Groundwater Potential Mapping in Semi-Arid Areas Using Integrated Remote Sensing, GIS, and Geostatistics Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
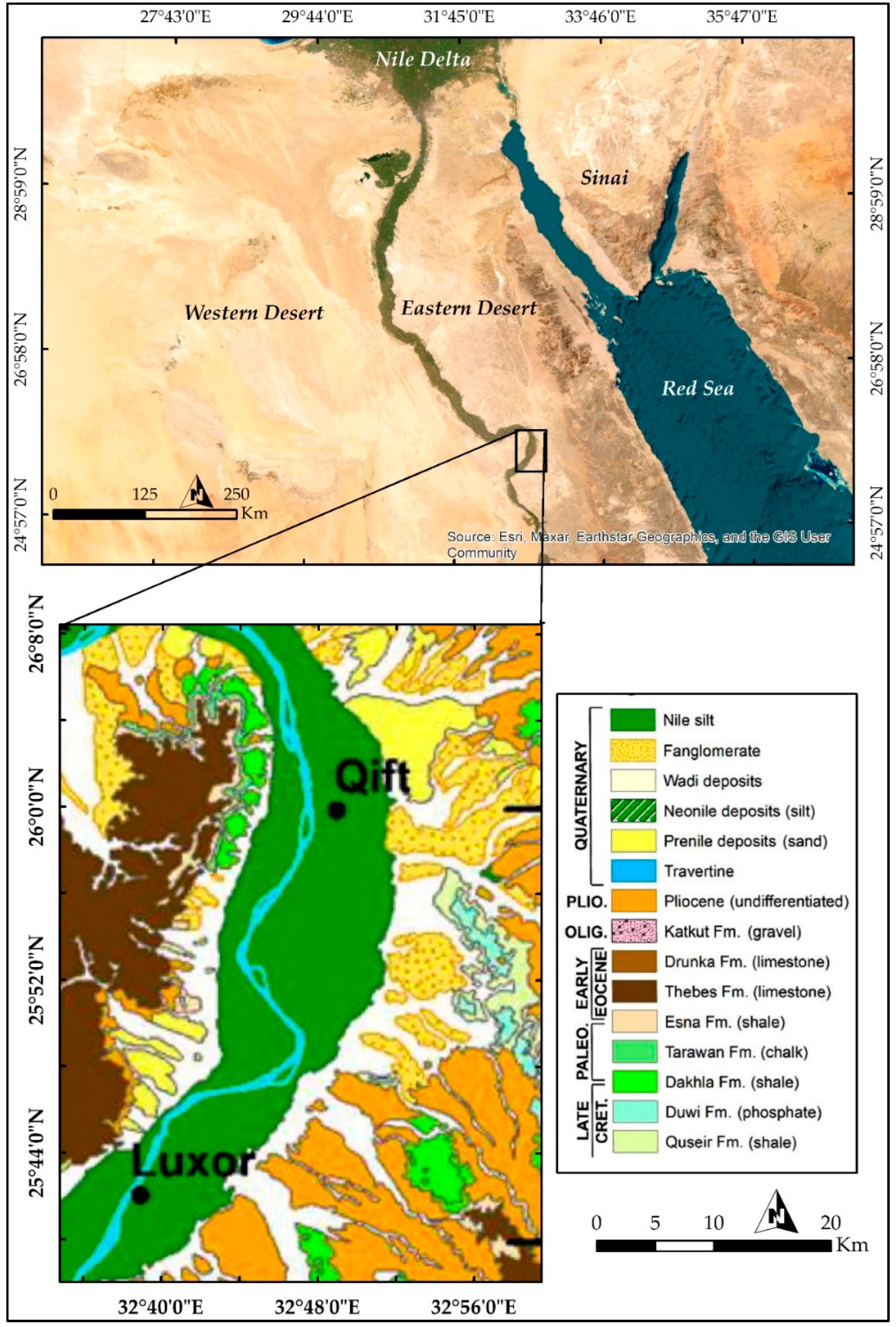
2.1. Study Area and Geological Setting
2.2. Data Collection and Preparation
2.3. Thematic Layer Generation
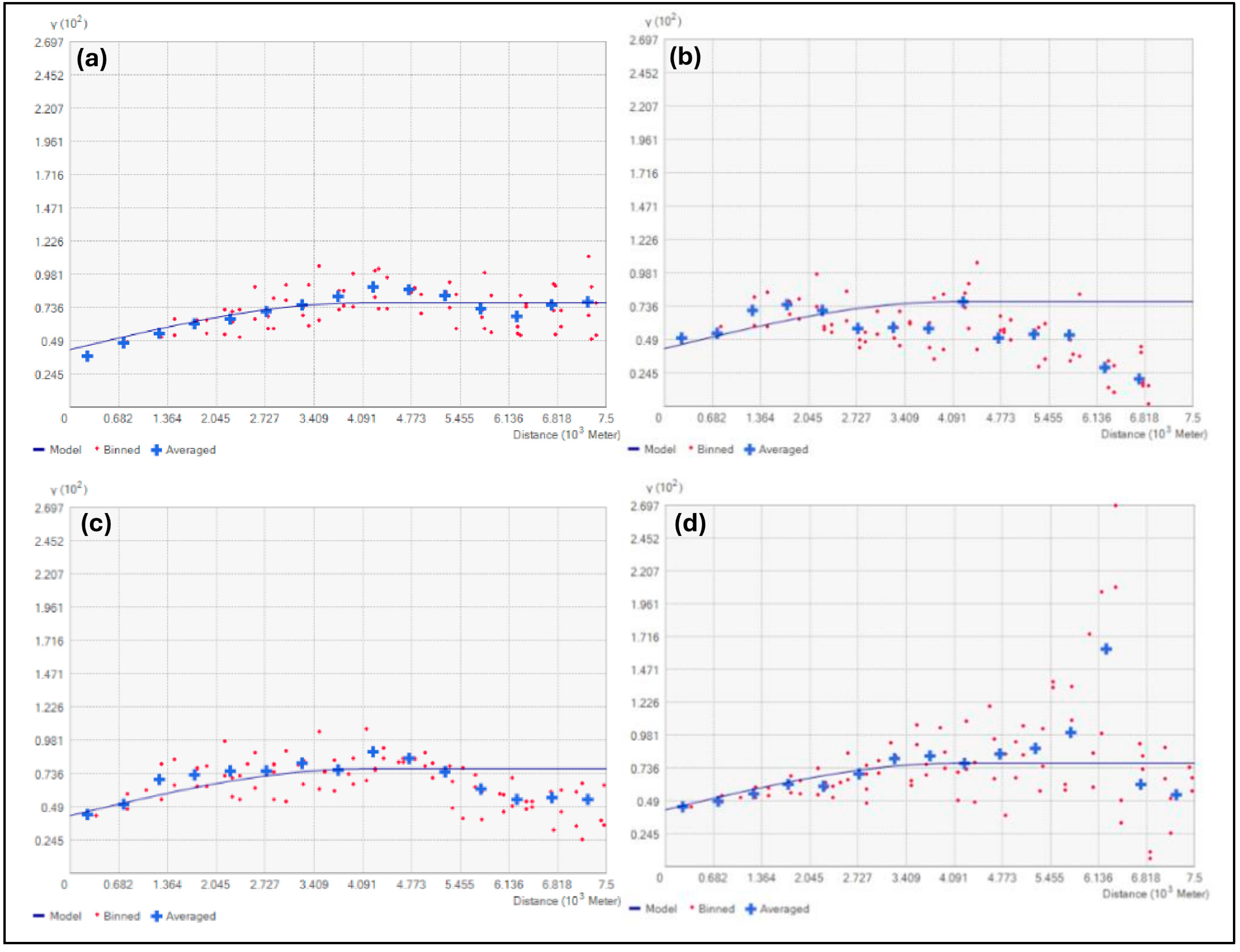
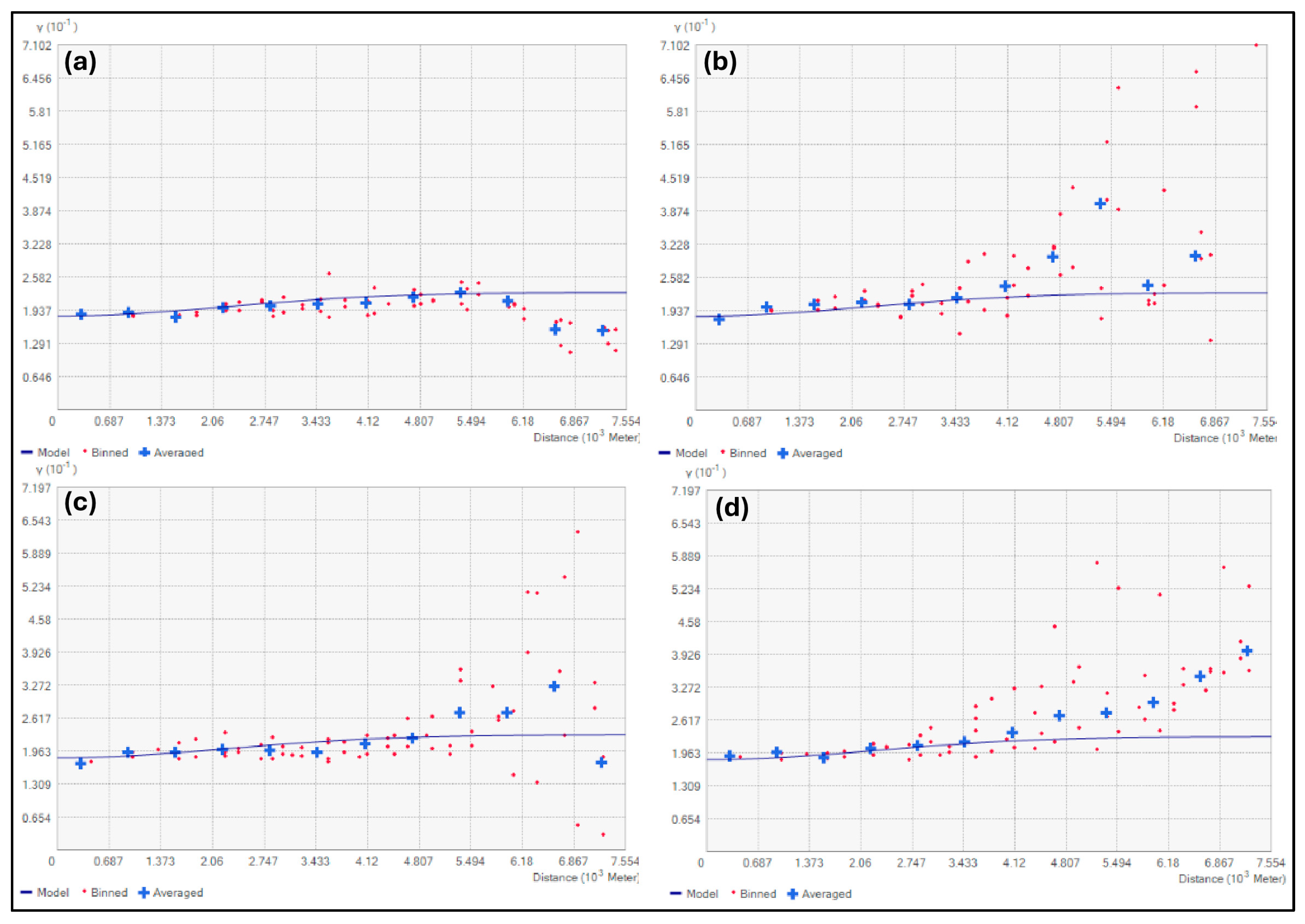
2.4. Geostatistical Analysis Theory
2.5. Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) and Groundwater Potential Mapping
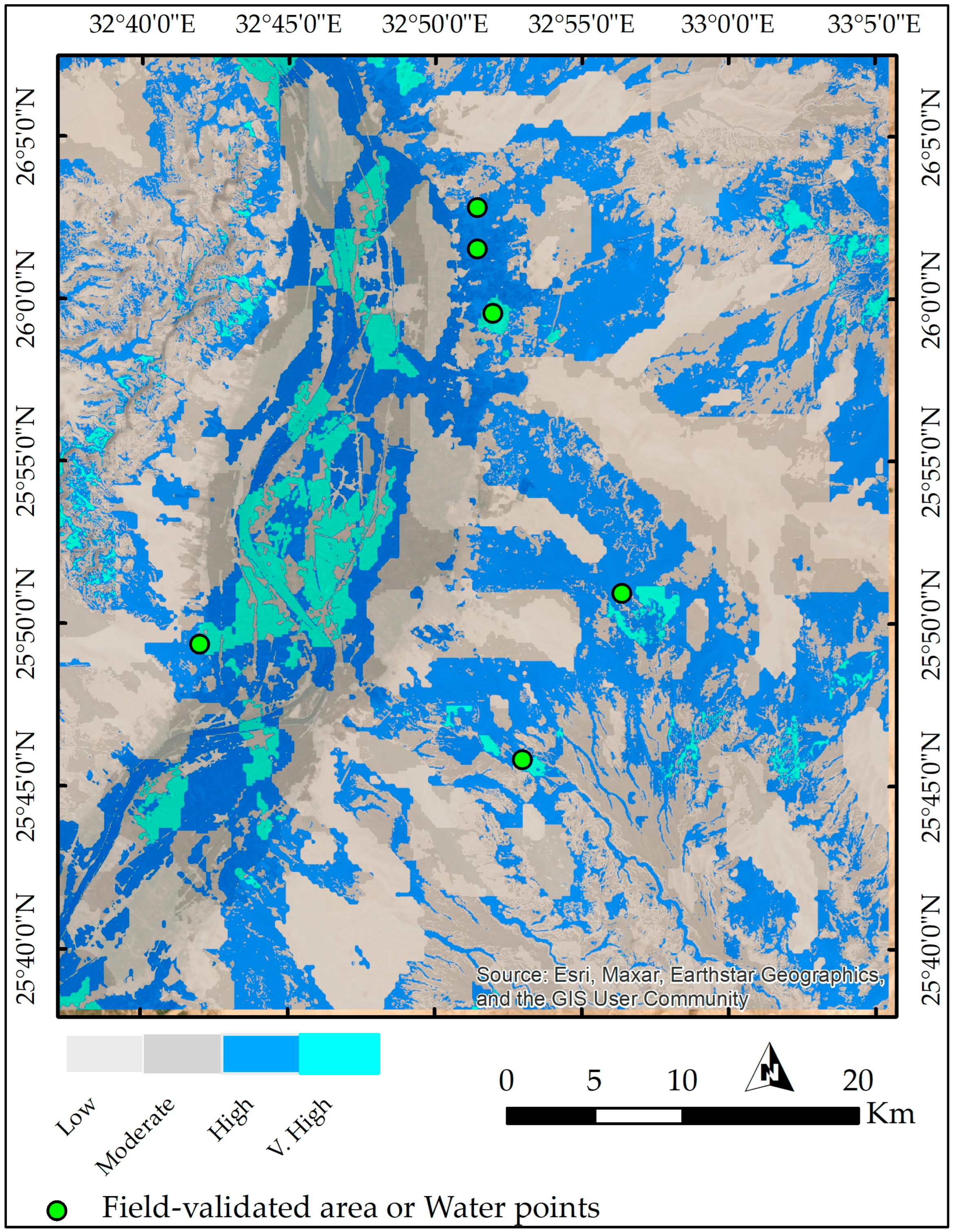
2.6. Validation and Accuracy Assessment
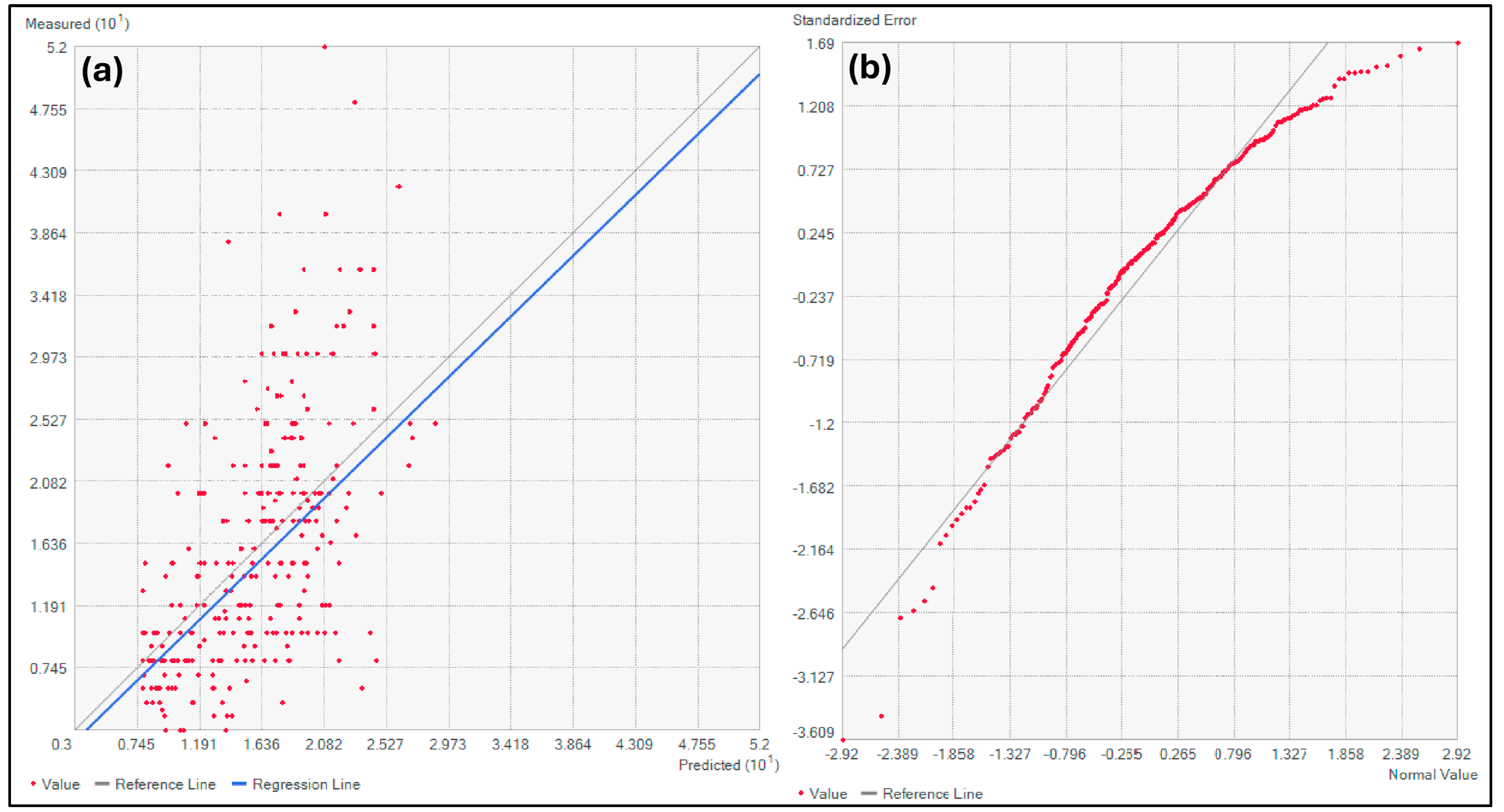
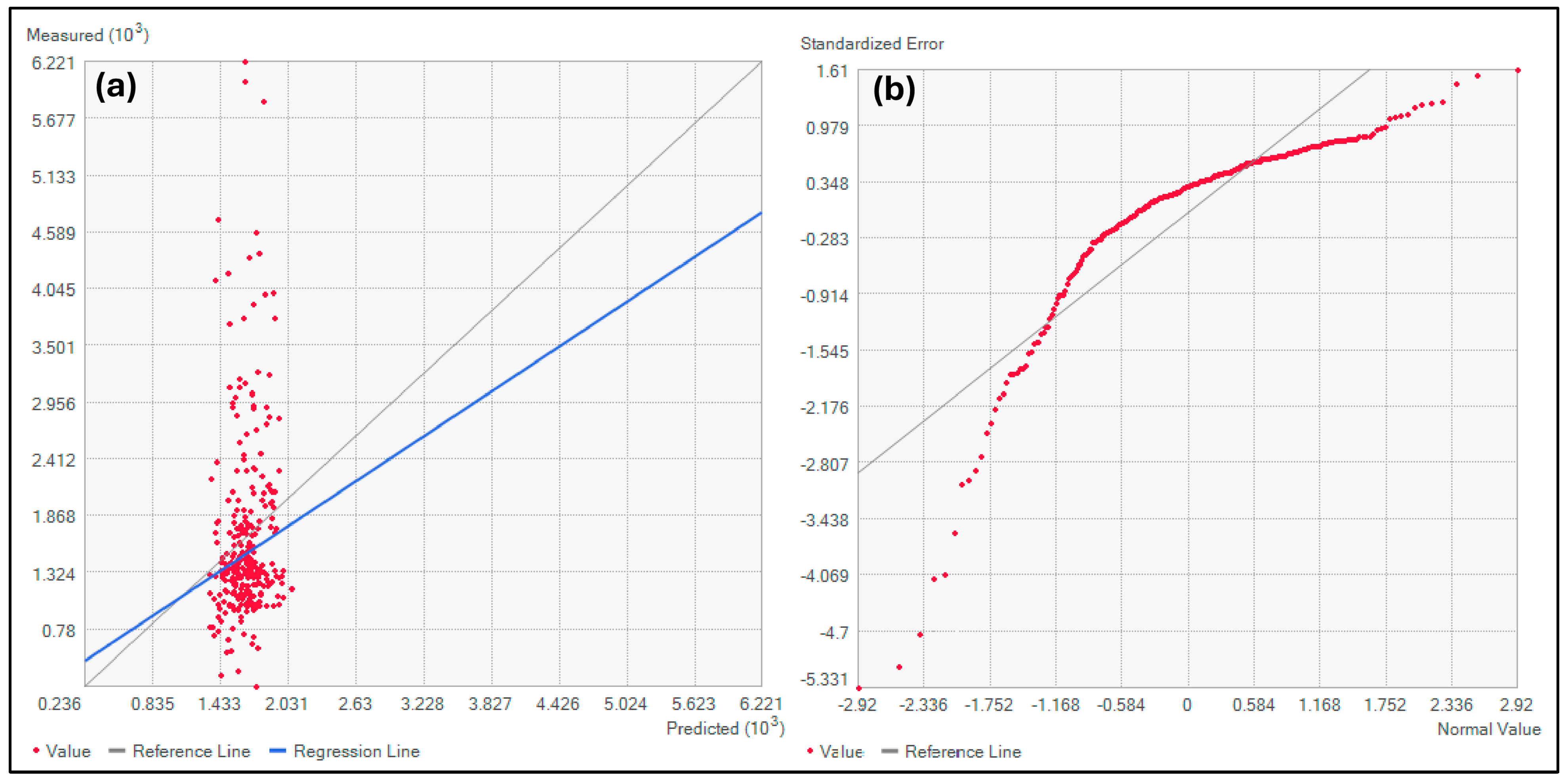
2.6.1. Geostatistical Model Validation
- Accuracy Metrics: Both the root mean square error (RMSE) and mean absolute error (MAE) were calculated to quantify prediction performance.
2.6.2. Field Validation
3. Results and Discussion
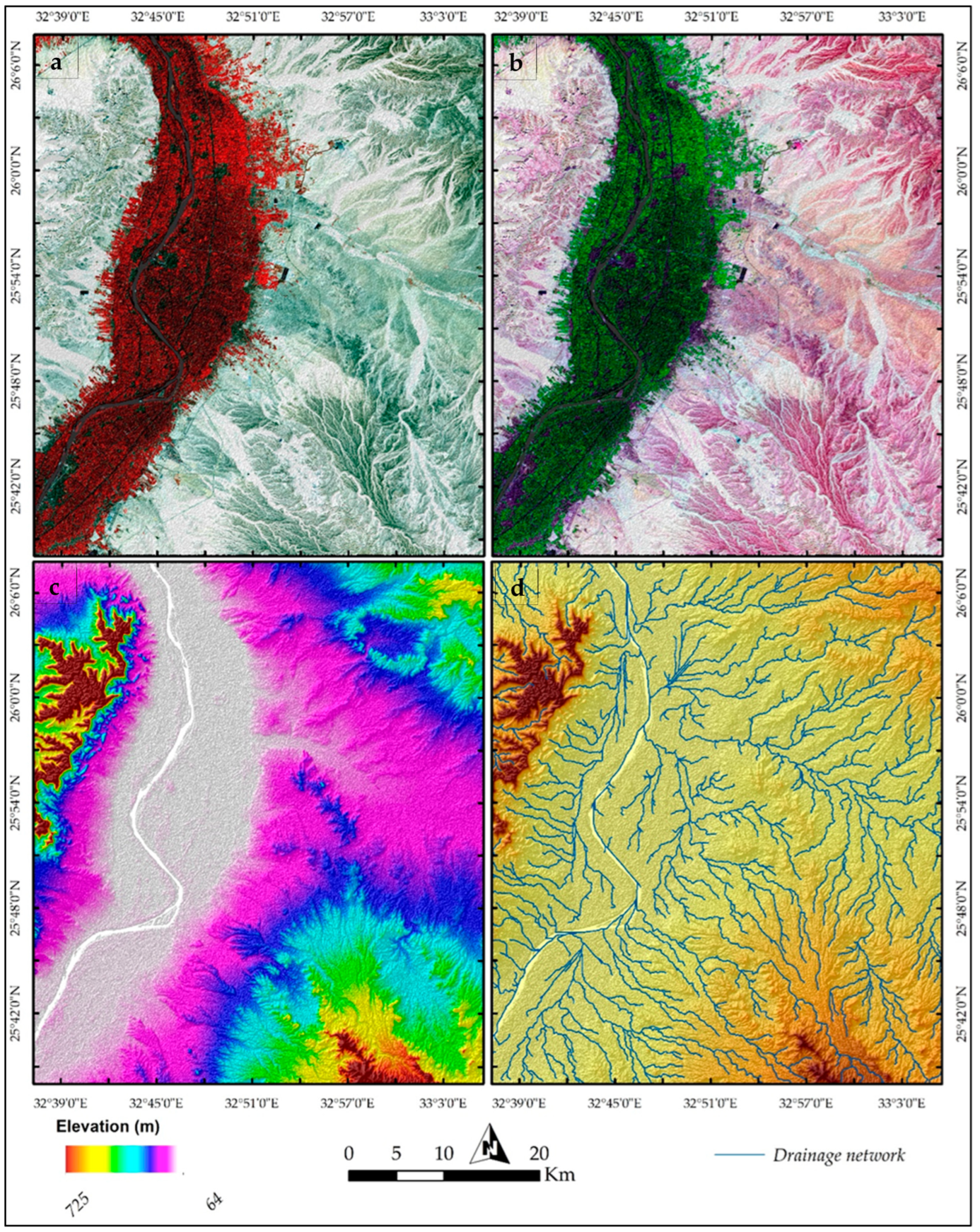
3.1. Remote Sensing
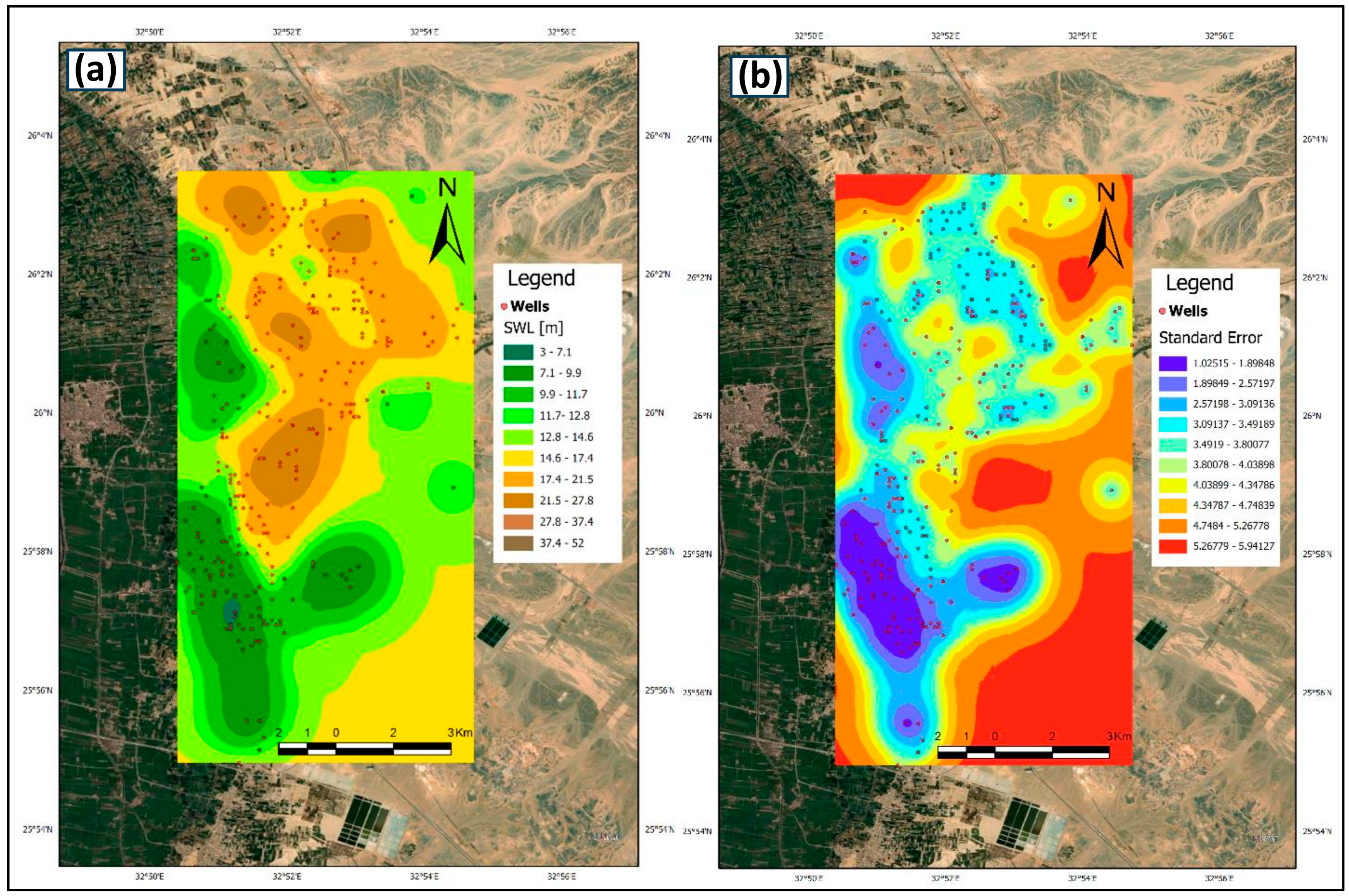
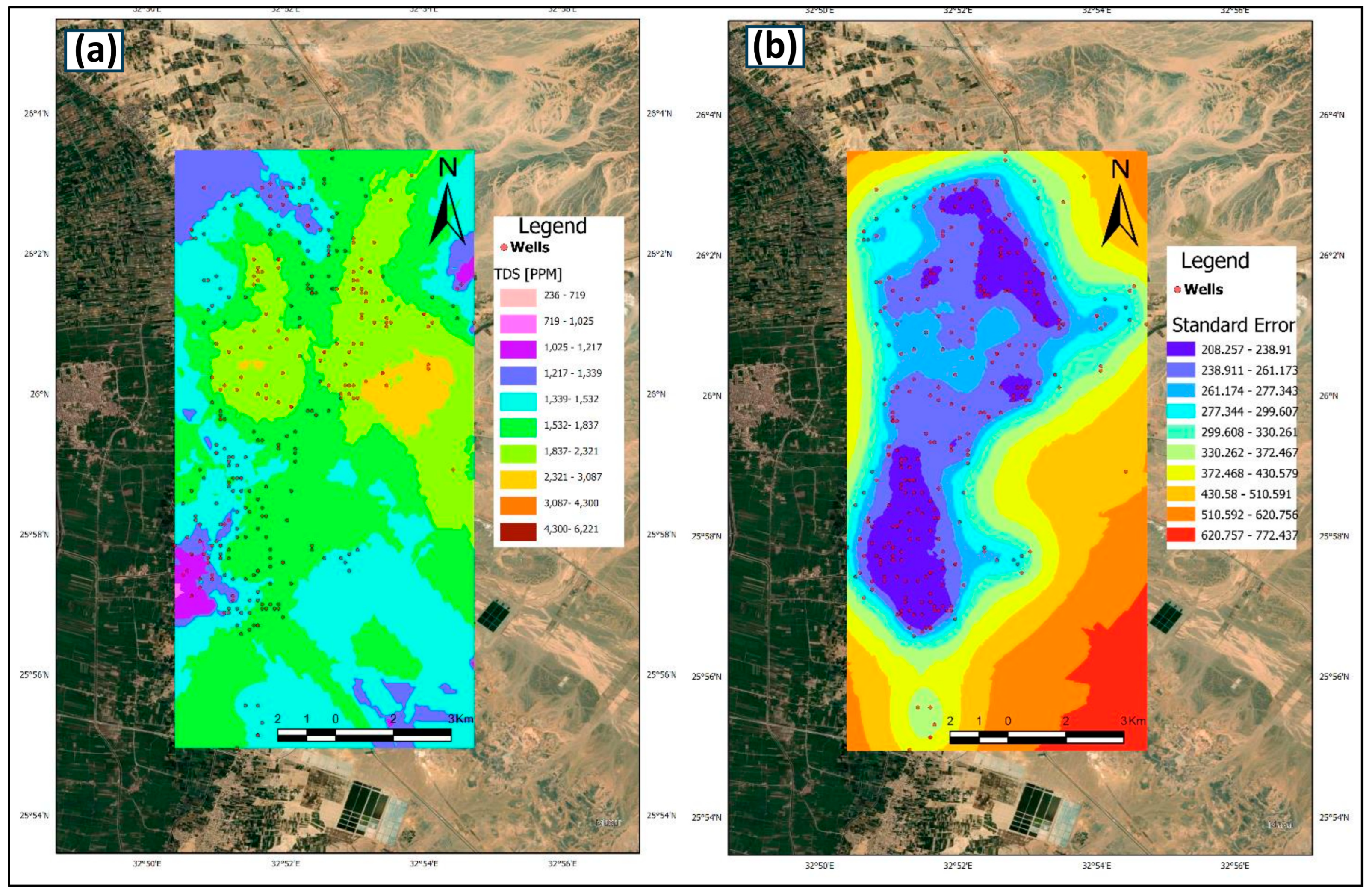
3.2. Geostatistical Analysis Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bera, A.; Das, S. Water Resource Management in Semi-Arid Purulia District of West Bengal, in the Context of Sustainable Development Goals. In Groundwater and Society: Applications of Geospatial Technology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 501–519. [Google Scholar]
- El-Rawy, M.; Makhloof, A.A.; Hashem, M.D.; Eltarabily, M.G. Groundwater Management of Quaternary Aquifer of the Nile Valley under Different Recharge and Discharge Scenarios: A Case Study Assiut. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 2563–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Agha, D.E.; Closas, A.; Molle, F. Survey of Groundwater Use in the Central Part of the Nile Delta. In Water and Salt Management in the Nile Delta; IWMI: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2015; pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Waseem, M.; Khurshid, T.; Abbas, A.; Ahmad, I.; Javed, Z. Impact of Meteorological Drought on Agriculture Production at Different Scales in Punjab, Pakistan. J. Water Clim. Change 2022, 13, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijeratne, V.P.I.S.; Li, G.; Mehmood, M.S.; Abbas, A. Assessing the Impact of Long-Term ENSO, SST, and IOD Dynamics on Extreme Hydrological Events (EHEs) in the Kelani River Basin (KRB), Sri Lanka. Atmosphere 2022, 14, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Waseem, M.; Ullah, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, J. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Meteorological and Hydrological Droughts and Their Propagations. Water 2021, 13, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulbalaji, P.; Padmalal, D.; Sreelash, K. GIS and AHP Techniques Based Delineation of Groundwater Potential Zones: A Case Study from Southern Western Ghats, India. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.S.; Jugran, D.K. Delineation of Groundwater Potential Zones and Zones of Groundwater Quality Suitable for Domestic Purposes Using Remote Sensing and GIS. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2003, 48, 821–833. [Google Scholar]
- Masoud, A.M.; Pham, Q.B.; Alezabawy, A.K.; Abu El-Magd, S.A. Efficiency of Geospatial Technology and Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis for Groundwater Potential Mapping in a Semi-Arid Region. Water 2022, 14, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, U.; Wagh, V.; Mukate, S.; Kadam, A.; Patil, S. Applications of Geospatial Analysis and Analytical Hierarchy Process to Identify the Groundwater Recharge Potential Zones and Suitable Recharge Structures in the Ajani-Jhiri Watershed of North Maharashtra, India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 17, 100733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferozur, R.M.; Jahan, C.S.; Arefin, R.; Mazumder, Q.H. Groundwater Potentiality Study in Drought Prone Barind Tract, NW Bangladesh Using Remote Sensing and GIS. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 8, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makonyo, M.; Msabi, M.M. Identification of Groundwater Potential Recharge Zones Using GIS-Based Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis: A Case Study of Semi-Arid Midlands Manyara Fractured Aquifer, North-Eastern Tanzania. Remote Sens. Appl. 2021, 23, 100544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Keese, K.E.; Flint, A.L.; Flint, L.E.; Gaye, C.B.; Edmunds, W.M.; Simmers, I. Global Synthesis of Groundwater Recharge in Semiarid and Arid Regions. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2006, 20, 3335–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbuZeid, K.; Elrawady, M. Sustainable Development of Non-Renewable Groundwater. In UNESCO Congress on Water Scarcity; University of Irvine: Irvine, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mir, R.; Azizyan, G.; Massah, A.; Gohari, A. Fossil Water: Last Resort to Resolve Long-Standing Water Scarcity? Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 261, 107358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu El-Magd, S.A.; Eldosouky, A.M. An Improved Approach for Predicting the Groundwater Potentiality in the Low Desert Lands; El-Marashda Area, Northwest Qena City, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 179, 104200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Singh, S.K.; Kundu, A.; Tyagi, K.; Menon, J.; Frederick, A.; Raj, A.; Lal, D. GIS-Based Multi-Criteria Approach to Delineate Groundwater Prospect Zone and Its Sensitivity Analysis. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uc Castillo, J.L.; Martínez Cruz, D.A.; Ramos Leal, J.A.; Tuxpan Vargas, J.; Rodríguez Tapia, S.A.; Marín Celestino, A.E. Delineation of Groundwater Potential Zones (GWPZs) in a Semi-Arid Basin through Remote Sensing, GIS, and AHP Approaches. Water 2022, 14, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgher, M.S.; Kumar, N.; Kumari, M.; Ahmad, M.; Sharma, L.; Naikoo, M.W. Groundwater Potential Mapping of Tawi River Basin of Jammu District, India, Using Geospatial Techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifediegwu, S.I. Assessment of Groundwater Potential Zones Using GIS and AHP Techniques: A Case Study of the Lafia District, Nasarawa State, Nigeria. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, I.A.; Sankar, K.; Dar, M.A. Deciphering Groundwater Potential Zones in Hard Rock Terrain Using Geospatial Technology. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.; Gupta, S.; Guin, S.; Kaur, H. Assessment of Groundwater Potential Zones Using Multi-Influencing Factor (MIF) and GIS: A Case Study from Birbhum District, West Bengal. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 4117–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Meshram, S.G.; Krishna, R.S.; Pradhan, B.; Shadeed, S.; Khedher, K.M.; Sepehri, M.; Ildoromi, A.R.; Alimerzaei, F.; Darabi, F. Identification of the Groundwater Potential Recharge Zones Using MCDM Models: Full Consistency Method (FUCOM), Best Worst Method (BWM) and Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP). Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 4727–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, U.; Yin, X.; Xu, Z.; Rasool, M.A.; Senapathi, V.; Hussain, M.; Siddique, J.; Trabucco, J.C. Mapping of Groundwater Productivity Potential with Machine Learning Algorithms: A Case Study in the Provincial Capital of Baluchistan, Pakistan. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, W.; Ghoneim, E.; Shew, R.; LaMaskin, T.; Al-Bloushi, K.; Hussein, S.; AbuBakr, M.; Al-Mulla, E.; Al-Awar, M.; El-Baz, F. Delineation of Groundwater Potential (GWP) in the Northern United Arab Emirates and Oman Using Geospatial Technologies in Conjunction with Simple Additive Weight (SAW), Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP), and Probabilistic Frequency Ratio (PFR) Techniques. J. Arid Environ. 2018, 157, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodley, T.; Seyam, M.; Abunama, T.; Bux, F. Delineation of Groundwater Potential Zones in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa Using Remote Sensing, GIS and AHP. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2022, 193, 104571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.M.C.; Ferolin, T.P. Groundwater Resource Exploration and Mapping Methods: A Review. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2023, 19, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, W.O. Review of Electrical and Gravity Methods of Near-Surface Exploration for Groundwater. Niger. J. Technol. Dev. 2014, 11, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Cheng, W.; Abdelkareem, M.; Al-Arifi, N. Mapping Prospective Areas of Water Resources and Monitoring Land Use/Land Cover Changes in an Arid Region Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. Water 2022, 14, 2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.H.; Mewafy, F.M.; Qian, W.; Faruwa, A.R.; Shebl, A.; Dabaa, S.; Saleem, H.A. Numerical Simulation of Geophysical Models to Detect Mining Tailings’ Leachates within Tailing Storage Facilities. Water 2024, 16, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebl, A.; Abdelaziz, M.I.; Ghazala, H.; Araffa, S.A.S.; Abdellatif, M.; Csámer, Á. Multi-Criteria Ground Water Potentiality Mapping Utilizing Remote Sensing and Geophysical Data: A Case Study Within Sinai Peninsula, Egypt. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2022, 25, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, L.; Rishi, M.S.; Singh, G.; Nath, S. Groundwater Potential Assessment of an Alluvial Aquifer in Yamuna Sub-Basin (Panipat Region) Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques in Conjunction with Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) and Catastrophe Theory. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbeih, S.F.; Madani, A.A.; Hagage, M. Groundwater Deterioration in Akhmim District, Upper Egypt: A Remote Sensing and GIS Investigation Approach. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2021, 24, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.M.; A, M.H.; Mohamed, M.R. Estimating Salinity Using Remote Sensing Data. J. Al-Azhar Univ. Eng. Sect. 2022, 17, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourghasemi, H.R.; Sadhasivam, N.; Yousefi, S.; Tavangar, S.; Ghaffari Nazarlou, H.; Santosh, M. Using Machine Learning Algorithms to Map the Groundwater Recharge Potential Zones. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 265, 110525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melese, T.; Belay, T. Groundwater Potential Zone Mapping Using Analytical Hierarchy Process and GIS in Muga Watershed, Abay Basin, Ethiopia. Glob. Chall. 2021, 6, 2100068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnous, M.O.; El-Rayes, A.E.; Geriesh, M.H.; Ghodeif, K.O.; Al-Oshari, F.A. Groundwater Potentiality Mapping of Tertiary Volcanic Aquifer in IBB Basin, Yemen by Using Remote Sensing and GIS Tools. J. Coast. Conserv. 2020, 24, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, M.; Birajdar, F. Advancements in Remote Sensing and GIS for Sustainable Groundwater Monitoring: Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions. Int. J. Res. Eng. Sci. Manag. 2024, 7, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, J.K.; Singh, S.K.; Ekanthalu, V.S. Integrating Remote Sensing, Geographic Information Systems and Global Positioning System Techniques with Hydrological Modeling. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1595–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejaur Rahman, M.; Rahman, A.; Saha, S.K. GIScience and Earth Observation Technology in Hydro-Geological Hazard Study—An Overview. In Advanced GIScience in Hydro-Geological Hazards: Applications, Modelling and Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 3–38. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, A.; Xue, L.; Islam, F.; Ahmed, N.; Qaysi, S.; Liu, S.; Alarifi, N.; Youssef, Y.M.; Abd-Elmaboud, M.E. Unveiling Groundwater Potential in Hangu District, Pakistan: A GIS-Driven Bivariate Modeling and Remote Sensing Approach for Achieving SDGs. Water 2024, 16, 3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchenna, A.; Achene, B.; Houria, B. Statistical Spatial Analysis of Traffic Accidents in the State of Constantine Using Geographic Information Systems(Gis). J. Al-Azhar Univ. Eng. Sect. 2022, 17, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embabi, N.S. Landscapes and Landforms of Egypt; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Beshr, A.M.; Kamel Mohamed, A.; ElGalladi, A.; Gaber, A.; El-Baz, F. Structural Characteristics of the Qena Bend of the Egyptian Nile River, Using Remote-Sensing and Geophysics. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2021, 24, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kazzaz, Y.A. Active Faulting Along Qena-Safaga Road, Eastern Desert, Egypt. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on the Geology of Africa, Assiut, Egypt, 23–25 November 1999; Volume 2, pp. 385–404. [Google Scholar]
- El-Gaby, S.; List, F.K.; Tehrani, R. Geology, Evolution and Metallogenesis of the Pan-African Belt in Egypt; Friedr. Vieweg & Sohn, Braunschweig: Wiesbaden, Germany, 1988; pp. 17–68. [Google Scholar]
- Akawy, A. Structural Geomorphology and Neotectonics of the Qina-Safaja District, Egypt. Neues Jahrb. Geol. Paläontologie-Abh. 2002, 226, 95–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akawy, A.; El Din, K.G. Middle Eocene to Recent Tectonics in the Qina Area, Upper Egypt. Neues Jahrb. Geol. Paläontologie-Abh. 2006, 240, 19–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoto, F.; Sy, O.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; Fernandez, V.; Colin, O.; Hoersch, B.; Meygret, A. Overview of Sentinel-2. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 1707–1710. [Google Scholar]
- Shebl, A.; Badawi, M.; Dawoud, M.; Abd El-Wahed, M.; El-Dokouny, H.A.; Csámer, Á. Novel Comprehensions of Lithological and Structural Features Gleaned via Sentinel 2 Texture Analysis. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 168, 106068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jotisankasa, A.; Torsri, K.; Supavetch, S.; Sirirodwattanakool, K.; Thonglert, N.; Sawangwattanaphaibun, R.; Faikrua, A.; Peangta, P.; Akaranee, J. Investigating Correlations and the Validation of SMAP-Sentinel L2 and In Situ Soil Moisture in Thailand. Sensors 2023, 23, 8828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismael, A. Geostatistical Modelling for Sulfur Element in Ghorabi Iron Ore Mine Area, Bahariya Oasis, Egypt. J. Al-Azhar Univ. Eng. Sect. 2021, 16, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikary, P.P.; Shit, P.K.; Santra, P.; Bhunia, G.S.; Tiwari, A.K.; Chaudhary, B.S. Geostatistics and Geospatial Technologies for Groundwater Resources in India; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; ISBN 3030623971. [Google Scholar]
- El-Rawy, M.; De Smedt, F. Estimation and Mapping of the Transmissivity of the Nubian Sandstone Aquifer in the Kharga Oasis, Egypt. Water 2020, 12, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigussie, W.; Hailu, B.T.; Azagegn, T. Mapping of Groundwater Potential Zones Using Sentinel Satellites (−1 SAR and -2A MSI) Images and Analytical Hierarchy Process in Ketar Watershed, Main Ethiopian Rift. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 160, 103632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, M.R.; Mousavi, S.M.; Rahimzadegan, M. Delineation of Groundwater Potential Zones Using Remote Sensing, GIS, and AHP Technique in Tehran–Karaj Plain, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Pardeshi, S.D. Integration of Different Influencing Factors in GIS to Delineate Groundwater Potential Areas Using IF and FR Techniques: A Study of Pravara Basin, Maharashtra, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Alshayef, M. Integration Based GIS Weighted Linear Combination (WLC) Model for Delineation Hydrocarbon Potential Zones in Ayad Area (Yemen) Using Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) Technique. SSRG Int. J. Geoinform. Geol. Sci. 2017, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Baharvand, S.; Rahnamarad, J.; Salman, S. Delineation of Groundwater Recharge Potential Zones Using Weighted Linear Combination Method (Case Study: Kuhdasht Plain, Iran). Geotech. Geol. 2016, 12, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Sophocleous, M. From Safe Yield to Sustainable Development of Water Resources—The Kansas Experience. J. Hydrol. 2000, 235, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Heap, A.D. A Review of Comparative Studies of Spatial Interpolation Methods in Environmental Sciences: Performance and Impact Factors. Ecol. Inform. 2011, 6, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrough, P.A. GIS and Geostatistics: Essential Partners for Spatial Analysis. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 2001, 8, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruybal, C.J.; Hogue, T.S.; McCray, J.E. Evaluation of Groundwater Levels in the Arapahoe Aquifer Using Spatiotemporal Regression Kriging. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 2820–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Statistical Index | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Mean | Std | Min | Max | Skewness | Kurtosis | IQR | Range | |
| SWL | 310 | 15.867 | 8.9 | 3 | 52 | 1.0080 | 0.8331 | 11 | 49 |
| TDS | 310 | 1661.5 | 909.7 | 236 | 6221 | 2.1856 | 2.1856 | 664 | 5985 |
| Parameters | SWL | TDS |
|---|---|---|
| Lag size | 500 | 500 |
| Number of lags | 12 | 12 |
| Nugget | 33 | 1.8 |
| Sill | 74 | 2.3 |
| Range | 4330 | 5475 |
| Index | Value |
|---|---|
| Count | 286 |
| Mean Absolute Error (MAE) | 0.040 |
| Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) | 3.135 |
| Mean Standardized | 0.015 |
| Root Mean Square Standardized (RMSS) | 0.935 |
| Index | Value |
|---|---|
| Count | 286 |
| Mean Absolute Error (MAE) | 1.305 |
| Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) | 186.862 |
| Mean Standardized | −0.002 |
| Root Mean Square Standardized (RMSS) | 1.036 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mostafa, A.E.-s.; Ali, M.A.M.; Ali, F.A.; Rabeiy, R.; Saleem, H.A.; Ali, M.A.H.; Shebl, A. Groundwater Potential Mapping in Semi-Arid Areas Using Integrated Remote Sensing, GIS, and Geostatistics Techniques. Water 2025, 17, 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131909
Mostafa AE-s, Ali MAM, Ali FA, Rabeiy R, Saleem HA, Ali MAH, Shebl A. Groundwater Potential Mapping in Semi-Arid Areas Using Integrated Remote Sensing, GIS, and Geostatistics Techniques. Water. 2025; 17(13):1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131909
Chicago/Turabian StyleMostafa, Ahmed El-sayed, Mahrous A. M. Ali, Faissal A. Ali, Ragab Rabeiy, Hussein A. Saleem, Mosaad Ali Hussein Ali, and Ali Shebl. 2025. "Groundwater Potential Mapping in Semi-Arid Areas Using Integrated Remote Sensing, GIS, and Geostatistics Techniques" Water 17, no. 13: 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131909
APA StyleMostafa, A. E.-s., Ali, M. A. M., Ali, F. A., Rabeiy, R., Saleem, H. A., Ali, M. A. H., & Shebl, A. (2025). Groundwater Potential Mapping in Semi-Arid Areas Using Integrated Remote Sensing, GIS, and Geostatistics Techniques. Water, 17(13), 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131909








