Multiscale Analysis of Seepage Failure Mechanisms in Gap-Graded Soils Using Coupled CFD-DEM Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
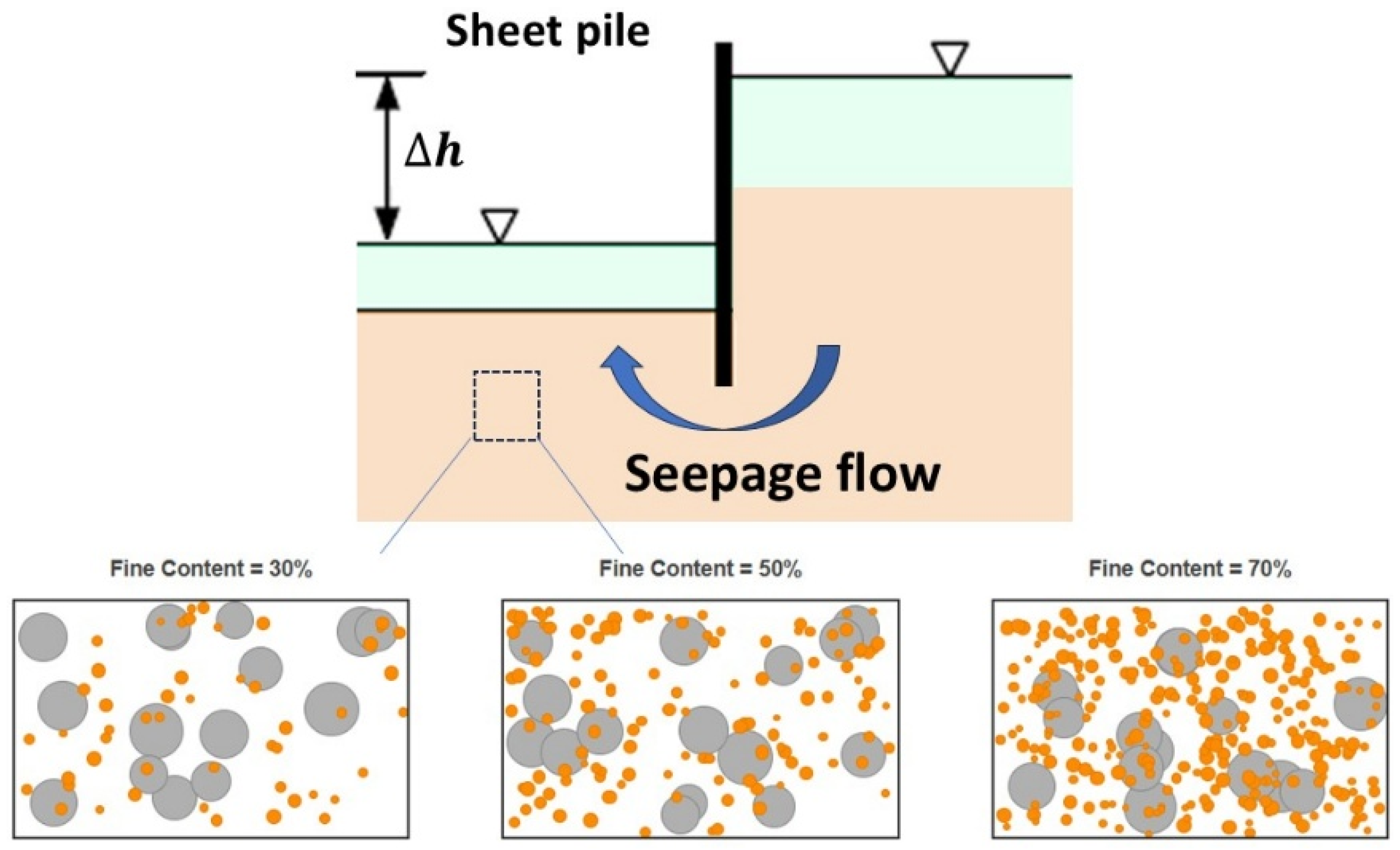
2. Methodology and Numerical Model Setup
2.1. Description of CFD-DEM
2.2. Simulation Process
2.2.1. Material Properties
2.2.2. Numerical Procedure
3. Macroscale Observations of Seepage Erosion
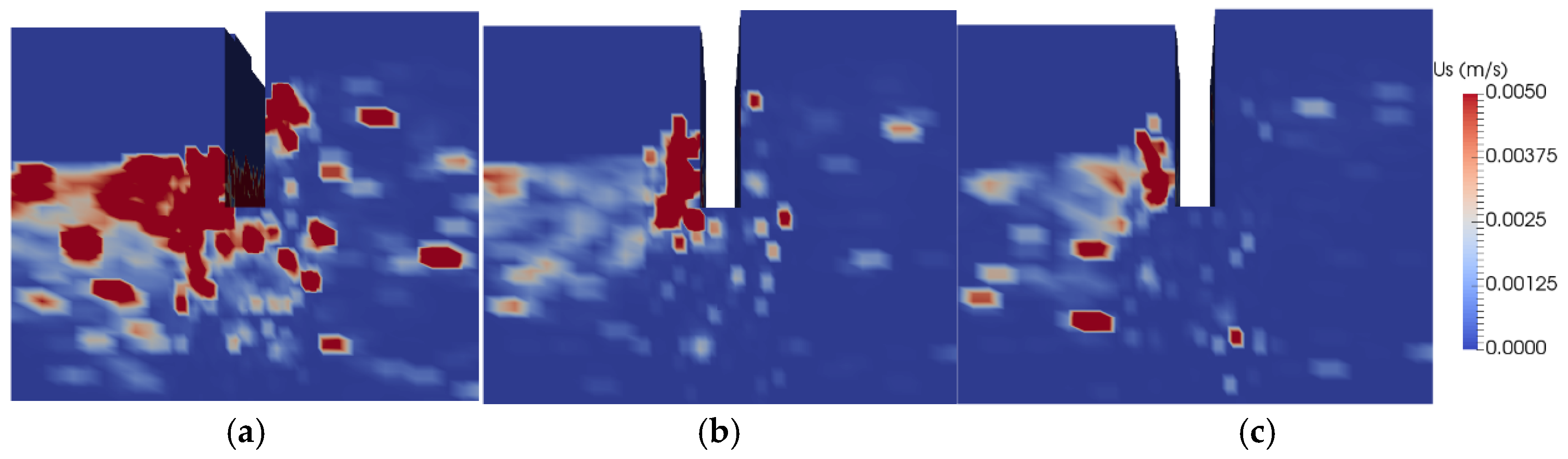
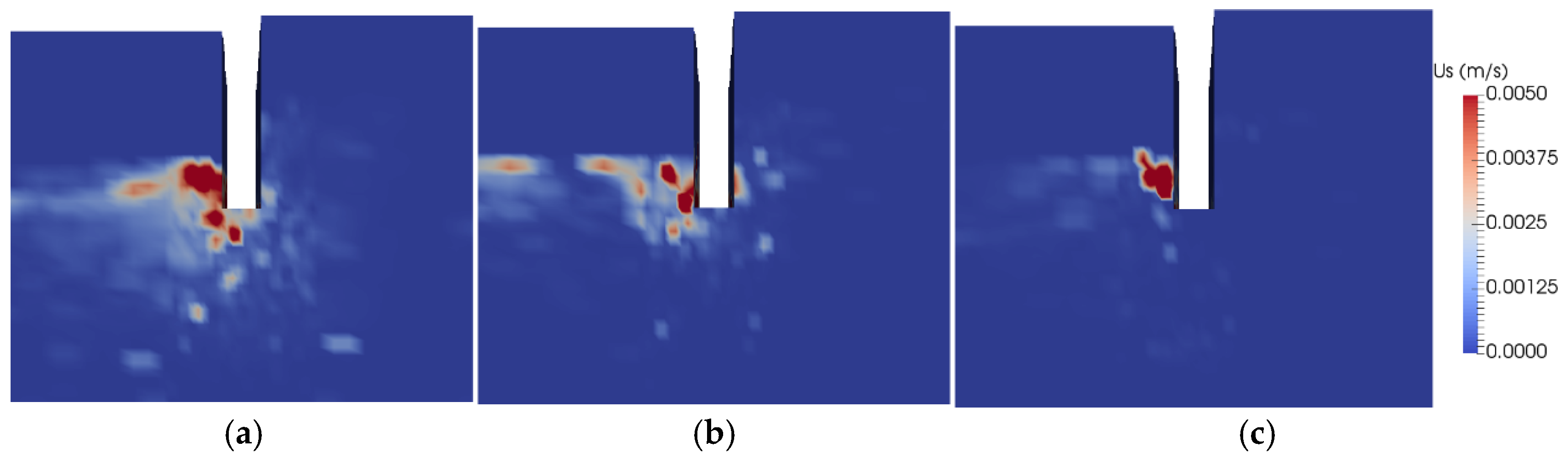
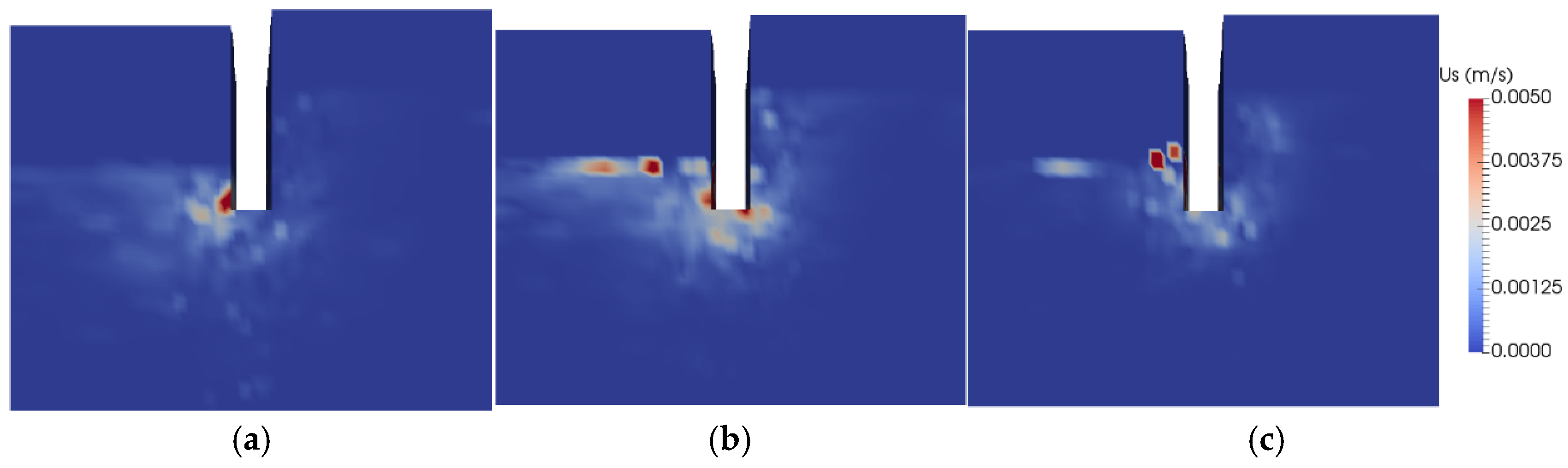
3.1. Spatial Distribution of Particle Velocity
3.2. Evolution of Eroded Mass Ratio
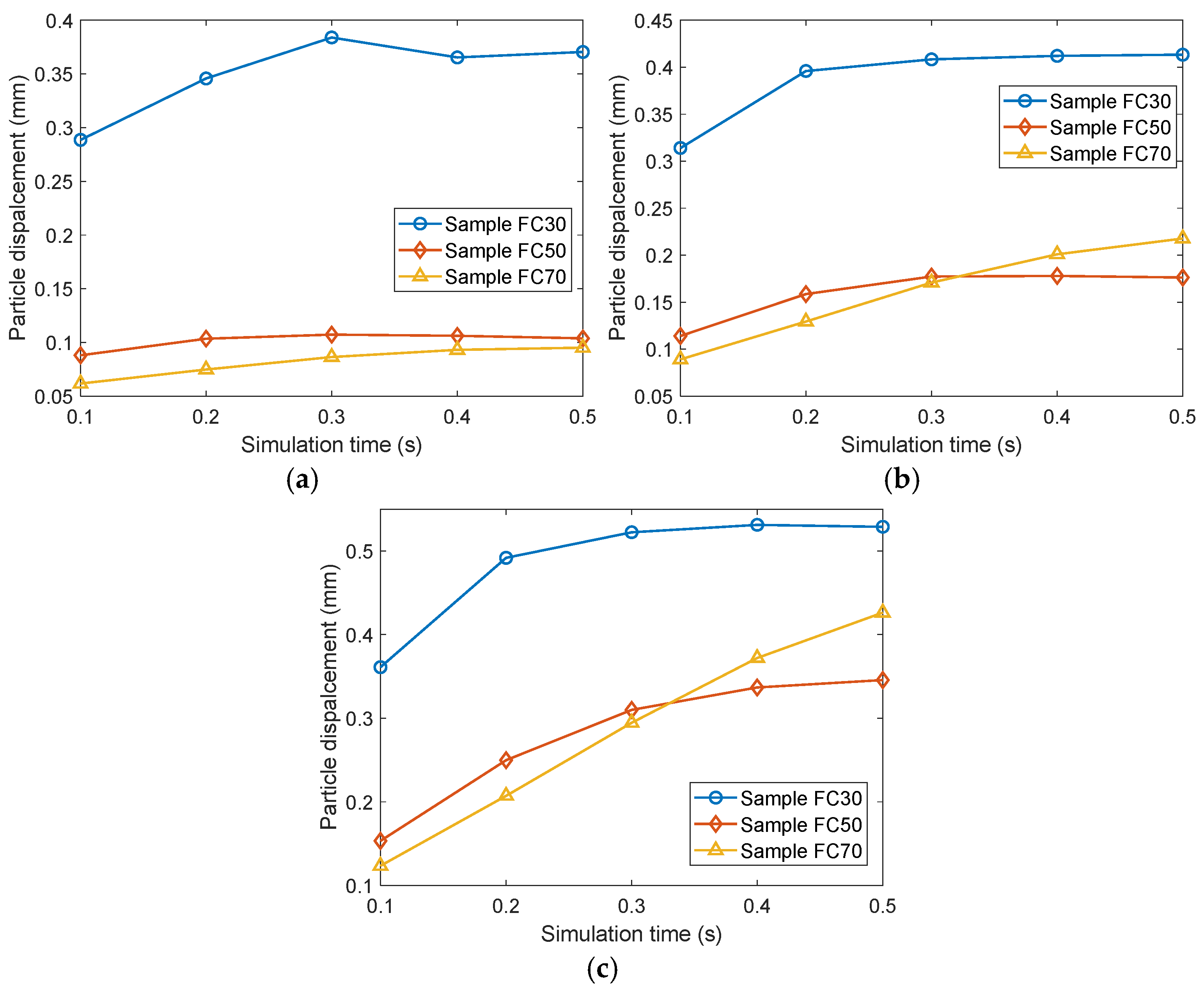
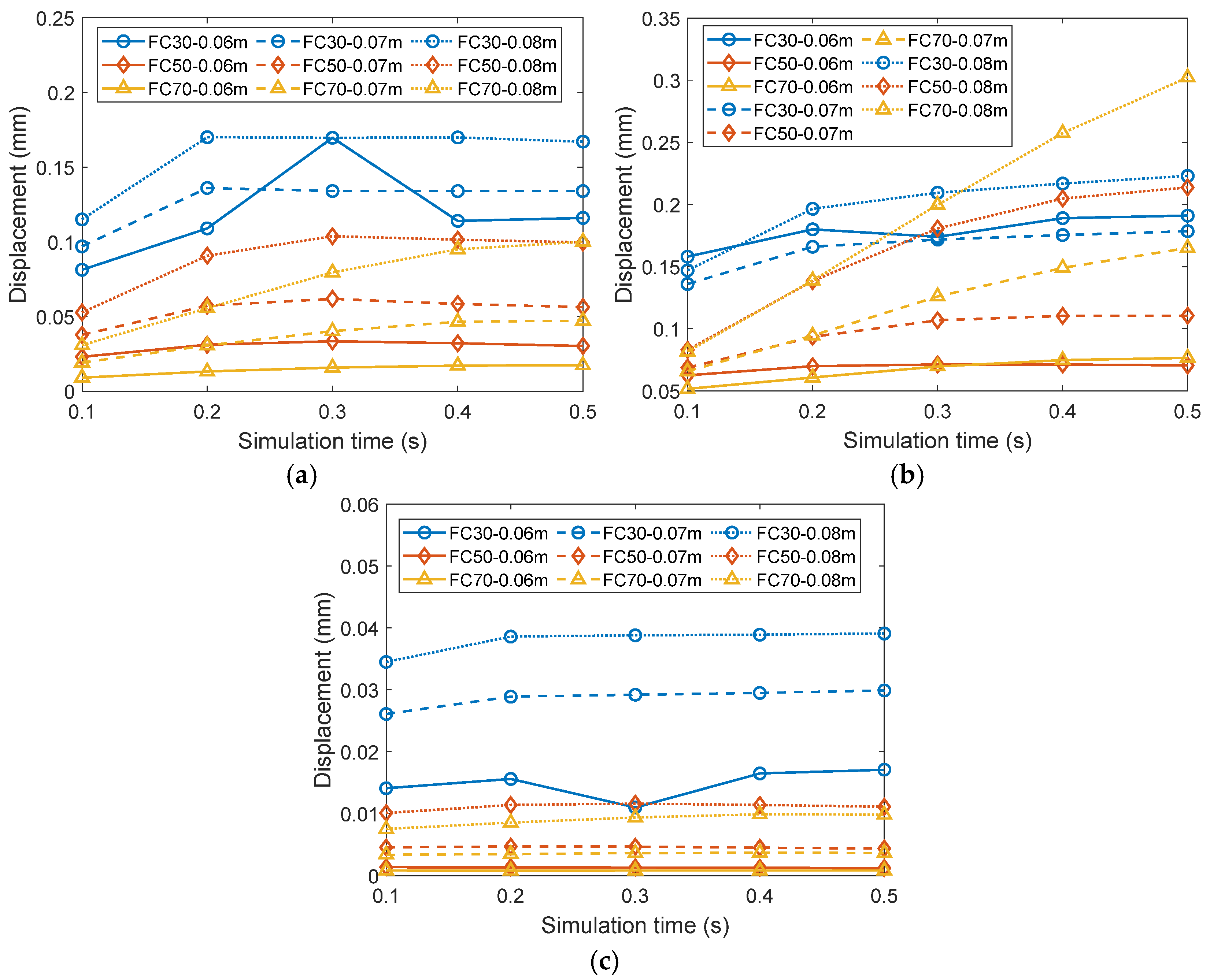
3.3. Evolution of Particle Migration
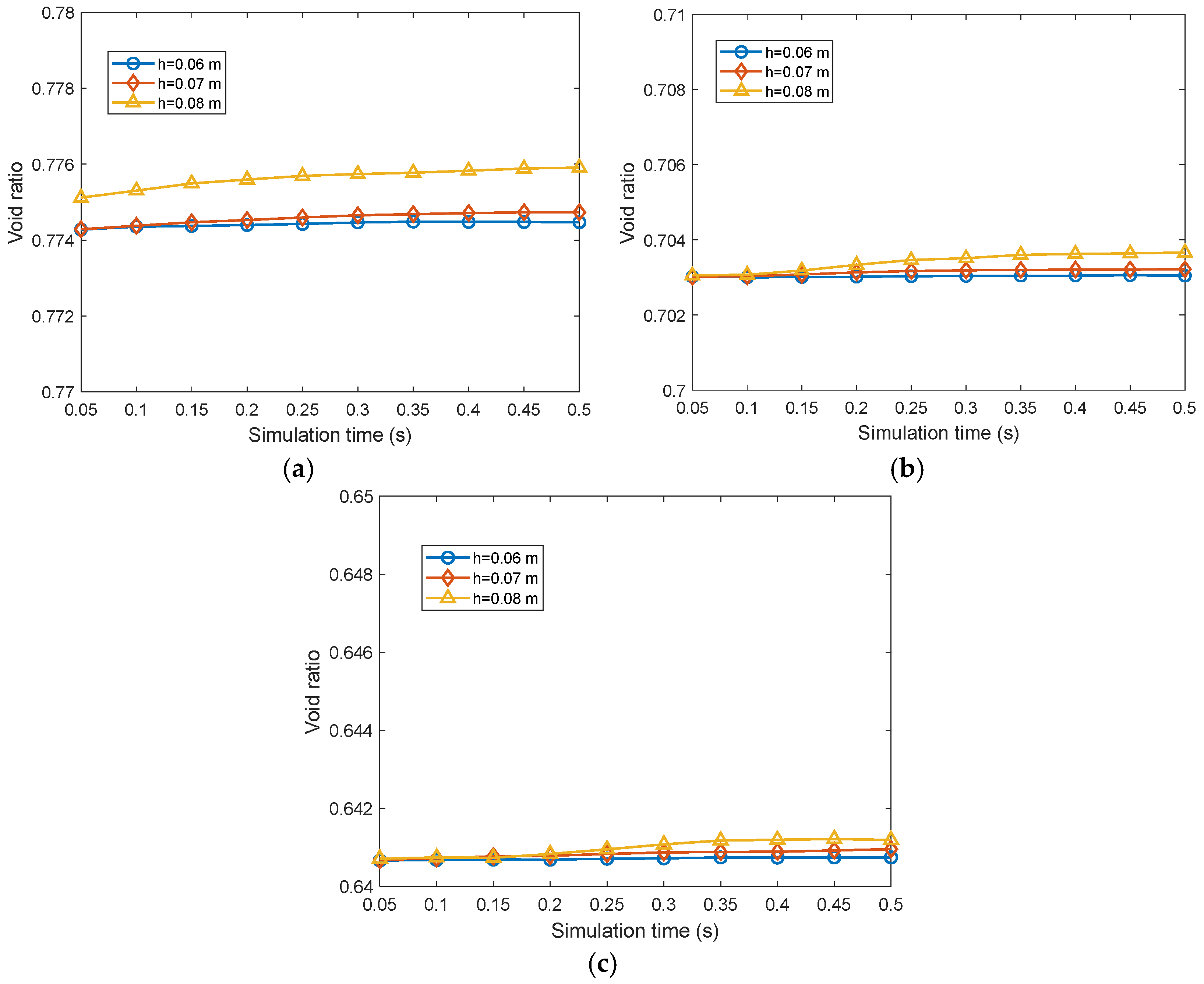
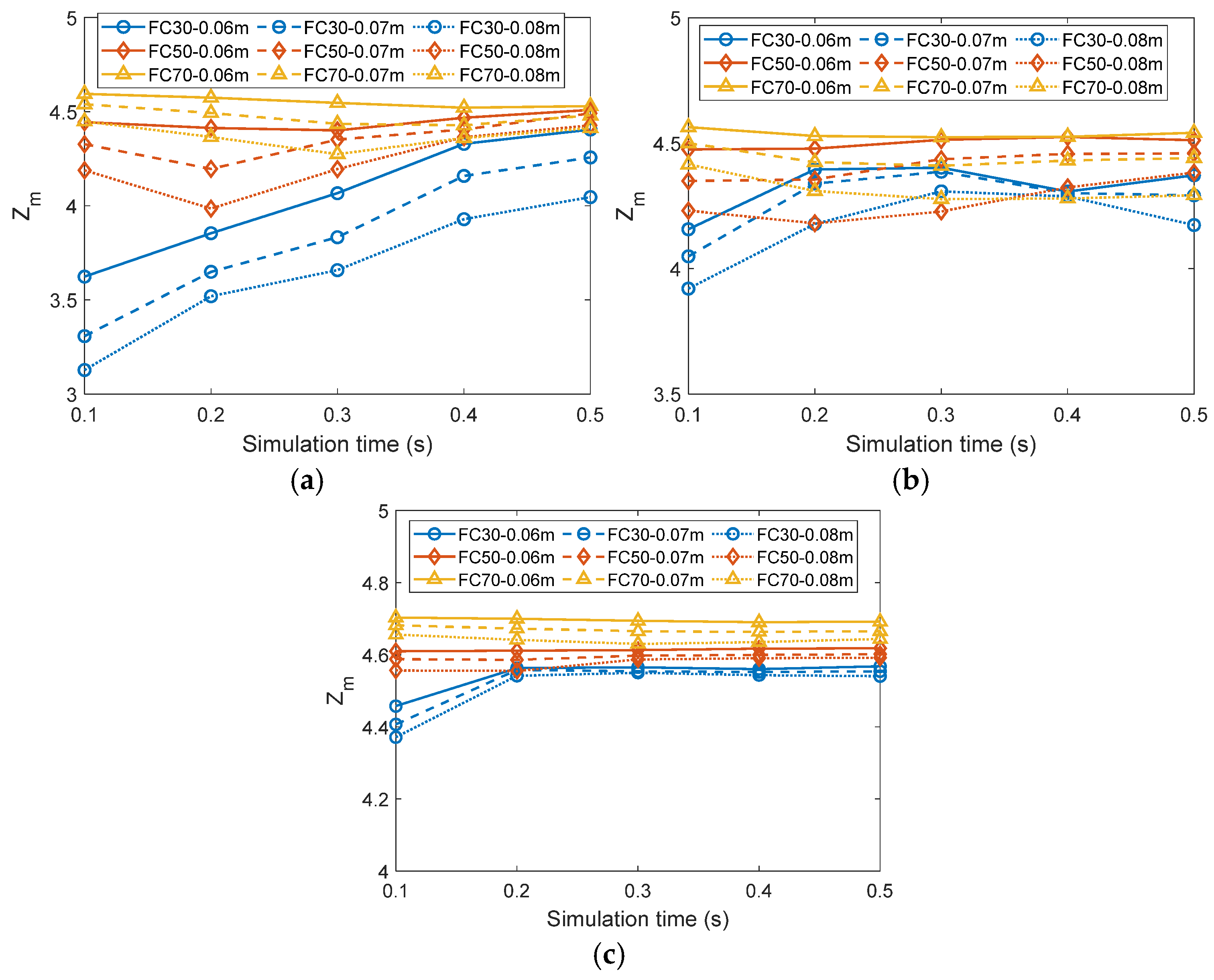
3.4. Evolution of Void Ratio
4. Particle-Scale Observations and Discussions
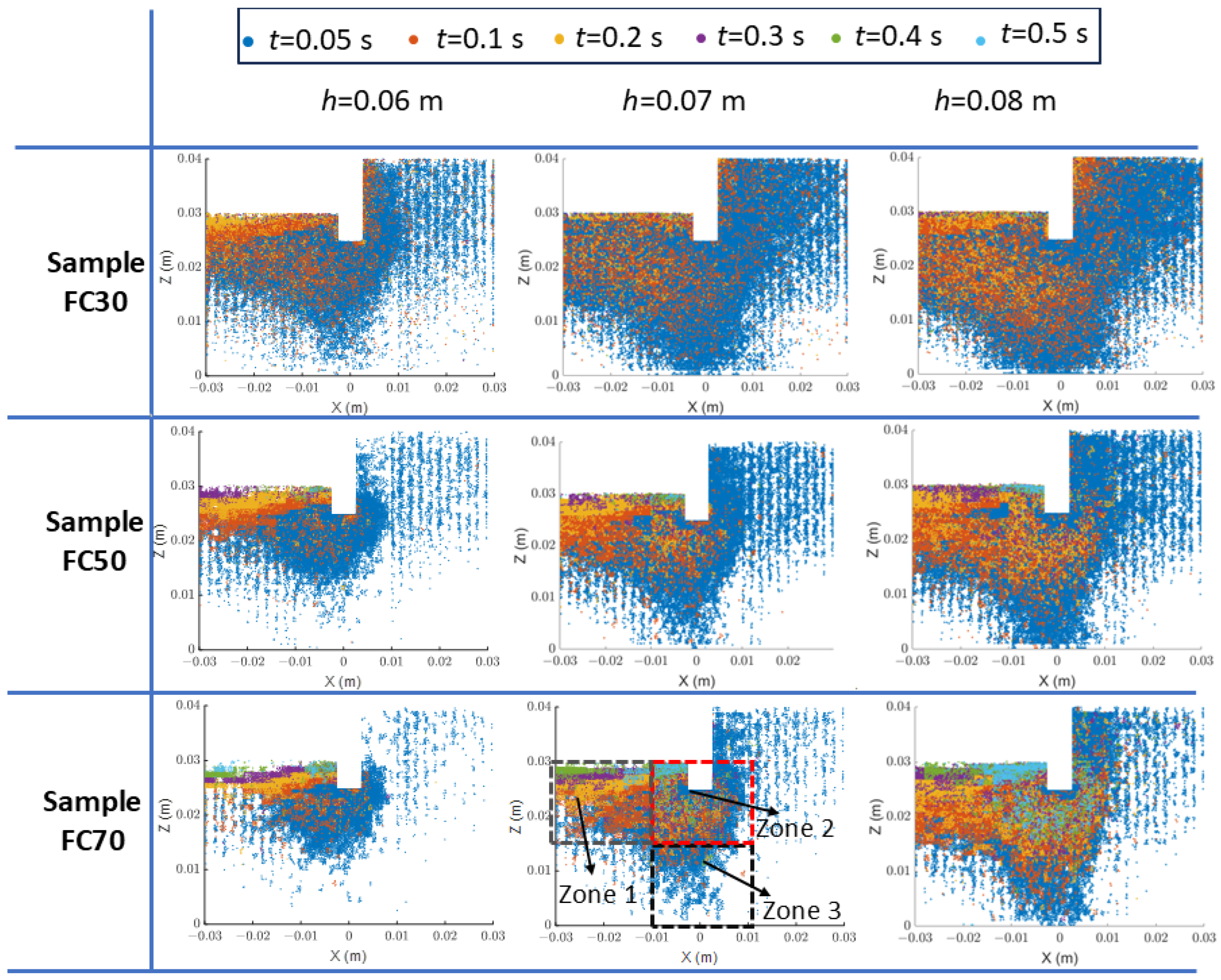
4.1. Initial Particle Position Tracking
4.2. Coordination Number
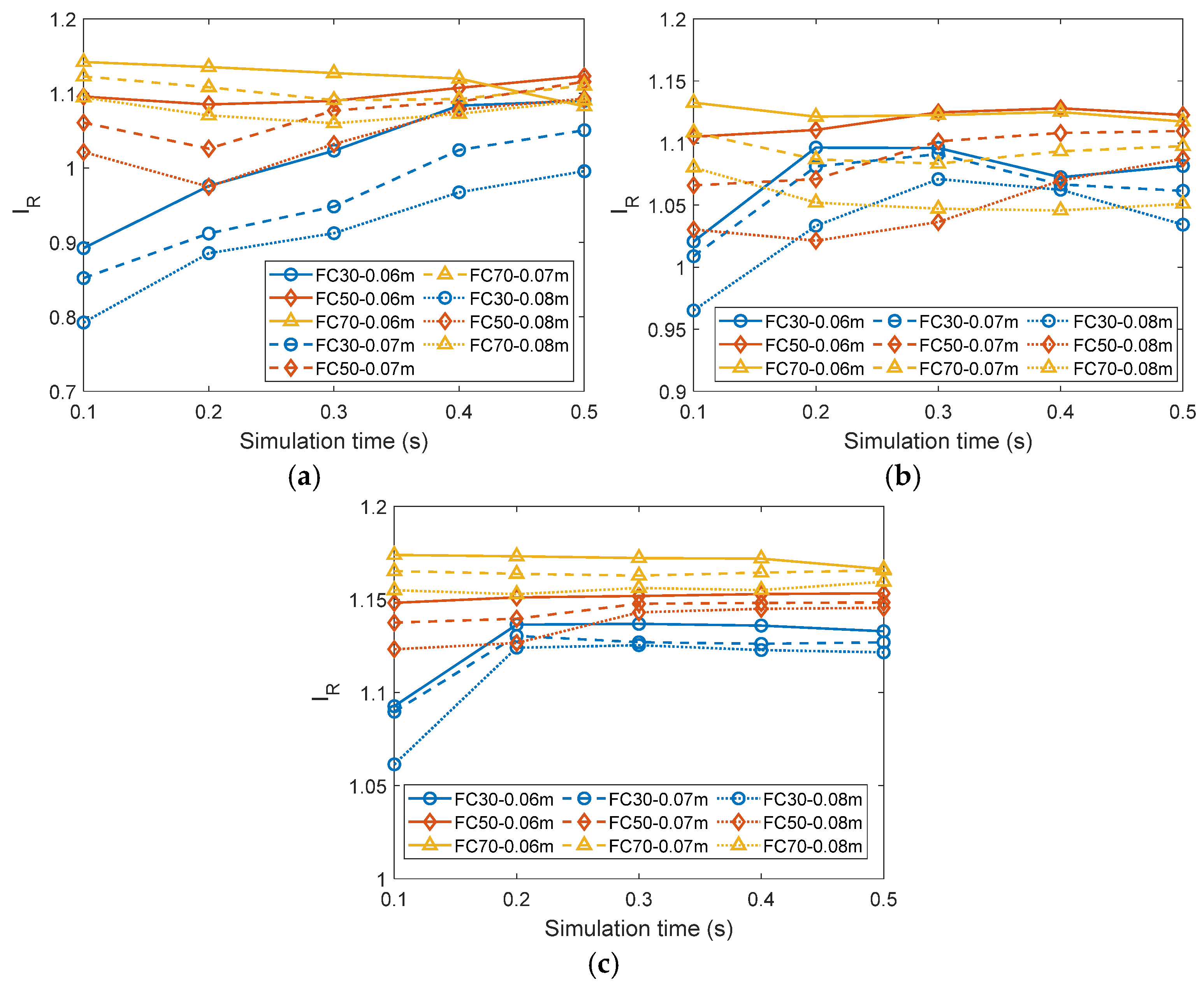
4.3. Mechanical Redundancy
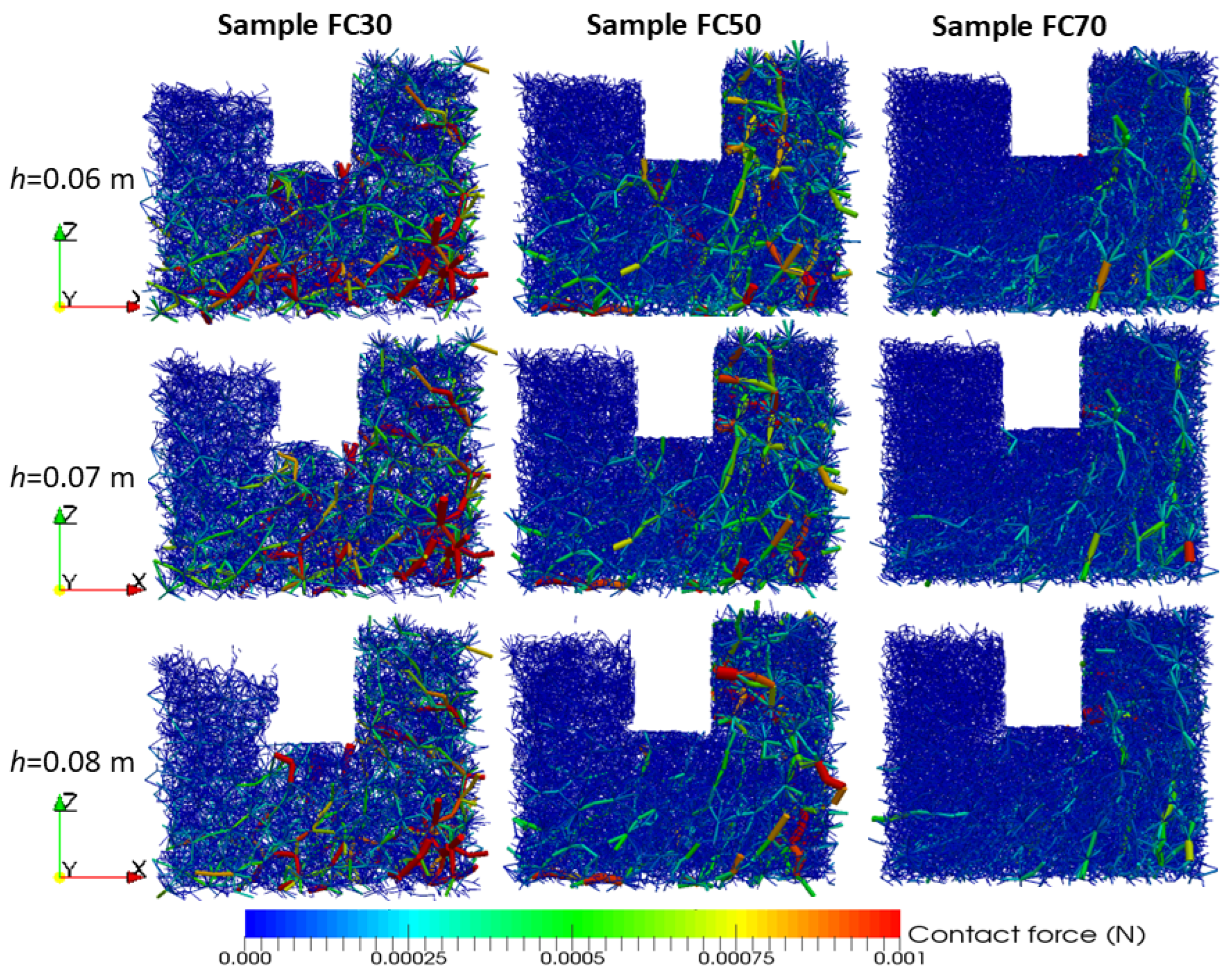
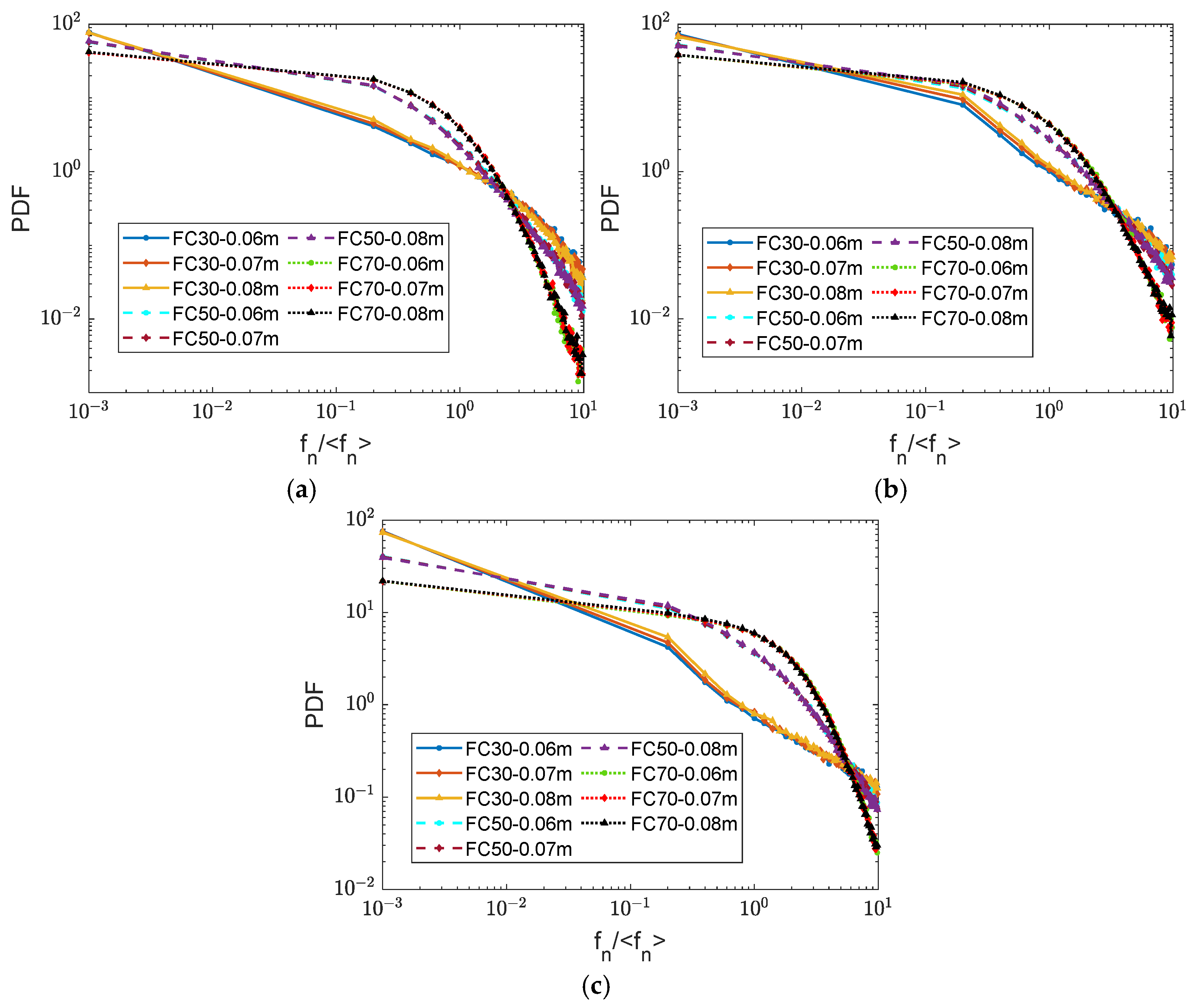
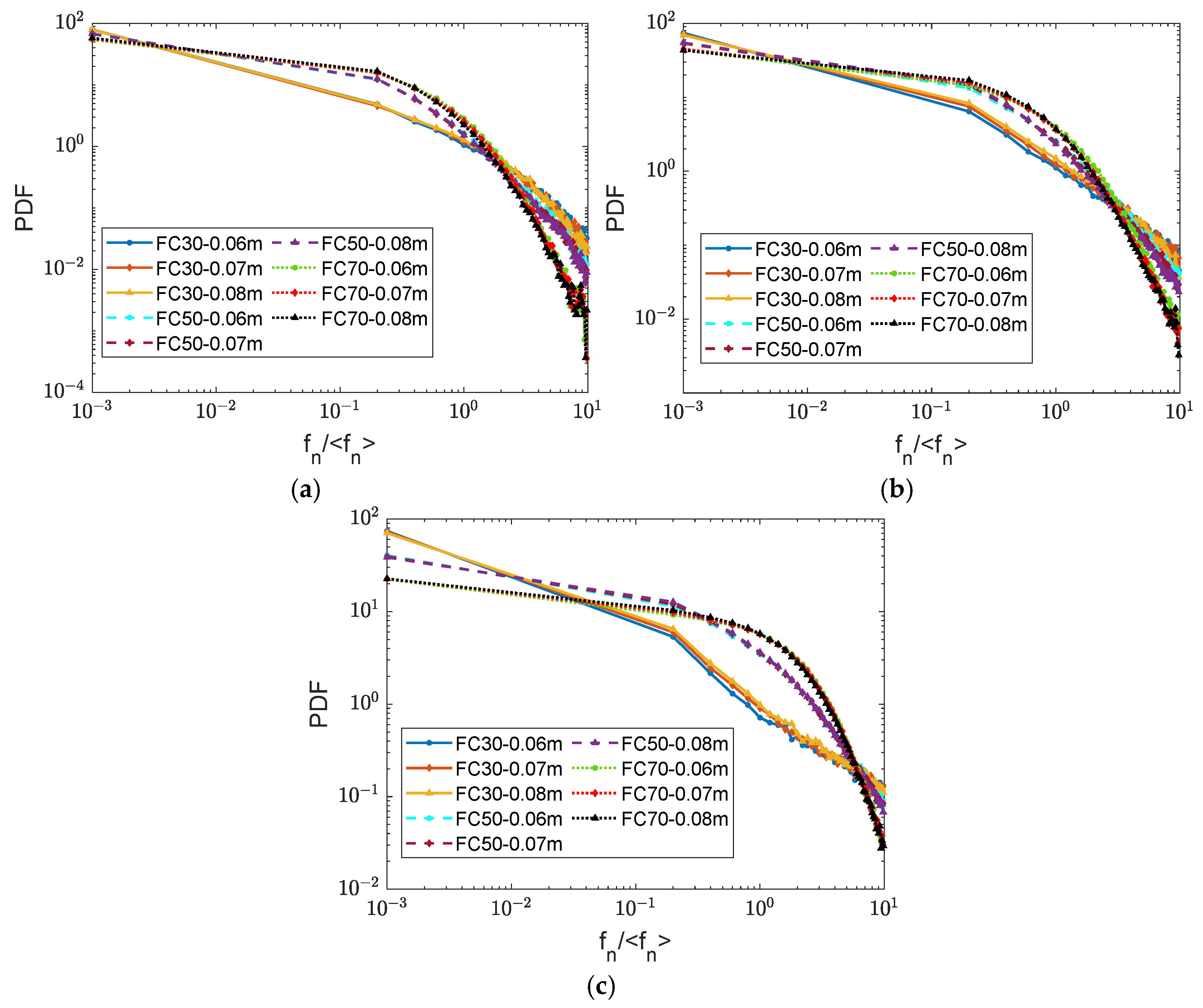
4.4. Contact Forces
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| DEM | Discrete element method |
| FC | Fines content |
| CN | Coordination number |
References
- Foster, M.; Fell, R.; Spannagle, M. The statistics of embankment dam failures and accidents. Can. Geotech. J. 2000, 37, 1000–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Liao, J.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y. Coupled seepage-damage effect in fractured rock masses: Model development and a case study. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 144, 104822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Liao, J.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, L. Mechanical behavior of sandstone during post-peak cyclic loading and unloading under hydromechanical coupling. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2023, 33, 927–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Tang, J.; Lin, H.; Wan, W. Transient pulse test and morphological analysis of single rock fractures. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2017, 91, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, S.; Xu, F. Evolution and modeling of mine water inflow and hazards characteristics in southern coalfields of China: A case of Meitanba mine. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, K.S.; Reddy, K.R. Critical appraisal of piping phenomena in earth dams. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2007, 66, 381–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, T.C.; Chahal, R.; Chiu, E.; Ofoegbu, G.I. Controlling constriction sizes of granular filters. Can. Geotech. J. 1985, 22, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendahmane, F.; Marot, D.; Rosquoët, F.; Alexis, A. Characterization of internal erosion in sand kaolin soils. Rev. Eur. Génie Civ. 2011, 10, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Kuwano, R. Laboratory testing for evaluation of the influence of a small degree of internal erosion on deformation and stiffness. Soils Found. 2018, 58, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, S.S.; Vaid, Y.P. Seepage forces and confining pressure effects on piping erosion. Can. Geotech. J. 2000, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.F.; Fell, R. Investigation of rate of erosion of soils in embankment dam. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2004, 130, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzaghi, K. Theoretical Soil Mechanics; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1943; pp. 235–264. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, T.; Verruijt, A. Seepage Failure of Sand behind Sheet Piles. The Mechanism and Practical Approach to Analyze. Soils Found. 1999, 39, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Nie, M.; Xiao, M. Flume-scale experiments on suffusion at bottom of cutoff wall in sandy gravel alluvium. Can. Geotech. J. 2017, 54, 1716–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundall, P.A.; Strack, O.D.L. A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies. Géotechnique 1979, 29, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholtes, L.; Hicher, P.Y.; Sibille, L. Multiscale approaches to describe mechanical responses induced by particle removal in granular materials. Comptes Rendus Méc. 2010, 338, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.H.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.Q.; Cui, P. Discrete numerical modelling of particle transport in granular filters. Comput. Geotech. 2013, 47, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shire, T.; O’Sullivan, C.; Hanley, K.J.; Fannin, R.J. Fabric and Effective Stress Distribution in Internally Unstable Soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, Y.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tanaka, T. Discrete particle simulation of two-dimensional fluidized bed. Powder Technol. 1993, 77, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.D.; Shan, T. A coupled CFD-DEM analysis of granular flow impacting on a water reservoir. Acta Mech. 2014, 225, 2449–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.; Liu, C.H.; Chang, C.M. Numerical investigation of rainfall-induced landslide in mudstone using coupled finite and discrete element analysis. Geofluids 2018, 1, 9192019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Jang, B.; Wu, C. Damming process and characteristics of landslide-debris avalanches. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 121, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shamy, U.; Denissen, C. Microscale characterization of energy dissipation mechanisms in liquefiable granular soils. Comput. Geotech. 2010, 37, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, K.; Shire, T.; O’Sullivan, C.; Nezamabadi, S.; Luding, S.; Delenne, J.Y. Coupled DEM-CFD Analysis of the Initiation of Internal Instability in a Gap-Graded Granular Embankment Filter. EPJ Web Conf. 2017, 140, 10005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, R.; Zhou, C.; Li, X.; Bate, B. Microscopic mechanism of the combined effects of confining pressure and fines content on suffusion in gap-graded underfilled soils. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LIGGGHTS. LIGGGHTS (R)-Public Documentation, Version 3.X. Available online: http://www.cfdem.com (accessed on 18 February 2015).
- OpenFOAM. OpenFOAM—The Open Source CFD Toolbox. The OpenFOAM Foundation. 2015. Available online: http://www.openfoam.org (accessed on 22 May 2015).
- Zhou, Z.; Kuang, S.; Chu, K.; Yu, A. Discrete particle simulation of particle-fluid flow: Model formulations and their applicability. J. Fluid Mech. 2010, 661, 482–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerst, K.; Roloff, C.; Medeiros de Souza, L.G.; Bartz, A.; Seidel-Morgenstern, A.; Thevenin, D.; Janiga, G. CFD-DEM simulations of a fluidized bed crystallizer. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 165, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Felice, R. The voidage function for fluid-particle interaction systems. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1994, 20, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Wang, J.-P. CFD-DEM simulations of seepage-induced erosion. Water 2020, 12, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q. Simulating the hydraulic heave phenomenon with multiphase fluid flows using CFD-DEM. Water 2020, 12, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, B.; Tang, Y.; Hu, T.; Ling, D. Microscopic mechanism and analytical modeling of seepage-induced erosion in bimodal soils. Comput. Geotech. 2022, 141, 104527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Mu, L.; Huang, M. A coupled CFD-DEM investigation into hydro-mechanical behaviour of gap-graded soil experiencing seepage erosion considering cyclic hydraulic loading. J. Hydrol. 2023, 624, 129908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yin, Z.Y. A coupled CFD-DEM investigation of suffusion of gap graded soil: Coupling effect of confining pressure and fines content. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 2020, 44, 2473–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, R.; Li, Z.; Zhou, C.; Li, X. A new method for preventing sidewall preferential flow in the internal erosion simulation using un-resolved CFD–DEM. Acta Geophys. 2024, 72, 3595–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kezdi, A. Soil Physics: Selected Topics; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1979; pp. 126–133. [Google Scholar]
- De Frias Lopez, R.; Silfwerbrand, J.; Jelagin, D.; Birgisson, B. Force transmission and soil fabric of binary granular mixtures. Geotechnique 2016, 66, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shamy, U.; Zeghal, M. Coupled continuum-discrete model for saturated granular soils. J. Eng. Mech. 2005, 131, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzaghi, K.; Peck, R.B. Soil Mechanics in Engineering; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1948; pp. 213–236. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Z.H.; Zhu, Y.G.; Zou, J.F.; Gong, J.; Liu, S.K. DEM study of the microscopic characteristics and internal stability of binary mixtures. Powder Technol. 2019, 352, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Zhang, P.; Shi, Z.; Huang, M. Coupled CFD-DEM investigation of erosion accompanied by clogging mechanism under different hydraulic gradients. Comput. Geotech. 2023, 153, 105058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, C. Numerical simulation of deviatoric shear deformation of granular media. Géotechnique 2000, 50, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruyt, N.P.; Rothenburg, L. Plasticity of granular materials: A structural-mechanics view. AIP Conf. Proc. 2009, 1145, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Qian, J.; Zhou, C. Macro- and micro-scale investigation of suffusion in gap-graded soils under multiple factors using CFD-DEM. Comput. Geotech. 2025, 186, 107381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjai, F.; Wolf, D.E.; Jean, M.; Moreau, J.-J. Bimodal character of stress transmission in granular packings. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, N.H.; Cheng, Y.P.; Thornton, C. Strong force networks in granular mixtures. Granul. Matter 2014, 16, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Young’s modulus | 5 MPa |
| Radii of particles | 0.25 mm |
| 1 mm | |
| Friction coefficient | 0.85 |
| Poission’s ratio | 0.45 |
| Restitution coefficient | 0.5 |
| Sample FC30 | Sample FC50 | Sample FC70 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fines content (FC) | 30% | 50% | 70% |
| Number of particles | 389,302 | 640,105 | 846,449 |
| Viscosity of Water | Density of Water | Viscosity of Air | Density of Air |
|---|---|---|---|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Q.; Ma, L.; Chang, S.; Yue, X.; Yuan, L. Multiscale Analysis of Seepage Failure Mechanisms in Gap-Graded Soils Using Coupled CFD-DEM Modeling. Water 2025, 17, 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162461
Xiao Q, Ma L, Chang S, Yue X, Yuan L. Multiscale Analysis of Seepage Failure Mechanisms in Gap-Graded Soils Using Coupled CFD-DEM Modeling. Water. 2025; 17(16):2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162461
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Qiong, Lu Ma, Shan Chang, Xinxin Yue, and Ling Yuan. 2025. "Multiscale Analysis of Seepage Failure Mechanisms in Gap-Graded Soils Using Coupled CFD-DEM Modeling" Water 17, no. 16: 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162461
APA StyleXiao, Q., Ma, L., Chang, S., Yue, X., & Yuan, L. (2025). Multiscale Analysis of Seepage Failure Mechanisms in Gap-Graded Soils Using Coupled CFD-DEM Modeling. Water, 17(16), 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162461






