Temporal Hydrological Responses to Progressive Land Cover Changes and Climate Trends in a Plateau Lake Basin in Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
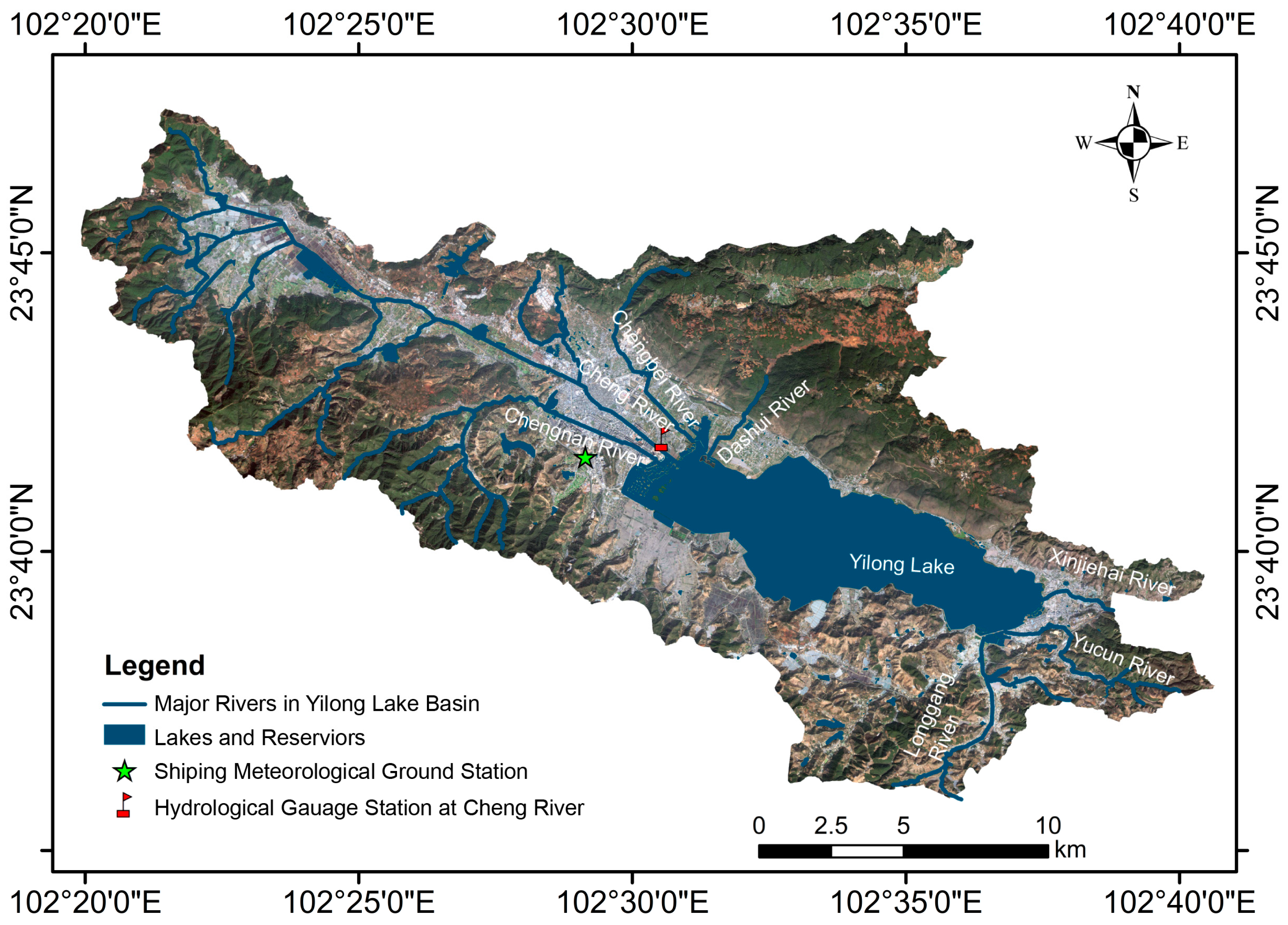
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Data Processing
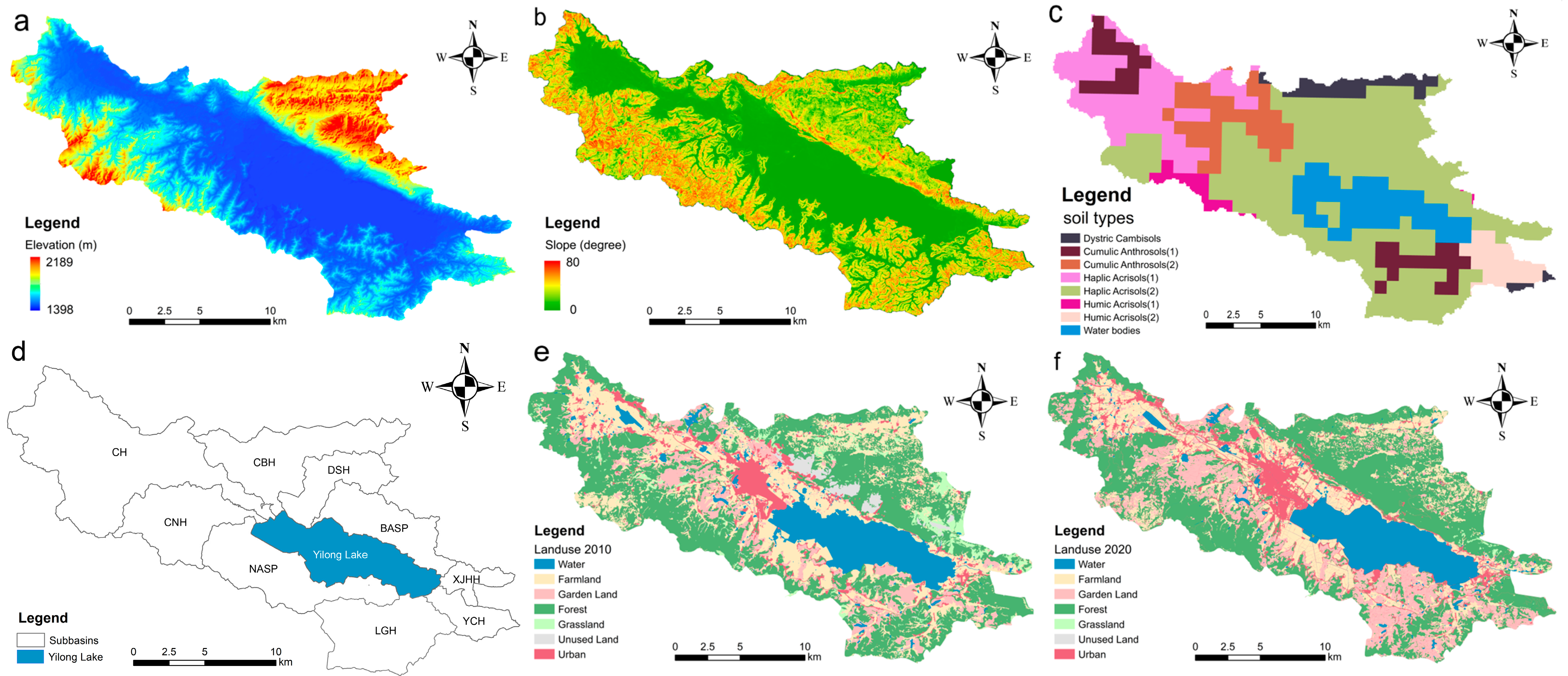
2.2.1. Geospatial Data
2.2.2. Climate Data
2.2.3. Streamflow Data
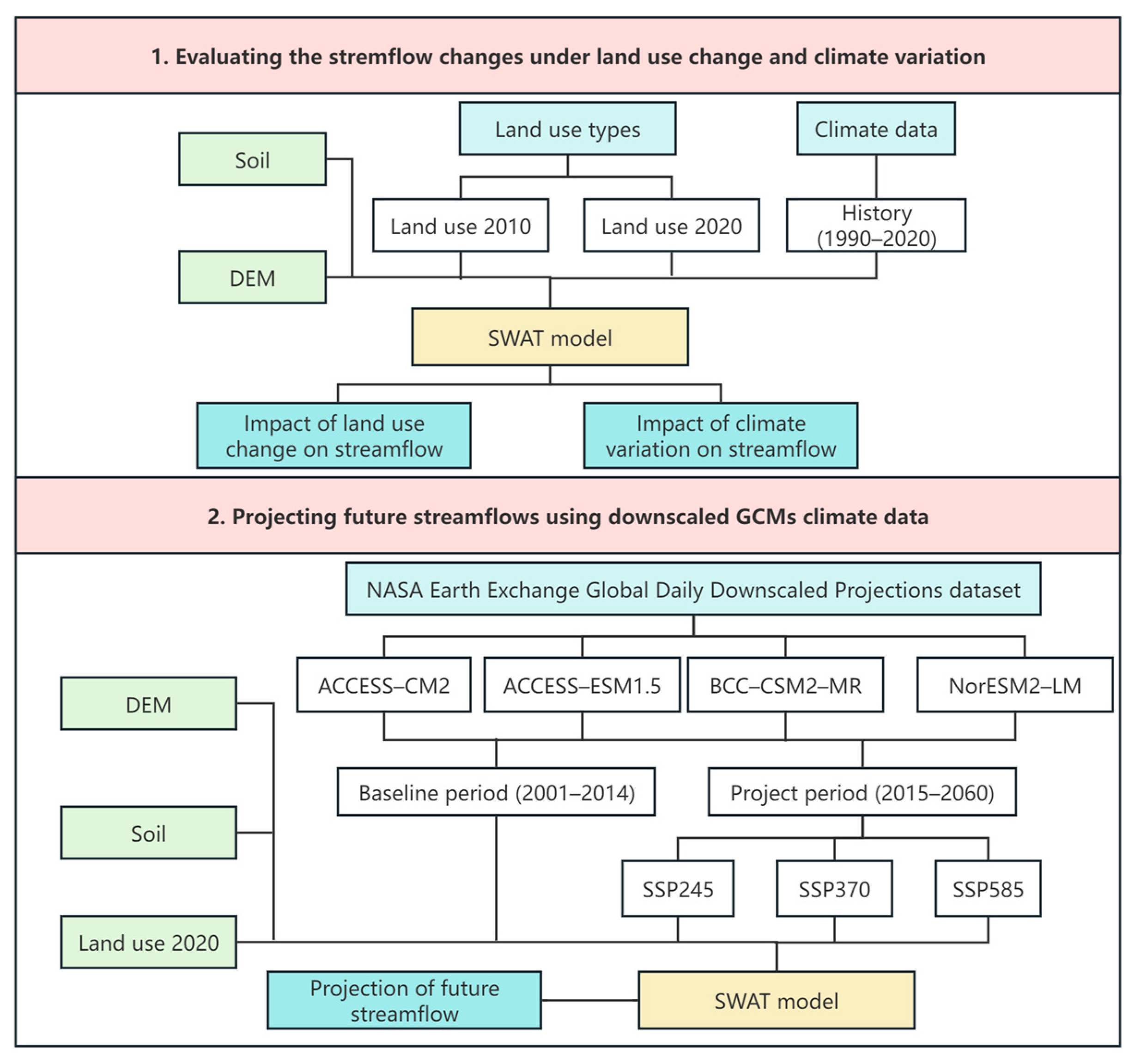
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Model Description and Setup
2.3.2. Calibration and Validation
3. Results
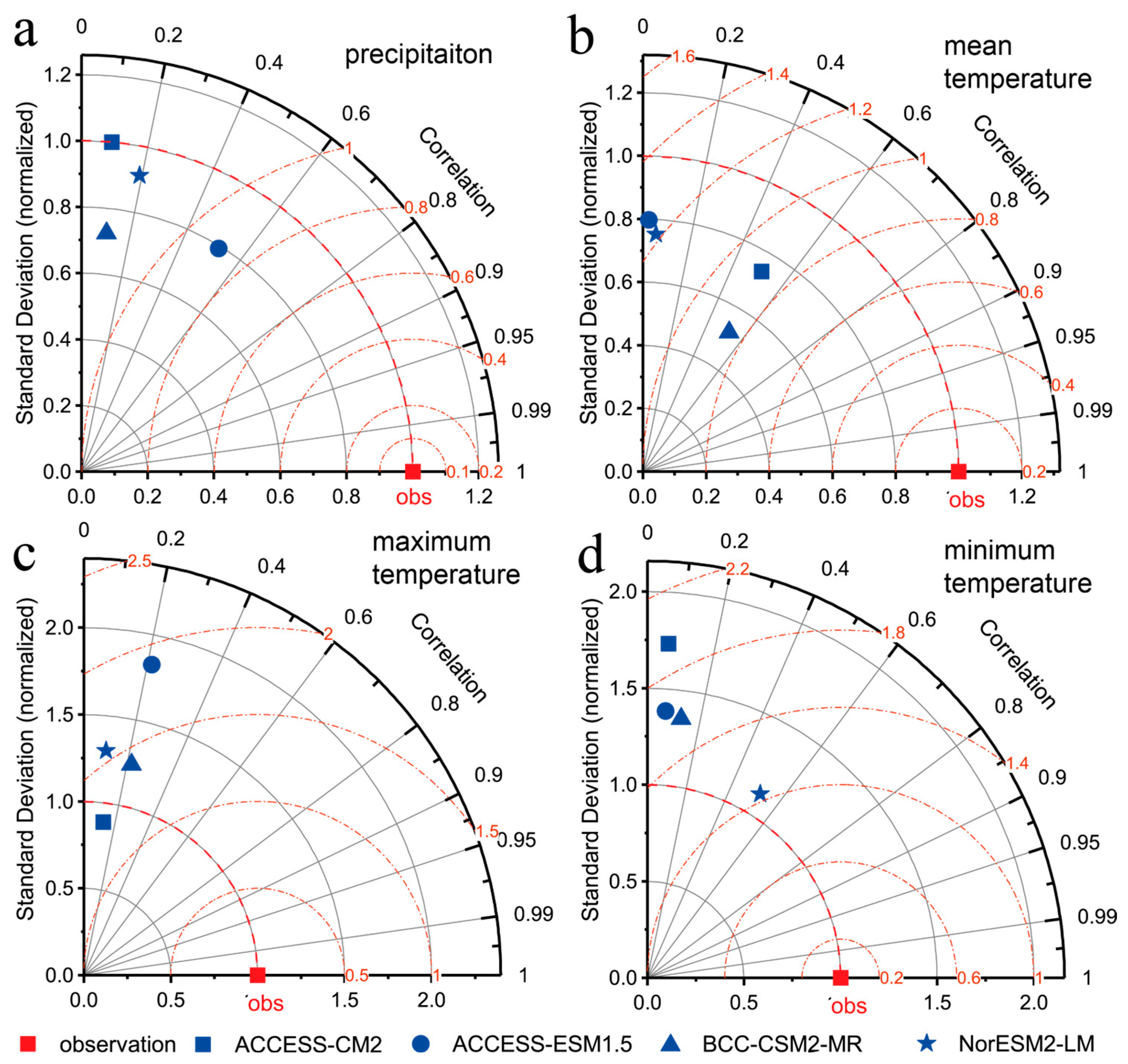
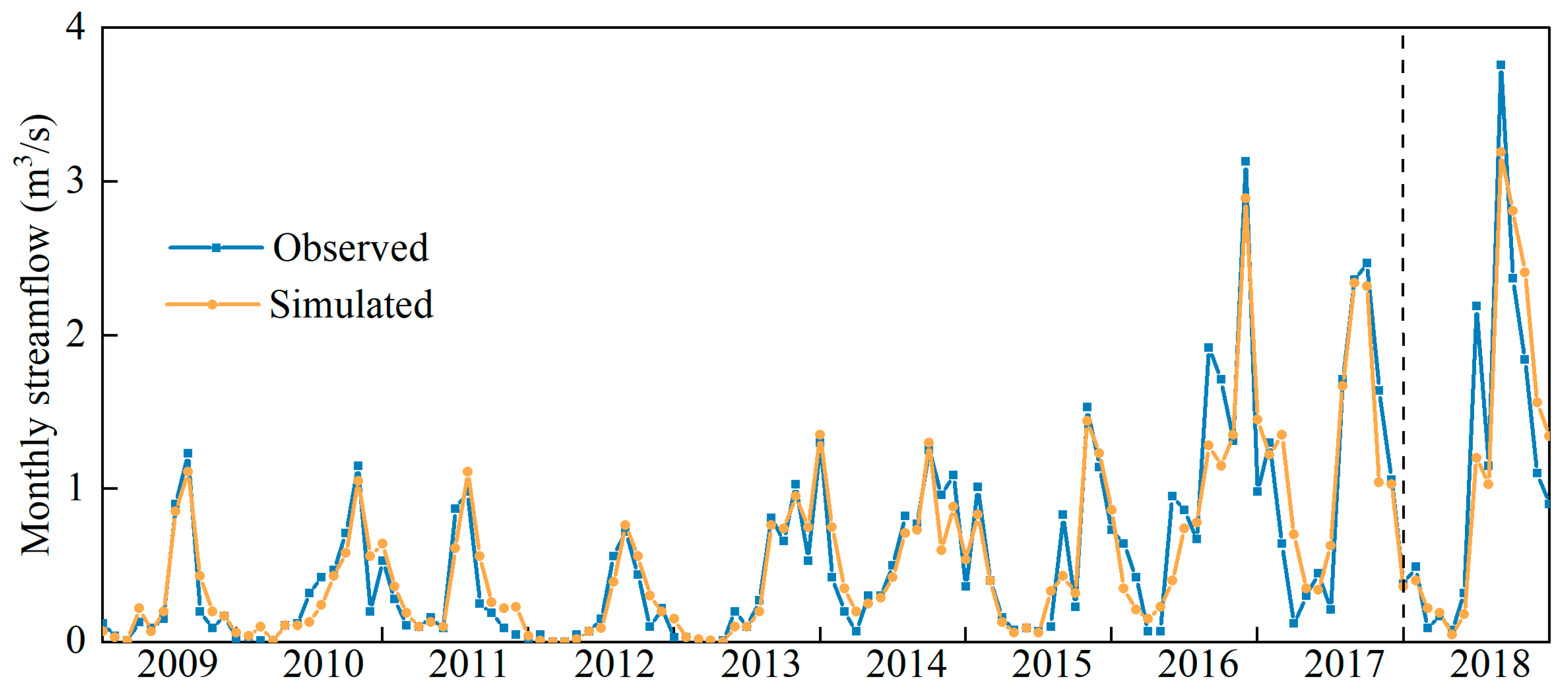
3.1. Model Performance
3.2. Hydrological Responses to Land Use Change
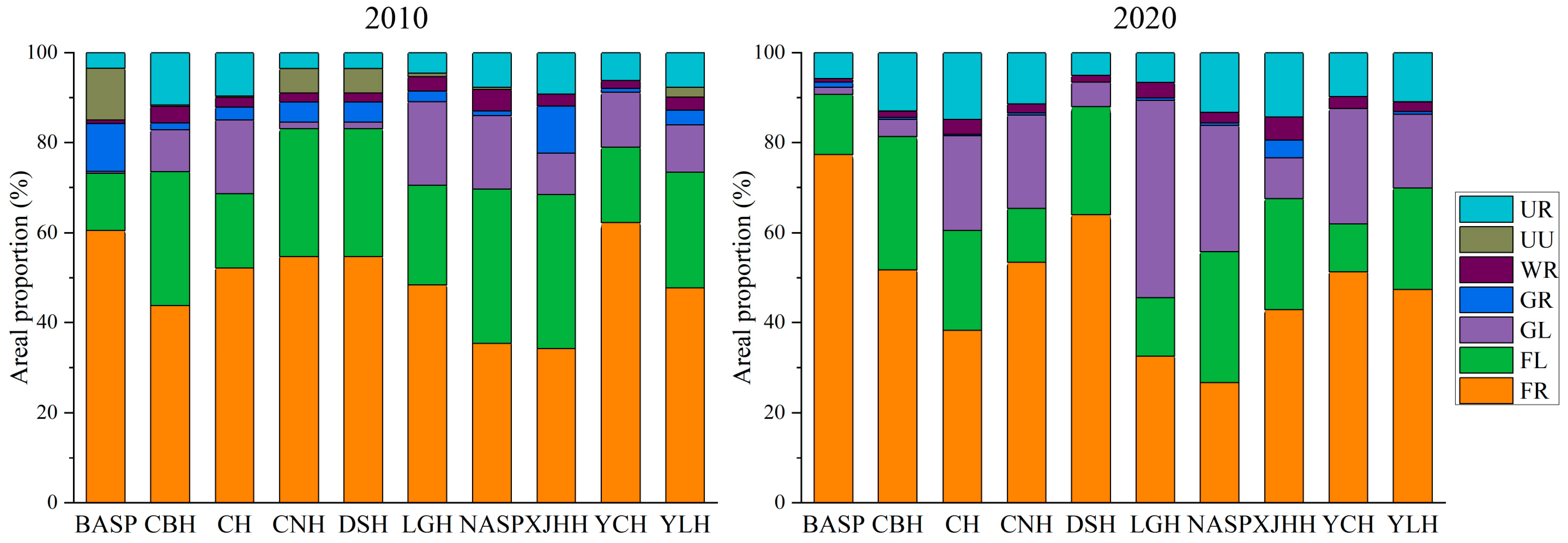
3.2.1. Landscape Patterns and Changes
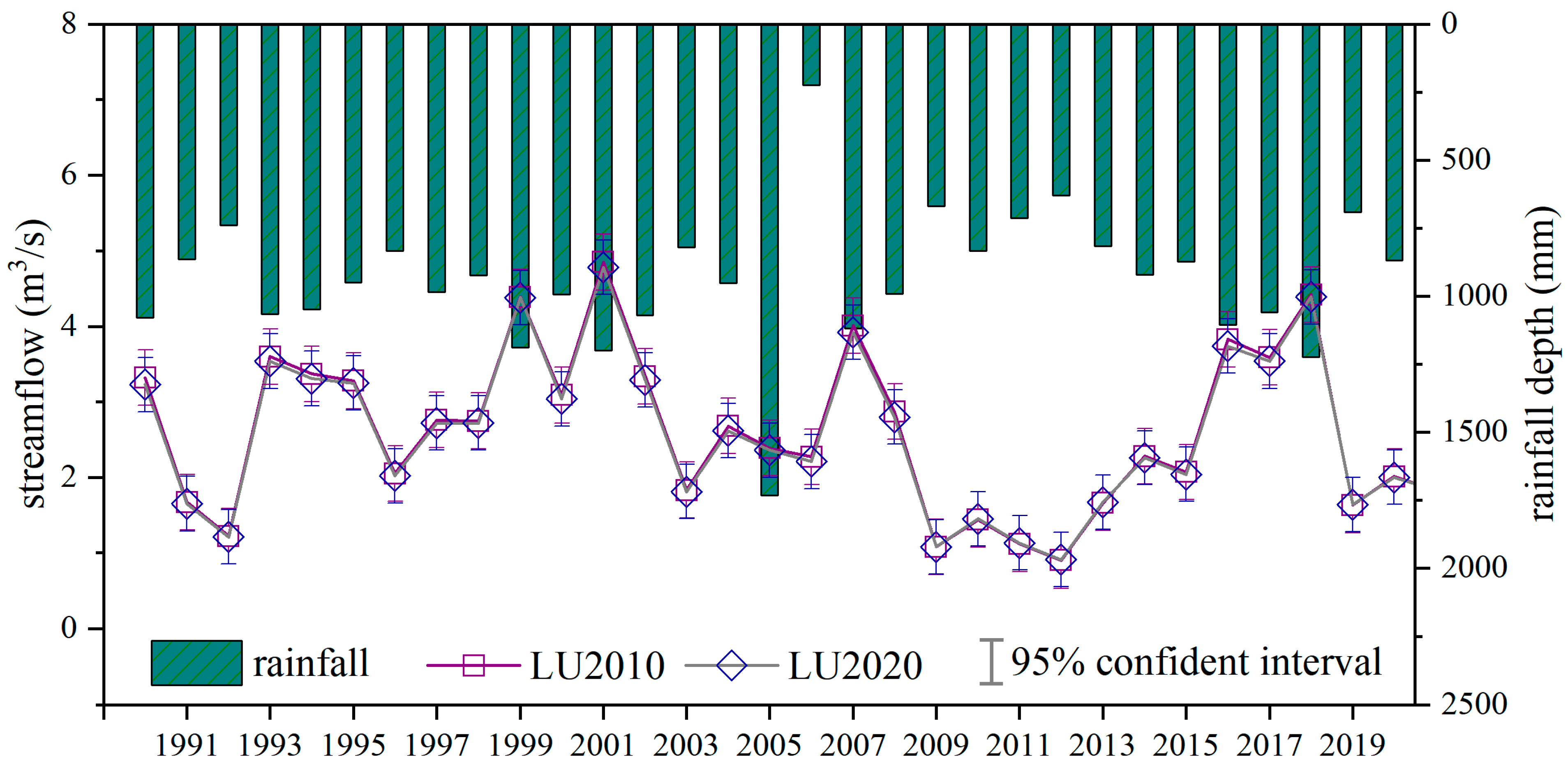
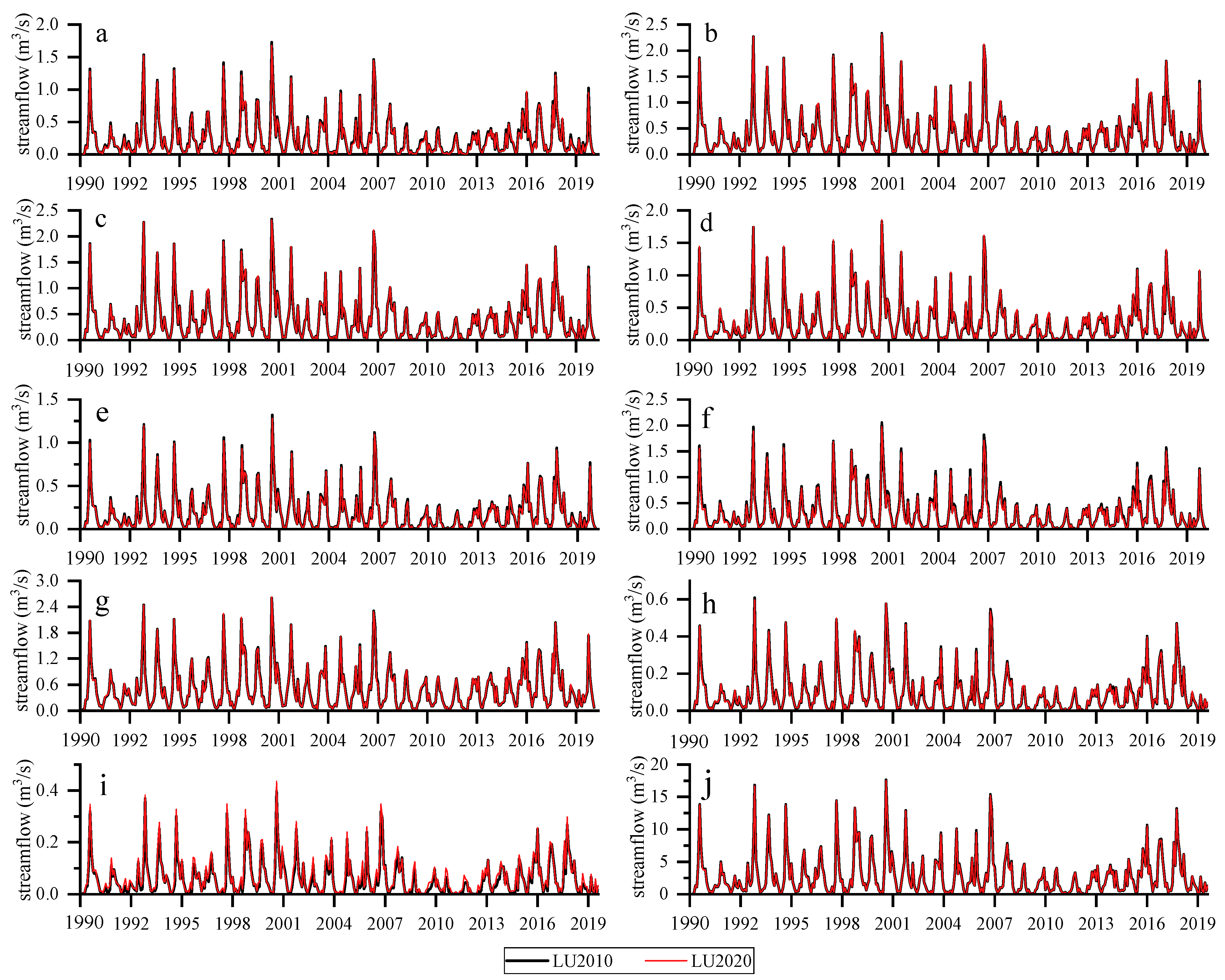
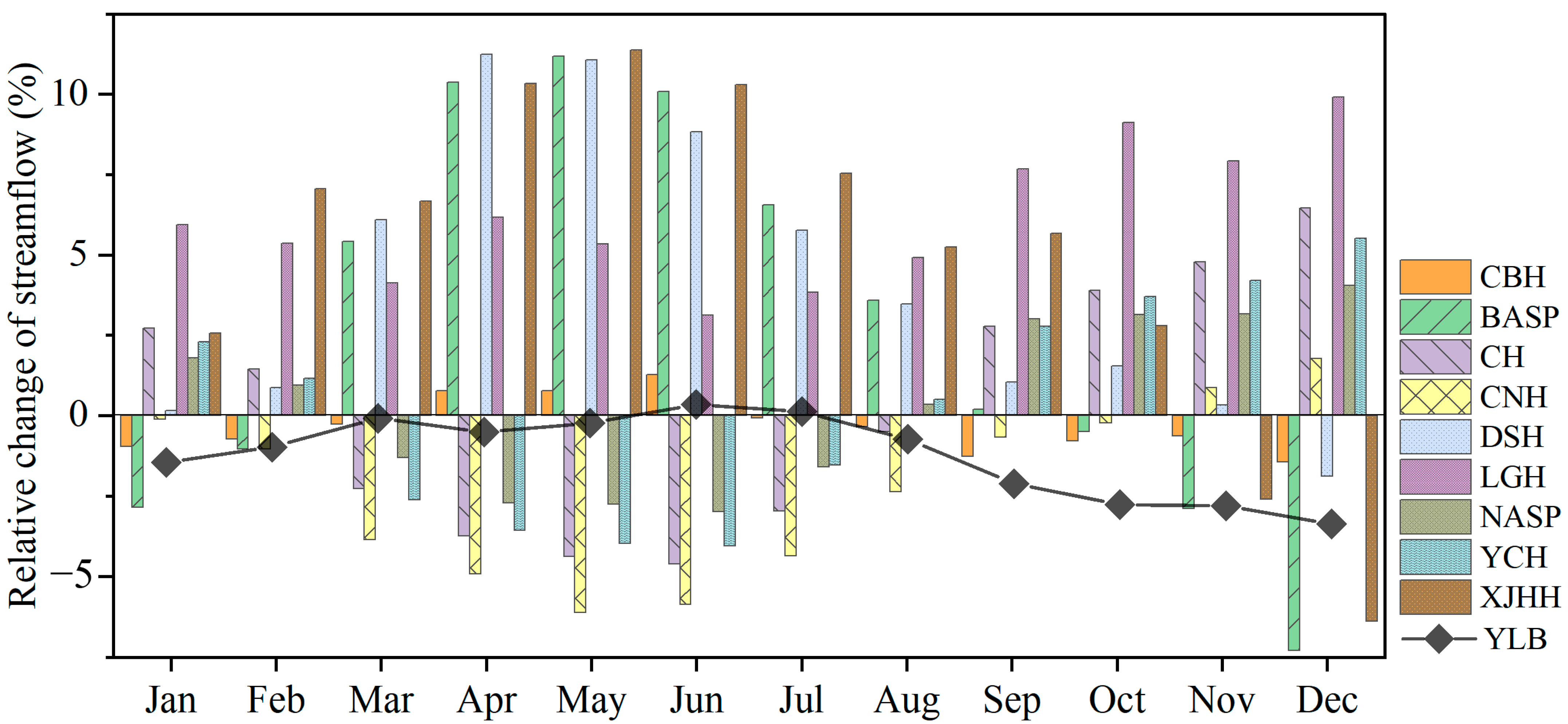
3.2.2. Streamflow Changes Response to Land Use Alternations
3.3. Projection of Future Streamflow Under Climate Change
3.3.1. Projected Future Temperature
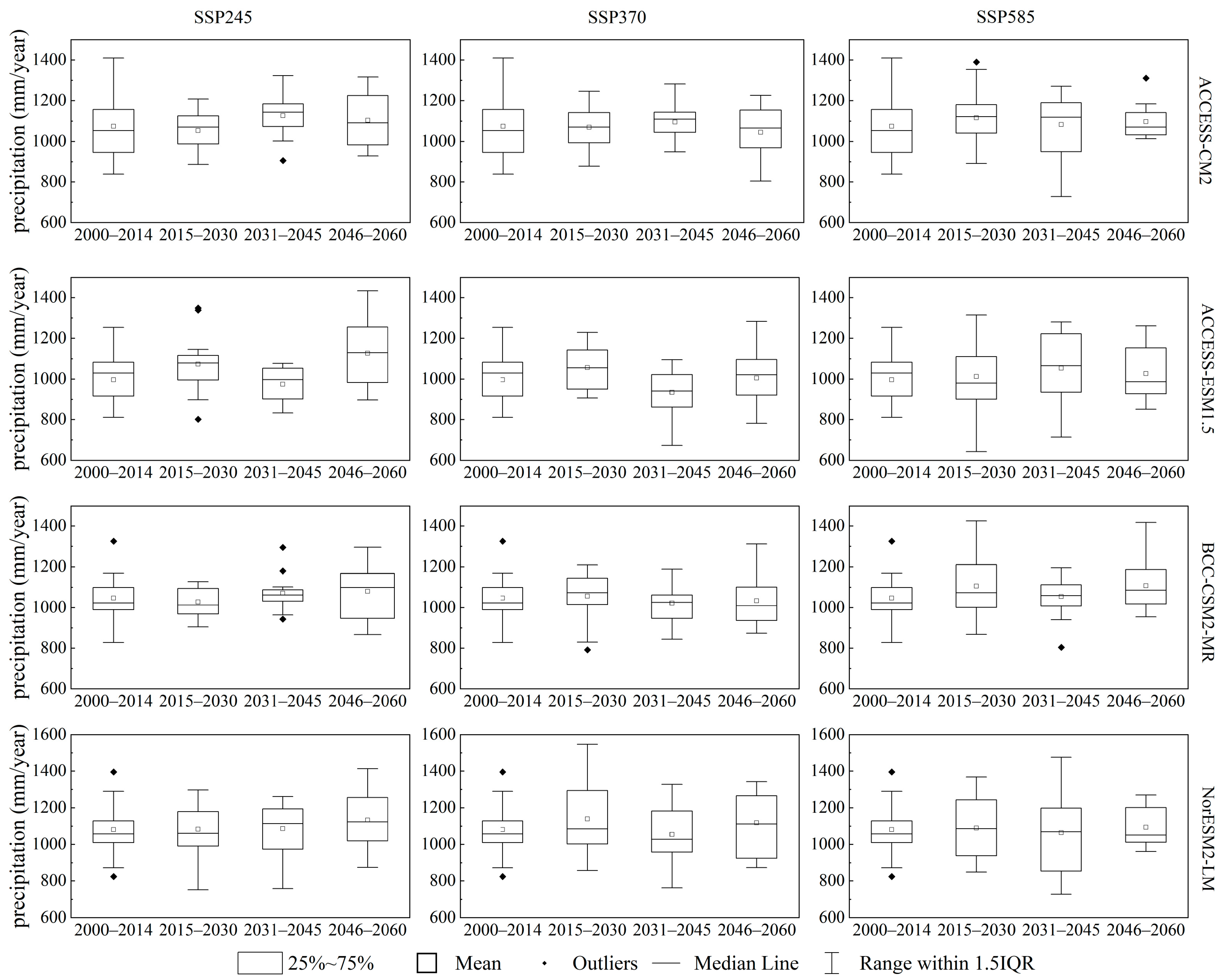
3.3.2. Projected Future Precipitation
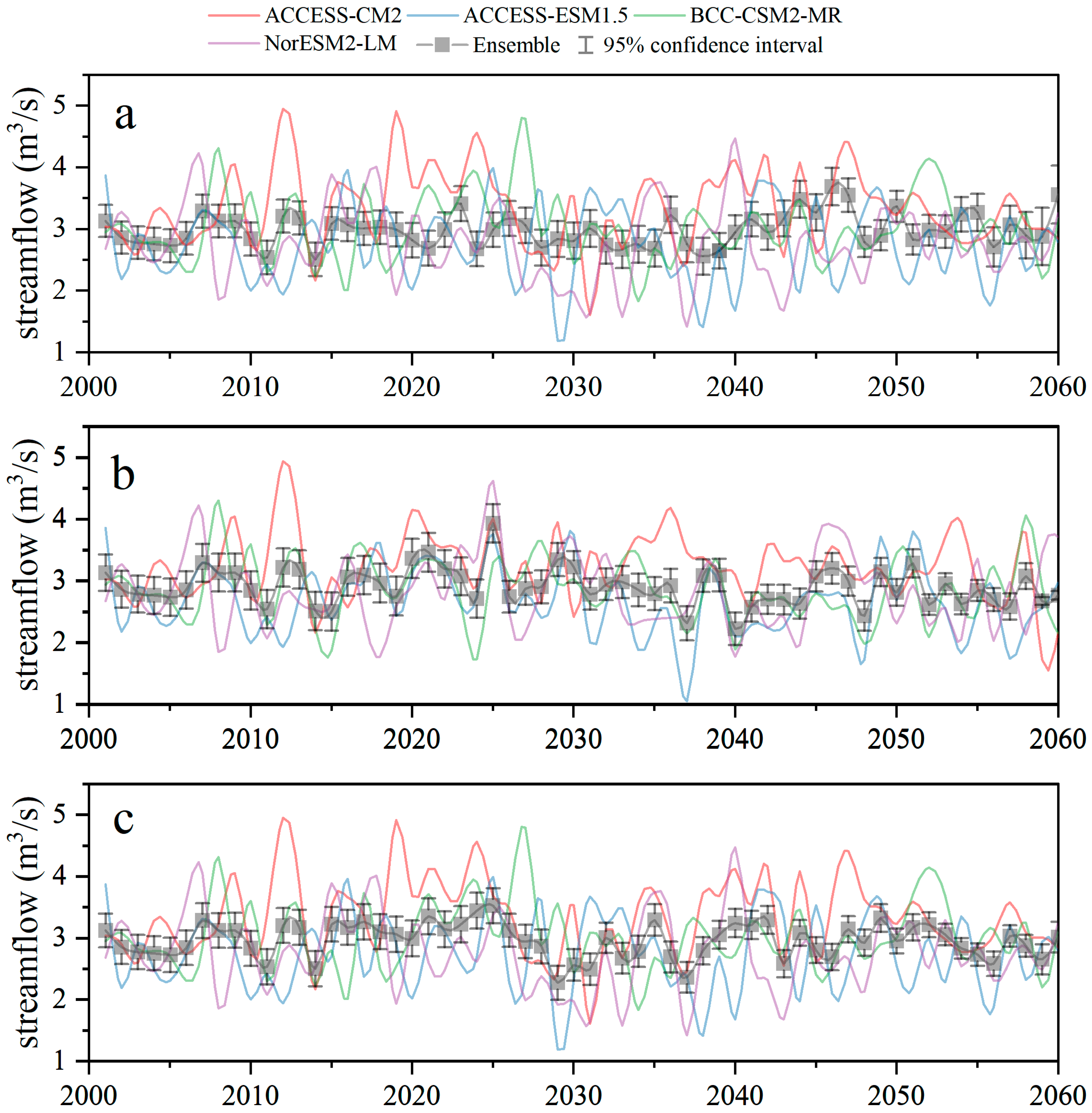
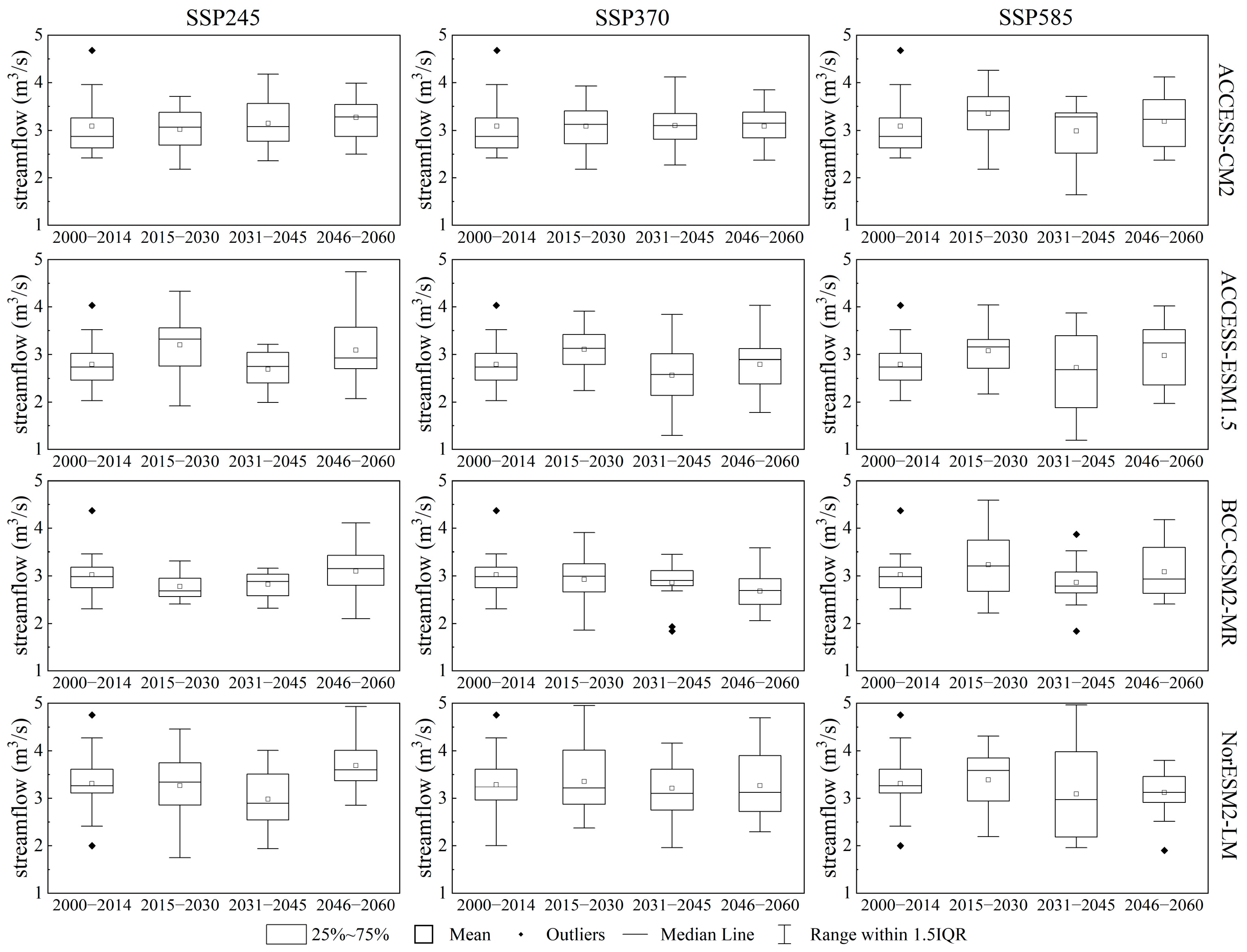
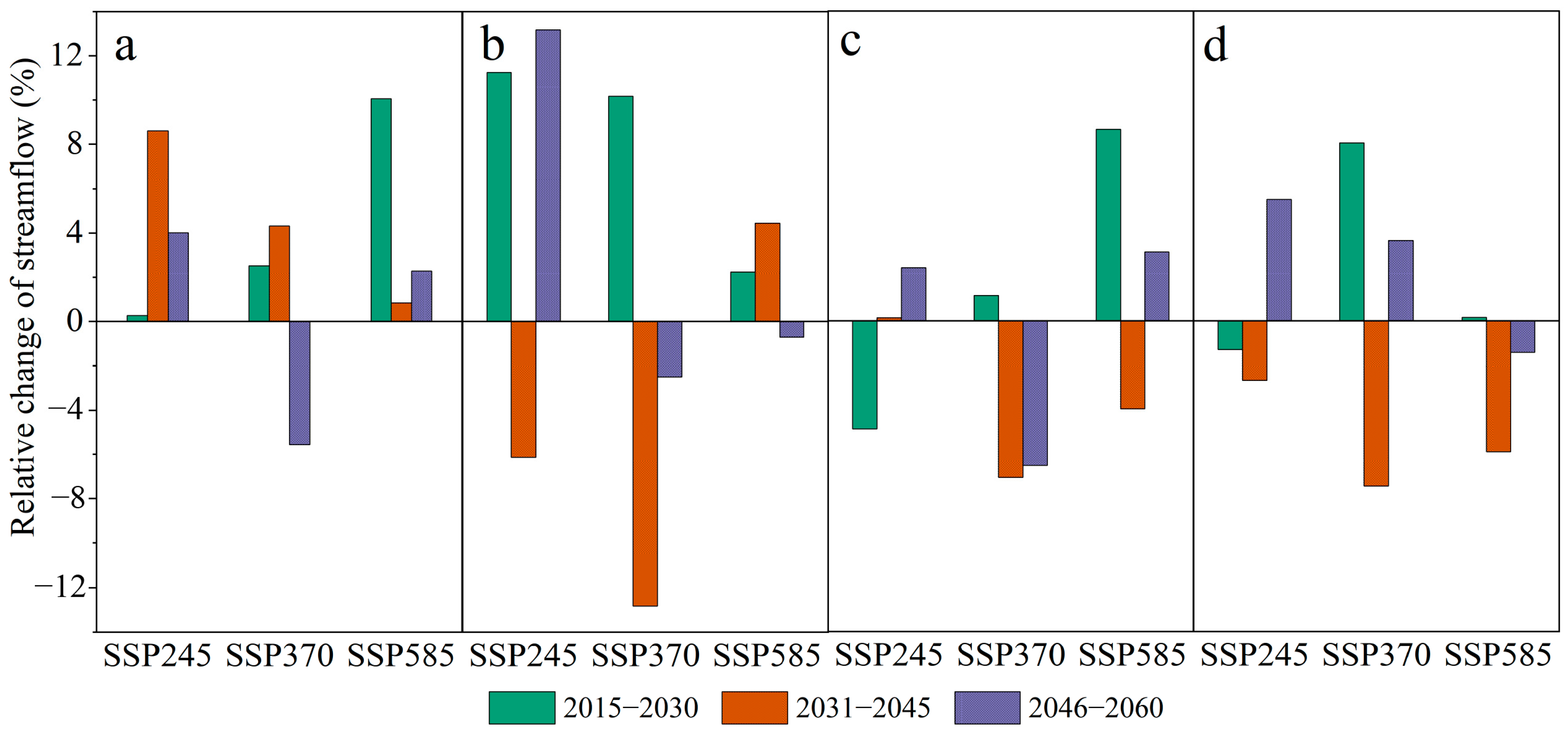
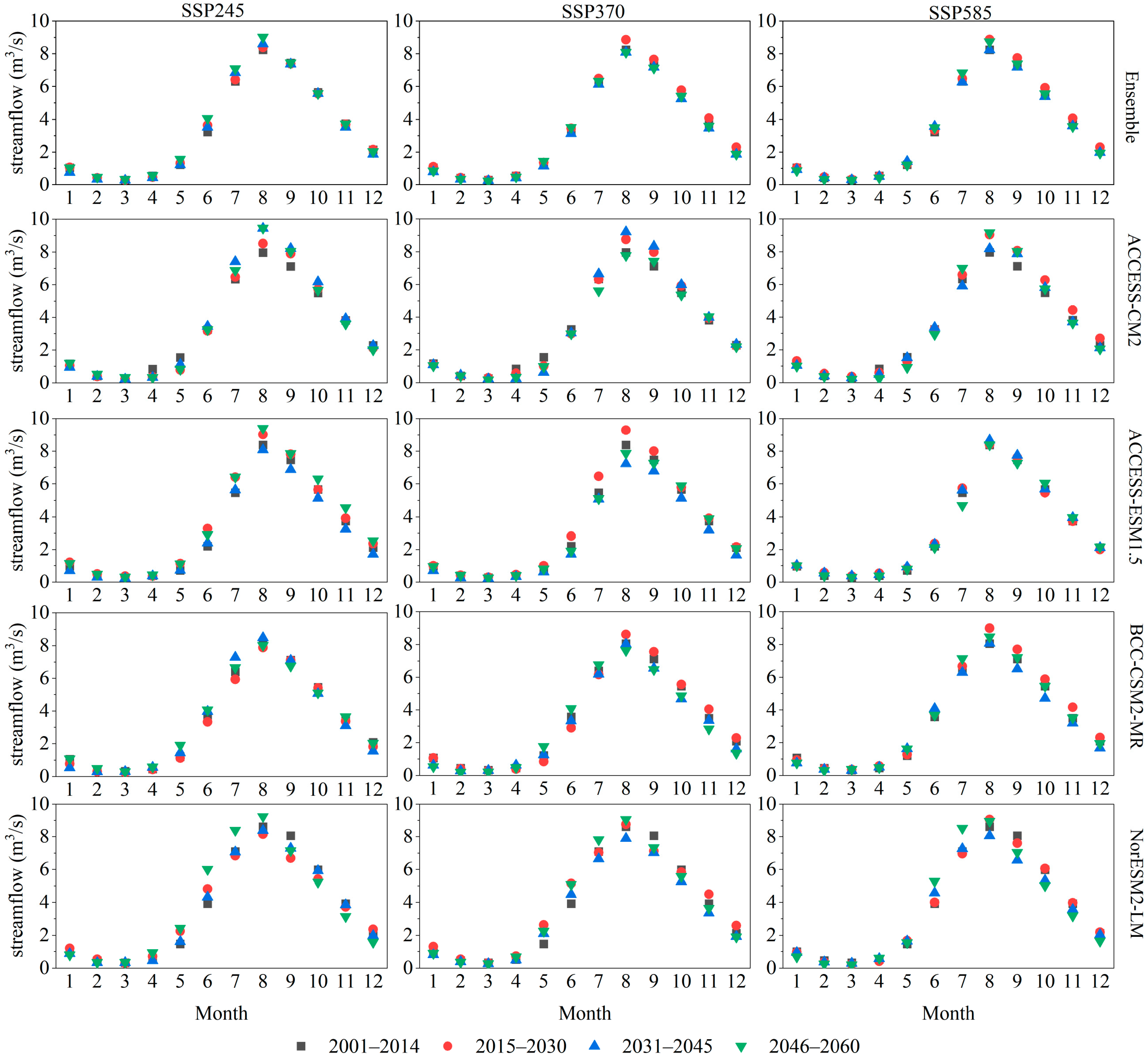
3.3.3. Projected Future Streamflow Dynamics
4. Discussion
4.1. Impacts of Land Use Change on Streamflow
4.2. Impacts of Climate Change on Streamflow and Future Hydrological Risks
4.3. Implications for Watershed Management and Sustainability
4.4. Uncertainties and Research Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Peng, P. Spatio-Temporal Changes of Land-Use/Land Cover Change and the Effects on Ecosystem Service Values in Derong County, China, from 1992–2018. Sustainability 2021, 13, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romulo, C.L.; Posner, S.; Cousins, S.; Hoyle Fair, J.; Bennett, D.E.; Huber-Stearns, H.; Richards, R.C.; McDonald, R.I. Global state and potential scope of investments in watershed services for large cities. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, S.; Luo, P.; Xie, D.; Zhu, W. Watershed Ecohydrological Processes in a Changing Environment: Opportunities and Challenges. Water 2022, 14, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P.J.; Williard, K.W.J.; Schoonover, J.E. Fundamentals of Watershed Hydrology. J. Contemp. Water Res. Educ. 2015, 154, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayitesi, N.M.; Guzha, A.C.; Mariethoz, G. Impacts of land use land cover change and climate change on river hydro-morphology—A review of research studies in tropical regions. J. Hydrol. 2022, 615, 128702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R.; et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, K.; Dong, Z. Effects of climate change and human activities on runoff in the Beichuan River Basin in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Catena 2019, 176, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cai, T.; Wen, Q.; Yin, C.; Han, J.; Zhang, Z. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Ecosystem Water Yield Services and Responses to Future Land Use Scenarios in Henan Province, China. Water 2024, 16, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yu, B.; Lintner, B.R.; Findell, K.L.; Zhang, Y. Projected increase in global runoff dominated by land surface changes. Nat. Clim. Change 2023, 13, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Hao, L.; Cao, Z.; Huang, X.; Qin, M.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, G. Combined effects of urbanization and climate change on watershed evapotranspiration at multiple spatial scales. J. Hydrol. 2020, 587, 124869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudin, L.; Salavati, B.; Furusho-Percot, C.; Ribstein, P.; Saadi, M. Hydrological impacts of urbanization at the catchment scale. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, Y.; Tesfamariam, S. Climate Change Impact and Adaptation for Urban Drainage Systems. In Climate Adaptation Engineering; Bastidas-Arteaga, E., Stewar, M.G., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 73–98. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Mohammad Yusoff, W.F.; Mohamed, M.F.; Jiao, S.; Dai, Y. Flood economic vulnerability and risk assessment at the urban mesoscale based on land use: A case study in Changsha, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhou, G.; Bruijnzeel, L.A.; Dai, A.; Wang, F.; Gentine, P.; Zhang, G.; Song, Y.; Zhou, D. Rising rainfall intensity induces spatially divergent hydrological changes within a large river basin. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Cai, Z.; Wu, F.; Jiang, Z.; Pepin, N.; Shen, S.S.P. Temperature dataset of CMIP6 models over China: Evaluation, trend and uncertainty. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 57, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Dong, Z.; Lei, G.; Yu, Z. Effects of land use change on runoff depth in the Songnen Plain, China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Laan, E.; Nunes, J.P.; Dias, L.F.; Carvalho, S.; Mendonca Dos Santos, F. Assessing the climate change adaptability of sustainable land management practices regarding water availability and quality: A case study in the Sorraia catchment, Portugal. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 165438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Song, P.; Hu, X.; Chen, C.; Wei, B.; Zhao, S. Coupled effects of land use and climate change on water supply in SSP–RCP scenarios: A case study of the Ganjiang River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhao, X.; Chen, P.; Zhu, B.; Cai, W.; Wu, W.; Guo, Q.; Iribagiza, M.R. Assessing the effects of combined future climate and land use/cover changes on streamflow in the Upper Fen River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 53, 101853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; He, D.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Sheng, H.; Guo, H.; Zhao, L.; Zou, R. Integrated SWAT model and statistical downscaling for estimating streamflow response to climate change in the Lake Dianchi watershed, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 1193–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Wang, M.; Chang, X.; Gao, W. Response of river-lake hydrologic regimes to local climate change in the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau region, China. Reg. Environ. Change 2020, 20, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Karthikeyan, R.; Bai, Z.; Srinivasan, R. Analysis of streamflow responses to climate variability and land use change in the Loess Plateau region of China. Catena 2017, 154, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Wang, X.; Fu, C. Impacts of land use/land cover and climate change on hydrological cycle in the Xiaoxingkai Lake Basin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 47, 101422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodine, T.G.; Conley, G.; Riihimaki, C.A.; Holland, C.; Beck, N.G. Modeling the impact of future rainfall changes on the effectiveness of urban stormwater control measures. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y. Dynamical downscaling simulation and future projection of precipitation over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 8227–8243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Tan, Z.; He, Q. Physics-Informed Neural Networks of the Saint-Venant Equations for Downscaling a Large-Scale River Model. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2022WR033168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, B.C.; Tebaldi, C.; van Vuuren, D.P.; Eyring, V.; Friedlingstein, P.; Hurtt, G.; Knutti, R.; Kriegler, E.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Lowe, J.; et al. The Scenario Model Intercomparison Project (ScenarioMIP) for CMIP6. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 3461–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.; Miao, C.; Duan, Q.; Tang, Q.; Di, Z.; Liao, W.; Wu, J.; Zhou, R. Sensitivity Analysis-Based Automatic Parameter Calibration of the VIC Model for Streamflow Simulations Over China. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR025968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, S.N.; Khoshravesh, M.; Valashedi, R.N. Assessing the effect of climate and land use changes on the hydrologic regimes in the upstream of Tajan river basin using SWAT model. Appl. Water Sci. 2023, 13, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassman, P.W.; Sadeghi, A.M.; Srinivasan, R. Applications of the SWAT Model Special Section: Overview and Insights. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aredo, M.R.; Hatiye, S.D.; Pingale, S.M. Impact of land use/land cover change on stream flow in the Shaya catchment of Ethiopia using the MIKE SHE model. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deen, T.A.; Arain, M.A.; Champagne, O.; Chow-Fraser, P.; Martin-Hill, D. Impacts of climate change on streamflow in the McKenzie Creek watershed in the Great Lakes region. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1171210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daba, M.H.; You, S. Quantitatively Assessing the Future Land-Use/Land-Cover Changes and Their Driving Factors in the Upper Stream of the Awash River Based on the CA–Markov Model and Their Implications for Water Resources Management. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Cao, X.; Huang, L.; Zhu, J. Temporal—Spatial Changes in Vegetation Coverage under Climate Change and Human Activities: A Case Study of Central Yunnan Urban Agglomeration, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, J.; Xiong, J.; Bian, J.; Jin, H.; Cheng, W.; Li, A.; García Mozo, H. Vegetation Change and Its Response to Climate Change in Yunnan Province, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2021, 2021, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio Chaparro Torres, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Lan, Y. Temporal analysis of land degradation and urban expansion in central Yunnan Province using remote sensing for supporting sustainable development goals 11/15. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 163, 112058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Wu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Yang, S. Study on Spatio-Temporal Changes of Land Use Sustainability in Southwestern Border Mountainous Provinces in Recent 20 Years Based on Remote Sensing Interpretation: A Case Study in Yunnan Province, China. Land 2022, 11, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, N.; Song, W.; Ma, J.; Chu, Y. Multi-Source Remote Sensing Analysis of Yilong Lake’s Surface Water Dynamics (1965–2022): A Temporal and Spatial Investigation. Water 2024, 16, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Xiao, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; An, B.; Sun, G.; Cheng, H.; Tang, J.; Li, H. Impact of the evolution of Plateau Lake landscape pattern on ecosystem service value in the Pearl River basin: A case study of Yilong Lake Basin in Yunnan Province, China. Acta Geophys. 2022, 71, 1391–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Li, Q.; Yang, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, J.; Sun, G. Analysis of Landscape Pattern Evolution and Driving Forces Based on Land-Use Changes: A Case Study of Yilong Lake Watershed on Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. Land 2022, 11, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H. Seasonal Water Quality Changes and the Eutrophication of Lake Yilong in Southwest China. Water 2022, 14, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrasher, B.; Wang, W.; Michaelis, A.; Melton, F.; Lee, T.; Nemani, R. NASA Global Daily Downscaled Projections, CMIP6. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.F.; Wang, G.; Silander, J.; Wilson, A.M.; Allen, J.M.; Horton, R.; Anyah, R. Statistical downscaling and bias correction of climate model outputs for climate change impact assessment in the U. S. Northeast. Glob. Planet. Change 2013, 100, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wei, L.; Tang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, T.; Lv, T. Future changes in extremes across China based on NEX-GDDP-CMIP6 models. Clim. Dyn. 2024, 62, 9587–9617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, T. Improving simulations of extreme precipitation events in China by the CMIP6 global climate models through statistical downscaling. Atmos. Res. 2024, 303, 107344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Gao, X.; Han, Z.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Giorgi, F. Bias correction of temperature and precipitation over China for RCM simulations using the QM and QDM methods. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 57, 1425–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Moriasi, D.N.; Gassman, P.W.; Abbaspour, K.C.; White, M.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Santhi, C.; Harmel, R.D.; van Griensven, A.; Liew, M.W.V.; et al. SWAT: Model Use, Calibration, and Validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1491–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Fu, Z. A coupling simulation and optimization method developed for environmental-economic management of Lake watershed. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 318, 115546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavilán, P.; Lorite, I.J.; Tornero, S.; Berengena, J. Regional calibration of Hargreaves equation for estimating reference ET in a semiarid environment. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 81, 257–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosznay, M. Generalization of SCS Curve Number Method. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1989, 115, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharki, S.; Taia, S.; Arjdal, Y.; Hack, J. Hydrological modeling of spatial and temporal variations in streamflow due to multiple climate change scenarios in northwestern Morocco. Clim. Serv. 2023, 30, 100388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Gitau, M.W.; Pai, N.; Daggupati, P. Hydrologic and Water Quality Models: Performance Measures and Evaluation Criteria. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1763–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Fu, Z.; Ji, Y.; Zhou, J. A spatiotemporal optimization method for nutrient control in lake watersheds. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, K.P.; Mukherjee, S.; Mishra, A.K.; Mann, M.E.; Williams, A.P. Climate change will accelerate the high-end risk of compound drought and heatwave events. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2219825120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, M.; Liang, Z.; Zhou, Q. Identification of Regime Shifts and Their Potential Drivers in the Shallow Eutrophic Lake Yilong, Southwest China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, T.G. Atmospheric circulation as a source of uncertainty in climate change projections. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Krysanova, V.; Benestad, R.E.; Hov, Ø.; Piniewski, M.; Otto, I.M. Uncertainty in climate change impacts on water resources. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 79, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Libera, D.A.; Kheimi, M.; Sankarasubramanian, A.; Wang, D. The Roles of Climate Forcing and Its Variability on Streamflow at Daily, Monthly, Annual, and Long-Term Scales. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR027111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Mahmud, I. pyMannKendall: A python package for non parametric Mann Kendall family of trend tests. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwarakish, G.S.; Ganasri, B.P.; De Stefano, L. Impact of land use change on hydrological systems: A review of current modeling approaches. Cogent Geosci. 2015, 1, 1115691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sun, Y.; Yuan, W.; Lyu, S.; Wan, F. Streamflow responses to climate change and LUCC in a semi-arid watershed of Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Arid Land 2017, 9, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, I.; Mujumdar, P.P. Isolating the impacts of land use and climate change on streamflow. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 3633–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achugbu, I.C.; Olufayo, A.A.; Balogun, I.A.; Dudhia, J.; McAllister, M.; Adefisan, E.A.; Naabil, E. Potential effects of Land Use Land Cover Change on streamflow over the Sokoto Rima River Basin. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtar, A.; He, H.; Alsafadi, K.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Keo, S.; Bai, C.; Abuarab, M.; Zhang, C.; Elbagoury, K.; et al. Evapotranspiration as a response to climate variability and ecosystem changes in southwest, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Gao, W.; Chang, X. Predicting hydrological alterations to quantitative and localized climate change in plateau regions: A case study of the Lake Dianchi Basin, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2021, 36, 969–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Luo, L.; Pan, M.; He, F.; Luo, C.; Meng, D.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Gong, F.; Wu, G.; et al. Estimations of Water Volume and External Loading Based on DYRESM Hydrodynamic Model at Lake Dianchi. Water 2022, 14, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Khoury, I.; Boithias, L.; Labat, D. A Review of the Application of the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) in Karst Watersheds. Water 2023, 15, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Land Use/Land Cover Categories in Data Source | Land Use Types Defined in Data Source | Land Use Types Defined in SWAT Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Codes | Types | Codes | SWAT LULC Description | |
| Farmland | 011 | paddy field | RICE | rice |
| 012 | irrigated field | CANA | spring canola, argentine | |
| 013 | non-irrigated field | CORN | corn | |
| Garden land | 021 | orchard | ORCD | orchard |
| 022 | tea garden | ORCD | orchard | |
| 023 | other garden | ORCD | orchard | |
| Forest | 031 | woodland | PINE | pine |
| 032 | shrub land | RNGB | range, brush | |
| 033 | other forest | FRSD | forest, deciduous | |
| Grassland | 043 | other grass | HAY | hay |
| Transportation | 101 | railway land | UTRN | transportation |
| 102 | highway land | UTRN | transportation | |
| 104 | rural roads | UTRN | transportation | |
| Water and utilities | 111 | river | WATR | water |
| 112 | lake | WATR | water | |
| 113 | reservoir | WATR | water | |
| 114 | pond | WATR | water | |
| 116 | tidal flat | WATR | water | |
| 117 | ditch | WATR | water | |
| 118 | hydraulic construction land | UINS | institutional | |
| Other | 122 | facility agricultural land | UINS | institutional |
| 127 | barren | BARR | barren | |
| Residential land | 202 | town | URMD | residential medium density |
| 203 | village | URLD | residential low density | |
| Mining land | 204 | mining land | UIDU | industrial |
| Public administration and public service land | 205 | scenic spots and special sites | UINS | institutional |
| No. | Model | Developed Country | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ACCESS-CM2 | Australia | 1.875° × 1.25° |
| 2 | ACCESS-ESM1.5 | Australia | 1.875° × 1.25° |
| 3 | BCC-CSM2-MR | China | 1.1250° × 1.1250° |
| 4 | NorESM2-LM | Norway | 1.0° × 1.0° |
| Data Type | Data Period | Resolution/Scale | Data Source | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| dem | - | 2.5 m (grid) | multi-source remote sensing image fusion | Yunnan Geological Data Center |
| land cover/land use data | 2010 | 1:10,000 | the 2nd national land resource survey with correction | Yunnan Geological Data Center |
| 2020 | 1:5000 | the 3rd national land resource survey with correction | ||
| soil data | - | 1000 m (grid) | Chinese Soil Dataset based on the World Soil Database (HWSD) (v1.1) | National Cryosphere Desert Data Center (https://www.ncdc.ac.cn/portal/metadata/a948627d-4b71-4f68-b1b6-fe02e302af09, accessed on 10 April 2022) |
| historical meteorological data (precipitation, average temperature, maximum temperature, and minimum temperature) | 1990–2020 | daily | Shiping Meteorological Ground Station | Meteorological Bureau of Shiping County |
| projected meteorological data (daily humidity, daily precipitation, daily averaged surface wind speed, daily mean temperature, daily maximum temperature, and daily minimum temperature) | 2000–2060 | daily | NEX-GDDP-CMIP6 dataset | NASA Center for Climate Simulation (https://www.nccs.nasa.gov/services/data-collections/land-based-products/nex-gddp-cmip6, accessed on 8 May 2024) |
| historical streamflow data | 2009–2018 | monthly | Cheng River (CR) gauge station | Shiping Water Authority |
| water system’s shape file (major reservoirs, ponds, and ditches) | - | - | local survey | Yunnan Geological Data Center |
| Parameter | p-Value | t-Stat | Method | Initial Range | Fitted Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R_CN2.mgt | 0.002 | 6.879 | R_relative | −0.5…0.5 | −0.23 |
| V_ALPH_BF.gw | 0.008 | −3.480 | V_replace | 0…1 | 0.21 |
| V_GW_DELAY.gw | 0.070 | 1.871 | V_replace | 30…300 | 172 |
| V_GWQMN.gw | 0.882 | 0.164 | V_replace | 0…5 | 3.63 |
| V_GW_REVAP.gw | 0.853 | −0.230 | V_replace | 0.02…0.2 | 0.145 |
| V_ESCO.hru | 0.534 | −0.591 | V_replace | 0…0.5 | 0.028 |
| V_CH_N2.rte | 0.027 | 2.298 | V_replace | 0…0.3 | 0.134 |
| V_CH_K2.rte | 0.483 | 0.722 | V_replace | 5…200 | 187 |
| R_SOL_AWC.sol | 0.070 | 1.904 | R_relative | 0…1 | 0.41 |
| R_SOL_K.sol | 0.437 | 0.821 | R_relative | 0…3 | 0.97 |
| V_SURLAG.bsn | 0.193 | 1.313 | V_replace | 0.05…24 | 20.36 |
| R_SOL_Z.sol | 0.576 | 0.558 | R_relative | −0.5…5 | 4.13 |
| V_EPCO.hru | 0.147 | 1.445 | R_relative | −0.5…0.5 | −0.29 |
| GCMs | Statistic Indexes | SSP245 | SSP370 | SSP585 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACCESS-CM2 | Mean value (°C) | 9.79 | 9.89 | 9.95 |
| Trend (°C/year) | +0.043 | +0.054 | +0.044 | |
| Standard deviation (°C) | 0.68 | 0.71 | 0.88 | |
| Coefficient of variation | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.09 | |
| ACCESS-ESM1.5 | Mean value (°C) | 9.74 | 9.62 | 10.01 |
| Trend (°C/year) | +0.040 | +0.060 | +0.045 | |
| Standard deviation (°C) | 0.62 | 0.74 | 0.89 | |
| Coefficient of variation | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.09 | |
| BCC-CSM2-MR | Mean value (°C) | 9.22 | 9.28 | 9.35 |
| Trend (°C/year) | +0.035 | +0.046 | +0.040 | |
| Standard deviation (°C) | 0.55 | 0.60 | 0.68 | |
| Coefficient of variation | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07 | |
| NorESM2-LM | Mean value (°C) | 8.77 | 8.66 | 9.09 |
| Trend (°C/year) | +0.025 | +0.034 | +0.022 | |
| Standard deviation (°C) | 0.60 | 0.54 | 0.75 | |
| Coefficient of variation | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.08 |
| GCMs | Statistic Indexes | SSP245 | SSP370 | SSP585 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACCESS-CM2 | Mean value (mm/year) | 1093 | 1069 | 1098 |
| Trend (mm/year) | +1.912 | −1.093 | −1.24 | |
| Standard deviation (mm) | 112 | 103 | 128 | |
| Coefficient of variation | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.12 | |
| ACCESS-ESM1.5 | Mean value (mm/year) | 1058 | 999 | 1030 |
| Trend (mm/year) | +1.617 | +0.014 | −1.54 | |
| Standard deviation (mm) | 145 | 128 | 162 | |
| Coefficient of variation | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.16 | |
| BCC-CSM2-MR | Mean value (mm/year) | 1058 | 1037 | 1089 |
| Trend (mm/year) | +1.641 | +0.582 | −0.38 | |
| Standard deviation (mm) | 98 | 108 | 124 | |
| Coefficient of variation | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.11 | |
| NorESM2-LM | Mean value (mm/year) | 1080 | 1104 | 1082 |
| Trend (mm/year) | +0.012 | −0.564 | −0.60 | |
| Standard deviation (mm) | 141 | 167 | 162 | |
| Coefficient of variation | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| SSP | GCMs | 2001–2060 | 2015–2030 | 2031–2045 | 2046–2060 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zc | p | Trend | Zc | p | Trend | Zc | p | Trend | Zc | p | Trend | ||
| SSP245 | ACCESS-CM2 | 1.97 | 0.05 | ↑ | 1.58 | 0.11 | - | 0.89 | 0.37 | - | −1.39 | 0.17 | - |
| ACCESS-ESM1.5 | 0.52 | 0.60 | - | −1.17 | 0.24 | - | 0.00 | 1.00 | - | 1.98 | 0.05 | ↑ | |
| BCC-CSM2-MR | 0.43 | 0.66 | - | −0.54 | 0.59 | - | 0.00 | 1.00 | - | −1.98 | 0.05 | ↓ | |
| NorESM2-LM | 1.20 | 0.23 | - | 1.13 | 0.26 | - | 0.00 | 1.00 | - | −0.79 | 0.43 | - | |
| Ensemble | 1.42 | 0.16 | - | 0.45 | 0.65 | - | 0.20 | 0.84 | - | −0.45 | 0.66 | - | |
| SSP370 | ACCESS-CM2 | 0.94 | 0.35 | - | 1.67 | 0.10 | ↑ | −0.59 | 0.55 | - | −0.40 | 0.69 | - |
| ACCESS-ESM1.5 | −0.96 | 0.34 | - | −0.05 | 0.96 | - | −0.74 | 0.46 | - | 0.69 | 0.49 | - | |
| BCC-CSM2-MR | −1.82 | 0.07 | ↓ | 0.81 | 0.42 | - | −1.19 | 0.24 | - | 0.25 | 0.80 | - | |
| NorESM2-LM | −0.93 | 0.36 | - | 0.95 | 0.34 | - | −1.98 | 0.05 | ↓ | −0.50 | 0.62 | - | |
| Ensemble | −0.40 | 0.16 | - | 1.44 | 0.15 | - | −2.33 | 0.02 | ↓ | 0.15 | 0.88 | - | |
| SSP585 | ACCESS-CM2 | 0.61 | 0.55 | - | 0.68 | 0.50 | - | 1.93 | 0.05 | ↑ | −1.39 | 0.17 | - |
| ACCESS-ESM1.5 | −0.23 | 0.82 | - | −1.35 | 0.18 | - | −0.99 | 0.32 | - | −0.89 | 0.37 | - | |
| BCC-CSM2-MR | 0.46 | 0.65 | - | 3.11 | 0.00 | ↑ | 0.05 | 0.96 | - | 1.24 | 0.22 | - | |
| NorESM2-LM | −0.96 | 0.34 | - | −1.67 | 0.10 | ↓ | 1.54 | 0.13 | - | 1.73 | 0.08 | ↑ | |
| Ensemble | −0.37 | 0.71 | - | 0.63 | 0.53 | - | 1.98 | 0.05 | ↑ | −0.10 | 0.92 | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, Z.; Wu, Y.; He, W.; She, N.; Shao, H.; Fan, C. Temporal Hydrological Responses to Progressive Land Cover Changes and Climate Trends in a Plateau Lake Basin in Southwest China. Water 2025, 17, 1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131890
Bao Z, Wu Y, He W, She N, Shao H, Fan C. Temporal Hydrological Responses to Progressive Land Cover Changes and Climate Trends in a Plateau Lake Basin in Southwest China. Water. 2025; 17(13):1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131890
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Zhengduo, Yuxuan Wu, Weining He, Nian She, Hua Shao, and Chao Fan. 2025. "Temporal Hydrological Responses to Progressive Land Cover Changes and Climate Trends in a Plateau Lake Basin in Southwest China" Water 17, no. 13: 1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131890
APA StyleBao, Z., Wu, Y., He, W., She, N., Shao, H., & Fan, C. (2025). Temporal Hydrological Responses to Progressive Land Cover Changes and Climate Trends in a Plateau Lake Basin in Southwest China. Water, 17(13), 1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131890






