Abstract
Excessive nitrogen accumulation from aquaculture poses a significant threat to water quality in river–lake systems. This study investigated the Taipu River and five interconnected lakes to analyze the forms, spatial distribution, and ecological impact of nitrogen in both water and surface sediments. Sediment total nitrogen (TN), ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N), and nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N) were measured, with aquaculture-dominated lakes such as Xueluoyang Lake and Caodang Marsh exhibiting significantly higher sedimentary TN concentrations than the Taipu River. In Xueluoyang Lake, the average TN content reached 1037.3 mg/kg—1.87 times higher than in the river—highlighting the legacy effect of historical intensive aquaculture. Correlation analyses showed strong associations between sediment NH4+-N and NO3−-N and nitrogen levels in overlying water, confirming sediments as a major endogenous nitrogen source. Multivariate statistical methods, including Pearson’s correlation, hierarchical clustering, and principal component analysis, were applied to elucidate spatial patterns and key influencing factors. Water quality evaluation indices and sediment organic pollution assessments revealed widespread TN exceedance, particularly in dry seasons, with water quality deteriorating to Class V or worse. These results underscore the need for strengthened control of sedimentary nitrogen release and effective management of agricultural non-point source pollution to restore and protect water quality in river–lake systems.
1. Introduction
Rivers and lakes, serving distinct hydrological, ecological, and socio-economic functions, are conventionally studied as separate systems. However, under intensive anthropogenic disturbances, increasing quantities of nitrogen, phosphorus, and other pollutants have been introduced into river–lake systems and subsequently deposited in sediments. Under highly fluctuating hydrological conditions, these systems exhibit significant mutual water quality influences, particularly between interconnected rivers and lakes. The persistent input and long-term accumulation of nitrogen and phosphorus contaminants in water bodies have transformed sediments into refractory internal loadings [1]. Research demonstrated that when environmental conditions change in lacustrine systems, internal loading can be released into overlying water through diffusion, advection, and sediment resuspension processes, resulting in “secondary pollution” that severely degrades water quality.
Recent studies have systematically investigated sediment–water nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in interconnected river–lake systems across China. For instance, Ma et al. demonstrated that water-level fluctuations significantly influence phosphorus fraction distribution and potential release risks in Yangtze-connected lakes [2]. In the Poyang Lake Basin, anthropogenic stressors were identified as dominant sources of phosphorus contamination, highlighting the importance of integrated management [3]. Le et al. applied phosphate oxygen isotope tracing to clarify phosphorus source pathways in dense river–lake networks, while Liu et al. verified the role of system connectivity in reducing TN in urban lakes [4,5]. Beyond China, recent international studies have also revealed critical insights into sediment–water nutrient dynamics. In Poland, Janicka et al. analyzed a river–lake system and found significant seasonal and spatial variability in nitrogen and phosphorus forms, with sediment accumulation processes playing a key role in internal nutrient retention [6]. Similarly, Potasznik et al. investigated cascading river–lake systems and highlighted that macrophytes and sediments jointly regulate the nutrient fluxes in catchment-scale aquatic environments [7]. These findings provided valuable comparative references for assessing nutrient behaviors and internal loading risks in the Taipu River Basin.
To protect river–lake ecosystems, China has recently implemented multiple fishery withdrawal and lake restoration policies, such as the Opinions of the General Office of the State Council on Firmly Advancing the Ten-Year Fishing Ban on the Yangtze River. These policies emphasized reducing aquaculture impacts on lacustrine ecosystems through measures including net enclosure removal and cage elimination, while enhancing aquatic vegetation restoration and ecological compensation to improve water self-purification capacity. In the Taihu Lake Basin, for instance, policy implementation has significantly reduced surface water nitrogen and phosphorus inputs and improved water quality in several lakes [8]. Nevertheless, despite substantial post-implementation water quality improvements, TN remains a frequent exceedance [9].
The Taipu River is situated within a densely interconnected river network, featuring numerous tributaries and over twenty lakes directly or indirectly connected to it. The Grand Canal traverses this region north–south, forming a complex river–lake continuum system. However, nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations in the interconnected lakes adjacent to the Taipu River generally exceed those in the main river channel, suggesting significant mutual hydroecological impacts at their confluence zones [10]. Previous studies have revealed distinct spatial distribution patterns of nitrogen and phosphorus pollution within the Taipu River Basin, a Yangtze River tributary, with pollutant concentrations demonstrating strong environmental sensitivity. These findings underscore the urgent need for effective pollution control measures in such interconnected river–lake systems [11]. Research in the Chaohu Lake Basin has demonstrated that non-point source pollution substantially degrades regional water quality, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus inputs from specific tributaries, highlighting the critical ecological impacts of pollutant transfer within river–lake continuums [12]. Furthermore, studies on Yangtze River water diversion into Taihu Lake have indicated that hydrological regime alterations significantly affect water quality parameters and phytoplankton habitats, suggesting potential cumulative ecosystem impacts from tributary-derived pollutants in lacustrine systems [13]. Therefore, systematic investigation of pollution characteristics and ecological effects becomes imperative for elucidating the direct/indirect impacts of peripheral lake inputs on the Taipu River and identifying optimal environmental monitoring targets within specified river–lake spatial domains.
This study focused on two critical aquaculture-dominated lakes adjacent to the Taipu River, employing comparative and statistical analyses of nitrogen species in both the aqueous and sedimentary phases. Through comprehensive characterization of TN distribution patterns and speciation, we systematically identified the dominant TN sources within the aquatic system and elucidated mechanisms sustaining elevated TN concentrations post-pollution control interventions.
Different from previous studies that primarily focused on isolated lakes or rivers, this study provides an integrated assessment of endogenous nitrogen pollution in a densely interconnected river–lake system. By combining multi-season field sampling, sediment–water interaction analysis, and multivariate statistical techniques, we offer new insights into the legacy effects of aquaculture and spatial drivers of internal nitrogen loading in the Taipu River Basin.
Therefore, this study aims to analyze the seasonal and spatial distribution patterns of nitrogen species in both the water and sediments of a highly interconnected river–lake system, investigate the sediment–water interaction mechanisms governing internal nitrogen cycling, and identify the influence of aquaculture and hydrological conditions on nitrogen accumulation and release.
By integrating multi-seasonal field sampling with statistical and spatial analysis, this study provides new insights into endogenous nitrogen dynamics under real eutrophication pressures. The findings are expected to contribute to the scientific understanding of sediment-driven nitrogen pollution and future management strategies in similar river–lake environments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Taipu River is located in the plain river network region of the Taihu Lake Basin. It originates from East Taihu Lake and discharges into the Huangpu River, spanning 57 km between 120°28′15″ E–121°4′44″ E and 31°0′35″ N–31°1′42″ N. The surrounding terrain is characterized by low relief, extensive Quaternary overburden, and minimal bedrock exposure. Hydrologically, the river has an average discharge of 300 m3/s, flow velocities ranging from 0.03 to 0.33 m/s, and a sediment accumulation rate of 4.2 cm/a. In contrast, the lake areas were largely stagnant or slow-flowing, particularly during the dry season, exhibiting typical shallow lake hydrodynamics in low-gradient regions. As a critical hydrological nexus, the Taipu River connects with 205 lakes and several major waterways, including the Grand Canal, Lanxi Pond, Maxi Creek, and Ditang Creek. The Grand Canal intersects the Taipu River in a north–south orientation. Lanxi Pond and Ditang Creek feed into Yingdouhu Lake from the south and west, respectively. Yingdouhu Lake discharges northeastward into the Taipu River and southeastward into the Sujia Canal, eventually merging with Maxi Creek near Wangjiangjing before entering Jiaxing, Zhejiang Province.
Based on archival research and field investigations, five representative lakes hydrologically connected to the Taipu River were selected as study sites, which were categorized by functional type:
- Aquaculture-dominated lakes: Historically intensive aquaculture zones (Xueluoyang Lake and Yangjiadang Lake);
- Urban lakes: Proximate to built-up areas with intense anthropogenic pressures (Caodang Marsh and Yingdouhu Lake);
- Suburban lakes: Non-aquacultural systems distal from urban centers (Fenhu Lake).
Key characteristics of the selected lakes:
- Xueluoyang Lake: Former 4-hectare net-enclosed aquaculture zone, now undergoing fishery withdrawal and ecological restoration;
- Caodang Marsh and Yingdouhu Lake: Subject to dense urban populations in surrounding areas;
- Yangjiadang Lake: Northern embankment adjacent to 60 hectares of fishponds created using dredged sediments from Taipu River, bordered by agricultural lands and aquaculture ponds with high eutrophication risks;
- Fenhu Lake: Transects the lower Taipu River reach through direct hydrological connectivity.
2.2. Sample Collection and Analytical Methods
2.2.1. Sample Collection and Pretreatment
Water and sediment samples from the Taipu River were collected via an equidistant sampling method at 4 km intervals. The distribution of lake sampling points was determined according to the method specified in the Guidelines for Lake Sediment Investigation [14]. To comprehensively assess seasonal variation, water and sediment samples were collected during three representative hydrological seasons in 2021: the dry season (January), the normal season (April), and the wet season (July). Based on the representativeness and regional functional considerations, seven sampling points were selected along the Taipu River and 17 points across five interconnected lakes during the dry season. In the normal and wet seasons, sampling intensity increased to 10 points along the Taipu River while maintaining 17 points across the lakes, yielding a total of 78 samples across all three seasons (Figure 1). For river sampling, a strict 4 km equidistant protocol was implemented. In each lake, triplicate sampling points were systematically positioned at the inlet of lake, middle of lake, and outlet of lake to ensure spatial coverage of hydrodynamic and biogeochemical gradients.
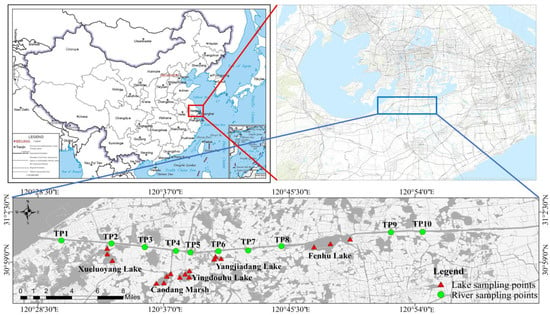
Figure 1.
Location and sampling site.
Surface water samples (0.3–0.5 m below the water surface) were collected using a plexiglass water sampler and preserved in pre-cleaned 500 mL polyethylene bottles. Immediately after collection, 2 mL of 0.8 mol/L HNO3 was added to acidify samples for metal stabilization. All samples were transported to the laboratory under dark, low-temperature (4 °C) conditions and analyzed within 48 h to minimize post-sampling alterations. Concurrent in situ measurements of physicochemical parameters—including water temperature, dissolved oxygen (DO), conductivity, fluorescent dissolved organic matter (fDOM), oxidation-reduction potential (ORP), turbidity, and chlorophyll-a (Chl-a)—were performed using a calibrated portable multi-parameter water quality sonde (EXO2, YSI, Yellow Springs, OH, USA) to ensure real-time environmental representativeness.
Sediment samples were collected simultaneously with water samples at the same sampling points as the water samples. A Peterson grab sampler was employed as the sampling tool. On-site sediment samples were collected from the boat with a minimum of 2 kg (wet weight) while recording information such as longitude, latitude, and color. The samples were then sealed in clean resealable bags and stored under low-temperature (4 °C) conditions. After being transported to the laboratory, the samples underwent pretreatment processes including freeze-drying, grinding, and sieving (60 mesh and 100 mesh) before being preserved for subsequent analysis.
The sediments at all sampling sites were visually assessed during collection. Most samples consisted predominantly of fine-grained silt and clay, suggesting deposition under low-energy hydrodynamic conditions. In aquaculture-dominated areas, the surface sediments appeared to be dark gray to black and emitted a slight sulfurous odor, indicating an anaerobic environment. Although detailed granulometric and redox potential measurements were not conducted, these characteristics are consistent with previous observations in similarly impacted lake systems.
2.2.2. Analytical Methods
The concentrations of NH4+-N and TN in water were determined following the water quality–determination of ammonia nitrogen–Nessler’s reagent spectrophotometry (HJ 535—2009) [15] and water quality–determination of total nitrogen–alkaline potassium persulfate digestion UV spectrophotometric method (HJ 636—2012) [16], respectively. Sediment TN and total organic carbon (TOC) were analyzed according to soil quality–determination of total nitrogen–modified Kjeldahl method (HJ 717—2014) [17] and soil-determination of organic carbon–potassium dichromate oxidation spectrophotometric method (HJ 615—2011) [18], respectively. NH4+-N and NO3−-N in sediments were extracted using an extraction method [14]. Briefly, 10 g of freeze-dried sediment (sieved through a 10 mesh) was weighed into a 200 mL plastic bottle, mixed with 50 mL of 1 mol/L NaCl extractant at a soil-to-water ratio of 1:5, and oscillated at 180 r/m for 30 min at 25 °C. The solid–liquid mixture was transferred to a 50 mL centrifuge tube for centrifugation for five minutes at a speed of 3000 r/m. After centrifugation, the supernatant was filtered (0.45 μm membrane). For NH4+-N analysis, 10 mL of supernatant was added to a 25 mL colorimetric tube with Nessler’s reagent, and the absorbance was measured at 420 nm. For NO3−-N determination, 25 mL of the filtrate was acidified with 1 mL of 1.8 mol/L H2SO4 in a 50 mL colorimetric tube, and the absorbance was measured at 220 nm and 275 nm for calculation.
The detection limits of the analytical methods used in this study were as follows: 0.025 mg/L for NH4+-N in water, 0.05 mg/L for TN in water, 48 mg/kg for TN in sediments, and 0.06% for TOC in sediments, based on the Chinese environmental standards (HJ 535—2009, HJ 636—2012, HJ 717—2014, and HJ 615—2011). For NH4+-N and NO3−-N in sediment extracts, which were measured using Nessler’s reagent and UV spectrophotometry at 420 nm and 220/275 nm, respectively, after NaCl extraction, the estimated detection limits were approximately 0.3 mg/kg and 0.5 mg/kg, respectively, according to commonly reported method performance in similar studies.
2.3. Water Quality Index Method
The water quality index method is divided into the single-factor water quality index (Pi) and the comprehensive water quality index (Iwq) [19,20]. The specific calculation methods were provided in Supplementary Materials Text 1.
2.4. The Organic Index (OI) Method
The OI method is commonly used as an indicator of the environmental condition of sediment in water bodies [21]. The calculation method was provided in Supplementary Materials Text 2.
2.5. Data Analysis
Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin (KMO) and Bartlett’s sphericity test, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), correlation analysis, and hierarchical clustering were all performed using SPSS 26. The schematic diagram of the study area and the distribution of sampling points were created using ArcGIS 10.6 software. The calculation method for the coefficient of variation [22] was provided in Supplementary Materials Text 3.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. River and Lake Water Quality Analysis
The basic physicochemical properties of the overlying water quality, as tested on-site, were summarized in Table A1, including common water quality indicators such as temperature, pH, DO, and electrical conductivity. The results showed that the water quality in the Taipu River and its connected lakes varied significantly across different seasons and hydrological periods (e.g., wet season, normal season, and dry season). These variations directly affected the distribution characteristics of nitrogen. Table A2 summarizes the concentrations of NH4+-N and TN during the dry, normal, and wet seasons. As shown in the table, the average NH4+-N concentration in the Taipu River ranged from 0.13 to 0.48 mg/L, while in the connected lakes, it ranged from 0.13 to 0.76 mg/L, with a high coefficient of variation [22], all exceeding 50%, indicating significant differences between sampling points. The overall water quality for NH4+-N was good, with all sampling points meeting the Class III surface water environmental quality standard [23] (Figure 2a,b). The average TN concentration in the Taipu River ranged from 1.35 to 2.64 mg/L, while in the connected lakes, it ranged from 1.32 to 4.21 mg/L, with a coefficient of variation between 5% and 60%.
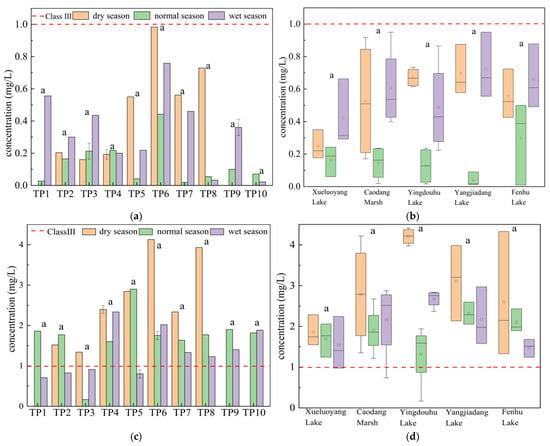
Figure 2.
(a) Spatiotemporal distribution of NH4+-N in the Taipu River; (b) in the connected lakes; (c) distribution of TN in the Taipu River; (d) in the connected lakes. “a” indicates no significant seasonal difference in concentrations at the corresponding site or lake.
Figure 2c,d show the spatiotemporal distribution of TN in the Taipu River and connected lakes. As observed, the average TN concentration in the main stream of the Taipu River was 1.90 mg/L, while in the connected lakes, the average TN concentration was 2.25 mg/L. The TN concentrations in both the river and lakes were the highest during the dry season and the lowest during the normal season. The TN pollution in the study area was relatively severe, classified as Class V or worse [23]. Overall, the highest TN concentrations occurred during the dry season, which may be attributed to factors such as lower temperatures, reduced water flow, and slower biochemical reaction rates during this period [24].
Spatially, there were no significant differences in TN concentrations across the river and lake water quality in the study area. The spatial variation of nutrients depended on land use types and urban development levels, with higher nitrogen concentrations typically occurring in urban and agricultural areas [25]. The TN concentration in Yingdouhu Lake, an urban lake, was approximately 1.36 times that of the Taipu River. Yingdouhu Lake is located in a developed economic area, with water inputs from Lanxi Tang and Ditang, as well as effluent from a sewage treatment plant entering from the south. Positioned at a river–lake junction, the convergence zone significantly influences the migration of pollutants. In the middle reaches of the Taipu River, near the river–lake water flow intersection, TN concentrations were relatively higher. Xueluoyang Lake, located near the upstream of the Taipu River, had the lowest TN concentration of 1.74 mg/L. Fenhu Lake had a TN concentration of 2.16 mg/L, Caodang Marsh had 2.28 mg/L, and Yangjiadang Lake had 2.53 mg/L. The coefficients of variation for Xueluoyang Lake, Caodang Marsh, Yingdouhu Lake, Yangjiadang Lake, and Fenhu Lake are 23.3%, 35.6%, 21.2%, 20.9%, and 24.4%, respectively, with Caodang Marsh exhibiting the greatest variation.
The overlying water quality was evaluated using the comprehensive water quality index method, which is widely applied in river water quality assessment in China. Jin et al. employed the comprehensive water quality index method to assess the pollution status of rivers in East Taihu Lake and combined it with the Monte Carlo simulation method to analyze the impacts of pollutants such as TN, total phosphorus, and petroleum hydrocarbons [26]. The study emphasized the importance of petroleum hydrocarbons in future water quality assessments. Hou et al. used the comprehensive water quality index method in the water quality assessment of the Ningxia section of the Yellow River, with results indicating that ammonia nitrogen was the primary pollutant affecting water quality, and the water quality was generally poor [27]. Zhang applied the comprehensive water quality index method in the lower reaches of the Liao River in Liaoning Province, and the study showed that this method provided more objective and effective information compared to other methods, enabling a more accurate assessment of water quality [28].
As shown in Table 1, the water quality of the Taipu River and Fenhu Lake should meet the Class III standard, while other lakes are classified as Class IV [23]. From the perspective of the Pi, NH4+-N and DO concentrations met the Class III water standard across all seasons. However, TN concentrations exceeded the standard severely. Except for the Taipu River and Xueluoyang Lake, all other lakes had water quality classified as worse than Class V in at least two seasons, with the poorest quality occurring during the dry season. Due to the relatively low Pi-values for NH4+-N and DO, the overall Iwq was reduced. Except for Taipu River, Yingdouhu Lake, and Fenhu Lake, the water quality of other rivers and lakes met the corresponding water quality classification.

Table 1.
Single-factor water quality index (Pi) and comprehensive water quality index (Iwq) (calculated as the average) for the three seasons in the connected rivers and lakes.
3.2. River and Lake Surface Sediment Analysis
3.2.1. Analysis of Surface Sediment TOC and Nitrogen Content
Table A3 summarizes the TOC content of sediments during the dry, normal, and wet seasons. Table A4 summarizes the contents of TN, NH4+-N, and NO3−-N in sediments during the same seasons. As shown in Table A2, the average TOC content in the Taipu River ranged from 0.86% to 1.0% across different hydrological periods. In the connected lakes, the average TOC content ranged from 0.52% to 2.6%. Overall, the coefficient of variation was relatively low, indicating that the distribution of TOC in the river and lakes was fairly uniform. The aquaculture-dominated lake, Xueluoyang Lake, had a higher TOC content (2.2%), which was twice as high as that of other rivers and lakes in the study area, indicating relatively higher organic pollution in aquaculture-dominated lakes. Table A5 presents the TOC content in the surface sediments of plain lakes. Compared to Table A5, the surface sediment TOC in the study area was generally within the normal range. Both Yangcheng Lake and Xueluoyang Lake, as aquaculture-dominated lakes, showed higher TOC contents, suggesting that organic pollution from aquaculture in lakes should not be overlooked. As shown in Table A4, the average TN content in the sediments ranged from 375.8 to 1322.2 mg/kg. The standard deviation for Caodang Marsh was relatively high, with an average of 379 mg/kg, while other regions showed lower coefficients of variation. The average NH4+-N content in the sediments ranged from 23.0 to 145.0 mg/kg, with the Taipu River showing a relatively high coefficient of variation of around 40%. The average NO3−-N content in the sediments ranged from 3.6 to 11.7 mg/kg, with the Taipu River and Yingdouhu Lake showing large coefficients of variation.
3.2.2. Evaluation of Organic Pollution Degree in Surface Sediments
Figure 3 assessed the evaluation of organic pollution degree in the surface sediments of the connected rivers and lakes. As shown in Figure 3, the aquaculture-dominated lake, Xueluoyang Lake, was categorized as moderately polluted (Class III), while the other rivers and lakes were in a relatively clean state (Class II) [21]. The organic nitrogen (ON) and OI in the aquaculture-dominated lake also indicated moderate pollution, suggesting that the organic ecological risk effect was significant and should be given attention.
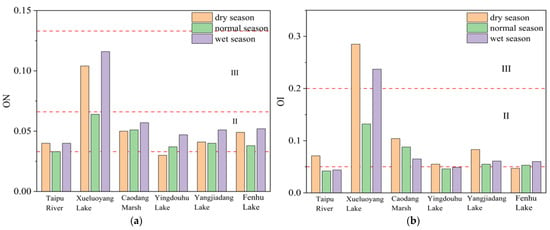
Figure 3.
(a) Evaluation of ON in surface sediments of connected rivers and lakes; (b) evaluation of OI in surface sediments of connected rivers and lakes. Specifically, “II” represents a relatively clean state, while “III” represents a moderately polluted state.
3.2.3. Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics of TN, NH4+-N, and NO3−-N in Surface Sediments
Figure 4a,b show the spatiotemporal distribution of TN content in the surface sediments of the connected rivers and lakes. As observed, the TN content in the main stream of the Taipu River was 554.88 mg/kg, while the TN content in the connected lakes was 623.3 mg/kg. The TN content in the sediment of the connected lakes was 1.12 times that of the Taipu River. The TN content in both the river and lakes was the highest during the wet season, which aligned with the findings of Memet Varol et al. on the surface sediment of the Tigris River [29]. During the wet season, the TN concentration in the overlying water was relatively low, while the TN content in the surface sediments was higher. This may be that the high temperatures during the wet season, along with specific environmental conditions, led to active physical and chemical reactions at the sediment–water interface. As a result, TN in the overlying water settled into the sediments, leading to a short-term increase in sediment TN content while the TN concentration in the overlying water decreases.
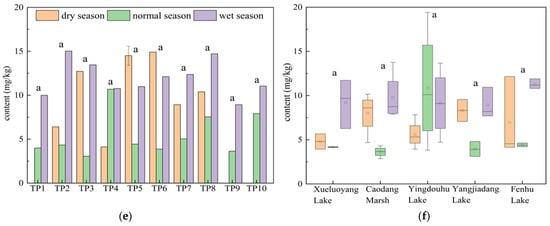
Figure 4.
(a) Spatiotemporal distribution of TN in surface sediments of the Taipu River; (b) in connected lakes; (c) NH4+-N in surface sediments of the Taipu River; (d) in connected lakes; (e) NO3−-N in surface sediments of the Taipu River; (f) in connected lakes. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between groups (p < 0.05). Specifically, “a” represents significantly different from all other groups, “b” represents significantly different from the group marked “b” (i.e., the “bc” group), “c” represents significantly different from groups marked “c” (i.e., “bc” and “cd” groups), “bc” represents not significantly different from either “b” or “c”, “cd” represents not significantly different from either “c” or “d”; “de” represents not significantly different from either “d” or “e”; “d” represents significantly different from the group marked “d” (i.e., the “cd” group), and “e” represents significantly different from all other groups and associated with the highest TOC value. Note: Groups that do not share any letter are significantly different; those that share at least one letter are not significantly different.
Spatially, the TN content in the upper reaches of the Taipu River significantly differed from the middle and lower reaches, but there was no significant difference when compared to the aquaculture-dominated lake upstream. The highest TN content in the upper reaches was approximately 888.0 mg/kg. The TN content in the aquaculture-dominated lake, Xueluoyang Lake, was the highest across all three hydrological seasons, with an average of 1037.3 mg/kg, showing a significant difference from the other four lakes. This value was 1.87 times the TN content in the Taipu River sediments. This was related to the area’s history of intensive cage aquaculture. Although Xueluoyang Lake has now undergone fishery-to-lake conversion, historically, it had more than 60 acres of cage aquaculture areas, with excessive feed inputs and a large amount of fish excretion, leading to the accumulation of high nitrogen content in the lake’s bottom sediments. Related studies indicated that marine fish farming in the Inner Danish waters had led to increased nitrogen and phosphorus release, with an associated rise in nutrient flux in the sediments [30]. Except for Xueluoyang Lake, the TN content in other lakes was relatively low. The TN content in Caodang Marsh was 629.33 mg/kg, with a coefficient of variation of 61.3%; Fenhu Lake had 533.21 mg/kg, with a coefficient of variation of 35.4%; Yangjiadang Lake had 519.48 mg/kg, with a coefficient of variation of 9.5%; and Yingdouhu Lake had 445 mg/kg, with a coefficient of variation of 21.5%. Caodang Marsh showed the highest coefficient of variation.
Nitrogen in sediments and water is most readily absorbed by plants in the form of NH4+-N, and it is mainly released into the overlying water through diffusion, sediment resuspension, and biological disturbance. Dissolved NH4+-N diffusing across the sediment–water interface is an important pathway for the release of endogenous nitrogen, and as NH4+-N is released, the risk of water eutrophication increases. Khirul et al. found that the interaction of nitrogen, iron, and sulfides in polluted marine sediments, along with biochemical cycling under hypoxic conditions, significantly promoted nitrogen release, especially the diffusion processes of ammonia nitrogen and nitrate, thereby driving eutrophication [31]. Xiao et al. observed that algal blooms significantly enhanced the concentrations of ammonia nitrogen and nitrate, promoting anaerobic ammonia oxidation and denitrification pathways, which in turn affected the eutrophication process in the water [32].
Figure 4c,d show the spatiotemporal distribution of NH4+-N content in the surface sediments of the connected rivers and lakes. As shown in the figure, the NH4+-N content in the main stream of the Taipu River was 54.53 mg/kg, accounting for 9.7% of the TN content. In the connected lakes, the NH4+-N content was 62.68 mg/kg, accounting for 10.0%. The NH4+-N content in the sediments of the connected lakes was 1.15 times that of the Taipu River. The NH4+-N content in both the river and lakes was the highest during the wet season, which was consistent with the findings of Wang et al. on the NH4+-N content in the sediments of the Danjiangkou Reservoir [33]. During the normal season, the DO concentration in the overlying water was relatively high and could penetrate to deeper layers of the sediment. The oxidative environment in the sediments increases the activity of aerobic microorganisms, which allows the organic matter in the sediment to be mineralized and decomposed. This led to the accumulation of NH4+-N in the sediment. By the wet season, ammonifying bacteria, under anaerobic conditions, mineralize ON in the sediments, resulting in a higher level of NH4+-N [34,35].
Spatially, there was no significant difference in the NH4+-N content between the river and the lakes. The NH4+-N content in the Taipu River was higher in the upstream section, decreased at TP4 and TP5, and slightly increased again near TP6, which followed a trend similar to that of TN. Among the five lakes, the aquaculture-dominated lake, Xueluoyang Lake, had the highest NH4+-N content, with an average of 78.75 mg/kg, accounting for 6.9% of TN, and a coefficient of variation of 15.5%. This was approximately 1.46 times higher than that of the Taipu River. Following Xueluoyang Lake were Yangjiadang Lake and Caodang Marsh, with NH4+-N contents that were relatively close, averaging 68.17 mg/kg and 67.26 mg/kg, accounting for 13.1% and 10.6% of TN, respectively, with coefficients of variation of 28.6% and 18.8%. Fenhu Lake and Yingdouhu Lake had lower NH4+-N contents. The distribution of sediment NH4+-N was closely related to the distribution of TN. Zhu et al. analyzed the release characteristics of nitrogen in sediments and pointed out that the release of NH4+-N from sediments is significantly correlated with TN, and that temperature and pH significantly influence its release dynamics [36]. The higher NH4+-N content in Xueluoyang Lake was associated with its higher TN content.
Figure 4e,f show the spatiotemporal distribution of NO3−-N content in the surface sediments of the connected rivers and lakes. As shown in the figure, the NO3−-N content in the main stream of the Taipu River was 9.12 mg/kg, accounting for 1.6% of TN. The NO3−-N content in the connected lakes was 7.37 mg/kg, accounting for 1.2% of TN. The NO3−-N content in both the river and lakes was the highest during the wet season and the lowest during the normal season. The NO3−-N content in the sediments of the connected lakes was approximately 0.80 times that of the Taipu River.
Spatially, there was no significant difference in the NO3−-N content between the river and the lakes. Among the five lakes, Yingdouhu Lake had the highest NO3−-N content, with an average of 8.58 mg/kg and a coefficient of variation of 38.2%, which was about 1.16 times that of the Taipu River. The proportion of NO3−-N was relatively low, and the content was quite similar across the lakes. Fenhu Lake had a coefficient of variation of 20.6%, Caodang Marsh had 21.4%, Yangjiadang Lake had 16.8%, and Xueluoyang Lake had 14.5%. The seasonal variation at the sampling points in the Taipu River was relatively large, but spatial differences were small.
3.3. Influence of Nitrogen in the Surface Sediments of Connected Lakes on the Taipu River
3.3.1. Influence of Nitrogen in the Surface Sediments of Connected Lakes on the Surface Sediments of the Taipu River
To clarify the differences and influence between the sediments of the connected lakes and the Taipu River, a hierarchical clustering analysis was conducted on 15 sampling points using the squared Euclidean distance as a measure, as shown in Figure 5 [37]. The results indicated that at a distance of 5, the river and lake sampling points can be divided into four categories:
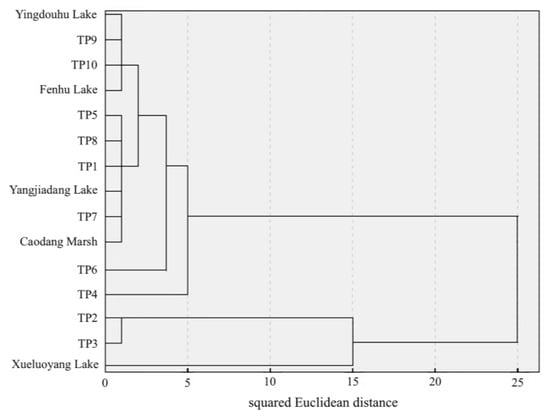
Figure 5.
Dendrogram of hierarchical clustering analysis for the connected rivers and lakes.
- Category 1: Yingdouhu Lake, Fenhu Lake, Yangjiadang Lake, Caodang Marsh, TP1, TP5–TP10;
- Category 2: TP4;
- Category 3: TP2, TP3;
- Category 4: Xueluoyang Lake.
At a distance of 15, Category 1 and Category 2 merged into one group, while Category 3 and Category 4 merged into another group. As the distance increases, at a distance of 25, all points were grouped into one category. This figure indicates that TP2, TP3, and TP4 on the Taipu River differ significantly from other sampling points on the river, and Xueluoyang Lake also shows considerable differences from the other four rivers and lakes. These sampling sites in category 1 were situated in relatively stagnant or slow-flowing areas, where hydrodynamic conditions were stable, which favored the accumulation of pollutants. Both the sediments and the overlying water exhibited elevated nitrogen concentrations. TP4 lay within a flow-confluence zone characterized by complex mixing dynamics and substantial influence from the Grand Canal. Consequently, its nitrogen pollution signature differed: sediment-bound nitrogen was high, whereas aqueous-phase nitrogen was comparatively low. TP2 and TP3 were located in the upper reaches of the Taipu River, directly connected to aquaculture-dominated lakes. The nitrogen accumulation in their sediments reflected the historical intensity of farming activities in the area. Xueluoyang Lake had a documented history of aquaculture-related pollution. The build-up and release of nitrogen in its sediments had a measurable impact on local water quality.
Based on the preliminary classification results from the cluster analysis, it can be concluded that the sampling points can generally be divided into two to four categories. To further identify the influencing factors in each region, PCA was employed for an in-depth investigation and validation. Before conducting the PCA analysis, the KMO and Bartlett’s test of sphericity were performed on the standardized pollution factor data samples. The test results indicated that the KMO statistic value was 0.591 and Bartlett’s test gave a p-value of 0.000. According to Kaiser’s criteria, a KMO value above 0.5 is the minimum acceptable threshold for factor analysis. Although 0.591 is considered to be common, the highly significant Bartlett’s test (p < 0.001) indicated sufficient correlations among variables. Therefore, principal component analysis was acceptable. Subsequently, the PCA was conducted using the varimax rotation method for the component loading matrix, and the component scores were calculated using the Anderson–Rubin method. Typically, PCA analysis focuses on components with an initial eigenvalue greater than one or close to one. Therefore, the number of principal components was determined using a scree plot without setting the number of factors. Based on the eigenvalue distribution, the eigenvalues of the first four principal components are all greater than one and could explain approximately 90% of the total variance. Starting from the fifth principal component, the eigenvalues fall below one and gradually level off, indicating less applicable for the overall variability. Therefore, the first four principal components were chosen for analysis, which was consistent with the results shown in Figure 5. The results of the hierarchical cluster analysis showed that the sampling sites could be grouped into four distinct categories based on the squared Euclidean distance. To further verify and explore the driving factors behind these spatial patterns, PCA was performed. Although the grouping patterns of hierarchical cluster analysis and PCA were not exactly identical, there was considerable overlap between them. For instance, TP2, TP3, TP4, and Xueluoyang Lake were consistently separated from the majority of other sampling sites in hierarchical clustering analysis and PCA. This cross-validation between methods reinforces the reliability of the identified spatial classifications and highlights the distinct sediment nitrogen characteristics in areas influenced by aquaculture, tributary mixing, or non-point source pollution.
Figure 6 shows the PCA analysis plot for the connected rivers and lakes. The principal component (PC) analysis revealed that PC1 explained 40.8% of the total variance, PC2 21.5%, PC3 15.9%, and PC4 11.7%. The cumulative variance explained by the first four principal components reaches approximately 90%. Based on the relative spatial positions and pairwise distances of the sampling points, the correlation between the points can be intuitively observed. Combined with the spatial characteristics of nitrogen, it was evident that TP4, TP6, TP2, and TP3 exhibited significant differences compared to other sampling points on the Taipu River.
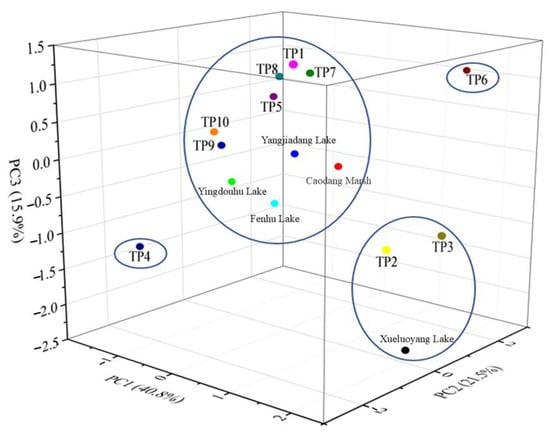
Figure 6.
PCA analysis chart of the connected rivers and lakes.
TP4 was located in a water flow mixing zone, with the Grand Canal to the south. Both the eastern and western sides of the Grand Canal had tributaries converging, and when pollutants passed through the water flow mixing zone, there was a significant presence of asymmetric water flow convergence areas with distinct three-dimensional characteristics [38]. The turbulent mixing in the water flow convergence zone was complex and had a strong entrainment effect on sediments and pollutants, making it a key node influencing the migration, diffusion, and distribution of pollutants.
By combining the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of surface sediment TN, NH4+-N, and NO3−-N, it can be observed that the TN content in TP6 sediments ranks second only to TP2 and TP3. Although TP6 was directly connected to Yangjiadang Lake, the PCA analysis did not group TP6 with Yangjiadang Lake, suggesting that other factors are influencing the nitrogen content in TP6. According to satellite map Figure A1 and field surveys, TP6 was surrounded by typical rural areas, with abundant farmland and villages nearby. This suggested that TP6 was significantly impacted by rural non-point source pollution. Agricultural and domestic pollution were the main sources of rural non-point source pollution. Ritter reviewed the sources of agricultural non-point source pollution and its impact on water quality, which primarily included erosion and sediment, animal waste, fertilizers, and pesticides [39]. Lu et al. reviewed the research progress on agricultural non-point source pollution and analyzed the impact of imbalanced fertilizer use and application structure over the past decade [40]. The article concluded that excessive fertilizer application and unreasonable application structures are the main causes of agricultural non-point source pollution. Cardiff et al. estimated the annual nitrogen loss from agricultural fields through edge-of-field monitoring combined with bromide tracer application, revealing the impact of nitrogen on groundwater and suggesting the practical use of this method for reducing agricultural nitrogen loss [41].
TP2 and TP3 were located in the upper reaches of the Taipu River, with TP2 directly connected to the aquaculture-dominated lake, Xueluoyang Lake. These three sampling points exhibited relatively low TN concentrations in the overlying water, while sediment nitrogen content was high. As shown in Figure A2, Xueluoyang Lake’s shores were rich in submerged plants, and the watershed area contains the Xueluoyang Lake Wetland. The lake’s shores were also surrounded by several villages and farmlands. Before 2019, Xueluoyang Lake experienced widespread cage aquaculture. Currently, the fish farming has been retired and the lake has been restored, but historically, there was a cage aquaculture area of over 4 hectares. The long-term excessive feeding and high fish excretion led to the accumulation of high nitrogen content in the lake sediments. Despite this, the TN concentration in the overlying water of Xueluoyang Lake was relatively low, possibly due to dredging, which has slowed the rate of nitrogen release from the sediment to the overlying water and improved the water quality. Jing et al. found that dredging weakens the ability of sediment NH4+-N to release into the overlying water, a result consistent with the findings of this study [42]. The PCA analysis grouped TP2, TP3, and Xueluoyang Lake into one category, suggesting that the TN content in the upper reaches of the Taipu River was significantly influenced by aquaculture-dominated lakes.
In summary, nitrogen-rich sediments originating from aquaculture and agricultural activities in connected lakes exerted a pronounced influence on the Taipu River’s surface sediments through hydrodynamic connectivity. In the lake–river interface zones (TP2, TP3), input from the aquaculture-dominated Xueluoyang Lake elevated sediment TN and NH4+-N despite low overlying-water TN. In the flow-confluence zone (TP4), intense mixing with Grand Canal waters produced heterogeneous nitrogen distributions between sediment and water. In the slow-flow deposition areas (Category 1: Fenhu, Yingdouhu, TP1, TP5–TP10), stable hydrodynamics facilitated the accumulation of both sediment-bound and aqueous nitrogen. Finally, rural non-point source pollution around TP6 similarly elevated sediment nitrogen, highlighting the combined effects of lake-derived and land-derived nitrogen loads. Collectively, these findings demonstrated that lake sediment nitrogen not only accumulated within lakes but also significantly altered the spatial pattern and magnitude of nitrogen pollution in the Taipu River, underscoring the need for integrated management of connected waterbodies.
3.3.2. Influence of Nitrogen in Surface Sediments of Connected Rivers and Lakes on Water Quality
Table 2 presents the correlations between different nitrogen forms in sediments and the physicochemical properties of the water. TN and NH4+-N in sediments exhibited a significant positive correlation (p < 0.01), while sediment TN showed a negative correlation with water TN (p < 0.05). Sediment NH4+-N was significantly positively correlated with sediment NO3−-N, water NH4+-N, ORP, and DO (p < 0.01). Sediment NO3−-N showed positive correlations with ORP, DO, and fDOM. Compared to sediment NO3−-N, sediment NH4+-N was more strongly influenced by sediment TN, and the content of sediment TN significantly affected sediment NH4+-N levels. The negative correlation between sediment TN and water TN suggests that, under certain conditions, these two forms can transform into one another. When TN in water settles into sediments, the water TN concentration decreases while the sediment TN content increases. NO3−-N showed limited correlation with other nitrogen species, being only positively correlated with NH4+-N. Water DO was significantly positively correlated with sediment nitrogen forms but negatively correlated with water NH4+-N, consistent with the findings of Jing et al. [42]. Specifically, higher DO concentrations favor the activity of aerobic microorganisms—such as ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB)—which promote the conversion of NH4+-N to NO2−-N and NO3−-N, thus enhancing nitrification [43]. This process not only increases NO3−-N accumulation in sediments but also reduces NH4+-N levels, thereby explaining the positive correlation between DO and sediment nitrogen forms. In addition, high DO levels can form an oxidized layer on the sediment surface, acting as a physical–chemical barrier that hinders the diffusion of NH4+-N from sediments and prevents its release into the overlying water [44]. This may explain the observed negative correlation between DO and water NH4+-N. Furthermore, elevated DO provides NO3−-N as a precursor for subsequent denitrification. Although denitrification typically occurs in anaerobic microzones, it depends on the availability of nitrate, indirectly enhancing nitrogen transformation and removal [45]. These results indicate that DO not only influences nitrogen transformation in sediments but also regulates its migration and release into the water column, playing a key role in nitrogen cycling in lake ecosystems.

Table 2.
Correlation between sediment nitrogen and water quality parameter (n = 67).
The zero to two centimeters layer of the sediment–water interface was a key zone for the cycling of nitrogen and other nutrients between sediments and the water. Canavan et al. used a reactive transport model (RTM) to study nitrogen cycling in coastal freshwater sediments, revealing the nitrogen transformation processes at the sediment interface and their impact on water nitrogen concentrations [46]. Nitrification and denitrification reactions at the sediment–water interface occurred in a vertically stratified manner, with these processes taking place only in the surface sediment layer [47]. Under anaerobic conditions, the decomposition of ON by facultative anaerobic and anaerobic bacteria led to the release of NH4+-N. Part of the NH4+-N was fixed in the mineral crystal layers of the sediment, while some was adsorbed by organic and inorganic colloids. The remaining portion was released into the overlying water to balance the ammonia concentration at the sediment–water interface, thereby increasing the nitrogen concentration and nutrient levels in the water [48]. Additionally, NO3−-N from the overlying water can also diffuse back into the anaerobic layer of the sediment, where it is reduced by denitrification to N2O, N2, and other gases that escape into the atmosphere [49]. The migration and transformation processes of nitrogen at the sediment–water interface are illustrated in Figure 7. It is important to note that sediment samples in this study were collected from the uppermost—5 cm layer using a standard dredge sampler. However, many key biogeochemical processes, such as nitrogen transformation and release, predominantly occur within the top 0–2 cm of the sediment–water interface. Given the deposition rate in this study area reaches approximately 4.2 cm/year, the sampled layer likely represents material deposited during the most recent year, and in some cases, possibly from just the previous season. Therefore, the results primarily reflect recent sediment dynamics rather than long-term accumulation patterns. This temporal limitation should be considered when comparing these findings with systems that have slower sedimentation rates or deeper biogeochemical activity layers.
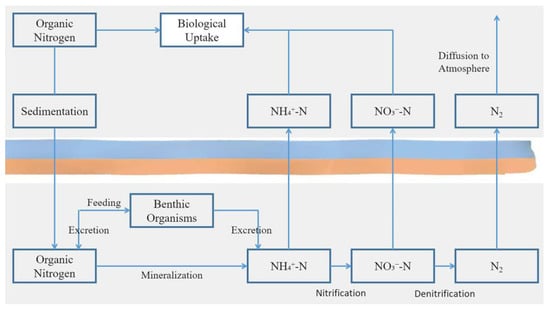
Figure 7.
Nitrogen transformation and migration processes at the sediment–water interface.
In the correlation analysis presented in Table 2, sediment NO3−-N was significantly positively correlated with NH4+-N, indicating that a vigorous transformation process exists between NO3−-N and NH4+-N in this river–lake system. Under aerobic conditions, NH4+-N generated from organic matter mineralization can be converted to NO2−-N through nitrification, which is further transformed into NO3−-N, while anaerobic conditions were unfavorable for the nitrification of NH4+-N [50,51]. Some researchers have suggested that the adsorbed NO3−-N in sediments mainly originates from the overlying water and showed a weaker correlation with sediment NH4+-N. In simple terms, this implied that sediments had a negative release capacity for NO3− from the water, i.e., they reduced the NO3− concentration in the overlying water [52,53]. For example, when the NO3− concentration in the water increases, denitrification in the anaerobic layer of the sediment intensifies, and more NO3− enters the sediment’s anaerobic layer, leading to a decrease in water NO3− concentrations. Conversely, when the NO3− concentration in the overlying water decreased, the denitrification process in the sediment’s anaerobic layer slowed down, resulting in reduced diffusion of NO3− from the water into the sediment, thereby regulating the nutrient levels in the aquatic ecosystem.
Studies have shown that the source of NO3−-N in lake sediments, whether it primarily originates from the overlying water or directly results from the mineralization of NH4+-N, may depend on the environmental conditions of the sediment. The intensity of organic matter mineralization in sediments varies in lakes with different nutrient levels [54]. In lightly polluted lake areas, biological and microbial activities in the sediment were frequent. When the nitrogen available for absorption in the overlying water was largely consumed and reduced, nitrogen in the sediment may be released to replenish it. In this case, both NO3−-N and NH4+-N can be directly utilized by biota [55,56]. Meanwhile, benthic organisms and microbial activity accelerate the mineralization of ON, with sediment NO3−-N primarily resulting from the direct transformation of NH4+-N during mineralization. For lakes or lake areas with more severe pollution, eutrophication led to the death of large amounts of aquatic plants, and the ON deposited in the sediment was decomposed by facultative anaerobic and anaerobic bacteria, releasing substantial amounts of NH4+-N [57,58]. Due to the lack of consumption by primary producers, the NH4+-N generated from mineralization was adsorbed and fixed by the sediment. The mineral fixation of NH4+-N results in the burial of nitrogen within the sediment, where it no longer participates in the nitrogen cycle in the short term. At this stage, NO3−-N in lake sediments primarily originated from the overlying water. This process was significant for reducing internal pollution loads and slowing down the eutrophication of the lake. However, it should be noted that nitrogen was merely buried in the sediment, and when the physicochemical properties of the sediment–water interface change, it may still be released back into the overlying water.
4. Conclusions
This study revealed that the water quality in the Taihu Lake Basin was generally poor, with TN concentrations in the water often exceeding Class V standards, reflecting significant nutrient enrichment. Sediment analyses showed that TN, NH4+-N, and NO3−-N levels exhibited pronounced seasonal variation, with the highest nitrogen content observed during the wet season, likely influenced by intensified physicochemical processes at the sediment–water interface. In aquaculture-dominated lakes such as Xueluoyang Lake, sediment nitrogen concentrations were notably elevated, and the level of organic pollution was severe.
A significant interaction was found between sediment and water column nitrogen, particularly regarding the transformation between NH4+-N and NO3−-N. These transformations, along with sediment nitrogen release, played a crucial role in shaping water nutrient levels, especially under eutrophic conditions. Spatial analysis revealed marked differences in nitrogen pollution across lakes and sections of the Taipu River, with agricultural and aquaculture activities contributing prominently to these situations. Xueluoyang Lake, affected by historical overfishing and intensive aquaculture, showed persistent sediment nitrogen accumulation, despite the recent cessation of fishing activities.
These findings have important implications for water and sediment management in river–lake systems. Targeted sediment dredging is recommended for areas such as Xueluoyang Lake, while buffer zones and constructed wetlands could help mitigate agricultural non-point source pollution. Enhanced seasonal monitoring is also necessary during periods of elevated nitrogen release risk.
However, for this study, sampling was restricted to three representative seasons within a single year, limiting its ability to reflect interannual variability. Furthermore, when comparing with regions that have lower deposition rates (e.g., a few millimeters per year), it is important to consider that such differences in temporal scale might affect the applicability of the results. Future research should therefore incorporate multi-year, high-frequency sampling, integrate microbial and isotope analysis, and utilize coupled hydrodynamic–biogeochemical models to improve the simulation and management of sediment–water nitrogen dynamics under varying environmental scenarios. Additionally, future studies should also consider the role of benthic macroinvertebrates in sediment mixing and nutrient cycling. Their presence or absence, particularly in organically enriched or anoxic environments, may significantly influence sediment–water interactions and should be included as a factor in future investigations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w17132000/s1, Text 1: Water quality indexing method; Table S1: Evaluation standards for water quality index method; Text 2: Eutrophication risk assessment method; Table S2: Evaluation standards for different levels of the organic pollution index method; Text 3: Calculation of the coefficient of variation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.L. and H.T.; methodology, J.H. and F.T.; software, J.H.; validation, J.H. and F.T.; formal analysis, J.H. and F.T.; investigation, F.T.; resources, F.L. and H.T.; data curation, J.H. and F.T.; writing—original draft preparation, J.H.; writing—review and editing, J.H. and Y.H.; visualization, J.H. and F.T.; supervision, Y.H. and F.L.; project administration, F.L., Y.H. and H.T.; funding acquisition, F.L. and H.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 21876111, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 22476107.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| NH4+-N | Ammonium nitrogen |
| NO3−-N | Nitrate nitrogen |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| DO | Dissolved oxygen |
| fDOM | Fluorescent dissolved organic matter |
| ORP | Oxidation-reduction potential |
| Chl-a | Chlorophyll-a |
| TOC | Total organic carbon |
| KMO | Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| PC | Principal component |
| AOB | Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria |
| NOB | Nitrite-oxidizing bacteria |
| RTM | Reactive transport model |
Appendix A

Table A1.
Statistical table of basic physicochemical properties for on-site water quality testing.
Table A1.
Statistical table of basic physicochemical properties for on-site water quality testing.
| Indicator | Taipu River | Xueluoyang Lake | Caodang Marsh | Yingdouhu Lake | Yangjiadang Lake | Fenhu Lake | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Temperature (°C) | Normal Season | 19.6 (19.4~19.9) | 19.8 (19.7~19.9) | 19.7 (19.3~20.3) | 22.8 (20.5~20.9) | 20.0 (19.9~20.1) | 20 (19.7~20.6) |
| Wet Season | 29.8 (29.1~30.5) | 29.3 (29.3~29.4) | 29.9 (29.8~30.1) | 30.53 (30.0~30.9) | 30.2 (30~30.6) | 30.3 (30.1~30.4) | |
| pH | Normal Season | 8.0 (7.8~8.3) | 8.54 (8.29~8.79) | 8.2 (7.9~8.6) | 7.8 (7.7~7.8) | 7.7 (7.7~7.7) | 7.9 (7.9~8.1) |
| Wet Season | 7.8 (7.7~7.9) | 7.9 (7.8~8.0) | 7.7 (7.6~8.0) | 7.6 (7.5~7.9) | 7.7 (7.7~7.8) | 7.7 (7.6~7.7) | |
| DO (mg/L) | Normal Season | 7.2 (6.8~8.4) | 9.2 (8.4~10.1) | 8.2 (7.2~9.5) | 6.9 (6.7~7.1) | 6.6 (6.5~6.7) | 7.5 (7.2~8.1) |
| Wet Season | 5.2 (4.7~6.1) | 6.4 (6.2~6.6) | 5.8 (4.3~7.6) | 5.4 (4.0~7.3) | 5.3 (4.8~6.1) | 5.0 (4.9~5.0) | |
| Chl-a (µg/L) | Normal Season | 7.0 (4.5~12.7) | 23.4 (12.7~34.1) | 10.7 (4.2~19.6) | 7.1 (6.4~7.8) | 5.9 (5.2~6.9) | 7.2 (6.6~7.7) |
| Wet Season | 4.7 (3.4~6.3) | 5.4 (4.7~6.1) | 5.7 (4.4~7.0) | 6.2 (3.8~10.9) | 4.1 (3.6~4.7) | 5.9 (5.3~6.4) | |
| Turbidity (NTU) | Normal Season | 38.2 (21.0~60.0) | 19.4 (15.0~23.9) | 84.1 (16.8~168.3) | 107.0 (95.4~126.6) | 82.8 (75.7~89.3) | 31.6 (28.0~35.9) |
| Wet Season | 24.4 (12.3~31.9) | 23.5 (18.7~28.2) | 42.7 (9.3~81.1) | 49.0 (36.0~68.6) | 30.6 (27.9~36.0) | 33.0 (24.9~41.2) | |
| fDOM (rfu) | Normal Season | 20.3 (17.9~23.2) | 31.6 (20.9 ~42.3) | 39.5 (26.1~51.3) | 45.5 (40.9~47.7) | 54.1 (52.7~56.9) | 25.4 (23.0~28.8) |
| Wet Season | 45.1 (36.0~51.2) | 51.2 (37.9~64.4) | 71.6 (67.5~77.0) | 83.6 (79.7~88.7) | 58.2 (53.0~61.6) | 49.3 (47.2~50.6) | |
| Electrical Conductivity (μs/cm) | Normal Season | 502.9 (450.9~545) | 461.5 (461.0~462.0) | 602.5 (569.0~632.0) | 700.1 (687.4~718.9) | 672.3 (666.9~679.1) | 530.3 (522.1~546.5) |
| Wet Season | 404.7 (377.5~429.4) | 391.7 (388.5~394.9) | 455.5 (433.6~476.7) | 503.9 (471.0~544.0) | 435.4 (420.3~455.4) | 419.9 (416.0~422.8) | |
| ORP (mV) | Normal Season | 172.1 (114.8~233.4) | 173.7 (158.3~189.1) | 175.4 (121.7~226.5) | 180.9 (167.1~189) | 190.5 (129.9~251.6) | 172.0 (122.9~229.9) |
| Wet Season | 273.7 (189.1~452.4) | 255.8 (247.4~264.2) | 231.0 (152.9~281.5) | 162.7 (68.6~276) | 262.4 (258.4~265) | 248.8 (236.2~256.7) | |
Note: The value outside the parentheses is the mean, while the value inside the parentheses represents the range from the minimum to the maximum.

Table A2.
Statistical concentrations of NH4+-N and TN in the water quality of the Taipu River and connected lakes.
Table A2.
Statistical concentrations of NH4+-N and TN in the water quality of the Taipu River and connected lakes.
| Indicator | Study Area | Mean | Median | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Normal | Wet | Dry | Normal | Wet | Dry | Normal | Wet | Dry | Normal | Wet | ||
| NH4+-N (mg/L) | Taipu River | 0.48 | 0.13 | 0.33 | 0.55 | 0.09 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 65% | 97% | 69% |
| Xueluoyang Lake | 0.26 | 0.16 | 0.42 | 0.26 | 0.19 | 0.31 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.21 | 47% | 57% | 49% | |
| Caodang Marsh | 0.53 | 0.15 | 0.63 | 0.51 | 0.16 | 0.54 | 0.37 | 0.11 | 0.29 | 71% | 73% | 46% | |
| Yingdouhu Lake | 0.67 | 0.13 | 0.49 | 0.67 | 0.13 | 0.43 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.28 | 9% | 91% | 58% | |
| Yangjiadang Lake | 0.70 | 0.24 | 0.76 | 0.64 | 0.02 | 0.67 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 22% | 80% | 35% | |
| Fenhu Lake | 0.56 | 0.30 | 0.66 | 0.52 | 0.39 | 0.61 | 0.15 | 0.26 | 0.20 | 27% | 86% | 30% | |
| TN (mg/L) | Taipu River | 2.64 | 1.72 | 1.35 | 2.40 | 1.77 | 1.28 | 1.08 | 0.66 | 0.57 | 41% | 38% | 42% |
| Xueluoyang Lake | 2.02 | 1.69 | 1.54 | 2.02 | 1.77 | 1.41 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.65 | 19% | 24% | 42% | |
| Caodang Marsh | 2.79 | 1.90 | 2.16 | 2.79 | 1.86 | 2.52 | 1.27 | 0.60 | 0.97 | 45% | 31% | 45% | |
| Yingdouhu Lake | 4.21 | 1.32 | 2.68 | 4.22 | 1.59 | 2.76 | 0.20 | 0.79 | 0.22 | 5% | 60% | 8% | |
| Yangjiadang Lake | 3.11 | 2.31 | 2.18 | 3.21 | 2.29 | 1.98 | 0.93 | 0.27 | 0.72 | 30% | 12% | 33% | |
| Fenhu Lake | 2.60 | 2.10 | 1.48 | 2.15 | 1.98 | 1.51 | 1.55 | 0.29 | 0.22 | 60% | 14% | 15% | |

Table A3.
Statistical analysis of TOC content in surface sediments of connected rivers and lakes.
Table A3.
Statistical analysis of TOC content in surface sediments of connected rivers and lakes.
| Study Area | Statistical Value | Dry | Normal | Wet | Statistical Value | Dry | Normal | Wet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taipu River | Maximum | 1.99% | 1.67% | 2.95% | Minimum | 0.31% | 0.24% | 0.64% |
| Xueluoyang Lake | 2.18% | 2.16% | 2.79% | 0.05% | 0.20% | 0.10% | ||
| Caodang Marsh | 2.76% | 1.97% | 2.57% | 1.20% | 0.77% | 0.63% | ||
| Yingdouhu Lake | 1.81% | 1.44% | 2.21% | 0.37% | 0.25% | 0.52% | ||
| Yangjiadang Lake | 1.60% | 1.65% | 2.54% | 0.11% | 0.30% | 0.68% | ||
| Fenhu Lake | 2.37% | 1.69% | 0.95% | 0.76% | 0.39% | 0.01% | ||
| Taipu River | Mean | 1.04% | 0.86% | 0.95% | Median | 1.49% | 1.22% | 1.76% |
| Xueluoyang Lake | 2.11% | 1.87% | 2.60% | 2.15% | 2.01% | 2.71% | ||
| Caodang Marsh | 0.52% | 0.54% | 1.31% | 1.67% | 1.21% | 1.94% | ||
| Yingdouhu Lake | 0.95% | 0.87% | 1.15% | 1.31% | 1.09% | 1.79% | ||
| Yangjiadang Lake | 1.40% | 1.05% | 1.30% | 1.53% | 1.36% | 2.08% | ||
| Fenhu Lake | 0.88% | 0.98% | 0.94% | 1.54% | 1.24% | 0.94% | ||
| Taipu River | Deviation | 1.44% | 1.18% | 1.61% | Coefficient of Variation | 21% | 20% | 37% |
| Xueluoyang Lake | 2.15% | 2.01% | 2.74% | 2% | 10% | 4% | ||
| Caodang Marsh | 1.71% | 1.16% | 1.93% | 72% | 64% | 33% | ||
| Yingdouhu Lake | 1.23% | 1.02% | 1.91% | 28% | 23% | 29% | ||
| Yangjiadang Lake | 1.59% | 1.38% | 2.39% | 7% | 22% | 33% | ||
| Fenhu Lake | 1.37% | 1.05% | 0.95% | 49% | 31% | 1% |

Table A4.
Statistical analysis of different forms of nitrogen in sediments of the Taipu River and connected lakes.
Table A4.
Statistical analysis of different forms of nitrogen in sediments of the Taipu River and connected lakes.
| Indicator | Study Area | Mean | Median | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Normal | Wet | Dry | Normal | Wet | Dry | Normal | Wet | Dry | Normal | Wet | ||
| TN (mg/kg) | Taipu River | 579.9 | 502.6 | 586.1 | 507.4 | 500.7 | 520.4 | 103.6 | 167.0 | 162.8 | 18% | 35% | 27% |
| Xueluoyang Lake | 1101.3 | 688.6 | 1322.2 | 1101.3 | 672.1 | 1302.4 | 113.2 | 34.6 | 90.6 | 10% | 5% | 7% | |
| Caodang Marsh | 654.9 | 553.2 | 680.5 | 635.2 | 532.2 | 646.7 | 409.3 | 423.7 | 305.4 | 62% | 77% | 45% | |
| Yingdouhu Lake | 375.8 | 406.2 | 553.3 | 326.3 | 392.2 | 567.3 | 143.0 | 71.3 | 88.8 | 38% | 18% | 16% | |
| Yangjiadang Lake | 485.0 | 434.2 | 639.4 | 485.0 | 476.0 | 644.0 | 13.5 | 98.1 | 21.4 | 3% | 23% | 3% | |
| Fenhu Lake | 544.7 | 415.5 | 639.5 | 556.3 | 406.3 | 504.3 | 295.6 | 56.7 | 246.5 | 54% | 14% | 39% | |
| NH4+-N (mg/kg) | Taipu River | 50.5 | 38.6 | 74.5 | 49.7 | 38.5 | 62.8 | 15.4 | 15.5 | 33.8 | 30% | 40% | 45% |
| Xueluoyang Lake | 56.3 | 35.9 | 145.0 | 56.3 | 37.1 | 134.8 | 9.2 | 3.0 | 32.0 | 16% | 8% | 22% | |
| Caodang Marsh | 75.8 | 32.7 | 93.4 | 78.0 | 34.9 | 90.0 | 8.7 | 6.9 | 22.3 | 12% | 21% | 24% | |
| Yingdouhu Lake | 69.1 | 23.5 | 64.9 | 61.7 | 23.0 | 59.0 | 18.4 | 5.3 | 33.5 | 27% | 22% | 52% | |
| Yangjiadang Lake | 63.0 | 24.0 | 117.5 | 63.0 | 22.4 | 119.8 | 37.4 | 5.4 | 4.5 | 59% | 23% | 4% | |
| Fenhu Lake | 39.1 | 23.0 | 100.0 | 46.9 | 21.7 | 92.0 | 16.5 | 5.7 | 67.2 | 42% | 25% | 67% | |
| NO3−-N (mg/kg) | Taipu River | 10.3 | 5.3 | 11.7 | 10.4 | 4.4 | 11.6 | 4.1 | 2.6 | 2.4 | 40% | 48% | 20% |
| Xueluoyang Lake | 4.8 | 4.4 | 9.2 | 4.8 | 4.2 | 9.7 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 2.8 | 26% | 11% | 30% | |
| Caodang Marsh | 8.0 | 3.6 | 9.8 | 8.6 | 3.7 | 8.8 | 2.3 | 0.6 | 2.7 | 29% | 17% | 28% | |
| Yingdouhu Lake | 5.6 | 10.9 | 9.1 | 5.3 | 10.1 | 9.1 | 1.6 | 6.6 | 3.8 | 29% | 61% | 42% | |
| Yangjiadang Lake | 8.3 | 3.9 | 8.9 | 8.3 | 3.9 | 8.2 | 1.8 | 0.8 | 1.8 | 21% | 21% | 20% | |
| Fenhu Lake | 7.0 | 4.4 | 11.3 | 4.5 | 4.4 | 11.2 | 4.5 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 65% | 5% | 5% | |

Table A5.
TOC content in surface sediments of plain lakes.
Table A5.
TOC content in surface sediments of plain lakes.
| Study Area | Taihu Zhushan Bay | Poyang Lake | Dongting Lake | Yangcheng Lake | Dianshan Lake |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOC Content | 0.80% | 1.15% | 1.3% | 2.8% | 0.79% |
Appendix B
Figure A1.
Satellite map of TP6 and Yangjiadang Lake (YJD). TP6 refers to the sixth sampling point along the Taipu River; YJD is the abbreviation for Yangjiadang Lake.
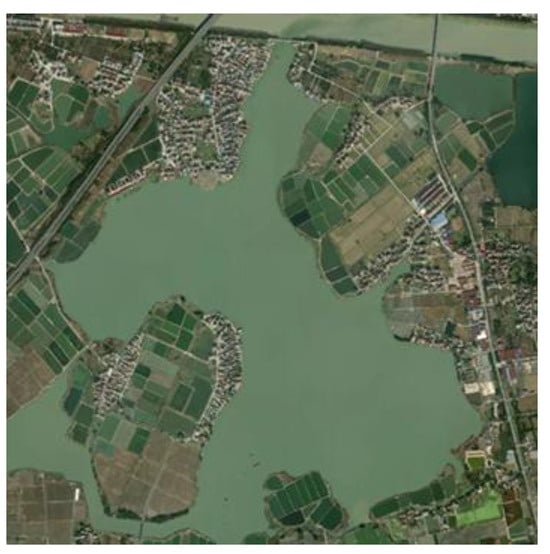

Figure A2.
Satellite map of Xueluoyang Lake.
References
- Song, K.; Adams, C.J.; Burgin, A.J. Relative importance of external and internal phosphorus loadings on affecting lake water quality in agricultural landscapes. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 108, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.Y.; Qi, X.; Zhou, S.Q.; Niu, H.F.; Zhang, T.X. Spatiotemporal distribution of phosphorus fractions and the potential release risks in sediments in a Yangtze River connected lake: New insights into the influence of water-level fluctuation. J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.W.; Chen, H.T.; Ma, C.; Gao, X.; Yang, C.; Sun, W.C.; Wang, Y.Q. A novel framework reveals anthropogenic stressors of phosphorus polluted river-lake connection water system in Poyang lake basin of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, F.; Ruan, X.H.; Wei, Z.; Wu, K.D.; Wei, H.Z.; Liu, C.Q. Tracing phosphorus sources in the river-lake system using the oxygen isotope of phosphate. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 175022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Huang, S.H.; Chen, H.; Zuo, M.B.; He, G.Y.; Wang, M.; Bai, S.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, D.D.; Ding, Y.L.; et al. Study on the Effect of Water System Connection on the Improvement of Water Quality of Inner Lakes in Town-Taking Seven Lakes in Yangshuo Urban Area of Guilin as an Example. Water 2025, 17, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicka, E.; Kanclerz, J.; Wiatrowska, K.; Budka, A. Variability of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Content and Their Forms in Waters of a River-Lake System. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 874754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriata-Potasznik, A.; Szymczyk, S.; Skwierawski, A. Influence of Cascading River-Lake Systems on the Dynamics of Nutrient Circulation in Catchment Areas. Water 2020, 12, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Xia, Y.Q.; Ti, C.P.; Shan, J.; Wu, Y.H.; Yan, X.Y. Thirty years of experience in water pollution control in Taihu Lake: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Li, K.X.; Li, S.Q.; Li, Z.H.; Wan, L.L.; Guo, W. Source tracing analysis of the exceedance of NH3-N and CODMn in shallow groundwater in the central typical area of the Yangtze river delta. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, B.H. Using δ15N and δ18O Signatures to Evaluate Nitrate Sources and Transformations in Four Inflowing Rivers, North of Taihu Lake. Water 2017, 9, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-Y.; Zhou, M.-H.; Xu, P.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.-L.; Lin, H.-Y.; Jiang, N.; Ren, B.; Zhang, B.-W. Spatial Distribution of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Nutrients in the Main Stream and Typical Tributaries of Tuojiang River and Fujiang River. Huan Jing Ke Xue= Huanjing Kexue 2023, 44, 3933–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, F.; Li, S.Y. Estimation on Emission of Nonpoint Source Pollution of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Different Catchments of the Chaohu Lake Basin, China. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Energy and Environmental Protection (ICEEP 2012), Hohhot, China, 23–24 June 2012; Volume 518–523, p. 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.Y.; Wu, S.Q.; Wu, X.F.; Xue, W.Y.; Yang, Q.Q.; Zhu, S.L.; Wang, F.F.; Chen, D. Effects of Water Diversion from Yangtze River to Lake Taihu on the Phytoplankton Habitat of the Wangyu River Channel. Water 2018, 10, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.X. (Ed.) Specification for Lake Sediment Survey; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- HJ 535-2009; Water Quality—Determination of Ammonia Nitrogen—Nessler’s Reagent Spectrophotometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- HJ 636-2012; Water Quality—Determination of Total Nitrogen—Alkaline Potassium Persulfate Digestion UV Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- HJ 717-2014; Soil Quality—Determination of Total Nitrogen—Modified Kjeldahl Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- HJ 615-2011; Soil—Determination of Organic Carbon—Potassium Dichromate Oxidation Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Xu, Z. Study on the Single-Factor Water Quality Identification Index Method for Rivers in China. J. Tongji Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2005, 33, 321–325. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z. Comprehensive water quality identification index for environmental quality assessment of surface water. J. Tongji Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2005, 33, 482–488. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, G. Status and Evaluation of OM, TN, and TP in Surface Sediments of Lake Taihu. J. Lake Sci. 1996, 8, 319–324. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, K. Mathematical Contributions to the Theory of Evolution. III. Regression, Heredity, and Panmixia. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1896, 187, 253–318. [Google Scholar]
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Makuwa, S.; Tlou, M.; Fosso-Kankeu, E.; Green, E. The effects of dry versus wet season on the performance of a wastewater treatment plant in North West Province, South Africa. Water SA 2022, 48, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.H.; Yu, R.H.; Kang, J.F.; Lü, C.W.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.H. Water pollution characteristics and influencing factors of closed lake in a semiarid area: A case study of Daihai Lake, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Li, Y.; Lu, L.; Zhang, D.; He, S.Y.; Shentu, J.L.; Chai, Q.W.; Huang, L. Water quality assessment of east Tiaoxi River, China, based on a comprehensive water quality index model and Monte-Carlo simulation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Zhang, Y.T.; Qian, H. Water quality assessment in China Ningxia Section of the Yellow River using water quality identification index method. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Energy Engineering and Environmental Protection (EEEP), Xiamen, China, 19–21 November 2019; Volume 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. Different Methods for the Evaluation of Surface Water Quality: The Case of the Liao River, Liaoning Province, China. Int. Rev. Spat. Plan. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 5, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, M. Temporal and spatial dynamics of nitrogen and phosphorus in surface water and sediments of a transboundary river located in the semi-arid region of Turkey. Catena 2013, 100, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maar, M.; Larsen, J.; Dahl, K.; Riemann, B. Modelling the environmental impacts of future offshore fish farms in the inner Danish waters. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2018, 10, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khirul, M.A.; Cho, D.; Kwon, S.H. Behaviors of nitrogen, iron and sulfur compounds in contaminated marine sediment. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Yang, J.-Y. Water Bloom Modified Sediment Nitrogen Transformation and Removal. Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2019, 40, 4018–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Han, Y.P.; Pan, L.D. Spatial-temporal variation of nitrogen and diffusion flux across the water-sediment interface at the hydro-fluctuation belt of Danjiangkou reservoir in China. Water Supply 2020, 20, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, M.I.; Sánchez-Montoya, M.D.; Vidal-Abarca, M.R.; Suárez, M.L.; Gómez, R. Implications of flow intermittency on sediment nitrogen availability and processing rates in a Mediterranean headwater stream. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 76, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.P.; Wang, L.Q.; Liang, T.; Huang, M.X. Nitrogen distribution and ammonia release from the overlying water and sediments of Poyang Lake, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Li, Q.; Zou, J.; Liu, M. Research On the Characteristics of Sediment and the Release Law of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Pollutants in Landscape Lake. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2186, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukpatu, J.; Udoinyang, E.; Udoh, J.P. The Use of Agglomerative Hierarchical Cluster Analysis for the Assessment of Mangrove Water Quality of Okoro River Estuary, Southeastern Nigeria. Int. J. Geol. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2015, 3, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, F.; Xu, N.; Li, P.; Wang, A. Numerical Modeling of the Dispersion Characteristics of Pollutants in the Confluence Area of an Asymmetrical River. Water 2023, 15, 3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, W.F. Reducing Impacts of Nonpoint Source Pollution from Agriculture: A Review. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 1988, 23, 645–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Liu, Z. A Review on the Agriculture Non-Point Source Pollution Research. Sci. J. Technol. 2023, 5, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardiff, M.; Schachter, L.; Krause, J.; Gotkowitz, M.; Austin, B. Quantifying Annual Nitrogen Loss to Groundwater Via Edge-of-Field Monitoring: Method and Application. Groundwater 2023, 61, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, L.D.; Wu, C.X.; Liu, J.T.; Wang, H.G.; Ao, H.Y. The effects of dredging on nitrogen balance in sediment-water microcosms and implications to dredging projects. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 52, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandra, P.S.; Clara, D.; Anja, W.; Bernhard, M.; Stefanie, S.; Schloter, M.; Florian, E. Seasonal dynamics of anaerobic oxidation of ammonium and denitrification in a dimictic lake during the stratified spring-summer period. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2022, 67, 1194–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Wei, Z.M.; Zhao, Y.; Xi, B.D.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhao, T.Z.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.Q. Environmental factors influencing the distribution of ammonifying and denitrifying bacteria and water qualities in 10 lakes and reservoirs of the Northeast, China. Microb. Biotechnol. 2015, 8, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, F.A.E.; Darchambeau, F.; Borges, A.V.; Morana, C.; De Brabandere, L.; Thamdrup, B.; Crowe, S.A. Denitrification, anaerobic ammonium oxidation, and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium in an East African Great Lake (Lake Kivu). Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavan, R.W.; Laverman, A.M.; Slomp, C.P. Modeling nitrogen cycling in a coastal fresh water sediment. Hydrobiologia 2007, 584, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koomklang, J.; Yamaguchi, H.; Ichimi, K.; Tada, K. A role for a superficial sediment layer in upward nutrient fluxes across the overlying water-sediment interface. J. Oceanogr. 2018, 74, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitzinger, S.; Harrison, J.A.; Böhlke, J.K.; Bouwman, A.F.; Lowrance, R.; Peterson, B.; Tobias, C.; Van Drecht, G. Denitrification across landscapes and waterscapes:: A synthesis. Ecol. Appl. 2006, 16, 2064–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upreti, K.; Rivera-Monroy, V.H.; Maiti, K.; Giblin, A.E.; Castañeda-Moya, E. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA) is marginal relative to denitrification in emerging-eroding wetlands in a subtropical oligohaline and eutrophic coastal delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 152942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetten, M.S.M.; Wagner, M.; Fuerst, J.; van Loosdrecht, M.; Kuenen, G.; Strous, M. Microbiology and application of the anaerobic ammonium oxidation (‘anammox’) process. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2001, 12, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caranto, J.D.; Vilbert, A.C.; Lancaster, K.M. Nitrosomonas europaea cytochrome P460 is a direct link between nitrification and nitrous oxide emission. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 14704–14709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Zhong, X.L. Sediment pollution and nitrogen release at the sediment-water interface in Changjiang River and its tributary, the lower Han River Basin. Water Environ. J. 2020, 34, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Cai, Q.; Qin, B.; Zheng, X. Preliminary Study on Nitrogen Migration Characteristics at the Sediment–Water Interface in Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu. J. Lake Sci. 1998, 10, 41–47. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- den Heyer, C.E. Organic Matter Mineralization in Lake Sediments: A Within and Among Lake Study. Master’s Thesis, McGill University, Montréal, QC, Canada, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, L.C.; Luo, W.G.; Zhu, S.L. Experiment on Sediment Ammonia Nitrogen Release of Chaohu Lake in Varying Hydrodynamic Disturbance. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.R. Research on nitrogen and phosphorus release from sediments in small inland freshwater lakes. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development (EESD 2013), Shanghai, China, 12–13 November 2013; Volume 864–867, pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.G.; Wu, C.; Xie, D.Y.; Ma, J. Sources, Migration, Transformation, and Environmental Effects of Organic Carbon in Eutrophic Lakes: A Critical Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.Y.; Liu, C.Q.; Cai, J.; Hu, Y.; Shao, K.Q.; Tang, X.M.; Gong, Y.; Yao, X.L.; Xu, Q.J.; Gao, G. Relationships between environmental factors and N-cycling microbes reveal the indirect effect of further eutrophication on denitrification and DNRA in shallow lakes. Water Res. 2023, 245, 120572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).