A Quantitative Assessment of the Impacts of Land Use and Natural Factors on Water Quality in the Red River Basin, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
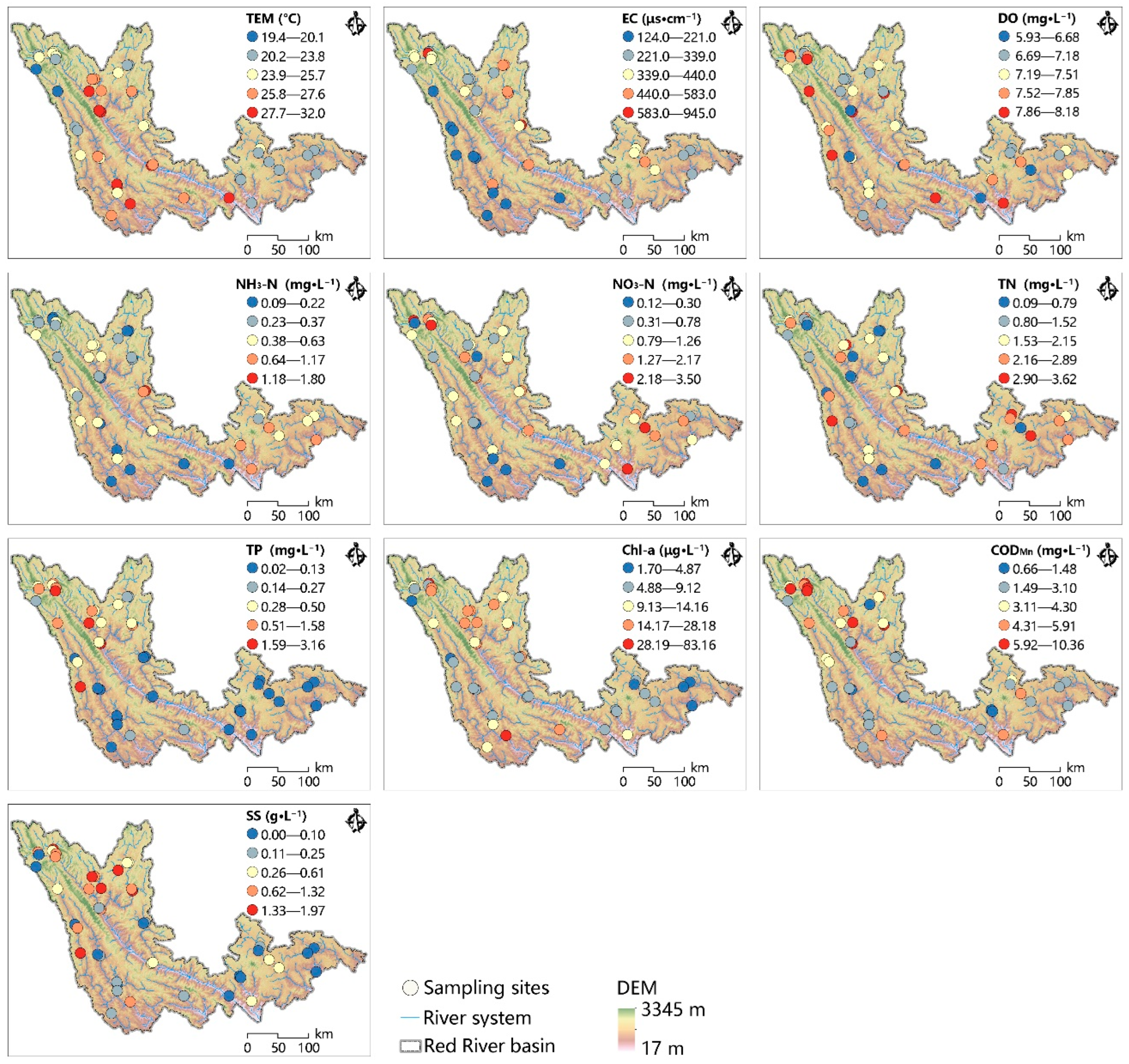
2.2. Water Sampling Measurements
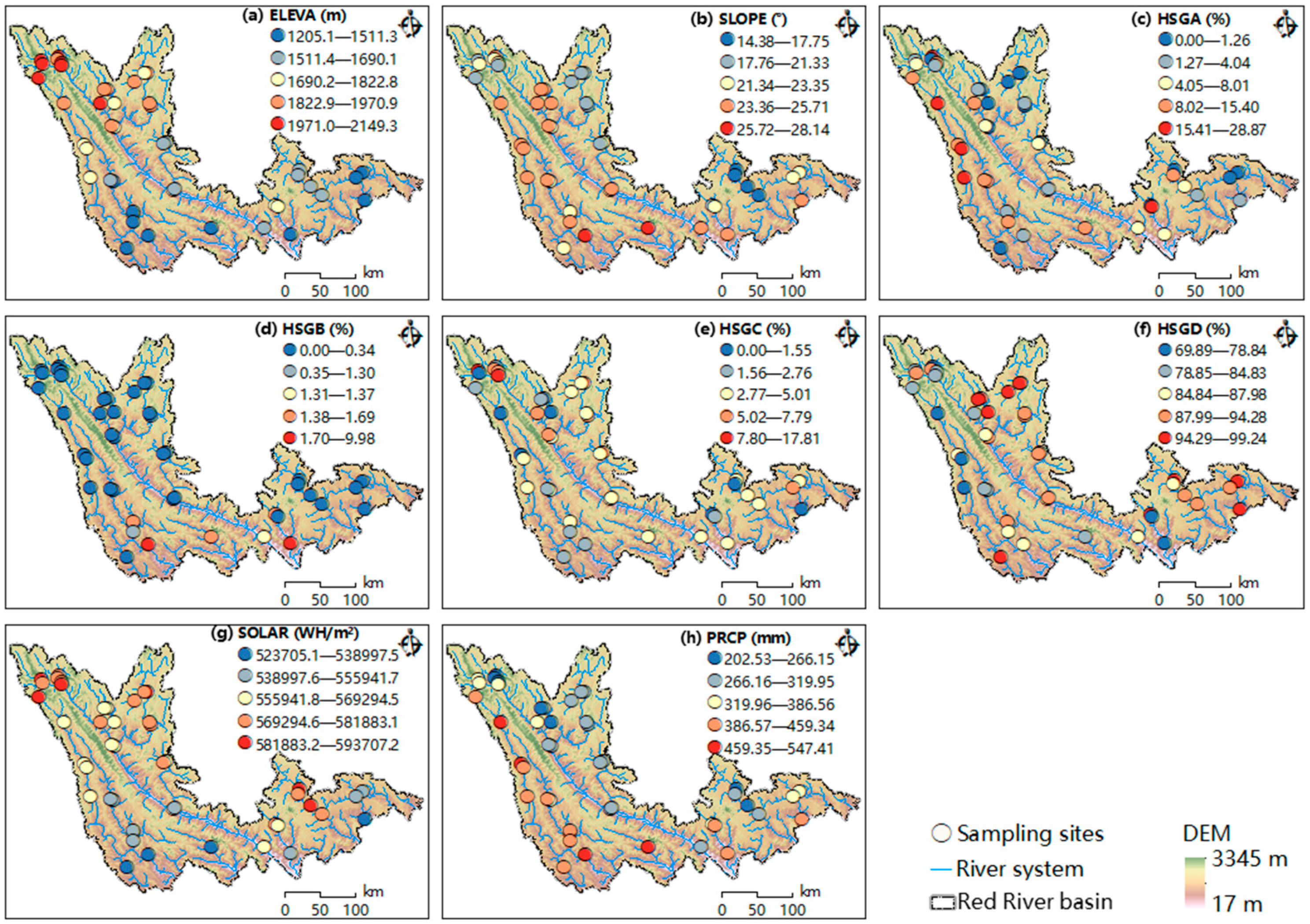
2.3. Land Use and Natural Factors Statistics
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Screening of Important Land Use Index
2.4.2. Effects of Land Use and Natural Environment on Water Quality
3. Results
3.1. The Best Prediction Model of Water Quality and Important Land Use Index
3.2. Characteristics of Water Quality, Land Use, and Natural Factors
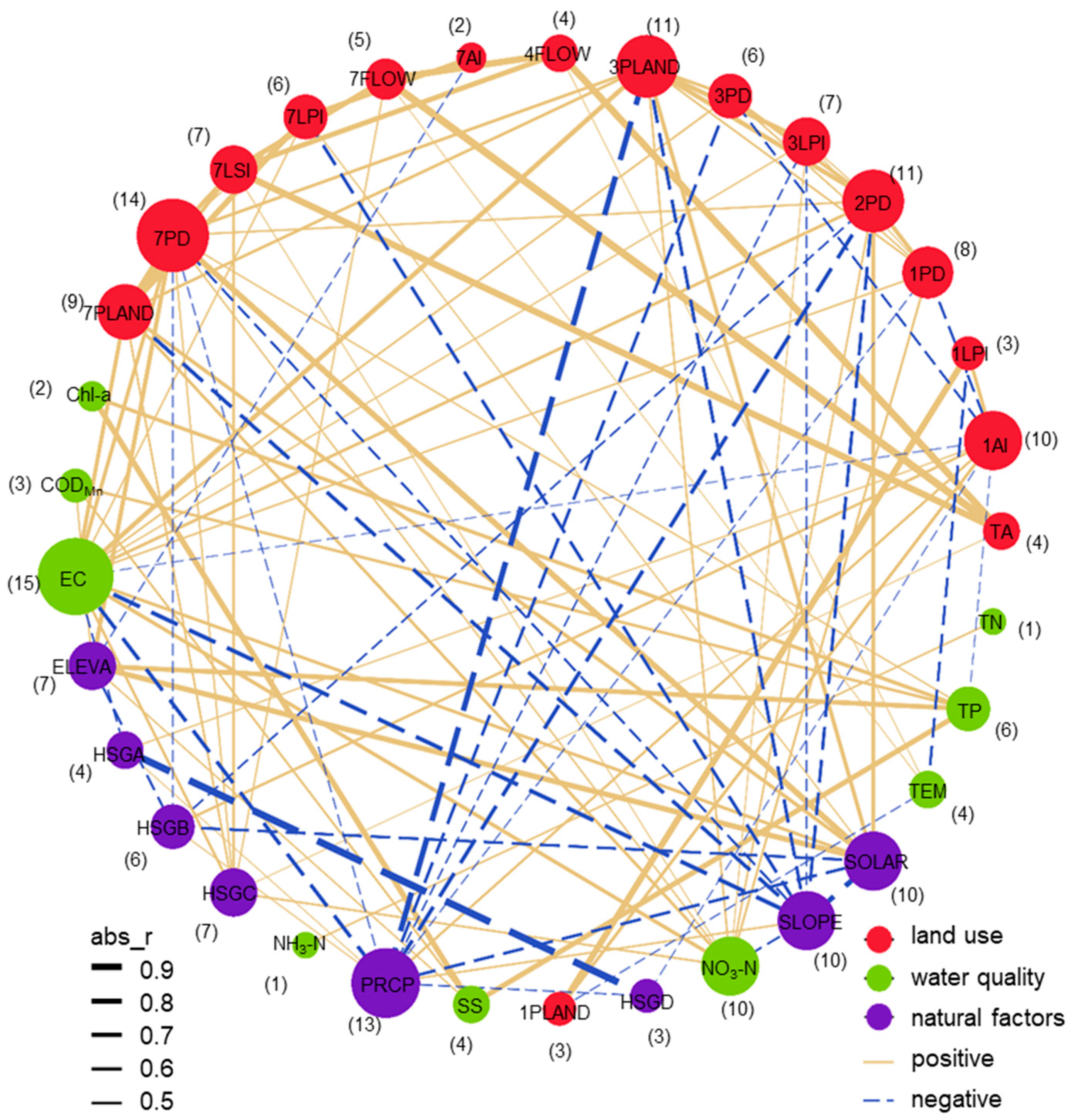
3.3. Correlation Between Land Use, Natural Factors, and Water Quality Parameters
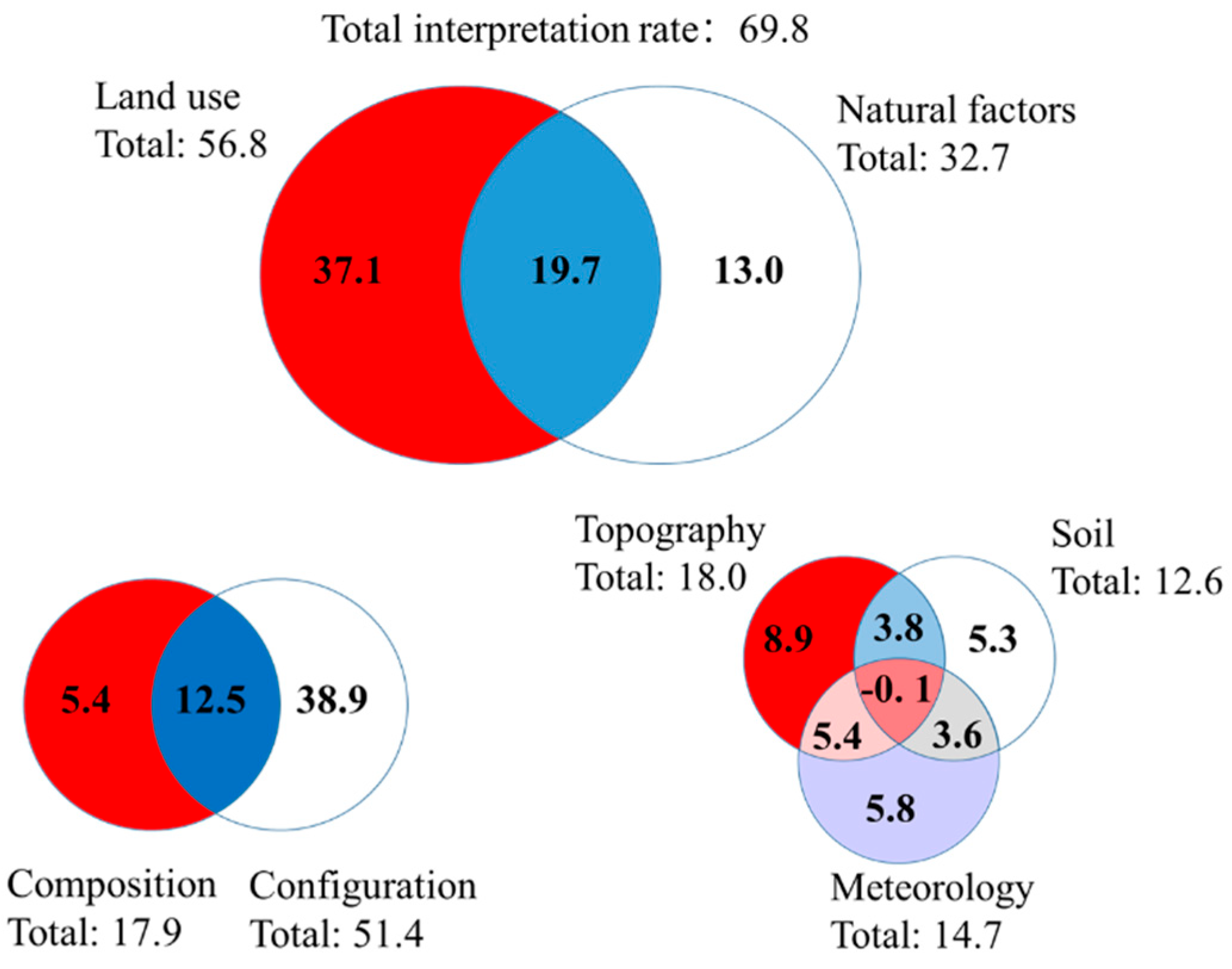
3.4. Mulivariate Drivers of Water Quality Variation from Land Use and Natural Factors
3.5. Variations in Water Quality Parameters in Response to Land Use and Natural Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Combined Effects of Land Use Composition, Land Use Configuration, and Natural Factors on Water Quality
4.2. Covariance Effect of Land Use and Natural Factors and Their Relative Impact on Water Quality
4.3. Variations in the Impact of Land Use and Natural Factors on Single Water Quality Parameters
4.4. Implications for Land Management in the Red River
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, A.; Wang, D.; Ning, Z.; Li, P.; Xu, T.; Zhu, B.; Peng, Q.; Jin, T.; Lin, J.; Zhang, D. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Water Quality in Xiangxi Bay under the Operation of the Three Gorges Reservoir. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2025, 270, 104518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A. Land Use and Water Quality. In Encyclopedia of Hydrological Sciences; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dalu, T.; Wasserman, R.J.; Tonkin, J.D.; Alexander, M.E.; Dalu, M.T.B.; Motitsoe, S.N.; Manungo, K.I.; Bepe, O.; Dube, T. Assessing Drivers of Benthic Macroinvertebrate Community Structure in African Highland Streams: An Exploration Using Multivariate Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Yang, X.; Cui, Z.; Ren, L.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, S. The Impact of Human Activities on Blue-Green Water Resources and Quantification of Water Resource Scarcity in the Yangtze River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Cai, H.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Y. Water Quality in Relation to Land Use in the Junshan Lake Watershed and Water Quality Predictions. Water Supply 2021, 21, 3602–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.K.; Oakes, R.M. Headwater Influences on Downstream Water Quality. Environ. Manag. 2008, 41, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunsaker, C.T.; Levine, D.A. Hierarchical Approaches to the Study of Water Quality in Rivers. BioScience 1995, 45, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Guo, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, R. Scale Effects on Spatially Varying Relationships between Urban Landscape Patterns and Water Quality. Environ. Manag. 2014, 54, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Ma, K.; Yang, L.; He, K. Testing a Dynamic Complex Hypothesis in the Analysis of Land Use Impact on Lake Water Quality. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 1313–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-W.; Hwang, S.-J.; Lee, S.-B.; Hwang, H.-S.; Sung, H.-C. Landscape Ecological Approach to the Relationships of Land Use Patterns in Watersheds to Water Quality Characteristics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Liu, K.; Li, L.; Xu, Z.X. Relationship of Land Use/Cover on Water Quality in the Liao River Basin, China. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 1484–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jin, Y.; Hao, Y.; Lu, J. Identification of the Control Factors Affecting Water Quality Variation at Multi-Spatial Scales in a Headwater Watershed. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 11129–11141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, H.Y.; Chuah, C.J.; Yong, E.L.; Snyder, S.A. Effects of Land Use Configuration, Seasonality and Point Source on Water Quality in a Tropical Watershed: A Case Study of the Johor River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Liu, W.; Liu, W.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Sun, M.; Yuan, Y. Regional Differences in the Impact of Land Use Pattern on Total Phosphorus Concentration in the Yangtze River Basin. Land 2025, 14, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.T.; Vo, L.D.; Nguyen, T.X.; Quang, N.X. The Interactive Effects of Natural Factor and Pollution Source on Surface Water Quality in the Lower Mekong River Basin, Southwestern Vietnam. Water Resour. 2020, 47, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, F.; Meng, W.; Wang, X.-Q. Water Quality Assessment and Source Identification of Daliao River Basin Using Multivariate Statistical Methods. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 152, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Westrich, B.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y. A Coupling Simulation Based on a Hydrodynamics and Water Quality Model of the Pearl River Delta, China. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VishnuRadhan, R.; David Thresyamma, D.; Sarma, K.; George, G.; Shirodkar, P.; Vethamony, P. Influence of Natural and Anthropogenic Factors on the Water Quality of the Coastal Waters around the South Andaman in the Bay of Bengal. Nat. Hazards 2015, 78, 309–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heathcote, A.J.; Filstrup, C.T.; Downing, J.A. Watershed Sediment Losses to Lakes Accelerating despite Agricultural Soil Conservation Efforts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Song, Z.; Lu, Y.; Weng, B.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gou, Y. Evaluation of Soil Erosion in the Changhua River Basin on Hainan Island Based on the Chinese Soil Loss Equation Model. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SCS. National Engineering Handbook, Section 4: Hydrology. In US Soil Conservation Service; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.L.; Juneng, L.; Kuswanto, H.; Do, H.X.; Zhang, F. Impacts of Solar Radiation Management on Hydro-Climatic Extremes in Southeast Asia. Water 2023, 15, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, A.; Bhat, S.U.; Jehangir, A. Local Determinants Influencing Stream Water Quality. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, D.A.; Tomasella, J. On the Ability of Large-Scale Hydrological Models to Simulate Land Use and Land Cover Change Impacts in Amazonian Basins. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 1831–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kang, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, F. Modelling Hydrological Response to Different Land-use and Climate Change Scenarios in the Zamu River Basin of Northwest China. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2008, 22, 2502–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, M. Quantifying Streamflow Change Caused by Forest Disturbance at a Large Spatial Scale: A Single Watershed Study. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W12525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Yin, L.; Shi, X.; Duan, X. Study on Characteristics of Landscape Pattern Evolution in Red River Basin. J. Yunnan Univ. 2017, 35, 780–788. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X. Ethnic Water Culture and Agricultural Civilization in the Reaches of Red River. Soc. Sci. Yunnan 2004, 6, 103–107+129. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; He, D.; Ye, C. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Runoff of Red River Basin in Yunnan. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.P.Q.; Garnier, J.; Gilles, B.; Sylvain, T.; Van Minh, C. The Changing Flow Regime and Sediment Load of the Red River, Viet Nam. J. Hydrol. 2007, 334, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Luo, X. Analysis of Variation in Runoff and Impacts Factors in the Yuanjiang-Red River Basin from 1956 to 2013. Resour. Sci. 2016, 38, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, R.B.; Gippel, C.J.; Finlayson, B.L.; Hart, B.T. Catchment-Wide Impacts on Water Quality: The Use of ‘Snapshot’ Sampling during Stable Flow. J. Hydrol. 1997, 199, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, L.; Liu, Q.; Peng, Q.; Kang, M. Impacts of Land Use on Surface Water Quality in a Subtropical River Basin: A Case Study of the Dongjiang River Basin, Southeastern China. Water 2015, 7, 4427–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A.; Ene, E. FRAGSTATS v4: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical and Continuous Maps. In Computer Software Program Produced by the Authors at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst; University of Massachusetts: Amherst, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 15. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Fang, H. Quantitative Analysis of Driving Factors in Soil Erosion Using Geographic Detectors in Qiantang River Catchment, Southeast China. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yisehak, K.; Belay, D.; Taye, T.; Janssens, G.P.J. Impact of Soil Erosion Associated Factors on Available Feed Resources for Free-Ranging Cattle at Three Altitude Regions: Measurements and Perceptions. J. Arid. Environ. 2013, 98, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Wang, Q.; Wu, J.; Huang, C.; Yu, D. Protective Function of Narrow Grass Hedges on Soil and Water Loss on Sloping Croplands in Northern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 139, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Cai, Q.; Liu, R.; Cao, M. The Influence of Topography and Land Use on Water Quality of Xiangxi River in Three Gorges Reservoir Region. Environ. Geol. 2009, 58, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRCS. Chapter 7–Hydrologic Soil Groups. In NRCS–National Engineering Handbook (NEH), Part 630–Hydrology; USDA NRCS: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S. 1-Km Monthly Precipitation Dataset for China (1901–2017); National Tibetan Plateau Data Center: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Molina, M.C.; Roa-Fuentes, C.A.; Zeni, J.O.; Casatti, L. The Effects of Land Use at Different Spatial Scales on Instream Features in Agricultural Streams. Limnologica 2017, 65, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cheng, F.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Q.; Cui, X. Urban Land-Use Type Influences Summertime Water Quality in Small- and Medium-Sized Urban Rivers: A Case Study in Shanghai, China. Land 2022, 11, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Jing, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cao, X.; Ma, L.; Zhuo, Y.; Wen, L.; Wang, L. How the Land Use/Cover Changes and Environmental Factors at Different Scales Affect Lake Water Quality in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1188927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, J. Effects of Land Use, Topography and Socio-Economic Factors on River Water Quality in a Mountainous Watershed with Intensive Agricultural Production in East China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuma, H.G.; Feyessa, F.F.; Demissie, T.A. Assessing the Impacts of Land Use/Land Cover Changes on Hydrological Processes in Southern Ethiopia: The SWAT Model Approach. Cogent Eng. 2023, 10, 2199508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hou, Z.; Liao, J.; Fu, L.; Peng, Q. Influences of the Land Use Pattern on Water Quality in Low-Order Streams of the Dongjiang River Basin, China: A Multi-Scale Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551–552, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L. Landscape Patterns and Topographic Features Affect Seasonal River Water Quality at Catchment and Buffer Scales. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, E.E.; Sheldon, F.; Darnell, R.; Bunn, S.E.; Harch, B.D. A Comparison of Spatially Explicit Landscape Representation Methods and Their Relationship to Stream Condition. Freshw. Biol. 2011, 56, 590–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Yue, C.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Z.; Lv, N.; Tang, Y. The Spatial Pattern of Land Use/Land Cover in the Water Supplying Area of the Middle- Route of the South-to-North Water Diversion (MR-SNWD) Project. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2006, 61, 633–644. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Yuan, B.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Guo, M.; Liu, Z. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Driving Factors of Surface Water Quality in the Jing River Basin of the Loess Plateau. Water 2024, 16, 3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Shao, Q.; Zuo, Q.; Cui, Y. Impact of Land Use and Urbanization on River Water Quality and Ecology in a Dam Dominated Basin. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, L.; Ma, F.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Liang, X. Localization Method for SWAT Model Soil Database Based on HWSD. China Water Wastewater 2014, 30, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, M.S.; Biju, A.; Benchamin, D. Assessment of Spatial and Temporal Variations in Water Quality Using Multivariate Statistical Analysis in the Munroe Island, Kerala, India. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Cui, Z. Effects of Land Use and Slope on Water Quality at Multi-Spatial Scales: A Case Study of the Weihe River Basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 57599–57616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelic, M.; Dolinaj, D.; Stankov, U.; Lescesen, I. Correlation Analysis of Impact of Natural Parameters on Water Quality of the River Danube near Novi Sad for the Period 2004–2011. Geogr. Pannonica 2013, 17, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson Mwaijengo, G.; Msigwa, A.; Njau, K.N.; Brendonck, L.; Vanschoenwinkel, B. Where Does Land Use Matter Most? Contrasting Land Use Effects on River Quality at Different Spatial Scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 134825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; He, J.; Li, X. Hydrological and Meteorological Droughts in the Red River Basin of Yunnan Province Based on SPEI and SDI Indices. Prog. Geogr. 2016, 35, 758–767. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, H.; Zhou, J. Study on the Geographic Distribution and Influencing Factors of Dai Settlements in Yunnan Based on Geodetector. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; He-Yang, Y.; Tang, H.; Chen, C.; He, K. Terrain Gradient Effect and Functional Zoning of Land Use Change in the Red River Basin of Yunnan Province. J. Yunnan Univ. Nat. Sci. 2024, 46, 276–287. [Google Scholar]
- Trinh, D.A.; Do, N.T.; Panizzo, V.N.; McGowan, S.; Salgado, J.; Large, A.R.G.; Henderson, A.C.G.; Vu, T.T. Anthropogenic Impacts on the Water Chemistry of a Transboundary River System in Southeast Asia. J. Asian Earth Sci. X 2024, 12, 100183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C. Evaluating Coupled Influences of Slope Class and Land Use Change on Water Quality Using Single and Composite Indices in an Agricultural Basin. CATENA 2025, 248, 108584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hou, L.; Qian, Y.; Wan, X. Effect of Zero Growth of Fertilizer Action on Ecological Efficiency of Grain Production in China under the Background of Carbon Emission Reduction. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Hydrologic Soil Group | Soil Types | Minimum Infiltration Rate (mm/h) | Permeability |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Yellow-brown earth, dark-brown earth, meadow soil, dark felty soil | >7.62 | Rapid |
| B | Humid-thermo ferralitic | 3.81–7.62 | Quick |
| C | Paddy soil | 1.27–3.81 | Moderate |
| D | Brown earth, torrid red soil, limestone soil, purplish soil, lateritic red earth, red earth, yellow earth | 0.00–1.27 | Slow |
| Parameters | Adjusted R2 | p | The Best Stepwise Multiple Regression (MLR) Model | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEM | 0.425 | <0.001 | TEM = 25.132 + 1.229 × 7FLOW − 0.953 × 1LPI | 1.109 |
| EC | 0.610 | <0.001 | EC = 348.131 + 78.351 × 3PLAND − 92.491 × 1AI + 68.779 × 7AI | 1.218 |
| DO | 0.357 | <0.001 | DO = 7.330 − 0.768 × TA + 0.533 × 4FLOW + 0.133 × 7PD | 9.877 |
| NH3-N | 0.340 | <0.001 | NH3-N = 0.434 + 0.158 × 3LPI + 0.136 × 1AI + 0.116 × 3PD | 1.024 |
| NO3-N | 0.593 | <0.001 | NO3-N = 1.113 + 0.647 × 7PLAND + 0.247 × 1PD − 0.272 × 7LPI | 1.904 |
| TP | 0.261 | 0.001 | TP = 0.499 + 0.339 × 7PD − 0.284 × 1LPI | 1.053 |
| TN | 0.090 | 0.025 | TN = 1.748 + 0.336 × 3LPI | 1.000 |
| CODMn | 0.224 | 0.002 | CODMn = 4.893 + 5.767 × 7LSI | 3.436 |
| SS | 0.212 | 0.003 | SS = 0.884 − 0.017 × 1PLAND + 0.104 × 2PD | 1.163 |
| Water Quality Parameter (Unit) | Minimum | Mean | Median | Max | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEM (°C) | 19.40 | 25.13 | 24.80 | 32.00 | 2.61 | 10.40 |
| EC (μs·cm−1) | 124 | 348 | 322 | 945 | 162.16 | 46.58 |
| DO (mg·L−1) | 5.930 | 7.330 | 7.350 | 8.180 | 0.51 | 6.96 |
| NH3-N (mg·L−1) | 0.092 | 0.435 | 0.367 | 1.801 | 0.30 | 69.69 |
| NO3-N (mg·L−1) | 0.121 | 1.113 | 0.923 | 3.500 | 0.75 | 67.67 |
| TP (mg·L−1) | 0.018 | 0.499 | 0.160 | 3.156 | 0.71 | 142.44 |
| TN (mg·L−1) | 0.093 | 1.750 | 1.754 | 3.616 | 1.00 | 57.10 |
| Chl-a (μg·L−1) | 1.704 | 14.259 | 9.521 | 83.158 | 14.35 | 100.66 |
| CODMn (mg·L−1) | 0.656 | 4.060 | 3.030 | 10.361 | 2.47 | 60.75 |
| SS (g·L−1) | 0.003 | 0.553 | 0.324 | 1.972 | 0.59 | 106.47 |
| Indicator (Unit) | Minimum | Mean | Median | Max | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (%) |
| 1PLAND (%) | 8.710 | 29.086 | 30.759 | 47.992 | 10.15 | 34.91 |
| 3PLAND (%) | 0.090 | 8.430 | 8.085 | 27.873 | 5.95 | 70.30 |
| 7PLAND (%) | 0.0002 | 0.830 | 0.609 | 3.110 | 0.71 | 85.59 |
| 1PD (n/km2) | 0.098 | 0.376 | 0.371 | 0.772 | 0.14 | 36.57 |
| 2PD (n/km2) | 0.304 | 2.945 | 2.951 | 6.982 | 1.65 | 56.13 |
| 3PD (n/km2) | 0.427 | 5.669 | 6.097 | 10.036 | 1.99 | 35.02 |
| 7PD (n/km2) | 0.000 | 0.054 | 0.046 | 0.197 | 0.04 | 79.73 |
| 1LPI (%) | 0.557 | 10.301 | 6.961 | 44.148 | 10.86 | 105.44 |
| 3LPI (%) | 0.007 | 0.670 | 0.273 | 6.472 | 1.15 | 170.95 |
| 7LPI (%) | 0.0002 | 0.174 | 0.112 | 0.884 | 0.19 | 109.50 |
| 7LSI | 1.000 | 15.169 | 9.456 | 61.019 | 13.60 | 89.68 |
| 1AI (%) | 88.520 | 92.248 | 92.169 | 96.271 | 1.74 | 1.89 |
| 7AI (%) | 81.290 | 88.844 | 89.362 | 94.449 | 3.26 | 3.67 |
| 4FLOW (m) | 6794 | 70,539 | 49,312 | 412,226 | 70,401.22 | 99.81 |
| 7FLOW (m) | 5978 | 77,055 | 54,129 | 390,403 | 77,545.25 | 100.64 |
| TA (ha) | 6461 | 329,285 | 144,158 | 3,220,281 | 576,299.70 | 175.02 |
| ELEVA (m) | 1205.140 | 1739.900 | 1762.659 | 2149.317 | 222.16 | 12.77 |
| SLOPE (°) | 14.380 | 22.446 | 22.835 | 28.145 | 2.73 | 12.15 |
| HSGA (%) | 0.000 | 6.972 | 4.044 | 28.869 | 7.28 | 104.45 |
| HSGB (%) | 0.000 | 0.578 | 0.000 | 9.980 | 1.88 | 325.83 |
| HSGC (%) | 0.000 | 4.105 | 3.831 | 17.811 | 3.00 | 73.17 |
| HSGD (%) | 69.891 | 88.345 | 90.595 | 99.245 | 7.19 | 8.14 |
| SOLAR (WH/m2) | 523,705 | 565,054 | 566,955 | 593,707 | 16,589.79 | 2.94 |
| PRCP (mm) | 202.533 | 350.580 | 323.436 | 547.412 | 84.86 | 24.20 |
| Explanatory Variable | Variance Explained Rate (%) | RDA Statistic | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-F | p-Value | |||
| All the indicators | Axis1 | 20.9 | 0.2 | 0.020 * |
| Axis2 | 18.5 | 0.3 | 0.002 ** | |
| All sorting axes | 69.8 | 2.1 | 0.002 ** | |
| Indicator group | Land use indicator | 56.8 | 2.3 | 0.002 ** |
| Natural factor | 32.7 | 2.6 | 0.002 ** | |
| Indicator category | Composition | 17.9 | 3.0 | 0.002 ** |
| Configuration | 51.4 | 2.5 | 0.002 ** | |
| Topography | 18.0 | 4.6 | 0.002 ** | |
| Soil | 12.6 | 2.0 | 0.006 ** | |
| Meteorology | 14.7 | 3.6 | 0.002 ** | |
| Response | Adjusted R2 | p | The Best Stepwise Multiple Regression (MLR) Model | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEM | 0.651 | <0.001 | TEM = 3.258 + 0.015 × 7FLOW − 0.072 × SOLAR − 0.066 × PRCP − 0.066 × 4FLOW − 0.03 × 1PD | 8.483 |
| EC | 0.651 | <0.001 | EC = 5.755 − 0.173 × PRCP + 0.132 × 7PLAND + 0.127 × 1PD − 0.113 × HSGA | 1.496 |
| DO | 0.395 | <0.001 | DO = 4.668 − 0.15 × TA + 0.10 × 4FLOW + 0.024 × 7PD | 9.877 |
| NH3-N | 0.181 | 0.002 | NH3-N = 0.343 + 0.082 × 3LPI | 1.000 |
| NO3-N | 0.536 | <0.001 | NO3-N = 0.688 + 0.193 × 7PLAND + 0.155 × 1PD | 1.009 |
| TP | 0.386 | <0.001 | TP = 0.327 + 0.204 × ELEVA − 0.117 × 1LPI | 1.000 |
| TN | 0.087 | 0.027 | TN = 0.936 + 0.134 × 1PD | 1.000 |
| Chl-a | 0.143 | 0.015 | Chl-a = 2.561 + 0.334 × SLOPE + 0.265 × ELEVA | 1.026 |
| CODMn | 0.137 | 0.007 | CODMn = 1.561 + 0.227 × ELEVA | 1.000 |
| SS | 0.301 | <0.001 | SS = 0.379 + 0.139 × ELEVA − 0.132 × 1PLAND | 1.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Tang, H.; Feng, X.; Han, Y.; He, Y.; Yan, L.; He, Y.; Yang, L.; He, K. A Quantitative Assessment of the Impacts of Land Use and Natural Factors on Water Quality in the Red River Basin, China. Water 2025, 17, 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131968
Chen C, Chen X, Tang H, Feng X, Han Y, He Y, Yan L, He Y, Yang L, He K. A Quantitative Assessment of the Impacts of Land Use and Natural Factors on Water Quality in the Red River Basin, China. Water. 2025; 17(13):1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131968
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Changming, Xingcan Chen, Hong Tang, Xuekai Feng, Yu Han, Yuan He, Liqin Yan, Yangyidan He, Liling Yang, and Kejian He. 2025. "A Quantitative Assessment of the Impacts of Land Use and Natural Factors on Water Quality in the Red River Basin, China" Water 17, no. 13: 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131968
APA StyleChen, C., Chen, X., Tang, H., Feng, X., Han, Y., He, Y., Yan, L., He, Y., Yang, L., & He, K. (2025). A Quantitative Assessment of the Impacts of Land Use and Natural Factors on Water Quality in the Red River Basin, China. Water, 17(13), 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131968






