GIS-Based Assessment of Stormwater Harvesting Potentials: A Sustainable Approach to Alleviate Water Scarcity in Rwanda’s Eastern Savanna Agroecological Zone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
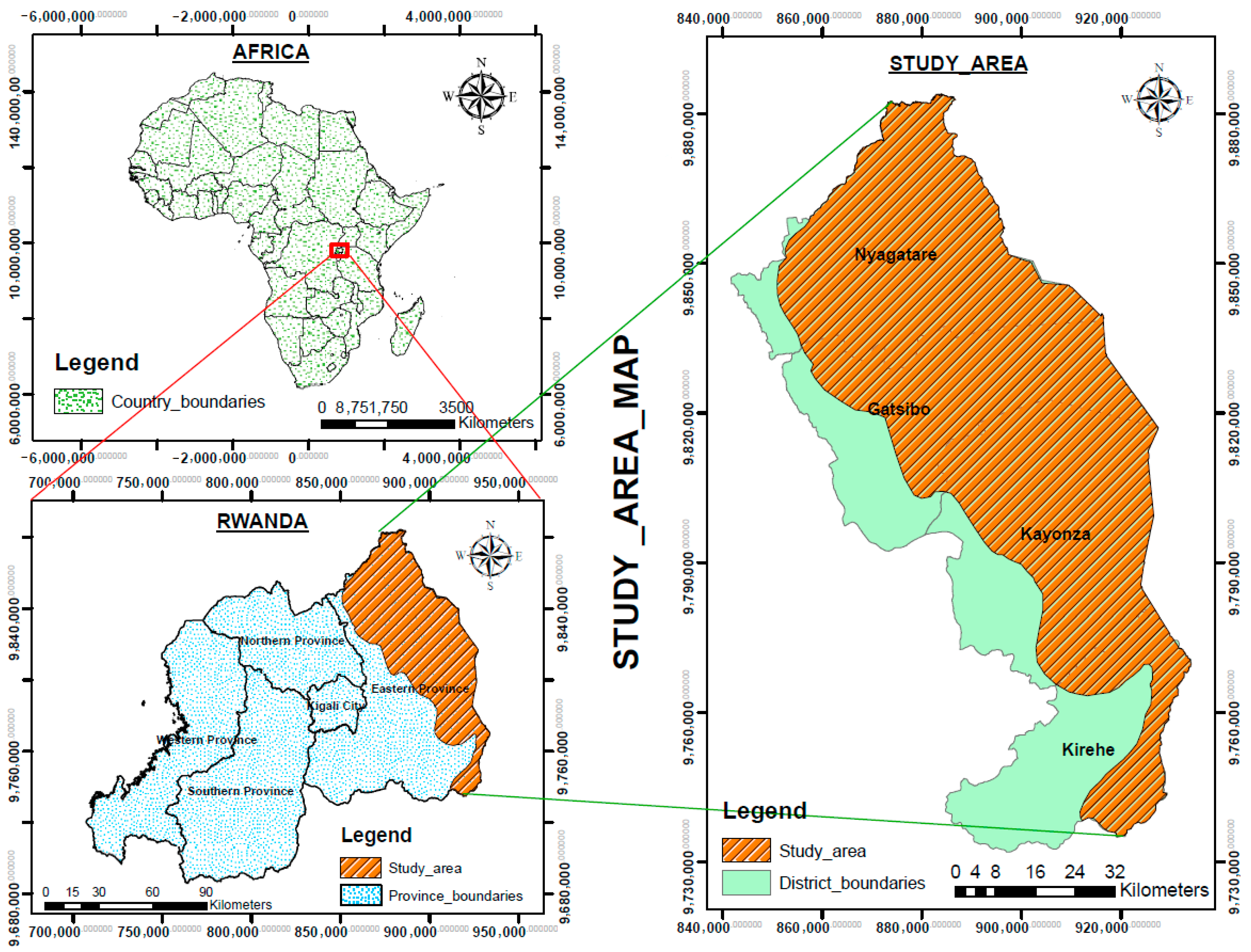
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Data Sources
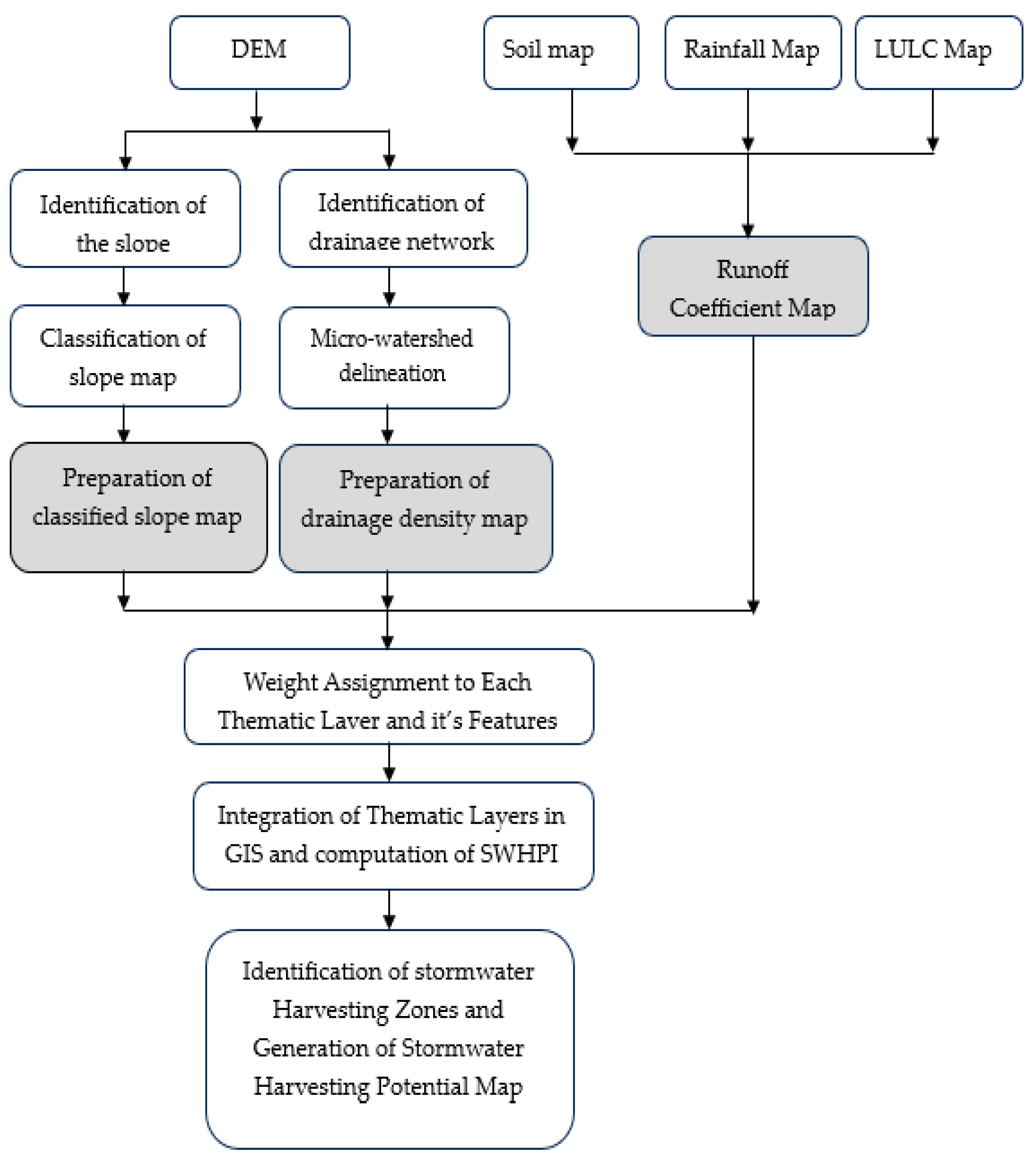
2.3. Methods
2.4. Data Collection and Preparation
2.5. GIS Mapping and Analysis
2.6. Calculation of Curve Numbers
2.7. Runoff Estimation
2.8. Weighted Overlay Analysis and Stormwater Storage Classification
2.9. Optimal Site Selection for Stormwater Harvesting Structures
3. Results
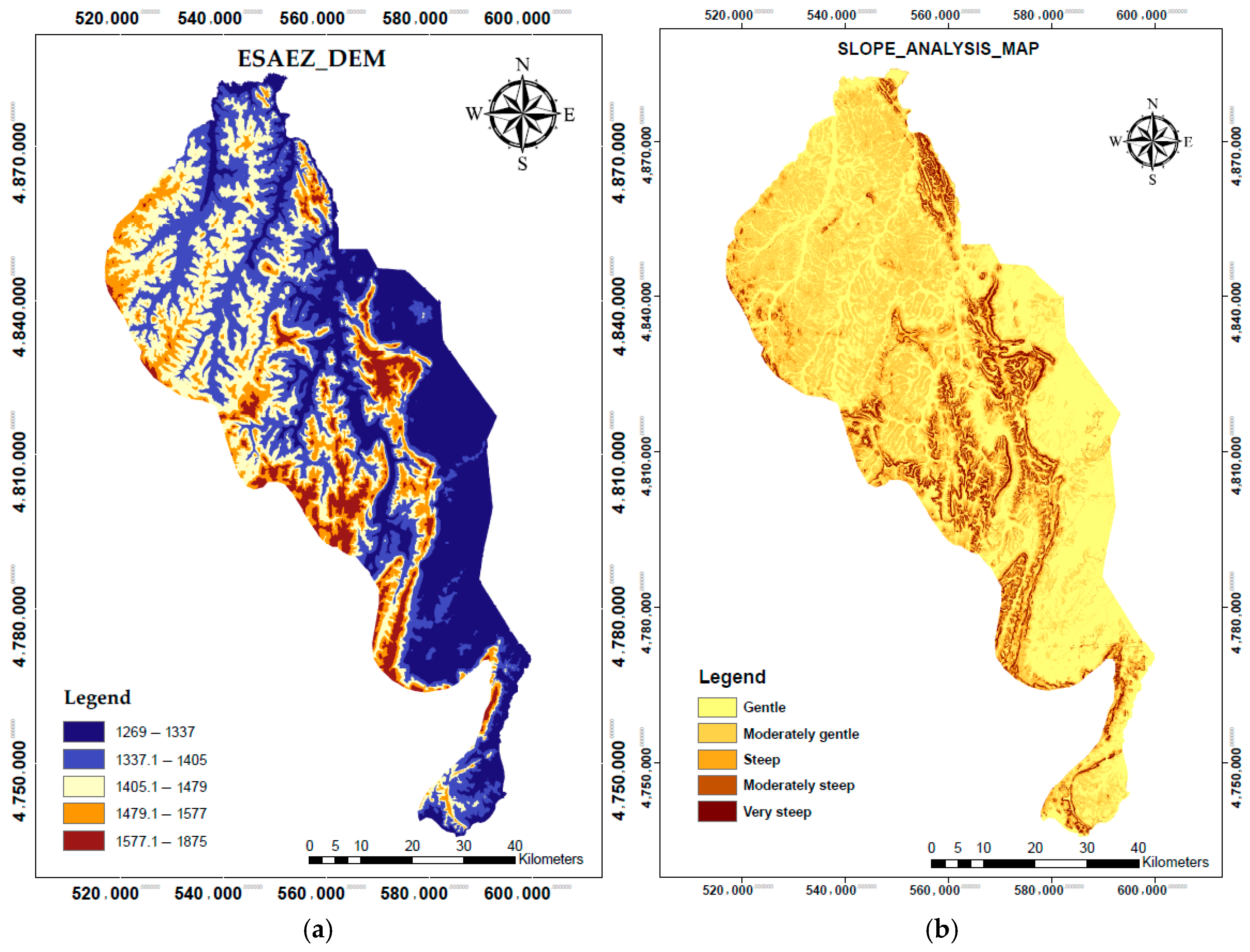
3.1. DEM and Land Slope
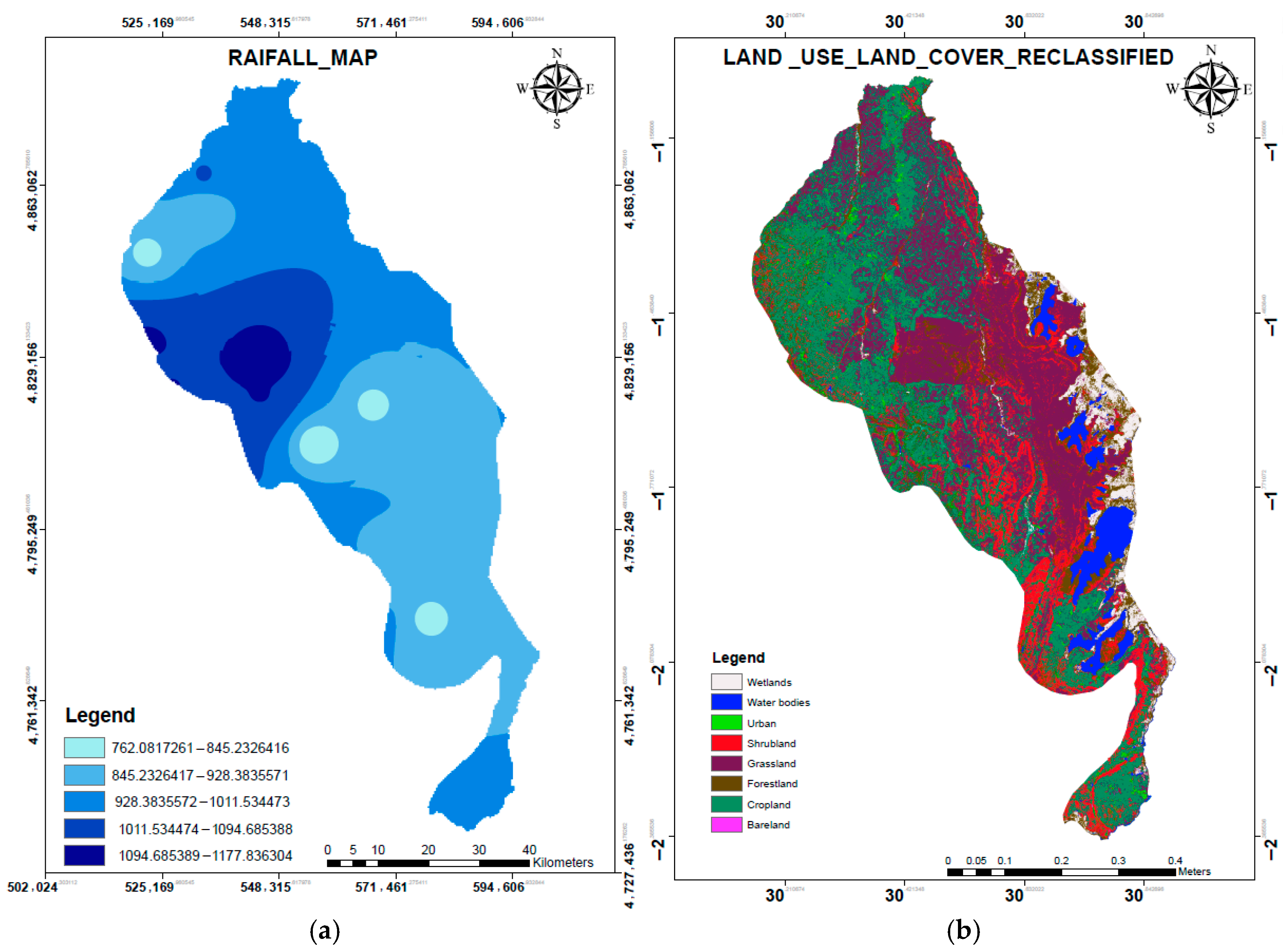
3.2. Rainfall and Land Use/Land Cover
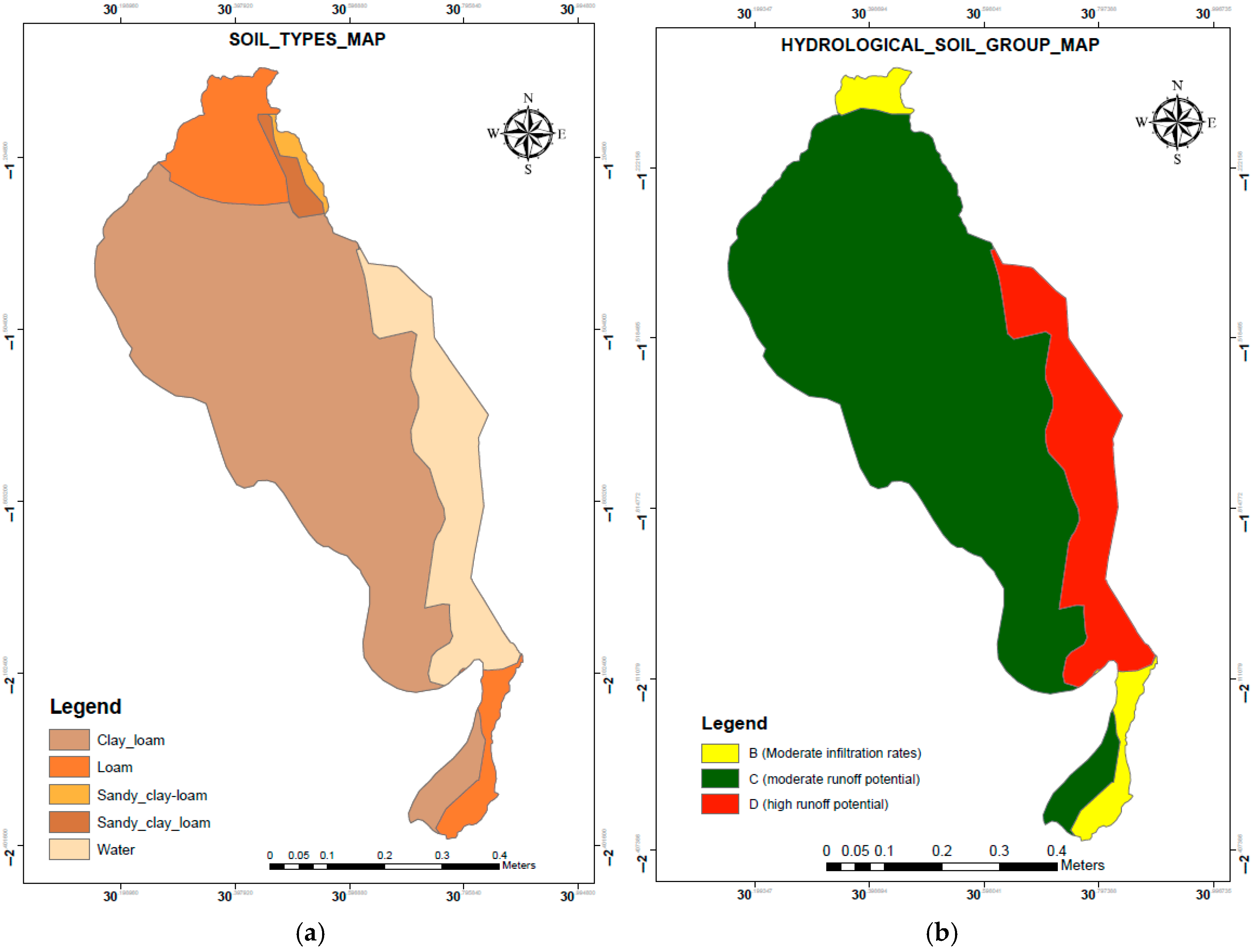
3.3. Soil Type and Hydrological Soil Groups
3.4. SCS-CN for the Combination of LULC and the HGS of the Study Area
| No. | LULC | Area km2 | Percentage (%) | HSG | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | ||||
| 1 | Cropland | 1557.158 | 32 | - | 78 | 85 | 89 |
| 2 | Grassland | 1739.047 | 36 | - | 69 | 79 | 84 |
| 3 | Forests/shrubland | 1018.623 | 21 | - | 55 | 70 | 77 |
| 4 | Build-up land/bareland | 95.544 | 2 | - | 80 | 82 | 86 |
| 5 | Open water/wetland | 435.722 | 9 | - | 99 | 99 | 99 |
| Total | 4846.094 | 100 | |||||
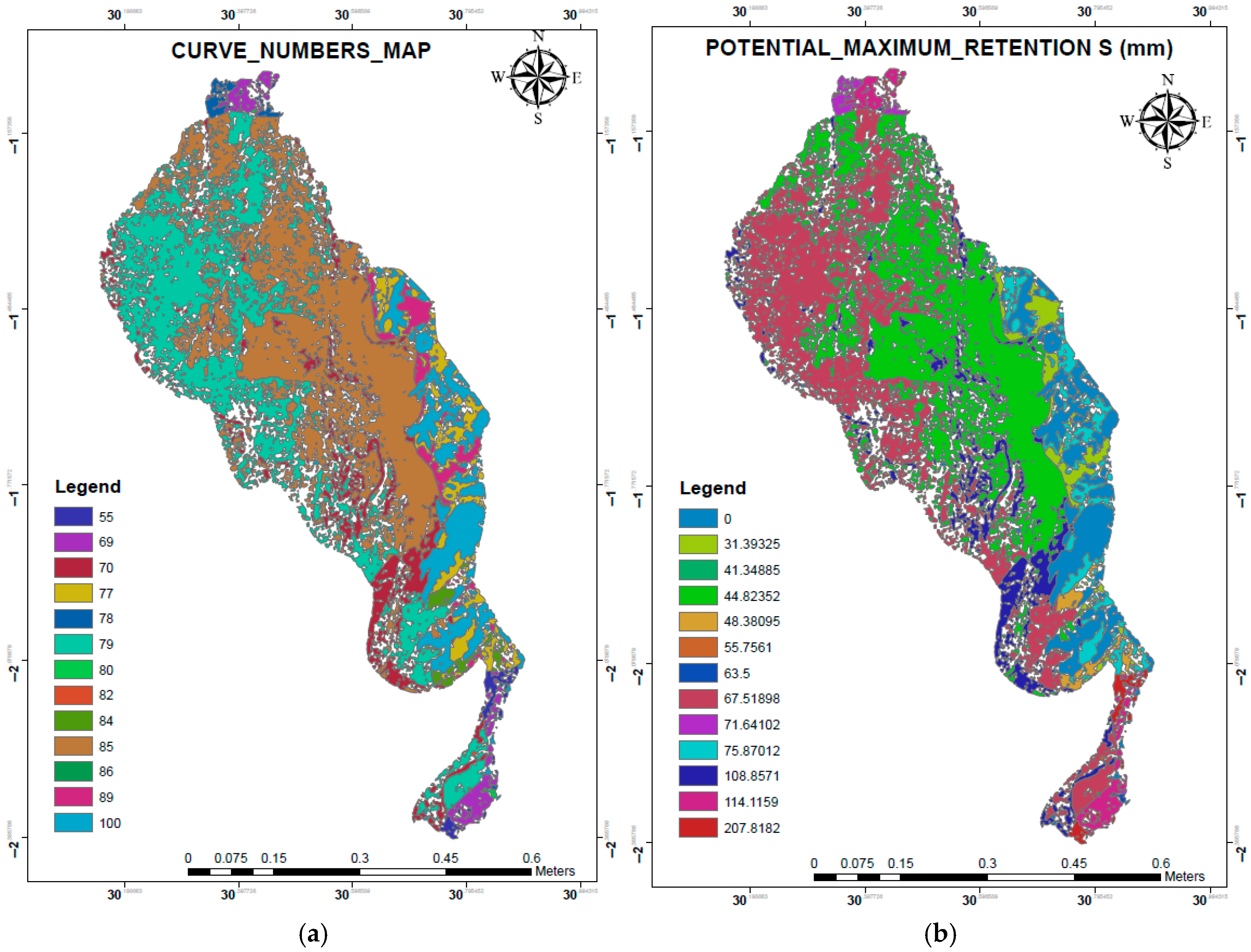
3.5. Curve Number and Potential Maximum Retention
3.6. Drainage Density
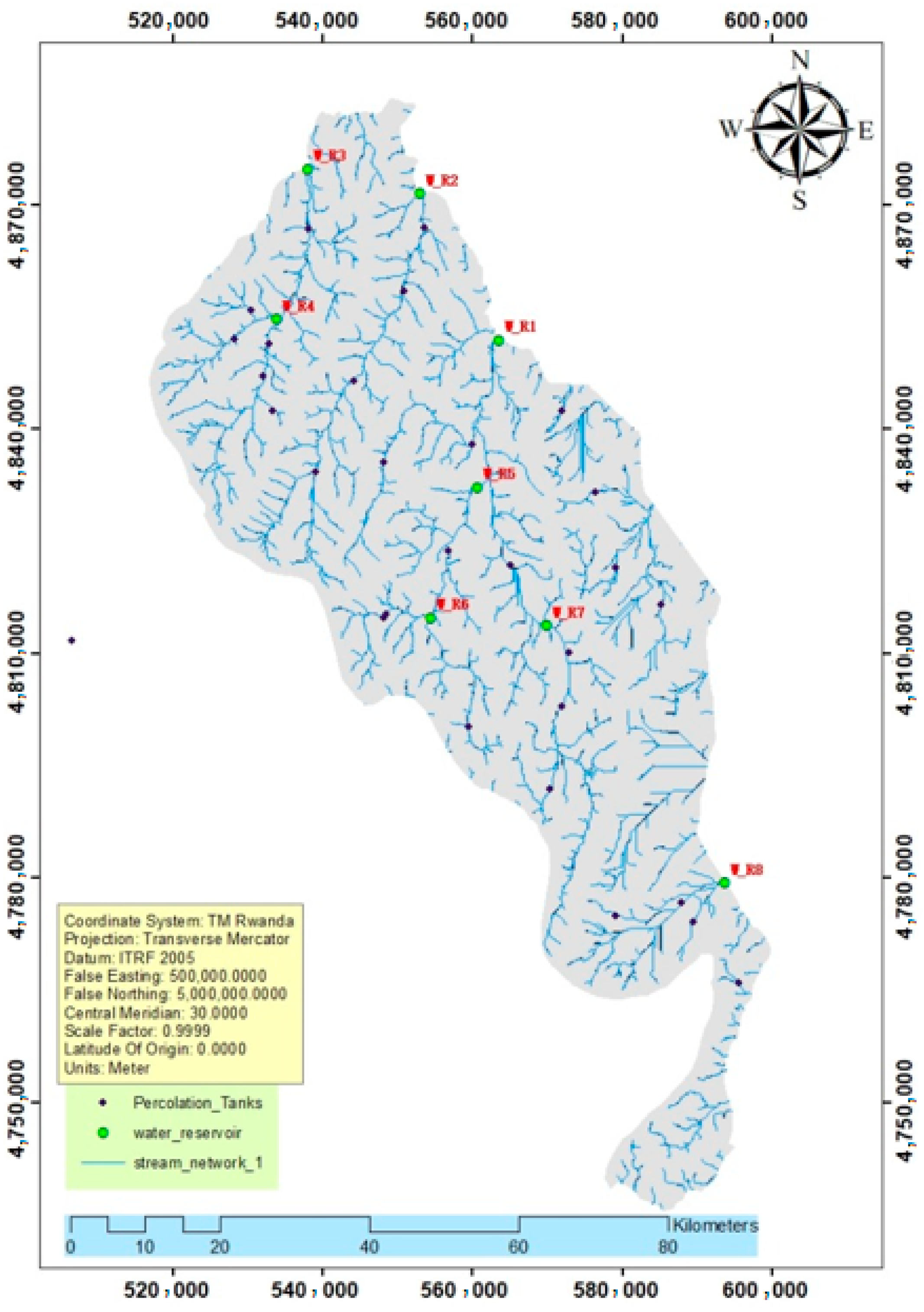
3.7. Estimated Volumes and Their Locations
4. Discussions
4.1. Terrain Slope Classification and Implications
4.2. Rainfall Distribution and Land Cover Characteristics
4.3. Soil Classification and Hydrological Implications
4.4. Discussion of LULC and HSG Distribution
4.5. Curve Number Distribution and Runoff Potential Analysis
4.6. Drainage Density and Hydrological Implications
4.7. Evaluation of Proposed Water Retention Sites
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RLMA | Rwanda Land Management Authority |
| RMA | Rwanda Meteorological Agency |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| LULC | Land Use/Land Cover |
| DSRM | Dynamic Soil Resource Mapping |
| RESAEZ | Rwanda Eastern Savanna Agroecological Zone |
References
- Jiang, S.C.; Lim, K.; Huang, X.; McCarthy, D.; Hamilton, A.J. Human and environmental health risks and benefits associated with use of urban stormwater. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2015, 2, 683–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.R.; Farrelly, M.A. Delivering sustainable urban water management: A review of the hurdles we face. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamdar, P.; Cook, S.; Sharma, A.; Corby, N.; O’Connor, J.; Perera, B. A GIS based screening tool for locating and ranking of suitable stormwater harvesting sites in urban areas. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 128, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Malla, R.; Sharma, M.; Panthi, J.; Lakhankar, T.; Krakauer, N.Y.; Pradhanang, S.M.; Dahal, P.; Shrestha, M.L. Impact of irrigation method on water use efficiency and productivity of fodder crops in nepal. Climate 2016, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, K.S.; Mishra, A.K.; Ahmad, N. Surface runoff estimation over heterogeneous foothills of Aravalli mountain using medium resolution remote sensing rainfall data with soil conservation system-curve number method: A case of semi-arid ungauged Manesar Nala watershed. Water Environ. J. 2017, 31, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curve Number Hydrology in Water Quality Modeling. Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/sites/default/files/2023-03/CURVE%20NUMBER%20HYDROLOGY%20IN%20WATER%20QUALITY%20MODELING.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2025).
- Ponce, V.M.; Richard, H.H. Runoff Curve Number: Has is it reached matyrity? J. Hydrol. Eng. 1996, 14–16. Available online: https://www.uvm.edu/~bwemple/HydroModel/ponce1996.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.-H.; Chen, L.-D.; Fang, N.-F.; Qin, D.-F.; Cai, C.-F. Research on the SCS-CN initial abstraction ratio using rainfall-runoff event analysis in the Three Gorges Area, China. Catena 2009, 77, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Singh, V.P. Soil Conservation Service Curve Number (SCS-CN) Methodology. In Water Science and Technology Library; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melesse, A.M.; Abtew, W.; Setegn, S.G.; Dessalegne, T. Hydrological Variability and Climate of the Upper Blue Nile River Basin. In Nile River Basin; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 3–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarboton, D.G. A new method for the determination of flow directions and upslope areas in grid digital elevation models. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fohrer, N.; Haverkamp, S.; Eckhardt, K.; Frede, H.-G. Hydrologic Response to land use changes on the catchment scale. Phys. Chem. Earth Part B Hydrol. Oceans Atmos. 2001, 26, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashaw, T.; Tulu, T.; Argaw, M.; Worqlul, A.W.; Tolessa, T.; Kindu, M. Estimating the impacts of land use/land cover changes on Ecosystem Service Values: The case of the Andassa watershed in the Upper Blue Nile basin of Ethiopia. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 31, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenta, A.A.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Tsubo, M.; Yasuda, H.; Kawai, T.; Ebabu, K.; Berihun, M.L.; Belay, A.S.; Sultan, D. Agroecology-based soil erosion assessment for better conservation planning in Ethiopian river basins. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadeed, S.; Almasri, M. Application of GIS-based SCS-CN method in West Bank catchments, Palestine. Water Sci. Eng. 2010, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizeyimana, J.C.; Lin, S.; Ndayisenga, F.; Twagirayezu, G.; Khan, J.; Marnn, P.; Kaku, D.U.; Musaed, B.; Al-Shaibah, A.; Hussein, A.R.; et al. Establishment of Rainfall Intensity-Duration-Frequency Equations and Curves Used to Design an Appropriate and Sustainable Hydraulic Structure for Controlling Flood in Nyabugogo Catchment-Rwanda. Available online: https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202106.0025/v1 (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Meshram, S.G.; Sharma, S.K. Prioritization of watershed through morphometric parameters: A PCA-based approach. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1505–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatya, D.; Walega, A.; Callahan, T.; Morrison, A.; Vulava, V.; Hitchcock, D.; Williams, T.; Epps, T. Storm event analysis of four forested catchments on the Atlantic coastal plain using a modified SCS-CN rainfall-runoff model. J. Hydrol. 2022, 608, 127772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Users and Uses Assessment in Rwanda. Available online: https://waterportal.rwb.rw/sites/default/files/2022-07/03-12-2020_Final%20Report_Water_Users_Assessment.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Askarizadeh, A.; Rippy, M.A.; Fletcher, T.D.; Feldman, D.L.; Peng, J.; Bowler, P.; Mehring, A.S.; Winfrey, B.K.; Vrugt, J.A.; AghaKouchak, A.; et al. From Rain Tanks to Catchments: Use of Low-Impact Development To Address Hydrologic Symptoms of the Urban Stream Syndrome. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11264–11280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockström, J.; Karlberg, L.; Wani, S.P.; Barron, J.; Hatibu, N.; Oweis, T.; Bruggeman, A.; Farahani, J.; Qiang, Z. Managing water in rainfed agriculture—The need for a paradigm shift. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, V.G.; Mein, R.G.; Mcmahon, T.A. Modelling the Urban Water Cycle Year First Available: 2000 Hardware Required: PC 486, 32 MB of RAM, CD-ROM Software Required: Windows 95 or Greater Program Language: Visual Basic 6.0 Program Size: 1.4 MB Availability and Cost: Contact CRC for Catchment Hydrology (Nominal Charge). 2001. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1364815201000299 (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- Ndirangu, M.D.; Chira, R.M.; Wang’ondu, V.; Kairo, J.G. Analysis of wave energy reduction and sediment stabilization by mangroves in Gazi Bay, Kenya. Bonorowo Wetl. 2017, 7, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. Nature-Based Solutions for Water World Water Assessment Programme; United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. FAO Statistical Programme of Work 2016–2017. 2016. Available online: https://www.fao.org/publications/en (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Pandey, U.J.; Pandey, S.; Gunn, R.; Lim, K.J.; Engel, B.; Harbor, J. Developing a Web-Enabled Tool to Assess Long-Term Hydrologic Impact of Land Use Change: Information Technologies Issues and a Case Study Developing a Web-Enabled Tool to Assess Long-Term Hydro-Logic Impacts of Land-Use Change: Information Technology Issues and a Case Study. 2000. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/241608160 (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Ndhlovu, G.; Woyessa, Y. Use of gridded climate data for hydrological modelling in the Zambezi River Basin, Southern Africa. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvin, K.; Dasgupta, D.; Krinner, G.; Mukherji, A.; Thorne, P.W.; Trisos, C.; Romero, J.; Aldunce, P.; Barret, K.; Blanco, G.; et al. IPCC, 2023: Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report, Summary for Policymakers. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Core Writing Team, Lee, H., Romero, J., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadese, S.; Soromessa, T.; Bekele, T.; Abbas, S. Analysis of the Current and Future Prediction of Land Use/Land Cover Change Using Remote Sensing and the CA-Markov Model in Majang Forest Biosphere Reserves of Gambella, Southwestern Ethiopia. Sci. World J. 2021, 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiruneh, G.A.; Meshesha, D.T.; Adgo, E.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Fenta, A.A.; Alemayehu, T.Y.; Ayana, G.; Reichert, J.M.; Tilahun, K. Geospatial modeling and mapping of soil organic carbon and texture from spectroradiometric data in Nile basin. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2023, 29, 100879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccartney, M.; Rex, W.; Bank, W.; Bank, W.H.Y.W.; Uhlenbrook, S. Change in Global Freshwater Storage. International Water Management Institute. Available online: https://www.iwmi.org/ (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Guyassa, E.; Frankl, A.; Zenebe, A.; Poesen, J.; Nyssen, J. Effects of check dams on runoff characteristics along gully reaches, the case of Northern Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. 2017, 545, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugiraneza, T.; Nascetti, A.; Ban, Y. Continuous monitoring of urban land cover change trajectories with landsat time series and landtrendr-google earth engine cloud computing. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, N.; Patrick, R.; Phenihas, T.; Rolland, A.; Placide, R.; Robert, M.O.M.; Silver, T.; Vestine, K.; Evrard, K.; Grüneberg, W.J. Evaluation of Performance of Introduced Yam Bean (Pachyrhizus spp.) in Three Agro-Ecological Zones of Rwanda. Trop. Plant Biol. 2017, 10, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsengimana, V.; Mukangango, M.; Habiyaremye, J.d.D.; Uwiduhaye, F.; Iradukunda, C.S.; Bigengimana, Y.; Nsanganwimana, F.; Cocozza, C. Status of Soil Physicochemical Properties in Forests and Savannas Restored Using the Ecosystem-Based Adaptation Approach in Eastern Rwanda. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2024, 2024, 6504201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iiyama, M.; Mukuralinda, A.; Ndayambaje, J.D.; Musana, B.; Ndoli, A.; Mowo, J.G.; Garrity, D.; Ling, S.; Ruganzu, V. Tree-Based Ecosystem Approaches (TBEAs) as multi-functional land management strategies—Evidence from rwanda. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molden, D.J.; Barker, R. Charlotte de Fraiture IHE Delft Institute for Water Education. 2007. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284491758 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Mbilinyi, B.; Tumbo, S.; Mahoo, H.; Mkiramwinyi, F. GIS-based decision support system for identifying potential sites for rainwater harvesting. Phys. Chem. Earth 2007, 32, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). United Nations Environmental Programme Annual Report 2012; United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), 2013; Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/8607/-UNEP%202013%20Annual%20Report2014UNEP%20AR%202013.nLR.pdf?sequence=8&%3BisAllowed=y%2C%20Chinese%7C%7Chttps%3A//wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/8607/-UNEP%202013%20Annual%20Report2014UNEP-AR-CHinese-low%20re (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Shuler, C.K.; Amato, D.W.; Gibson, V.; Baker, L.; Olguin, A.N.; Dulai, H.; Smith, C.M.; Alegado, R.A. Assessment of terrigenous nutrient loading to coastal ecosystems along a human land-use gradient, Tutuila, American Samoa. Hydrology 2019, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P.; Asce, F.; Woolhiser, D.A.; Asce, M. Mathematical Modeling of Watershed Hydrology. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2002, 7, 270–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahinda, J.M.; Taigbenu, A.; Boroto, R. Domestic rainwater harvesting as an adaptation measure to climate change in South Africa. Phys. Chem. Earth 2010, 35, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANNUAL REPORT. UN-Water Annual Report 2013. pp. 18–22. Available online: https://www.unwater.org/sites/default/files/app/uploads/2017/05/UN_Water_Annual_Report_2013.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Navarro, A.; Tauler, R.; Lacorte, S.; Barceló, D. Occurrence and transport of pesticides and alkylphenols in water samples along the Ebro River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2010, 383, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadono, T.; Ishida, H.; Oda, F.; Naito, S.; Minakawa, K.; Iwamoto, H. Precise Global DEM Generation by ALOS PRISM. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, II-4, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Liao, A.; Cao, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; He, C.; Han, G.; Peng, S.; Lu, M.; et al. Global land cover mapping at 30 m resolution: A POK-based operational approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, L.; Niu, Z.; Huang, X.; Fu, H.; Liu, S.; et al. Finer resolution observation and monitoring of global land cover: First mapping results with Landsat TM and ETM+ data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2607–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha; Polisgowdar, B. Rainfall-runoff estimation by SCS-CN method: A case study. Int. J. Res. Agron. 2024, 7, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alataway, A. SCS-CN and GIS-Based Approach for Estimating Runoff in Western Region of Saudi Arabia. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2023, 11, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ssekyanzi, G.; Ahmad, M.J.; Choi, K.-S. Geospatial Assessment of Stormwater Harvesting Potential in Uganda’s Cattle Corridor. Water 2025, 17, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekani, L.; Khaleghi, S.; Mahmoodi, M. Application of GIS in modeling Zilberchai basin runoff. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, 40, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.A.; Gk, V. Estimation of Runoff by using SCS Curve Number Method Integrated with GIS. Int. Adv. Res. J. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2017, 4, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Yusop, Z.; Yap, W.-S.; Tan, W.L.; Chow, M.F.; Ling, J.L. A calibrated, watershed-specific SCS-CN Method: Application to Wangjiaqiao watershed in the three Gorges Area, China. Water 2020, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molden, D.; Frenken, K.; de Fraiture, C.; Barker, R.; Svendsen, M.; Sadoff, C.; Finlayson, C. Publication—Trends in Water and Agricultural Development; Earthscan: London, UK, 2007; pp. 57–89, No. January; Available online: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9781849773799-5/trends-water-agricultural-development-david-molden-karen-frenken-randolph-barker-charlotte-de-fraiture-bancy-mati-mark-svendsen-claudia-sadoff-max-finlayson-sithara-attapatu-mark-giordano-arlene-inocencio-mats-lannerstad-nadia-manning-fran%C3%A7ois-molle-bert-smedema-domitille-vall%C3%A9e (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Pizarro-Tapia, R.; Valdés-Pineda, R.; Olivares, C.; González, P.A. Development of Upstream Data-Input Models to Estimate Downstream Peak Flow in Two Mediterranean River Basins of Chile. Open J. Mod. Hydrol. 2014, 4, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Changwony, C.; Sichangi, A.W.; Ngigi, M.M. Using GIS and Remote Sensing in Assessment of Water Scarcity in Nakuru County, Kenya. Adv. Remote Sens. 2017, 06, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Al-Weshah, R.A.; Sakarnah, Z.A. Flash Floods Assessment Urban Area: A Case Study Wadi Abdoun Basin, Jordan. Dirasat Hum. Soc. Sci. 2024, 51, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Shen, L. Spatial variability of global lake evaporation regulated by vertical vapor pressure difference. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 054006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somashekar, R.K.; Ravikumar, P.; Sowmya, S.V.; Dar, M.A.; Ravikumar, A.S. Runoff Estimation and Morphometric Analysis for Hesaraghatta Watershed Using IRS–1D LISS III FCC Satellite Data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2011, 39, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goli, Y.S.; Ye, J.; Ye, Y.; Kalgora, B. Impact of Ecological Related Innovations Enhancing the Efficiency of Corporate Environmental Responsibility. Am. J. Ind. Bus. Manag. 2020, 10, 191–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolekar, S.S.; Mishra, A.; Choudhari, P.; Choudhari, N.R. Identification of specific areas for water conservation measures using Geoinformatics approach. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aklan, M.; Al-Komaim, M.; de Fraiture, C. Site suitability analysis of indigenous rainwater harvesting systems in arid and data-poor environments: A case study of Sana’a Basin, Yemen. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 8319–8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, D.; Hatfield, J.L. Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bewket, W.; Stroosnijder, L. Effects of Agroecological Land Use Succession On Soil Properties in Chemoga Watershed, Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Geoderma 2003, 111, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurni, K.; Zeleke, G.; Kassie, M.; Tegegne, B.; Kassawmar, T.; Teferi, E.; Amdihun, A.; Mekuriaw, A.; Debele, B.; Deichert, G.; et al. Suggested Citation. Available online: https://www.eld-initiative.org/fileadmin/pdf/ELD-ethiopia_i_06_72dpi-D.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- Tebebu, T.Y.; Abiy, A.Z.; Zegeye, A.D.; Dahlke, H.E.; Easton, Z.M.; Tilahun, S.A.; Collick, A.S.; Kidnau, S.; Moges, S.; Dadgari, F.; et al. Surface and subsurface flow effect on permanent gully formation and upland erosion near Lake Tana in the northern highlands of Ethiopia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimanpour, S.M.; Soufi, M.; Zolfaghari, M.; Ahmadi, H. Investigation of topographic threshold relations of gully creation in various land use in fars province, Ir Iran. Indian J. Sci. Res. 2014, 3, 362–371. [Google Scholar]
- Tetzlaff, D.; Uhlenbrook, S. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences Significance of Spatial Variability in Precipitation for Process-oriented Modelling: Results from Two Nested Catchments Using Radar and Ground Station Data. 2005. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/296859919_Significance_of_spatial_variability_in_precipitation_for_process-oriented_modelling_results_from_two_nested_catchments_using_radar_and_ground_station_data (accessed on 25 April 2025).
- Kabelka, D.; Kincl, D.; Vopravil, J.; Krofta, K.; Kintl, A. Determination of C-factor for conventional cultivation and soil conservation technique used in hop gardens. Open Agric. 2024, 9, 20220301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremedhn, H.; Gebrewahid, Y.; Hadgu, G.; de Graaf, D.C. Projecting the impacts of climate change on habitat distribution of Varroa destructor in Ethiopia using MaxEnt ecological modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 968, 178904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solgi, A.; Najafi, A.; Ezzati, S.; Ferencik, M. Assessment of ground-based skidding impacts on the horizontally rate and extent of soil disturbance along the margin of the skid trail. Ann. For. Sci. 2016, 73, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazi, S.A.; Kazmi, J.H. Analysis of socio-environmental impacts of the loss of urban trees and vegetation in Lahore, Pakistan: A review of public perception. Ecol. Process. 2016, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitasova, H.; Barton, M.; Ullah, I.; Hofierka, J.; Harmon, R.S. GIS-Based Soil Erosion Modeling. In Treatise on Geomorphology: Volume 1–14; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 228–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leipard, A.R.; Kevern, J.T.; Richardson, J.R. Hydraulic characterization and design of permeable interlocking concrete pavement. In World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2015: Floods, Droughts, and Ecosystems—Proceedings of the 2015 World Environmental and Water Resources Congress; American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): Reston, VA, USA, 2015; pp. 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundalia, M.; Dholakia, M. Impact of Monthly Curve Number on Daily Runoff Estimation for Ozat Catchment in India. Open J. Mod. Hydrol. 2014, 4, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Historic, Archive Document: Do Not Assume Content Reflects Current Scientific Knowledge, Policies, or Practices. In The Yearbook of Agriculture; U.S. Government Printing Office, 1972; o-441-067. Available online: https://www.nal.usda.gov/exhibits/speccoll/files/original/59322c0b7c00bdf977b1f91978384f9d.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Montgomery, D.R.; Dietrich, W.E. Source areas, drainage density, and channel initiation. Water Resour. Res. 1989, 25, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN-Water Annual Report. 2008. Available online: https://www.unwater.org/sites/default/files/app/uploads/2017/05/UN-Water_Annual_Report_2008.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Yimer, E.A.; Yadollahi, S.; Riakhi, F.-E.; Alitane, A.; Weerasinghe, I.; Wirion, C.; Nossent, J.; van Griensven, A. A groundwater level-based filtering to improve the accuracy of locating agricultural tile drain and ditch networks. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 122, 103423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrechorkos, S.H.; Taye, M.T.; Birhanu, B.; Solomon, D.; Demissie, T. Future Changes in Climate and Hydroclimate Extremes in East Africa. Earth’s Future 2023, 11, e2022EF003011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.E.H.; Charbel, L.; Blond, N. L’impact du Terrassement des Versants sur L’érosion Dans le Pourtour Occidental du Plateau du Jord Tannourine-Aaqoura (Liban). Rev. Int. Geomat. 2023, 32, 53–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO Strategy Climate Change. Available online: http://www.wipo.int/amc/en/mediation/rules (accessed on 26 April 2025).
- Salman, Q.M.K.; Hamdan, A.N.A. Runoff Estimation for the Central Region of the Lesser Zab River Watershed Using the SCS-Curve Number Method and GIS. J. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 24, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, A.S.; Nicholls, R.J.; Clarke, D.; Savin, C.; Harrison, P.A. Integrated assessment of the food-water-land-ecosystems nexus in Europe: Implications for sustainability. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamene, L.; Adimassu, Z.; Aynekulu, E.; Yaekob, T. Estimating landscape susceptibility to soil erosion using a GIS-based approach in Northern Ethiopia. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2017, 5, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Tao, S.; Walsh, S.J.; Chen, X.; Bilsborrow, R.E.; An, L.; Song, C. Agent-based modeling of the effects of conservation policies on social-ecological feedbacks between cropland abandonment and labor migration. Landsc. Ecol. 2023, 38, 4247–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Maidment, R.; Tadesse, T.; Gadain, H.; Ceccato, P. Validation of the CHIRPS satellite rainfall estimates over eastern Africa. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 292–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBetrie, G.D.; Mohamed, Y.A.; van Griensven, A.; Srinivasan, R. Sediment management modelling in the Blue Nile Basin using SWAT model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Molden, D.; Cook, S.; Graphics, V.; Overview, A.; Waters, M.; Tobergte, D.; Curtis, S.; Tumbo, S.; Mutabazi, K. Measurements and Modelling of Evapotranspiration to Assess Agricultural Water Productivity in Basins with Changing Land Use Patterns: A Case Study in the Sao Francisco River Basin, Brasil; Teixeira, A.H.d.C., Ed.; 2008; Volume 23, Available online: http://www.cpatsa.embrapa.br/public_eletronica/downloads/OPB2046.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Belayneh, M.; Yirgu, T.; Tsegaye, D. Runoff and soil loss responses of cultivated land managed with graded soil bunds of different ages in the Upper Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. Ecol. Process. 2020, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Tariq, A.; Islam, F.; Aziz, S.; Waseem, L.A.; Ahmad, M.N.; Amin, M.; Amin, N.U.; Ali, S.; Aslam, M.; et al. Integrated study of GIS and Remote Sensing to identify potential sites for rainwater harvesting structures. Phys. Chem. Earth 2024, 134, 103574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euliss, N.H.; Gleason, R.A.; Laubhan, M.; Finocchiaro, R.; Browne, B.A.; Olness, A. Impact of U.S. Department of Interior and U.S. Department of Agriculture Programs on Ecological Services Derived from Restored Prairie Wetlands and Adjacent Grasslands; U.S. Geological Survey Northern Prairie Wildlife Research Center: Jamestown, ND, USA, 2004; p. 18.
- Meles, M.B.; Younger, S.E.; Jackson, C.R.; Du, E.; Drover, D. Wetness index based on landscape position and topography (WILT): Modifying TWI to reflect landscape position. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 255, 109863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshome, D.S.; Tolessa, T.; Gemeda, D.O.; Taddese, H.; You, S. Impact of land use/land cover (LU/LC) changes on ecosystem service values in Muger Sub-basin, Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Environ. Chall. 2024, 17, 101041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisanga, C.B.; Mubanga, K.H.; Sichigabula, H.; Banda, K.; Muchanga, M.; Ncube, L.; van Niekerk, H.J.; Zhao, B.; Mkonde, A.A.; Rasmeni, S.K. Modelling climatic trends for the Zambezi and Orange River Basins: Implications on water security. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2022, 13, 1275–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Neelin, J.D.; Hill, S.A.; Schiro, K.A.; Su, H. A Process Model for ITCZ Narrowing under Warming Highlights Clear-Sky Water Vapor Feedbacks and Gross Moist Stability Changes in AMIP Models. J. Clim. 2023, 36, 4913–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, S.A.; Pulla, S.T.; Williams, G.P.; Jones, N.L.; Mamane, B.; Sanchez, J.L. Correction: Evaluating Groundwater Storage Change and Recharge Using GRACE Data: A Case Study of Aquifers in Niger, West Africa. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeze, A.W.; Wubalem, A. Landslide Factor Optimization for Landslide Susceptibility Modeling. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/387218658 (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Tufa, A.H.; Kanyamuka, J.S.; Alene, A.; Ngoma, H.; Marenya, P.P.; Thierfelder, C.; Banda, H.; Chikoye, D. Analysis of adoption of conservation agriculture practices in southern Africa: Mixed-methods approach. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1151876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, A.; Tessema, A.; Ganewo, Z.; Haile, A. Climate change impacts on household food security and farmers adaptation strategies. J. Agric. Food Res. 2021, 6, 100197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Teku, D.; Sisay, T.; Mihret, B. Geospatial modeling of landslide susceptibility in Debek, South Wollo, Ethiopia: Comparative analysis of frequency ratio and analytical hierarchy process models for geohazards management. Front. Earth Sci. 2025, 13, 1557860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dile, Y.T.; Berndtsson, R.; Setegn, S.G.; Añel, J.A. Hydrological Response to Climate Change for Gilgel Abay River, in the Lake Tana Basin—Upper Blue Nile Basin of Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowing, J.; Payton, R.W. Integrating Indigenous and Scientific Knowledge on Soils: Recent Experiences in Uganda and Tanzania and Their Relevance to Participatory Land Use Planning Moses Tenywa Agricultural Innovation Systems Brokerage Association AGINSBA. 2004. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/267703517 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Twinomucunguzi, F.R.B.; Silvestri, G.; Kinobe, J.; Mugabi, A.; Isoke, J.; Nyenje, P.M.; Foppen, J.W.; Kulabako, R.N.; Kansiime, F. Socio-institutional drivers of groundwater contamination hazards: The case of on-site sanitation in the bwaise informal settlement, Kampala, Uganda. Water 2021, 13, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No | Primary Data | Spatial Resolution | Format | Source | Map Derived |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Digital Elevation Model | 10 m | Raster | Rwanda Land Management Authority | Slope, watershed, Drainage density, stream network |
| 2 | Land Use Land Cover | 90 m | Raster | Rwanda Land Management Authority | Land Use Land Cover map |
| 3 | Rainfall Data | - | Point source data | Rwanda Meteorological Agency | Rainfall map |
| 4 | Rwanda Soil Map | 5 × 5 Arc minutes | Vector | Digital Soil Map of the World (https://www.fao.org/soils-portal/data-hub/soil-maps-and-databases/faounesco-soil-map-of-the-world/en/ (accessed on 25 February 2025) | Soil texture and HSG maps |
| Thematic Layer | Feature Class | Range | Weight | Rank for Surface Water Storage | Rank for Groundwater Recharge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Runoff coefficient | >0.40 | Very high | 60 | 1 | 5 |
| 0.40–0.30 | High | 2 | 4 | ||
| 0.30–0.20 | Moderate | 3 | 3 | ||
| <0.20 | Low | 4 | 2 | ||
| Slope | 0–3% | Nearly level | 40 | 1 | 10 |
| 3–5% | Gentle | 2 | 9 | ||
| 5–10% | Moderately gentle | 4 | 8 | ||
| 10–15% | Steep | 6 | 6 | ||
| 15–20% | Moderately steep | 8 | 4 | ||
| >20% | Very steep | 10 | 2 |
| Check Dam | Farm Pond | Percolation Pond | Contour Bunding | Contour Trenching |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land slope: <15% | Land slope: <5% | Land slope: <10% | Land slope: <6% | Land slope: 10–25% |
| Soil: fine-textured soil | Soil: fine-textured soil | Soil: light-textured soil | Soil: light/medium-textured soil | Suitable sites: hilly areas |
| Drainage order: 1–4 | Drainage order: 1–4 | Drainage order: 1–4 | Rainfall: <800 mm | Rainfall: <800 mm |
| Description | X | Y | Volume (10 Million m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| W_R1 | 5634414 | 4851957 | 0.242 |
| W_R2 | 5529056 | 4871617 | 8.51 |
| W_R3 | 5378171 | 4874882 | 7.38 |
| W_R4 | 5337404 | 4854765 | 2 |
| W_R5 | 5605299 | 4832344 | 7.94 |
| W_R6 | 5542881 | 4814866 | 1.91 |
| W_R7 | 5697734 | 4813817 | 5.88 |
| W_R8 | 5937264 | 4779405 | 1.88 |
| Slope Class (%) | Description | Runoff Potential | Erosion Risk | Land Suitability | Recommended Conservation Practices | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–5 | Nearly flat | Low–Moderate | Low (Waterlogging risk) | Suitable for agriculture, infrastructure | Subsurface drainage, raised beds, controlled traffic farming | [4,83] |
| 5.01–10 | Gently sloping | Moderate | Low–Moderate | Ideal for rainfed cropping | Cover crops, mulching, and conservation tillage | [84] |
| 10.01–15 | Moderately steep | Moderate–High | Moderate | Conditional for agriculture (with management) | Strip cropping, agroforestry, and contour farming | [85] |
| 15.01–20 | Steep | High | High | Marginal for agriculture | Bench terracing, stone bunds, grass strips, check dams | [86] |
| >20 | Very steep | Very High | Very High | Unsuitable for agriculture | Exclusion from cultivation, afforestation, and natural regeneration | [5,9] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tuyishime, H.C.; Choi, K.S. GIS-Based Assessment of Stormwater Harvesting Potentials: A Sustainable Approach to Alleviate Water Scarcity in Rwanda’s Eastern Savanna Agroecological Zone. Water 2025, 17, 2045. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142045
Tuyishime HC, Choi KS. GIS-Based Assessment of Stormwater Harvesting Potentials: A Sustainable Approach to Alleviate Water Scarcity in Rwanda’s Eastern Savanna Agroecological Zone. Water. 2025; 17(14):2045. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142045
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuyishime, Herve Christian, and Kyung Sook Choi. 2025. "GIS-Based Assessment of Stormwater Harvesting Potentials: A Sustainable Approach to Alleviate Water Scarcity in Rwanda’s Eastern Savanna Agroecological Zone" Water 17, no. 14: 2045. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142045
APA StyleTuyishime, H. C., & Choi, K. S. (2025). GIS-Based Assessment of Stormwater Harvesting Potentials: A Sustainable Approach to Alleviate Water Scarcity in Rwanda’s Eastern Savanna Agroecological Zone. Water, 17(14), 2045. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142045









