Enhanced Pretreatment of Natural Rubber Industrial Wastewater Using Magnetic Seed Coagulation with Ca(OH)2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wastewater of Centrifuged Latex Production
2.2. Experiments of Magnetic Seed Coagulation (MSC)
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Fractal Structure
2.4.1. SEM Analysis
2.4.2. Fractal Dimension
2.4.3. Lacunarity Measurement
3. Results
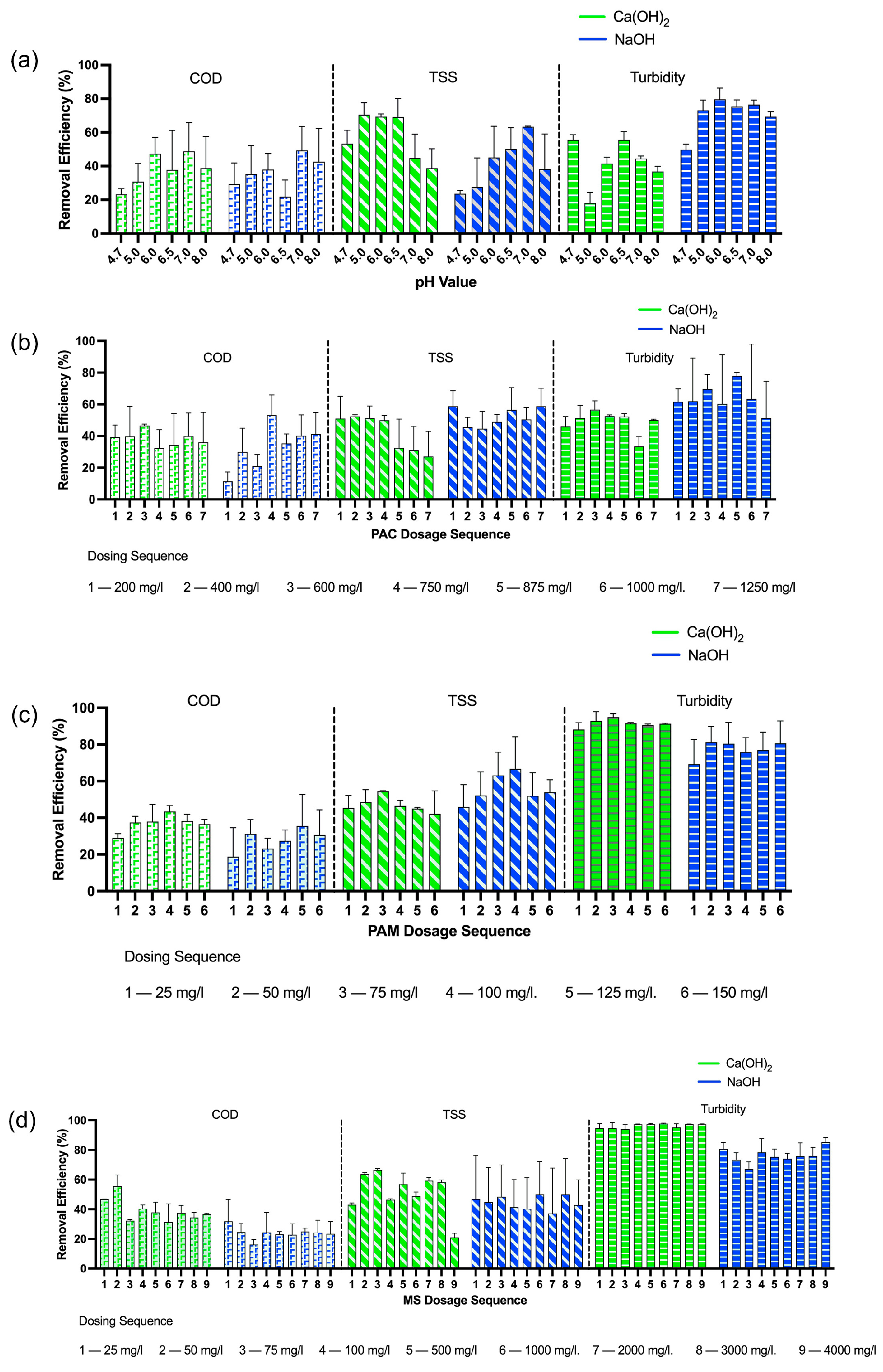
3.1. Optimization of MSC
3.1.1. pH
3.1.2. PAC
3.1.3. PAM
3.1.4. Magnetic Seeds (MS)
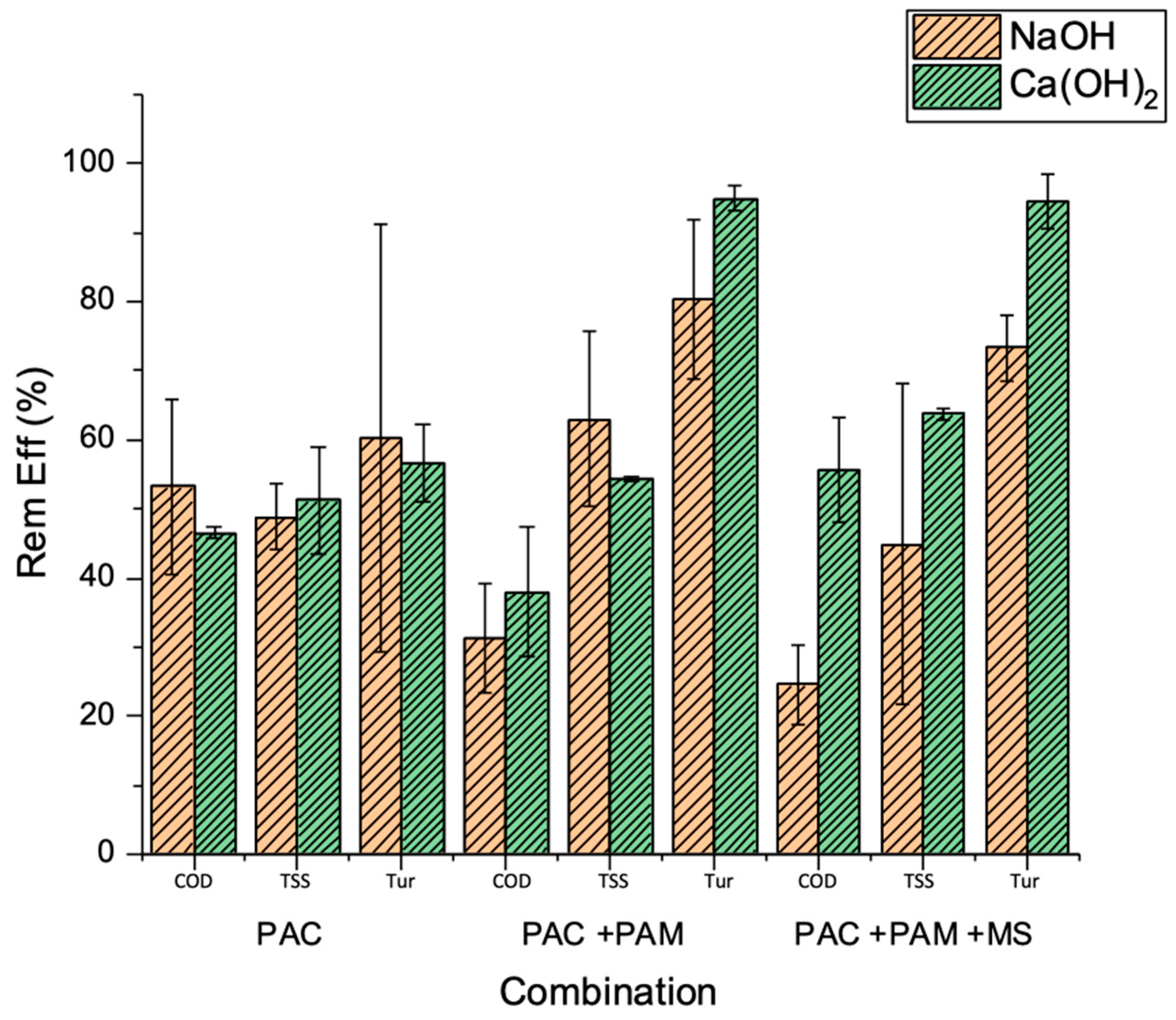
3.2. Pollutant Removal under Optimized MSC
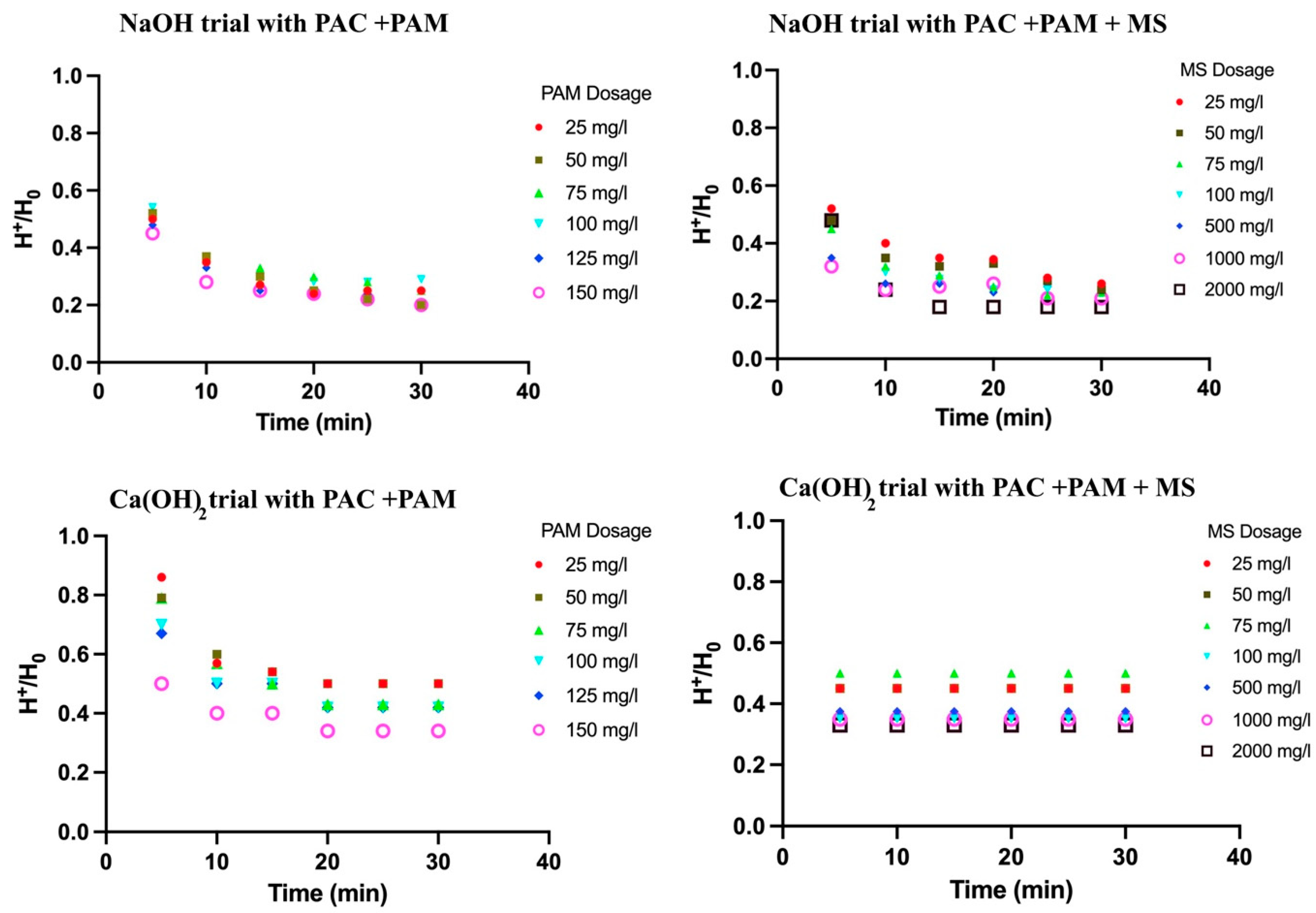
3.3. Settling Time of MSC with pH Adjustment
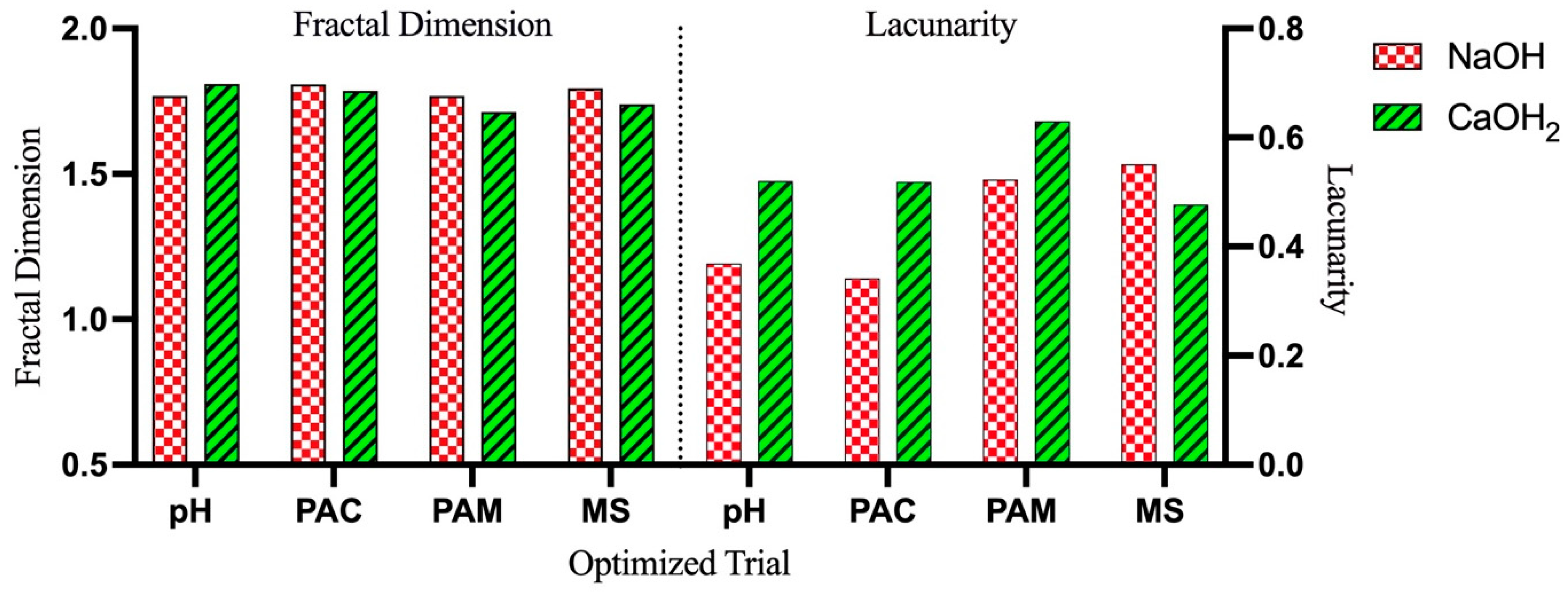
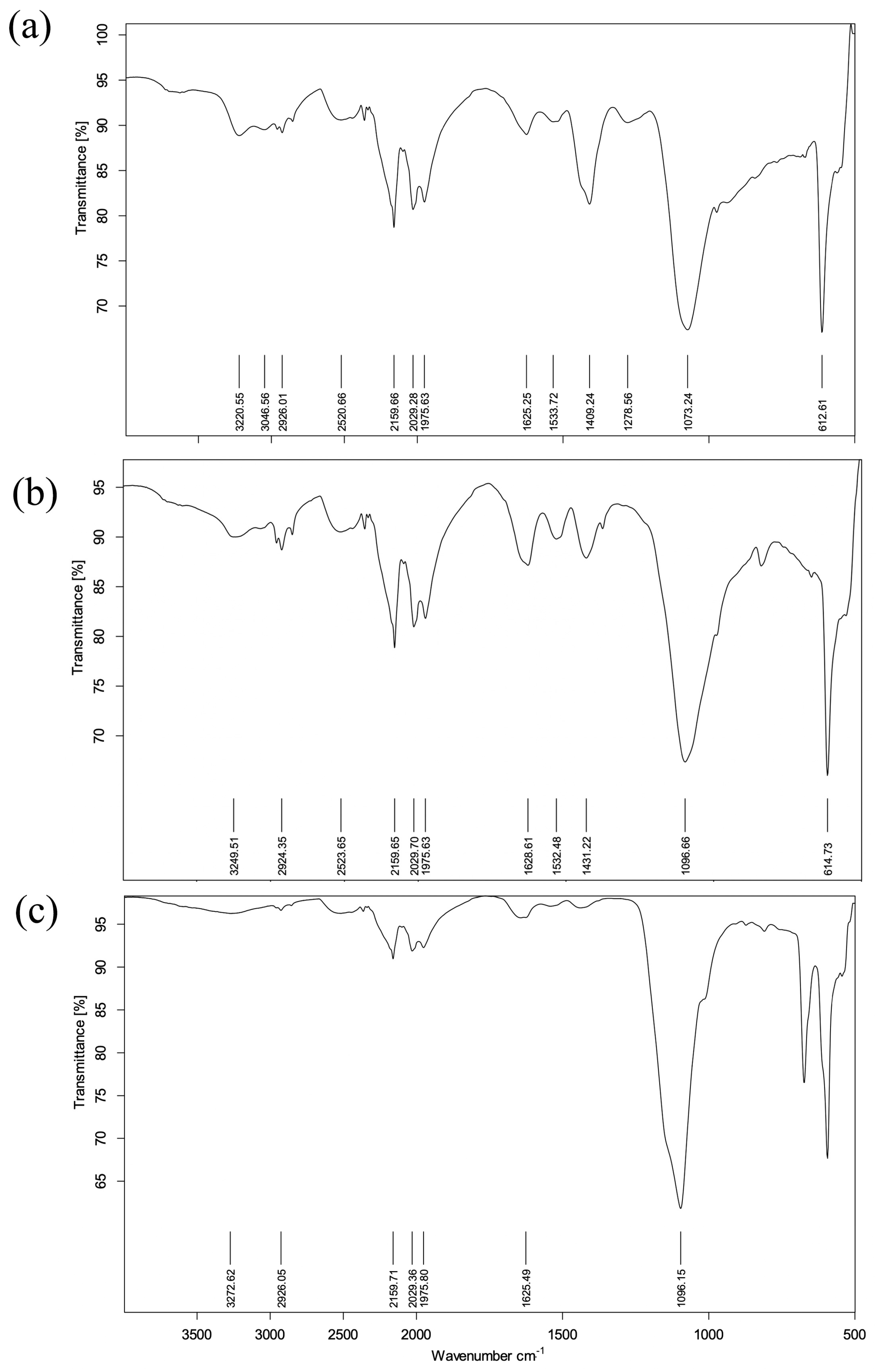
3.4. Fractal Structure Analysis
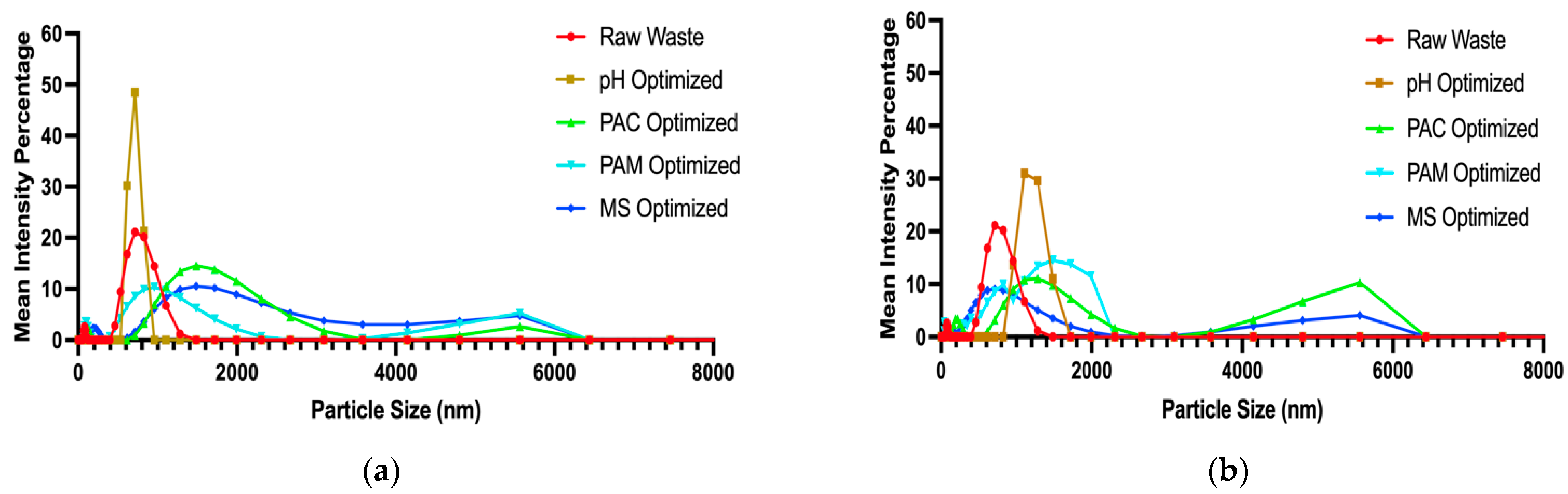
3.5. Removal of Dissolved Matter and Particle Size Optimization
4. Discussion
4.1. Proposed Mechanism of MSC Enhanced with pH Adjustment by Ca(OH)2
4.2. Life Cycle Analysis and Cost Analysis
4.3. Limitations of this Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rubber Reserach Institute of Sri Lanka. Hand Book of Rubber; Tillekeratne, L.M.K., Director, Nugawela, A., Seneviratne, W.M.G., Eds.; Rubber Research Institute: Agalawatta, Sri Lanka, 2003; Volume 2, ISBN 9559022067. [Google Scholar]
- Ngteni, R.; Hossain, M.S.; Kadir, M.O.A.; Asis, A.J.; Tajudin, Z. Kinetics and Isotherm Modeling for the Treatment of Rubber Processing Euent Using Iron (II) Sulphate Waste as a Coagulant. Water 2020, 12, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Census and Statistics, Ministry of Finance. Economic Statistics of Sri Lanka. 2023. Available online: www.statistics.gov.lk (accessed on 26 February 2024).
- Sri Lanka, C.B. Sri Lanka Export Development Board. Available online: https://www.srilankabusiness.com/news/merchandize-exports-reached-usd-13-bn-in-2022.html (accessed on 29 August 2023).
- Silalahi, H.; Agustina, T.; Sirait, E. Treatment of rubber industry wastewater by using fenton reagent and activated carbon. J. Teknol. 2017, 2, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, K.C.; Chan, M.K.; Chen, Y.M.; Subhramaniyun, P. Treatment of Rubber Industry Wastewater Review: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 52, 103559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H.; Klausen, L.H.; Moonhee, R.; Kang, S. Emerging High-Ammonia-nitrogen Wastewater Remediation by Biological Treatment and Photocatalysis Techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijerathna, W.S.M.S.K.; Wimalaweera, T.I.P.; Samarajeewa, D.R.; Lindamulla, L.M.L.K.B.; Rathnayake, R.M.L.D.; Nanayakkara, K.G.N.; Jegatheesan, V.; Wei, Y.; Jinadasa, K.B.S.N. Imperative Assessment on the Current Status of Rubber Wastewater Treatment: Research Development and Future Perspectives. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostermeyer, P.; Van Landuyt, J.; Bonin, L.; Folens, K.; Williamson, A.; Hennebel, T.; Rabaey, K. High Rate Production of Concentrated Sulfides from Metal Bearing Wastewater in an Expanded Bed Hydrogenotrophic Sulfate Reducing Bioreactor. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2022, 11, 100173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idris, J.; Som, A.M.; Musa, M.; Ku Hamid, K.H.; Husen, R.; Muhd Rodhi, M.N. Dragon Fruit Foliage Plant-Based Coagulant for Treatment of Concentrated Latex Effluent: Comparison of Treatment with Ferric Sulfate. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 230860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamoto, M.; Nagai, H.; Sato, S.; Takahashi, M.; Kawakami, S.; Choeisai, P.K.; Syutsubo, S.; Ohashi, A.; Yamaguchi, T. Rubber and Methane Recovery from Deproteinized Natural Rubber Wastewater by Coagulation Pre-Treatment and Anaerobic Treatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2012, 6, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoudinejad, M.; Rabori, M.M.; Dehghani, M.H. Treatment of Natural Rubber Industry Wastewater through a Combination of Physicochemical and Ozonation Processes Introduction 1 Treatment of Natural Rubber Industry Wastewater through a Combination of Physicochemical and Ozonation Processes. J. Adv. Environ. Health Res. 2015, 3, 242–249. [Google Scholar]
- El-taweel, R.M.; Mohamed, N.; Alrefaey, K.A.; Husien, S.; Abdel-Aziz, A.B.; Salim, A.I.; Mostafa, N.G.; Said, L.A.; Fahim, I.S.; Radwan, A.G. A Review of Coagulation Explaining Its Definition, Mechanism, Coagulant Types, and Optimization Models; RSM, and ANN. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2023, 6, 100358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Wu, Z.; Yu, J.; Xu, H.; Chen, M.; Wei, Y. Roles of Magnetic Coagulation in Black-Odor Water Restoration: An Insight into Dissolved Organic Matters. Water Cycle 2023, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xiao, F.; Wang, D.; Xu, X.; Zhou, Q. Comparison of Novel Magnetic Polyaluminum Chlorides Involved Coagulation with Traditional Magnetic Seeding Coagulation: Coagulant Characteristics, Treating Effects, Magnetic Sedimentation Efficiency and Floc Properties. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 182, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Jiao, Y.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Wei, Y. Insight into the Magnetic Lime Coagulation-Membrane Distillation Process for Desulfurization Wastewater Treatment: From Pollutant Removal Feature to Membrane Fouling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritigala, T.; Demissie, H.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, J.; Fan, H.; Li, J.; Wang, D.; Weragoda, S.K.; et al. Optimized Pre-Treatment of High Strength Food Waste Digestate by High Content Aluminum-Nanocluster Based Magnetic Coagulation. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 104, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, S.; Rui, X.; Xu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Lee, C.T.; Li, C. Enhanced Precipitation Performance for Treating High-Phosphorus Wastewater Using Novel Magnetic Seeds from Coal Fly Ash. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, M.; Yadav, R.S.; Feng, Y. Roles of Magnetic Particles in Magnetic Seeding Coagulation-Flocculation Process for Surface Water Treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendashteh, A.R.; Asghari Haji, F.; Chaibakhsh, N.; Yazdi, M.; Pendashteh, M. Optimized Treatment of Wastewater Containing Natural Rubber Latex by Coagulation-Flocculation Process Combined with Fenton Oxidation. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2017, 8, 4015–4023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Dieude-Fauvel Emilie, E.; Dentel, S.K. Physical Characteristics of Conditioned Anaerobic Digested Sludge—A Fractal, Transient and Dynamic Rheological Viewpoint. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Du, B.; Shi, B.; Wang, D. Fractal Analysis of Polyferric Chloride-Humic Acid (PFC-HA) Flocs in Different Topological Spaces. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 535-2009; Water Quality-Determination of Ammonia Nitrogen-Nessler’s Reagent Spectrophotometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- ISO 14040; Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Principles and Framework. International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO): Geneve, Switzerland, 2006.
- ISO 14044; Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Requirements and Guidelines. International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO): Geneve, Switzerland, 2006.
- Jin, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Dong, Y.; Li, J. Differences in Rheological and Fractal Properties of Conditioned and Raw Sewage Sludge. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhu, G.; Jiang, S.; Tshukudu, T.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, P.; He, Q. Investigations of Coagulation-Flocculation Process by Performance Optimization, Model Prediction and Fractal Structure of Flocs. Desalination 2011, 269, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, J.; Ngadi, M.O. Structure and Irregularities of Surface of Fried Batters Studied by Fractal Dimension and Lacunarity Analysis. Food Struct. 2016, 9, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jin, X.; Mi, S.; Tang, J. An Effective Method to Compute the Box-Counting Dimension Based on the Mathematical Definition and Intervals. Results Eng. 2020, 6, 100106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedi, A.; Gorczyca, B. Application of Fractal Dimensions to Study the Structure of Flocs Formed in Lime Softening Process. Water Res. 2011, 45, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Fan, B.; Peng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, J.; Luan, Z. Evaluation of Al30 Polynuclear Species in Polyaluminum Solutions as Coagulant for Water Treatment. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.-C.; Ahmad, M.; Yousaf, M.; Rahman, S.U.; Sharif, H.M.A.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, B.; Huang, Y. Strategic analysis on development of simultaneous adsorption and catalytic biodegradation over advanced bio-carriers for zero-liquid discharge of industrial wastewater. Chemosphere 2023, 332, 138871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ge, X.; Wang, D.; Tang, H. Distinct Coagulation Mechanism and Model between Alum and High Al13-PACl. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 305, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, S.; Chiang, P.-C.; Shah, K.J. Evaluation and Optimization of Enhanced Coagulation Process: Water and Energy Nexus. Water-Energy Nexus 2019, 2, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Huang, X.; Yu, Z.; Chen, P.; Cao, X. Application Progress of Enhanced Coagulation in Water Treatment. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 20231–20244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrill, L.; Mara, E.; Fern, A. Coagulation—Flocculation as a Pretreatment Process at a Landfill Leachate Nitrification—Denitrification Plant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Xu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, W.; Song, K. Science of the Total Environment Effective Removal by Coagulation of Contaminants in Concentrated Leachate from Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Power Plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Song, H.; Zhang, T.; Yao, S.; Wang, Y. Magnetic Technologies and Green Solvents in Extraction and Separation of Bioactive Molecules Together with Biochemical Objects: Current Opportunities and Challenges. Separations 2022, 9, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoczyński, L.; Ratnaweera, H.; Kosobucka, M.; Smoczyński, M. Image Analysis of Sludge Aggregates. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 122, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernitsky, D.J.; Edzwald, J.K. Solubility of Polyaluminium Coagulants. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.—AQUA 2003, 52, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroszyński, T. Removal of Organic Solvents From Wastewaters By Means of Physico-Chemical Methods. Physicochem. Methods Water Wastewater Treat. 1980, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.S. Operating Cost Reduction of In-Line Coagulation/Ultrafiltration Membrane Process Attributed to Coagulation Condition Optimization for Irreversible Fouling Control. Water 2018, 10, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Ge, C.; Sun, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, H. Identification of Organic Pollutants and Heavy Metals in Natural Rubber Wastewater and Evaluation Its Phytotoxicity and Cytogenotoxicity. Chemosphere 2024, 349, 140503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Liu, R.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, L. Treatment of an Alkaline Butyl Rubber Wastewater by the Process of Coagulation and Flocculation—Hydrolysis Acidification—Biological Contact Oxidation—MBR. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2013, 12, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melián, E.P.; Santiago, D.E.; León, E.; Reboso, J.V.; Herrera-Melián, J.A. Treatment of Laundry Wastewater by Different Processes: Optimization and Life Cycle Assessment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, J.; Zhao, X.; Dong, Q.; Wang, X.; Wei, L.; Yang, S.S.; Sun, H.; Ren, N.Q.; Bai, S. Towards the Carbon Neutrality of Sludge Treatment and Disposal in China: A Nationwide Analysis Based on Life Cycle Assessment and Scenario Discovery. Environ. Int. 2023, 174, 107927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, C.J.; Karkou, E.; Vlad, O.; Vyrkou, A.; Savvakis, N.; Arampatzis, G.; Angelis-Dimakis, A. Life cycle environmental impact assessment of slaughterhouse wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 200, 550–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Raw Wastewater | Pretreated Wastewater with Ca(OH)2 | Pretreated Wastewater with NaOH |
|---|---|---|---|
| COD, mg/L | 34,875 ± 2652 | 20,248 ± 824 | 25,893 ± 2000 |
| BOD5, mg/L | 11,150 ± 1485 | 6467 ± 972 | 7805 ± 678 |
| TOC, mg/L | 12,034 ± 1617 | 7438 ±1068 | 8238 ± 1543 |
| TN, mg/L | 4137 ± 1103 | 3529 ± 312 | 3830 ± 534 |
| NO3−–N, mg/L | 1461 ± 245 | 113 ± 37 | 485 ± 248 |
| NO2−–N, mg/L | 50.45 ± 24.67 | 35.55 ± 20.18 | 42.67 ± 33.48 |
| NH3–N, mg/L | 2583 ± 810 | 1545 ± 97 | 2256 ± 398 |
| PO43−–P, mg/L | 995 ± 333 | 156 ± 35 | 390 ± 152 |
| TSS, mg/L | 5695 ± 2595 | 1275 ± 45 | 2093 ± 22 |
| SO42−–S, mg/L | 3130 ± 1032 | 425 ± 181 | 1126 ± 348 |
| EC, mS/cm | 28.35 ± 8.56 | 24.55 ± 8.67 | 26.60 ± 9.14 |
| Turbidity | 2620 ± 205 | 87 ± 7 | 708 ± 126 |
| pH | 5.02 ± 0.81 | 6.50 ± 0.25 | 7.00 ± 0.50 |
| Indicator | MSC with Ca(OH)2 | MSC with NaOH | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fossil resource scarcity | 1.55999 × 10−1 | −6.88316 × 10−1 | USD2013 |
| Freshwater ecotoxicity | 6.68386 × 10−14 | 5.72752 × 10−13 | species.yr |
| Freshwater eutrophication | −1.85415 × 10−7 | −1.33689 × 10−7 | species.yr |
| Global warming, Human health | 1.38058 × 10−6 | 3.65916 × 10−7 | DAILY |
| Human carcinogenic toxicity | 2.52249 × 10−9 | −1.54105 × 10−8 | DAILY |
| Human non-carcinogenic toxicity | 3.00235 × 10−8 | 3.50142 × 10−8 | DAILY |
| Optimization Step | Cost (USD/m3) | |
|---|---|---|
| NaOH | Ca(OH)2 | |
| pH Optimization | 1.88 | 0.41 |
| PAC Optimization | 0.38 | 0.30 |
| PAM Optimization | 0.20 | 0.30 |
| MS Optimization | 0.03 | 0.07 |
| Total | 2.49 | 1.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wimalaweera, I.P.; Wei, Y.; Ritigala, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, H.; Weerasooriya, R.; Jinadasa, S.; Weragoda, S. Enhanced Pretreatment of Natural Rubber Industrial Wastewater Using Magnetic Seed Coagulation with Ca(OH)2. Water 2024, 16, 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060847
Wimalaweera IP, Wei Y, Ritigala T, Wang Y, Zhong H, Weerasooriya R, Jinadasa S, Weragoda S. Enhanced Pretreatment of Natural Rubber Industrial Wastewater Using Magnetic Seed Coagulation with Ca(OH)2. Water. 2024; 16(6):847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060847
Chicago/Turabian StyleWimalaweera, Ishanka Prabhath, Yuansong Wei, Tharindu Ritigala, Yawei Wang, Hui Zhong, Rohan Weerasooriya, Shameen Jinadasa, and Sujithra Weragoda. 2024. "Enhanced Pretreatment of Natural Rubber Industrial Wastewater Using Magnetic Seed Coagulation with Ca(OH)2" Water 16, no. 6: 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060847
APA StyleWimalaweera, I. P., Wei, Y., Ritigala, T., Wang, Y., Zhong, H., Weerasooriya, R., Jinadasa, S., & Weragoda, S. (2024). Enhanced Pretreatment of Natural Rubber Industrial Wastewater Using Magnetic Seed Coagulation with Ca(OH)2. Water, 16(6), 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16060847







