Algal Community Dynamics in Three Water Intakes of Poyang Lake: Implications for Drinking Water Safety and Management Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
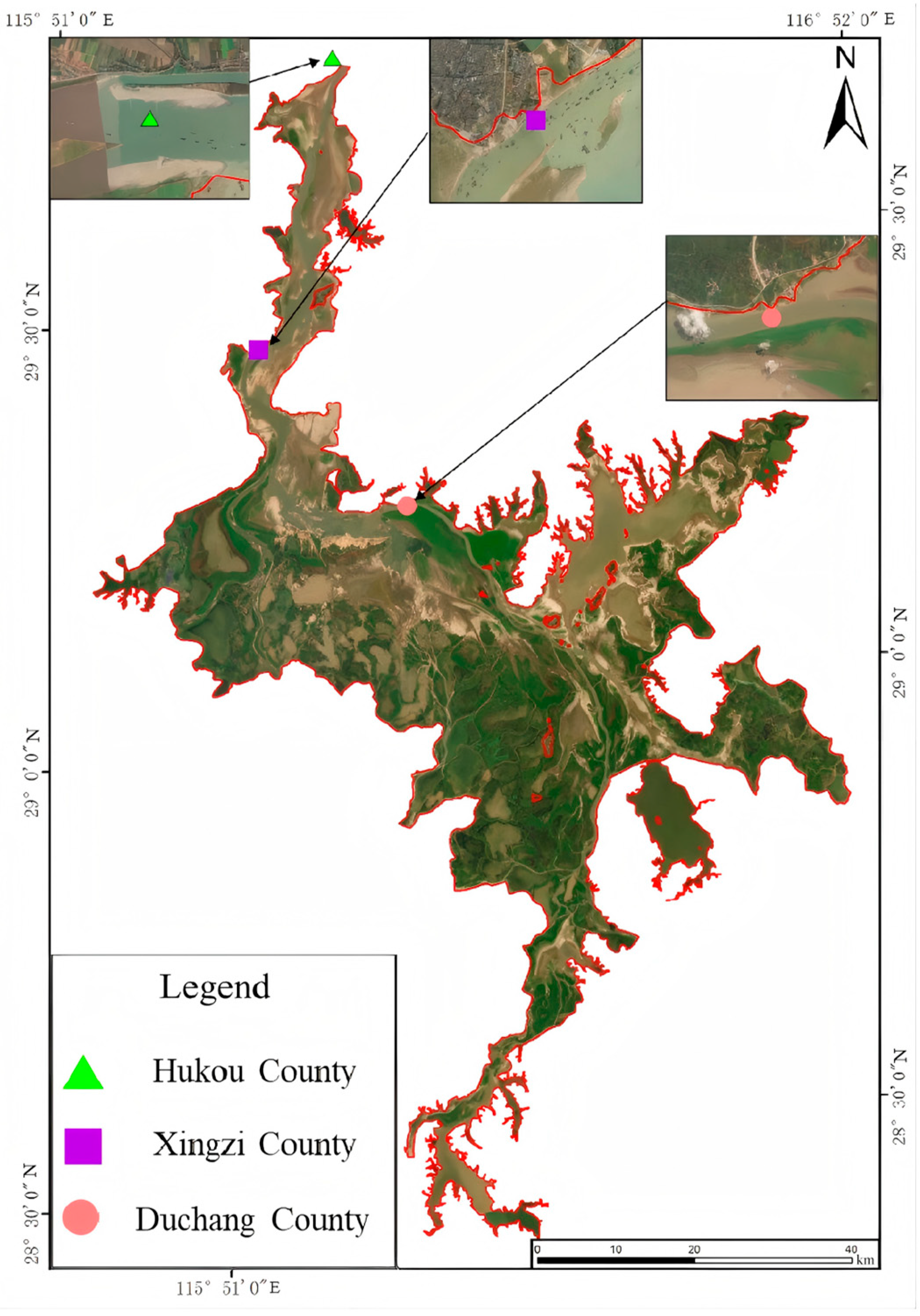
2.1. Overview of the Study Area and Point Placement
2.2. Sampling and Processing
2.2.1. Water Quality Sample Collection and Processing
2.2.2. Phytoplankton Sampling and Treatment
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis of Data
2.3. Evaluation Methodology
2.3.1. Algae Data Processing
2.3.2. Comprehensive Nutritional Status Index (TLI) Approach
2.3.3. Dominant Algal Species
2.3.4. Water Quality Evaluation Criteria
3. Results
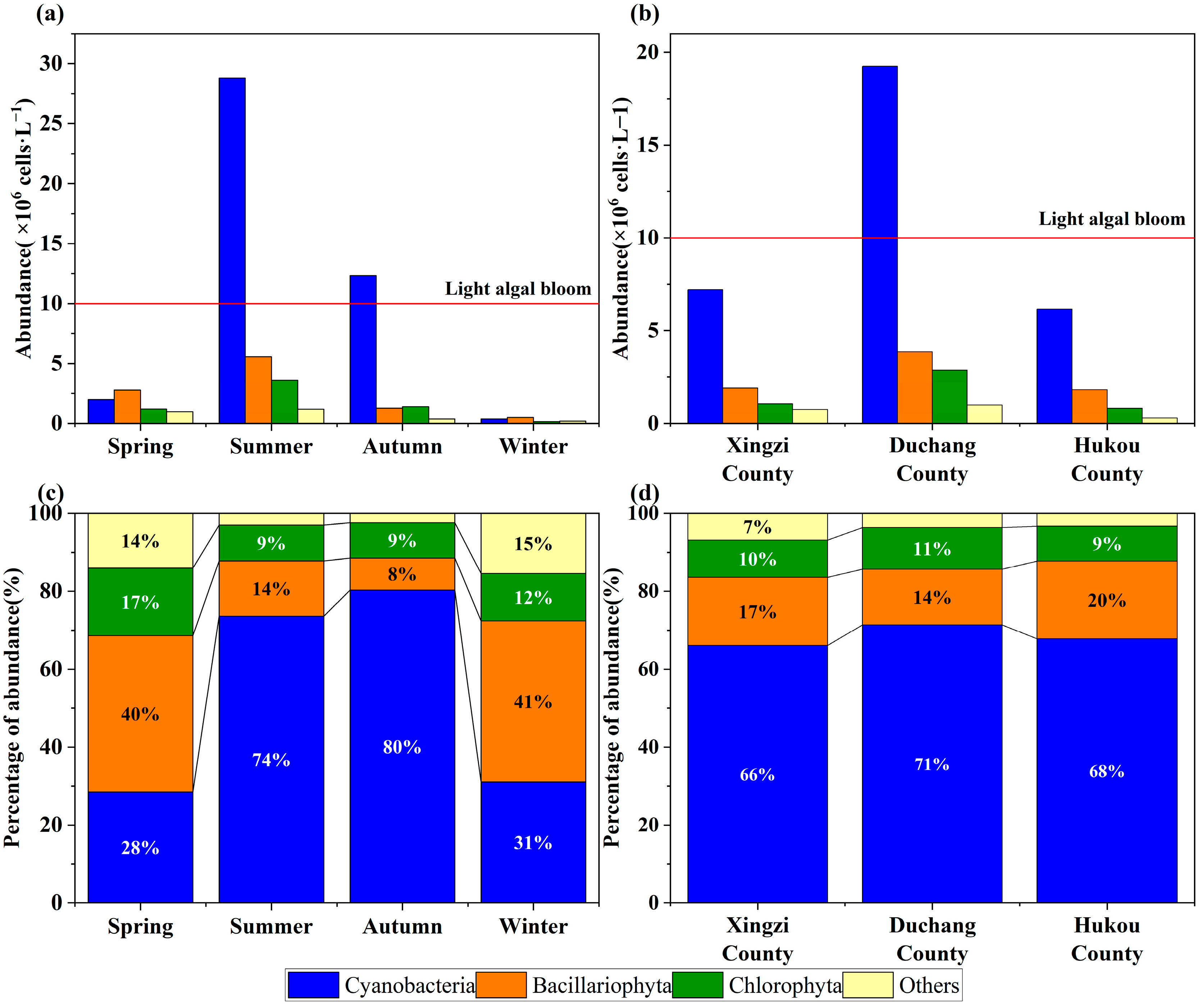
3.1. Phytoplankton Community Structure Characteristics
3.2. Eutrophication and Water Quality Assessment
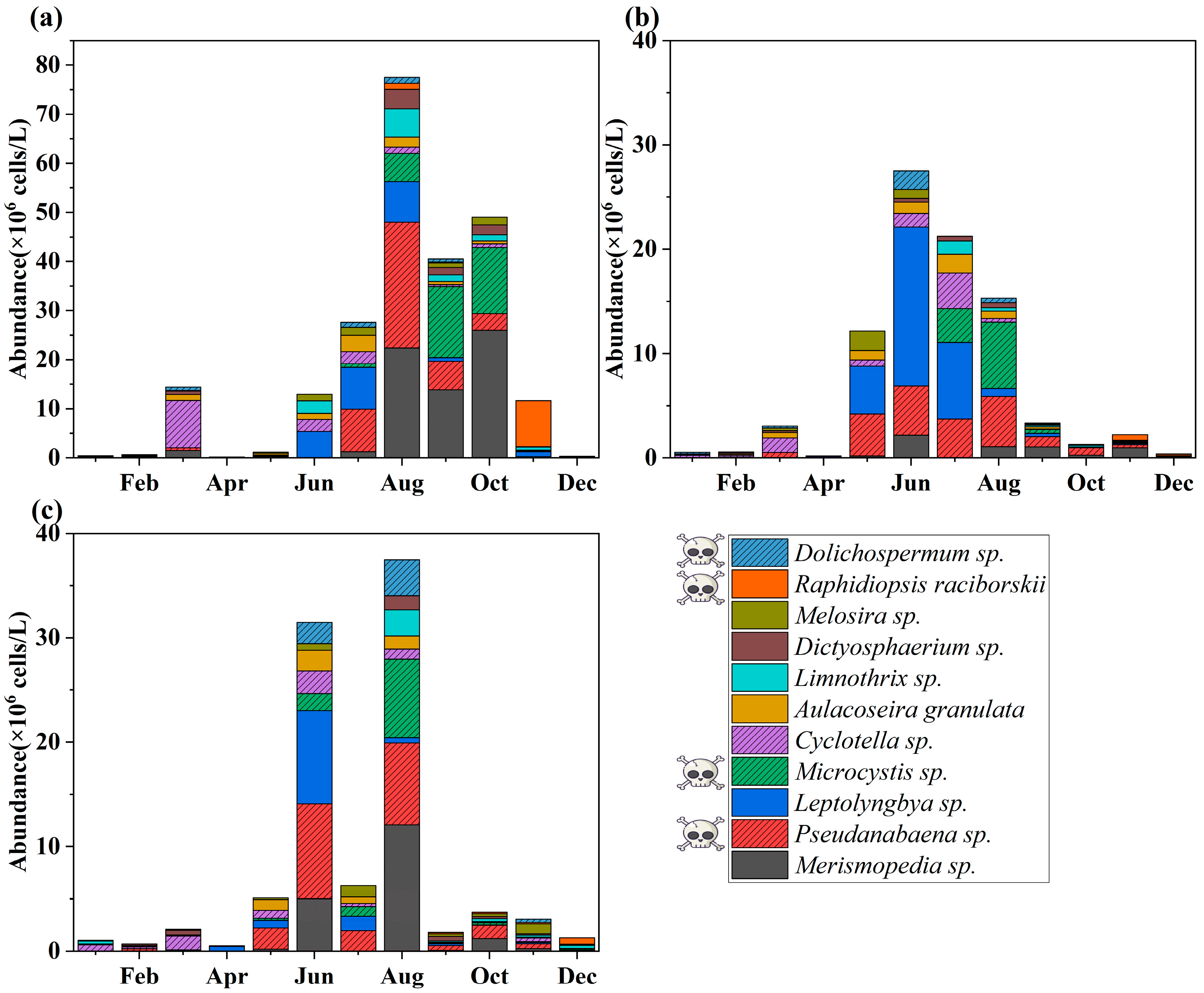
3.3. Spatial–Temporal Succession of Dominant Species
3.4. Potential Impacts of Harmful Algae on Water Safety
| Algal Species | Toxins | Per-Cell Production | Toxicity Magnitude (For Mice) | Environmental/Human Health Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dolichospermum sp. | ATX-a | 0.23 mg/kg | ATX-a is an extracellular neurotoxin [28]; | |
| STX | The toxic dose of STX for 1 mouse unit: 0.189 μg [29] | STX is a type of highly toxic algal toxin [29] | ||
| MCs | Unspecified types | Hepatotoxic potential [30] | ||
| Pseudanabaena sp. | MCs (partial producers) [31] | Hepatotoxic potential [30] | ||
| Microcystis sp. | MCs (MC-LR is the main variant) | 0.1–1.38 pg/cell [31] | MC-LR:0.05–0.1 mg/kg intraperitoneal [13] | MC-LR: predominant congener with hepatotoxicity and chronic carcinogenic risk [13] |
| Raphidiopsisraciborskii | CYN | 0.01–0.11 μg/106 cells [32] | LD50: 0.2 mg/kg intraperitoneal [33]; 4.4~6.9 mg/kg oral [34] | CYN: cytotoxic water-soluble alkaloid; inhibits protein/glutathione synthesis; potential carcinogen [35] |
| Odor Compounds | Algal Species | Odor Threshold (ng·L−1) | Odor Perception |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heptanal, 2,4-decadienal [24] | Cyclotella sp. | Fishy odor | |
| GSM | Dolichospermum sp. | (4~10 [25]) | Earthy-musty odor |
| 2-MIB | Dolichospermum sp., Pseudanabaena sp. | 10 [25] | Earthy-musty odor |
| β-cyclocitral | Microcystis sp. | 19 [25] | Grassy odor |
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of Algal Community Distribution and Eutrophication Assessment
4.2. Potential Impacts of Algae on Drinking Water Safety and Mitigation Measures
4.3. Risk Identification Methods for Algal Blooms in Drinking Water Sources
- (1)
- Identification of Key Monitoring Areas
- (2)
- Determination of High-Risk Periods
- (3)
- Harmful Algae Warnings
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y.J.; Mao, B.; Jia, S.; Wang, C.; Ji, X.; Lv, Q. Revealing nitrate sources seasonal difference between groundwater and surface water in China’s largest fresh water lake (Poyang Lake): Insights from sources proportion, dynamic evolution and driving forces. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 178134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q. Healthy Yangtze River and Ecological Poyang Lake: Keynote Address at the Symposium on Conservation and Management of Lakes in the Yangtze River Basin. Yangtze River 2009, 40, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, G.; Peng, N.; Zhong, J.; Yang, P.; Zou, B.; Chen, H.; Lou, Q.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, W. Effect of metals on microcystin abundance and environmental fate. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 226, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, B.; Liu, X.; Wu, Z.; Cai, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, J. Water-level fluctuations are key for phytoplankton taxonomic communities and functional groups in Poyang Lake. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.S.; He, H.; Cai, Y.J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.W. Spatial distribution of chlorophyll a and its relationship with the environment during summer in Lake Poyang: A Yangtze-connected lake. Hydrobiologia 2014, 732, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.J.; Dieterle, D.A.; Lenes, J. A numerical analysis of carbon dynamics of the Southern Ocean phytoplankton community: The roles of light and grazing in effecting both sequestration of atmospheric CO2 and food availability to larval krill. Deep-Sea Res. 2001, 48, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.Q.; Zhu, G.W.; Gao, G. Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, M.A.; Carey, C.; Hamilton, D.P.; Huisman, J.; Paerl, H.W.; Wood, S.A.; Wulff, A. Perspective: Advancing the research agenda for improving understanding of cyanobacteria in a future of global change. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Xu, D.; Liu, K.; Zhou, Y.-F. Characteristics of Periphytic Algae Communities in Wuli Lake, Lake Taihu. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2015, 37, 346–352. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, S.S.; Liu, J.F.; Chen, Y.W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, H. Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Phytoplankton Community Structure in Poyang Lake. J. Nanchang Inst. Technol. 2024, 43, 42–50+64. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Torres, A.; Pivokonsky, M.; Henderson, R.K. The impact of cell morphology and algal organic matter on algal floc properties. Water Res. 2019, 163, 114887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, N.R.H.; Granville, A.M.; Henderson, R.K. Understanding variability in algal solid-liquid separation process outcomes by manipulating extracellular protein-carbohydrate interactions. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.R.; Beversdorf, L.J.; Weirich, C.A.; Bartlett, S.L. Cyanobacterial Toxins of the Laurentian Great Lakes, Their Toxicological Effects, and Numerical Limits in Drinking Water. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.C.; Dreher, T.W.; Li, R.H. An overview of diversity, occurrence, genetics and toxin production of bloom-forming Dolichospermum (Anabaena) species. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Fang, S.; Li, K.; Wu, Z.; Min, X.; Liu, J.; Xing, J.; Deng, Y.; Guo, Y. Temporal distribution patterns of phytoplankton and their drivers in Lake Poyang (China)–A monthly study from 2011 to 2019. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Ye, H.; Lin, K.; Qi, S.; Hu, B.; Luo, J. Assessment of water-related ecosystem services based on multi-scenario land use changes: Focusing on the Poyang Lake Basin of southern China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartory, D.P.; Grobbelaar, J.U. Extraction of chlorophyll a from freshwater phytoplankton for spectrophotometric analysis. Hydrobiologia 1984, 114, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wei, Y. The Freshwater Algae of China: Systematics, Taxonomy and Ecology; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 1–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.C.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhang, J.H. Lake Eutrophication Evaluation Method and Classification Standard. Environ. Monit. China 2002, 18, 47–49. [Google Scholar]
- McNaughton, S.J. Relationships among Functional Properties of Californian Grassland. Nature 1967, 216, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DB44/T 2261-2020; Technical Specification for Classification and Monitoring of Algal Blooms. Guangdong Provincial Administration for Market Regulation: Guangzhou, China, 2020.
- Yuan, L.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, D.; Luo, L.; Liu, J. Seasonal and Spatial Variations of Microcystins and Their Relationships with Physiochemical and Biological Factors in Poyang Lake. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 450–459. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Chu, H.; Tang, Y.; Yang, F. Long-term low-dose microcystin-LR exposure induces renal injury in mice by activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J. South. Med. Univ. 2022, 42, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, W.; Ma, X.G. Analysis of algae-derived odor problem in Hongsheng Reservoir. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2022, 16, 3975–3983. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, y.; Liang, J.; Song, G.; Bi, Y. Spatiotemporal Dynamic Characteristics of Odor-Causing Substances in the Main Canal of the Middle Route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. In Proceedings of the 2019 Annual Conference of the Chinese Hydraulic Engineering Society, Zhengzhou, China, 18–20 September 2019; Volume 9, pp. 334–342. [Google Scholar]
- Izaguirre, G.; Taylor, W.D. A Pseudanabaena species from Castaic Lake, California, that produces 2-methylisoborneol. Water Res. 1998, 32, 1673–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Qi, M.; Ren, R.; Liu, J.; Sun, X.; Xie, P.; Chen, J. The relationships between odors and environmental factors at bloom and non-bloom area in Lake Taihu, China. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 569–576. [Google Scholar]
- Puddick, J.; van Ginkel, R.; Page, C.D.; Murray, J.S.; Greenhough, H.E.; Bowater, J.; Selwood, A.I.; Wood, S.A.; Prinsep, M.R.; Truman, P.; et al. Acute toxicity of dihydroanatoxin-a from Microcoleus autumnalis in comparison to anatoxin-a. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Jia, X.P.; Yang, M.L.; Li, J.; Wu, H.; Zhou, Y. Discussion on several issues in the Kunming mouse bioassay for paralytic shellfish toxins. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2001, 2, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Oudra, B.; Loudiki, M.; Vasconcelos, V.; Sabour, B.; Sbiyyaa, B.; Oufdou, K.; Mezrioui, N. Detection and quantification of microcystins from cyanobacteria strains isolated from reservoirs and ponds in Morocco. Environ. Toxicol. 2002, 17, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Dietrich, D.R.; Cary, S.C. Increasing Microcystis cell density enhances microcystin synthesis: A mesocosm study. Inland Waters 2012, 2, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Fan, L.; Wu, Y.; Qin, W.; Shang, T.; Cheng, N.; Lei, L. Low dominance of toxic genotype within the Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii population and its affecting factors in tropical reservoirs of southern China- a case study of Zhuhai city. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2024, 48, 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Banker, R.; Carmeli, S.; Werman, M.; Teltsch, B.; Porat, R.; Sukenik, A. Uracil moiety is required for toxicity of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin cylindrospermopsin. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health-Part A 2001, 62, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seawright, A.A.; Nolan, C.C.; Shaw, G.R.; Chiswell, R.K.; Norris, R.L.; Moore, M.R.; Smith, M.J. The oral toxicity for mice of the tropical cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska). Environ. Toxicol. 1999, 14, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froscio, S.M.; Hurnpage, A.R.; Wickramasinghe, W.; Shaw, G.; Falconer, I.R. Interaction of the cyanobacterial toxin cylindrospermopsin with the eukaryotic protein synthesis system. Toxicon 2008, 51, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimaud, G.M.; Mairet, F.; Sciandra, A.; Bernard, O. Modeling the temperature effect on the specific growth rate of phytoplankton: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio-Technol. 2017, 16, 625–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, P.M.; Ibelings, B.W.; Bormans, M.; Huisman, J. Artificial mixing to control cyanobacterial blooms: A review. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.Q.; Liu, Y.B.; Shi, Q.H. Research, Development, Utilization and Protection of Poyang Lake in the 60 Years since the Founding of New China. J. Jiangxi Agric. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2009, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, K.; Liu, X.; Duan, M.; Chen, Y. Distribution and its influencing factors of bloom-forming cyanobacteria in Poyang Lake. China Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 261–267. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, G.; Zou, H.; Chen, N.; Xia, Y. Analysis on the Current Situation of Phytoplankton in the Typical River Lake Ecotone of Lake Poyang. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 4954–4964. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, F.; Liu, J.-T.; Yang, P.; Wen, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Characteristics of Cyanobacteria and the Driving Factors in Poyang Lake. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2024, 33, 605–614. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Yin, H. Analysis of influencing factors of phytoplankton at different hydrological periods at the outlet of Poyang Lake. Express Water Resour. Hydropower Inf. 2025, 46, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Jiang, M.; Xu, L.; Hu, S.; You, H.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L. Spatial and temporal characteristics of phytoplankton in Lake Poyang and its response to extreme flood and drying events. J. Lake Sci. 2024, 36, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Y.; Gao, Y.; Jia, J.J.; Kun, S.D.; Lyu, S.X.; Li, Z.X.; Lu, Y.; Wen, X.F. Water level as the key controlling regulator associated with nutrient and gross primary productivity changes in a large floodplain-lake system (Lake Poyang), China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 599, 126414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, F.; Ge, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Song, Y.; Zhang, D.; Lin, X.; Chen, S. The relationship of phytoplankton community structure and related environmental factors in upstream reservoirs of Xinjiang. J. Tarim Univ. 2024, 36, 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, K.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y. Spatial distribution characteristics of periphytic algae community of Lake Poyang in the high water level phase. J. Lake Sci. 2021, 33, 102–110. [Google Scholar]
- Johnk, K.D.; Huisman, J.; Sharples, J.; Sommeijer, B.; Visser, P.M.; Stroom, J.M. Summer heatwaves promote blooms of harmful cyanobacteria. Glob. Change Biol. 2008, 14, 495–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Liu, J.; Hu, F.; Wen, C.; Wen, H.; Wu, J.; Fu, S.; Dai, G. Influence of wind field on surface cyanobacteria density of Lake Poyang in wet season, China. J. Lake Sci. 2024, 36, 377–391. [Google Scholar]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Z. Effect of Wind-Induced Wave on Concentration of Colloidal Nutrient and Phytoplankton in Lake Taihu. Environ. Sci. 2007, 28, 506–511. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Cheng, J.; Mo, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Bi, S. Spatio-temporal variation of phytoplankton community and its relationship with environmental factors in Danjiangkou reservoir. J. Lake Sci. 2023, 35, 821–832. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, L.; Liu, D.; Duan, J.; Hu, Z.; Pan, J.; Lu, X.; Cui, S.; Liu, Q. Temporal and spatial changes of phytoplankton communities and their relationship with environmental factors in Qiandao Lake. J. Shanghai Ocean. Univ. 2024, 33, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Chen, H.M.; Wang, R.C.; Li, X.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, M. Analysis of the Causes for the Large Bloom Area in Taihu Lake in 2017. J. Lake Sci. 2019, 31, 621–632. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Park, M.S.; Hu, Q. Influences of cellular characteristics and media properties on membrane microalgal harvesting: A comparative study using Scenedesmus acuminatus cultivated at a pilot scale. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 1679–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.R.; Jia, R.B. Study on the Release Characteristics of Algal Toxins from Cells Destroyed by Chemical Oxidation. China Water Wastewater 2006, 13, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, Z.A.; Alamri, S.; Hashem, M. Endotoxin removal efficiency in conventional drinking water treatment plants, a case study in Egypt. Water SA 2022, 48, 180–186. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Z.; Kuai, J.; Wang, B.; Zhou, G. Progress and its application of slow/controlled release fertilizers in agricultural production. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2023, 42, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.Y.; Xu, S.T.; Cong, H.B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F. Removal of algal toxins in pressure-enhanced coagulation-sedimentation-filtration algae removal process. Water Wastewater Eng. 2015, 51, 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Climate-Blooms like it hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Kraemer, B.M.; Lenters, J.D.; Merchant, C.J.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S.; Schladow, S.G.; Weyhenmeyer, G.A. Global lake responses to climate change. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohdi, E.; Abbaspour, M. Harmful algal blooms (red tide): A review of causes, impacts and approaches to monitoring and prediction. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1789–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Zhu, W.; Wang, R.C.; Feng, G.Y.; Xue, Z.P. Rapid horizontal accumulation and bloom formation of the cyanobacterium Microcystis under wind stress. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X. Automatic recognition and classification of microalgae using an inception-v3 convolution neural network model. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 4625–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Chla | TP | TN | SD | CODMn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rij | 1 | 0.84 | 0.82 | −0.83 | 0.83 |
| rij2 | 1 | 0.7056 | 0.6724 | 0.6889 | 0.6889 |
| Water Quality Grade | Water Bloom Levels | Cyanobacterial Cell Density (Cells·L−1) | Trophic Levels | Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | No blooms | [0, 2.0 × 106) | Oligotrophic | [0, 30] |
| II | No significant bloom | [2.0 × 106, 1.0 × 107) | Mesotrophic | (30, 50] |
| III | Mild bloom | [1.0 × 107, 5.0 × 107) | Lightly eutrophic | (50, 60] |
| IV | Moderate bloom | [5.0 × 107, 1.0 × 108) | Moderately eutrophic | (60, 70] |
| V | Severe bloom | ≥1.0 × 108 | Heavily eutrophic | >70 |
| Site | Mean Density (Cells·L−1) | Peak-to-Mean Ratio | Coefficient of Variation (CV) | Months Exceeding Mild Bloom Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duchang County | 2.70 × 107 | 2.03 | 1.16 | 5 (June–October) |
| Hukou County | 0.91 × 107 | 3.47 | 1.09 | 4 (May–August) |
| Xingzi County | 1.09 × 107 | 4.32 | 1.47 | 2 (June, August) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, X. Algal Community Dynamics in Three Water Intakes of Poyang Lake: Implications for Drinking Water Safety and Management Strategies. Water 2025, 17, 2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17132034
Li B, Li J, Hu Y, Cheng S, Li S, Zhang X. Algal Community Dynamics in Three Water Intakes of Poyang Lake: Implications for Drinking Water Safety and Management Strategies. Water. 2025; 17(13):2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17132034
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bo, Jing Li, Yuehang Hu, Shaozhe Cheng, Shouchun Li, and Xuezhi Zhang. 2025. "Algal Community Dynamics in Three Water Intakes of Poyang Lake: Implications for Drinking Water Safety and Management Strategies" Water 17, no. 13: 2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17132034
APA StyleLi, B., Li, J., Hu, Y., Cheng, S., Li, S., & Zhang, X. (2025). Algal Community Dynamics in Three Water Intakes of Poyang Lake: Implications for Drinking Water Safety and Management Strategies. Water, 17(13), 2034. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17132034









