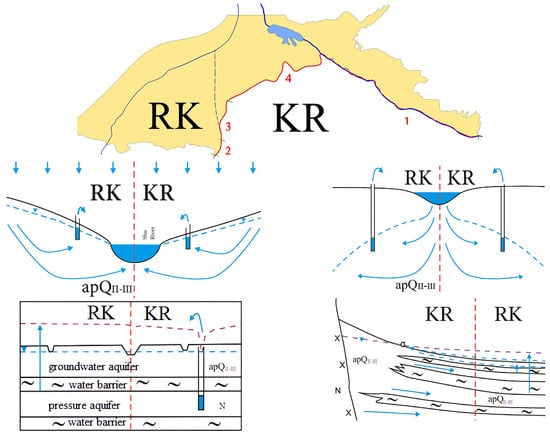
Figure 8.
Types of transboundary groundwater flows in the Shu transboundary aquifer system. 1—Transboundary groundwater flow of the Shu River Valley. 2—Transboundary groundwater flow of the Aspara River. 3—Transboundary groundwater flow in the foothill plain of the Kyrgyz Alatau. 4—Transboundary groundwater flow of the Shuya foothill plain. The blue arrows indicate the direction of groundwater flows, and the black wave indicates the aquifer barrier. The red dotted line indicates the separation of the state border of Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan. The purple dotted line indicates the dynamic groundwater level. The blue dotted lines indicate the static groundwater level.
Transboundary groundwater flow in the Shu River Valley. A significant section of the border with Kyrgyzstan, about 85 km long, runs along the Shu River—one of the major rivers of Zhambyl Region (see Figure 8, Section 1). The Middle–Upper Quaternary alluvial-proluvial aquifer is hydraulically connected to the river via the Holocene alluvial aquifer. The groundwater flow is drained by the Shu River, and its direction coincides with the river’s flow. The net transboundary groundwater flow is essentially zero. Changes in the underground runoff (due to abstraction or increase due to irrigation) only affect the discharge of the Shu River itself.
Transboundary groundwater flow from the Aspara River alluvial fan. The state border follows the Aspara River in the zone of groundwater formation, as shown in Figure 8, Section 2. The radially diverging groundwater flow from the Middle–Upper Quaternary alluvial-proluvial complex in Kazakhstan is directed to the north–northwest.
A similar flow in Kyrgyzstan is directed to the north-northeast. Withdrawal of river flow from the main river channel may reduce the recharge of groundwater in the recharge zone of the Middle–Upper Quaternary alluvial–proluvial aquifer complex.
Transboundary groundwater flow of the piedmont plain of the Kyrgyz Alatau. The state border runs along the Aspara River in the groundwater discharge zone (see Figure 8, Section 3). There is currently no transboundary groundwater flow in this area. However, such a flow may arise during groundwater extraction due to a decline in piezometric levels. On the Kazakh side near the border, the Aspara groundwater field has been explored and is under exploitation. A drop in abstraction levels may lead to a decrease in groundwater levels in the neighboring territory. In Kyrgyzstan, groundwater fields have also been explored. The exploitation of all identified fields at their approved abstraction rates will likely occur under interacting groundwater withdrawal conditions.
Transboundary groundwater flow of the Shu piedmont plain. The state border crosses the piedmont plain of the Kyrgyz Alatau in a zone of confined and semi-confined water, where groundwater is secondarily submerged and discharged into rivers (see Figure 8, Section 4). The transboundary groundwater flow is almost entirely formed in the neighboring state. The flow rate entering Kazakhstan from Kyrgyzstan is estimated at approximately 1.25 m3/s. Known sources of groundwater contamination exist on the Kyrgyz side, and there is a potential for contaminated groundwater to migrate into Kazakhstan.
In summary, the following conclusions can be drawn for the Shu Transboundary Aquifer System. The unified unconfined and confined–unconfined hydrogeological system consists of two main aquifer complexes: the Middle–Upper Quaternary alluvial–proluvial (apQII–III) and Neogene (N); the border crosses all hydrogeological zones typical for piedmont artesian basins in arid regions; Several groundwater deposits have been explored on both sides of the border within the Shu basin, with resource assessments carried out under conditions of potential wellfield interaction. Monitoring of groundwater levels on the opposite side of the border is required during exploitation; it is recommended to develop coordinated and joint transboundary groundwater management with Kyrgyzstan.
4. Discussion
Zhambyl Region is not considered water-deficient in terms of sources for domestic and drinking water supply, except for certain districts in the northern and northeastern parts, which are relatively poorly provided with water resources. Due to favorable hydrogeological conditions, water supply for domestic and drinking purposes is primarily ensured through groundwater from alluvial–proluvial Quaternary deposits of alluvial fans and the piedmont plains of the Kyrgyz Alatau, as well as from the alluvial deposits of the Shu, Talas, Assy, and Kuragaty River Valleys. These resources are widely used for supplying water to cities, rural settlements, and industrial and agricultural facilities.
The hydrological regime of the Shu and Talas rivers is characterized by snow and glacier-fed flow. The glaciated area in the Shu and Talas basins totals 762 km2. Glaciers have a significant influence on the hydrological regime of these rivers: fluctuations in flow from year to year are relatively smoothed, and the degree of glaciation determines about 50–60% of the rivers’ annual runoff. As elevation decreases, the proportion of seasonal snow increases to 70%, and the share of rainfall ranges from 2% to 11% depending on altitude.
The total water resources of the Shu and Talas River Basins are estimated at 4.67 km3, of which 3.36 km3 is formed on the territory of the Kyrgyz Republic (considered in this study) and 1.29 km3 in Kazakhstan. The transboundary basins of Zhambyl Region are divided into the Shu and Talas basins. The Talas Transboundary Basin includes the North Talas and South Talas transboundary aquifers.
The Shu Basin is characterized by a classical scheme of groundwater formation in piedmont depressions. In the foothills, within the alluvial fan area, there is a recharge zone for groundwater due to infiltration of surface runoff. At the boundary between the alluvial fans and the piedmont plain, there is an intensive discharge zone through springs, evapotranspiration, and groundwater outflow into small rivers such as Karasu. Below this zone lies the confined water area and a secondary submergence of groundwater to depths of 10–15 m. Groundwater in this zone primarily discharges into the Karasu rivers, contributing to their flow.
The hydrogeological system includes several hydrogeological subdivisions, among which aquifers and complexes of interest for recharge, transit, and discharge of transboundary flows are identified.
Within the Shu Basin boundary, the following transboundary aquifers are distinguished:
Transboundary groundwater flow of the Shu River Valley;
Transboundary groundwater flow of the Aspara River alluvial fan;
Transboundary groundwater flow of the Kyrgyz Alatau piedmont plain;
Transboundary groundwater flow of the Shu piedmont plain.
Analysis of the formation conditions of transboundary groundwater flows in the Shu Basin allows us to conclude:
The unified unconfined and confined–unconfined hydrogeological system consists of two main aquifer complexes—the Middle–Upper Quaternary alluvial–proluvial complex and the Neogene complex.
The border intersects all hydrogeological zones typical for piedmont artesian basins in arid regions.
Several groundwater fields have been explored on both sides of the border, and their resource assessments have been carried out under conditions of wellfield interaction. Monitoring groundwater levels on the adjacent side is required during operation.
There are no large industrial enterprises in the populated areas. Some villages have repair workshops and small processing and canning plants for agricultural products.
Landfills, livestock farm sites, and storage areas for lubricants at field stations represent potential hotspots for organic and chemical contamination of surface and groundwater. The main potential sources of pollution include the filtration fields of the sugar factory, as well as irrigated areas where various fertilizers and agrochemicals may be used.
The obtained results indicate a combination of geogenic and anthropogenic factors determining the quality of groundwater in the studied settlements. High concentrations of Na+, Cl−, and SO42− are primarily caused by geogenic leaching of salts from rocks (halite, anhydrite, and carbonates). Significant concentrations of lithium, strontium, fluoride, and arsenic also have a natural origin—associated with the mineralogy of the region [39,40,57].
At the same time, elevated levels of nitrates, nitrites, and phosphates (according to the analysis data) may indicate the influence of agricultural and domestic wastewater. The use of mineral fertilizers and manure in irrigated areas leads to soil enrichment with nitrates, which then percolate into groundwater. Similarly, untreated or insufficiently treated domestic sewage from settlements can introduce additional nitrogen and chlorides. Thus, the combined impact of agricultural runoff and domestic pollution exacerbates eutrophication and mineralization of groundwater, especially in areas with scattered wells and boreholes. Overall, regular monitoring and a targeted water management policy will create the prerequisites for sustainable management of groundwater resources in the Zhambyl Region.
5. Conclusions
The results of the conducted study allowed for a comprehensive assessment of groundwater quality at 11 water intakes located in the Kordai, Shu, and Merke Districts of the Zhambyl Region of the Republic of Kazakhstan. The analysis covered a wide range of macro- and microcomponents in accordance with the standards established by Order No. 26 of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated 20 February 2023, as well as GOST and ST RK ISO 6332-2008.
Water samples were collected in the Kordai, Shu, and Merke Districts of the Zhambyl Region to assess compliance with sanitary and epidemiological requirements for water sources, water intake points for domestic drinking purposes, domestic water supply, recreational water use, and water safety. Chemical-analytical studies were conducted to evaluate the compliance of water samples with drinking water standards.
The results determined the chemical composition and mineralization of groundwater, which ranged from 0.18 to 0.93 g/L. The pH of the waters was predominantly neutral. Water hardness ranged from soft to hard. Elevated concentrations of fluoride (up to 2.3 mg/L or 1.53 times the MAC) were noted in the village of Sarybulak, Kordai District. In the Andas Batyr area of the Merke District, a high concentration of arsenic was recorded (4.8 times the MAC). These waters are not used for drinking water supply.
Given the growing water stress and climate change, the results of this study confirm the necessity of implementing systematic monitoring using unified standards, integrating GIS analyses to assess the spatial distribution of pollutants, and developing adaptive strategies for the protection and rational use of groundwater.
This study can serve as a basis for decision-making in the fields of water supply, groundwater protection, and transboundary water resources management, especially in the context of achieving UN Sustainable Development Goal No. 6—ensuring availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.T., M.A., A.A., and D.Y.; methodology, Y.M., V.R., and I.R.; software, K.K. and Y.S.; validation, D.A., K.K., and Y.S.; formal analysis, S.T., M.A., and A.A.; investigation, Y.M., V.R., I.R., and D.A.; resources, S.T., K.K., and Y.S.; data curation, M.A. and A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, S.T., M.A., A.A., and D.Y.; writing—review and editing, S.T. and D.Y.; visualization, Y.M., V.R., I.R. and D.A.; supervision, D.Y.; project administration, D.Y.; funding acquisition, S.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Science Committee of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan (“Risk assessment of the likelihood of transboundary problems in the use and protection of fresh groundwater in the Zhambyl Region from Kyrgyzstan”, AP23489813).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| GOST | State Standard |
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization |
| KR | Kyrgyz Republic (Kyrgyzstan) |
| MAC | Maximum Allowable Concentration |
| MPC | Maximum Permissible Concentrations |
| RK | Republic of Kazakhstan (Kazakhstan) |
| SDG | Sustainable Development Goal |
| ST RK | Standard of the Republic of Kazakhstan |
| TDS | Total Dissolved Solids |
Appendix A

Table A1.
The results of chemical and analytical studies of samples from 11 water intakes within the Shu transboundary groundwater basin.
Table A1.
The results of chemical and analytical studies of samples from 11 water intakes within the Shu transboundary groundwater basin.
| Sampling Location | Karasu Village | Otegen Village | Auhatty Village | Sortobe Village | Kordai Village | Sarybulak Village | Kainar Village | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The coordinates of the sampling points | 42°59′41.88″ N, 74°53′03.24″ E. | 42°57′45.94″ N, 74°59′56.70″ E. | 42°54′00.30″ N, 75°09′20.86″ E. | 42°52′00.48″ N, 75°13′49.26″ E. | 43°01′25.33″ N, 74°43′53.76″ E. | 43°15′10.73″ N, 74°18′01.60″ E. | 43°17′41.23″ N, 74°12′55.37″ E. | |
| Date of sampling | 26 September 2024 | 27 September 2024 | 28 September 2024 | 29 September 2024 | 2 October 2024 | 3 October 2024 | 4 October 2024 | |
| pH | 8.0 | 8.04 | 8.16 | 8.24 | 8.21 | 8.19 | 8.15 | |
| Dry residue, mg/dm3 | 495 | 268 | 277 | 169 | 345 | 445 | 738 | |
| Cations, mg/dm3 | Na+ | 55.0 | 46.1 | 18.4 | 9.0 | 56.3 | 85.3 | 87.5 |
| K+ | 2.9 | 15.8 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 2.6 | 2.4 | 3.6 | |
| Ca2+ | 88.1 | 24.0 | 64.1 | 44.0 | 50.1 | 56.1 | 114.1 | |
| Mg2+ | 34.0 | 14.6 | 18.2 | 7.3 | 19.5 | 23.1 | 46.2 | |
| NH4+ | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |
| Fe sum | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |
| Anions, mg/dm3 | CO3− | <6.0 | <6.0 | <6.0 | <6.0 | <6.0 | <6.0 | <6.0 |
| HCO3− | 311.2 | 189.2 | 231.9 | 152.5 | 219.7 | 256.3 | 244.1 | |
| Cl− | 25.9 | 17.7 | 11.3 | 7.1 | 18.8 | 14.2 | 21.3 | |
| SO42− | 157.8 | 69.6 | 53.1 | 28.4 | 106.6 | 151.9 | 369.6 | |
| NO3− | 13.0 | 4 | 14 | 6 | 8 | 18 | 35 | |
| NO2− | <0.005 | <0.005 | <0.005 | <0.005 | <0.005 | <0.005 | <0.005 | |
| F, mg/dm3 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 2.3 | 1.0 | |
| Mineralization, mg/dm3 | 697 | 388 | 422 | 262 | 490 | 617 | 930 | |
| Hardness | total | 7.2 | 2.4 | 4.7 | 2.8 | 4.1 | 4.7 | 9.5 |
| carbonates | 5.1 | 2.4 | 3.8 | 2.5 | 3.6 | 4.2 | 4.0 | |
| SiO2, mg/dm3 | 7.1 | 6 | 7.7 | 5.3 | 7.3 | 7.3 | 7.8 | |
| Overall stiffness, moll/dm3 | 7.2 | 2.4 | 4.7 | 2.8 | 4.1 | 4.7 | 9.5 | |
| Permanganate oxidizability mg oxygen/dm3 | 0.52 | 0.64 | 0.32 | 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | |
| Petroleum products, mg/dm3 | 0.005 | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | |
| Surfactants, mg/dm3 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | |
| Phenolic index, mg/dm3 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |
| Al, mg/dm3 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | |
| Be, mg/dm3 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | |
| B, mg/dm3 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.2 | |
| Cd, mg/dm3 | 0.0001 | 0.0004 | 0.001 | 0.0009 | 0.0009 | 0.001 | 0.0001 | |
| Co, mg/dm3 | 0.0190 | 0.0084 | 0.0099 | 0.0048 | 0.0086 | 0.010 | 0.019 | |
| Si, mg/dm3 | 7.14 | 6.0 | 7.7 | 5.3 | 7.3 | 7.3 | 7.8 | |
| Li, mg/dm3 | 0.016 | 0.008 | 0.005 | 0.0038 | 0.01 | 0.017 | 0.0033 | |
| Mn, mg/dm3 | 0.016 | 0.0430 | 0.0120 | 0.0140 | 0.0160 | 0.0160 | 0.0230 | |
| Pb, mg/dm3 | 0.001 | 0.0200 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.0035 | 0.001 | |
| Cu, mg/dm3 | 0.0250 | 0.0130 | 0.0130 | 0.0180 | 0.0110 | 0.0130 | 0.016 | |
| Mo, mg/dm3 | 0.0570 | 0.0190 | 0.0330 | 0.0230 | 0.0900 | 0.0410 | 0.0230 | |
| As, mg/dm3 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |
| Ni, mg/dm3 | 0.027 | 0.0066 | 0.0130 | 0.0081 | 0.0120 | 0.0140 | 0.0230 | |
| Hg, mg/dm3 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |
| Se, mg/dm3 | 0.0001 | 0.0028 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0055 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |
| Ag, mg/dm3 | 0.0140 | 0.0001 | 0.0052 | 0.0007 | 0.0035 | 0.0041 | 0.0100 | |
| Sr, mg/dm3 | 1.034 | 0.1825 | 0.400 | 0.0181 | 0.509 | 0.601 | 2.411 | |
| Zn, mg/dm3 | 0.0017 | 0.0005 | 0.0028 | 0.0020 | 0.0017 | 0.0023 | 0.0039 | |
| Date of sampling | 5 October 2024 | 6 October 2024 | 9 October 2024 | 10 October 2024 | Kazakhstan | WHO | ||
| The coordinates of sampling points | 43°15′28.44″ N, 74°01′39.95″ E. | 43°02′21.77″ N, 73°33′30.66″ E. | 42°56′58.86″ N, 73°29′24.09″ E. | 42°48′26.35″ N, 73°29′38.84″ E. | - | - | ||
| pH | 8.09 | 8.01 | 8.22 | 8.11 | 6.0–9.0 | 6.2–8.5 | ||
| Dry residue, mg/dm3 | 187 | 114 | 132 | 118 | - | - | ||
| Cations, mg/dm3 | Na+ | 37.4 | 21.5 | 17.1 | 4.2 | 200 | 200 | |
| K+ | 1.5 | 0.7 | 1.2 | 0.7 | ||||
| Ca2+ | 20.0 | 16.0 | 18.0 | 30.0 | - | 200 | ||
| Mg2+ | 7.3 | 4.9 | 10.9 | 7.3 | - | 50 | ||
| NH4+ | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 2.0 | 0.50 | ||
| Fe sum | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.3 | 0.3 | ||
| Anions, mg/dm3 | CO3− | <6.0 | <6.0 | <6.0 | <6.0 | - | ||
| HCO3− | 122.0 | 109.8 | 140.3 | 128.1 | - | |||
| Cl− | 12.8 | 3.2 | 2.1 | 2.8 | 350 | 250 | ||
| SO42− | 53.1 | 14.0 | 13.2 | 9.1 | 500 | 250 | ||
| NO3− | 4.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 45 | 50 | ||
| NO2− | <0.005 | <0.005 | <0.005 | <0.005 | 3.0 | 0.50 | ||
| F, mg/dm3 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 1.5 | ||
| Mineralization, mg/dm3 | 267 | 181 | 216 | 193 | 1000.0 | |||
| Hardness | total | 1.6 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 2.1 | 7.0 | ||
| carbonates | 1.6 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 2.1 | ||||
| SiO2, mg/dm3 | 7.0 | 6.1 | 7.6 | 4.5 | - | - | ||
| Overall stiffness, moll/dm3 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 2.1 | - | - | ||
| Permanganate oxidizability mg oxygen/dm3 | 0.16 | 0.84 | 0.36 | 0.12 | 5.0 | -- | ||
| Petroleum products, mg/dm3 | 0.005 | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.033 | 0.1 | |||
| Surfactants, mg/dm3 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | - | - | ||
| Phenolic index, mg/dm3 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | - | - | ||
| Al, mg/dm3 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | - | - | ||
| Be, mg/dm3 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | - | - | ||
| B, mg/dm3 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | - | - | ||
| Cd, mg/dm3 | 0.0007 | 0.0006 | 0.0009 | 0.0008 | 0.001 | - | ||
| Co, mg/dm3 | 0.0040 | 0.0016 | 0.0043 | 0.0026 | - | - | ||
| Si, mg/dm3 | 7.0 | 6.1 | 7.6 | 4.5 | - | - | ||
| Li, mg/dm3 | 0.006 | 0.0039 | 0.0046 | 0.002 | - | - | ||
| Mn, mg/dm3 | 0.0046 | 0.0035 | 0.0087 | 0.0064 | - | - | ||
| Pb, mg/dm3 | 0.0160 | 0.0046 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.03 | 0.01 | ||
| Cu, mg/dm3 | 0.0093 | 0.0048 | 0.0099 | 0.0092 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||
| Mo, mg/dm3 | 0.0210 | 0.0130 | 0.0150 | 0.0160 | - | - | ||
| As, mg/dm3 | 0.0001 | 0.015 | 0.0001 | 0.240 | - | - | ||
| Ni, mg/dm3 | 0.0032 | 0.0017 | 0.0044 | 0.0026 | - | - | ||
| Hg, mg/dm3 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | - | - | ||
| Se, mg/dm3 | 0.0029 | 0.0011 | 0.0019 | 0.0029 | - | - | ||
| Ag, mg/dm3 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0052 | 0.0001 | - | - | ||
| Sr, mg/dm3 | 0.190 | 0.123 | 0.080 | 0.027 | - | - | ||
| Zn, mg/dm3 | 0.0003 | 0.0004 | 0.0006 | 0.0014 | 5.0 | 5.0 | ||
References
- Davamani, V.; John, J.E.; Poornachandhra, C.; Gopalakrishnan, B.; Arulmani, S.; Parameswari, E.; Santhosh, A.; Srinivasulu, A.; Lal, A.; Naidu, R. A Critical Review of Climate Change Impacts on Groundwater Resources: A Focus on the Current Status, Future Possibilities, and Role of Simulation Models. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.A.; Zuniga-Teran, A.A.; Megdal, S.B.; Quanrud, D.M.; Christopherson, G. Assessing the Relationship Between Groundwater Availability, Access, and Contamination Risk in Arizona’s Drinking Water Sources. Water 2025, 17, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasechko, S.; Seybold, H.; Perrone, D.; Fan, Y.; Shamsudduha, M.; Taylor, R.G.; Fallatah, O.; Kirchner, J.W. Rapid Groundwater Decline and Some Cases of Recovery in Aquifers Globally. Nature 2024, 625, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeter, S.A.; Orme, A.M.; Lehmann, K.; Lehmann, R.; Chaudhari, N.M.; Küsel, K.; Wang, H.; Hildebrandt, A.; Totsche, K.U.; Trumbore, S.; et al. Hydroclimatic Extremes Threaten Groundwater Quality and Stability. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Q.; Fan, H.; Cao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Luo, J.; Yao, Y. Groundwater Quality Evolution across China. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, S.; Subba Rao, N.; Chaudhary, M.; Das, R. Assessing Sources of Groundwater Quality and Health Risks Using Graphical, Multivariate, and Index Techniques from a Part of Rajasthan, India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 27, 101356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misstear, B.; Vargas, C.R.; Lapworth, D.; Ouedraogo, I.; Podgorski, J. A Global Perspective on Assessing Groundwater Quality. Hydrogeol. J. 2023, 31, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assessment of Groundwater Quality in the Alluvial Aquifer Using GIS and Water Quality Indices in the Feija Plain, South-East Morocco. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2025, 16, 16–33. [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.; Nasim, I.; Ahmad, M.; Nawaz, R.; Tahir, A.; Irshad, M.A.; Al-Mutairi, A.A.; Irfan, A.; Al-Hussain, S.A.; Zaki, M.E.A. Human Health Risk Assessment of Drinking Water Using Heavy Metal Pollution Index: A GIS-Based Investigation in Mega City. Appl. Water Sci. 2025, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etuk, M.; Re, V.; Viaroli, S.; Raco, B.; Igwe, O. Assessing Groundwater Quality and Solute Sources in Highly Anthropized Areas. The Case of Abuja Federal Capital Territory, Nigeria. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2025, 29, 101425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsudduha, M.; Lee, J.; Joseph, G.; Bahuguna, A.; Wijesundera, S.; Nair, S.S.; Hoo, Y.R.; Wang, Q.; Ayling, S.C.E. Assessing the Water Quality Hazard and Challenges to Achieving the Freshwater Goal in Sri Lanka. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammons, S.; Madrigal, J.M.; Manley, C.K.; Spaur, M.; Hofmann, J.N.; Sandler, D.P.; Freeman, L.E.B.; Ward, M.H.; Jones, R.R. Nitrate and Disinfection By-Products in Drinking Water and Risk of Ovarian Cancer. Environ. Epidemiol. 2025, 9, e382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus Laureano, J.; do Nascimento, E.L.; Ramos, C.F.; da Silva Lopes, D.; Pavanello, L.F.S.; de Oliveira Lima, T.; Mendonça, A.G.; da Rosa, A.L.D.; da Costa Junior, W.A.; Recktenvald, M.C.N.d.N.; et al. Assessment of Risk to Human Health Associated with the Consumption of Contaminated Groundwater in the Western Brazilian Amazon. Environ. Geochem. Health 2025, 47, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, A.; Ali, M.; Ali, N.; Khan, A.; Zairov, R.; Sinyashin, O.; Wang, Y.; Zafar, S.; Khan, F.-A. A Comprehensive Analysis of the Impact of Arsenic, Fluoride, and Nitrate–Nitrite Dynamics on Groundwater Quality and Its Health Implications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 487, 137093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapworth, D.; Boving, T.; Brauns, B.; Dottridge, J.; Hynds, P.; Kebede, S.; Kreamer, D.; Misstear, B.; Mukherjee, A.; Re, V.; et al. Groundwater Quality: Global Challenges, Emerging Threats and Novel Approaches. Hydrogeol. J. 2023, 31, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, D.D.; Manning, N.F.; Jacquemin, S.J.; Johnson, L.T. A Tale of Two Tributaries: Source Delineation of Chloride in a Distressed Watershed (Grand Lake St. Marys, Ohio). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Yun, Q.; Jiang, G.; Teng, D.; Zhou, G.; Cao, Y. A Review of Chloride Ions Removal from High Chloride Industrial Wastewater: Sources, Hazards, and Mechanisms. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 353, 120184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.; Fanelli, R.M.; Sekellick, A.J. High-Frequency Data Reveal Deicing Salts Drive Elevated Specific Conductance and Chloride along with Pervasive and Frequent Exceedances of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Aquatic Life Criteria for Chloride in Urban Streams. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nas, B.; Berktay, A. Groundwater Quality Mapping in Urban Groundwater Using GIS. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 160, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, M.K.; Shekhar, A.; Jenifer, M.A. Assessing Groundwater Quality for Drinking Water Supply Using Hybrid Fuzzy-GIS-Based Water Quality Index. Water Res. 2020, 179, 115867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machiwal, D.; Cloutier, V.; Güler, C.; Kazakis, N. A Review of GIS-Integrated Statistical Techniques for Groundwater Quality Evaluation and Protection. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, R.; Sakizadeh, M. Comparison of Interpolation Methods for the Estimation of Groundwater Contamination in Andimeshk-Shush Plain, Southwest of Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 2758–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- On Approval of Sanitary Rules “Sanitary and Epidemiological Requirements to Water Sources, Places of Water Intake for Domestic and Drinking Purposes, Domestic and Drinking Water Supply and Places of Cultural and Domestic Water Use and Safety of Water Bodi. Available online: https://adilet.zan.kz/kaz/ (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- On Approval of Hygienic Standards of Safety Indicators of Domestic and Cultural Water Use//Order of the Minister of Health of the Republic of Kazakhstan. DSM-138. № 30713. Table 1. 24.11.2022. Available online: https://adilet.zan.kz/kaz/ (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- Krasnopyorova, M.; Gorlachev, I.; Kharkin, P.; Severinenko, M.; Zheltov, D. Study of the Trace Element Composition of Drinking Water in Almaty City and Human Health Risk Assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliyeva, K.; Punys, P.; Zhaparkulova, Y. The Impact of Climate Change on Hydrological Regime of the Transboundary River Shu Basin (Kazakhstan–Kyrgyzstan): Forecast for 2050. Water 2021, 13, 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seraya, N.; Daumova, G.; Petrova, O.; Garcia-Mira, R.; Polyakova, A. Ecological Status of the Small Rivers of the East Kazakhstan Region. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.T.; Li, Y.P.; Huang, G.H.; Wang, S.G.; Wang, P.P. A Multi-Perspective Input-Output Model for the Energy-Water Nexus in Kazakhstan. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 49, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozenbayeva, A.; Yerezhepkyzy, R.; Yessetova, S.; Jangabulova, A.; Beissenbayeva, M. Legal Regulation of Transboundary Water Resources of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Environ. Dev. 2022, 44, 100781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.J.; Li, Y.P.; Liu, J.; Huang, G.H.; Ding, Y.K.; Sun, J.; Zhang, H. Identifying Optimal Virtual Water Management Strategy for Kazakhstan: A Factorial Ecologically-Extended Input-Output Model. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, G.I.; Nagabhatla, N.; Londono-Escudero, C.; Vignola, R. Transboundary Aquifer Management Across the Americas: Hydro-Diplomacy as an Accelerator of Adaptive Groundwater Governance Amid Climate Change Challenges. Water 2024, 16, 3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Villaseñor, E.; Megdal, S. The U.S.-Mexico Transboundary Aquifer Assessment Program as a Model for Transborder Groundwater Collaboration. Water 2021, 13, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Villaseñor, E.M.; Megdal, S.B.; Shamir, E. Prioritizing Transboundary Aquifers in the Arizona–Sonora Region: A Multicriteria Approach for Groundwater Assessment. Water 2025, 17, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.; Olivares, R.; Varner, T.S.; Kulkarni, H.V.; Carmona, G.; Lima, C.; Hollan, S.; Datta, S. Hydrogeochemical Assessment of Groundwater in Transboundary Aquifers along the US-Mexico Border and Drinking Water Quality Implications for Texas Colonias. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 27, 101377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, A.; Pétré, M.-A.; Fraser, C.; Petersen-Perlman, J.D.; Sanchez, R.; Movilla, L.; Pietersen, K. Why Do We Need to Care about Transboundary Aquifers and How Do We Solve Their Issues? Hydrogeol. J. 2023, 31, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Ruan, H.; Wang, T.; Yu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Kulmatov, R. Sustainable Use of Groundwater Resources in the Transboundary Aquifers of the Five Central Asian Countries: Challenges and Perspectives. Water 2020, 12, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapiyev, V.; Wade, A.J.; Shahgedanova, M.; Saidaliyeva, Z.; Madibekov, A.; Severskiy, I. The Hydrochemistry and Water Quality of Glacierized Catchments in Central Asia: A Review of the Current Status and Anticipated Change. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 38, 100960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Jayakumar, R.; Shrestha, S.; Han, Z. Assessment of Transboundary Aquifer Resources in Asia: Status and Progress towards Sustainable Groundwater Management. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 20, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenova, D.; Sarsekova, D.; Absametov, M.; Murtazin, Y.; Sagin, J.; Trushel, L.; Miroshnichenko, O. The Study of Groundwater in the Zhambyl Region, Southern Kazakhstan, to Improve Sustainability. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazhiyev, S.; Murtazin, Y.; Sotnikov, Y.; Rakhimova, V.; Adenova, D.; Abdizhalel, M.; Yerezhep, D. Geoinformation and Analytical Support for the Development of Promising Aquifers for Pasture Water Supply in Southern Kazakhstan. Water 2025, 17, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOST 26449.1-85; Stationary Distillation Desalting Units. Methods of Saline Water Chemical Analysis. USSR National Committee on Standards: Moscow, Russia, 1985.
- ST RK 1015-2000; WATER Gravimetric Method for Determination of Sulfate Content in Natural and Waste Waters. Committee for Standardization, Metrology and Certification of the Ministry of Energy, Industry and Trade of the Republic of Kazakhstan (Gosstandart): Astana, Kazakhstan, 2000.
- GOST 33045-2014; WATER Methods for Determination of Nitrogen-Containing Substances. Standartinform: Moscow, Russia, 2014.
- ST RK ISO6332-2008; Water Quality. Determination of Iron Content. Spectrometric Method Using 1,10-Phenanthroline. Committee for Standardization, Metrology and Certification of the Ministry of Energy, Industry and Trade of the Republic of Kazakhstan, (Gosstandart): Astana, Kazakhstan, 2008.
- ST RK 2727-2015; Water Quality Method for Determination of Fluorides. Committee for Standardization, Metrology and Certification of the Ministry of Energy, Industry and Trade of the Republic of Kazakhstan (Gosstandart): Astana, Kazakhstan, 2015.
- ST RK ISO10523-2013; Water Quality. Determination of pH. Committee for Standardization, Metrology and Certification of the Ministry of Energy, Industry and Trade of the Republic of Kazakhstan (Gosstandart): Astana, Kazakhstan, 2013.
- GOST 23268.16-78; Drinking Medicinal, Medicinal-Table and Natural Table Mineral Water. Methods of Determination of Iodid-Ions. Methods of Saline Water Chemical Analysis. USSR National Committee on Standards: Moscow, Russia, 1978.
- Taylor, R.G.; Scanlon, B.; Döll, P.; Rodell, M.; van Beek, R.; Wada, Y.; Longuevergne, L.; Leblanc, M.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Edmunds, M.; et al. Ground Water and Climate Change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The United Nations World Water Development Report 2022: Groundwater: Making the Invisible Visible//UNESCO, Paris. Available online: https://www.unwater.org/publications/un-world-water-development-report-2022 (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- Xue, Y.; Niu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Jia, L.; Guo, S. Current Status and Future Research of Groundwater Under Climate Change: A Bibliometric Analysis. Water 2024, 16, 3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yessenzholov, B.; Khussainov, A.; Kakabayev, A.; Plachinta, I.; Bayazitova, Z.; Kyzdarbekova, G.; Zhamkenov, U.; Ramazanova, M. Assessment of Hydrometeorological Impacts of Climate Change on Water Bodies in Northern Kazakhstan. Water 2024, 16, 2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedden-Nicely, D.R.; Kaiser, K.E. Water Governance in an Era of Climate Change: A Model to Assess the Shifting Irrigation Demand and Its Effect on Water Management in the Western United States. Water 2024, 16, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsz, A.A.; Sobkowiak, L.; Styszyńska, A.; Wrzesiński, D.; Perz, A. The Thermal State of the North Atlantic Ocean and Hydrological Droughts in the Warta River Catchment in Poland during 1951–2020. Water 2023, 15, 2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, S.A.; Irvine, D.J.; Rau, G.C.; Bayer, P.; Menberg, K.; Blum, P.; Jamieson, R.C.; Griebler, C.; Kurylyk, B.L. Global Groundwater Warming Due to Climate Change. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepikova, M.; Bense, V.; Le Borgne, T.; Guihéneuf, N.; Bour, O. Impact of Groundwater Extraction on Subsurface Thermal Regimes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2025, 20, 54048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, D.J.; Singha, K.; Kurylyk, B.L.; Briggs, M.A.; Sebastian, Y.; Tait, D.R.; Helton, A.M. Groundwater-Surface Water Interactions Research: Past Trends and Future Directions. J. Hydrol. 2024, 644, 132061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenova, D.; Tazhiyev, S.; Sagin, J.; Absametov, M.; Murtazin, Y.; Trushel, L.; Miroshnichenko, O.; Zaryab, A. Groundwater Quality and Potential Health Risk in Zhambyl Region, Kazakhstan. Water 2023, 15, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).