Forecasting Tibetan Plateau Lake Level Responses to Climate Change: An Explainable Deep Learning Approach Using Altimetry and Climate Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
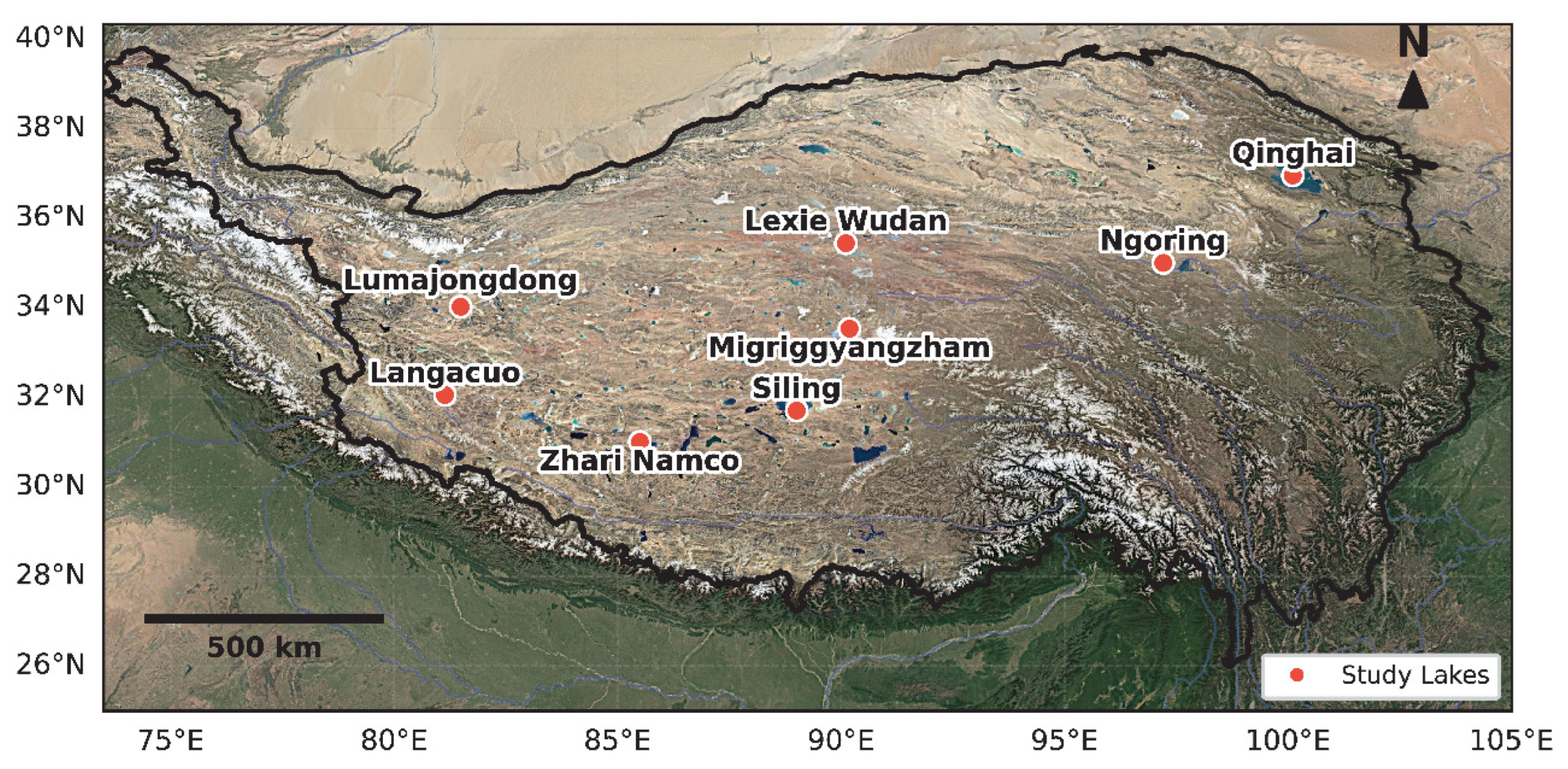
2.1. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.2. Deep Learning Framework
2.3. Model Validation and Interpretation
2.4. Mechanistic Attribution of Hydrological Trends Using Explainable AI
2.5. Scenario Analysis and Uncertainty Quantification
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of CMIP6 Model Performance
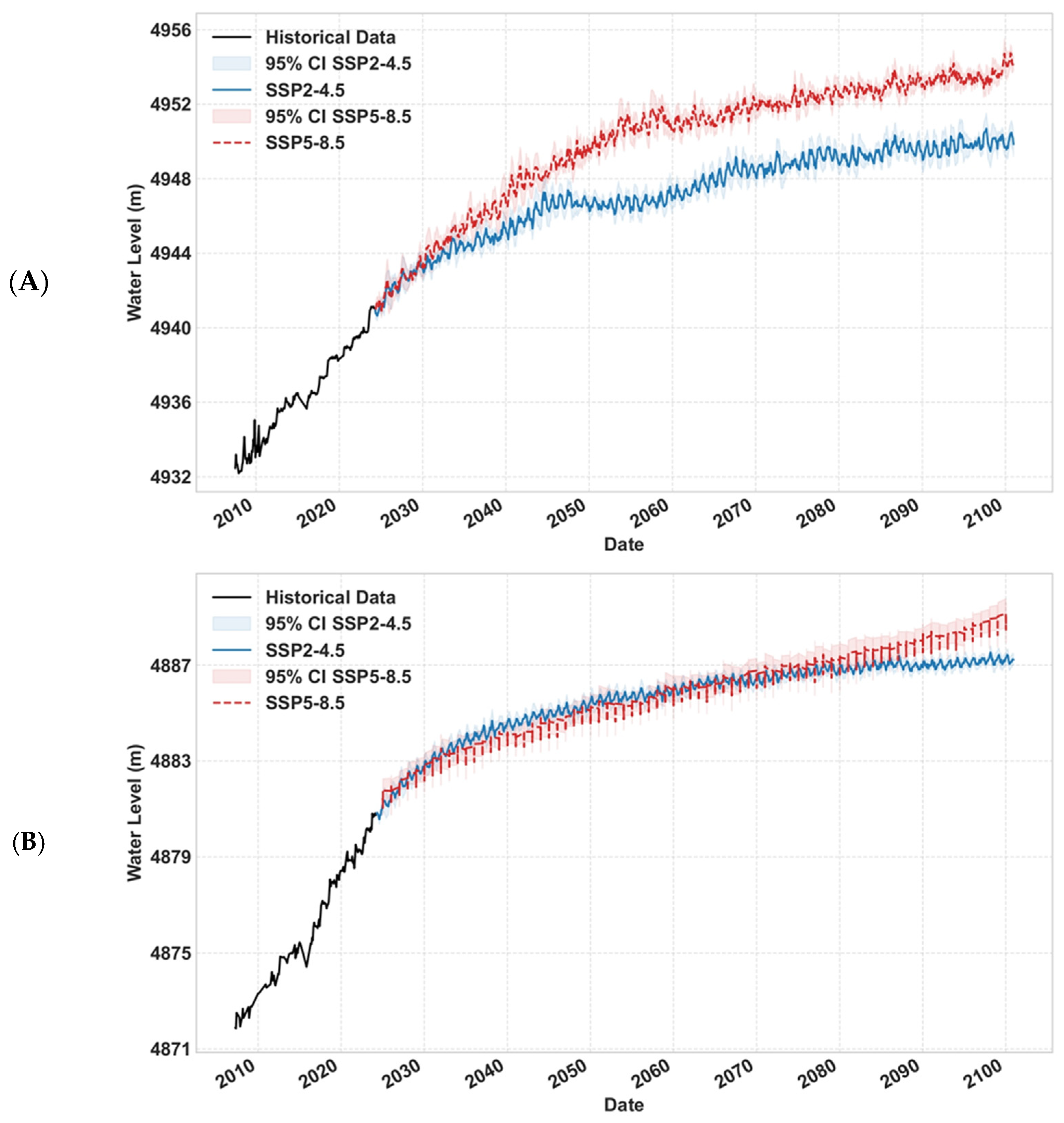
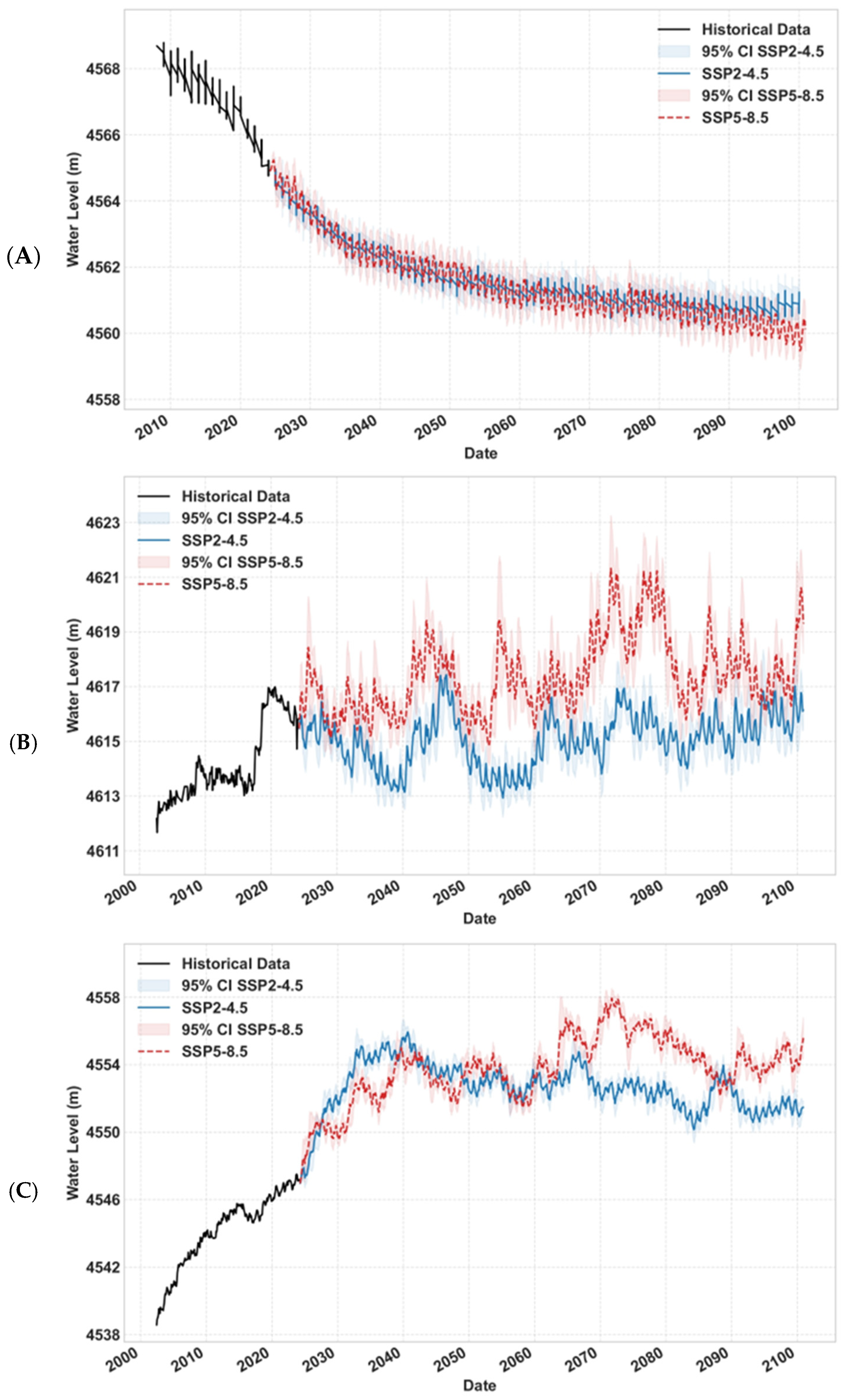
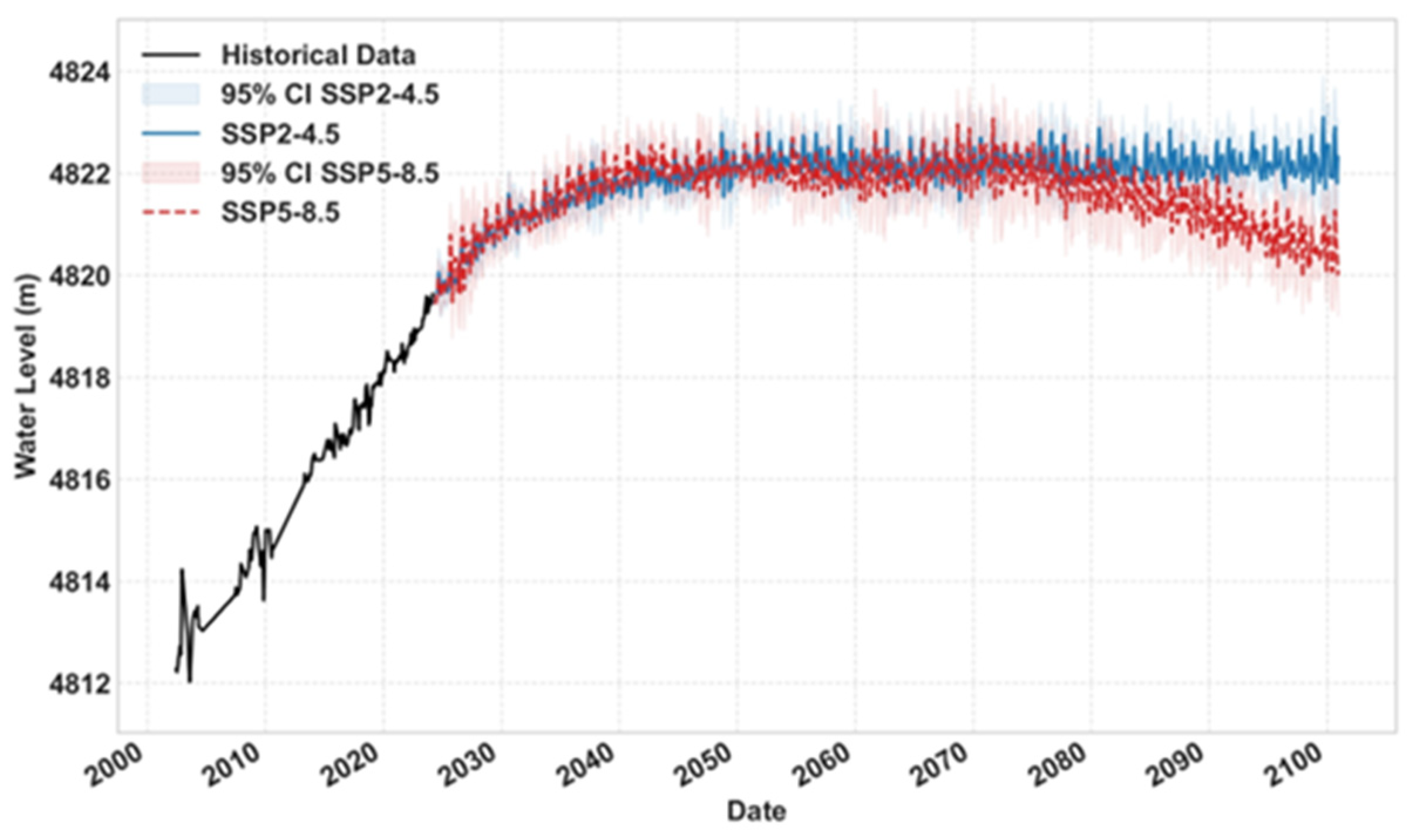
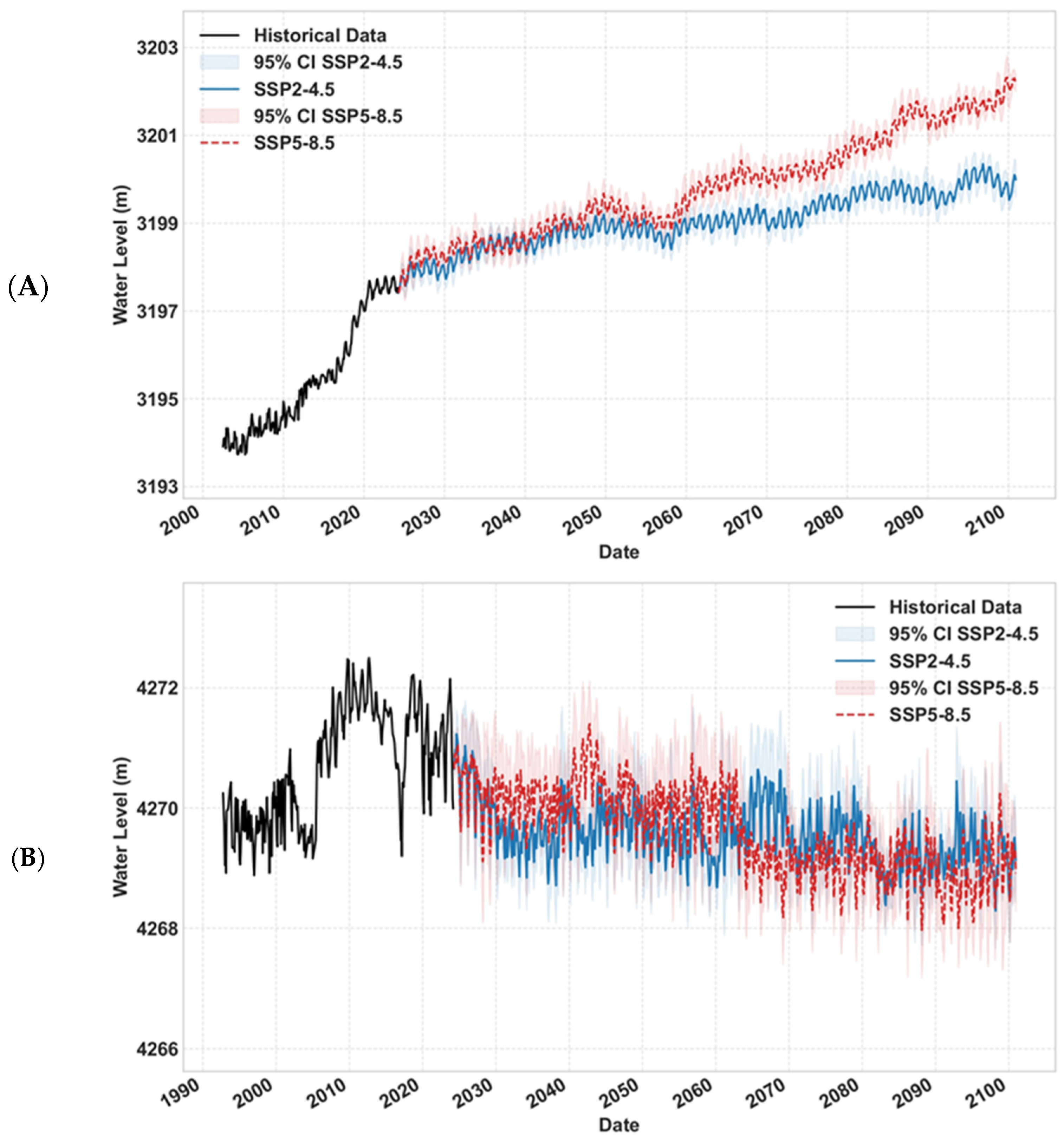
3.2. Hydrological Projections Under Climate Scenarios
4. Discussion
4.1. Divergent Hydrological Regimes and Climatic Drivers
- (a)
- Northern Glacier-Fed Lakes
- (b)
- Southern Evaporation-Dominated Lakes
- (c)
- Western Transitional Lakes
- (d)
- Eastern Morphometry-Controlled Lakes
4.2. Implications for Ecosystems and Water Security
4.3. Future Research Directions
4.4. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xue, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, Q. Land–Climate Interaction over the Tibetan Plateau. In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Climate Science; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorino, P.; Elia, A.C.; Pizzul, E.; Bertoli, M.; Renzi, M.; Prearo, M. The Old and the New on Threats to High-Mountain Lakes in the Alps: A Comprehensive Examination with Future Research Directions. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Kraemer, B.M.; Lenters, J.D.; Merchant, C.J.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S. Global Lake Responses to Climate Change. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kurbaniyazov, A.; Kirillin, G. Changing Pattern of Water Level Trends in Eurasian Endorheic Lakes as a Response to the Recent Climate Variability. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Mengmeng, W.; Tao, Z.; Wenfeng, C. Progress in Remote Sensing Monitoring of Lake Area, Water Level, and Volume Changes on the Tibetan Plateau. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 26, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Shum, C.; Yi, S.; Yang, K.; Xie, H.; Feng, W.; Bolch, T.; Wang, L.; Behrangi, A. Lake Volume and Groundwater Storage Variations in Tibetan Plateau’s Endorheic Basin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 5550–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Xie, H.; Yang, K.; Zhu, L.; Shum, C.K.; Bolch, T.; Yi, S.; Allen, S.; Jiang, L.; et al. Response of Tibetan Plateau Lakes to Climate Change: Trends, Patterns, and Mechanisms. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 208, 103269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Ju, J.; Qiao, B.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Yang, R.; Ma, Q.; Guo, L.; Pang, S. Physical and Biogeochemical Responses of Tibetan Plateau Lakes to Climate Change. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, W.; Li, J. Change in Precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau Projected by Weighted CMIP6 Models. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 39, 1133–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ye, A.; Wang, Y. Enhanced Spatial Dry–Wet Contrast in the Future of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Hydrol. Process 2025, 39, e70087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; You, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Kang, S.; Zhai, P. Integrated Warm-Wet Trends over the Tibetan Plateau in Recent Decades. J. Hydrol. 2024, 639, 131599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrifield, A.L.; Brunner, L.; Lorenz, R.; Humphrey, V.; Knutti, R. Climate Model Selection by Independence, Performance, and Spread (ClimSIPS v1.0.1) for Regional Applications. Geosci. Model Dev. 2023, 16, 4715–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xie, H.; Duan, S.; Tian, M.; Yi, D. Water Level Variation of Lake Qinghai from Satellite and in Situ Measurements under Climate Change. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2011, 5, 053532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancamaria, S.; Frappart, F.; Leleu, A.-S.; Marieu, V.; Blumstein, D.; Desjonquères, J.-D.; Boy, F.; Sottolichio, A.; Valle-Levinson, A. Satellite Radar Altimetry Water Elevations Performance over a 200 m Wide River: Evaluation over the Garonne River. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 128–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Nielsen, K.; Andersen, O.B.; Bauer-Gottwein, P. Monitoring Recent Lake Level Variations on the Tibetan Plateau Using CryoSat-2 SARIn Mode Data. J. Hydrol. 2017, 544, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Huang, B.; Ke, L.; Richards, K.S. Seasonal and Abrupt Changes in the Water Level of Closed Lakes on the Tibetan Plateau and Implications for Climate Impacts. J. Hydrol. 2014, 514, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Duan, Z. Monitoring Spatial-Temporal Variations of Lake Level in Western China Using ICESat-1 and CryoSat-2 Satellite Altimetry. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agar, P.; Roohi, S.; Voosoghi, B.; Amini, A.; Poreh, D. Sea Surface Height Estimation from Improved Modified, and Decontaminated Sub-Waveform Retracking Methods over Coastal Areas. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-Y.; Yang, S. Evaluation of CMIP6 for Historical Temperature and Precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau and Its Comparison with CMIP5. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2020, 11, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Li, C.; Tian, F. Evaluation of Temperature and Precipitation Simulations in CMIP6 Models over the Tibetan Plateau. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2020EA001620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, R.W.; Naz, I.; Shu, H.; Yan, J.; Quddoos, A.; Tariq, A.; Davis, J.B.; Al-Saif, A.M.; Soufan, W. Multi-Temporal Image Analysis of Wetland Dynamics Using Machine Learning Algorithms. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, R.W.; Shu, H.; Naz, I.; Quddoos, A.; Yaseen, A.; Gulshad, K.; Alarifi, S.S. Machine Learning-Based Wetland Vulnerability Assessment in the Sindh Province Ramsar Site Using Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, G.; Yi, S.; Chen, W. Seasonal Trends and Cycles of Lake-Level Variations over the Tibetan Plateau Using Multi-Sensor Altimetry Data. J. Hydrol. 2022, 604, 127251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.07874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (Ed.) Linking Global to Regional Climate Change. In Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 1363–1512. ISBN 978-1-00-915788-9. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (Ed.) Ocean, Cryosphere and Sea Level Change. In Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 1211–1362. ISBN 978-1-00-915788-9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Song, C.; Reager, J.T.; Yao, F.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Sheng, Y.; MacDonald, G.M.; Brun, F.; Schmied, H.M.; Marston, R.A. Recent Global Decline in Endorheic Basin Water Storages. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (Ed.) Water Cycle Changes. In Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 1055–1210. ISBN 978-1-00-915788-9. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, G.; Woolway, R.I.; Yang, K.; Wada, Y.; Wang, J.; Crétaux, J.-F. Widespread Societal and Ecological Impacts from Projected Tibetan Plateau Lake Expansion. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Dai, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, C. MTMF Method for Hydromagnesite Determination Based on Landsat8 and ZY1-02D Data: A Case Study of the Jiezechaka Salt Lake in Tibet. Aquat. Geochem. 2024, 30, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fang, P.; Que, Y.; Zhu, L.-J.; Duan, Z.; Tang, G.; Liu, P.; Ji, M.; Liu, Y. A Dataset of Lake-Catchment Characteristics for the Tibetan Plateau. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2022, 14, 3791–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, G.; Yang, R.; Liu, C.; Yang, K.; Qiao, B.; Han, B. Lake Variations on Tibetan Plateau of Recent 40 Years and Future Changing Tendency. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2019, 34, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Lutz, A.F.; Andrade, M.; Bahl, A.; Biemans, H.; Bolch, T.; Hyde, S.; Brumby, S.; Davies, B.; Elmore, A. Importance and Vulnerability of the World’s Water Towers. Nature 2020, 577, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-J.; Li, X.-Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.-F.; Wu, X.-C.; Wang, P.; Lin, H.; Zhang, G.-H.; Miao, C.-Y. Evapotranspiration and Its Dominant Controls along an Elevation Gradient in the Qinghai Lake Watershed, Northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Luo, Z.; Nazli, S.; Shi, L. Hydrologic Response and Prediction of Future Water Level Changes in Qinghai Lake of Tibet Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 57, 102168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Feng, L.; Wang, X.; Pi, X.; Xu, W.; Woolway, R.I. Global Lakes Are Warming Slower than Surface Air Temperature Due to Accelerated Evaporation. Nat. Water 2023, 1, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.-J.; He, J.-S.; Yang, R.-H.; Wu, H.-J.; Wang, X.-L.; Jiao, L.; Tang, Z.; Yao, Y.-J. Range Shifts in Response to Climate Change of Ophiocordyceps Sinensis, a Fungus Endemic to the Tibetan Plateau. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 206, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shaibah, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Tong, Z.; Zhang, M.; El-Zeiny, A.; Faichia, C.; Hussain, M.; Tayyab, M. Modeling Water Quality Parameters Using Landsat Multispectral Images: A Case Study of Erlong Lake, Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Teng, H.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wan, D.; Shi, Z. Future Habitat Shifts and Economic Implications for Ophiocordyceps Sinensis under Climate Change. Ecol. Evol. 2025, 15, e71327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Lake | Variable | RMSE Reduction (%) | Extreme Event Improvement (95th %ile, %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lexie Wudan | Runoff | 11.4% | 90.3% |
| Precipitation | 17.7% | 97% | |
| Temperature | 34.6% | 90.6% | |
| Evaporation | 38.0% | 98.30% | |
| Lumajang Dong | Runoff | 47.89% | 88.5% |
| Precipitation | 13.6% | 64.5% | |
| Temperature | 26.94% | 66.7% | |
| Evaporation | 0.81% | 81.8% | |
| Zhari Namco | Precipitation | 30.5% | 96.5 |
| Temperature | 26.6% | 95.2% | |
| Evaporation | 19.0% | 98.6% | |
| Runoff | 17.1% | 85.9% | |
| Langacuo | Precipitation | 10.3% | 87.5% |
| Temperature | 19.6% | 74.5% | |
| Evaporation | 14.3% | 11.2% | |
| Runoff | 20.8% | 99.3% | |
| Ngoring | Precipitation | 4.8% | 79.2% |
| Temperature | 12.9% | 98.8% | |
| Evaporation | 13.4% | 98.3% | |
| Runoff | 1.1% | 93.4% | |
| Siling | Precipitation | 49.0% | 94.8% |
| Temperature | 30.4% | 96.3% | |
| Evaporation | 43.0% | 100.0% | |
| Runoff | 0.6% | 78.9% | |
| Qinghai | Precipitation | 7.1% | 96.2% |
| Temperature | 47.2% | 91.0% | |
| Evaporation | 2.6% | 98.9% | |
| Runoff | 19.7% | 96.2% | |
| Migriggyangzham | Precipitation | 15.2% | 84.3% |
| Temperature | 6.6% | 89.3% | |
| Evaporation | 1.8% | 100.0% | |
| Runoff | 3.8% | 94.5% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gholami, A.; Zhang, W. Forecasting Tibetan Plateau Lake Level Responses to Climate Change: An Explainable Deep Learning Approach Using Altimetry and Climate Models. Water 2025, 17, 2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162434
Gholami A, Zhang W. Forecasting Tibetan Plateau Lake Level Responses to Climate Change: An Explainable Deep Learning Approach Using Altimetry and Climate Models. Water. 2025; 17(16):2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162434
Chicago/Turabian StyleGholami, Atefeh, and Wen Zhang. 2025. "Forecasting Tibetan Plateau Lake Level Responses to Climate Change: An Explainable Deep Learning Approach Using Altimetry and Climate Models" Water 17, no. 16: 2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162434
APA StyleGholami, A., & Zhang, W. (2025). Forecasting Tibetan Plateau Lake Level Responses to Climate Change: An Explainable Deep Learning Approach Using Altimetry and Climate Models. Water, 17(16), 2434. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162434






