The Diversity of Geochemical and Ecotoxicological Indices of Alluvial Deposits Reflects the Pattern of Landforms: The Case of the Vistula River Valley in the Małopolski Gorge (Poland)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
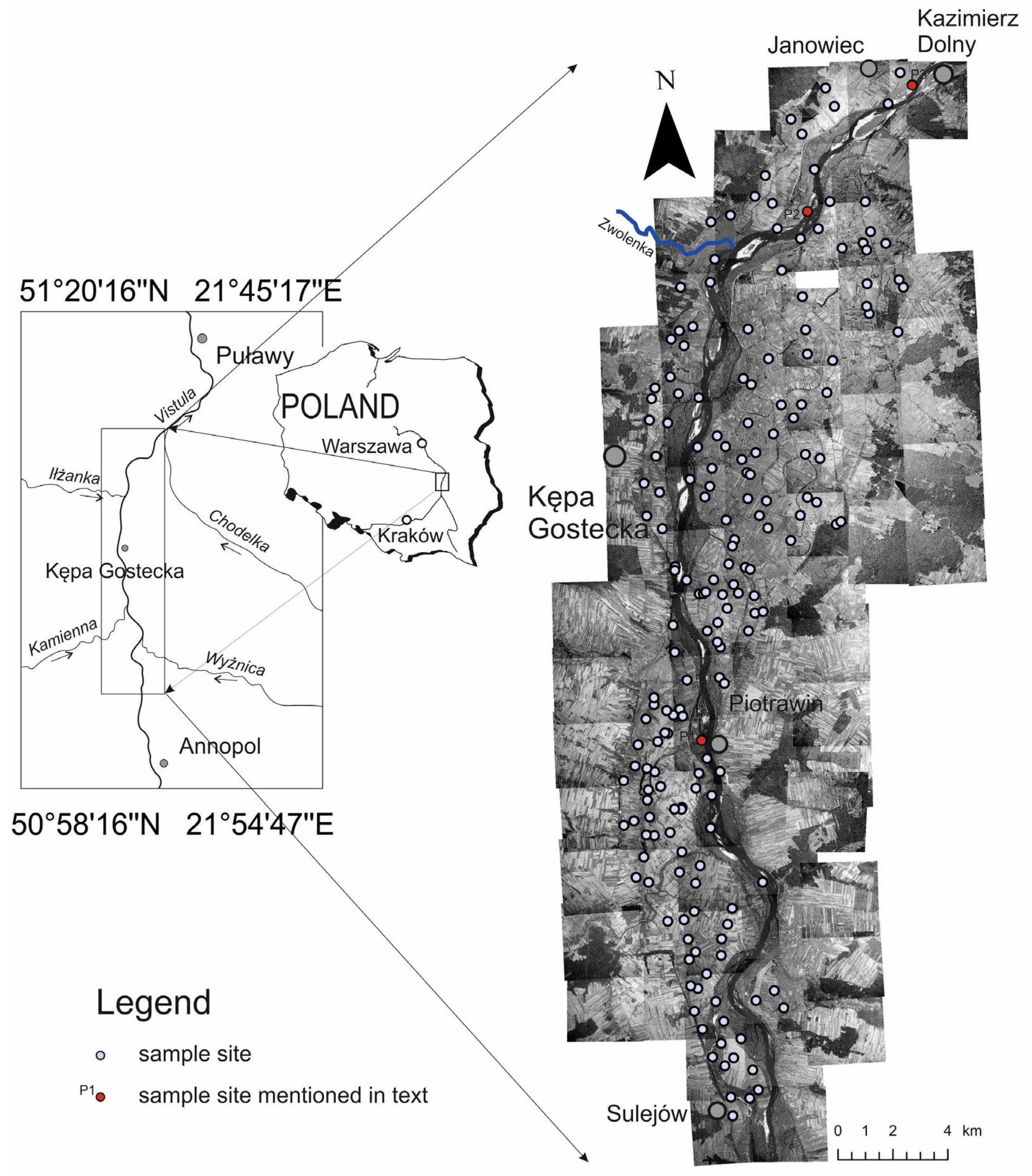
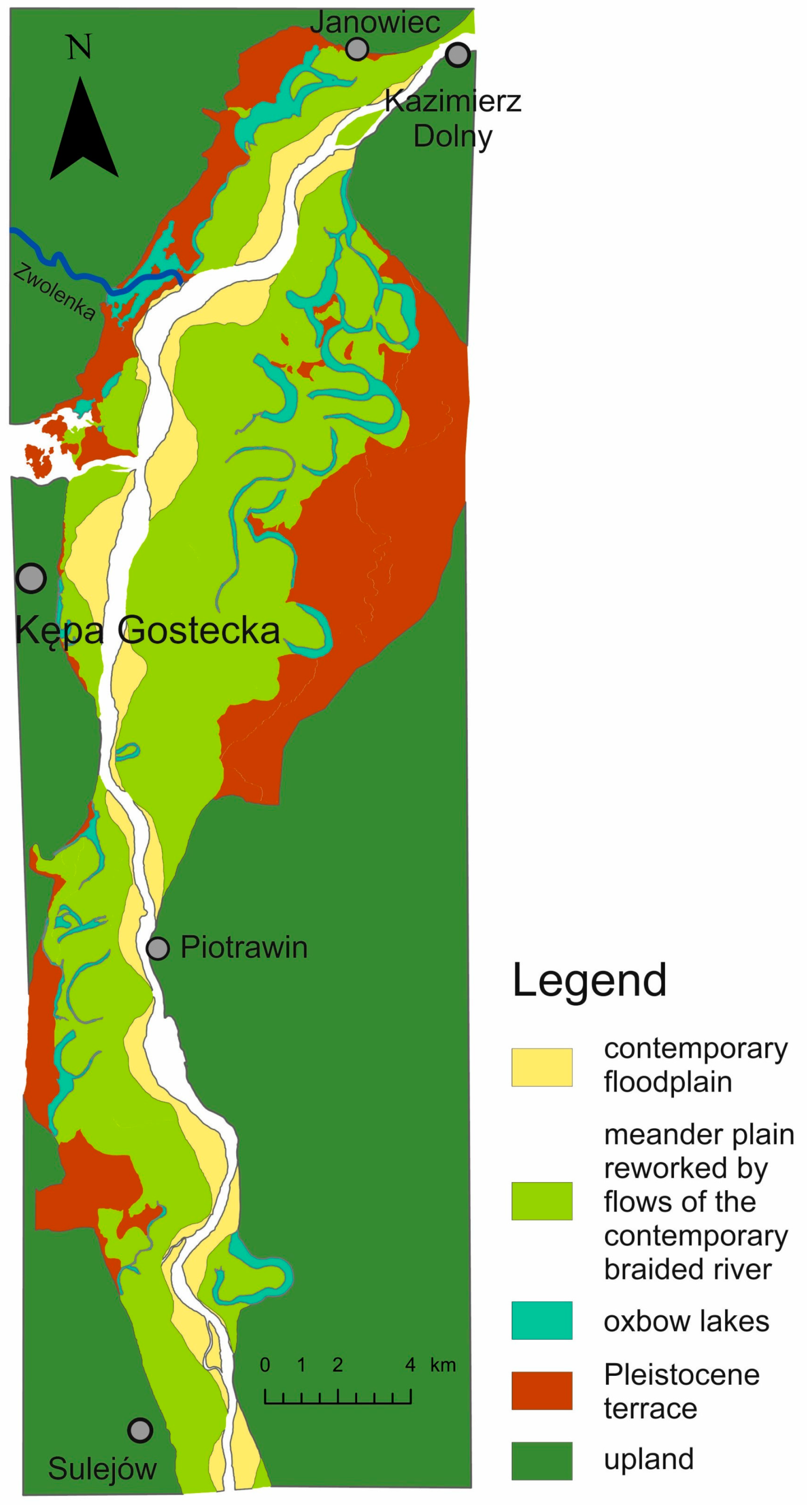
2. Study Area
3. Methods
4. Results
4.1. Lithology
4.2. Trace Elements Contents
4.3. Geochemical Indices
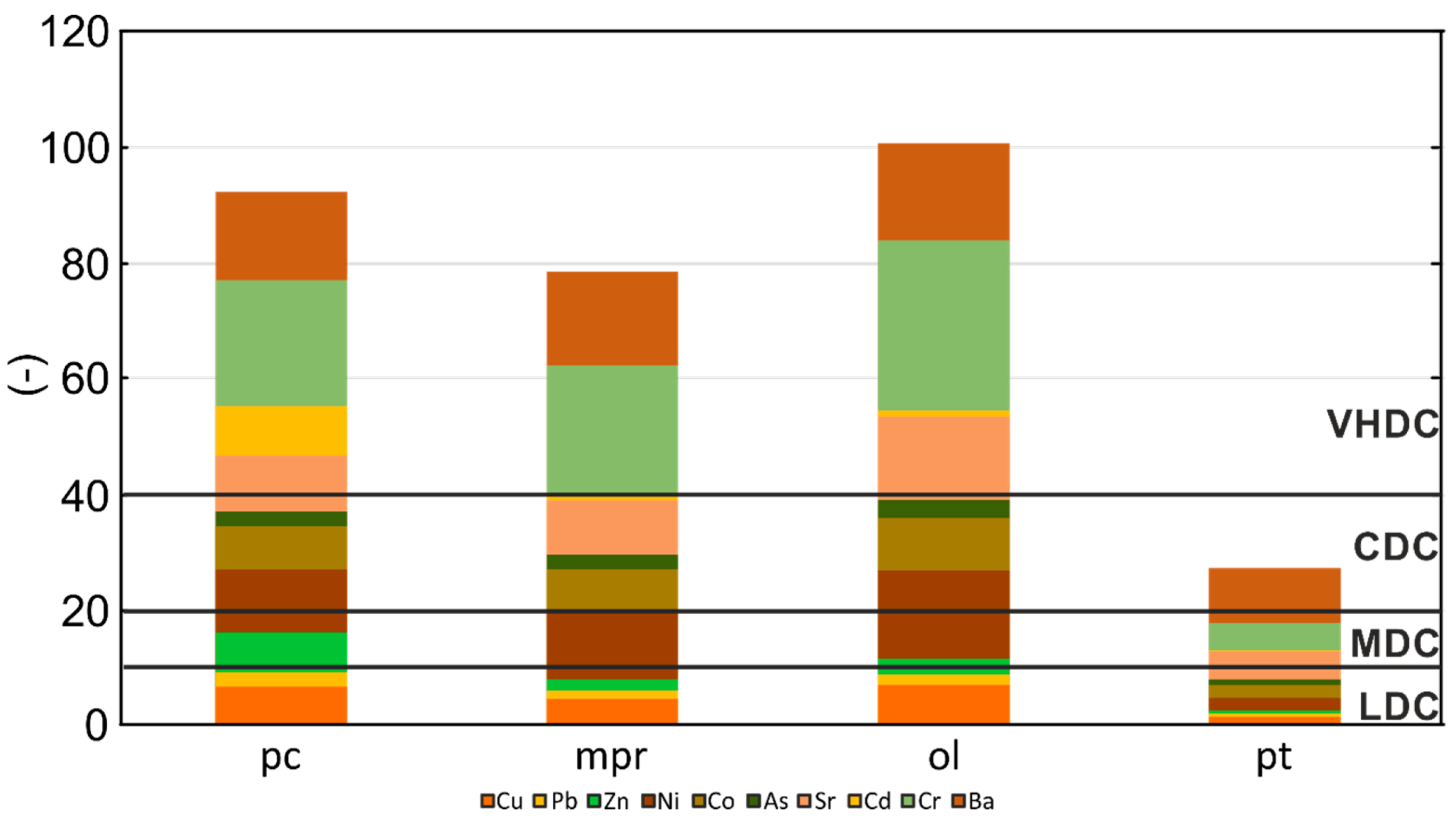
4.4. Integrated Geochemical Indices
4.5. Geochemical Indices of Ecological Risk
5. Discussion
5.1. General Contamination by Trace Elements
5.2. Nature and Origin of Trace Elements in the Studied Section of the Vistula Valley Sediments
5.3. Ecological Risks
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lecce, S.A.; Pavlowsky, R.T. Floodplain storage of sediment contaminated by mercury and copper from historic gold mining at Gold Hill, North Carolina, USA. Geomorphology 2014, 206, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.W. Trace metal storage in recent floodplain sediments along the Dill River, central Germany. Geomorphology 2015, 235, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Mao, L.; Sun, R.; Du, J.; Tan, Z.; Ding, M. Contamination Evaluation and Source Identification of Heavy Metals in the Sediments from the Lishui River Watershed, Southern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helios-Rybicka, E. Impact of mining and metallurgical industries on the environment in Poland. Appl. Geochem. 1996, 11, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenaers, H.; Schouten, C.J.; Rang, M.C. Variability of the metal content of flood deposits. Environ. Geol. 1988, 11, 95–106. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Bermejo, J.C.; Beltran, R.; Gomez Ariza, J.L. Spatial variations of heavy metals contamination in sediments from Odiel river (Southwest Spain). Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forstner, U.; Wittmann, G.T.W. Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1979; pp. 1–257. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, C.W. Heavy metal storage in near channel sediments of the Lahn River, Germany. Geomorphology 2004, 61, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.R. The role of fluvial geomorphic processes in the dispersal of heavy metals from mine sites. J. Geochem. Explor. 1997, 58, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Feng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wei, J.; Qiao, R.; Bi, F.; Liu, N.; Zhang, X. Graphene-based aerogels in water and air treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Bi, F.; Qiao, R.; Jiang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. PVP-modified spindle-shaped MIL-88B (Fe) to enhance the degradation of tetracycline by activated peroxodisulfate: A comparative study and mechanistic investigation. Prog. Nat. Sci Mater. Int. 2024, 33, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haris, H.; Looi, L.J.; Aris, A.Z.; Mokhtar, N.F.; Ayob, N.A.A.; Yusoff, F.M.; Salleh, A.B.; Praveena, S.M. Geo-accumulation index and contamination factors of heavy metals (Zn and Pb) in urban river sediment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 39, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskuła, J.; Sojka, M.; Fiedler, M.; Wróżyński, R. Analysis of Spatial Variability of River Bottom Sediment Pollution with Heavy Metals and Assessment of Potential Ecological Hazard for the Warta River, Poland. Minerals 2021, 11, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrot, N.; Wojciechowska, E.; Mohsin, M.; Kuittinen, S.; Pappinen, A.; Rezania, S. Trace Metal Contamination of Bottom Sediments: A Review of Assessment Measures and Geochemical Background Determination Methods. Minerals 2021, 11, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorbiłowicz, M.; Skorbiłowicz, E.; Górska, M. The Content of Heavy Metals in Bottom Sediments of Selected Rivers of the Podlasie Province as an Impact Assessment of the Towns they are Adjacent with. J. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 19, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.R.; Orbock Miller, S. Contaminated Rivers: A Geomorphological-Geochemical Approach to Site Assessment and Remediation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 1–418. [Google Scholar]
- Falkowska, E.; Falkowski, T. Trace metals distribution pattern in floodplain sediments of a lowland river in relation to contemporary valley bottom morphodynamics. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2015, 40, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciszewski, D.; Malik, I.; Wardas, M. Geomorphological influences on heavy metal migration in fluvial deposits: The Mała Panew River valley (southern Poland). Przegl. Geol. 2004, 52, 163–174, (In Polish with English Summary). [Google Scholar]
- Falkowska, E.; Falkowski, T.; Tatur, A.; Kałmykow-Piwińska, A. Floodplain morphodynamics and distribution of trace elements in overbank deposits, Vistula River Valley Gorge near Solec nad Wisłą, Poland. Acta Geol. Pol. 2016, 66, 541–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annammala, K.V.; Mohamad, N.A.; Sugumaran, D.; Masilamani, L.S.; Liang, Y.Q.; Jamal, M.H.; Yusop, Z.; Yusoff, A.R.M.; Nainar, A. Sediment clues in flood mitigation: The key to determining the origin, transport, and degree of heavy metal contamination. Hydrol. Res. 2021, 52, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audry, S.; Schâffer, J.; Blanc, G.; Jouanneau, J.M. Fifty-year sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution (Cd, Zn, Cu, Pb) in the Lot River reservoir (France). Environ. Pollut. 2004, 132, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yacoub, C.; Miralles, N.; Valderrama, C. Experimental study of mobility and kinetic characterisation of trace elements in contaminated sediments from a river basin in Northern Peru. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2015, 21, 828–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Chi-Lung, Y. Abundance of chemical elements in the earth’s crust and its major tectonic units. Int. Geol. Rev. 1970, 12, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Deng, J.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liqiang, Y. Calculating Pollution Indices by Heavy Metals in Ecological Geochemistry Assessment and a Case Study in Parks of Beijing. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2008, 19, 230–241. [Google Scholar]
- Håkanson, L. An Ecological Risk Index for Aquatic Pollution Control: A Sedimentological Approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, E.; Zhang, B.; Bai, X.; Lei, P.; Qiao, X.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Wu, G.; Gao, Y. Pollution characteristics and ecological risks associated with heavy metals in the Fuyang river system in North China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 281, 116994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Xiao, R.; Zhao, Q.; Jia, J.; Cui, B.; Liu, X. Heavy metal fractions and ecological risk assessment in sediments from urban, rural and reclamation-affected rivers of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, X.; Gui, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Guo, W. Ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediment from the Liaohe River protected area, China. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.T.; Lee, C.W. Application of multiple ecological risk indices for the evaluation of heavy metal contamination in a coastal dredging area. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 214, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, E.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, E.; Yang, F.; Wei, C.; Shen, J. Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal pollution and ecological risk in lake sediment by combining total concentration and chemical partitioning. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 269, 116212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokr, M.S.; Baroudy, A.A.E.; Fullen, M.A.; El-Beshbeshy, T.R.; Ali, R.R.; Elhalim, A.; Guerra, A.J.T.; Jorge, M.C.O. Mapping of heavy metal contamination In alluvial soils of the Middle Nile Delta of Egypt. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2016, 24, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, B.P.; Tiwari, G.; Prasad, J. Pedogenic influence on profile distribution of total and DTPA—Extractable micronutrients in rice growing hydric soils of Majuli river island, Assam, India. Span. J. Soil Sci. SJSS 2017, 7, 59–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiński, M. Objaśnienia do Szczegółowej Mapy Geologicznej Polski. 1:50,000. Arkusz Kazimierz Dolny (746); Państwowy Instytut Geologiczny—Państwowy Instytut Badawczy: Warsaw, Poland, 2023; pp. 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiński, M. Objaśnienia do Szczegółowej Mapy Geologicznej Polski. 1:50,000. Arkusz Opole Lubelskie (783); Państwowy Instytut Geologiczny—Państwowy Instytut Badawczy: Warsaw, Poland, 2023; pp. 1–63. [Google Scholar]
- Włodek, M.; Gaździcka, E. Objaśnienia do Szczegółowej Mapy Geologicznej Polski. 1:50,000. Arkusz Annopol (820); Państwowy Instytut Geologiczny—Państwowy Instytut Badawczy: Warsaw, Poland, 2009; pp. 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Pożaryski, W. Pleistocene in the Vistula River gorge across the Southern Uplands. Pr. Inst. Geol. 1953, 9, 1–134. [Google Scholar]
- Pożaryski, W. Osady rzeczne w przełomie Wisły przez wyżyny południowe. Pr. Inst. Geol. 1955, 12c, 1–96. [Google Scholar]
- Pożarski, W.; Kalicki, T. Evolution of the gap section of the Vistula valley in the Late Glacial and Holocene. In Evolution of the Vistula River Valley During the Last 15,000 Years; Geographical Studies Special Issue 8; Starkel, L., Ed.; IGiPZ PAN: Wrocław, Poland, 1955; pp. 111–137. [Google Scholar]
- Starkel, L. Historia Doliny Wisły od Ostatniego Zlodowacenia do Dziś; IGiPZ PAN: Warsaw, Poland, 2001; pp. 1–263. [Google Scholar]
- Falkowski, T. Naturalne Czynniki Stabilizujące Wybrane Odcinki Strefy Korytowej Wisły Środkowej [Factors of Natural Stability of the Middle Vistula River Channel Zones]; Wydawnictwo SGGW: Warsaw, Poland, 2006; pp. 1–128, (In Polish with English Summary). [Google Scholar]
- Falkowski, E. History and prognosis for the development of bed configurations of selected sections of Polish Lowland rivers. Biul. Geol. 1971, 12, 5–121, (In Polish with English Summary). [Google Scholar]
- Starkel, L. The reflection of hydrologic changes in fluvial environment of the temperate zone during the last 15,000 years. In Background to Paleohydrology: A Perspective; Gregory, K.J., Ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1983; pp. 213–235. [Google Scholar]
- Myślińska, E. Laboratoryjne Badania Gruntów i Gleb [Laboratory Soil Investigations]; Wydawnictwa Uniwersytetu Warszawskiego: Warsaw, Poland, 2010; pp. 1–278. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Wyżga, B.; Ciszewski, D. Hydraulic controls on the entrapment of heavy metal-polluted sediments on a floodplain of variable width, the upper Vistula River, southern Poland. Geomorphology 2010, 117, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kałmykow-Piwińska, A.; Falkowska, E. Data Needed for Assessment of Trace Elements Contamination of the Vistula River Valley in the Małopolski Gorge. Application of Geochemical and Ecotoxicological Indices. RepOD V1. 2024. Available online: https://repod.icm.edu.pl/dataset.xhtml?persistentId=doi:10.18150/ZCY6PZ (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Chester, R.; Stoner, J.H. Pb in Particulates from the Lower Atmosphere of the Eastern Atlantic. Nature 1973, 245, 27–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buat-Menard, P.; Chesselet, R. Variable influence of the atmospheric flux on the trace metal chemistry of oceanic suspended matter. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1979, 42, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergin, M.; Saydam, C.; Basturk, O.; Erdem, E.; Yoruk, R. Metal concentrations in surface sediments from the two coastal inlets (Golden Horn Estuary and Izmit Bay) of the northeastern Sea of Marmara. Chem. Geol. 1991, 91, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G. Schwermetalle in den Sedimenten des Rheins—Veränderungen seit 1971. Umschau 1979, 24, 778–783. [Google Scholar]
- Zgłobicki, W.; Telecka, M.; Skupiński, S. Assessment of microscale variation of heavy metal pollution of the Bystrzyca River alluvia downstream from Lublin. Pol. J. Soil Sci. 2016, 49, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lis, J.; Pasieczna, A.; Mojski, J.E.; Przeniosło, S.; Sylwestrzak, H.; Strzelecki, R.; Wołkowicz, S. Atlas Geochemiczny Polski; Państwowy Instytut Geologiczny—Państwowy Instytut Badawczy: Warsaw, Poland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Qing, X.; Yutong, Z.; Shenggao, L. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 120, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol. Mar. Res. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.R.L. Physical Processes of Sedimentation; G. Allen & Unwin: London, UK, 1970; pp. 1–248. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Santos, M.; Probst, A.; García-García, J.; Ruiz-Romera, E. Influence of anthropogenic inputs and a highmagnitude flood event on metal contamination pattern in surface bottom sediments from the Deba River urban catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 514, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Sun, B.; Zeng, D.; Wei, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, B. Vertical distribution of trace elements in the sediment cores from major rivers in east China and its implication on geochemical background and anthropogenic effects. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 139, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, M.; Ayrault, S.; Evrard, O.; Laceby, J.P.; Gateuille, D.; Lefevre, I.; Mouchel, J.M.; Meybeck, M. Investigating the metal contamination of sediment transported by the 2016 Seine River flood (Paris, France). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, G.F.; Apostolatos, C. Use of sedimentary metals to predict metal concentrations in black mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) tissue and risk to human health (SydneyEstuary, Australia). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5481–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kałmykow-Piwińska, A.; Falkowska, E. Morphodynamic conditions of heavy metal concentration in deposits of the Vistula River valley near Kępa Gostecka (central Poland). Open Geosci. 2020, 12, 1036–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowska, E. Glacial morphogenesis of uplands of the Warta Glaciation in Poland as a control on heavy metal distribution in deposits. Geol. Q. 2009, 53, 293–304. [Google Scholar]
- Sokołowska, G.; Szwarczewski, P. Metale ciężkie w różnowiekowych osadach aluwialnych Bzury. Prz. Geol. 1998, 46, 417–420. [Google Scholar]
- Szwarczewski, P. Wybrane geochemiczne i teksturalne cechy osadów w dolinie Utraty jako efekt działalności człowieka—Współczesnej i w przeszłości. Pr. Stud. Geogr. 2003, 33, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Szwarczewski, P.; Smolska, E. Cechy geochemiczne osadów stokowych I fluwialnych na północno-zachodnim Mazowszu. Pr. Stud. Geogr. 2013, 51, 105–123. [Google Scholar]
- Czajka, A. Sedymentacja pozakorytowa aluwiów w strefie między wala Wisły w Kotlinie Oświęcimskiej. Prz. Geol. 2000, 48, 263–267. [Google Scholar]
- Czajka, A. Środowisko Sedymentacji Osadów Przykorytowych Rzek Uregulowanych na Przykładzie Górnej Odry i Górnej Wisły; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Śląskiego: Katowice, Poland, 2007; pp. 1–97. [Google Scholar]
- Jarosz, D. Zanieczyszczenie wód I Powietrza W Polsce W Latach 1945–1970 Jako Problem władzy I społeczeństwa. Polska 1944/45-1989 Studia I materiały 2018, 15, 37–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, M.; Jaskuła, J.; Siepak, M. Heavy metals in bottom sediments of reservoirs in the lowland area of western Poland: Concentrations, distribution, sources and ecological risk. Water 2019, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plak, A.; Bartmiński, P.; Dębicki, R. Wpływ transportu publicznego na zawartość wybranych metali ciężkich w glebach sąsiadujących z ulicami Lublina. Proc. ECOpole 2010, 4, 167–171. [Google Scholar]
- Bojanowski, M.J.; Dubicka, Z.; Minoletti, F.; Olszewska-Nejbert, D.; Surowski, M. Stable C and O isotopic study of the Campanian chalk from the Mielnik section (eastern Poland): Signals from bulk rock, belemnites, benthic foraminifera, nannofossils and microcrystalline cements. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2017, 465, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prognoza Oddziaływania na Środowisko Programu Ochrony Środowiska dla gminy Zwoleń na lata 2017–2020 z uwzględnieniem lat 2024–2027, Zwoleń, Poland. 2021, pp. 1–31. Available online: https://bip.zwolen.pl/upload/2021.11.29%20Prognoza%20oddzia%C5%82ywania%20na%20%C5%9Brodowisko%20program%20ochrony%20%C5%9Brodowiska.pdf (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Liao, J.; Cui, X.; Feng, H.; Yan, S. Environmental Background Values and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Watershed Sediments: A Comparison of Assessment Methods. Water 2022, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slukovskii, Z.I. Geoecological assessment of small rivers in the big industrial city based on the data on heavy metal content in bottom sediments. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2015, 40, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asare, A.; Asamoah, B.D.; Sanful, P.O. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contaminants Using Pollution Indices in Ankobra River at Prestea Huni-Valley District, Ghana. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2019, 7, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krampah, F.; Nyarko, S.Y.; Danlogo, K.; Sanful, P. Application of Pollution Indices in the Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of Surface Sediments of River Bonsa, Ghana. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2019, 7, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Wang, J.; Pan, H.; Yang, C.; Qu, J.; Lu, N.; Yuan, X. Heavy metals in Yinma River sediment in a major Phaeozems zone, Northeast China: Distribution, chemical fraction, contamination assessment and source apportionment. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astatkie, H.; Ambelu, A.; Mengistie, E. Contamination of Stream Sediment with Heavy Metals in the Awetu Watershed of Southwestern Ethiopia. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 658737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciazela, J.; Siepak, M.; Wojtowicz, P. Tracking heavy metal contamination in a complex river-oxbow lake system: Middle Odra Valley, Germany/Poland. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, S. 18th–20th century flood-induced changes in the landscapes of the Mała Wisła Valley within the Oświęcimska Basin. Geogr. Pol. 2012, 85, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruszczak, H. Changes of the Vistula river course and development of the flood plain in the border zone of the South-Polish uplands and Middle-Polish lowlands in historical times. Landf. Anal. 1997, 1, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kazimierowicz, Z.; Kazimierowicz, J. Badania zawartości metali ciężkich w zlewni rzeki Biebrzy i jej trzech dopływów. Inż. Ekol. 2014, 40, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Maciołek, H.; Zielińska, A.; Domarecki, T. Oddziaływanie geobiologiczno-chemiczne kadmu i ołowiu na środowisko przyrodnicze. J. Ecol. Health 2013, 17, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, C.J.; Hahn, J.; Opp, C. Spatial Connections between Microplastics and Heavy Metal Pollution within Floodplain Soils. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharjee, A.; Ahmed, Z.; Kumar, P.; Alam, R.; Rahman, M.S.; Simal-Gandara, J. Assessment of the Ecological Risk from Heavy Metals in the Surface Sediment of River Surma, Bangladesh: Coupled Approach of Monte Carlo Simulation and Multi-Component Statistical Analysis. Water 2022, 14, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Class | Index Value | Sediment Quality |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | <0 | Unpolluted |
| 1 | 0–1 | From unpolluted to moderately polluted |
| 2 | 1–2 | Moderately polluted |
| 3 | 2–3 | From moderately polluted to strongly polluted |
| 4 | 3–4 | Strongly polluted |
| 5 | 4–5 | From strongly polluted to extremely polluted |
| 6 | >5 | Extremely polluted |
| Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) | Org (%) | CaCO3 (%) | Fe/Al (-) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| the entire study area | ||||||
| Maximum | 100 | 80 | 48 | 36.90 | 5.90 | 0.82 |
| Minimum | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.14 |
| Mean | 37 | 43 | 20 | 3.26 | 0.60 | 0.44 |
| Median | 34 | 48 | 18 | 2.47 | 0.00 | 0.44 |
| Standard deviation | 27 | 18 | 12 | 4.40 | 1.18 | 0.10 |
| contemporary floodplain (28 samples) | ||||||
| Maximum | 100 | 56 | 31 | 7.77 | 5.90 | 0.63 |
| Minimum | 13 | 0 | 0 | 0.28 | 0.00 | 0.19 |
| Mean | 54 | 31 | 15 | 3.00 | 1.73 | 0.44 |
| Median | 52 | 31 | 17 | 2.92 | 1.20 | 0.45 |
| Standard deviation | 23 | 16 | 8 | 1.83 | 1.79 | 0.11 |
| meander plain reworked by flows of the braided river (130 samples) | ||||||
| Maximum | 100 | 75 | 48 | 7.45 | 2.68 | 0.70 |
| Minimum | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.22 |
| Mean | 36 | 44 | 20 | 2.56 | 0.22 | 0.44 |
| Median | 31 | 48 | 18 | 2.16 | 0.00 | 0.43 |
| Standard deviation | 26 | 18 | 11 | 1.42 | 0.48 | 0.08 |
| oxbow lakes (22 samples) | ||||||
| Maximum | 40 | 80 | 48 | 36.90 | 3.75 | 0.82 |
| Minimum | 1 | 33 | 15 | 1.43 | 0.00 | 0.32 |
| Mean | 10 | 57 | 33 | 9.43 | 0.98 | 0.51 |
| Median | 7 | 56 | 34 | 5.70 | 0.00 | 0.49 |
| Standard deviation | 11 | 11 | 9 | 11.16 | 1.42 | 0.12 |
| Pleistocene terrace (12 samples) | ||||||
| Maximum | 95 | 53 | 20 | 1.82 | 1.19 | 0.47 |
| Minimum | 33 | 5 | 0 | 0.61 | 0.00 | 0.14 |
| Mean | 68 | 23 | 10 | 1.19 | 0.40 | 0.29 |
| Median | 72 | 18 | 9 | 1.17 | 0.00 | 0.27 |
| Standard deviation | 23 | 17 | 7 | 0.51 | 0.56 | 0.09 |
| Element | Cu | Pb | Zn | Ni | Co | As | Sr | Cd | Cr | Ba |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The entire study area | ||||||||||
| Maximum | 75.1 | 78.76 | 862.8 | 68.2 | 17.7 | 14.0 | 399 | 13.17 | 125 | 499 |
| Minimum | 1.5 | 4.20 | 4.1 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 19 | 0.01 | 1 | 56 |
| Mean | 17.7 | 17.94 | 77.8 | 29.4 | 8.5 | 6.2 | 85 | 0.53 | 54 | 325 |
| Median | 16.2 | 16.30 | 56.9 | 28.7 | 8.3 | 6.0 | 84 | 0.20 | 52 | 333 |
| Standard deviation | 10.7 | 10.09 | 101.9 | 14.8 | 3.8 | 2.9 | 37 | 1.57 | 29 | 86 |
| Contemporary floodplain (28 samples) | ||||||||||
| Maximum | 75.1 | 78.76 | 862.8 | 54.6 | 16.1 | 13.2 | 143 | 13.17 | 119 | 441 |
| Minimum | 2.0 | 4.60 | 9.4 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 24 | 0.08 | 4 | 126 |
| Mean | 23.7 | 28.12 | 199.9 | 28.5 | 8.6 | 6.5 | 85 | 2.38 | 54 | 315 |
| Median | 19.9 | 24.82 | 126.5 | 29.35 | 9.0 | 6.3 | 85 | 1.02 | 52 | 320 |
| Standard deviation | 18.3 | 19.50 | 219.1 | 15.1 | 4.0 | 3.3 | 28 | 3.56 | 32 | 86 |
| meander plain reworked by flows of the braided river (130 samples) | ||||||||||
| Maximum | 40.5 | 39.80 | 240.6 | 68.2 | 16.4 | 14.0 | 114 | 2.05 | 125 | 499 |
| Minimum | 3.0 | 5.20 | 7.7 | 3.5 | 1.5 | 0.1 | 32 | 0.01 | 5 | 149 |
| Mean | 16.3 | 16.29 | 57.5 | 30.0 | 8.7 | 6.1 | 82 | 0.22 | 56 | 335 |
| Median | 15.0 | 15.45 | 52.2 | 28.1 | 8.4 | 5.9 | 84 | 0.17 | 52 | 338 |
| Standard deviation | 7.6 | 5.32 | 29.9 | 12.9 | 3.2 | 2.5 | 16 | 0.22 | 25 | 72 |
| oxbow lakes (22 samples) | ||||||||||
| Maximum | 34 | 25.05 | 108.1 | 57.7 | 17.7 | 14 | 399 | 0.51 | 106 | 478 |
| Minimum | 8.3 | 8.80 | 17.1 | 7.8 | 1.8 | 2.7 | 55 | 0.08 | 5 | 56 |
| Mean | 24.7 | 20.47 | 76.7 | 40.2 | 10.3 | 8.1 | 127 | 0.27 | 72 | 348 |
| Median | 26.4 | 22.08 | 80.6 | 43.3 | 11.8 | 8.8 | 98 | 0.27 | 78 | 392 |
| Standard deviation | 6.3 | 4.29 | 25.6 | 13.9 | 4.7 | 2.9 | 82 | 0.10 | 27 | 114 |
| Pleistocene terrace (12 samples) | ||||||||||
| Maximum | 10.6 | 12.27 | 27.1 | 12.3 | 6.2 | 4.9 | 84 | 0.09 | 26 | 302 |
| Minimum | 1.5 | 4.20 | 4.1 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 1.1 | 19 | 0.01 | 1 | 114 |
| Mean | 5.5 | 7.35 | 14.1 | 5.6 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 42 | 0.04 | 12 | 195 |
| Median | 4.5 | 6.80 | 11.7 | 4.6 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 36 | 0.04 | 9 | 179 |
| Standard deviation | 3.1 | 2.56 | 7.8 | 3.8 | 1.7 | 1. 3 | 19 | 0.03 | 8 | 52 |
| Cu | Pb | Zn | Ni | Co | As | Sr | Cd | Cr | Ba | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| silt | 0.5898 | 0.3856 | 0.1839 | 0.7529 | 0.7585 | 0.6617 | 0.7408 | 0.0487 | 0.7338 | 0.8129 |
| clay | 0.7358 | 0.5075 | 0.2797 | 0.8977 | 0.8851 | 0.7125 | 0.6680 | 0.0960 | 0.9000 | 0.8972 |
| Org | 0.8451 | 0.6961 | 0.5161 | 0.8652 | 0.8470 | 0.7255 | 0.7020 | 0.3488 | 0.8695 | 0.8304 |
| CaCO3 | 0.4279 | 0.5379 | 0.5847 | 0.1945 | 0.2316 | 0.2678 | 0.5279 | 0.5265 | 0.2295 | 0.0960 |
| Fe/Al. | 0.8382 | 0.7091 | 0.5176 | 0.8687 | 0.8908 | 0.8559 | 0.7391 | 0.3558 | 0.8919 | 0.8455 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kałmykow-Piwińska, A.; Falkowska, E. The Diversity of Geochemical and Ecotoxicological Indices of Alluvial Deposits Reflects the Pattern of Landforms: The Case of the Vistula River Valley in the Małopolski Gorge (Poland). Water 2025, 17, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010064
Kałmykow-Piwińska A, Falkowska E. The Diversity of Geochemical and Ecotoxicological Indices of Alluvial Deposits Reflects the Pattern of Landforms: The Case of the Vistula River Valley in the Małopolski Gorge (Poland). Water. 2025; 17(1):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010064
Chicago/Turabian StyleKałmykow-Piwińska, Agnieszka, and Ewa Falkowska. 2025. "The Diversity of Geochemical and Ecotoxicological Indices of Alluvial Deposits Reflects the Pattern of Landforms: The Case of the Vistula River Valley in the Małopolski Gorge (Poland)" Water 17, no. 1: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010064
APA StyleKałmykow-Piwińska, A., & Falkowska, E. (2025). The Diversity of Geochemical and Ecotoxicological Indices of Alluvial Deposits Reflects the Pattern of Landforms: The Case of the Vistula River Valley in the Małopolski Gorge (Poland). Water, 17(1), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010064






