Abstract
Global warming and intensified human activities increase flood disasters, causing annual casualties and economic losses. Mountain shadows are a major source of interference in floodwater extraction from SAR imagery, severely impacting the accuracy of water body detection. This study proposes an innovative approach based on the Inverted Exponential Shadow Removal Model (IESRM). This model can adaptively and dynamically adjust the slope threshold according to the terrain characteristics. It is easy to use, eliminating the need for manual parameter setting. The experimental results demonstrate the following: (1) Water body detection tests across diverse terrains (mountains, plains, and foothill plains) show robust results even in complex foothill regions, with an overall accuracy of 94.51% and a Kappa coefficient of 0.86. (2) A comparative analysis with the shadow formation mechanism method and the HAND (Height Above Nearest Drainage) method revealed that the inverted exponential function model achieved the highest accuracy, with an overall accuracy of 96.46% and a Kappa coefficient of 0.89. The IESRM provides an innovative solution for removing mountain shadows, enhancing SAR imagery-based flood monitoring in complex terrains. It offers timely and accurate data support for flood disaster management agencies.
1. Introduction
Flood disasters rank among the top ten natural disasters globally and are the most impactful disasters to the affected population [1,2,3,4]. Flood disasters also hold the highest frequency and fatality rates worldwide [5,6,7]. In 2024, China experienced frequent extreme weather events, particularly heavy rainfall-induced floods, which caused severe destruction to social and economic systems. According to data released by the National Disaster Reduction Committee and the Ministry of Emergency Management, the national average precipitation in the first half of 2024 reached 316.9 mm, exceeding the historical average by 13.9%. During this period, nineteen regional heavy rainfall events occurred, characterized by both high frequency and extremity, leading to widespread flooding across multiple areas. These floods affected a total of 14.34 million people, resulting in 230 fatalities or disappearances, the emergency relocation of 742,000 individuals, the collapse of 21,000 houses, and damage to 1.33 million hectares of croplands. The direct economic losses were estimated at CNY 59.2 billion. Under these severe circumstances, developing accurate and efficient flood disaster monitoring systems and enhancing emergency response capabilities are crucial for mitigating the impacts of such disasters.
Remote sensing, particularly synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imagery, has been extensively utilized for flood monitoring due to its resilience under all-weather conditions [8,9]. However, mountain shadows in SAR imagery exhibit weak reflectance characteristics similar to water bodies, leading to spectral confusion and misclassification [8,10]. As tourism grows, mountainous regions have increasingly become a crucial pillar of economic development [11]. Simultaneously, the rapid expansion of the photovoltaic industry has led to increasing land use constraints, resulting in the widespread siting of photovoltaic power stations in mountainous and hilly areas, particularly in southwestern China [12]. Once these regions experience flood disasters, the resulting damage and losses can be immeasurable. Therefore, efficiently removing mountain shadows from SAR imagery while preserving the integrity of mountainous water body information remains a critical challenge in flood monitoring. To address this issue, numerous researchers have explored various methods for mountain shadow removal [13]. The use of auxiliary information from topographic data, such as Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) [14], to remove mountain shadows in the preprocessing or postprocessing stages of flood detection has seen widespread application. Commonly used methods include the shadow formation mechanism, the HAND (Height Above Nearest Drainage) model, and the slope threshold method.
The shadow formation mechanism method simulates mountain shadow regions based on SAR radar imaging geometric parameters (such as satellite orbit azimuth and incidence angle) and DEM data and subsequently removes them [15]. Although this method is grounded in imaging principles and offers certain theoretical advantages, its application is hindered by the need for precise radar imaging parameters and complex mathematical modelling, making its implementation cumbersome [16]. The HAND (Height Above Nearest Drainage) method utilizes DEM data to compute terrain-relative height, effectively masking non-water areas when an appropriate HAND threshold is set [17]. Typically, the HAND threshold is set to 15 m [18], whereas in flat areas, the threshold is generally lower [19]. Furthermore, researchers have attempted to optimize mountain shadow removal by incorporating Digital Surface Model (DSM) data. For example, Chen et al. proposed a method combining topological separation with a DSM-based local search algorithm, effectively eliminating most misclassified areas. However, residual jagged noise remains at the boundaries of certain water body regions [20].
The slope threshold method has been widely applied in mountain shadow removal due to its simplicity and efficiency [14,21,22]. This method calculates slope values from DEM data and sets a predefined threshold to distinguish mountain shadow regions [23]. Among commonly used thresholds, a 5° slope threshold is widely adopted [2,6,24]. However, this threshold varies significantly across different terrain conditions [21]. Liu et al. applied a 10° slope threshold for water body extraction in the Yangtze River Basin [24], whereas Hansana et al. utilized a 3° slope threshold for flood monitoring across the entire territory of Laos [25]. Farhadi et al. conducted a study in Khuzestan Province, Iran, where the slope threshold was gradually increased from 0% to 20% [26]. The accuracy assessment results indicated that a 15% slope threshold (8.53°) was optimal for this study area. Lin et al. conducted a comparative analysis of 5°, 10°, and 15° slope thresholds across different terrain complexities, including plains, mountainous areas, and mixed terrains. The results demonstrated that the 5° slope threshold effectively removed mountain shadows and improved water body extraction accuracy in mountainous and mixed-terrain regions. However, it also led to the misclassification of 17% of actual water bodies [27].
Overall, existing mountain shadow removal methods have improved the accuracy of water body extraction in SAR imagery to a certain extent. However, they still face challenges such as complex processing workflows, high user dependency [28], and the erroneous removal of mountainous water bodies due to fixed threshold settings, which introduce systematic misclassification errors in mountainous regions during flood disaster monitoring [24]. For instance, these limitations hinder disaster assessment in mountainous tourist areas and photovoltaic infrastructure sites [11]. Given these limitations, further optimization of mountain shadow removal methods is necessary.
This study proposes an improvement based on the slope threshold method, developing a classification model using the elevation–slope characteristics of water body and shadow samples. To achieve dynamic threshold segmentation, the inverted exponential function is introduced, resulting in the Inverted Exponential Shadow Removal Model (IESRM). Compared to conventional slope threshold methods, which rely on fixed or empirical slope thresholds, the IESRM adaptively adjusts the classification threshold as a function of elevation, thereby improving adaptability across complex terrains. Building on this foundation, the IESRM also differs significantly from other mainstream shadow removal approaches such as the HAND model and the shadow formation mechanism. It avoids extensive parameter tuning, manual threshold setting, and reliance on multiple software tools. Instead, it supports fully automated and lightweight deployment directly on the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform using globally available DEM data. These innovations collectively improve both the classification accuracy and the operational efficiency of flood monitoring in mountainous areas. IESRM application code in GEE is available at https://github.com/Aces14222/IESRM-Application-Code (accessed on 13 May 2025). The main objectives of this study include the following:
- Adaptive Thresholding: The model applies dynamic threshold segmentation for slope values, enhancing its adaptability across different terrain conditions.
- Efficiency and Simplicity: The model operates efficiently on the GEE platform, enabling rapid execution to support timely flood disaster response.
- Water Body Integrity: The method effectively removes mountain shadows while preserving mountainous water bodies, making it suitable for flood monitoring in mountainous regions.
2. Study Area and Dataset
2.1. Study Area
This study focuses on the Mentougou and Fangshan Districts in Beijing and Zhuozhou City in Hebei Province, situated at the junction of the northwestern North China Plain and the foothills of the Taihang Mountains. Mentougou, situated to the west of Beijing, is characterized by a chain of interconnected mountains. Fangshan, in southwestern Beijing, features undulating terrain with middle and low mountains, as well as hilly terrain in the northwest, transitioning into flat alluvial plains in the southeast. Zhuozhou, situated at the foot of the Taihang Mountains in northeastern Hebei, has a predominantly flat terrain that gently slopes from northwest to southeast [29].
From 29 July to 9 August 2023, this region experienced severe flooding caused by the combined influence of Typhoon Doksuri and contrasting air masses [8]. The diverse topographic features of the area, such as ruggedness and relief, facilitates rapid water convergence following rainfall, thereby exacerbating the risks of flooding and increasing the potential for misclassification between water bodies and mountain shadows in SAR imagery [30]. Consequently, this region serves as an ideal experimental site for assessing the efficacy of mountain shadow removal methods in flood-prone areas. The location and topographic features of the study area are shown in Figure 1.
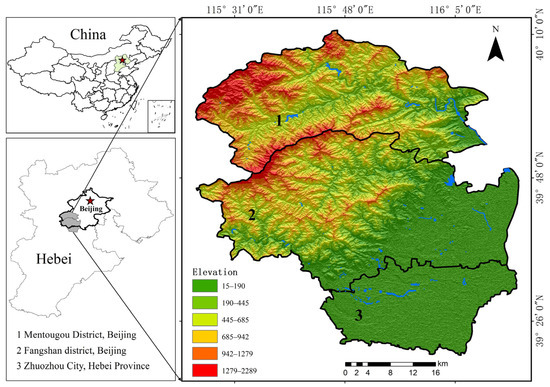
Figure 1.
Study area.
2.2. Dataset
In model construction and its application, this study utilized Sentinel-1 data with VV and VH polarizations, acquired on 5 August 2023, during the flooding period. The imagery has a spatial resolution of 10 m and was accessed through the GEE platform. Preprocessing steps, including thermal noise removal, radiometric calibration, and terrain correction, were automatically applied within the GEE platform, reducing the need for manual intervention [31]. This study utilizes Sentinel-2 imagery, specifically the Red (B4), Green (B3), and Blue (B2) bands, each with a spatial resolution of 10 m [26]. To ensure the temporal consistency and quality of the selected Sentinel-2 imagery, data acquired after August 5th was chosen, with cloud coverage below 20% (acquisition date: 15 August).
For terrain data, this study employed the DEM from the SRTM dataset, with an original spatial resolution of 30 m, also accessed through GEE. To ensure resolution consistency across datasets, the DEM data was resampled to a 10-m resolution using bilinear interpolation, and all data were reprojected to the GCS_WGS_1984 coordinate system [32]. An overview of all datasets, including their source, resolution, acquisition date, and usage, is summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Overview of datasets used in this study.
3. Methodology
The technical workflow of this study is shown in Figure 2. Data retrieval and processing were completed on the GEE platform. The scatter plot of sample points was generated using the Matplotlib library (version 3.7.1) in a Python environment (version 3.10). The model construction process is highlighted in blue in the figure. The following section will provide a detailed description of the model construction process.
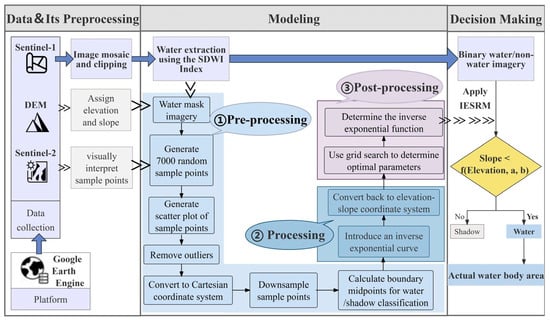
Figure 2.
Workflow.
3.1. Pre-Processing
3.1.1. Sample Point Generation
Sentinel-1 SAR imagery was utilized in this study to extract water bodies using the Sentinel-1 Dual-Polarized Water Index (SDWI). The SDWI enhances water body detection by calculating the difference between the dual-polarized VV and VH backscatter data from Sentinel-1 [33]. The mathematical formulation of the SDWI is expressed as follows.
Here, VH and VV represent the dual-polarized backscatter data from Sentinel-1, and SDWI is the result of the mathematical band operation. This operation generates a binary map distinguishing water bodies from non-water areas [22]. A mask was generated based on the water body areas delineated using the SDWI index. Using this mask, 7000 random sample points were generated. Additionally, DEM data retrieved from GEE was used to calculate slope values, which, along with elevation values, were assigned as attributes to these sample points. To ensure the robustness and generalizability of the boundary function model, the sample points were carefully distributed across diverse terrain types, including plains, hills, mid-low mountains, and high mountains [34]. All sample points were manually interpreted to determine whether each point represented an actual water body or mountain shadow, and they were subsequently labelled. A total of 5263 mountain shadow points and 1737 water body points were identified through visual interpretation. The visualization of these sample points is shown in Figure 3a.
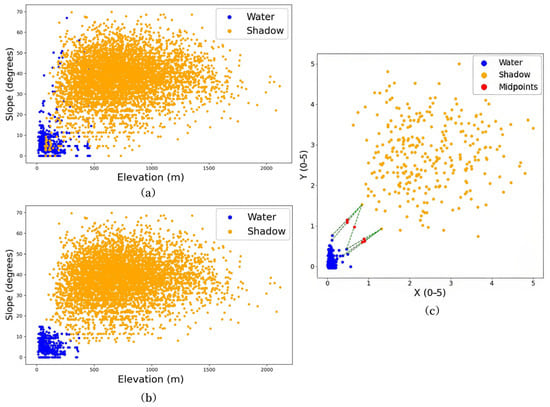
Figure 3.
Pre-processing of model training samples. (a) Distribution of water and shadow sample points in the elevation–slope space. (b) Sample distribution after outlier removal. (c) Extraction of midpoints between water and shadow samples after down-sampling and Cartesian coordinate transformation.
3.1.2. Removal of Outliers in Sample Points
During the visual interpretation of sample points, slope calculations were influenced by measurement errors and spatial resolution limitation of SRTM data, resulting in the presence of outliers. These outliers were primarily attributed to inaccuracies in manual interpretation. Such errors, often random in nature, introduced deviations from the expected normality in the data distribution [35]. To address this issue, the interquartile range (IQR) method, a robust and widely used approach for outlier detection in non-normally distributed data, was employed to identify and remove these anomalies from the scatter plot [36].
The IQR method is particularly effective against extreme values and is straightforward to implement. In this study, more conservative thresholds were applied, setting the first quartile (Q1) at 10% (0.1) and the third quartile (Q3) at 90% (0.9). This adjustment accounted for the distinct distribution characteristics of the two sample categories: water body samples were predominantly concentrated in areas with low elevation and slope, whereas shadow samples exhibited more skewed distribution. Using traditional IQR parameters might misclassify numerous valid data points as outliers [37]. After outlier removal using the interquartile range (IQR) method, some shadow points in low-elevation, low-slope areas remained confused with water body points. These shadow points were manually excluded. A total of 42 sample points were removed, including 11 water body sample points and 31 mountain shadow sample points. The distribution of sample points after outlier removal is illustrated in Figure 3b.
3.1.3. Coordinate System Transformation and Calculation of Boundary Midpoints
To better fit the classification boundary, this study calculated the boundary midpoints between two classes of sample points to determine the parameter range of the inverted exponential function. Due to the large size of the sample point set after outlier removal, it was impractical to calculate the boundary midpoints for all points directly. Therefore, down-sampling was performed to reduce the computational complexity [38].
The elevation–slope coordinate system was converted to a planar Cartesian system to facilitate mathematical operations, under the condition that the spatial positions of the sample points remained unchanged. This transformation was necessary because midpoints calculated using the distance formula in the elevation–slope coordinate system do not accurately reflect the classification boundary between the two classes of sample points. Specifically, the transformation was implemented in two steps. First, the coordinate range of the water body points was computed and then expanded to include the range of shadow points, ensuring that all data points were contained within a unified global coordinate frame. Second, a linear mapping function was defined to convert values from the original range to a Cartesian coordinate system. This mapping preserved the order and relative positions of the original points by applying proportional scaling and translation, effectively enabling accurate and efficient computation of midpoints based on Euclidean geometry. This approach avoids distortion that may arise from nonlinearities in the elevation–slope space and ensures that boundary fitting is conducted under geometrically consistent assumptions.
In the new coordinate system, each sample point was assigned new coordinates, and the Euclidean distance formula was used to calculate all distances between pairs of points from the two classes. To balance representativeness and computational efficiency, six nearest sample point pairs were selected. These calculated boundary midpoints were then used to construct the boundary function model, providing initial conditions for function fitting and ensuring the accurate delineation of mountain shadow and water body regions. Figure 3c illustrates the midpoints between water and shadow samples.
3.2. Processing
Building on previous studies that used a 5° slope or other linear functions, this study introduces the inverted exponential function, which offers superior fitting accuracy for distinguishing mountain shadows from water bodies. The form and mathematical expression of the inverted exponential function are illustrated in Figure 4. We observed that the boundary between water and mountain shadow samples exhibits a naturally decaying trend: as elevation increases, the slope threshold required to differentiate shadow regions gradually decreases. This decaying relationship can be effectively represented by the concave shape of the inverted exponential function. In addition, the two parameters of the function, a and b, play a key role in shaping the threshold boundary. Their definitions and implications are detailed below.
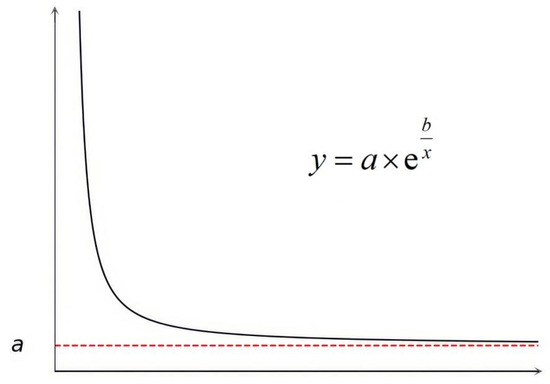
Figure 4.
The shape and expression of the inverted exponential function, with the red dashed line indicating its horizontal asymptote.
Parameter a determines the final horizontal position of the inverted exponential function curve, with y asymptotically approaching a as x approaches infinity, forming a horizontal asymptote. This characteristic reflects the existence of a slope threshold in the inverted exponential function (in the elevation–slope coordinate system), as shown by the red dashed line in Figure 4. This feature effectively simulates the gradual disappearance of mountain shadows in low-slope areas, drawing on existing slope threshold methods [39].
Parameter b, on the other hand, controls the rate at which the function decays. Larger values of b result in a faster decay of the curve at smaller x values. Given that slope values do not exceed 90°, the x-value in the inverted exponential function will not drop below a specific limit. This introduces an elevation threshold, ensuring that mountain shadows below this threshold are not misclassified as water bodies. This behavior aligns with the observation that mountain shadows are absent in low-altitude areas, such as plains [40].
Compared to existing slope threshold methods, which use linear functions, the concave shape of the inverted exponential function provides a more precise boundary for distinguishing water bodies from mountain shadows. The coordinate system is reverted to the elevation–slope system, and the down-sampled points are restored, preparing for the next step of optimizing parameters a and b.
3.3. Post-Processing
Grid search is a systematic method for hyperparameter optimization, widely utilized in machine learning and statistical modelling [41]. Its core principle involves discretizing the model’s hyperparameters and exhaustively searching through a predefined parameter grid to identify the optimal parameter combination [42].
In this study, grid search was applied to optimize the two critical parameters, a and b, of the inverted exponential function [43]. The search ranges for these parameters were defined as a ∈ [3, 5] and b ∈ [150, 180]. These ranges were not arbitrarily assigned but were systematically derived based on the calculated classification midpoints, which were used to fit the inverted exponential function curve and determine the upper and lower bounds for parameters a and b. To enhance precision, the range values were subsequently refined and finalized using a tail removal rounding method.
The defined intervals [3, 5] and [150, 180] were linearly divided to generate a set of candidate parameter values. Each candidate parameter pair was then evaluated using a classification rule: if the slope value (slope) of a sample exceeds the function value f (Elevation, a, b), it was classified as shadow (label 1); otherwise, it was classified as water (label 0). For each parameter combination, the classification results were compared to the true labels, and the accuracy metrics were computed to assess the classification performance. The parameter pair that yielded the highest accuracy was selected as the optimal combination, providing the best values for a and b.
3.4. Mountain Shadow Removal and Accuracy Evaluation
The final result of the IESRM is a function. In practical applications, there is no longer a need to use grid search to determine the parameters a and b; instead, the model can be directly applied to identify water bodies and mountain shadows. Specifically, the elevation value of each pixel within the water body regions of the imagery is substituted into the function. If the pixel’s slope value exceeds the function value f (Elevation, a, b), the pixel is identified as a mountain shadow and classified as a non-water region.
This study employed a confusion matrix to validate the accuracy of the final water body extraction imagery. Evaluation metrics derived from the confusion matrix included overall classification accuracy, producer’s accuracy, user’s accuracy, and the Kappa coefficient. The flood mapping results were assessed for accuracy using sample point data obtained through visual interpretation of optical imagery [44].
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Results and Analysis of the IESRM
4.1.1. Results of the IESRM
The optimal parameters identified using the grid search method were a = 4.16 and b = 170.00, leading to the establishment of the following optimal model, where x denotes the elevation (in meters) and y represents the dynamic slope threshold (in degrees):
This inverse exponential function strictly decreases with respect to elevation, indicating that the slope threshold for removing mountain shadows becomes progressively lower at higher elevations. Figure 5 illustrates how the proposed model effectively captures the spatial distribution patterns of water bodies and mountain shadows within the slope-elevation domain. The model’s primary strength lies in its ability to dynamically adjust the segmentation threshold through an exponential function, effectively mitigating the influence of mountain shadows. Specifically, when the slope reaches 90°, the elevation threshold is approximately 55.31 m. Under the practical assumption that slopes exceeding 90° are unrealistic, the model inherently excludes mountain shadows below an elevation of 55.31 m. This finding aligns with natural geographical principles, as low-altitude regions generally lack the conditions necessary to form extensive mountain shadows [45].
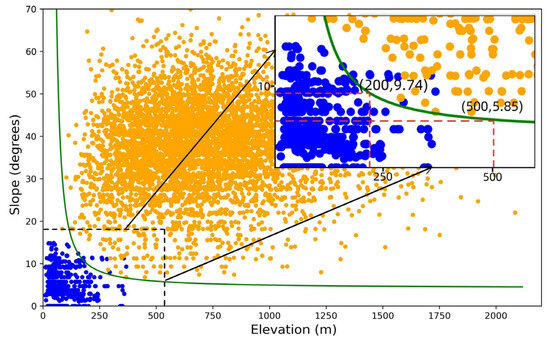
Figure 5.
Results of the IESRM model and its dynamic threshold segmentation.
As the elevation increases to x = 200 m, the terrain transitions from plains to hills, and the conditions for excluding mountain shadows become increasingly stringent due to the rising complexity of the topography. At this elevation, the slope threshold dynamically decreases to approximately y = 9.74° [24]. Subsequently, when the elevation increases to x = 500 m, the terrain transitions into the foothill region, where water bodies and mountain shadows are most likely to be confused. At this point, the slope threshold is y ≈ 5.85°, and this conservative slope threshold helps reduce the misclassification of water bodies. As the elevation reaches x = 1000 m, the threshold y ≈ 4.93°. This threshold closely aligns with the conventional slope threshold of 5° which is commonly adopted in studies of complex terrains [2,14,23,46], thereby validating the model’s adaptability and accuracy in mountainous conditions [47].
Compared to traditional static slope threshold segmentation methods, the proposed model dynamically adjusts the segmentation criteria through an inverted exponential function. This dynamic adjustment enables effective shadow removal across diverse terrain complexities [40]. By demonstrating superior generalizability and applicability [48], the model ensures both accuracy and robustness under varying slope and elevation conditions. As a result, it offers an innovative and effective solution for automating mountain shadow removal in SAR imagery, paving the way for improved flood monitoring.
4.1.2. Accuracy Analysis of the IESRM Training Set
The model achieved a peak accuracy of 98% on the test dataset. As detailed in Table 2, the IESRM successfully classified 1737 water body points and 5263 mountain shadow points, with only a minimal number of misclassified samples. Specifically, 35 mountain shadow points were incorrectly identified as water bodies, while 105 water body points were misclassified as mountain shadows. These results demonstrate the model’s high classification accuracy and model consistency, as further corroborated by its Kappa coefficient of 0.95.

Table 2.
Accuracy metrics for the IESRM on the training dataset.
4.2. Analysis of Mountain Shadow Removal Results in the Study Area
4.2.1. Accuracy Analysis of the IESRM Validation Set
In this study, DEM was first retrieved from the GEE to calculate slope data. The elevation and slope data were then spatially registered with the preliminary flood imagery, and the IESRM was applied for subsequent analysis. The effectiveness of the optimized IESRM in removing mountain shadows was evaluated using Sentinel-2 data acquired on August 15 through manual visual interpretation. A total of 8000 validation sample points were randomly generated across the entire study area to ensure unbiased spatial coverage. These points were manually labeled and divided into two categories: non-water bodies (6341 samples) and water bodies (1660 samples). Among them, 145 non-water samples were misclassified as water, while 138 water samples were incorrectly identified as non-water. The model achieved an overall accuracy of 96.46%, with a Kappa coefficient of 0.98. The detailed accuracy metrics are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Accuracy metrics for the IESRM on the test dataset in the study area under flood scenarios.
For water body classification, the producer’s accuracy was 91.63%, reflecting a high detection capability in water body regions. However, some water bodies were misclassified. In plain areas, due to the imagery being captured during the flood period, the scenes included discontinuous patches of accumulated water, as shown in Figure 6d for plain puddles and highway sample points. These areas were prone to misclassification caused by mixed pixel interference [49]. In mountainous regions, misclassification was more common in river areas. Narrow rivers surrounded by high terrain often experienced SAR signal occlusion due to mountains [3], forcing the estimation of river boundaries based on terrain data. This increased the likelihood of misclassification, as seen in Figure 6c for mountain river sample points [50]. Additionally, the accuracy of the IESRM was limited by the resolution of the SRTM data. Resampled elevation and slope data did not fully match the actual features of water bodies, leading to occasional inaccuracies. By contrast, larger water bodies such as reservoirs and lakes in mountainous regions were less frequently misclassified, as illustrated in Figure 6a.
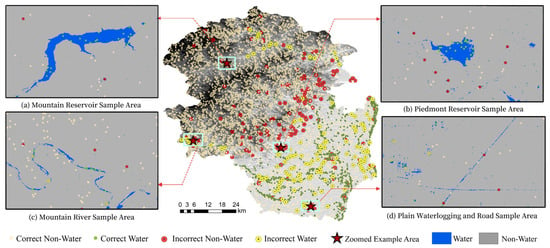
Figure 6.
Spatial distribution of correctly and incorrectly classified water and non-water sample points across the study area, with four representative subregions highlighting common areas of misclassification.
For non-water body classification, the producer’s accuracy reached 97.45%, reflecting a high degree of precision. Misclassification of non-water bodies primarily stemmed from two factors. First, certain features with low radar backscatter signatures, such as highways and building roofs, exhibited specular reflection under specific incident angles, resembling the appearance of water bodies [51]. Highway intersections within plain puddle regions exemplify classic examples of this type of misclassification, as shown in Figure 6d [52]. Additionally, terrain features such as gullies and roads in mountainous regions, which resemble river-like topography, contributed to further misclassification [53]. These errors, often observed as scattered patches in the imagery, are exemplified by reservoir sample points in foothill areas, as shown in Figure 6b.
4.2.2. Accuracy Analysis for Different Terrain
This study selected Mentougou District, Fangshan District, and Zhuozhou City as the study areas due to their typical flood disaster background and complex terrain, with a “half mountainous, half plain” landscape [8]. These diverse topographical conditions provide an ideal experimental scenario for evaluating the accuracy of the IESRM. To further analyze the impact of terrain on the model, separate accuracy evaluations were conducted for each of the three administrative districts, as shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Mentougou District, Fangshan District and Zhuozhou City accuracy assessment comparison table.
The results indicate that terrain characteristics significantly affect classification accuracy. The IESRM displayed notable differences in performance across varying terrain conditions. Specifically, Zhuozhou City, dominated by flat terrain, achieved the highest overall classification accuracy, with a Kappa coefficient of 0.92. This high accuracy is attributed to the flat topography, which minimizes uncertainty factors during classification. In Mentougou District, characterized by mountainous terrain, the model performed exceptionally well in non-water body classification, achieving a producer’s accuracy of 0.99. This result underscores the effectiveness of the IESRM in mitigating the impact of mountain shadows in mountainous regions. In Fangshan District, which features the most complex terrain, the overall accuracy was the lowest among the three areas but still reached 0.95. The primary misclassifications occurred in foothill areas, where the complex topography caused water bodies and mountain shadows to exhibit similar elevation and slope characteristics, leading to classification deviations.
In conclusion, the RESRM demonstrated robust performance across large areas with diverse terrain conditions, maintaining high classification accuracy and showcasing its reliability across various topographical scenarios.
4.3. Quantitative Analysis
To further evaluate the effectiveness of the IESRM in removing mountain shadows, a region measuring 5320 m × 4928 m, located directly west of Mentougou District, was selected for quantitative analysis. This area, characterized by complex terrain and abundant water bodies, provides an ideal setting to demonstrate the model’s effectiveness in mitigating mountain shadow interference in the context of flood disasters. Within this area, 300 random sample points were generated to quantify the model’s performance. The water body extraction results before and after shadow removal were compared, and changes in accuracy metrics were analyzed to assess the model’s impact on improving classification accuracy and enhancing flood monitoring capabilities. The accuracy comparison results are shown in Figure 7.
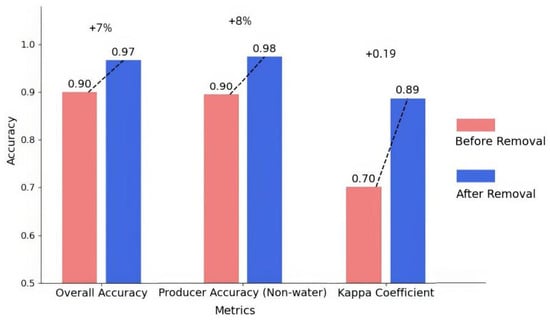
Figure 7.
Accuracy improvement after the application of IESRM.
Before shadow removal, the overall classification accuracy for the selected region was 90%, with a Kappa coefficient of 0.70. After applying the IESRM, these metrics improved significantly to 97% and 0.89, reflecting increases of 7% and 0.19, respectively. These results clearly demonstrate that the IESRM substantially enhances flood monitoring accuracy. Misclassification of non-water bodies in this region was primarily concentrated in areas affected by mountain shadows. The producer’s accuracy for non-water bodies increased from 0.90 to 0.98, further confirming the model’s effectiveness in mitigating mountain shadow interference. As illustrated in Figure 8c, the model’s capability to remove mountain shadows (highlighted in red) is visually apparent and highly effective.
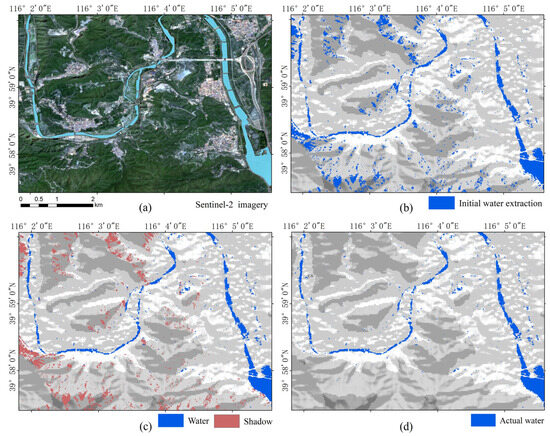
Figure 8.
Quantitative comparison of water body extraction results. (a) Sentinel-2 reference imagery of the study area. (b) Initial water extraction using SDWI from Sentinel-1 imagery. (c) Classification results showing water and misclassified mountain shadow regions before shadow removal. (d) Corrected water body classification after applying the IESRM.
4.4. Comparison of Different Methods
To further validate the efficacy of the IESRM in removing mountain shadows, as well as its prompt responsiveness under rainfall-induced flood conditions, this study compared it with two prevalent and exemplary mountain shadow removal methods: the shadow formation mechanism method and the Height Above Nearest Drainage (HAND) method. To ensure comparability, the three methods were evaluated under identical conditions, including the use of the same flood imagery, DEM dataset, validation sample points, and accuracy metrics (e.g., Kappa, user’s accuracy).
In this study, the core parameters of the shadow formation mechanism method were extracted from Sentinel-1 data files downloaded from the European Space Agency’s website (https://dataspace.copernicus.eu, accessed on 6 November 2024). Specifically, the azimuth <platformHeading> and the incidence angle <incidenceAngleMidSwath> were identified, with values of −13.4552 and 38.9822, respectively. Given that the azimuth in ArcGIS is calculated clockwise from true north with a range of 0–360 degrees [44], the azimuth was converted to approximately 346 degrees, and the elevation angle was approximated to 39 degrees [54]. Using the ‘Hillshade’ tool in ArcGIS 10.6 software, these incidence and azimuth parameters were applied to delineate mountain shadow regions. The simulated mountain shadow regions were then removed using GEE, resulting in the final water body areas [55].
For the HAND method, DEM was used in GEE to calculate flow direction and accumulation, generating river network data and identifying channels within the watershed [28]. Subsequently, the HAND data layer was formulated by calculating the elevation difference of each pixel relative to the nearest river channel based on the DEM [19]. Finally, the application of the HAND method requires a predetermined HAND threshold. In terrains characterized by complexity, the HAND threshold is typically set to 15 m [18,56]. Therefore, this study adopted a HAND threshold of 15 m to exclude areas with high HAND values while retaining water body areas with low HAND values. The ensuing HAND map served as the basis for delineating water bodies after mountain shadow removal.
Three regions with notable mountain shadow noise were selected within the study area as case illustrative regions to compare the efficacy of the three methods. These regions are: Region1, a reservoir nestled amidst mountainous terrain; Region2, the central segment of a mountain river; and Region3, a river in the foothill plain area. The results of the three methods are shown in Figure 9. A direct comparison indicates that the shadow formation mechanism method performs poorly, leaving substantial residual mountain shadows and erroneously removing water bodies. This is primarily due to the mathematical and geometric complexity associated with delineating mountain shadow boundaries utilizing radar imaging parameters and DEM data, which requires detailed calculations of azimuth and incidence angles for each pixel [57]. The method involves extensive computational demands and complex processing procedures, requiring multiple operations such as data downloads, local processing, and reliance on various software tools. According to our testing, executing the full processing pipeline using the shadow formation mechanism required approximately 15–20 min per region, including DEM preprocessing, Sentinel-1 data downloads, radar angle parameter retrieval, and threshold setting, far exceeding the time cost of the other two methods. This reliance on multiple tools significantly reduces processing efficiency, making it unsuitable for rapid response scenarios, particularly in applications like flood disaster management where real-time data processing is critical.
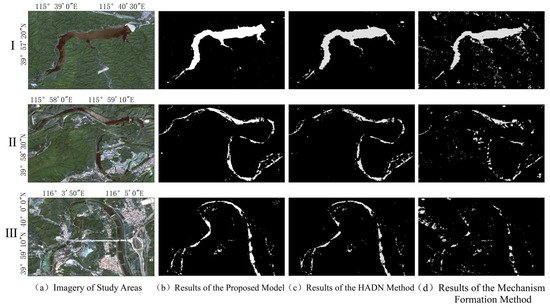
Figure 9.
Comparative analysis of water body extraction results using three different methods. Areas I, II, and III, selected from three representative sections of the Qingshui River in Mentougou District, were used as sampling regions for this comparison. (a) Optical imagery of the three sampling areas. (b) Results of the IESRM. (c) Results of the HAND method. (d) Results of the mechanism formation method.
In contrast, GEE-based methods offer substantial advantages in terms of processing efficiency [58,59,60]. Their cloud-based processing capabilities enable automated computation without the necessity of data downloads or local software installations, significantly reducing data processing time [61,62].
The HAND method, while simple to operate and fully automatable within GEE [61], exhibits limitations in specific scenarios. For example, in Region1, the HAND method inadvertently eliminated water bodies in the northeast corner of the reservoir. Similarly, in Region2, the HAND method removed substantial sections of the river, leaving ‘gaps’ and incomplete river contours. In Region3, however, the HAND method produced relatively ‘clean’ results with minimal residual mountain shadows, demonstrating its effectiveness in mountain shadow removal. Nonetheless, the HAND method primarily considers elevation characteristics, which often leads to the misclassification of water bodies as non-water at the edges of mountainous water bodies, thereby undermining the integrity of water body extraction. Additionally, the threshold-setting procedure for HAND relies heavily on user judgment and experience. This dependency can result in inaccurate threshold selection, leading to misclassification errors that subsequently impair the completeness and accuracy of the extracted water bodies.
In contrast, the IESRM proposed in this study integrates both elevation and slope characteristics. It improves upon fixed slope threshold methods, such as the 5° threshold, by enabling the model to adaptively adjust the threshold based on terrain features. This enhances the model’s adaptability and accuracy in complex terrains, avoiding errors and omissions caused by uniform threshold settings, and thereby effectively preserving the integrity of water bodies in mountainous areas. Furthermore, the application process of the IESRM is straightforward and efficient, significantly reducing user involvement complexity. It requires no parameter or threshold settings, thereby minimizing reliance on user judgment and ensuring consistency and reliability across various application scenarios [63]. This innovation makes the IESRM highly user-friendly and adaptable, providing an innovative and efficient solution for mountain shadow removal.
To further ascertain the comparative performance of the three methods in practical applications, this study conducted an accuracy evaluation of the extraction outcomes. The evaluation confirmed that the proposed inverted exponential function model outperformed the other methods in terms of accuracy. Detailed results are presented in Table 5.

Table 5.
Performance comparison of water body extraction methods based on confusion matrix, accuracy metrics, and Kappa coefficient.
To further evaluate whether the observed differences in classification performance were statistically significant, McNemar’s tests were conducted between the proposed IESRM method and each of the baseline methods. As shown in Table 6, both pairwise comparisons yielded statistically significant results: IESRM vs. HAND (χ2 = 45.31, p < 0.001) and IESRM vs. the shadow formation mechanism (χ2 = 1381.92, p < 0.000001). These results provide robust statistical support for the conclusion that the IESRM method offers a significant improvement in classification accuracy over the baseline approaches.

Table 6.
Results of McNemar’s test comparing classification outcomes between the proposed IESRM method and two baseline methods (HAND and formation mechanism).
5. Conclusions
This study proposes an innovative approach to mountain shadow removal using an inverted exponential function model, based on elevation and slope data samples. The new method allows for the adaptive selection of slope thresholds under different terrain conditions, providing a new solution to the challenge of effectively removing mountain shadows.
The results indicate the following:
- Accuracy evaluations were conducted in three regions with geographically diverse regions (Mentougou District, Fangshan District, and Zhuozhou City). Despite the complex terrain of Fangshan District, which posed significant challenges for shadow removal, the ultimate processing outcomes results were still satisfactory, achieving an overall accuracy and Kappa coefficient of 94.51% and 0.86, respectively. These results underscore the model’s applicability and robustness under complex terrain conditions.
- Compared to the mechanism formation method and the HAND method, the inverted exponential function model demonstrated the superior performance, achieving an overall accuracy and Kappa coefficient of 96.46% and 0.89, respectively. The application of this model to flood disaster detection significantly reduces the interference of mountain shadows.
The IESRM dynamically adjusts segmentation criteria, enabling adaptive threshold settings for terrains ranging from flat to complex, thereby ensuring precise removal of mountain shadows. The principal advantage of this model is its elimination of the need for supplementary parameter settings, significantly reducing reliance on user operations. It is particularly suited for rapid response scenarios in flood disasters. However, inherent limitations exist in this method. The quality of DEM data determines the efficacy of shadow removal using the IESRM model. In this study, the resolution of SAR imagery was higher than that of the DEM data. During image registration and shadow removal in steep slope areas, resampling may have introduced errors. Future research endeavors could enhance the model’s performance by incorporating higher-resolution DEM data or leveraging real-time high-resolution DEMs using interferometric SAR technology [64]. To address this limitation, future research could enhance the model’s performance by incorporating higher-resolution DEMs or integrating with advanced elevation sources such as TanDEM-X or LiDAR-based datasets.
Author Contributions
Methodology, H.S., F.M. and J.L.; validation, F.M. and J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, H.S. and S.W.; writing—review and editing, F.M., J.L. and H.S.; funding acquisition, F.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Shandong Top Talent Special Foundation (grant number 0031504), the Jinan City and University Integration Development Project (grant number JNSX2023065), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 42171113).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the European Space Agency (ESA) for providing free access to Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data and also extend their gratitude to NASA for providing free access to the SRTM data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bhatt, C.M.; Rao, G.S.; Farooq, M.; Manjusree, P.; Shukla, A.; Sharma, S.V.S.P.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Begum, A.; Bhanumurthy, V.; Diwakar, P.G.; et al. Satellite-based assessment of the catastrophic Jhelum floods of September 2014, Jammu & Kashmir, India. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2016, 8, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, E.; Peter, B.G.; Munoz, D.F.; Moftakhari, H.; Moradkhani, H. Fast Flood Extent Monitoring With SAR Change Detection Using Google Earth Engine. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4201419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R. Design optimization of PV power station with complex terrain—A case study of mountain PV project in Shaanxi. Eng. J. Wuhan Univ. 2023, 56, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Wang, Y.; Jin, S.; Chen, Q. Spatial-Temporal Variations and Severity of the 2020 Catastrophic Floods in the Yangtze River Basin from Sentinel-1 SAR Data. Water 2024, 16, 3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.S.; Maneta, M.M.; Sain, S.R.; Madaus, L.E.; Hacker, J.P. The role of climate and population change in global flood exposure and vulnerability. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toma, A.; Șandric, I.; Mihai, B.-A. Flooded area detection and mapping from Sentinel-1 imagery. Complementary approaches and comparative performance evaluation. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2024, 57, 2414004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costache, R.; Arabameri, A.; Elkhrachy, I.; Ghorbanzadeh, O.; Pham, Q.B. Detection of areas prone to flood risk using state-of-the-art machine learning models. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2021, 12, 1488–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, L. SAR-based dynamic information retrieving of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei flood-inundation happened in July 2023, North China. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2024, 15, 2366361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, P.; Chen, L.; Xu, M.; Guo, X.; Zhao, L. A new multi-source remote sensing image sample dataset with high resolution for flood area extraction: GF-FloodNet. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2023, 16, 2522–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanama, V.S.K.; Rao, Y.S.; Bhatt, C.M. Change detection based flood mapping using multi-temporal Earth Observation satellite images: 2018 flood event of Kerala, India. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 54, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanama, V.S.K.; Rao, Y.S.; Bhatt, C.M. Rapid monitoring of cyclone induced flood through an automated approach using multi–temporal Earth Observation (EO) images in RSS CloudToolbox platform. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 54, 589–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Niu, B.; Ren, Y.; Su, S.; Wang, J.; Shi, H.; Yang, J.; Han, M. A 10-m national-scale map of ground-mounted photovoltaic power stations in China of 2020. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wang, Z.; He, G. AP Shadow Net: A Remote Sensing Shadow Removal Network Based on Atmospheric Transport and Poisson’s Equation. Entropy 2022, 24, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cian, F.; Delgado Blasco, J.M.; Ivanescu, C. Improving rapid flood impact assessment: An enhanced multi-sensor approach including a new flood mapping method based on Sentinel-2 data. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 369, 122326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-J.; Wei, Y.-M.; Wang, S.-Y.; Zhou, Q.-L. Extracting the flood extent from SAR imagery on basis of DEM. J. Nat. Disasters 2002, 11, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Prasath, V.S.; Haddad, O. Radar shadow detection in synthetic aperture radar images using digital elevation model and projections. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 083628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioresita, F.; Puissant, A.; Stumpf, A.; Malet, J.-P. A Method for Automatic and Rapid Mapping of Water Surfaces from Sentinel-1 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sghaier, M.O.; Hadzagic, M.; Patera, J. Fusion of SAR and multispectral satellite images using multiscale analysis and dempster-shafer theory for flood extent extraction. In Proceedings of the 2019 22th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2–5 July 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.X.; Chen, B.; Sun, H.Q. Research progress and prospect of flood detection based on SAR satellite images. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2023, 25, 1933–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, S. Automatic monitoring of surface water dynamics using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data with Google Earth Engine. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 113, 103010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVries, B.; Huang, C.; Armston, J.; Huang, W.; Jones, J.W.; Lang, M.W. Rapid and robust monitoring of flood events using Sentinel-1 and Landsat data on the Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Ji, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, L. Flood Monitoring in the Middle and Lower Basin of the Yangtze River Using Google Earth Engine and Machine Learning Methods. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cian, F.; Marconcini, M.; Ceccato, P. Normalized Difference Flood Index for rapid flood mapping: Taking advantage of EO big data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 712–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Gao, Y.N. Surface water extraction in Yangtze River Basin based on sentinel time series image. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 26, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansana, P.; Guo, X.; Zhang, S.; Kang, X.; Li, S. Flood Analysis Using Multi-Scale Remote Sensing Observations in Laos. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, H.; Ebadi, H.; Kiani, A.; Asgary, A. Introducing a new index for flood mapping using Sentinel-2 imagery (SFMI). Comput. Geosci. 2025, 194, 105742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Di, L.; Tang, J.; Yu, E.; Zhang, C.; Rahman, M.S.; Shrestha, R.; Kang, L. Improvement and Validation of NASA/MODIS NRT Global Flood Mapping. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticehurst, C.; Karim, F. Towards developing comparable optical and SAR remote sensing inundation mapping with hydrodynamic modelling. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2023, 44, 2912–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Liu, J.Q.; Liu, X.X.; Li, S.T.; Kang, X.D. Flood monitoring and analysis based on time-series SAR image for complex area. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2024, 28, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadoud, M.A.; Khalil, A.; Kotaridis, I.; Husein, H.H.; Costache, R. Morphometric analysis for flash flood hazard mapping: A case study of the Abu Al-Ward River Basin. DYSONA-Appl. Sci. 2025, 6, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moxon, S.D.G. Mapping Mangrove Forests: Processing and Visualization of Multi-Sensor Earth Observation Data for the Colombian Pacific Coast. Master’s Thesis, Palacký University Olomouc, Olomouc, Czech Republic, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.T.; Feng, Q.L.; Jin, D.J. Application of random forest and Sentinel—1/2 in the information extraction of impervious layers in Dongying City. Remote Sens. Nat. Resour. 2021, 33, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.C.; Xue, D.J.; Li, C.G.; Zheng, J.; Li, W.Q. Study on new method for water area information extraction based on Sentinel-1 data. People’s Yangtze River 2019, 50, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, T.; Weng, X.; Holail, S.; Hao, C.; Xia, G.-S. DAM-Net: Flood detection from SAR imagery using differential attention metric-based vision transformers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 212, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Qin, N.; Zhang, Y.; McGrath, H.; Fortin, M.; Li, J. A rapid high-resolution multi-sensory urban flood mapping framework via DEM upscaling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 301, 113956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinutha, H.; Poornima, B.; Sagar, B. Detection of outliers using interquartile range technique from intrusion dataset. In Information and Decision Sciences: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on FICTA; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 511–518. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, J. A Robust Skewed Boxplot for Detecting Outliers in Rainfall Observations in Real-Time Flood Forecasting. Adv. Meteorol. 2019, 2019, 1795673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Sui, H.; Liu, J. Siam-DWENet: Flood inundation detection for SAR imagery using a cross-task transfer siamese network. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 116, 103132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, M.-J. Rapid Change Detection of Flood Affected Area after Collapse of the Laos Xe-Pian Xe-Namnoy Dam Using Sentinel-1 GRD Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Liu, D. A local thresholding approach to flood water delineation using Sentinel-1 SAR imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 159, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayed, H.A.; Atiya, A.F. Speed up grid-search for parameter selection of support vector machines. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 80, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstra, J.; Bengio, Y. Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2012, 13, 281–305. [Google Scholar]
- Riazi, M.; Khosravi, K.; Shahedi, K.; Ahmad, S.; Jun, C.; Bateni, S.M.; Kazakis, N. Enhancing flood susceptibility modeling using multi-temporal SAR images, CHIRPS data, and hybrid machine learning algorithms. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 162066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, S.W.; Gober, P.; Brazel, A.; Grossman-Clarke, S.; Weng, Q. Per-pixel vs. object-based classification of urban land cover extraction using high spatial resolution imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1145–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropatsch, W.G.; Strobl, D. The generation of SAR layover and shadow maps from digital elevation models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1990, 28, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, X.; Lei, Y.; Chang, T.; Zhang, J.; Peng, Y. Probabilistic structure analysis of fluctuating wind speed based on field measurement of super typhoon Doksuri. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2024, 253, 105878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahtahmassebi, A.; Yang, N.; Wang, K.; Moore, N.; Shen, Z. Review of shadow detection and de-shadowing methods in remote sensing. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 403–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, F.; Zhang, T.; You, H.J. Automatic extraction of flood inundation areas from SAR images: A case study of Jilin, China during the 2017 flood disaster. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 5050–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, J.; Gessner, U.; Klein, I.; Yesou, H.; Lai, X.; Oppelt, N.; Kuenzer, C. Analyzing Water Dynamics Based on Sentinel-1 Time Series—A Study for Dongting Lake Wetlands in China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.H.; Wu, Y.Q.; Zhou, J.J. SAR River Image Segmentation Based on Reciprocal Gray Entropy and Improved Chan-Vese Model. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2015, 44, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, H.; Abe, T.; Ohki, M. SAR-Based Flood Monitoring for Flatland with Frequently Fluctuating Water Surfaces: Proposal for the Normalized Backscatter Amplitude Difference Index (NoBADI). Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Jin, S. Backscatter characteristics analysis for flood mapping using multi-temporal Sentinel-1 images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavus, B.; Kocaman, S. Flood Mapping in Mountainous Areas Using Sentinel-1 & 2 Data and Glcm Features. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 1575–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, T.; Winter, R.; Schreier, G. Terrain influences in SAR backscatter and attempts to their correction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1991, 29, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón, D.; Khan, U.T.; Armenakis, C. Flood risk mapping using GIS and multi-criteria analysis: A greater Toronto area case study. Geosciences 2018, 8, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, M.A.; Kilsby, C.G.; Moore, P. Multi-temporal synthetic aperture radar flood mapping using change detection. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2017, 11, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Fu, H.; Sun, C.; Wang, S. Shadow Detection and Compensation from Remote Sensing Images under Complex Urban Conditions. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demissie, B.; Vanhuysse, S.; Grippa, T.; Flasse, C.; Wolff, E. Using Sentinel-1 and Google Earth Engine cloud computing for detecting historical flood hazards in tropical urban regions: A case of Dar es Salaam. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2023, 14, 2202296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, B.G.; Cohen, S.; Lucey, R.; Munasinghe, D.; Raney, A.; Brakenridge, G.R. Google Earth Engine Implementation of the Floodwater Depth Estimation Tool (FwDET-GEE) for rapid and large scale flood analysis. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 19, 1501005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Chen, S.; Miao, Z.; Xu, Y.; Ye, M.; Lu, P. Automatic Flood Monitoring Method with SAR and Optical Data Using Google Earth Engine. Water 2025, 17, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.N.; Tian, J.Y.; Li, X.J.; Wang, L.; Gong, H.L.; Chen, B.B.; Li, X.C.; Guo, J.H. Benefits of Google Earth Engine in remote sensing. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 26, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twele, A.; Cao, W.; Plank, S.; Martinis, S. Sentinel-1-based flood mapping: A fully automated processing chain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 2990–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldhuset, K. Combination of stereo SAR and InSAR for DEM generation using TanDEM-X spotlight data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 4362–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).