Optimal Control of Iron Release in Drinking Water Distribution Systems Fed with Desalinated Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Equipment
2.2. Experimental Procedure
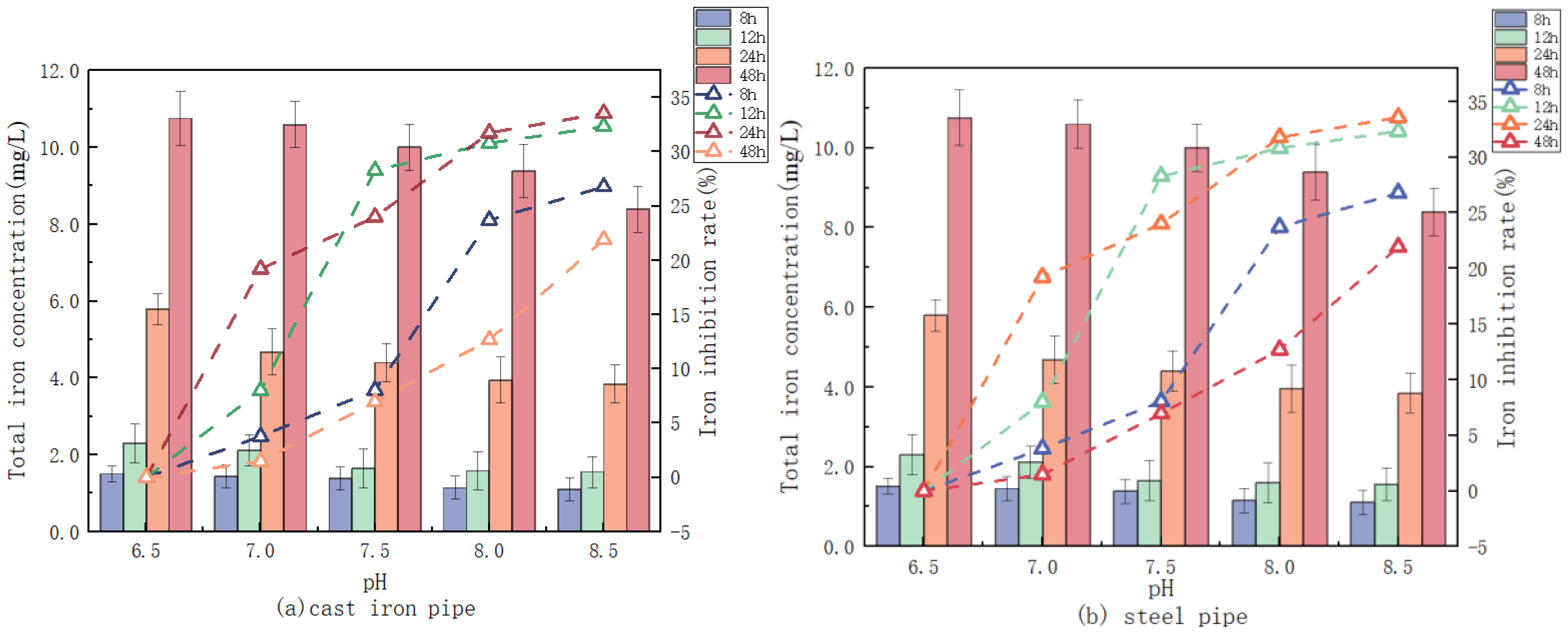
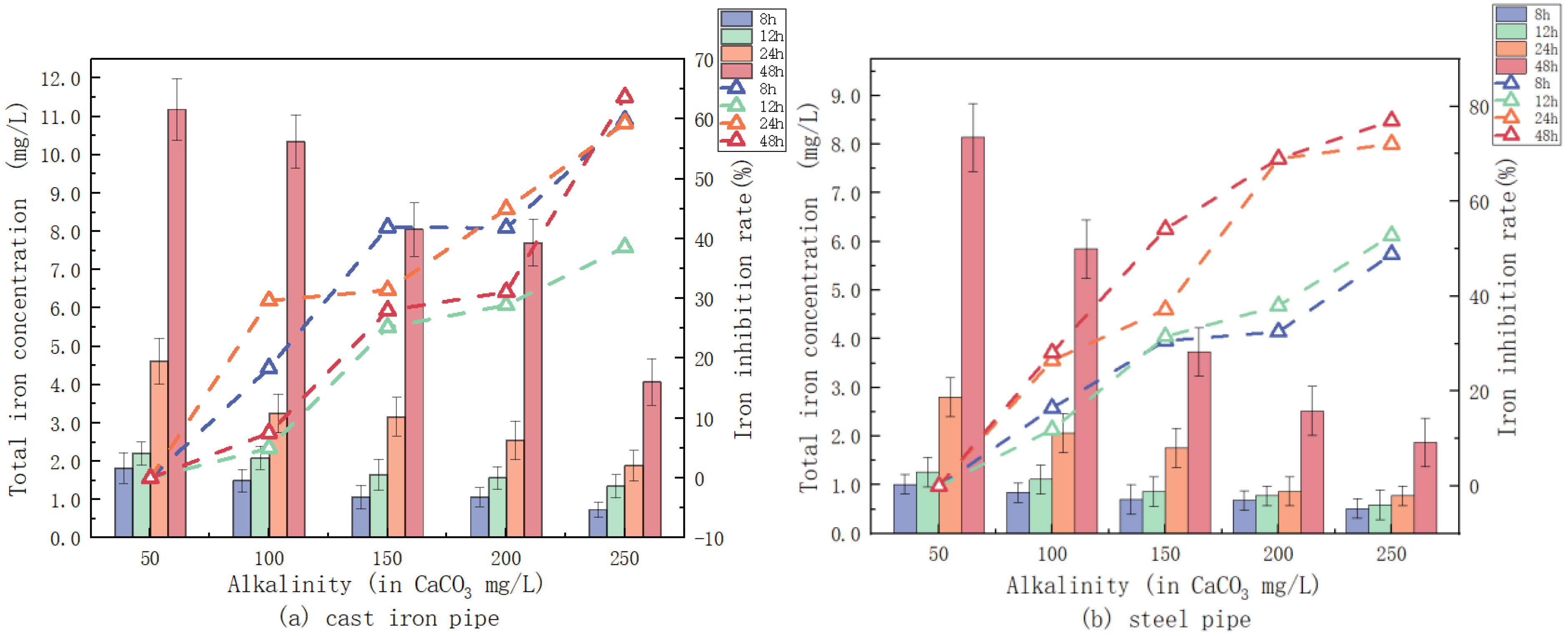
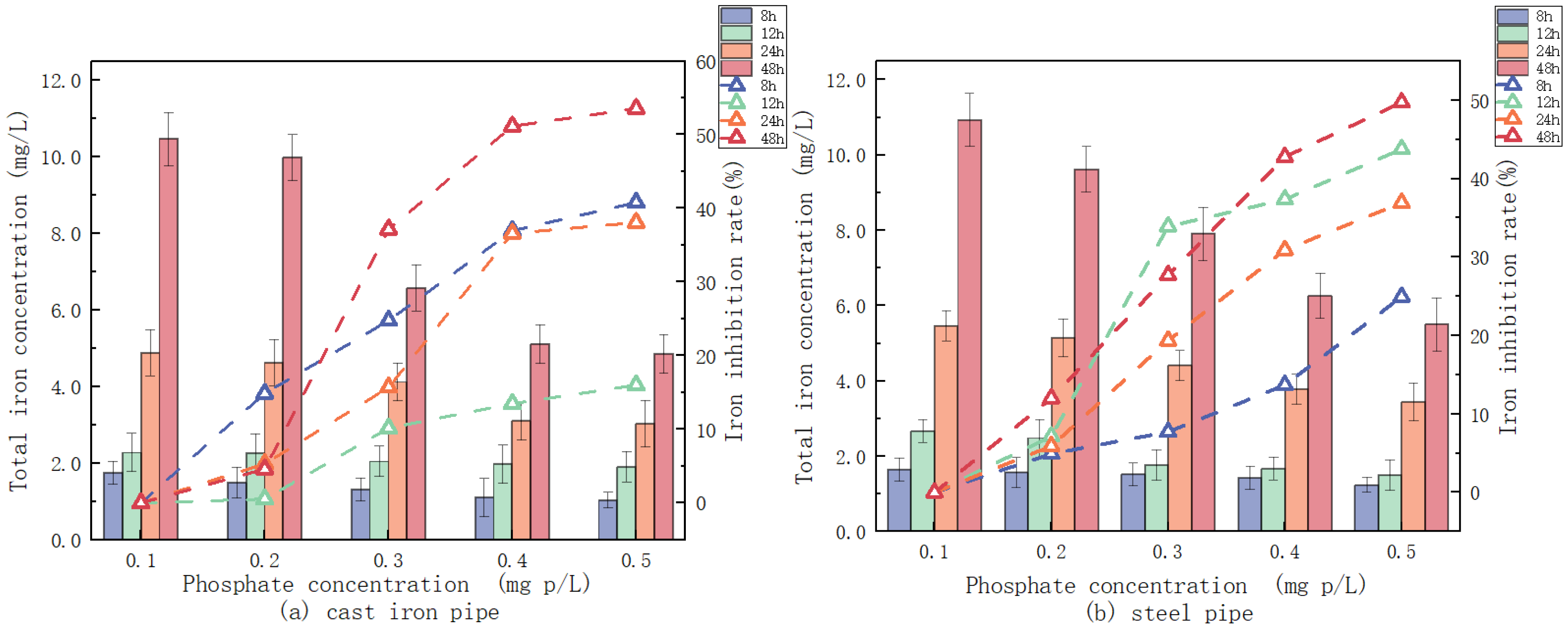
2.2.1. Effect of pH, Alkalinity, and Phosphate on Iron Release
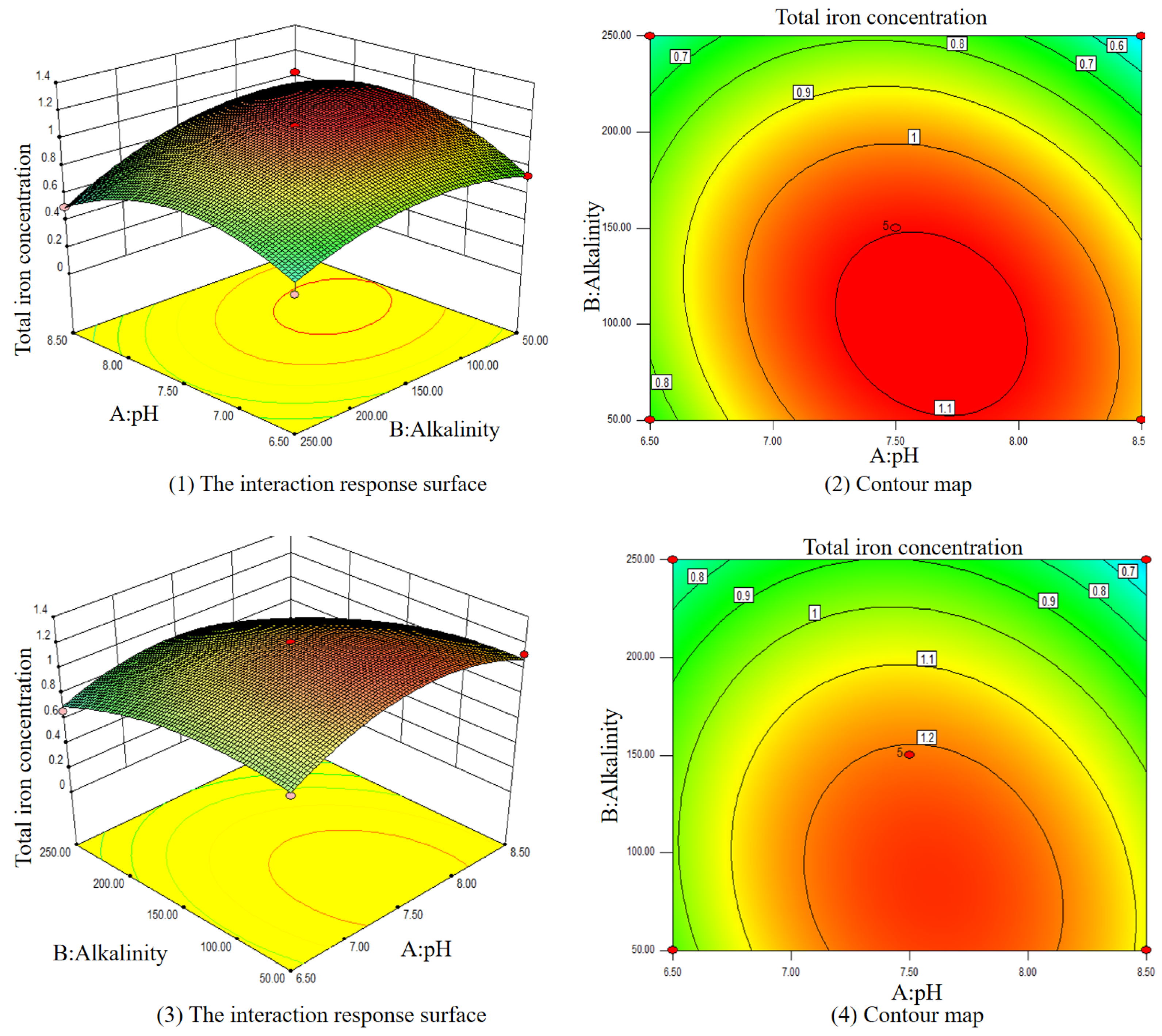
2.2.2. Optimal Control of Iron Release
2.3. Experimental Water and Test Indicators
2.4. Characterization of Pipe Scale
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Pipe Scales
3.1.1. Micro-Morphology (SEM)
3.1.2. Elemental Composition (XRF)
3.1.3. Chemical Composition (XRD)
3.2. Variations in Total Iron Concentrations Under Different pH, Alkalinity, and Phosphate Levels
3.2.1. pH Influence on the Release of Iron
3.2.2. Alkalinity Influence on the Release of Iron
3.2.3. Phosphate Influence on the Release of Iron
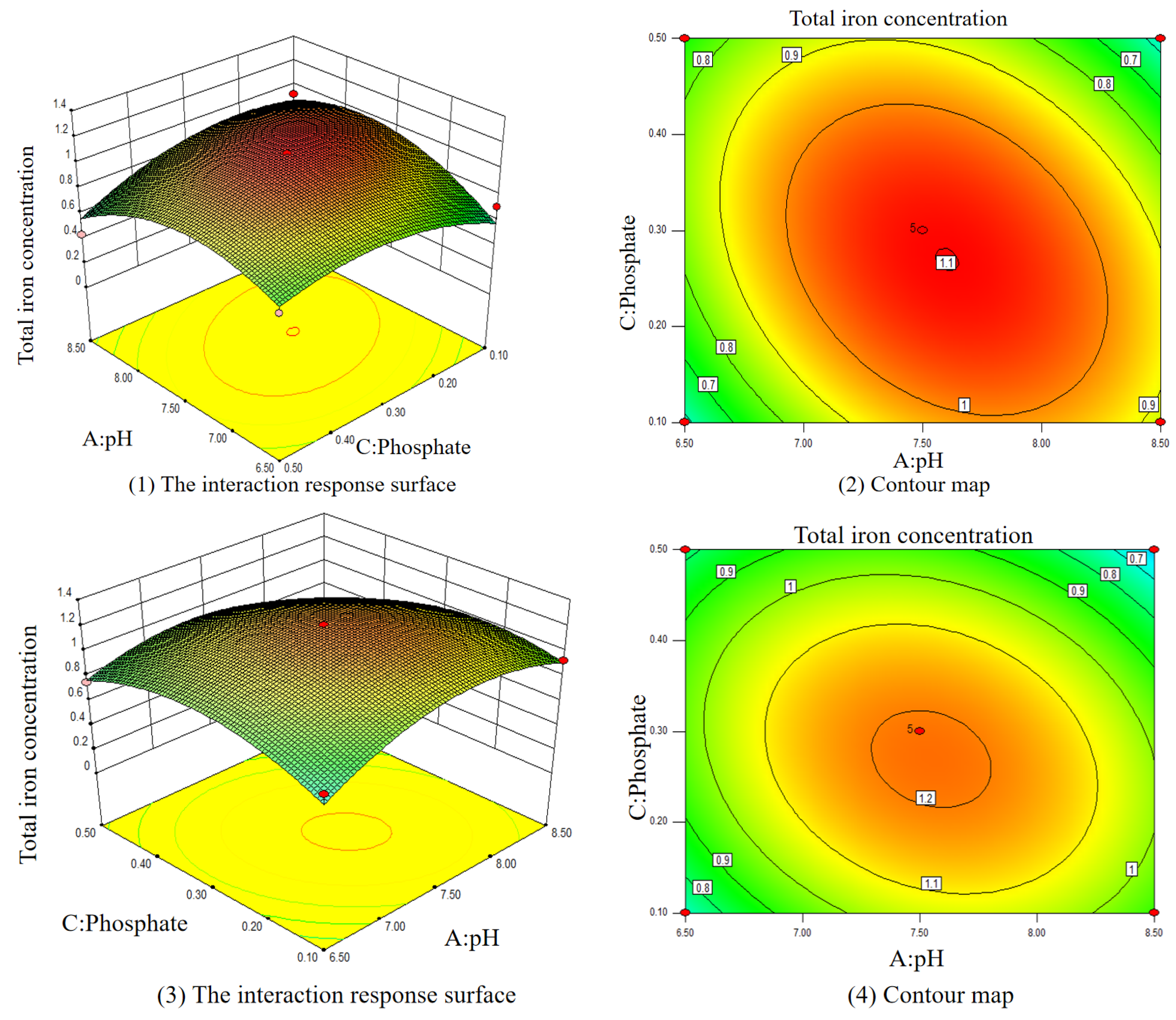
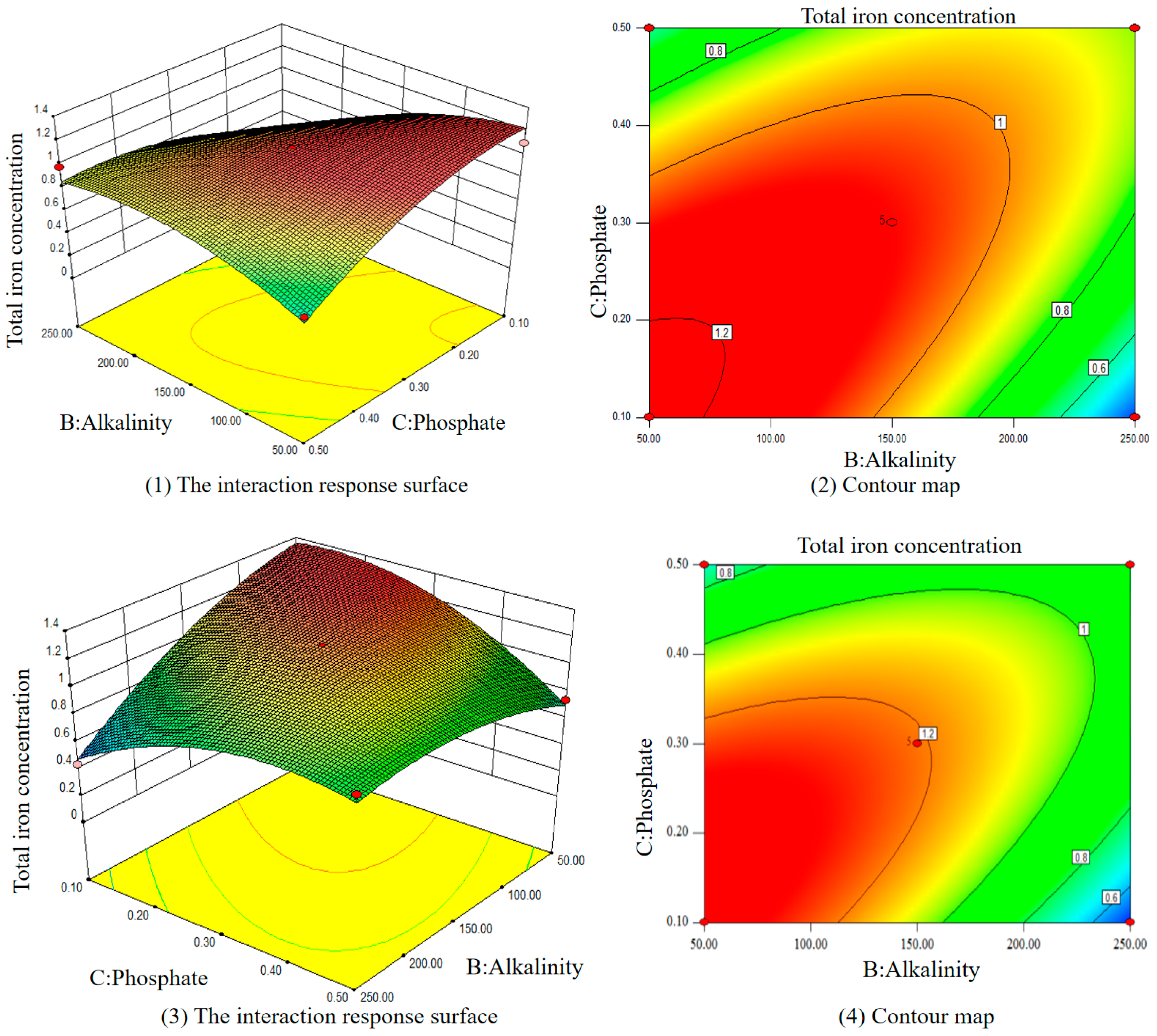
3.3. Optimal Condition of Iron Release Control
3.3.1. Variance Analysis
3.3.2. Effects of Multiple Varied Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Lin, X.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Li, L.; Qiang, Z. Modeling iron release from cast iron pipes in an urban water distribution system caused by source water switch. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 110, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, S.; Smith, K.; Yu, K.; Hu, H.; Jiang, W.; Li, Y. Characterization of corrosion scale formed on stainless steel delivery pipe for reclaimed water treatment. Water Res. 2016, 88, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avramidi, M.; Loizou, C.; Kyriazi, M.; Malamis, D.; Kalli, K.; Hadjicharalambous, A.; Kollia, C. Optimization of the Quality of Reclaimed Water from Urban Wastewater Treatment in Arid Region: A Zero Liquid Discharge Pilot Study Using Membrane and Thermal Technologies. Membranes 2025, 15, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhimathi, G.; Chellaswamy, C.; Geetha, T.S.; Arunmozhi, S.A. Integrating Regression and Boosting Techniques for Enhanced River Water Quality Monitoring in the Cauvery Basin: A Seasonal and Sustainable Approach. Water Environ. Res. 2025, 97, e70128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C. Early period corrosion and scaling characteristics of ductile iron pipe for ground water supply with sodium hypochlorite disinfection. Water Res. 2020, 176, 115742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, P.; Snoeyink, V.L.; Lytle, D.A.; Kriven, W.M. Iron Corrosion Scales: Model for Scale Growth, Iron Release, and Colored Water Formation. J. Environ. Eng. 2004, 130, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Han, B.; Chen, R.; Shi, B. Structural transformation and potential toxicity of iron-based deposits in drinking water distribution systems. Water Res. 2019, 165, 114999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C. Iron release in drinking water distribution systems by feeding desalinated seawater: Characteristics and control. Desalinat. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 9728–9735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M. Controlling corrosion in drinking water distribution systems: A grand challenge for the 21st century. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, X.; Fan, A.; Fu, L.; Gao, C. An innovative beneficial reuse of seawater concentrate using bipolar membrane electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 449, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Liu, X. The key drivers for the changes in global water scarcity: Water withdrawal versus water availability. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musie, W.; Gonfa, G. Fresh water resource, scarcity, water salinity challenges and possible remedies: A review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaner, A.; Tripler, E.; Hadas, E.; Ben-Gal, A. Feasibility of desalination as an alternative to irrigation with water high in salts. Desalination 2017, 416, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehri, A.A.; Duranceau, S.J.; Taylor, J.S.; Stone, E.D. Investigating iron release in distribution systems with blend variations of source waters and phosphate inhibitors. Desalination Water Treat. 2009, 8, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnhack, L.; Penn, R.; Lahav, O. Quality criteria for desalinated water and introduction of a novel, cost effective and advantageous post treatment process. Desalination 2008, 221, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahav, O.; Salomons, E.; Ostfeld, A. Chemical stability of inline blends of desalinated, surface and ground waters: The need for higher alkalinity values in desalinated water. Desalination 2009, 239, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnhack, L.; Voutchkov, N.; Lahav, O. Fundamental chemistry and engineering aspects of post-treatment processes for desalinated water—A review. Desalination 2011, 273, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, S.A.; Dietz, J.D.; Mutoti, G.; Taylor, J.S.; Randall, A.A.; Cooper, C. Red Water Release in Drinking Water Distribution Systems. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2005, 97, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Schonberger, K.D.; Korshin, G.V.; Ferguson, J.F.; Meyerhofer, P.; Desormeaux, E.; Luckenbach, H. Effects of blending of desalinated water with treated surface drinking water on copper and lead release. Water Res. 2010, 44, 4057–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Lee, K.; Lee, J.S.; Ko, Y.H. Persistent organic alkalinity in the ocean. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2024, 387, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeek, S.A.; Hale, C.; Bedoya-Lora, F.E.; Campbell, K.S.; Kelsall, G.H.; Hankin, A. Protectiveness and stability of iron carbonate films on carbon steel in mildly alkaline aqueous alkanolamine CO2 environments. Corros. Sci. 2023, 227, 111773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Schonberger, K.D.; Peng, C.Y.; Ferguson, J.F.; Desormeaux, E.; Meyerhofer, P.; Luckenbach, H.; Korshin, G.V. Effects of blending of desalinated and conventionally treated surface water on iron corrosion and its release from corroding surfaces and pre-existing scales. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3817–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W. Study on the Chemical Stability of Water Quality in Urban Water Supply Systems and Its Control Methods. Master’s Thesis, Hunan University, Changsha, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lytle, D.A.; Snoeyink, V.L. The effect of pH and dissolved inorganic carbon on the properties of iron colloldal suspensions. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2003, 52, 165–181.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytle, D.A.; Sarin, P.; Snoeyink, V.L. The effect of chloride and orthophosphate on the release of iron from a cast iron pipe section. J. Water Supply: Res. Technol. 2005, 54, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darre, C.N.; Toor, S.G. Desalination of Water: A Review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2018, 4, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Y.; Semiat, R.; Rahardianto, A. A perspective on reverse osmosis water desalination: Quest for sustainability. AIChE J. 2017, 63, 1771–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytle, D.A.; Snoeyink, V.L. Effect of orthophosphates and polyphosphates on the properties of iron particles and sus-pensions. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2002, 94, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

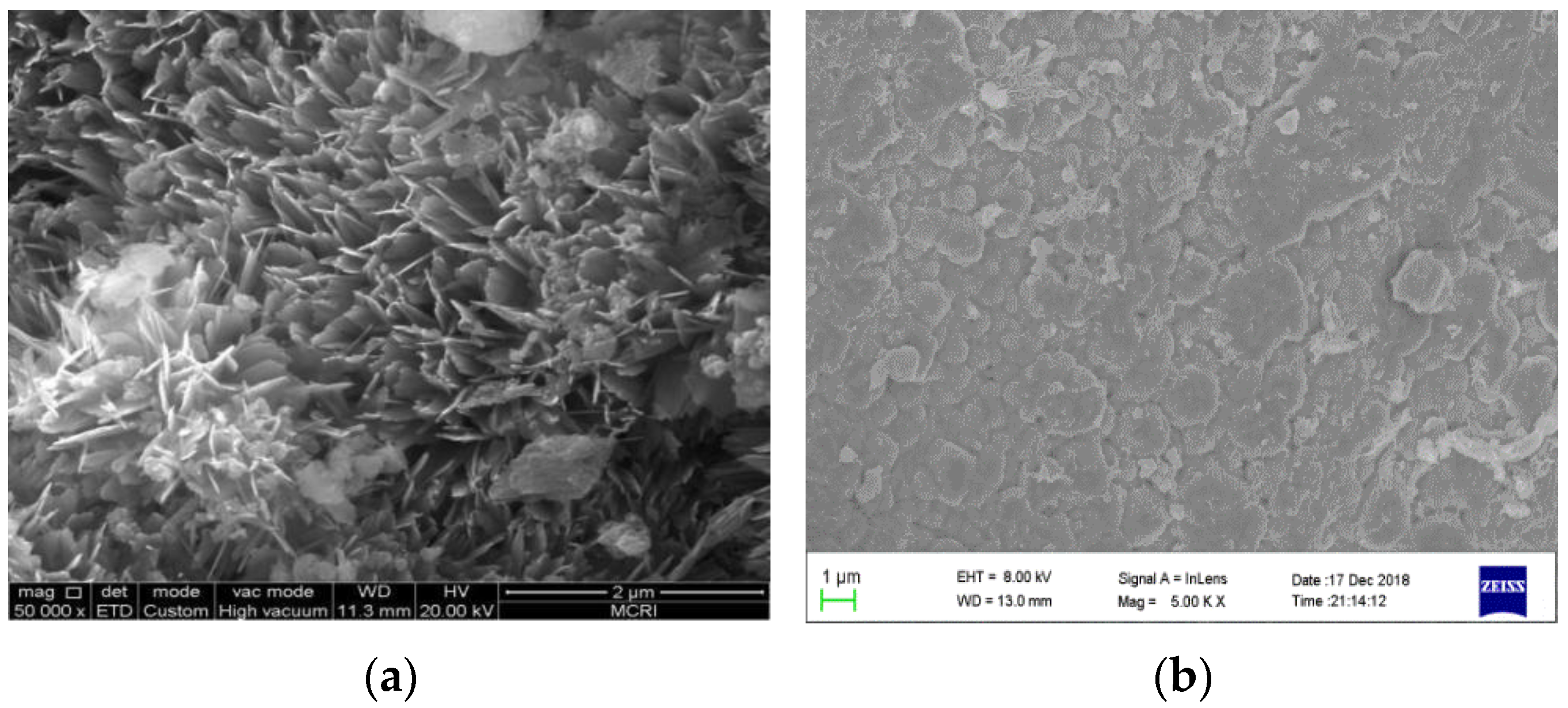
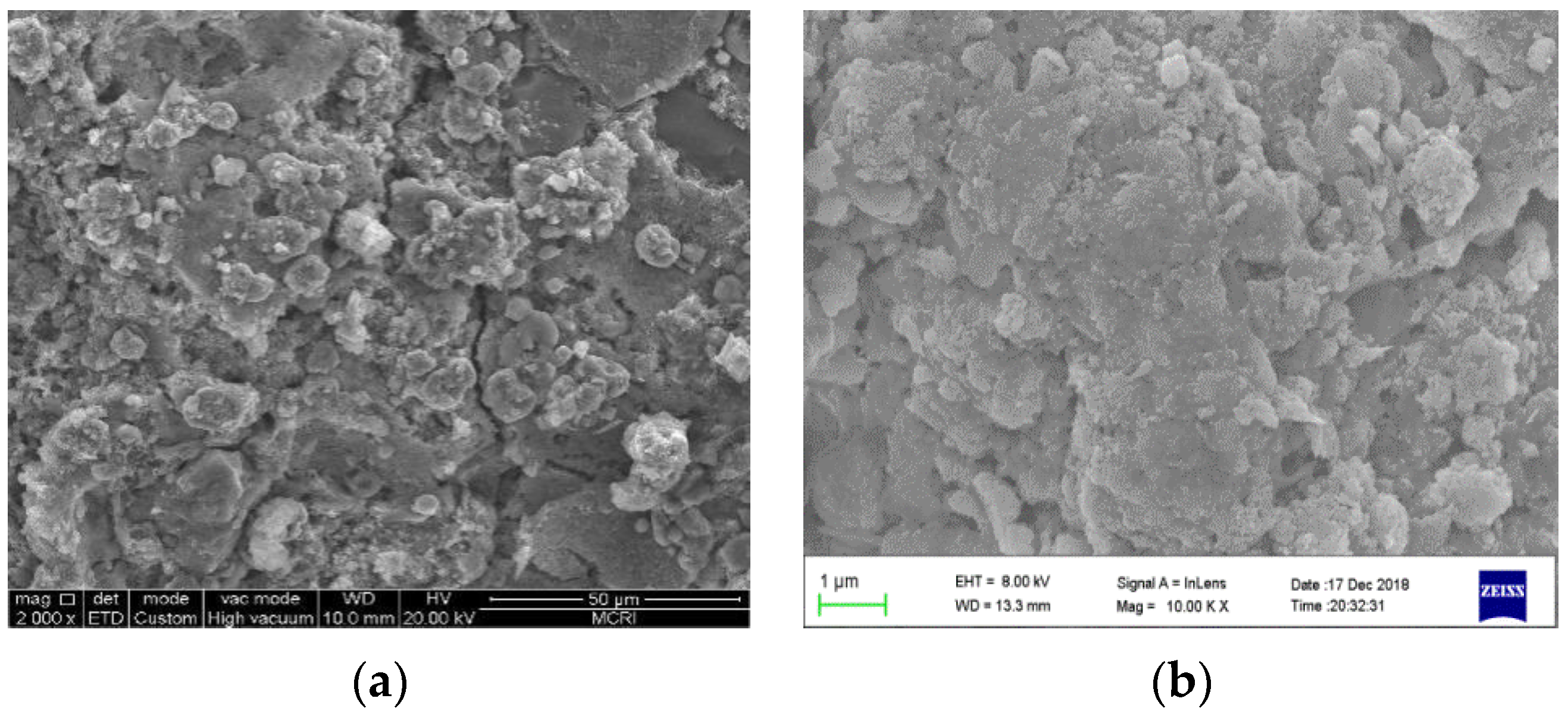
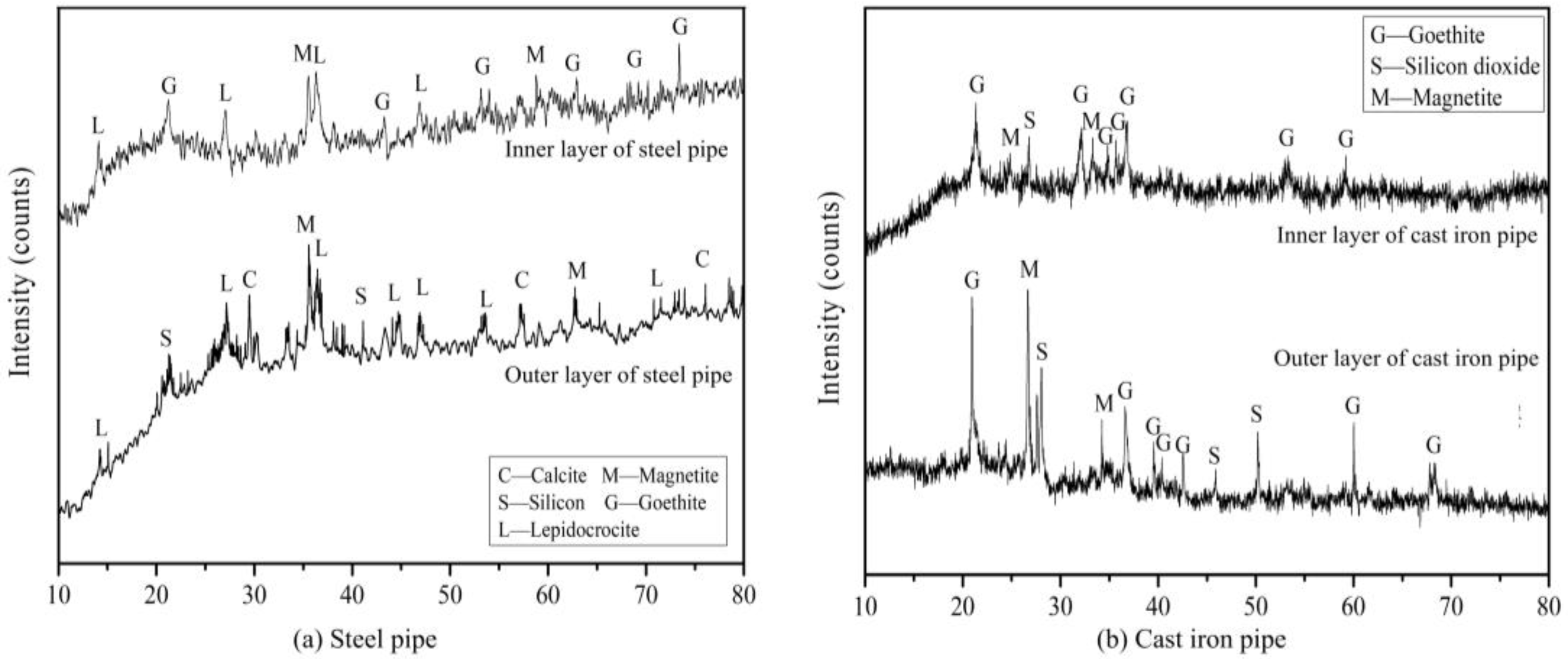
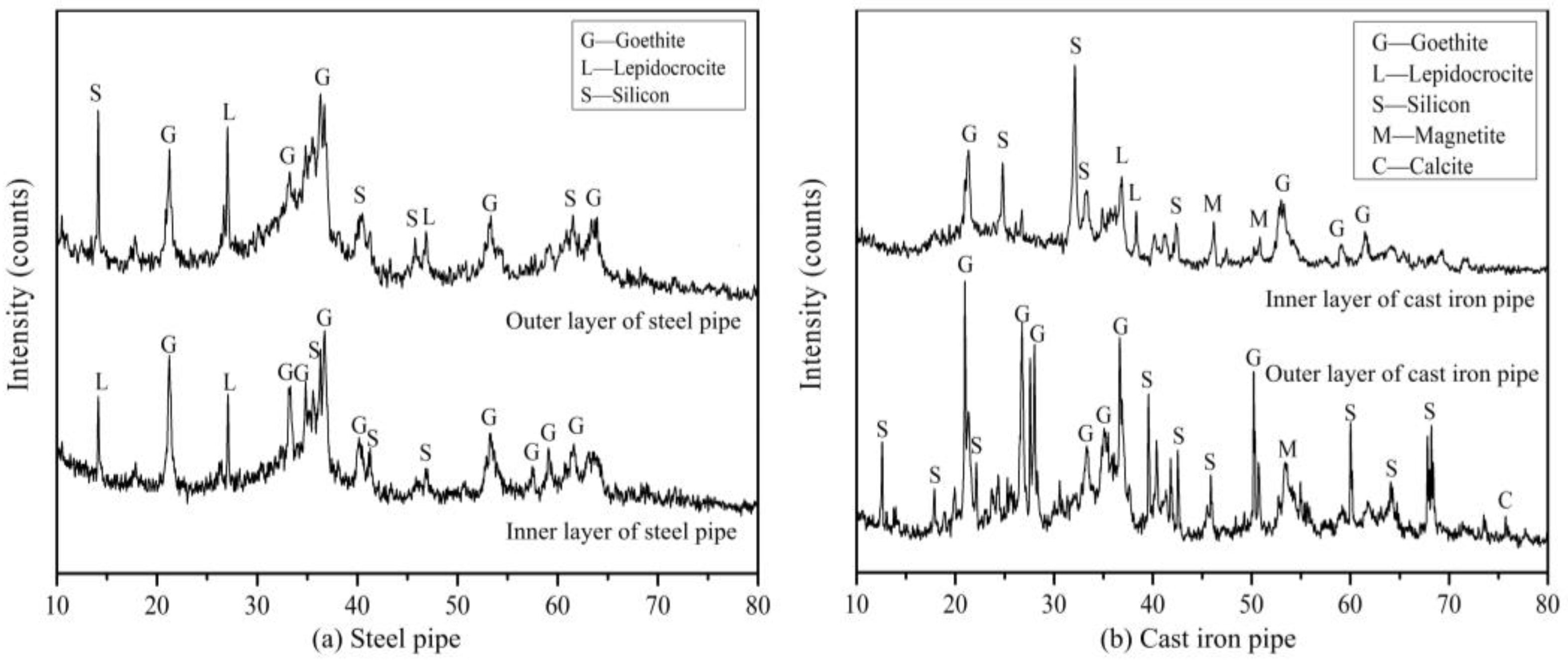
| Group | pH | Alkalinity (CaCO3 mg/L) | Phosphate (P mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7.5 | 150 | 0.3 |
| 2 | 7.5 | 250 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 7.5 | 150 | 0.3 |
| 4 | 7.5 | 150 | 0.3 |
| 5 | 8.5 | 150 | 0.1 |
| 6 | 8.5 | 50 | 0.3 |
| 7 | 7.5 | 250 | 0.1 |
| 8 | 7.5 | 50 | 0.5 |
| 9 | 6.5 | 150 | 0.5 |
| 10 | 6.5 | 50 | 0.3 |
| 11 | 8.5 | 150 | 0.5 |
| 12 | 6.5 | 250 | 0.3 |
| 13 | 7.5 | 150 | 0.3 |
| 14 | 6.5 | 150 | 0.1 |
| 15 | 7.5 | 50 | 0.1 |
| 16 | 8.5 | 250 | 0.3 |
| 17 | 7.5 | 150 | 0.3 |
| Parameter | Content |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.0 |
| Iron content | <0.03 |
| Na+ (mg/L) | 80 |
| Cl− | 50 |
| SO42− | 10 |
| Alkalinity (CaCO3 mg/L) | 5 |
| Hardness (CaCO3 mg/L) | 5 |
| Turbidity | <0.1 |
| Corrosion Layer | State | Fe | O | Si | Ca | Cr | Mg | Mn | Al | S | Cl | Zn | Na |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel pipe inner layer | before | 56.0 | 42 | 0.31 | 0.96 | — | — | 0.32 | 0.11 | 0.33 | 0.04 | 0.05 | — |
| after | 97.3 | — | 1.65 | 0.19 | — | — | — | 0.38 | 0.33 | 0.19 | — | — | |
| Steel pipe outer layer | before | 54.4 | 40 | 0.96 | 1.96 | — | — | 0.36 | 0.55 | 0.36 | 0.05 | — | 0.1 |
| after | 92.5 | — | 4.52 | 0.77 | — | 0.2 | 0.35 | 1.21 | 0.36 | — | 0.1 | — | |
| Cast iron pipe inner layer | before | 89.6 | — | 3.83 | 2.17 | — | 0.26 | 0.32 | 1.07 | 2.84 | — | — | 0.22 |
| after | 90.1 | — | 3.52 | 1.43 | — | 0.2 | 0.42 | 0.92 | 2.84 | — | — | 0.28 | |
| Cast iron pipe outer layer | before | 42.2 | — | 38.4 | 1.61 | 0.1 | 1.34 | 0.22 | 9.29 | 10.3 | — | 0.06 | 1.04 |
| after | 52.1 | — | 30.6 | 1.31 | 0.1 | 1.3 | 0.44 | 9.29 | 0.44 | — | 0.1 | 0.93 |
| Project | Quadratic Sum | Variance | Mean Square | F-Number | p Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| model | 1.09 | 9 | 0.12 | 9.66 | 0.0034 | notable |
| A | 0.0077501 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.62 | 0.4578 | quiet |
| B | 0.175 | 1 | 0.17 | 13.93 | 0.0073 | notable |
| C | 0.012 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.97 | 0.3577 | quiet |
| AB | 0.023 | 1 | 0.02 | 1.85 | 0.2157 | quiet |
| AC | 0.053 | 1 | 0.05 | 4.25 | 0.0782 | notable |
| BC | 0.300 | 1 | 0.30 | 23.92 | 0.0018 | notable |
| A2 | 0.243 | 1 | 0.24 | 19.38 | 0.0031 | notable |
| B2 | 0.107 | 1 | 0.11 | 8.52 | 0.0224 | notable |
| C2 | 0.117 | 1 | 0.12 | 9.31 | 0.0185 | notable |
| residual | 0.088 | 7 | 0.01 | |||
| pure error | 0 | 4 | ||||
| total departure | 1.179 | 16 |
| Project | Quadratic Sum | Variance | Mean Square | F-Number | p Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| model | 1.18 | 9 | 0.13 | 37.97 | <0.0001 | notable |
| A | 0.000648 | 1 | 0.00 | 0.19 | 0.6776 | quiet |
| B | 0.246 | 1 | 0.25 | 71.39 | <0.0001 | notable |
| C | 0.030 | 1 | 0.03 | 8.81 | 0.0208 | notable |
| AB | 0.014 | 1 | 0.01 | 3.94 | 0.0876 | quiet |
| AC | 0.034 | 1 | 0.03 | 9.88 | 0.0163 | notable |
| BC | 0.282 | 1 | 0.28 | 81.81 | <0.0001 | notable |
| A2 | 0.240 | 1 | 0.24 | 69.49 | <0.0001 | notable |
| B2 | 0.076 | 1 | 0.08 | 22.18 | 0.0022 | notable |
| C2 | 0.199 | 1 | 0.20 | 57.66 | 0.0001 | notable |
| residual | 0.024 | 7 | 0.00 | |||
| pure error | 0 | 4 | ||||
| total departure | 1.202 | 16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jia, P.; Fan, M.; Wan, T.; Ji, Y.; Zhu, J. Optimal Control of Iron Release in Drinking Water Distribution Systems Fed with Desalinated Water. Water 2025, 17, 2474. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162474
Feng Y, Zhang H, Jia P, Fan M, Wan T, Ji Y, Zhu J. Optimal Control of Iron Release in Drinking Water Distribution Systems Fed with Desalinated Water. Water. 2025; 17(16):2474. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162474
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Yongjia, Hui Zhang, Peixin Jia, Mingzhou Fan, Tao Wan, Yimeng Ji, and Jingyu Zhu. 2025. "Optimal Control of Iron Release in Drinking Water Distribution Systems Fed with Desalinated Water" Water 17, no. 16: 2474. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162474
APA StyleFeng, Y., Zhang, H., Jia, P., Fan, M., Wan, T., Ji, Y., & Zhu, J. (2025). Optimal Control of Iron Release in Drinking Water Distribution Systems Fed with Desalinated Water. Water, 17(16), 2474. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162474






