Harnessing the Potential of Extracellular Polymeric Substances in Enhancing ANAMMOX Processes: Mechanisms, Strategies, and Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Characteristics, Compositions, and Extraction of ANAMMOX-Derived Extracellular Polymeric Substances
2.1. Characteristics of ANAMMOX-Derived Extracellular Polymeric Substances
2.2. Compositions of ANAMMOX-Derived Extracellular Polymeric Substances
2.3. Extraction Methods of ANAMMOX-Derived Extracellular Polymeric Substances
3. Roles and Mechanisms of Extracellular Polymeric Substances in ANAMMOX Processes
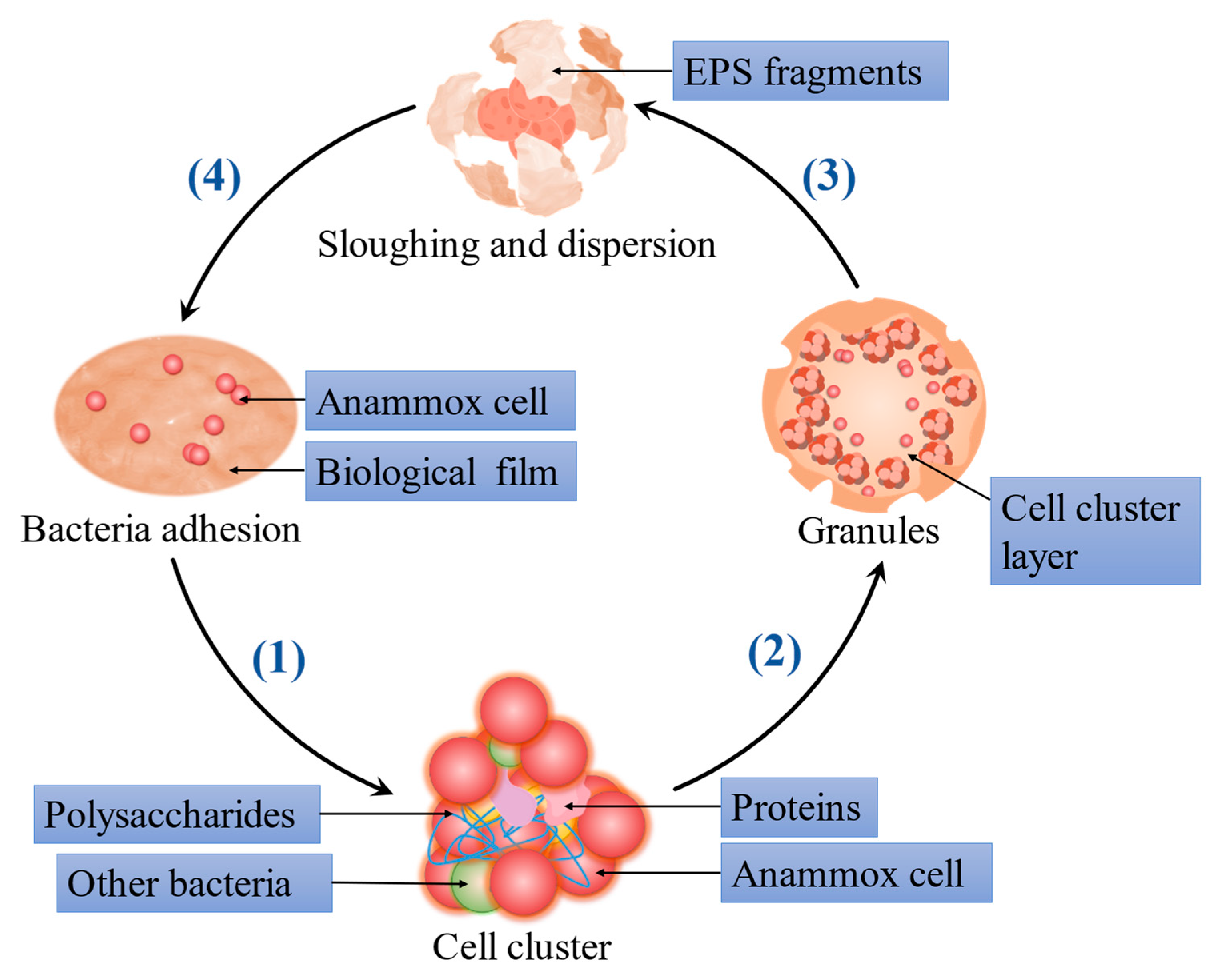
3.1. Extracellular Polymeric Substances Facilitate ANAMMOX Biofilm and Granule Formation
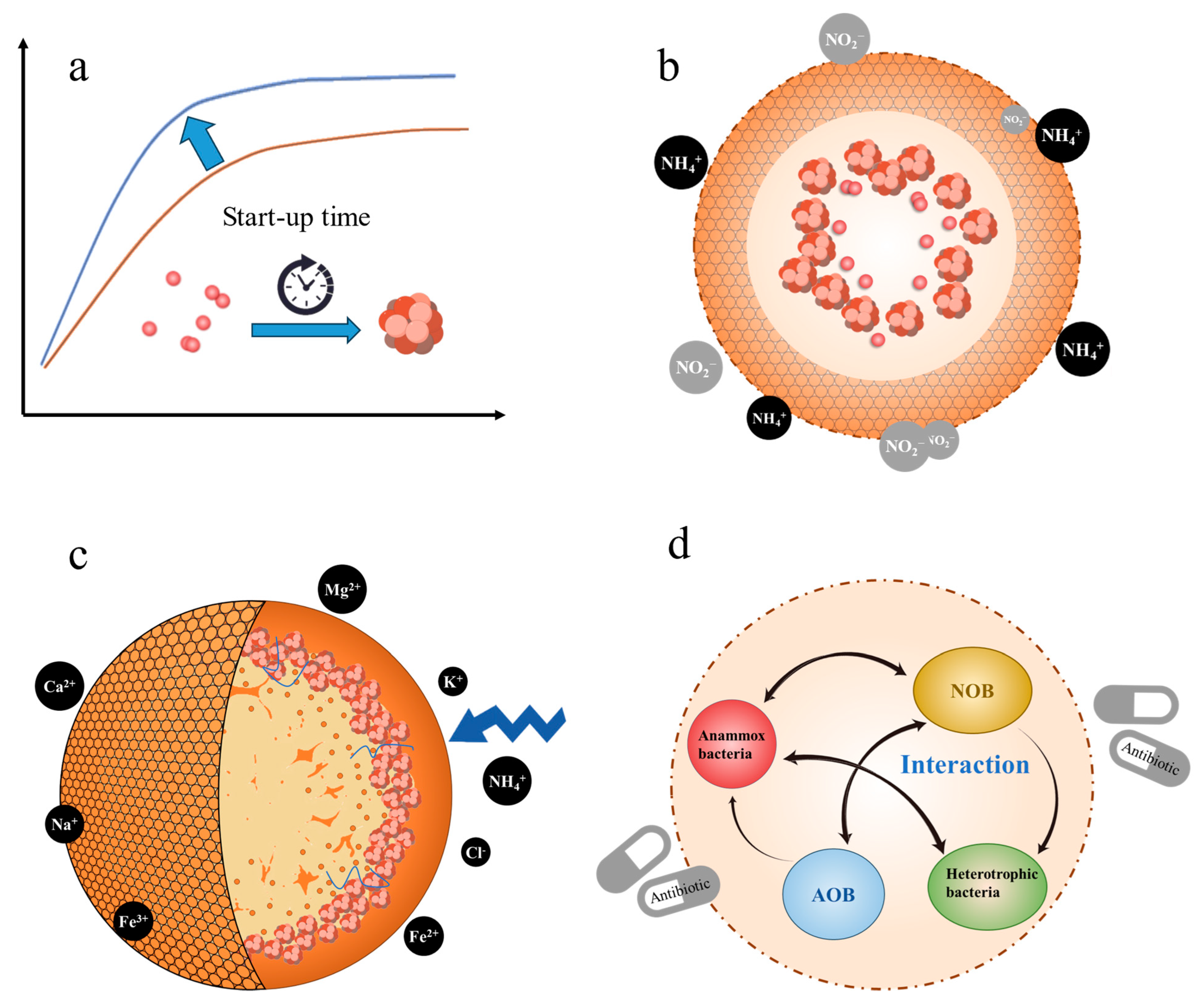
3.2. Extracellular Polymeric Substances Enhance ANAMMOX Activity and Stability
4. Extracellular Polymeric Substances Supplementation Strategies to Improve ANAMMOX Performance
4.1. Extracellular Polymeric Substances Supplementation during the Start-Up of ANAMMOX Reactors
4.2. Extracellular Polymeric Substances Supplementation under Substrate Inhibition Stress
4.3. Extracellular Polymeric Substances Supplementation under Salinity Stress
4.4. Extracellular Polymeric Substances Supplementation under Antibiotic Stress
5. Challenges and Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strous, M.; Fuerst, J.; Kramer, E.; Logemann, S.; Muyzer, G.; Pas-Schoonen, K.; RI, W.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M. Missing Litotroph Identified as New Planctomycete. Nature 1999, 400, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strous, M.; Pelletier, E.; Mangenot, S.; Rattei, T.; Lehner, A.; Taylor, M.W.; Horn, M.; Daims, H.; Bartol-Mavel, D.; Wincker, P.; et al. Deciphering the Evolution and Metabolism of an Anammox Bacterium from a Community Genome. Nature 2006, 440, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Z.; Qiao, S.; Zhou, J.; Tang, X.; Zhang, J. Fast Start-up of Anammox Process with Appropriate Ferrous Iron Concentration. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 170, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jetten, M.S.M.; Wagner, M.; Fuerst, J.; van Loosdrecht, M.; Kuenen, G.; Strous, M. Microbiology and Application of the Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidation (‘Anammox’) Process. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2001, 12, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Okabe, S. Anammox-Based Technologies for Nitrogen Removal: Advances in Process Start-up and Remaining Issues. Chemosphere 2015, 141, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.-Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.-G.; Du, X.-N.; Huang, B.-C.; Jin, R.-C. A Review of Anammox-Based Nitrogen Removal Technology: From Microbial Diversity to Engineering Applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 127896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Peng, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Deng, L.; Li, W.; Kao, C. Mainstream Partial Denitrification-Anammox (PD/A) for Municipal Sewage Treatment from Moderate to Low Temperature: Reactor Performance and Bacterial Structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Martínez, A.; Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Kruglova, A.; Vilpanen, M.; Kuokkanen, A.; Mikola, A.; Heinonen, M. Performance and Microbial Community Structure of a Full-Scale ANITATMMox Bioreactor for Treating Reject Water Located in Finland. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaka, K.; Kimura, Y.; Matsuura, M.; Osaka, T.; Tsuneda, S. First Full-Scale Nitritation-Anammox Plant Using Gel Entrapment Technology for Ammonia Plant Effluent. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 122, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, S.; Mozooni, M.; Rathsack, K.; Böllmann, J.; Martienssen, M. Effect of Increasing Salinity to Adapted and Non-Adapted Anammox Biofilms. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 2880–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Yu, D.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, G.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y. A Novel Process of Salt Tolerance Partial Denitrification and Anammox (ST-PDA) for Treating Saline Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 345, 126472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, X.; Du, R. Feasibility of Partial-Denitrification/ Anammox for Pharmaceutical Wastewater Treatment in a Hybrid Biofilm Reactor. Water Res. 2022, 208, 117856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.-J.; Jin, J.-A.; Yu, Y.; Lu, H.-F.; Jin, R.-C. Feasibility of Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidation Process for Treatment of Pretreated Printed Circuit Board Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 388, 129766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotti, T.; Kleerebezem, R.; Lubello, C.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Physiological and Kinetic Characterization of a Suspended Cell Anammox Culture. Water Res. 2014, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.-Y. Enhancing Start-up Strategies for Anammox Granular Sludge Systems: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 166398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.-C.; Yang, G.-F.; Yu, J.-J.; Zheng, P. The Inhibition of the Anammox Process: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Y. Determining the Mechanism for Biomass Segregation between Granules and Flocs in Anammox Granular System from the Prospective of EPS. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 475, 146028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Q.; Wang, Y. Characterization of Stratified EPS and Their Role in the Initial Adhesion of Anammox Consortia. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, J.; Lian, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Xing, Y.; Wang, T. Effects of Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) and N-Acyl-L-Homoserine Lactones (AHLs) on the Activity of Anammox Biomass. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 129, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Zhou, J.; Qiao, S.; Wei, H. Application of Low Intensity Ultrasound to Enhance the Activity of Anammox Microbial Consortium for Nitrogen Removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4290–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Yao, H.; Rong, H.; Li, S. Responses of Anammox Process to Elevated Fe(III) Stress: Reactor Performance, Microbial Community and Functional Genes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 414, 125051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. The Biofilm Matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, G.-P.; Yu, H.-Q.; Li, X.-Y. Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) of Microbial Aggregates in Biological Wastewater Treatment Systems: A Review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Wu, P.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; et al. A Critical Review of Improving Mainstream Anammox Systems: Based on Macroscopic Process Regulation and Microscopic Enhancement Mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingender, J.; Neu, T.R.; Flemming, H.-C. (Eds.) Microbial Extracel Lular Polymeric Substances; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; ISBN 978-3-642-64277-7. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.-J.; Zheng, P.; Wang, C.-H.; Mahmood, Q.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Chen, X.-G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.-W. Performance of High-Loaded ANAMMOX UASB Reactors Containing Granular Sludge. Water Res. 2011, 45, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.-T.; Zheng, P.; Shen, L.-D. Growth and Metabolism Characteristics of Anaerobic Ammonium-Oxidizing Bacteria Aggregates. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 5575–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janga, N.; Ren, X.; Kim, G.; Ahn, C.; Cho, J.; Kim, I.S. Characteristics of Soluble Microbial Products and Extracellular Polymeric Substances in the Membrane Bioreactor for Water Reuse. Desalination 2007, 202, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; An, X.; Wang, S.; Xue, C.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Kabutey, F.T.; Wang, K. Effect of Hydraulic Retention Time on Deterioration/Restarting of Sludge Anaerobic Digestion: Extracellular Polymeric Substances and Microbial Response. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, M.; Wang, Z.; She, Z.; Chang, Q.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Y.; Yang, N. Effect of Salinity on Extracellular Polymeric Substances of Activated Sludge from an Anoxic–Aerobic Sequencing Batch Reactor. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2789–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, P.; Izadi, P.; Eldyasti, A. Holistic Insights into Extracellular Polymeric Substance (EPS) in Anammosx Bacterial Matrix and the Potential Sustainable Biopolymer Recovery: A Review. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotti, T.; Carretti, E.; Berti, D.; Montis, C.; Del Buffa, S.; Lubello, C.; Feng, C.; Malpei, F. H ydrogels Formed by Anammox Extracellular Polymeric Substances: Structural and Mechanical Insights. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Wang, S.; Fu, L.; Fang, F.; Guo, J. Characterization of Extracellular Polymeric Substances by Microscopic Imaging Techniques in Wastewater Biotreatment: A Review. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2022, 39, 493–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Yang, Q.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Y. Stratification of Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) for Aggregated Anammox Microorganisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3260–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. Composition Analysis of Fractions of Extracellular Polymeric Substances from an Activated Sludge Culture and Identification of Dominant Forces Affecting Microbial Aggregation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, S.-Q.; Sun, N.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H. Distribution of Extracellular Polymeric Substances in Anammox Granules and Their Important Roles during Anammox Granulation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 101, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Abzac, P.; Bordas, F.; Joussein, E.; van Hullebusch, E.; Lens, P.N.L.; Guibaud, G. Characterization of the Mineral Fraction Associated to Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) in Anaerobic Granular Sludges. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Meng, F.; Chen, G.-H. Spectroscopic Characterization of Extracellular Polymeric Substances from a Mixed Culture Dominated by Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria. Water Res. 2015, 68, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, A.; Fang, F.; Chen, Y.; Yan, P.; Guo, J.; Ma, T.; Shen, Y. Importance of Exopolysaccharide Branched Chains in Determining the Aggregation Ability of Anammox Sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boleij, M.; Pabst, M.; Neu, T.R.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Lin, Y. Identification of Glycoproteins Isolated from Extracellular Polymeric Substances of Full-Scale Anammox Granular Sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13127–13135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, B.; Liu, S. Metagenomic Approaches to Understanding Bacterial Communication during the Anammox Reactor Start-Up. Water Res. 2018, 136, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z. Role of Extracellular Polymeric Substance in Determining the High Aggregation Ability of Anammox Sludge. Water Res. 2015, 75, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Zhao, L.; Feng, L.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.; Hu, T.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wei, L.; You, S. Mechanistic Insight into the Aggregation Ability of Anammox Microorganisms: Roles of Polarity, Composition and Molecular Structure of Extracellular Polymeric Substances. Water Res. 2024, 254, 121438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, M.; Peng, Y. Characterization of EPS Compositions and Microbial Community in an Anammox SBBR System Treating Landfill Leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Xia, X.; Nie, W.; Qin, B.; Hou, T.; Lin, A.; Yao, S.; Zhuang, L. Bidirectional Extracellular Electron Transfer Pathways of Geobacter Sulfurreducens Biofilms: Molecular Insights into Extracellular Polymeric Substances. Environ. Res. 2024, 245, 118038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boleij, M.; Seviour, T.; Wong, L.L.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Lin, Y. Solubilization and Characterization of Extracellular Proteins from Anammox Granular Sludge. Water Res. 2019, 164, 114952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Abzac, P.; Bordas, F.; Van Hullebusch, E.; Lens, P.N.L.; Guibaud, G. Extraction of Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) from Anaerobic Granular Sludges: Comparison of Chemical and Physical Extraction Protocols. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1589–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comte, S.; Guibaud, G.; Baudu, M. Relations between Extraction Protocols for Activated Sludge Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) and Complexation Properties of Pb and Cd with EPS: Part II. Consequences of EPS Extraction Methods on Pb2+ and Cd2+ Complexation. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2006, 38, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comte, S.; Guibaud, G.; Baudu, M. Relations between Extraction Protocols for Activated Sludge Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) and EPS Complexation Properties: Part, I. Comparison of the Efficiency of Eight EPS Extraction Methods. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2006, 38, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Lotti, T.; Lin, Y.; Malpei, F. Extracellular Polymeric Substances Extraction and Recovery from Anammox Granules: Evaluation of Methods and Protocol Development. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 374, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, F.; Wang, F.; Shao, L.; He, P. Deciphering Pretreatment-Induced Repartition among Stratified Extracellular Biopolymers and Its Effect on Anaerobic Biodegradability and Dewaterability of Waste Activated Sludge. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3014–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicer-Nàcher, C.; Domingo-Félez, C.; Mutlu, A.G.; Smets, B.F. Critical Assessment of Extracellular Polymeric Substances Extraction Methods from Mixed Culture Biomass. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5564–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.-M.; Sheng, G.-P.; Luo, H.-W.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, S.-J.; Xu, J.; Zeng, R.J.; Wu, J.-G.; Yu, H.-Q. Contribution of Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) to the Sludge Aggregation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4355–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Ma, H.; Li, Y.-Y. Anammox-Based Granulation Cycle for Sustainable Granular Sludge Biotechnology from Mechanisms to Strategies: A Critical Review. Water Res. 2023, 228, 119353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Huang, Y.; Meng, F.; Jin, C. Development of a Quartz Sand Protocol for Exoproteome Exploration from Anammox Consortia. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 14330–14339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, S.; Tang, X.; Wang, C.; Niu, Z.; Feng, Y. Insight into C-Di-GMP Regulation in Anammox Aggregation in Response to Alternating Feed Loadings. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9155–9164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Meng, Y.; Sheng, B.; Zhou, Z.; Jin, C.; Meng, F. Linking Exoproteome Function and Structure to Anammox Biofilm Development. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1490–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; He, J. Biofilms: The Microbial “Protective Clothing” in Extreme Environments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xue, H.; Wang, H.; Ma, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, Y. High Adhesion Ability of Anammox Granular Microbes Directly Revealed by QCM-D Technique. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkelsen, L.H.; Nielsen, P.H. Quantification of the Bond Energy of Bacteria Attached to Activated Sludge Floc Surfaces. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, P.; Jiang, J. Impacts of Hydrodynamic Shear Force on Nucleation of Flocculent Sludge in Anaerobic Reactor. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3029–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Yang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, M.; Long, M.; Fang, F.; Guo, J. The Differences in Characteristics of Extracellular Polymeric Substances of Flocs and Anammox Granules Impacted Aggregation. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-Q.; Liu, Y.; Tay, J.-H. The Effects of Extracellular Polymeric Substances on the Formation and Stability of Biogranules. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 65, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Cao, S.; Niu, M.; Li, B.; Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Performance of Partial-Denitrification Process Providing Nitrite for Anammox in Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) and Upflow Sludge Blanket (USB) Reactor. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 122, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Dong, W.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Xie, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. Response of Nitrite Accumulation to Elevated C/NO– 3-N Ratio during Partial Denitrification Process: Insights of Extracellular Polymeric Substance, Microbial Community and Metabolic Function. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 384, 129269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, C.E.; Nuijten, G.H.L.; de Graaf, R.M.; Jacobson, T.B.; Pabst, M.; Stevenson, D.M.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Noguera, D.R.; McMahon, K.D.; Amador-Noguez, D.; et al. Autotrophic and Mixotrophic Metabolism of an Anammox Bacterium Revealed by in Vivo 13C and 2H Metabolic Network Mapping. ISME J 2021, 15, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Fang, F.; Yan, P.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Ma, T.; Shen, Y. The Branched Chains and Branching Degree of Exopolysaccharides Affecting the Stability of Anammox Granular Sludge. Water Res. 2020, 178, 115818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Zheng, L.; Sun, D.-Z. Functions and Behaviors of Activated Sludge Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS): A Promising Environmental Interest. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 18, 420–427. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, R.; Zhu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, S.; Lu, H. Active Assimilators of Soluble Microbial Products Produced by Wastewater Anammox Bacteria and Their Roles Revealed by DNA-SIP Coupled to Metagenomics. Environ. Int. 2022, 164, 107265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Bishop, P.L. Biodegradability of Biofilm Extracellular Polymeric Substances. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lan, S.; Hao, S.; Dong, T.; Peng, Y.; Yang, J. Microbial Driving Mechanism for Simultaneous Removal of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in a Pure Anammox Reactor under Ferrous Ion Exposure. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 362, 127844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qin, Y. Fe(II) Improving Sulfurized Anammox Coupled with Autotrophic Denitrification Performance: Based on Interspecies and Intracellular Electron Transfer. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 364, 128051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Jin, H.; Han, M.; Lou, J. Iron-Mediated DAMO–Anammox Process: Revealing the Mechanism of Electron Transfer. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 356, 120750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, C.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, N. Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidation (Anammox) Promoted by Pyrogenic Biochar: Deciphering the Interaction with Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Beer, D.; O’Flaharty, V.; Thaveesri, J.; Lens, P.; Verstraete, W.; de Beer, D. Distribution of Extracellular Polysaccharides and Flotation of Anaerobic Sludge. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1996, 46, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Z.; Xu, J.-J.; Shi, Z.-J.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Ji, Z.-Q.; Deng, R.; Jin, R.-C. Short-Term Impacts of Cu, CuO, ZnO and Ag Nanoparticles (NPs) on Anammox Sludge: CuNPs Make a Difference. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 235, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yu, J.-J.; Jia, X.-Y.; Jin, R.-C. Enhancement of Anammox Performance by Cu(II), Ni(II) and Fe(III) Supplementation. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.-F.; Ma, W.-J.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Li, S.-T.; Zhao, J.-W.; Li, J.-P.; Liu, Q.; Fan, N.-S.; Huang, B.-C.; Jin, R.-C. A Spectra Metrology Insight into the Binding Characteristics of Cu2+ onto Anammox Extracellular Polymeric Substances. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Lu, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Yi, X.; Huang, M. Response Mechanism of a Highly Efficient Partial Nitritd Functional Genes. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krembs, C.; Eicken, H.; Junge, K.; Deming, J.W. High Concentrations of Exopolymeric Substances in Arctic Winter Sea Ice: Implications for the Polar Ocean Carbon Cycle and Cryoprotection of Diatoms. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2002, 49, 2163–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Bai, Y.-H.; Xia, W.-J.; Ni, S.-K.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Fan, N.-S.; Huang, B.-C.; Jin, R.-C. Exogenous Extracellular Polymeric Substances as Protective Agents for the Preservation of Anammox Granules. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-X.; Liao, Q.; Yu, C.; Xiao, R.; Tang, C.-J.; Chai, L.-Y.; Duan, C.-S. Physicochemical and Microbial Properties of Settled and Floating Anammox Granules in Upflow Reactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 123, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Yang, S.F. Influence of Loosely Bound Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) on the Flocculation, Sedimentation and Dewaterability of Activated Sludge. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Jiang, C.; Xu, S.; Gu, L.; Wang, D.; Zuo, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; et al. Insight into Nitrogen Removal Performance of Anaerobic Ammonia Oxidation in Two Reactors: Comparison Based on the Aspects of Extracellular Polymeric Substances and Microbial Community. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 185, 108526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Zuo, J.; Jiang, C.; Wang, D.; Gu, L.; Zhang, S.; Lu, H.; Wang, D.; Xu, S.; Bai, Z.; et al. Fast Start-up of Anammox Process: Effects of Extracellular Polymeric Substances Addition on Performance, Granule Properties, and Bacterial Community Structure. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 338, 117836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Duan, H.; Wei, W.; Ni, B.-J.; Laloo, A.; Yuan, Z. Achieving Stable Mainstream Nitrogen Removal via the Nitrite Pathway by Sludge Treatment Using Free Ammonia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9800–9807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Dong, J.; Wang, Z.; Ma, K.; Xu, X.; Alvarezc, P.J.J.; Zhu, L. Stability of Aerobic Granular Sludge under Condition of Low Influent C/N Ratio: Correlation of Sludge Property and Functional Microorganism. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 270, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.-L.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Wang, Q.-R. Nitrogen Removal Performance of Anaerobic Ammonia Oxidation Co-Culture Immobilized in Different Gel Carriers. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 2379–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, F.; Yang, M.-M.; Wang, H.; Yan, P.; Chen, Y.-P.; Guo, J.-S. Effect of High Salinity in Wastewater on Surface Properties of Anammox Granular Sludge. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Qi, P.; Qiang, Z.; Dong, H.; Gao, D.; Wang, D. Is Anammox a Promising Treatment Process for Nitrogen Removal from Nitrogen-Rich Saline Wastewater? Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 270, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Ma, B.; Song, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Y. Can Anammox Process Be Adopted for Treating Wastewater with High Salinity Exposure Risk? Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Yu, J.; Jeong, S.; Kim, J.; Park, S.; Bae, H.; Rhee, S.-K.; Unno, T.; Ni, S.-Q.; Lee, T. Differences in the Effects of Calcium and Magnesium Ions on the Anammox Granular Properties to Alleviate Salinity Stress. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yu, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Tang, P.; Huang, S. A Novel Control Strategy for the Partial Nitrification and Anammox Process (PN/A) of Immobilized Particles: Using Salinity as a Factor. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Li, Y.; Shan, X.; Abbas, G.; Zeng, Z.; Kang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, P.; Zhang, M. A Holistic Analysis of ANAMMOX Process in Response to Salinity: From Adaptation to Collapse. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 215, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; You, J.; Yin, S.; Yang, H.; He, S.; Feng, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wei, L. Extracellular Polymeric Substances-Antibiotics Interaction in Activated Sludge: A Review. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2023, 13, 100212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.-Q.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Wang, C.-J.; Bai, Y.-H.; Wu, D.; Wu, J.; Tian, G.-M.; Shi, M.-L.; Mahmood, Q.; Jin, R.-C. Expression of the NirS, HzsA, and Hdh Genes and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Response to Recovery of Anammox Process Inhibited by Oxytetracycline. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 681, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.-J.; Huang, D.-Q.; Bai, Y.-H.; Shen, Y.-Y.; Lin, X.-Z.; Huang, Y.; Ling, Y.-R.; Fan, N.-S.; Jin, R.-C. How Anammox Process Resists the Multi-Antibiotic Stress: Resistance Gene Accumulation and Microbial Community Evolution. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, N.-S.; Fu, J.-J.; Huang, D.-Q.; Ma, Y.-L.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Jin, R.-C.; Zheng, P. Resistance Genes and Extracellular Proteins Relieve Antibiotic Stress on the Anammox Process. Water Res. 2021, 202, 117453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.-Q.; Qian, H.; Li, P.-Y.; Zhao, J.-Q.; Sun, Y.-Q.; Jin, R.-C. Insight into the Evolution of Microbial Community and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Anammox Process Induced by Copper after Recovery from Oxytetracycline Stress. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 330, 124945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Narita, Y.; Gao, L.; Ali, M.; Oshiki, M.; Okabe, S. Maximum Specific Growth Rate of Anammox Bacteria Revisited. Water Res. 2017, 116, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan-Díaz, X.; Olmo, L.; Pérez, J.; Carrera, J. Coupling Anammox and Heterotrophic Denitrification Activity at Mainstream Conditions in a Single Reactor Unit. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 134087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, L.; Jiang, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Su, J.; Sun, H.; Xu, S.; Zhuang, X. Harnessing the Potential of Extracellular Polymeric Substances in Enhancing ANAMMOX Processes: Mechanisms, Strategies, and Perspectives. Water 2024, 16, 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091242
Fan L, Jiang C, Wang X, Yang Y, Xie Y, Su J, Sun H, Xu S, Zhuang X. Harnessing the Potential of Extracellular Polymeric Substances in Enhancing ANAMMOX Processes: Mechanisms, Strategies, and Perspectives. Water. 2024; 16(9):1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091242
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Lijing, Cancan Jiang, Xu Wang, Yang Yang, Yawen Xie, Jiaqi Su, Hong Sun, Shengjun Xu, and Xuliang Zhuang. 2024. "Harnessing the Potential of Extracellular Polymeric Substances in Enhancing ANAMMOX Processes: Mechanisms, Strategies, and Perspectives" Water 16, no. 9: 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091242
APA StyleFan, L., Jiang, C., Wang, X., Yang, Y., Xie, Y., Su, J., Sun, H., Xu, S., & Zhuang, X. (2024). Harnessing the Potential of Extracellular Polymeric Substances in Enhancing ANAMMOX Processes: Mechanisms, Strategies, and Perspectives. Water, 16(9), 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091242







