Modeling the Effects of Underground Brine Extraction on Shallow Groundwater Flow and Oilfield Fluid Leakage Pathways in the Yellow River Delta
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Regional Geology and Hydrogeology
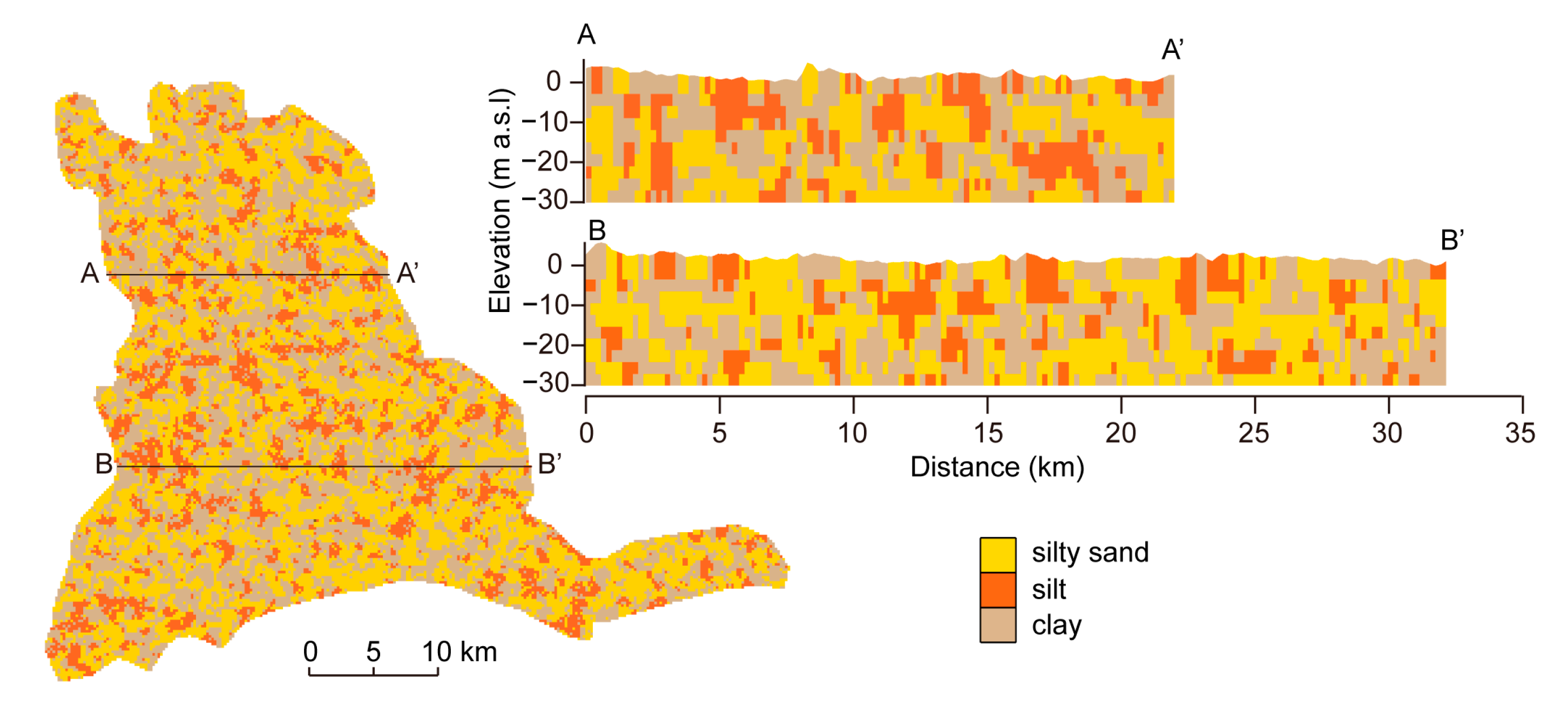
2.2. Stratigraphy Simulation Based on Transition Probability
2.3. Variable-Density Groundwater Flow Model
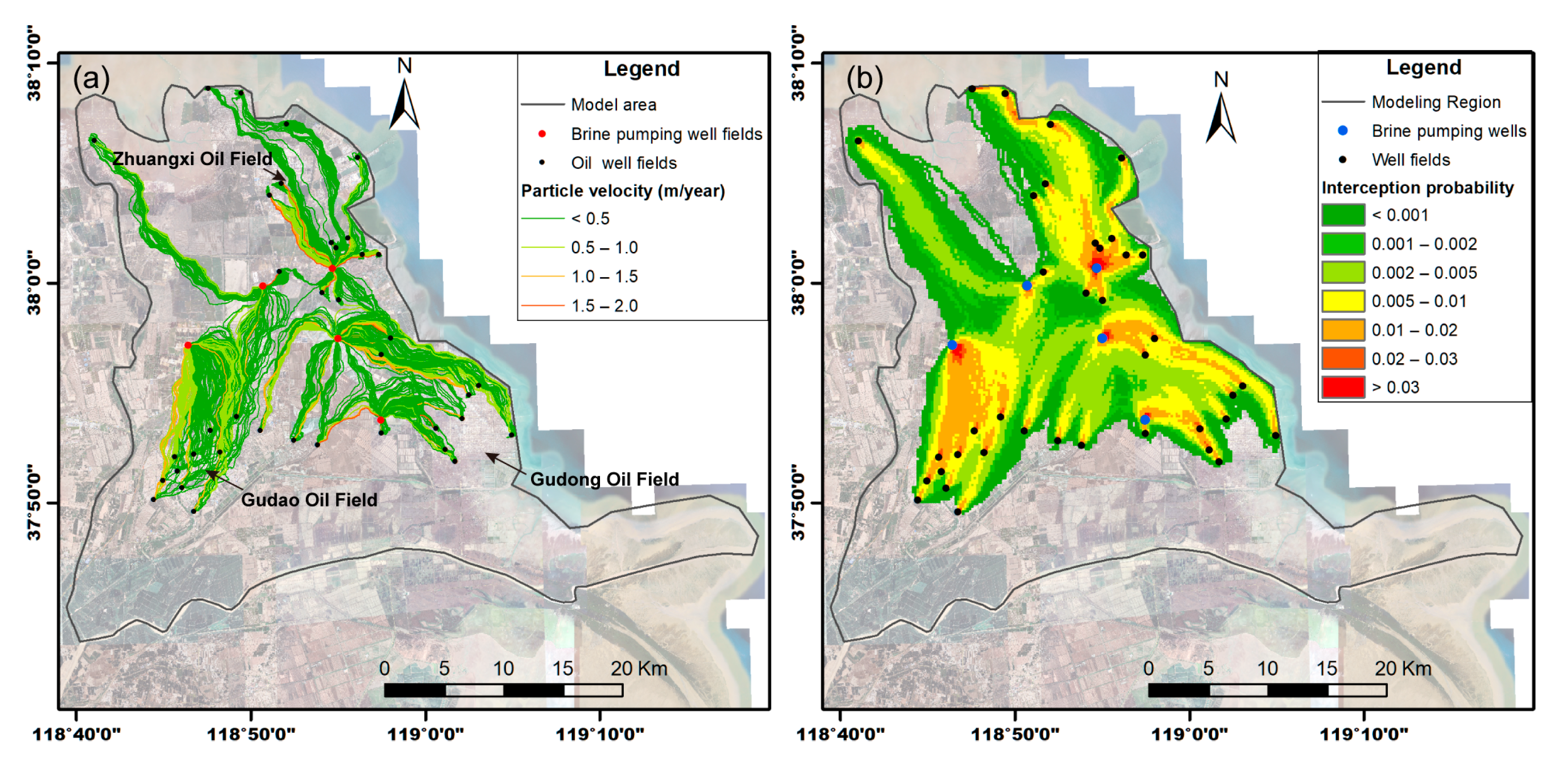
2.4. Delineating Flowpaths Through Particle Tracking
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sediment Stratigraphy
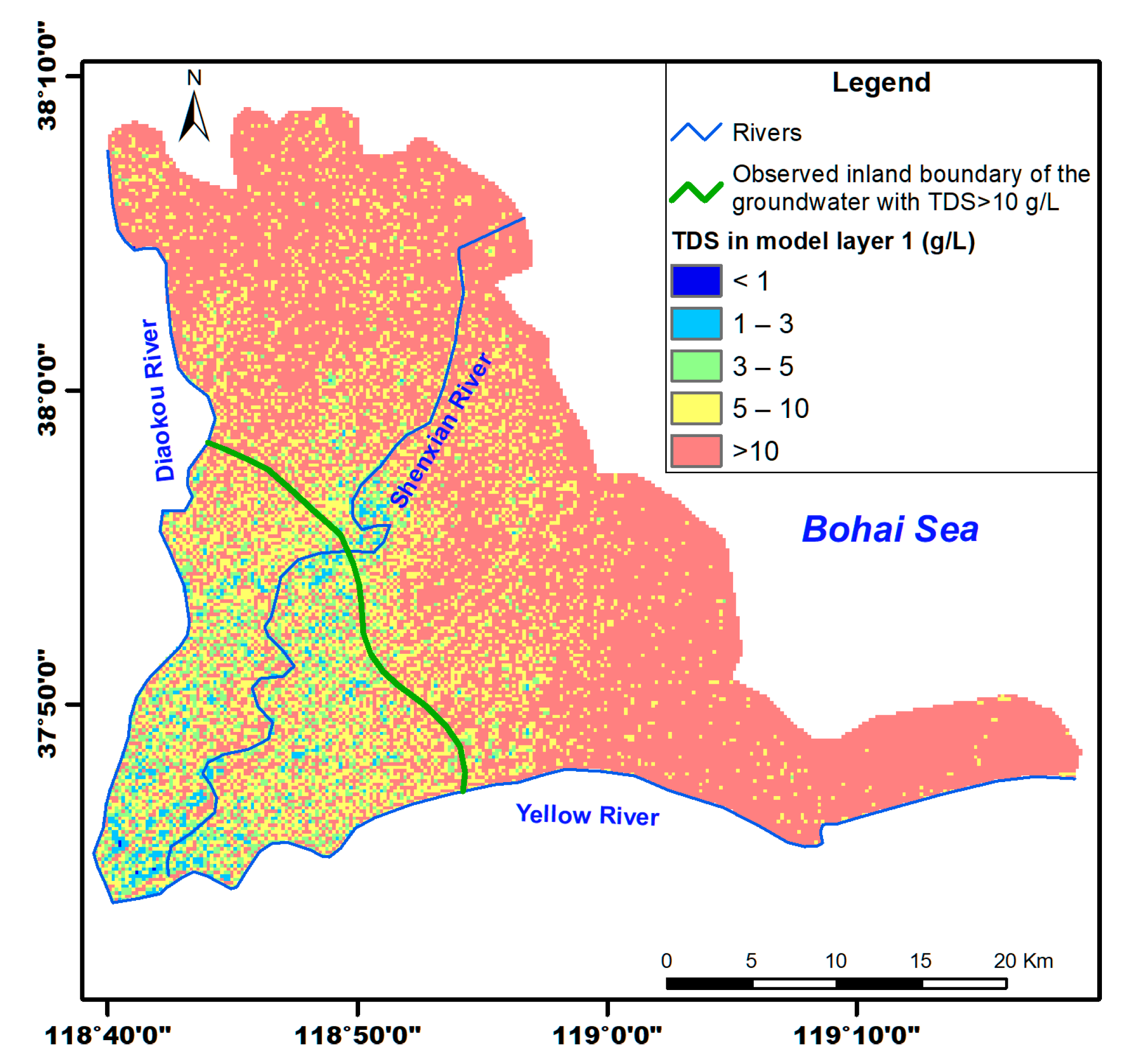
3.2. Groundwater Salinity in Predevelopment Conditions
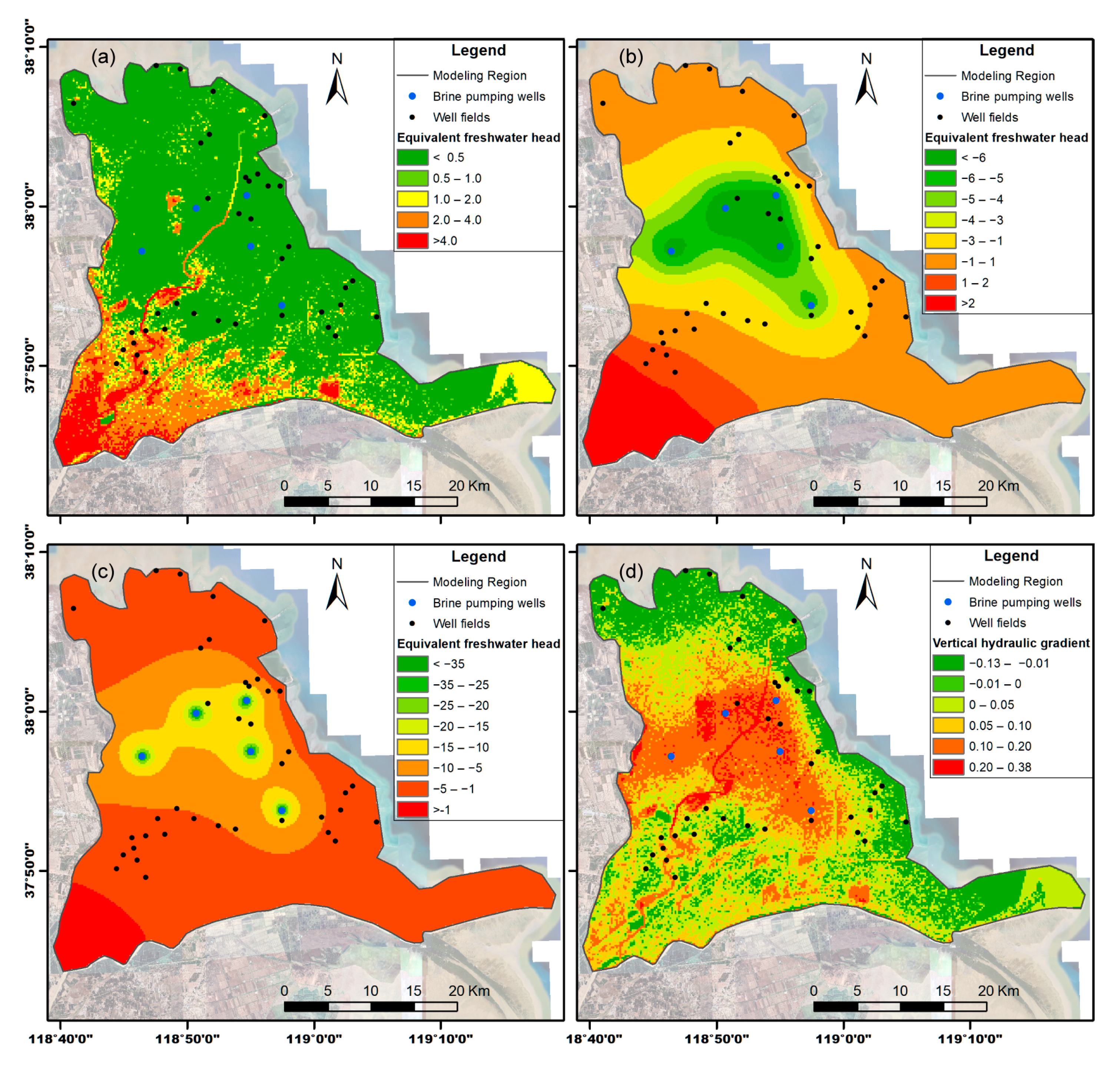
3.3. Groundwater Flow and Salinity Affected by Brine Extraction
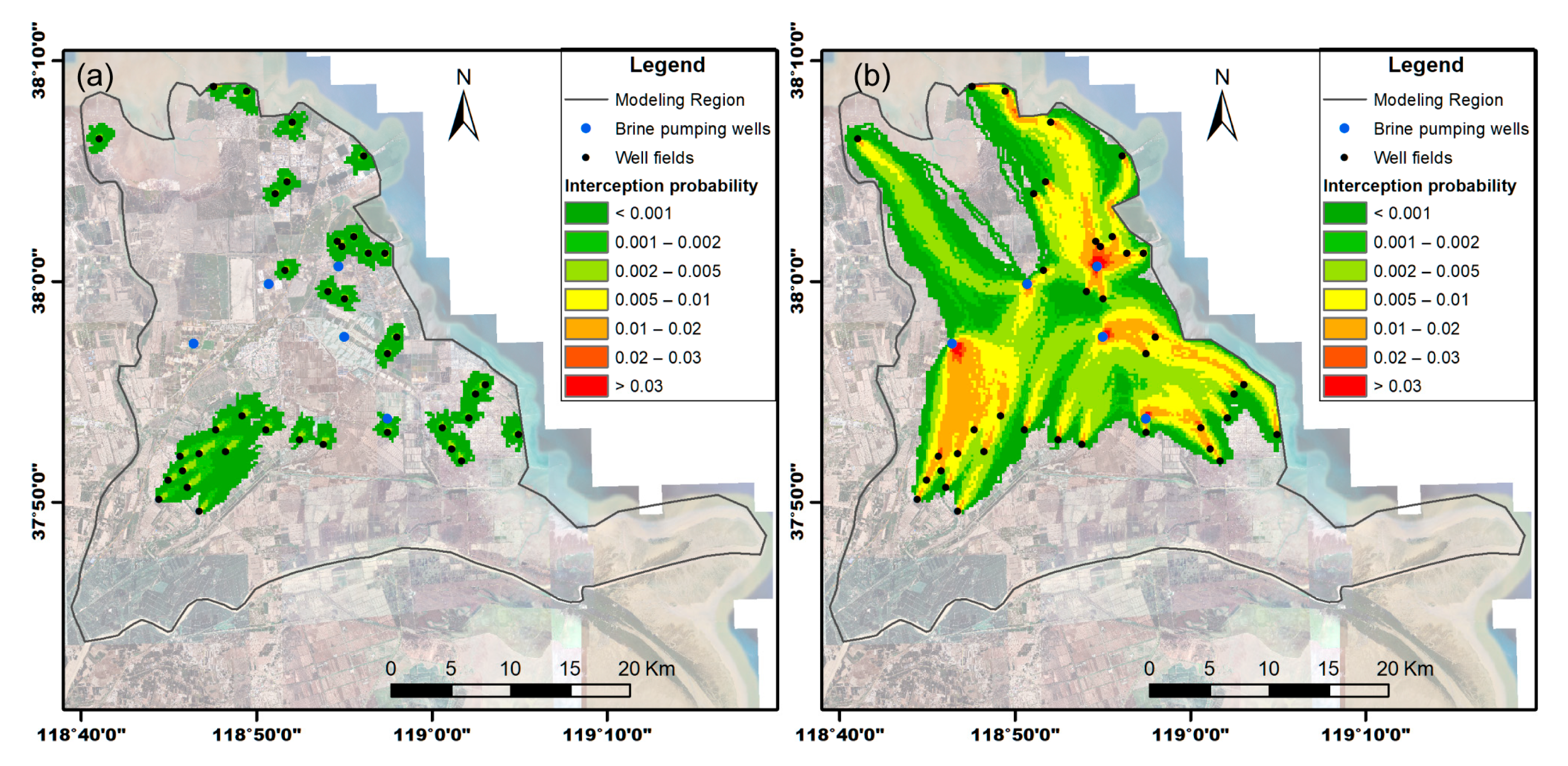
3.4. Potential Impacts on Brine Disposal Water Transport
3.5. Implication for Groundwater Monitoring
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhan, L.; Xin, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Li, L. Sustained upward groundwater discharge through salt marsh tidal creeks. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2024, 9, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Bi, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, K.; Bai, Z.; Zhou, X. Correlating severe land subsidence and confined brine aquifer compaction in the Yellow River Delta, China, with Sentinel-1A/1B satellite images. Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol. 2023, 41, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Fan, X.; Wang, L.; Tang, Y.; Huang, L. Detection of soil salinity distribution and its change in the Yellow River Delta comparing 2006 and 2022. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 4288–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Liu, Y.; Fan, J.; Lu, M.; Zang, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, B.; Huang, X.; Lai, J.; Wu, H. The salinization process and its response to the combined processes of climate change-human activity in the Yellow River Delta between 1984 and 2022. Catena 2023, 231, 107301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Min, T.; Dai, X. The Spatio-Temporal Dynamic Patterns of Shallow Groundwater Level and Salinity: The Yellow River Delta, China. Water 2023, 15, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Liu, H. Natural and anthropogenic hazards in the Yellow River Delta, China. Nat. Hazards 2017, 85, 1907–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Makoto, T.; Liu, G.; Kunihide, M.; Shin-ichi, O.; Tomochika, T.; Yoshihirom, F. Nitrate pollution of groundwater in the Yellow River Delta, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 15, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, Y.; Li, J.; Hou, Y.; Hao, H.; Xiao, N.; Zhi, Q. Characteristics, Source and Risk Assessment of Soil Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons around Oil Wells in the Yellow River Delta, China. Water 2023, 15, 3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zou, S.; Ye, S.; Xie, Z. Spatial distribution of heavy metals and their potential sources in the soil of Yellow River Delta: A traditional oil field in China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianrong, C.; Yanjun, L.; Sujie, Y. The concentrations and sources of PAHs and PCBs in soil from an oil field and estuary in the Yellow River Delta, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1028299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzer, C.; Ottinger, M.; Liu, G.; Sun, B.; Baumhauer, R.; Dech, S. Earth observation-based coastal zone monitoring of the Yellow River Delta: Dynamics in China’s second largest oil producing region over four decades. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 55, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Fu, J.; Zhang, J. Borehole casing failure analysis in unconsolidated formations: A case study. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2007, 59, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, P.B.; Landon, M.K.; Stephens, M.J.; Taylor, K.A.; Gillespie, J.M.; Davis, T.A.; Shimabukuro, D.H. Fluid migration pathways to groundwater in mature oil fields: Exploring the roles of water injection/production and oil-well integrity in California, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 166400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Liu, B.; Peng, X.; Shu, L.; Li, S.; Shen, Y. Groundwater response to water diversion and surface-water management scenarios in the Yellow River Delta wetland reserve, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2023, 31, 1829–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.; Overeem, I.; Tanaka, A.; Syvitski, J.P.M. Land subsidence at aquaculture facilities in the Yellow River delta, China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 3898–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Xia, X.; Bi, H.; Huang, H.; Ding, R.; Zhao, L. Land subsidence of the Yellow River Delta in China driven by river sediment compaction. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 142165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Hoey, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C. Land Subsidence over Oilfields in the Yellow River Delta. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1540–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, H. Characterization and mechanism of regional land subsidence in the Yellow River Delta, China. Nat. Hazards 2013, 68, 687–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Wang, K.; Liang, B.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Shi, B. Modeling the Morphological Responses of the Yellow River Delta to the Water-Sediment Regulation Scheme: The Role of Impulsive River Floods and Density-Driven Flows. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2022WR033003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, F.; Li, J.; Luo, B.; Huang, C. Geochemical and isotopic evidence of shallow groundwater salinization in a reclaimed coastal zone: The Yellow River Delta, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, F.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, C.; Ouyang, Z. Impact of water diversion on the hydrogeochemical characterization of surface water and groundwater in the Yellow River Delta. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 48, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Xue, C. Sedimentary Geology of the Yellow River Delta; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1997. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hou, G.; Gao, M.; Ye, S.; Zhao, G. Source of salt and the salinization process of shallow groundwater in the Yellow River Delta. Earth Sci. Front. 2022, 29, 145–154, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Gao, X.; Tian, Z.; Liu, C.; Wu, Z.; Li, C.; Kong, S. The genesis of groundwater chemistry in Yellow River Delta—A cases study of Gudao Town, Dongying City, Shandong Province. Earth Sci. Front. 2025, 32, 469–483, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Siena, M.; Riva, M. Impact of geostatistical reconstruction approaches on model calibration for flow in highly heterogeneous aquifers. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2020, 34, 1591–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, M. The role of different sources of uncertainty on the stochastic quantification of subsurface discharges in heterogeneous aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carle, S.F. T-PROGS: Transition Probability Geostatistical Software; University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- McKnight, S.V.; Boutt, D.F.; Munk, L.A. Impact of hydrostratigraphic continuity on brine-to-freshwater interface dynamics; implications from a two-dimensional parametric study in an arid and endorheic basin. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.; Zheng, C. A lithofacies approach for modeling non-Fickian solute transport in a heterogeneous alluvial aquifer. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Koch, J.; Sonnenborg, T.O.; Jørgensen, F.; Schamper, C.; Christian Refsgaard, J. Transition probability-based stochastic geological modeling using airborne geophysical data and borehole data. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 3147–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Wang, D.; Tian, X.; Bi, X.; Zheng, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, Z. Estuarine groundwater level response to and recovery from extreme precipitation events: Typhoon Lekima in the Yellow River Delta. J. Hydrol. 2024, 632, 130918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissmann, G.S.; Zhang, Y.; LaBolle, E.M.; Fogg, G.E. Dispersion of groundwater age in an alluvial aquifer system. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1198–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissmann, G.S.; Fogg, G.E. Multi-scale alluvial fan heterogeneity modeled with transition probability geostatistics in a sequence stratigraphic framework. J. Hydrol. 1999, 226, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Dai, Z.; Gong, H.; Gable, C.; Teatini, P. Statistic inversion of multi-zone transition probability models for aquifer characterization in alluvial fans. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016, 30, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, C.D., Jr.; Thorne, D.T.; Dausman, A.M.; Sukop, M.C.; Guo, W. SEAWAT, version 4; A Computer Program for Simulation of Multi-Species Solute and Heat Transport; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2007.
- Yuan, R.; Song, X.; Liu, G. Study on recharge of precipitation infiltration in the upper alluvial plain of the modern Yellow River Delta. J. Nat. Resour. 2010, 25, 1777–1785, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Sumner, D.M.; Jacobs, J.M. Utility of Penman-Monteith, Priestley-Taylor, reference evapotranspiration, and pan evaporation methods to estimate pasture evapotranspiration. J. Hydrol. 2005, 308, 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaap, M.G.; Leij, F.J.; van Genuchten, M.T. ROSETTA: A computer program for estimating soil hydraulic parameters with hierarchical pedotransfer functions. J. Hydrol. 2001, 251, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Geological Survey. Investigation and Assessment of Sustainable Utilization of Groundwater Resources in the North China Plain; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Liu, G.; Shu, L.; Liu, Q. Field measuring the hydraulic conductivity of different sediments in Yellow River Delta. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2008, 19, 6–10, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Doherty, J. PEST: Model Independent Parameter Estimation, Fifth Edition of User Manual; Watermark Numerical Computing: Brisbane, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pollock, D.W. User Guide for MODPATH Version 6—A Particle-Tracking Model for MODFLOW, Techniques and Methods; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, D.; Janardhanan, S.; Pagendam, D.E.; Gladish, D.W. Probabilistic Groundwater Flow, Particle Tracking and Uncertainty Analysis for Environmental Receptor Vulnerability Assessment of a Coal Seam Gas Project. Water 2020, 12, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassam, D.; Sreekanth, J.; Mallants, D.; Gonzalez, D.; Doble, R.; Pickett, T. Stochastic Assessment of Groundwater Contamination Risks From Onshore Gas Development Using Computationally Efficient Analytical and Numerical Transport Models. Front. Water 2022, 3, 799738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y. Particle Tracking Using Dynamic Water-Level Data. Water 2020, 12, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, L.; Colombo, L.; Formentin, G. Null-space Monte Carlo particle tracking to assess groundwater PCE (Tetrachloroethene) diffuse pollution in north-eastern Milan functional urban area. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, L.; Alberti, L.; Mazzon, P.; Antelmi, M. Null-Space Monte Carlo Particle Backtracking to Identify Groundwater Tetrachloroethylene Sources. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hong, T.; Meng, L.; Xiao, L.; Li, Y.; Bi, X. Identification of wetland conservation and restoration priorities in regions of oil extraction in the Yellow River Delta using circuit theory modelling. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

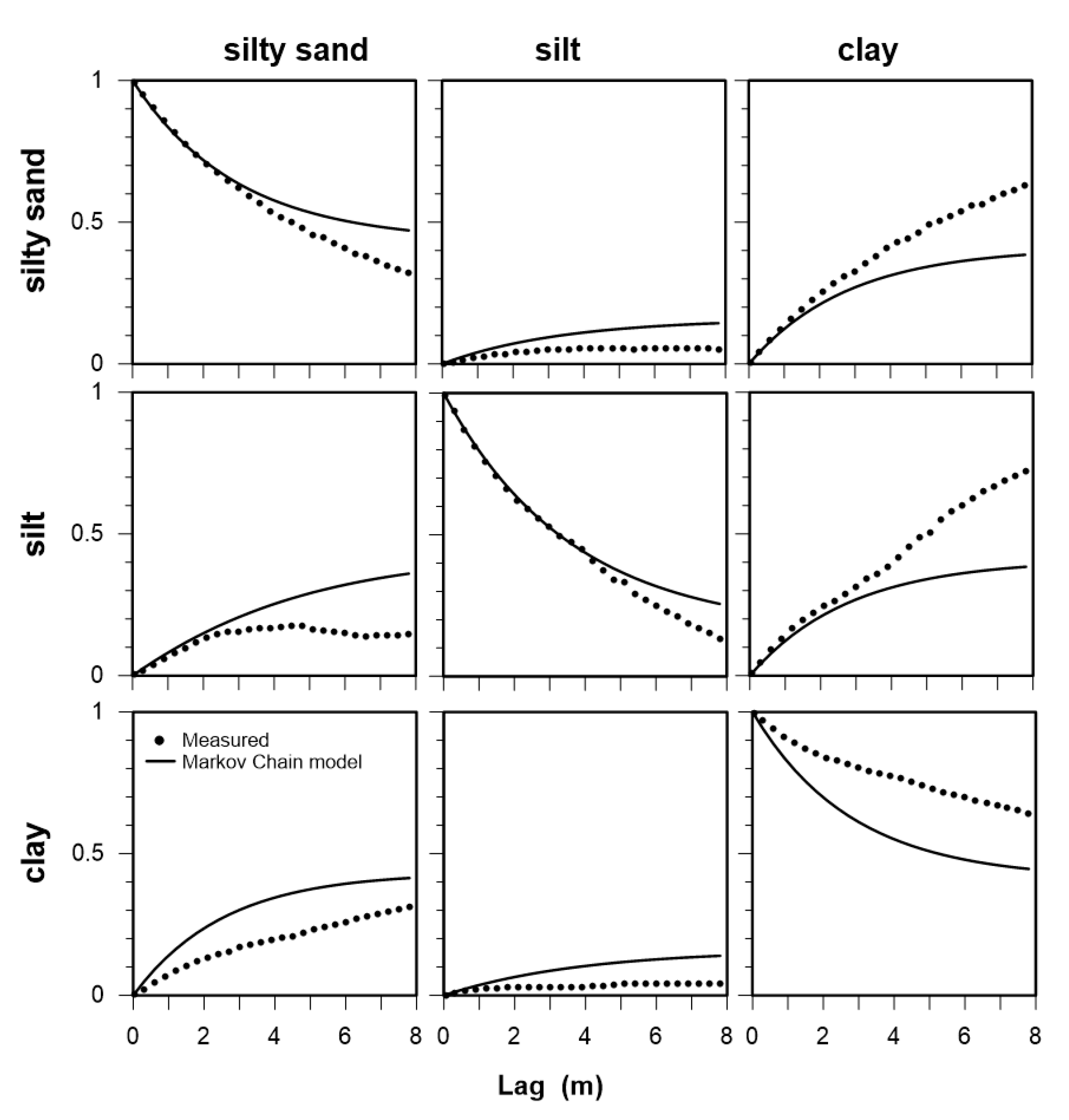

| Sediment Type | Vertical Direction | Horizontal Direction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silty Sand | Silt | Clay | Silty Sand | Silt | Clay | |
| Silty sand | 5.137 m | 0.244 | 0.756 | 500.0 m | 0.244 | 0.756 |
| Silt | 0.375 | 4.290 m | 0.625 | 0.375 | 400.0 m | 0.625 |
| Clay | 0.804 | 0.195 | 4.734 m | 0.789 | 0.211 | 455.4 m |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Yuan, X.; He, H.; Li, G.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Gu, Z.; Guan, C.; Cao, G. Modeling the Effects of Underground Brine Extraction on Shallow Groundwater Flow and Oilfield Fluid Leakage Pathways in the Yellow River Delta. Water 2025, 17, 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131943
Zhao J, Yuan X, He H, Li G, Zhang Q, Wang Q, Gu Z, Guan C, Cao G. Modeling the Effects of Underground Brine Extraction on Shallow Groundwater Flow and Oilfield Fluid Leakage Pathways in the Yellow River Delta. Water. 2025; 17(13):1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131943
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jingang, Xin Yuan, Hu He, Gangzhu Li, Qiong Zhang, Qiyun Wang, Zhenqi Gu, Chenxu Guan, and Guoliang Cao. 2025. "Modeling the Effects of Underground Brine Extraction on Shallow Groundwater Flow and Oilfield Fluid Leakage Pathways in the Yellow River Delta" Water 17, no. 13: 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131943
APA StyleZhao, J., Yuan, X., He, H., Li, G., Zhang, Q., Wang, Q., Gu, Z., Guan, C., & Cao, G. (2025). Modeling the Effects of Underground Brine Extraction on Shallow Groundwater Flow and Oilfield Fluid Leakage Pathways in the Yellow River Delta. Water, 17(13), 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131943





