Monitoring the Permeability and Evaluating the Impact of Cleaning on Two Permeable Pavement Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Experimental Design
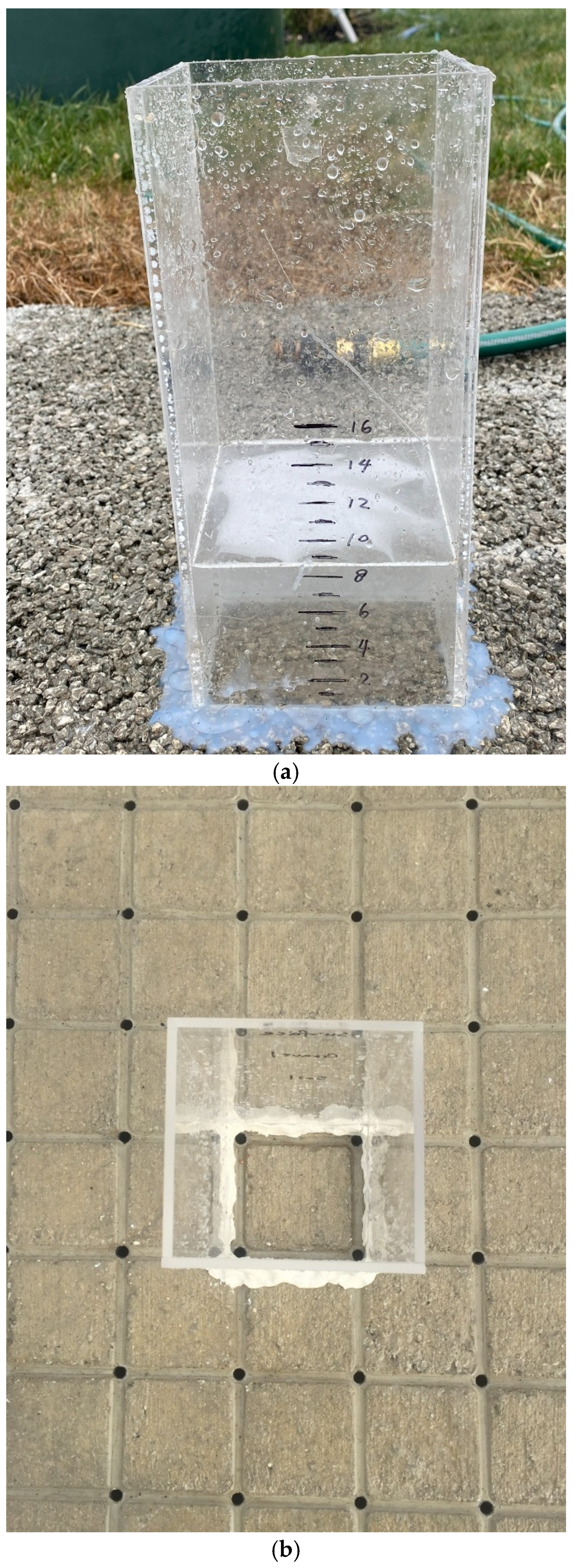
2.1. Permeability Measurement
2.2. Pavement Maintenance, Cleaning, and Operation Process
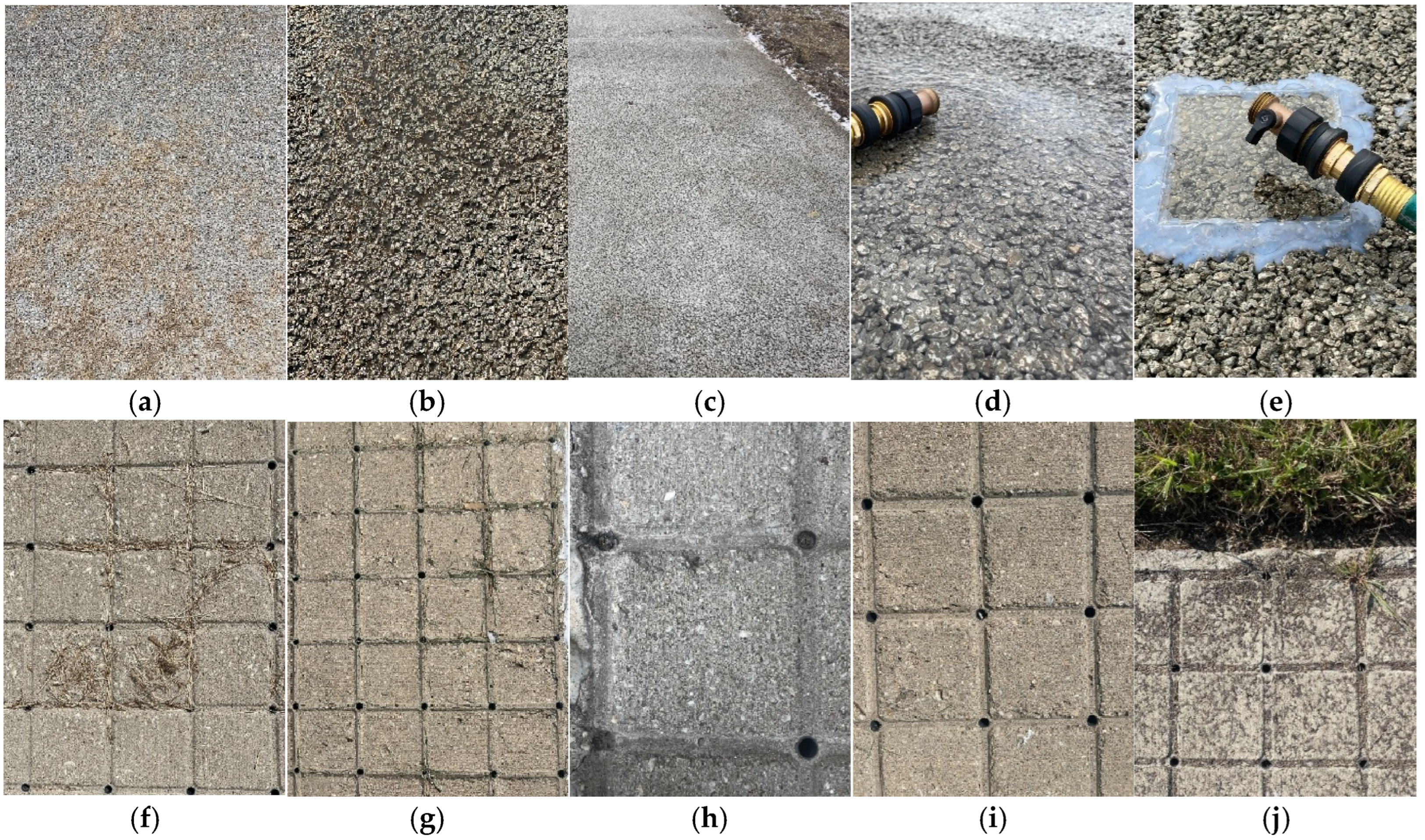
2.3. Visual Inspection of the Pavement Site
3. Results and Discussion
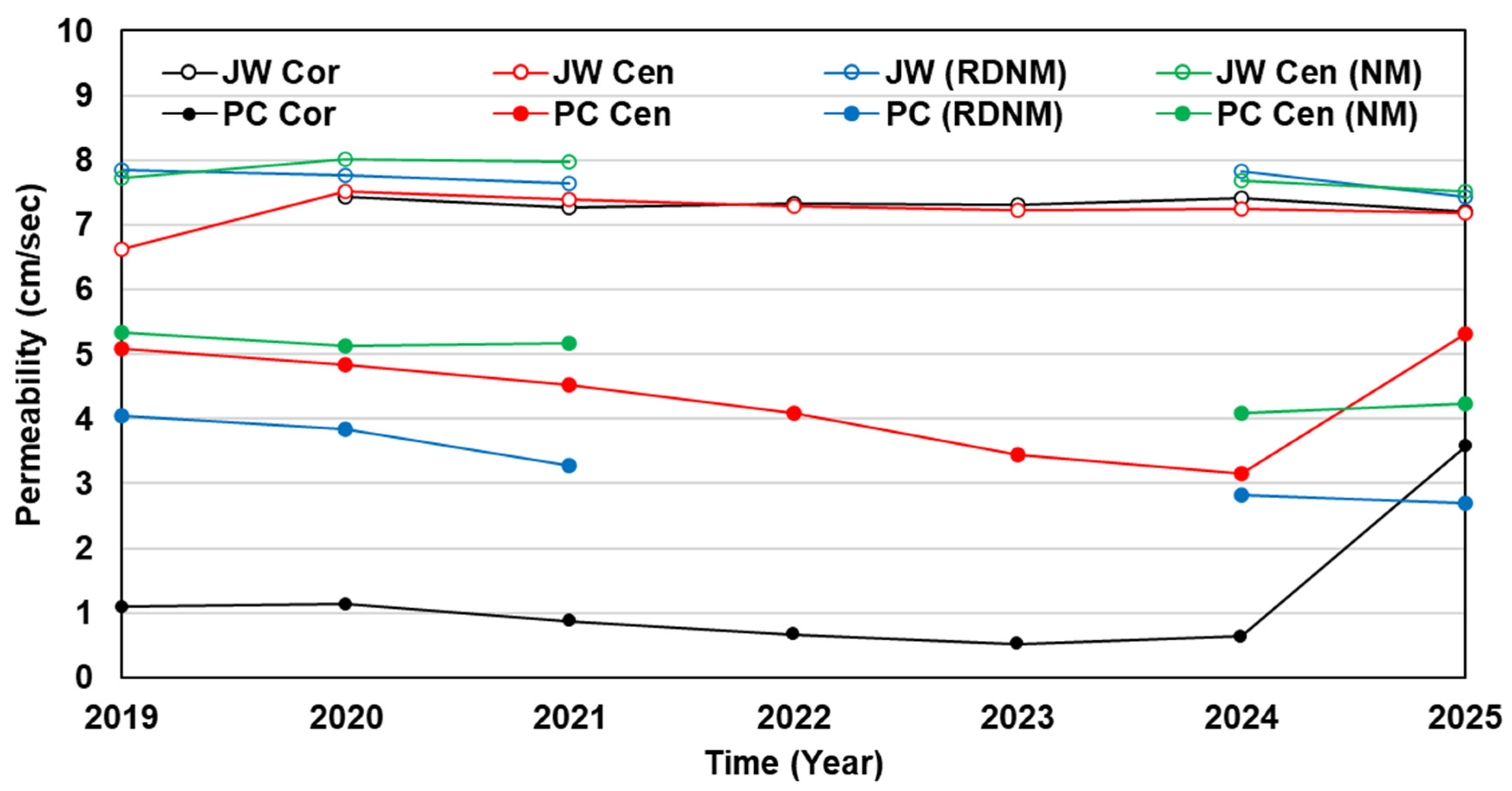
3.1. Permeability Trend of PC and JW
3.2. Permeability of PC and JW Before and After Maintenance
3.3. Observations on PC and JW
3.3.1. Visual Inspection on the Surface of Pavements
3.3.2. Permeability at Various Locations
3.3.3. Operation of the Pressure Washer
3.3.4. Observations Inside JW Aqueducts
3.3.5. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalnay, E.; Cai, M. Impact of urbanization and land-use change on climate. Nature 2003, 423, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buyantuyev, A.; Wu, J. Urban heat islands and landscape heterogeneity: Linking spatiotemporal variations in surface temperatures to land-cover and socioeconomic patterns. Landsc. Ecol. 2010, 25, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Arthur, S.T. The impact of land use—Land cover changes due to urbanization on surface microclimate and hydrology: A satellite perspective. Glob. Planet. Change 2000, 25, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Long, H. The economic and environmental effects of land use transitions under rapid urbanization and the implications for land use management. Habitat Int. 2018, 82, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterthwaite, D. The implications of population growth and urbanization for climate change. Environ. Urban. 2009, 21, 545–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, S.; Watson, J.E.M.; Salazar, A.; Thatcher, M.; McAlpine, C.A. The impact of urbanization and climate change on urban temperatures: A systematic review. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 1921–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, C.L.; Gibbons, C.J. Impervious Surface Coverage: The Emergence of a Key Environmental Indicator. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1996, 62, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, M.L.; Dinis-Almeida, M.; Fael, C.S. Permeable pavements—Green infrastructures as a flood mitigation measure. Acta Hortic. 2018, 1215, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stempihar, J.J.; Pourshams-Manzouri, T.; Kaloush, K.E.; Rodezno, M.C. Porous Asphalt Pavement Temperature Effects for Urban Heat Island Analysis. Transp. Res. Rec. 2012, 2293, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, D.B.; Leavitt, J. Field Evaluation of Permeable Pavement Systems for Improved Stormwater Management. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1999, 65, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrappa, A.K.; Biligiri, K.P. Pervious concrete as a sustainable pavement material–research findings and future prospects: A state-of-the-art review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, H.M.; Akib, S.; Karim, M.R. Permeable pavement and stormwater management systems: A review. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 2649–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäckström, M. Ground temperature in porous pavement during freezing and thawing. J. Transp. Eng. 2000, 126, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rubaei, A.M.; Stenglein, A.L.; Viklander, M.; Blecken, G.-T. Long-term hydraulic performance of porous asphalt pavements in northern Sweden. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2013, 139, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.M.; Chen, J.W.; Chen, T.H.; Lecher, T.; Davidson, P.C. Measurement of permeability and comparison of pavements. Water 2019, 11, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.; Akin, M.; Shi, X. Permeable concrete pavements: A review of environmental benefits and durability. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 1605–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruppu, U.; Rahman, A.; Rahman, M.A. Permeable pavement as a stormwater best management practice: A review and discussion. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illinois Department of Natural Resources. Model Stormwater Management Ordinance. Version 1. Office of Water Resources. 2015. Available online: https://dnr.illinois.gov/content/dam/soi/en/web/dnr/waterresources/documents/il-model-stormwater-ordinance.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Razzaghmanesh, M.; Beecham, S. A review of permeable pavement clogging investigations and recommended maintenance regimes. Water 2018, 10, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, R.J.; Al-Rubaei, A.M.; Blecken, G.T.; Viklander, M.; Hunt, W.F. Maintenance measures for preservation and recovery of permeable pavement surface infiltration rate: The effects of street sweeping, vacuum cleaning, high pressure washing, and milling. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 169, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Lin, Z.; Li, L.; Wu, Q. Pore characteristics of pervious concrete and their influence on permeability attributes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 327, 126074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Ge, X.; Tong, B.; Schaefer, V.; Wang, K.; Li, C. The quantitative assessment of clogging and cleaning effects on the permeability of pervious concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 335, 127455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Wille, K. Linking pore system characteristics to the compressive behavior of pervious concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 70, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kia, A.; Wong, H.S.; Cheeseman, C.R. High-strength clogging resistant permeable pavement. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Kozak, J.; Hundal, L.; Cox, A.; Zhang, H.; Granato, T. In-situ infiltration performance of different permeable pavements in an employee used parking lot—A four-year study. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 167, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, T.; Tajudin, A.N.; Wulaningtyas, A.H.; Andika, N.; Irawan, M.Z.; Widyatmoko, I. Recent developments in mitigating clogging in permeable pavements: A state-of-the-art review. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2025, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boogaard, F.; Lucke, T.; Beecham, S. Effect of age of permeable pavements on their infiltration function. Clean Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, E.Z. A Field Study to Evaluate Permeable Pavement Surface Infiltration Rates, Runoff Quantity, Runoff Quality, and Exfiltrate Quality. Master’s Thesis, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA, 2005. Available online: https://repository.lib.ncsu.edu/items/c837c72a-b432-42a5-98eb-11f4b49f8b9d (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Lucke, T.; Beecham, S. Field investigation of clogging in a permeable pavement system. Build. Res. J. 2011, 39, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcaida, A.K.; Nguyen, T.H.; Ahn, J. Investigation of particle-related clogging of sustainable concrete pavements. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.M.; Chen, J.W.; Lecher, T.; Chen, T.H.; Davidson, P. Assessment of clogging of permeable pavements by measuring change in permeability. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Architecture and Building Research Institute of Taiwan. Manual of Low Embodied-Carbon Building Rating System; Architecture and Building Research Institute of Taiwan: Taiwan, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- China Municipality. Sponge City Construction: Practical Technical Handbook; China Building Materials Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cooley, L.A., Jr. Permeability of superpave mixtures: Evaluation of field permeameters. In NCAT Report 99-1; National Center for Asphalt Technology (NCAT): Auburn, AL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- C1701/C1701M; Standard Test Method for Infiltration Rate of in Place Pervious Concrete. American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM): West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.





| Pavement Type | Application | Maintenance | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porous asphalt (PA) | Traffic/pedestrian surfaces and infiltration | Vacuum, pressure wash, mill, and seasonal upkeep |
|
| Concrete grid pavement (CGP) | Lots, driveways, and access roads | Vacuum removal of debris |
|
| Permeable interlocking concrete pavers (PICPs) | Roads, parking, and pedestrian zones | Surface joint cleaning |
|
| Concrete block pavers (CBPs), plastic grids, and pervious/porous pavement | Lots, paths, driveways, and turf | No method |
|
| Permeable pavers (PPs) | Employee parking lot | Spray, sweep, and vacuum; jet wash and suction |
|
| Permeable concrete pavements (PCPs) | LID zones, low traffic, and pedestrian areas | Hose rinse and vacuum |
|
| Clogging-resistant pavement (CRP) | Urban drainage and low-traffic areas | CRP’s design resists clogging |
|
| Pad | Left | Middle | Right | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area 1 | Crl | Ctr | Crr | Crl | Ctr | Crr | Crl | Ctr | Crr |
| Measurement | 2 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 |
| 2020 | 1.38 | 4.50 | 1.02 | 1.82 | 5.45 | 2.05 | 0.32 | 4.54 | 0.25 |
| 2021 | 0.76 | 4.26 | 0.40 | 1.65 | 5.22 | 1.94 | 0.41 | 4.09 | 0.14 |
| 2022 | 0.22 | 3.75 | 0.28 | 1.52 | 4.74 | 1.72 | 0.28 | 3.82 | 0 |
| 2023 | 0 | 3.22 | 0 | 1.32 | 4.22 | 1.46 | 0.35 | 2.89 | 0 |
| Pad | Left | Middle | Right | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area 1 | Crl | Ctr | Crr | Crl | Ctr | Crr | Crl | Ctr | Crr |
| Measurement | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 2020 | 7.05 | 7.67 | 7.28 | 7.32 | 7.04 | 7.13 | 7.13 | 7.86 | 7.62 |
| 2021 | 7.26 | 7.62 | 7.86 | 7.39 | 7.12 | 7.35 | 7.05 | 7.44 | 7.02 |
| 2022 | 6.90 | 7.39 | 7.59 | 7.26 | 6.82 | 7.28 | 7.33 | 7.66 | 7.48 |
| 2023 | 7.12 | 7.28 | 8.17 | 7.57 | 7.11 | 7.52 | 7.04 | 7.26 | 7.11 |
| Pavement | PC | JW | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pad | Left | Middle | Right | Left | Middle | Right | |||||||||||||
| Location 1 | Crl | Ctr | Crr | Crl | Ctr | Crr | Crl | Ctr | Crr | Crl | Ctr | Crr | Crl | Ctr | Crr | Crl | Ctr | Crr | |
| Measurement | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| Before Wash | 08/2024 | 0.13 | 2.80 | 0.37 | 1.28 | 4.25 | 1.56 | 0.51 | 2.44 | 0 | 7.52 | 6.78 | 7.34 | 7.04 | 7.30 | 7.52 | 6.95 | 7.63 | 6.85 |
| After Wash | 09/2024 | 2.87 | 5.58 | 2.55 | 4.60 | 5.70 | 4.43 | 4.50 | 5.05 | 2.54 | 7.30 | 6.67 | 7.28 | 7.62 | 7.22 | 7.94 | 7.20 | 7.19 | 7.63 |
| 04/2025 | 3.09 | 5.42 | 2.49 | 4.41 | 5.53 | 4.04 | 4.74 | 4.99 | 2.69 | 6.98 | 6.64 | 7.58 | 7.12 | 7.65 | 7.25 | 6.98 | 7.28 | 7.25 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perez, O.; Chen, L.-M.; Chen, J.-W.; Lecher, T.J.; Simpson, L.A.; Chen, T.-H.; Davidson, P.C. Monitoring the Permeability and Evaluating the Impact of Cleaning on Two Permeable Pavement Systems. Water 2025, 17, 2140. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142140
Perez O, Chen L-M, Chen J-W, Lecher TJ, Simpson LA, Chen T-H, Davidson PC. Monitoring the Permeability and Evaluating the Impact of Cleaning on Two Permeable Pavement Systems. Water. 2025; 17(14):2140. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142140
Chicago/Turabian StylePerez, Oscar, Lu-Ming Chen, Jui-Wen Chen, Timothy J. Lecher, Lane A. Simpson, Ting-Hao Chen, and Paul C. Davidson. 2025. "Monitoring the Permeability and Evaluating the Impact of Cleaning on Two Permeable Pavement Systems" Water 17, no. 14: 2140. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142140
APA StylePerez, O., Chen, L.-M., Chen, J.-W., Lecher, T. J., Simpson, L. A., Chen, T.-H., & Davidson, P. C. (2025). Monitoring the Permeability and Evaluating the Impact of Cleaning on Two Permeable Pavement Systems. Water, 17(14), 2140. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142140







