Abstract
The presence of ibuprofen (IBP) and paracetamol (PAR) contaminants in wastewater has become an emerging issue. Traditional wastewater treatment facilities have not been adequately upgraded to remove these micropollutants. This study focused on screening and identifying effective rhizobacteria capable of assisting plants in eliminating ibuprofen and paracetamol from wastewater using constructed wetlands. A total of 28 rhizobacteria were isolated from both the roots and the surrounding sand of Scirpus grossus after 30 days of pharmaceutical exposure. Among these, three isolates (Gram-negative Enterobacter aerogenes, Gram-positive Bacillus flexus, and Paenibacillus alvei) showed high tolerance to IBP and PAR with initial removal efficiencies > 75%. The addition of these three isolated rhizobacteria to a constructed wetland (planted with Scirpus grossus, 5-day HRT, 2 L/min aeration) assists the removal of IBP and PAR from wastewater. Bioaugmentation of rhizobacteria showed an increment of IBP removal (↑13%) from water (residual of 10 µg/L) and PAR (↑20%) from sand (residual 2.3 µg/L) as compared to the non-bioaugmented systems. The addition of rhizobacteria also showed the ability to significantly enhance the translocation of PAR into the shoot system of S. grossus, suggesting assisted phytoextraction mechanisms, while the removal of IBP in wetlands is suggested to occur via rhizodegradation. It is recommended that future research be conducted to elucidate the microbial degradation pathways and analyze the intermediate metabolites to accurately depict the pharmaceutical degradation mechanisms and evaluate their ecological risks.
1. Introduction
The occurrence of pharmaceutical residues in wastewater poses a significant challenge for wastewater treatment technologies [1]. Various sources of pharmaceutical compounds in the environment include households, industries, hospitals, and pharmacies [2,3], where common drugs such as paracetamol (PAR) and ibuprofen (IBP) are widely used, subsequently excreted, and improperly disposed of [4,5]. Currently, wastewater treatment facilities are not designed to effectively eliminate these organic micropollutants, which typically have high water solubility and low biodegradability. Consequently, their persistence in the environment is maintained [3,6]. The accumulation of pharmaceuticals in surface water may raise ecological and health concerns, including being the cause of chronic toxicities, endocrine-disrupting diseases, and accumulation in aquatic organisms [7,8].
Adsorption [9] and filtration [10] are widely recognized methodologies for mitigating the contamination of water by IBP and PAR. Electrocoagulation and photocatalysis have emerged as promising alternative technologies [11,12]. Despite the demonstrated efficacy of these technologies, there are escalating concerns regarding the chemicals utilized and the resultant treatment residues that may contribute to additional environmental pollution [13,14]. The high consumption of energy by applying these technologies also needs to be considered [15]. Nature-based treatments (biodegradation) are gaining popularity as sustainable alternatives [16]. Among the nature-based methods, phytoremediation (constructed wetland) using macrophytes offers environmentally friendly and relatively lower operational and maintenance costs for pharmaceutical-contaminated wastewater [17,18]. However, its practical application in wastewater treatment requires critical evaluation. Biodegradation can result in the formation of intermediate compounds, which can pose greater toxicity than the original pollutant [19,20]. Compared to physicochemical treatment, such as the Advanced Oxidation Process (AOP), biological processes are often slower and may not be economically viable at a larger scale [21,22]. In real wastewater treatment cases, these limitations must be carefully considered.
It is worth taking note that in phytoremediation, both biological and chemical degradation processes can naturally co-occur and interact, including microbial transformation and abiotic oxidation [23,24], particularly where treated or untreated wastewater introduces pharmaceutical residues. Wetlands planted with Typha angustifolia removed 95.1% of ibuprofen from an initial concentration of 1000 ng/L [25], while Phragmites australis removed 99% of ibuprofen from an initial concentration of 24 µg/L [26]. Spirodela polyrhiza was also reported to remove 97.7% of paracetamol from spiked wastewater (25 µg/L) [27]. Based on these previous findings, macrophytes showed good potential for removing pharmaceutical compounds from wastewater in wetland systems. The high pharmaceuticals removal performance occurred due to the plant uptake capability and also the interaction with rhizobacterial communities, which is currently limitedly studied [28].
Nevertheless, the majority of existing research primarily focuses on the uptake of pharmaceuticals by plant roots from effluents [14,29,30], while investigations regarding translocation, accumulation, and the influence of rhizobacterial additions remain insufficiently addressed [31]. In addition to that, the use of native Malaysian plant species of Scirpus grossus to remove pharmaceuticals in wetlands is currently limited. To bridge this research gap, the objective of the present study was to assess the potential of S. grossus in removing IBP and PAR from pilot-scale constructed wetlands. This research also aimed to analyze the effect of adding resistant isolated rhizobacterial species on the performance of the constructed wetland in removing IBP and PAR. The results obtained from this study are expected to provide an alternative option for pharmaceutical-containing wastewater treatment, while also contributing to the general knowledge of phytoremediation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material Acquisition and Initial Maintenance
The specimens used in this study (S. grossus) were obtained from Tasik Chini, Pahang, Malaysia. These plants underwent propagation within the UKM conservatory prior to the initiation of their second generation. A cohort of healthy, 30-day-old plants was acclimatized to the sand medium during the initial phase of the project.
2.2. Initial HRT Optimization
This research was conducted in a greenhouse at Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM), located within an open, natural environment. The experimental setup was replicated to facilitate the functioning of three constructed wetlands (CWs) planted with S. grossus (T1 exhibiting a hydraulic retention time of 3 days, T2 at 4 days, and T3 at 5 days) under ambient conditions of 30 ± 5 °C with 10 h of sunlight. The subfloor wetland reactors were engineered to accommodate a total effluent volume of 45 L, characterized by dimensions of 1 m in width, 1 m in length, 60 cm in height, and a thickness of 0.5 cm. Three identical reactors were utilized, each comprising a sand–gravel layer constructed from fiberglass. The layers within the sand strata, arranged from the base to the top, included the following: (i) a 15 cm layer of gravel with particle sizes ranging from 10 to 20 mm, (ii) a 5 cm layer of fine sand with a particle diameter of 2 mm, and (iii) a 1 cm layer of gravel with diameters between 1 and 5 mm. The total mass of the sand was recorded as 77 kg. A 22.5 cm thick gravel layer, with particle sizes ranging from 10 to 20 mm, was employed to stabilize both the inlet and outlet flows. The main study concentrated on plants that had undergone a 30-day acclimatization period. Each vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland (VSSFCW) received twenty healthy S. grossus plants that had successfully completed the acclimatization process. Figure 1 depicts that each reactor was meticulously designed for continuous operation, with discharge rates of 15, 11.25, and 9 L/day, corresponding to hydraulic retention times of 3, 4, and 5 days, respectively. All analyses in this research were conducted in triplicate. The optimum HRT condition was selected based on the removal of IBP and PAR, and the results of the validation run (with and without rhizobacterial addition, following Section 2.5) are presented in this article.

Figure 1.
Schematic of a pilot-scale system in Bukit Puteri on the UKM campus.
2.3. Isolation and Characterization of Rhizobacteria
During 30 days of microbial testing of S. grossus exposure to pharmaceutical-contaminated wastewater, a mixture of IBP and PAR (600 and 60 µg/L concentration, respectively) was placed in a continuous subsurface flow (SSF) system. The concentrations were determined by the maximum concentration of these compounds that were previously analyzed in domestic effluent in the Bangi Area, Malaysia. Isolation of rhizobacteria was conducted following a previous method [32]. Three samples of roots were taken from each VSSFCW (T1, T2, and T3) outlet. About 10 g of S. grossus roots and their surroundings were placed in a 250 mL Schott bottle filled with 100 mL of sterilized distilled water. The sample underwent incubation in a rotary shaker (Model SI-100D, Protech, Shah Alam, Malaysia) at a temperature of 37 °C and a speed of 150 rpm for a duration of 1 h. Serial dilution was utilized to achieve three appropriate dilutions for plating. Subsequently, 1 mL of the sample was transferred into 9 sterile saline solutions, facilitating the attainment of dilutions up to 10−4. Subsequently, 0.1 mL of each of the three dilutions (10−2 and 10−4 dilutions) was carefully pipetted into a sterilized Petri dish containing tryptic soy agar (TSA) (Difco, Tucker, GA, USA). The sample was disseminated in triplicate to the Petri dishes inside a laminar-flow cabinet using a hockey stick on the TSA. The dishes were then incubated in an inverted position at 37 °C for 24 h. The count and recording of colonies spanning from more than 20 to 300 cells were conducted. The results were expressed as colony-forming units (CFU) per milliliter by multiplying the number of colonies calculated by the product of the dilution and the quantity plated [33]. The colonies were isolated from the S. grossus root and adjacent soil and cultivated for 24 h in separate TSA. Differences in colony morphology, such as colors and shapes, were used to differentiate among isolated rhizobacteria colonies. The morphology of each cell was observed under a light microscope (Nikon-E100, Tokyo, Japan). Cellular morphology was identified, and biochemical tests (catalase, Gram stain, motility, and oxidase) were conducted on the pure cultures of bacteria.
To identify the rhizobacteria that were resistant to pharmaceuticals, a mineral salt medium (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) was employed to conduct a test for the root colonies. It contained concentrations of mixed pharmaceuticals (IBP and PAR) of 600 and 60 µg/L, respectively, in which S. grossus could grow and survive. The composition of the mineral salt medium (MSM) that was used is as follows: MgSO4·7H2O, 0.2 g/L; NH4Cl, 0.2 g/L; K2HPO4, 0.5 g/L; KH2PO4, 0.5 g/L; NaCl, 0.2 g/L; CaCl2·2H2O, 0.0225 g/L, supplemented with micronutrients CoCl·6H2O, 0.42 g/L; NaMoO4·2H2O, 0.15 g/L; ZnCl2, 0.23 g/L; AlCl3·6H2O, 0.05 g/L; CuSO4·H2O, 0.03 g/L; MnSO4·H2O, 0.13 g/L. The pH was adjusted to 7.0, and the solution was autoclaved at 121 °C for 20 min. The isolated bacteria were streaked with sterilized TSA (SDFO, San Mateo County, CA, USA) (50 mL) and incubated in a rotary agitator (Protech, SI-100D model, Malaysia) at 150 rpm (37 °C) for approximately 18 to 24 h.
Pure cultures were prepared in 50 mL of sterilized tryptic soya broth (Difco, USA) and incubated in a rotary shaker (Protech, Model SI-100D, Malaysia) at 37 °C and 150 rpm for 18–24 h following a growth period of 24 h. The sample was then placed in an Eppendorf Centrifuge model 5810 R, operating at 4000 rpm and 4 °C for a duration of 10 min (USA). To enable standard inoculation from the particle, the supernatants were isolated. The bacteria were incubated in a 250 mL conical flask containing 50 mL of MSM with a 10% standard inoculation of rhizobacteria for the purpose of screening. The flask underwent incubation at 37 °C with a shaking speed of 150 rpm for a duration of 5 days. The samples underwent analysis for bacterial growth (CFU/mL count) utilizing the following ratings: good (+++), fair (++), poor (+), and no growth (−) [34].
DNA was extracted from the selected prospective bacterial species using a Molecular Biology Kit (Promega Kit, Madison, WI, USA). The extraction was conducted in accordance with the protocol provided in the kit. The DNA amplification protocol was followed by the use of an amplification kit (Promega, USA) to conduct DNA amplification. The 16S rRNA was amplified using the Universal primers primer pair in a ready-to-use polymerase chain reaction (PCR) Master Mix (Promega) following genomic extraction: 27 F (5′TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAG) and 1492 R (5′GTCTCGTGGGCTCGGAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAG). The process was amplified using a master cycler (Epgradient S, Eppendorf, and Version 3608). The protocol for amplification consisted of 35 cycles, which included denaturation at 94 °C for 1 min, annealing at 45 °C for 50 s, and elongation at 68 °C for 50 s. Additionally, the amplification procedure began with an initial step at 94 °C for 10 min [33]. The PCR results were purified with a Pure Link TM Quick PCR Purification Kit [35], and the base pair of the amplified DNA was determined by the agarose gel electrophoresis technique, applying a Gene RulerTM 1 kb DNA as the Ladder Marker Method of DNA extraction. The Sanger method was used to sequence the obtained 16S rRNA gene (First BASE Laboratories Sdn Bhd, Seri Kembangan, Malaysia). When the 16S rRNA sequences were obtained, the sequences were compared with other bacterial 16S rRNA databases from the National Centre for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov).
BLAST version 2.17.0 was performed using DNA sequences from previous phases and sequence alignment techniques. The phylogenetic tree of the selected bacteria was constructed using the top 10 highest similarities identified after further blast processing with the MEGA X program, as reported by the NCBI Gene Bank [36]. The phylogenetic tree and the BLAST endpoint exhibiting the highest recognition similarity were utilized to determine the bacterial species. The construction of a phylogenetic tree consists of four clear steps: first, one must identify and gather a set of homologous DNA or protein sequences; second, these sequences need to be aligned; third, a tree is estimated based on the aligned sequences; and finally, the tree is visualized to effectively convey the essential information to others. A phylogenetic tree consists of branches linking nodes, with interior nodes indicating likely ancestors and external nodes representing contemporary sequences. The lengths of the branches represent the estimated amount of change occurring between two nodes. A phylogenetic tree estimates the relationships between taxa (or sequences) and their potential common ancestors.
2.4. Selected Rhizobacterial Biodegradation Examination
The biodegradation test evaluates the ability of the selected rhizobacteria from the isolation stage to break down the combination of IBP and PAR (utilizing HPLC analysis, Agilent HPLC 1200, Santa Clara, CA, USA). MSM broth was prepared with pharmaceutical concentrations of 600 and 60 µg/L, consisting of 50 mL of MSM containing IBP and PAR (10%, v/v) along with a 5 mL inoculum of rhizobacteria at an optical density (OD) of 550 nm, combined with 45 mL of MSM for this stage. The solution was transferred into a 250 mL conical flask and incubated overnight at 37 °C for a duration of 5 days while being agitated at 150 rpm in a shaker. On days 0 and 5, three conical flasks containing MSM broth were collected for each bacterium via centrifugation (Eppendorf Centrifuge 5810, Enfield, CT, USA) at 4000 rpm and 4 °C for a duration of 10 min. The samples were extracted and collected via solid-phase extraction (SPE) after a 5-day incubation period.
To concentrate IBP and PAR from the water sample, 200 mg/6 mL Oasis hydrophilic–lipophilic balanced (HLB) cartridges from Waters Company were used. The HLB cartridges contained 3 mL of deionized water adjusted to pH 2, along with 3 mL of acetonitrile and 3 mL of methanol. The sample was passed through the cartridge at a controlled flow rate using a vacuum manifold. After percolation, the HLB cartridge was washed with 10 mL of deionized water, and the eluent was discarded. Following this, the cartridge was allowed to rest for 1 h [37]. HPLC measurements were performed by eluting the analyte using 4 mL of acetonitrile, which was then collected in a vial. The eluted sample for IBP and PAR determination was measured using HPLC (Agilent 1200 Series, USA) through a standard calibration curve. A Zorbax C18 column with dimensions of 250 mm, 4.6 mm, and 5 mm was utilized at a UV wavelength of 230 nm, specifically at 254 nm. The mobile phases utilized consisted of water and methanol, operating at a flow rate of 1 L/min with a ratio of 60:40. The removal of the pharmaceutical mixture for each sampling at days 0 and 5 was calculated using the Equation (1).
where C0 is the pharmaceutical concentration (µg/L) at day 0 and C1 is the pharmaceutical concentration (µg/L) at day 5.
2.5. Addition of Rhizobacteria Under Optimum Conditions
Rhizobacteria (Enterobacter aerogenes, Bacillus flexus, and Paenibacillus alvei) were added in a validation run of the pilot-constructed wetland under optimized conditions (HRT 5 days, 18 days of operation, aeration 2 L/min [38]) to study the influence of bioaugmentation on the phytoremediation process. The operations, with and without rhizobacterium addition, were compared for 18 days. The significant factors analyzed were pharmaceutical concentrations in water, sand, and plants.
Water, sand, and plant samples were taken on days 3, 7, 12, and 18 during the validation run. The concentration of ibuprofen and paracetamol in the water sample was accomplished through the use of 500 mg/6 mL Oasis hydrophilic–lipophilic balanced (HLB) extraction cartridges (Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA) in the solid-phase extraction (SPE) (Jones Chromatography, Lakewood, CO, USA). Each HLB cartridge was preconditioned with 3 mL of deionized water, methanol, and acetonitrile at a pH of 2. The sample was subsequently extracted through the cartridge at a controlled flow rate using a vacuum manifold. The HLB cartridge was cleansed with 10 mL of deionized water during percolation, and the eluent was discarded. The cartridge was then left to sit for 1 h [37]. Ultimately, the analyte was eluted into a 1.5 mL sample vial for HPLC detection using 4 mL of acetonitrile. The mechanism of action during the treatment period of ibuprofen by Scirpus grossus was associated with adsorption and filtration. Subsequently, paracetamol and ibuprofen were extracted from the samples. In accordance with EPA Method 3550C, an ultrasonic solvent extraction process was implemented. Initially, sand samples were combined with sodium sulphate (R&M Chemicals, Bristol, UK) [39]. Subsequently, they were immersed in 50 mL of methanol (solvent) and sonicated at a temperature of 50 °C for 30 min using an ultrasound chamber (Kwun Wah International Ltd., Shenzhen, China) to eliminate epiphytes. The samples were subsequently purified using glass fiber, the distilled solvent was transferred to a 15 mL vial, and the extract was concentrated and analyzed in a 2 mL HPLC volume. The plant absorption of paracetamol and ibuprofen was ascertained by combining 1 g of the top part (shoot) and bottom part (roots) of each desiccated plant with 50 mL of methanol (solvent) (Merck, Germany) in a 100 mL Schott bottle [40]. Using an ultrasonic cleanser (Kwun Wah International Ltd., China), the sample was extracted from the vial. The extraction procedure was conducted at a temperature of 50 °C for 30 min, and the resulting liquid was subsequently filtered through glass fiber. The filtrate was poured into a 15 mL vial and exposed to a fume chamber for 3–4 days to guarantee the complete evaporation of water and methanol traces. Prior to conducting HPLC analysis, the extract was filtered to a volume of 2 mL using the same method as that employed for water and sediment.
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was implemented with an Agilent 1200 Series system (Agilent Technologies, USA) to conduct quantitative analyses of paracetamol and ibuprofen in plant, sediment, and water samples. The analysis was performed using a Zorbax C18 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) and was conducted in accordance with a standard calibration curve. Sample injection was performed directly into the nebulizer using an autosampler (CETAC ASX 520, Teledyne Technologies, Omaha, NE, USA). In a 60:40 (v/v) ratio, the mobile phase was composed of deionized water and methanol, with a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. Micrograms per liter (μg/L) was used to express the concentrations of paracetamol and ibuprofen in the samples. The initial concentration and final concentration were compared to determine the removal efficiency of each pharmaceutical compound, as outlined in Equation (1). The accumulation in the plant was calculated based on Equation (2):
where Canalyzed is the pharmaceutical concentration (µg/L), Vextract is the extracted volume, and Mplant is the mass of the plant part (root or shoot) taken for extraction.
2.6. Statistical Analyses
A homogeneity and normality analysis was conducted on all data that was obtained. Using one-way ANOVA, a correlation study was conducted to ascertain whether a relationship existed between the factors and the pertinent answer. The Tukey HSD test was employed to conduct post hoc research on each significant factor in order to identify significant variations from the collected findings. SPSS Version 21 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) was employed to conduct all statistical analyses. Substantial variations in the findings were demonstrated by p < 0.05, and inferences were derived at a confidence interval of 95% [41].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Isolation and Characterization of Rhizobacteria
During the isolation stage, 28 different bacterial colonies were obtained from the root area and adjacent soil of S. grossus exposed to pharmaceutical compounds. Table 1 summarizes the findings of biochemical testing (Gram stain, catalase, oxidase, and motility).

Table 1.
Biochemical characterization of isolated rhizobacteria (+: positive results, −: negative result).
Gram staining indicated that 17 of the S. grossus rhizobacteria were classified as Gram-positive, while 11 were identified as Gram-negative. Seventeen isolated rhizobacteria showed a positive response for the oxidase test, while sixteen showed a positive response for the catalase test. Nineteen isolates showed a positive result for the motility test.
3.2. Screening of Rhizobacteria Through Pharmaceutical Exposure
The bacterial growth results revealed that 6 of the 30 isolated rhizobacteria grew well (+++) in the pharmaceutical-contaminated medium. Table 2 summarizes the growth of rhizobacteria in the IBP- and PAR-contaminated medium.

Table 2.
Growth of rhizobacteria after five days of exposure to pharmaceutical compounds (+: poor, ++: fair, +++: good).
3.3. Removal of Pharmaceuticals by Selected Rhizobacteria
Six of the twenty-eight isolated rhizobacteria exhibited good growth on TSA, and these rhizobacteria were subsequently subjected to degradation assays. The results indicated that all six bacteria can degrade IBP and PAR during pharmaceutical exposure (Figure 2). The removals by bacteria C1, C2, and C7 were 78%, 89%, and 93%, respectively. Meanwhile, the removals by A2, A4, and B2 were only 50%, 48%, and 23%, respectively. Bacteria C1, C2, and C7 had the best degradation. Based on these findings, C1, C2, and C7 were chosen in the subsequent experiment to test for pharmaceutical degradation as a monoculture (Figure 3 and Figure 4).
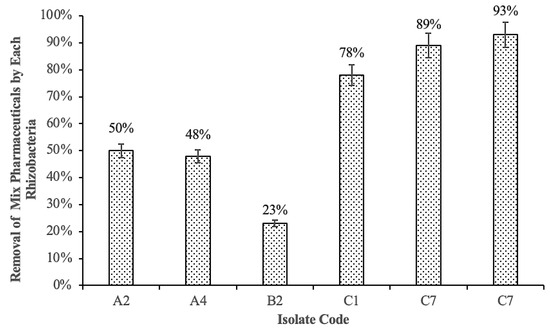
Figure 2.
Removal of mix pharmaceuticals (IBP and PAR) by each rhizobacteria.
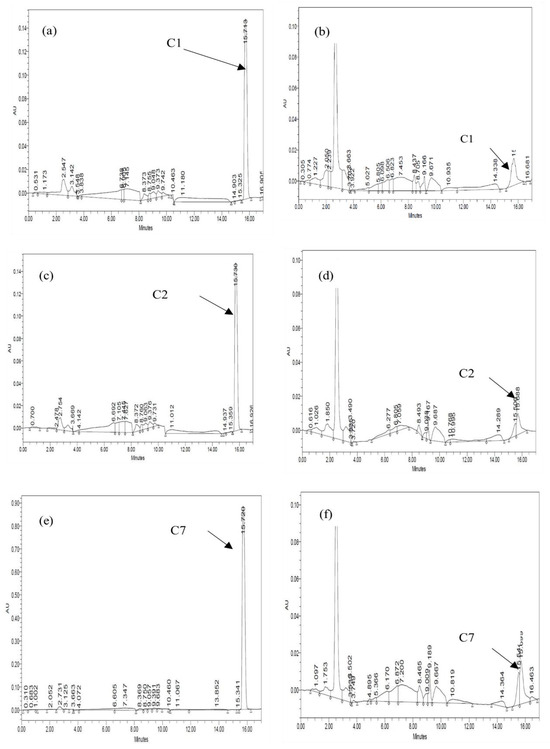
Figure 3.
Chromatogram of ibuprofen extracted at days 0 and 5 for monoculture: (a) C1 day 0, (b) C1 day 5, (c) C2 day 0, (d) C2 day 5, (e) C7 day 0, and (f) C7 day 5.
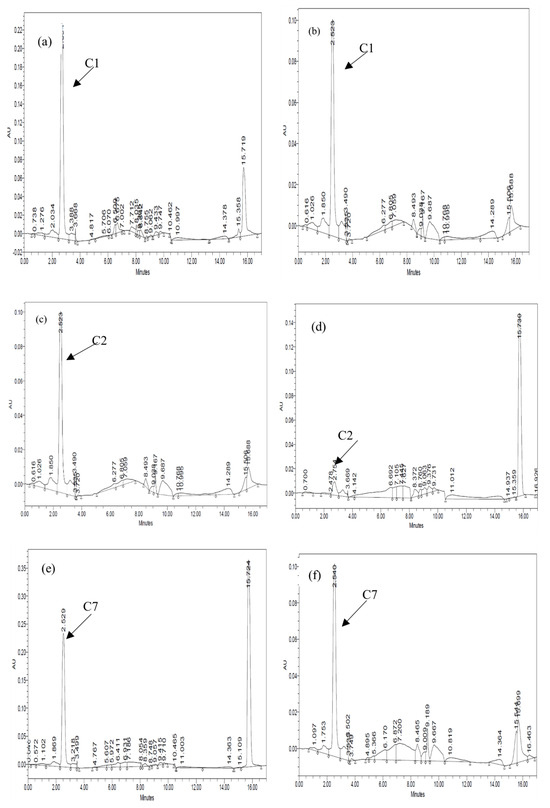
Figure 4.
Chromatogram of paracetamol extracted at 0 and 120 h for monoculture: (a) C1 day 0, (b) C1 day 5, (c) C2 day 0, (d) C2 day 5, (e) C7 day 0, and (f) C7 day 5.
The rate and extent of biodegradation were interpreted based on the HPLC chromatograms for residual pharmaceuticals. Figure 3 and Figure 4 show the resolved peaks in the pharmaceuticals’ chromatograms that were peak eluting, and they represented residual IBP and PAR. After five days of exposure, the HPLC chromatograms showed a lower signal than the zero-day chromatogram. The results indicate that all three bacterial strains can degrade IBP and PAR. Consequently, each bacterium exhibited varying efficiencies in breaking down the pharmaceutical compounds.
3.4. Identification of Selected Rhizobacteria
The three selected rhizobacteria from the screening test were identified using PCR techniques, and the 16S rRNA gene sequences of the isolated strains were submitted to the GenBank sequence database and identified, as detailed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Identification of isolated strains based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing.
A phylogenetic tree was generated to fully identify the rhizobacteria C1, C2, and C7. The phylogenetic tree revealed that the 16s rRNA sequence for the E. aerogenes isolate C1 was closely related to E. aerogenes strain S2-1, which was supported by 90% of the bootstrap value because they belonged to a similar genus (Figure 5). Consequently, this bacterium was generally identified as Enterobacter sp. strain C1. Given that the neighbor-joining tree was constructed based on the genetic distance between species, the branch length of this phylogenetic tree revealed how often divergence had occurred. Thus, a greater branch length corresponded with a greater degree of divergence. A more comprehensive molecular and biochemical analysis is required to identify Enterobacter sp. strain C1, as the current results do not allow for a specific species to be associated with the bacterium. In the future, the bacterium will be further identified to the species level by incorporating a variety of identification methods, including the determination of its genomic DNA content, DNA hybridization, and fatty acid profile.
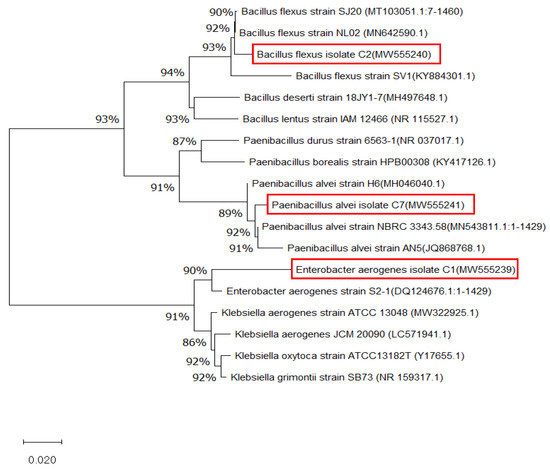
Figure 5.
A phylogram (neighbor-joining method) showing the genetic relationship between three bacteria (inside the red boxes), Enterobacter aerogenes, Bacillus flexus, and Paenilbacillus alvei, and other related reference microorganisms based on the 16s rRNA gene sequence analysis.
The phylogenetic analysis showed that B. flexus isolate C2 (Gram-positive) was genetically related to B. flexus strain NL02, which was supported by 94% of the bootstrap value. The length of these branches represented genetic distance. Going horizontally, it can be seen that Bacillus deseti strain 18JY1-7 and Bacillus lentus strain IAM 12466 were more distantly related to all of the other B. flexus, so it was the length of horizontal lines that was important in foreign genetic distances. The isolate C2 was identified as B. flexus and grouped into a similar clade to other B. flexus because the BLAST result revealed 99% similarity with those species. The isolate C7 (Gram-negative) was closely related to P. alvei NBRC3343.58 with a bootstrap value of 92%. Therefore, this isolate was assigned as P. alvei strain C7. Therefore, point 0.02 referred to nucleotides per site in the alignment that gave a measure of the scale of genetic distance between each of the bacterial groups.
3.5. Removal Efficiency of the Pharmaceuticals in Water and Sand During the Validation Run with and Without Rhizobacteria
3.5.1. Removal of Ibuprofen and Paracetamol from Water
Th initial HRT optimization test showed that the constructed wetland with HRT 5 (5 days) showed the best removal of IBP and PAR [38,42]. During the validation run, the IBP and PAR concentrations in the water decreased in all treatments (with and without rhizobacteria addition), and the removal efficiency increased throughout the tested period. In treatment tank 1, with rhizobacteria addition, the IBP and PAR concentration ranges were 138–10 and 3–0.8 µg/L, with removal efficiencies of 93% and 83% after 18 days of treatment, respectively (Figure 6). For treatment tank 2 without rhizobacteria addition, the concentration of IBP in the water decreased from 102 µg/L to 50 µg/L, and that of PAR decreased from 2.7 µg/L to 0.5 µg/L at the end of the study. Their removal efficiencies were 80% and 90.70%, respectively (Figure 6).
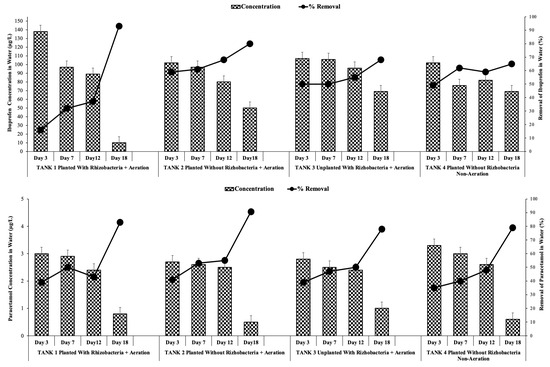
Figure 6.
Ibuprofen and paracetamol concentrations and removals in water under optimum conditions with and without rhizobacteria addition.
Statistical analysis revealed that rhizobacteria addition provided a significant difference in the concentrations of IBP and PAR in water. Meanwhile, in treatment tank 3 (unplanted with rhizobacteria addition), the concentration of IBP and PAR in the water was 107–69 and 2.8–1 µg/L, respectively. These values were still higher than those in treatment tank 4 without rhizobacteria addition, which were 102–69 and 3–0.6 µg/L, respectively. Therefore, rhizobacteria addition can enhance the degradation of IBP and PAR.
3.5.2. Removal of Ibuprofen and Paracetamol from Sand
IBP and PAR concentrations in the pilot-scale treatment tank 1 with rhizobacteria addition ranged within 70–10 and 2.70–2.30 µg/L, respectively, with removal efficiencies of 89 and 95% after 18 days of treatment (Figure 7). Statistical analysis revealed that rhizobacteria addition provided a significant difference between sand IBP and PAR concentrations and removal efficiency (p < 0.05).
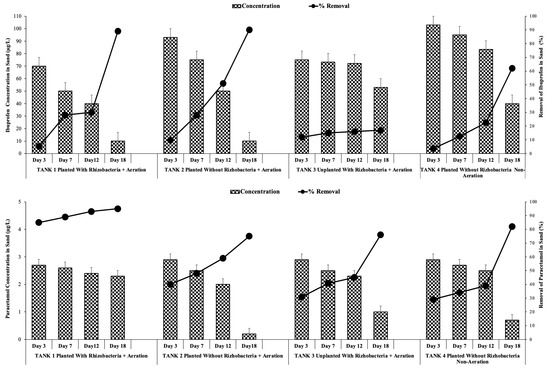
Figure 7.
Ibuprofen concentrations and removals in sand under optimum conditions with and without rhizobacteria addition.
The bioaugmentation of rhizobacteria resulted in an 89.95% removal efficiency of IBP and PAR in tank 1, which was higher than the removal efficiency in tank 2 without rhizobacteria addition (84.75%). Meanwhile, the removal of IBP and PAR from sand in tank 3 (71.76%) and tank 4 (62.82%) were lower than tank 1 and 2. Statistical analysis further demonstrated that phytoremediation with rhizobacteria addition significantly differed (p > 0.05) from that without rhizobacteria addition. These findings were consistent with those of Nguyen et al. [43], who demonstrated that the introduction of a bacterium consortium can notably enhance the degradation of pharmaceuticals in soil. Notable variations in IBP or PAR removal throughout the 18-day treatment period are highlighted by the presence or absence of rhizobacteria under 5-day HRT. Table 4 summarizes the removal of IBP and PAR from sand and water, respectively.

Table 4.
Ibuprofen and paracetamol removal in water and sand under optimal conditions without and with rhizobacterium additions.
It is intriguing that the removal of IBP from sediment (91%) and PAR from water (90%) was marginally higher in the absence of rhizobacteria addition than in the addition of rhizobacteria (83% and 89%, respectively) (Table 4). Although initially unexpected, these results may be attributed to microbial competition and abiotic factors in the rhizosphere environment [44,45]. In the case of IBP in sand, passive adsorption and physicochemical entrapment may be the primary mechanisms responsible for IBP retention, particularly in light of the hydrophobic character of IBP and its propensity to bind to particulate matter [46]. It is possible that the microenvironment was altered by the addition of rhizobacteria, which could have resulted in a reduction in adsorption affinity or a promotion of desorption by producing exudates [47,48]. For the case of PAR, its increased solubility and decreased affinity for solid particulates in water may render it more susceptible to spontaneous hydrolytic or photolytic degradation, which may be more effective under abiotic conditions [49,50]. These findings also suggested that the removal of IBP was more likely to occur due to the rhizodegradation mechanisms, while the removal of PAR was more likely to occur via assisted phytoextraction mechanisms (also discussed in Section 3.5.3).
3.5.3. Plant Uptake of Ibuprofen and Paracetamol (Shoots and Roots)
The results showed that IBP and PAR were detected inside the plant, indicating that IBP and PAR were adsorbed and accumulated in the roots and the shoots. This finding was consistent with that of previous research, indicating that plants can rapidly absorb xenobiotics and other pharmaceutical compounds [31]. Figure 8 shows that IBP and PAR concentrations in the roots and shoots were increased until day 18. Overall, pharmaceutical concentrations were on average higher in the upper part than in the root in both modes (with and without rhizobacteria addition), implying that IBP and PAR were absorbed and translocated to the upper part [51].
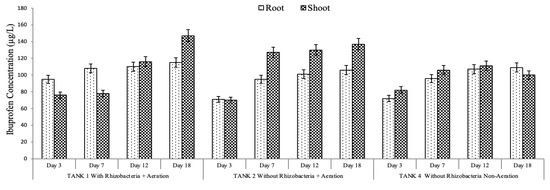
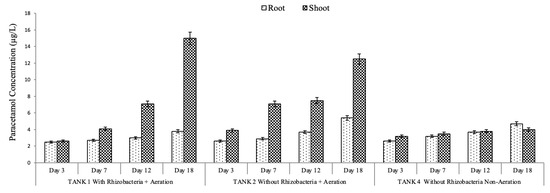
Figure 8.
Ibuprofen and paracetamol concentrations in the plant under optimum conditions without and with rhizobacterium addition.
However, another study found that pharmaceuticals (PAR, caffeine, and triclosan) were accumulated in the greater duckweed rhizosphere [27]. The rhizosphere offered a perfect environment for microbes that aid in pharmaceutical degradation. Previous studies have also shown that rhizospheres boost the number and activity of microorganisms owing to the diverse organic substrates provided by plant roots [52]. It is worth mentioning that the removal of IBP and PAR from water and sand (Figure 6 and Figure 7) does not directly match the plant uptake (Figure 8). This apparent inconsistency suggests that the main removal mechanism is not exclusively reliant on plant uptake but also encompasses substantial contributions from microbial degradation and rhizosphere-mediated transformation activities. PAR and IBP are recognized to undergo biodegradation through enzymatic routes facilitated by rhizospheric bacteria, resulting in their conversion into intermediate or final metabolites that might be undetectable in plant tissues [53,54]. The addition of rhizobacteria in the constructed wetland system augments transformation processes by activating co-metabolic pathways and promoting microbial enzyme synthesis [55]. Furthermore, the limited accumulation of these chemicals in shoot tissues indicates that transfer from roots to aerial parts is low [24], with a significant portion of the contaminant likely maintained or degraded in the rhizosphere or on the root surface. Based on the obtained findings, it is suggested that IBP was removed by rhizodegradation mechanisms, in which the rhizosphere’s microorganisms played an important role in the pharmaceutical compound’s removal [56]. The removal of PAR was suggested to occur via an assisted phytoextraction mechanism, in which rhizobacteria assist the degradation of pharmaceuticals to boost the subsequent uptake by plants [24,57].
4. Conclusions
The elevated levels of ibuprofen (IBP) and paracetamol (PAR) pollutants in wastewater have become a significant concern. The addition of rhizobacteria in constructed wetlands showed a promising alternative for pharmaceutical-contaminated wastewater. Three isolates from the rhizosphere of Scirpus grossus (Enterobacter aerogenes, Bacillus flexus, and Paenibacillus alvei) exhibited significant resistance to IBP and PAR. The incorporation of these three isolated rhizobacteria into a constructed wetland facilitates the removal of IBP and PAR from wastewater. Bioaugmentation resulted in a 13% increase in IBP removal from water and a 20% increase in PAR removal from sand compared to non-bioaugmented systems. The incorporation of rhizobacteria considerably improved the translocation of PAR into the shoot system of S. grossus, indicating the involvement of aided phytoextraction processes, whereas the elimination of IBP in wetlands is proposed to occur through rhizodegradation. Elucidation of the microbial degradation pathways is suggested to be conducted in the future to clearly portray the pharmaceutical degradation mechanisms in the constructed wetland. Additionally, analysis and assessment of the intermediate metabolites will be very useful to evaluate the ecological risks of the treated wastewater.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.R.S.A.; data curation, O.A.A.F. and S.B.K.; formal analysis, O.A.A.F.; funding acquisition, S.R.S.A., H.A.H., A.R.O., and N.‘I.I.; resources, S.R.S.A. and M.F.I.; supervision, S.R.S.A., H.A.H., A.R.O., and H.M.E.; validation, S.B.K.; visualization, S.B.K.; writing—original draft, O.A.A.F. and S.B.K.; writing—review editing, S.B.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia through a DIP-2024-001 research grant.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Samal, K.; Mahapatra, S.; Hibzur Ali, M. Pharmaceutical Wastewater as Emerging Contaminants (EC): Treatment Technologies, Impact on Environment and Human Health. Energy Nexus 2022, 6, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; He, J.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y. Adsorptive Removal of PPCPs from Aqueous Solution Using Carbon-Based Composites: A Review. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 3585–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL Falahi, O.A.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Hasan, H.A.; Othman, A.R.; Ewadh, H.M.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Imron, M.F. Occurrence of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Domestic Wastewater, Available Treatment Technologies, and Potential Treatment Using Constructed Wetland: A Review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 168, 1067–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.L.; Hooda, P.S.; Barker, J.; Barton, S.; Swinden, J. Ecotoxic Pharmaceuticals, Personal Care Products, and Other Emerging Contaminants: A Review of Environmental, Receptor-Mediated, Developmental, and Epigenetic Toxicity with Discussion of Proposed Toxicity to Humans. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 336–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhoy, I.S.; Daughton, C.G. Beyond the Medicine Cabinet: An Analysis of Where and Why Medications Accumulate. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Othman, A.R.; Hasan, H.A. Contaminants of Emerging Concern (CECs) in Aquaculture Effluent: Insight into Breeding and Rearing Activities, Alarming Impacts, Regulations, Performance of Wastewater Treatment Unit and Future Approaches. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.H.A.; Barros, R. Pharmaceuticals in Water: Risks to Aquatic Life and Remediation Strategies. Hydrobiology 2023, 2, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayode-Afolayan, S.D.; Ahuekwe, E.F.; Nwinyi, O.C. Impacts of Pharmaceutical Effluents on Aquatic Ecosystems. Sci. Afr. 2022, 17, e01288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choong, C.E.; Ibrahim, S.; Basirun, W.J. Mesoporous Silica from Batik Sludge Impregnated with Aluminum Hydroxide for the Removal of Bisphenol A and Ibuprofen. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 541, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakr, A.R.; Rahaman, M.S. Crossflow Electrochemical Filtration for Elimination of Ibuprofen and Bisphenol a from Pure and Competing Electrolytic Solution Conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zghoul, T.M.; Al-Qodah, Z.; Al-Jamrah, A. Performance, Modeling, and Cost Analysis of Chemical Coagulation-Assisted Solar Powered Electrocoagulation Treatment System for Pharmaceutical Wastewater. Water 2023, 15, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qodah, Z.; Al-Zghoul, T.M.; Jamrah, A. The Performance of Pharmaceutical Wastewater Treatment System of Electrocoagulation Assisted Adsorption Using Perforated Electrodes to Reduce Passivation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 20434–20448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maryam, B.; Buscio, V.; Odabasi, S.U.; Buyukgungor, H. A Study on Behavior, Interaction and Rejection of Paracetamol, Diclofenac and Ibuprofen (PhACs) from Wastewater by Nanofiltration Membranes. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 18, 100641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negarestani, M.; Motamedi, M.; Kashtiaray, A.; Khadir, A.; Sillanpää, M. Simultaneous Removal of Acetaminophen and Ibuprofen from Underground Water by an Electrocoagulation Unit: Operational Parameters and Kinetics. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nippatla, N.; Philip, L. Electrocoagulation-Floatation Assisted Pulsed Power Plasma Technology for the Complete Mineralization of Potentially Toxic Dyes and Real Textile Wastewater. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 125, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retnadhas, S.; Ducat, D.C.; Hegg, E.L. Nature-Inspired Strategies for Sustainable Degradation of Synthetic Plastics. JACS Au 2024, 4, 3323–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, Y.; Yun, J.; Zhang, G.; Zabed, H.M.; Qi, X. A Review on Constructed Wetlands-Based Removal of Pharmaceutical Contaminants Derived from Non-Point Source Pollution. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 26, 102504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Pant, A.; Dutta, K.; Rani, R.; Vithanage, M.; Daverey, A. Phytoremediation of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products Using the Constructed Wetland. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2024, 6, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahy, N.; Priyadarshini, A.; Sahoo, M.M.; Verma, A.K.; Daverey, A.; Sahoo, N.K. A Comprehensive Review on Eco-Toxicity and Biodegradation of Phenolics: Recent Progress and Future Outlook. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 27, 102423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, L.; Nian, K.; Long, T. Production of Higher Toxic Intermediates of Organic Pollutants during Chemical Oxidation Processes: A Review. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppan, N.; Padman, M.; Mahadeva, M.; Srinivasan, S.; Devarajan, R. A Comprehensive Review of Sustainable Bioremediation Techniques: Eco Friendly Solutions for Waste and Pollution Management. Waste Manag. Bull. 2024, 2, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiangyu, B.; Chao, L.; Shilong, H.; Jiping, Z.; Hu, J. Combining Advanced Oxidation Processes with Biological Processes in Organic Wastewater Treatment: Recent Developments, Trends, and Advances. Desalin. Water Treat. 2025, 323, 101263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, S.B.; Ahmad, A.; Said, N.S.M.; Imron, M.F.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Othman, A.R.; Purwanti, I.F.; Hasan, H.A. Macrophytes as Wastewater Treatment Agents: Nutrient Uptake and Potential of Produced Biomass Utilization toward Circular Economy Initiatives. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryal, M. Phytoremediation Strategies for Mitigating Environmental Toxicants. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, T.; Kelly, B.C.; Gin, K.Y.H. Bioaccumulation Behaviour of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in a Constructed Wetland. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahl, S.; Nivala, J.; van Afferden, M.; Müller, R.A.; Reemtsma, T. Effect of Design and Operational Conditions on the Performance of Subsurface Flow Treatment Wetlands: Emerging Organic Contaminants as Indicators. Water Res. 2017, 125, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Campos, L.C. Removal of Selected Emerging PPCP Compounds Using Greater Duckweed (Spirodela polyrhiza) Based Lab-Scale Free Water Constructed Wetland. Water Res. 2017, 126, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Wu, B.; Ng, W.J.; Appan, A.; Tan, S.K. Phytoextraction, Phytotransformation and Rhizodegradation of Ibuprofen Associated with Typha angustifolia in a Horizontal Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetland. Water Res. 2016, 102, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, S.N.; Ighalo, J.O.; Aniagor, C.O.; Igwegbe, C.A. Removal of Ibuprofen from Aqueous Media by Adsorption: A Comprehensive Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Ngo, H.H. Micropollutants Removal and Health Risk Reduction in a Water Reclamation and Ecological Reuse System. Water Res. 2018, 138, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klampfl, C.W. Metabolization of Pharmaceuticals by Plants after Uptake from Water and Soil: A Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 111, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreshtha, K.; Prakash, A.; Pandey, P.K.; Pal, A.K.; Singh, J.; Tripathi, P.; Mitra, D.; Jaiswal, D.K.; de los Santos-Villalobos, S.; Tripathi, V. Isolation and Characterization of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria from Cacti Root under Drought Condition. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2025, 8, 100319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaruzzaman, M.A.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Hasan, H.A.; Hassan, M.; Othman, A.R.; Idris, M. Characterisation of Pb-Resistant Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) from Scirpus grossus. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 23, 101456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwanti, I.F.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Titah, H.S.; Tangahu, B.V. Identification of Acid and Aluminium Resistant Bacteria Isolated from Aluminium Recycling Area. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 945–954. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, A.R.; Ismail, N.S.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Hasan, H.A.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Sharuddin, S.S.N.; Ismail, N.‘I. Potential of Indigenous Biosurfactant-Producing Fungi from Real Crude Oil Sludge in Total Petroleum Hydrocarbon Degradation and Its Future Research Prospects. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, S.B.; Imron, M.F.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Othman, A.R.; Purwanti, I.F.; Hasan, H.A. Treatment of Real Aquaculture Effluent Using Bacteria-Based Bioflocculant Produced by Serratia marcescens. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, H.A.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Al-Attabi, A.W.N.; Nash, D.A.H.; Anuar, N.; Abd Rahman, N.; Sulistiyaning Titah, H. Removal of Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, COD and Nitrogen Compounds from Pharmaceutical Wastewater Using Aerobic Suspension-Sequencing Batch Reactor (ASSBR). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 157, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL Falahi, O.A.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Hasan, H.A.; Othman, A.R.; Ewadh, H.M.; Al-Baldawi, I.A.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Imron, M.F.; Ismail, N.I. Simultaneous Removal of Ibuprofen, Organic Material, and Nutrients from Domestic Wastewater through a Pilot-Scale Vertical Sub-Surface Flow Constructed Wetland with Aeration System. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 43, 102214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Baldawi, I.A.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Anuar, N.; Mushrifah, I. Bioaugmentation for the Enhancement of Hydrocarbon Phytoremediation by Rhizobacteria Consortium in Pilot Horizontal Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semreen, M.H.; Shanableh, A.; Semerjian, L.; Alniss, H.; Mousa, M.; Bai, X.; Acharya, K. Simultaneous Determination of Pharmaceuticals by Solid-Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry: A Case Study from Sharjah Sewage Treatment Plant. Molecules 2019, 24, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imron, M.F.; Firdaus, A.A.F.; Flowerainsyah, Z.O.; Rosyidah, D.; Fitriani, N.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Hasan, H.A.; Wibowo, Y.G. Phytotechnology for Domestic Wastewater Treatment: Performance of Pistia stratiotes in Eradicating Pollutants and Future Prospects. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 51, 103429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osama, O.A.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Hasan, H.A.; Othman, A.R.; Ewadh, H.M.; Al-Baldawi, I.A.; Sharuddin, S.S.N.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Ismail, N.I. Elimination of Mixed Ibuprofen and Paracetamol from Spiked Domestic Wastewater via a Pilot Continuous Aerated Sub-Surface Constructed Wetland System. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 50, 103308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.M.; Afzal, M.; Ullah, I.; Shahid, N.; Baqar, M.; Arslan, M. Removal of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products Using Constructed Wetlands: Effective Plant-Bacteria Synergism May Enhance Degradation Efficiency. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 21109–21126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; He, Y.; Chen, Y. Rhizosphere Microbiome Regulation: Unlocking the Potential for Plant Growth. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2025, 8, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Li, D.; Ding, J.; Xiao, X.; Liang, Y. Microbial Coexistence in the Rhizosphere and the Promotion of Plant Stress Resistance: A Review. Environ. Res. 2023, 222, 115298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbat, C.; Pinna, A.; Andres, Y.; Villot, A.; Awad, S. Adsorption of Ibuprofen from Aqueous Solution onto a Raw and Steam-Activated Biochar Derived from Recycled Textiles Insulation Panels at End-of-Life: Kinetic, Isotherm and Fixed-Bed Experiments. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Motesharezadeh, B.; Hosseini, H.M.; Alikhani, H.; Zolfaghari, A.A. Root-Induced Changes of Zn and Pb Dynamics in the Rhizosphere of Sunflower with Different Plant Growth Promoting Treatments in a Heavily Contaminated Soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Agrawal, S.; Bhat, S.A.; Américo-Pinheiro, J.H.P.; Shahi, S.K.; Kumar, S. Environmental Impact, Health Hazards, and Plant-Microbes Synergism in Remediation of Emerging Contaminants. Clean. Chem. Eng. 2022, 2, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, D.; Tzvetkov, G.; Kaneva, N. Degradation of Paracetamol in Distilled and Drinking Water via Ag/ZnO Photocatalysis under UV and Natural Sunlight. Water 2023, 15, 3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Zavala, M.Á.; Jaber Lara, C.R. Degradation of Paracetamol and Its Oxidation Products in Surface Water by Electrochemical Oxidation. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mininni, A.N.; Pietrafesa, A.; Calabritto, M.; Di Biase, R.; Brunetti, G.; De Mastro, F.; Murgolo, S.; De Ceglie, C.; Salerno, C.; Dichio, B. Uptake and Translocation of Pharmaceutically Active Compounds by Olive Tree (Olea europaea L.) Irrigated with Treated Municipal Wastewater. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1382595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Baldawi, I.A.; Mohammed, A.A.; Mutar, Z.H.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Jasim, S.S.; Almansoory, A.F.; Ismail, N.’I. Application of Phytotechnology in Alleviating Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) in Wastewater: Source, Impacts, Treatment, Mechanisms, Fate, and SWOT Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 319, 128584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Langenhoff, A.A.M.M.; Sutton, N.B.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M.M.; Blokland, M.H.; Chen, F.; Huber, C.; Schröder, P. Metabolism of Ibuprofen by Phragmites australis: Uptake and Phytodegradation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4576–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, K.M.; Girardi, C.; Miltner, A.; Gehre, M.; Schäffer, A.; Kästner, M. Contribution of Microorganisms to Non-Extractable Residue Formation during Biodegradation of Ibuprofen in Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 445–446, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.Z.; Singh, K.; Chandra, R. Recent Advances of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) for Eco-Restoration of Polluted Soil. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2024, 23, 100845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.U.; Khan, A.N.; Waris, A.; Ilyas, M.; Zamel, D. Phytoremediation of Pollutants from Wastewater: A Concise Review. Open Life Sci. 2022, 17, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badar, Z.; Shanableh, A.; El-Keblawy, A.; Mosa, K.A.; Semerjian, L.; Al Mutery, A.; Hussain, M.I.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Tsombou, F.M.; Ayyaril, S.S.; et al. Assessment of Uptake, Accumulation and Degradation of Paracetamol in Spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) under Controlled Laboratory Conditions. Plants 2022, 11, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).