Intelligent Optimized Diagnosis for Hydropower Units Based on CEEMDAN Combined with RCMFDE and ISMA-CNN-GRU-Attention
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CEEMDAN Algorithm
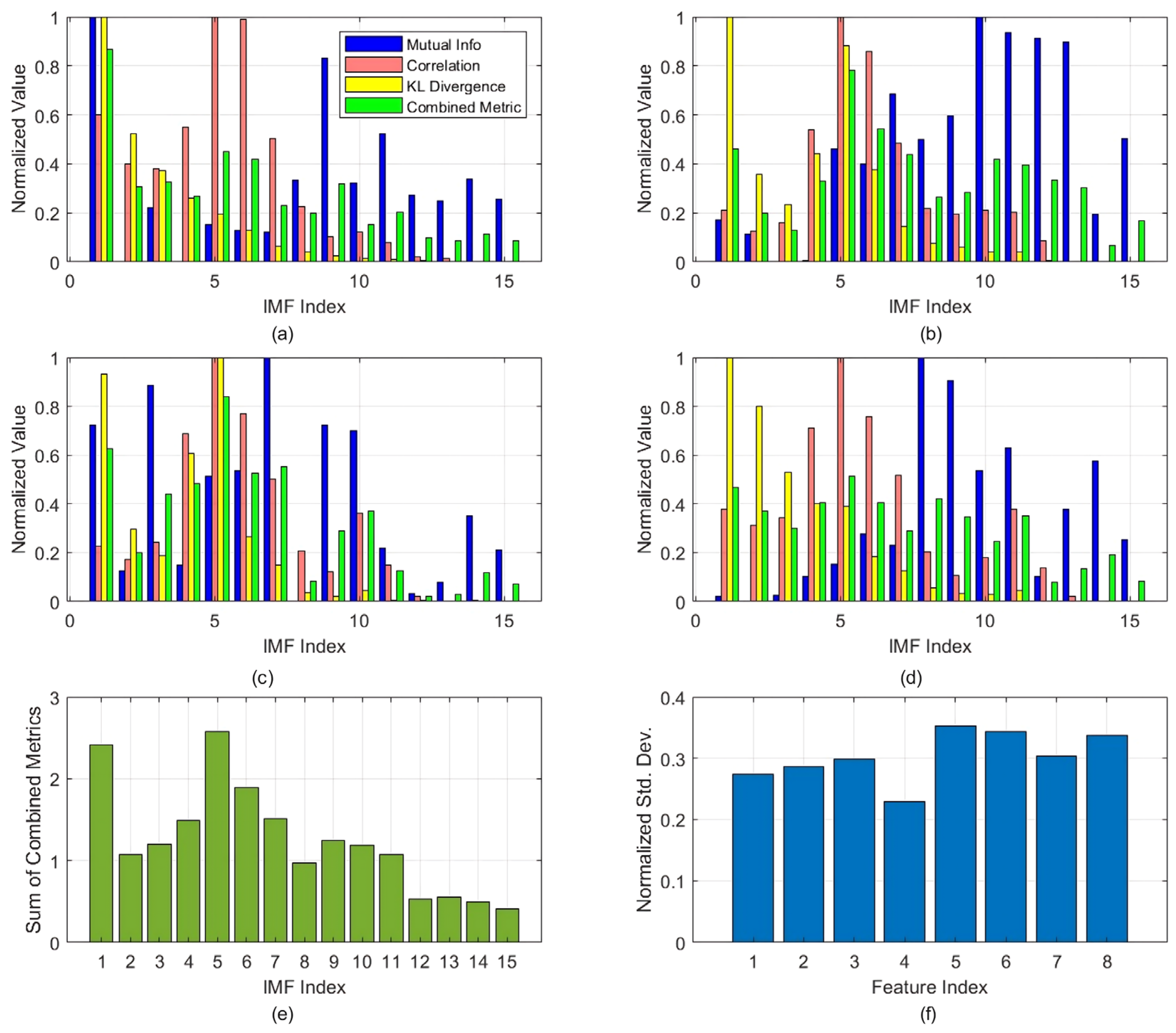
2.2. Selection of Mode Decomposition Components
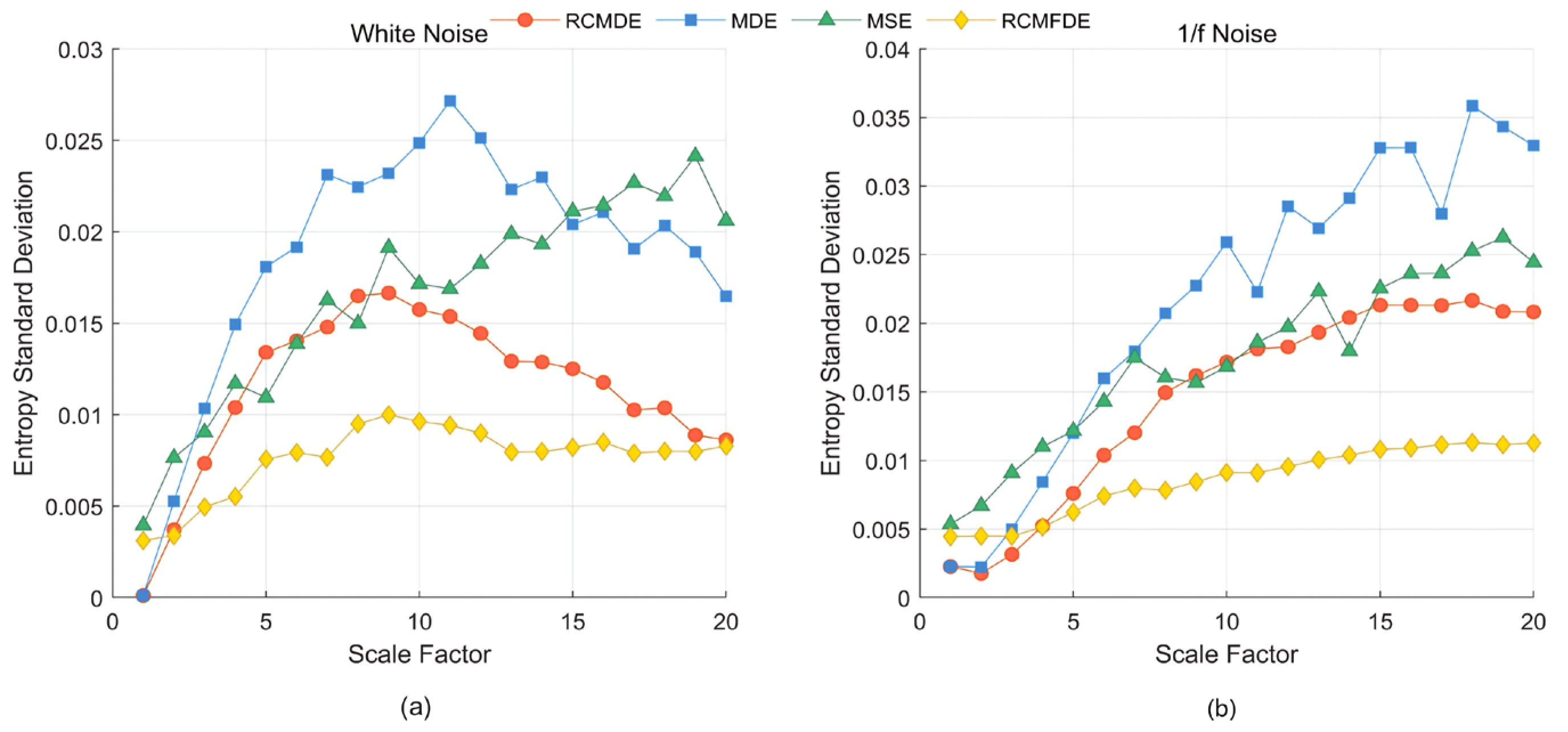
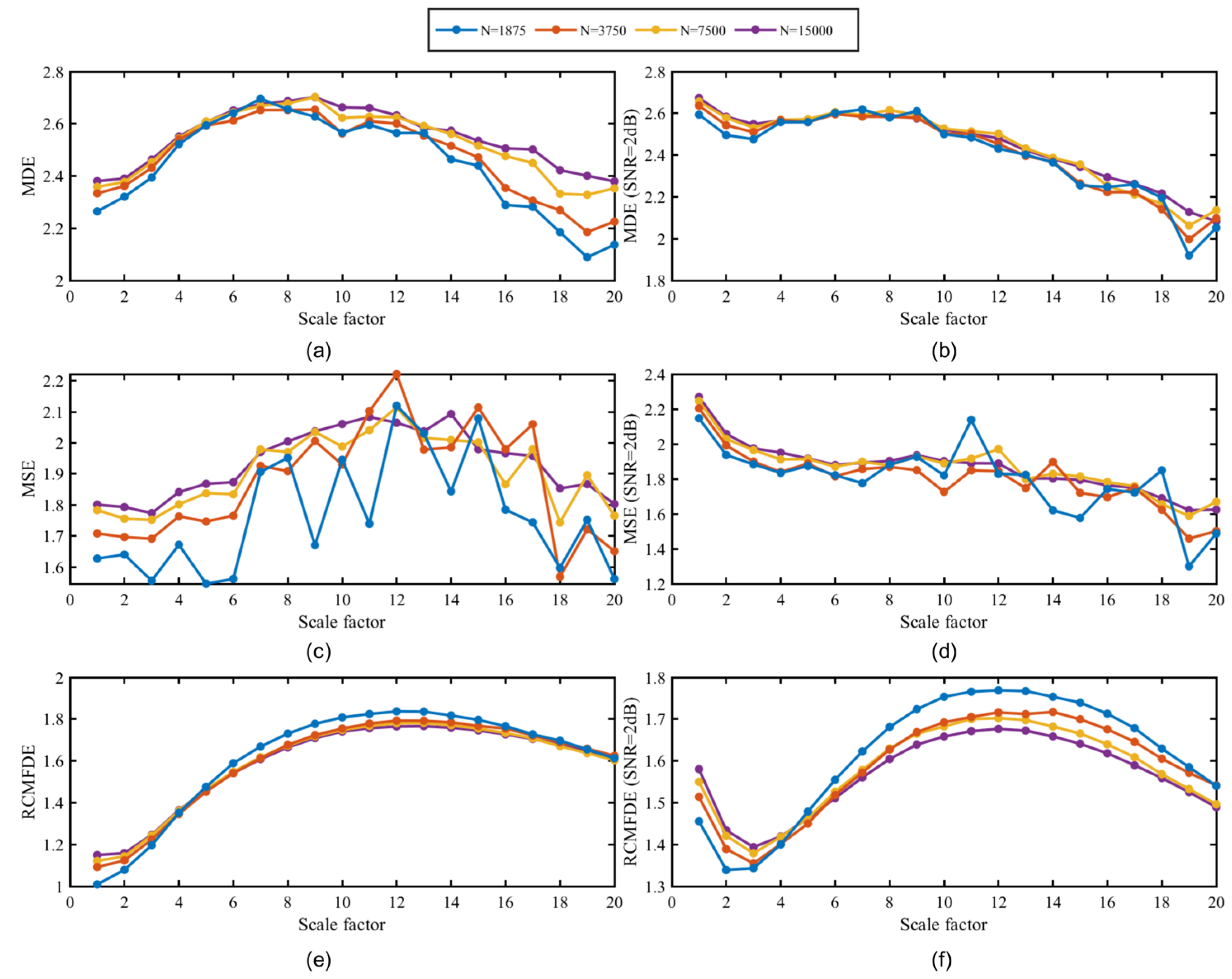
2.3. Refined Composite Multiscale Fluctuation Dispersion Entropy (RCMFDE)
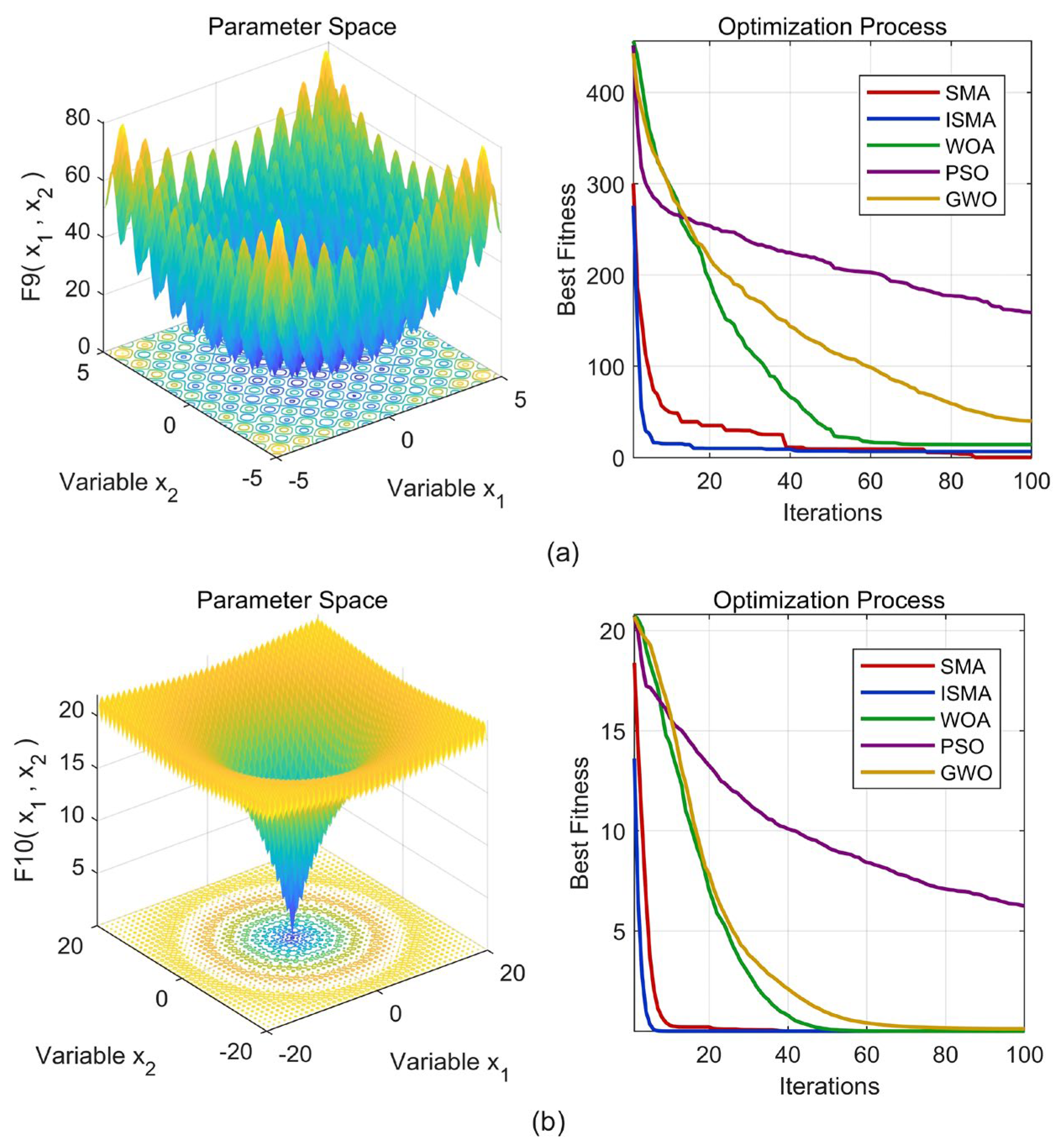
2.4. Establishment of the ISMA Algorithm
2.5. CNN-GRU-Attention Model
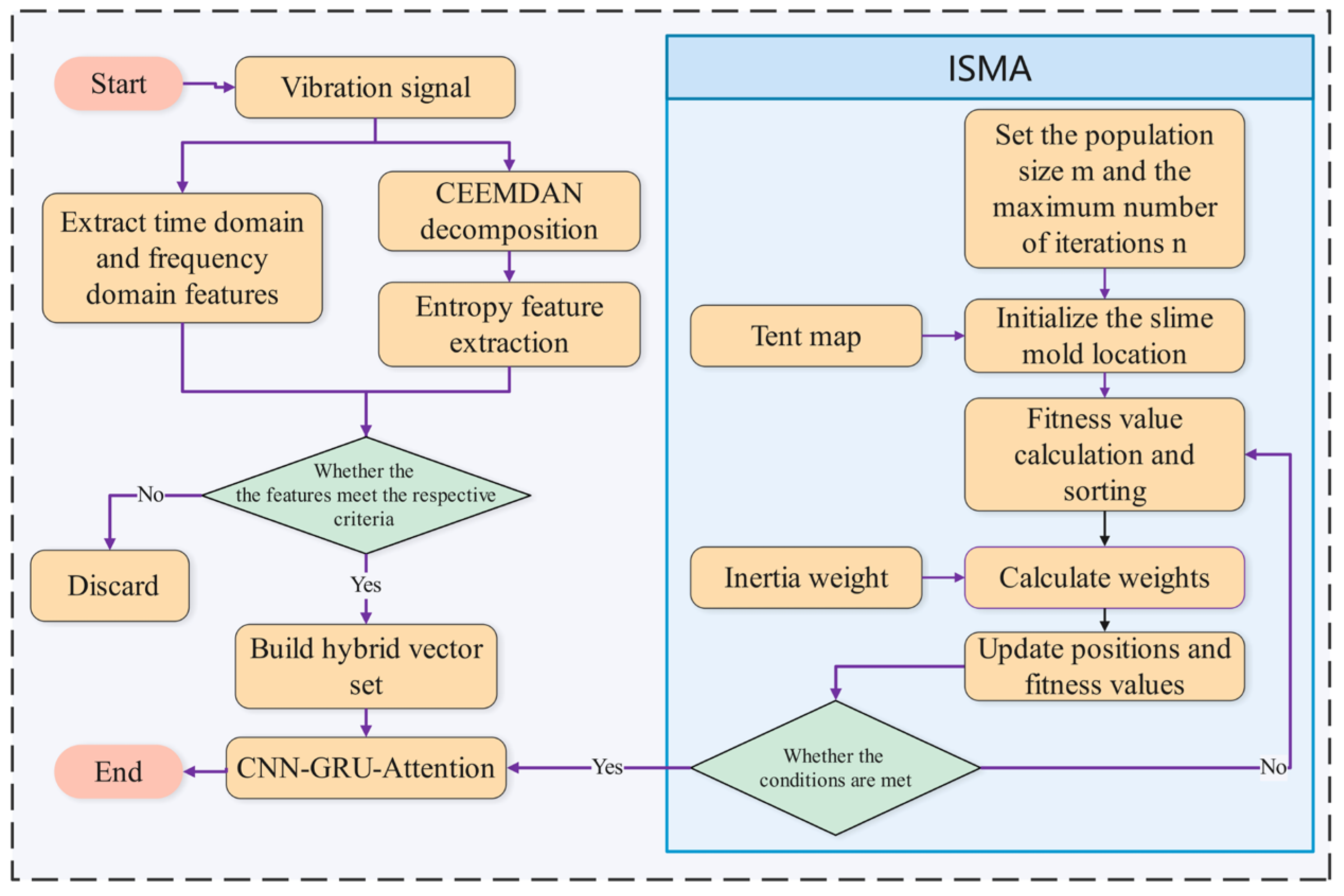
2.6. Proposed Model
3. Results and Discussion
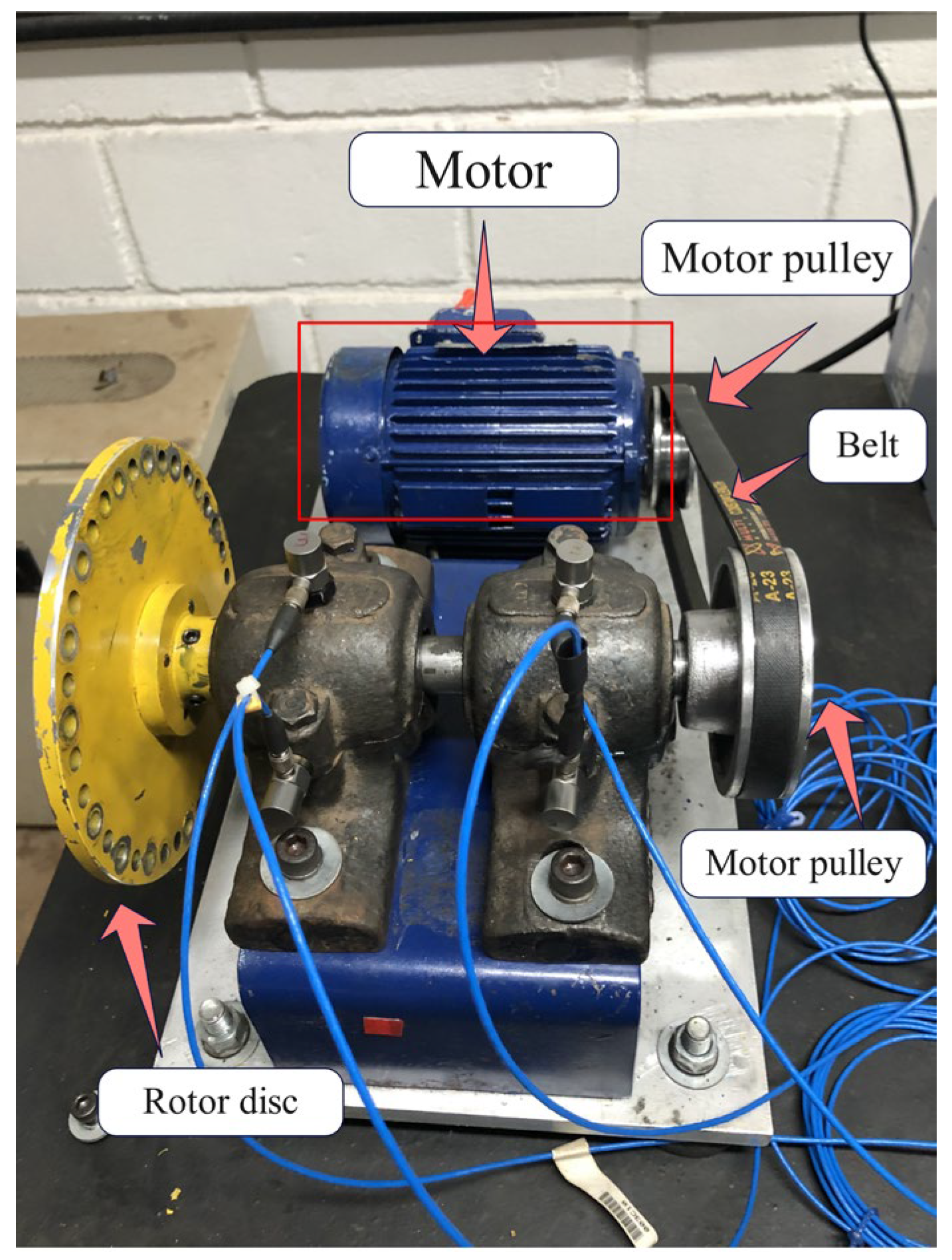
3.1. Simulation Experiments
3.2. CEEMDAN Decomposition
3.3. Constructing the Hybrid Feature Vector Set
3.4. RCMFDE Performance Analysis
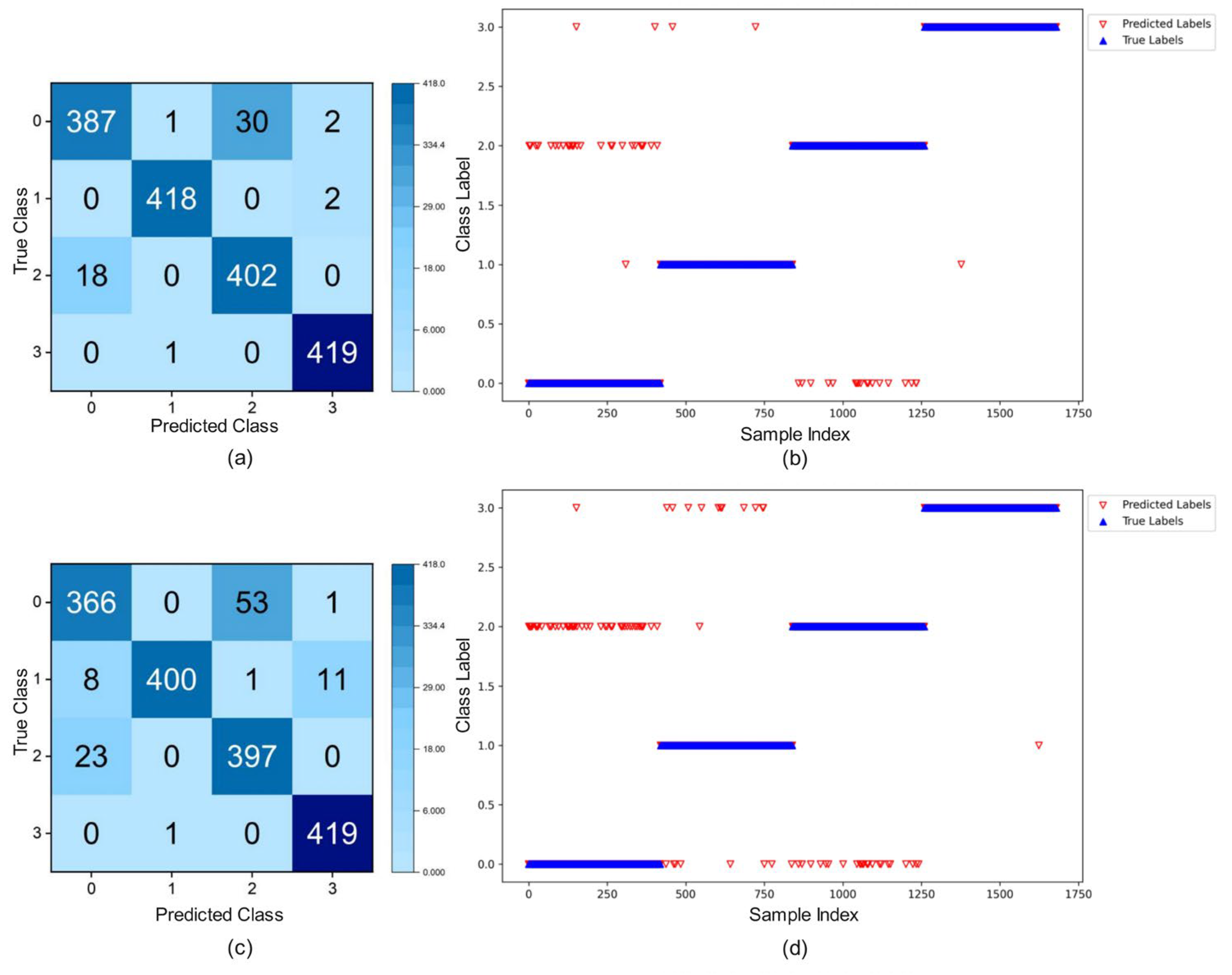
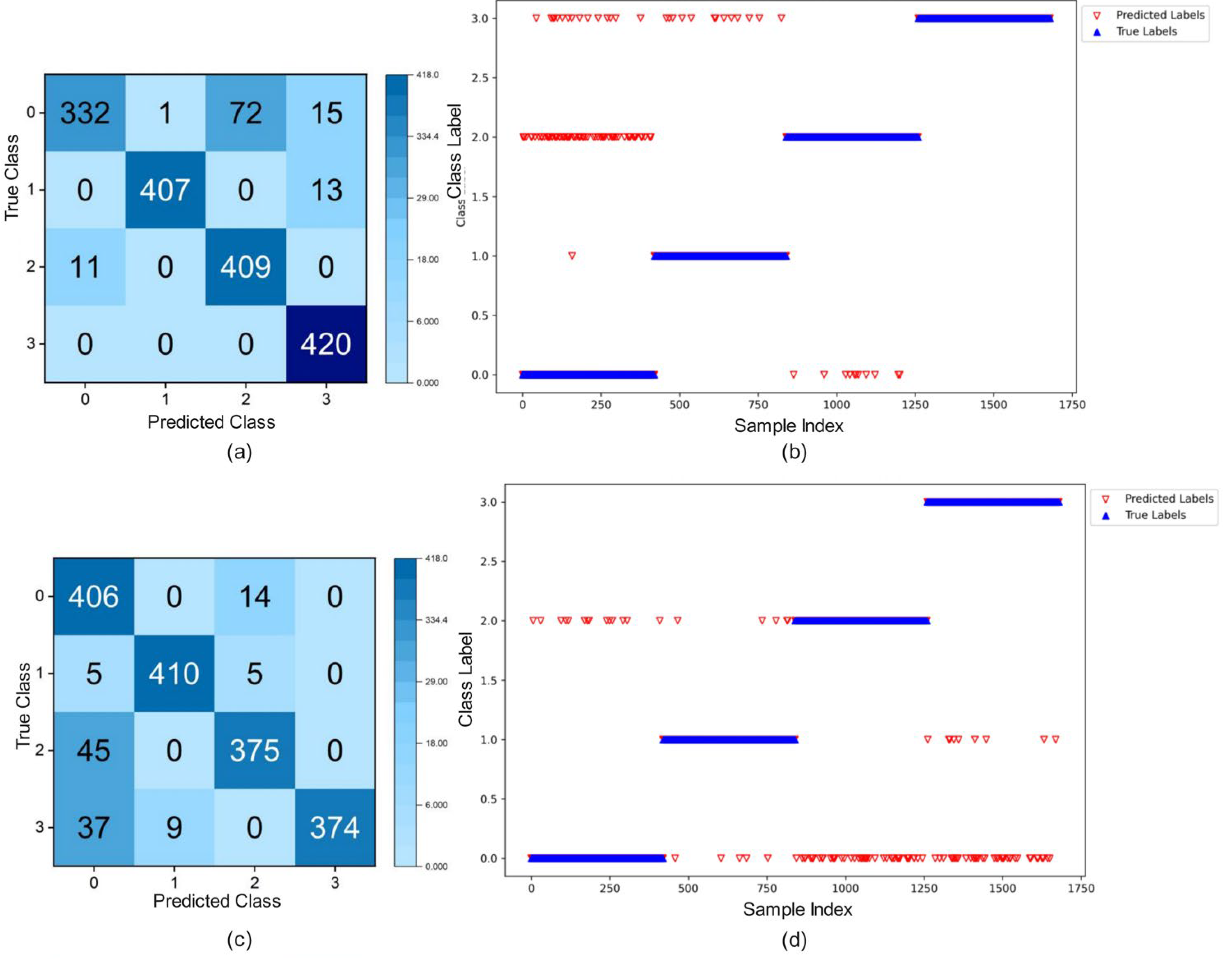
3.5. Intelligent Diagnosis of the ISMA-CNN-GRU-Attention Models
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Leng, M.; Wang, Z.; Wan, X.; Chen, C. A state of the art in digital twin for intelligent fault diagnosis. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2025, 63, 102963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Lu, Q.; Wu, T. Improved non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm III for Efficient of Multi-bjective Cascade Reservoirs Scheduling under Different Hydrological Conditions. J. Hydrol. 2025, 656, 132998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, T.B.; Todros, K. Blind separation of noisy piecewise-stationary mixtures via probability measure transform. Signal Process. 2023, 208, 108967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Xu, N.; Cui, X.; Wu, J. Interpretable prediction, classification and regulation of water quality: A case study of Poyang Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Cheng, W.; Wen, W.; Liu, Y. Application of Time-Frequency Analysis in Rotating Machinery Fault Diagnosis. Shock Vib. 2023, 2023, 9878228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Shang, Z.; Xu, H.; Wen, J.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, X.; Gao, R.X. Wavelet transform for rotary machine fault diagnosis:10 years revisited. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 200, 110545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S. Enhance carbon emission prediction using bidirectional long short-term memory model based on text-based and data-driven multimodal information fusion. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 471, 143301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Lv, S.; Ma, Z. Differential time-frequency mode decomposition and its application in rotating machinery fault diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2025, 229, 112571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhao, R.; Yan, K.; Wang, W. Accurate prediction of water quality in urban drainage network with integrated EMD-LSTM model. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 354, 131724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, W.; Shen, C.; Cheng, L.; Xia, M. Intelligent machine fault diagnosis with effective denoising using EEMD-ICA-FuzzyEn and CNN. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2022, 61, 8252–8264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z. A multi-source data-driven model of lake water level based on variational modal decomposition and external factors with optimized bi-directional long short-term memory neural network. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2023, 167, 105766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Zhang, S.; Dong, W.; Zhang, X.; Ma, W. A new hybrid method for bearing fault diagnosis based on CEEMDAN and ACPSO-BP neural network. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2023, 37, 5597–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Gu, W.; Zhou, T.; Hao, P.; Jiang, J. Leak aperture recognition of natural gas pipeline based on variational mode decomposition and mutual information. Measurement 2025, 242, 116017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Chen, Z.; Hua, R.; Hu, S.; Fan, C.; Xiao, X. Research on diagnosis method of centrifugal pump rotor faults based on IPSO-VMD and RVM. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2023, 55, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Technol. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wu, T.; Lu, W. A hybrid data-driven deep learning prediction framework for lake water level based on the fusion of meteorological and hydrological multi-source data. Nat. Resour. Res. 2024, 33, 163–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, C.; Lin, J.; Guo, L. A Novel Feature for Fault Classification of Rotating Machinery: Ternary Approximate Entropy for Original, Shuffle and Surrogate Data. Machines 2023, 11, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Yao, L.; Qi, X.; Zhang, J. Data-driven fault diagnosis for wind turbines using modified multiscale fluctuation dispersion entropy and cosine pairwise-constrained supervised manifold mapping. Knowl. Based Syst. 2021, 228, 107276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azami, H.; Arnold, S.E.; Sanei, S.; Chang, Z.; Sapiro, G.; Escudero, J.; Zhou, X.; Huang, S. Multiscale fluctuation-based dispersion entropy and its applications to neurological diseases. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 68718–68733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Z.; Yao, Z. Enhancing carbon price point-interval multi-step-ahead prediction using a hybrid framework of autoformer and extreme learning machine with multi-factors. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 270, 126467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yao, L.; Cai, Y. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis using generalized refined composite multiscale sample entropy and optimized support vector machine. Measurement 2020, 156, 107574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Du, W.; Li, C.; Guo, X.; Liu, Z. Fault diagnosis of rotating machinery with high-dimensional imbalance samples based on wavelet random forest. Measurement 2025, 248, 116936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Meng, G.; Wang, A.; Zhang, X.; Ding, J. Application of rotating machinery fault diagnosis based on deep learning. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021, 3083190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalai, J.; Mózes, F.E. Intelligent digital signal processing and feature extraction methods. In New Approaches in Intelligent Image Analysis; Kountchev, R., Nakamatsu, K., Eds.; Intelligent Systems Reference Library; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 108, pp. 59–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Zhao, M.; Lin, J.; Liang, K. A comprehensive review on convolutional neural network in machine fault diagnosis. Neurocomputing 2020, 417, 36–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, Y.; Xiao, B.; Jing, Q.; Yun, Z. Stability and safety study of pumped storage units based on time-shifted multi-scale cosine similarity entropy. J. Energy Storage 2024, 95, 112611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Han, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, M.; Lin, Q. Short-term runoff prediction with GRU and LSTM networks without requiring time step optimization during sample generation. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, T.; Li, J. Experimental and MPM modelling of widened levee failure under the combined effect of heavy rainfall and high riverine water levels. Comput. Geotech. 2025, 184, 107259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czako, Z.; Sebestyen, G.; Hangan, A. AutomaticAI—A hybrid approach for automatic artificial intelligence algorithm selection and hyperparameter tuning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 182, 115225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, S. A novel interval decomposition correlation particle swarm optimization-extreme learning machine model for short-term and long-term water quality prediction. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 130034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Shen, B. A novel swarm intelligence optimization approach: Sparrow search algorithm. Syst. Sci. Control Eng. 2020, 8, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qiu, W.; Hu, X.; Wang, W. A rolling bearing fault diagnosis technique based on fined-grained multi-scale symbolic entropy and whale optimization algorithm-MSVM. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 4209–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Guan, M. Effects of urban drainage inlet layout on surface flood dynamics and discharge. J. Hydrol. 2024, 632, 130890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashishtha, G.; Chauhan, S.; Singh, M.; Kumar, R. Bearing defect identification by swarm decomposition considering permutation entropy measure and opposition-based slime mould algorithm. Measurement 2021, 178, 109389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Q.; Shen, N. HKTSMA: An Improved Slime Mould Algorithm Based on Multiple Adaptive Strategies for Engineering Optimization Problems. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 28, 4436–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Chen, S.; Dong, S.; Qin, J. Modeling abrupt changes in mine water inflow trends: A CEEMDAN-based multi-model prediction approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 439, 140809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X. A new filter feature selection algorithm for classification task by ensembling pearson correlation coefficient and mutual information. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 131, 107865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Heidari, A.A.; Xue, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Chen, W. Boosting quantum rotation gate embedded slime mould algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 181, 115082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Shao, H.; Zhong, X.; Deng, Q.; Yang, X.; Xuan, J. Unsupervised domain-share CNN for machine fault transfer diagnosis from steady speeds to time-varying speeds. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 62, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, L.; Susto, G.A.; Brito, J.N.; Duarte, M. Mechanical faults in rotating machinery dataset (normal, unbalance, misalignment, looseness). Mendeley Data 2023, V3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azami, H.; Escudero, J. Amplitude- and fluctuation-based dispersion entropy. Entropy 2018, 20, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin, L.; Rongsheng, Z.; Qian, H.; Yongyong, Z.; Qiang, F.; Xiuli, W. Fault diagnosis of horizontal centrifugal pump orifice ring wear and blade fracture based on complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise-singular value decomposition algorithm. J. Vib. Control 2024, 30, 5228–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| State | Sample Length | Number of Samples | Label |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 25,000 | 2100 | 0 |
| Looseness | 25,000 | 2100 | 1 |
| Misalignment | 25,000 | 2100 | 2 |
| Unbalance | 25,000 | 2100 | 3 |
| Group | State |
|---|---|
| Group 1 | Normal |
| Group 2 | Looseness |
| Group 3 | Misalignment |
| Group 4 | Imbalance |
| No. | State |
|---|---|
| 1 | Kurtosis |
| 2 | Peak Value |
| 3 | Crest Factor |
| 4 | Skewness |
| 5 | Mean Frequency |
| 6 | Root Mean Square Frequency |
| 7 | Frequency Skewness |
| 8 | Frequency Kurtosis |
| NO. | Model | No Noise | SNR = 2 db |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CEEMDAN-RCMFDE-SMA-CNN-GRU-Attention | 94.17% | 93.15% |
| 2 | CEEMDAN-RCMFDE-ISMA-CNN-GRU-Attention | 96.79% | 93.33% |
| 3 | CEEMDAN-MDE-SMA-CNN-GRU-Attention | 90.65% | 89.52% |
| 4 | CEEMDAN-MDE-ISMA-CNN-GRU-Attention | 93.63% | 92.02% |
| 5 | CEEMDAN-MSE-ISMA-CNN-GRU-Attention | 92.20% | — |
| 6 | CEEMDAN-RCMFDE-ISMA-CNN-GRU | 95.42% | — |
| 7 | (Correlation coefficient selection) IMF + CEEMDAN-RCMFDE-ISMA-CNN-GRU-Attention | 95.18% | — |
| 8 | (KL divergence selection) IMF + CEEMDAN-RCMFDE- ISMA-CNN-GRU-Attention | 90.18% | — |
| 9 | (MI selection) IMF+CEEMDAN-RCMFDE- ISMA-CNN-GRU-Attention | 94.40% | |
| 10 | IMF (without time-domain and frequency-domain features) + CEEMDAN-RCMFDE-ISMA-CNN-GRU-Attention | 94.29% | — |
| 11 | CEEMDAN-SVD-PSO-BP [43] | 88.99% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Meng, H.; Wang, R.; Wang, P. Intelligent Optimized Diagnosis for Hydropower Units Based on CEEMDAN Combined with RCMFDE and ISMA-CNN-GRU-Attention. Water 2025, 17, 2125. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142125
Zhang W, Meng H, Wang R, Wang P. Intelligent Optimized Diagnosis for Hydropower Units Based on CEEMDAN Combined with RCMFDE and ISMA-CNN-GRU-Attention. Water. 2025; 17(14):2125. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142125
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wenting, Huajun Meng, Ruoxi Wang, and Ping Wang. 2025. "Intelligent Optimized Diagnosis for Hydropower Units Based on CEEMDAN Combined with RCMFDE and ISMA-CNN-GRU-Attention" Water 17, no. 14: 2125. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142125
APA StyleZhang, W., Meng, H., Wang, R., & Wang, P. (2025). Intelligent Optimized Diagnosis for Hydropower Units Based on CEEMDAN Combined with RCMFDE and ISMA-CNN-GRU-Attention. Water, 17(14), 2125. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142125






