Simulating Aquifer for Nitrate Ion Migration Processes in Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of the Polymeric Material
2.3. Procedure
The Dynamic Study
2.4. Kinetics Studies
2.5. Calculation of Barrier Parameters
Hydraulic Conductivity
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Characterization of Polymeric Materials
3.1.1. SEM-EDAX
3.1.2. FTIR
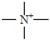 has no characteristic bands. The appearance of a peak at 2923 cm−1 may be due to the group —CH2– (acrylic) stretching vibration, asymmetric, C-H bond (reticulated resin).
has no characteristic bands. The appearance of a peak at 2923 cm−1 may be due to the group —CH2– (acrylic) stretching vibration, asymmetric, C-H bond (reticulated resin).3.1.3. XRD Diffraction
3.2. Kinetics Evaluation
Experimental Determination of Curves in Dynamic Regime and Calculation of Kinetic Parameters of the Process
- -
- Determining the thickness of the reactive medium layer along the barrier;
- -
- Determination of the standing time of the water;
- -
- The evaluation of the economic potential as a result of the adequate design of the operating parameters, which cannot be modified during the remediation.
3.3. Calculation of the Yield (η) of Nitrate Ion Removal
3.4. Calculation of Barrier Parameters
3.4.1. Hydraulic Conductivity
3.4.2. Flow Rate through the Section, or Filtration Rate
3.4.3. Barrier Permeability (K)
3.5. Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Havlin, J.L.; Tisdale, S.L.; Nelson, W.L.; Beaton, J.D. Soil Fertility and Fertilizers: An Introduction to Nutrient Management, 6th ed.; Pearson: Bloomington, MN, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, R.M.; Blowes, D.W.; Gillham, R.W.; Schultz, D.; Sivavec, T.; Puls, R.; Vogan, J.L.; Powell, P.D.; Landis, R. Permeable Reactive Barrier Technologies for Contaminant Remediation, EPA/600/R-98/125; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1998.
- Noubactep, C. Metallic iron for environmental remediation: A review of reviews. Water Res. 2015, 85, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noubactep, C. Comments on “Mechanism study of nitrate reduction by nano zero valent iron” by Hwang et al. [J. Hazard. Mater. (2010), doi:10.1016/jjhazmat.2010.10.078]. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 946–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chekli, L.; Bayatsarmadi, B.; Sekine, R.; Sarkar, B.; Shen, A.M.; Scheckel, K.G.; Skinner, W.; Naidu, R.; Shon, H.K.; Lombi, E.; et al. Analytical characterisation of nanoscale zero valent iron: A methodological review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 903, 13–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.-H.; Kim, D.-G.; Shin, H.-S. Mechanism study of nitrate reduction by nano zero valent iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Lva, L.; Zhang, W.; Du, Q.; Pan, B.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Q. Nitrate reduction using nanosized zero-valent iron supported by polystyrene resins: Role of surface functional groups. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2191–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jianga, Z.; Zhanga, S.; Pana, B.; Wangc, X.; Lva, L.; Zhanga, W.; Zhang, Q. A fabrication strategy for nanosized zero valent iron (nZVI)—Polymeric anion exchanger composites with tunable structure for nitrate reduction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 233–234, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiruvenkatachari, R.; Vigneswaran, S.; Naidu, R. Permeable reactive barrier for groundwater remediation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2008, 14, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badmus, K.O.; Coetsee-Hugo, E.; Swart, H.; Petrik, L. Synthesis and characterisation of stable and efficient nano zero valent iron. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 23667–23684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirbas, E.; Kobya, M.; Senturk, E.; Ozkan, T. Adsorption kinetics for the removal of chromium (VI) from aqueo*us solutions on the activated carbons prepared from agricultural wastes. Water SA 2004, 309, 533–539. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Yi, S.; He, H.; Long, C.; Li, A. Preparation of nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on chelating resin with nitrogen donor atoms for simultaneous reduction of Pb2+ and . Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 230, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimache, A.N.; Iancu, I. General Elements of Hydraulics; Conspress: Bucureşti, Romainia, 2014; ISBN 978-973-100-357-3. [Google Scholar]
- Nield, D.A.; Bejan, A. Convection in Porous Media, 3rd ed.; Springer: Greer, SC, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0387-29096-6/0-387-29096-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.A.; Nakayama, A.; Pop, I. Conjugate free convection of non-Newtonian fluids about a vertical cylindrical fin in porous media. Heat Mass Transf. 1995, 30, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, L.; Chu, S.; Luo, M.; Liu, J. Zeolite supported Fe/Ni bimetallic nanoparticles for simultaneous removal of nitrate and phosphate: Synergistic effect and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 347, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.W.; Mirza, M.L.; Bhatti, T.M. Removal of Cr(VI) using iron nanoparticles supported on porous cation-exchange resin. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 157, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Elliott, D.W.; Zhang, W. Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles for Abatement of Environmental Pollutants: Materials and Engineering Aspects. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2006, 31, 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Long, C.; Li, A. Selective reduction of nitrate into nitrogen using Fe–Pd bimetallic nanoparticle supported on chelating resin at near-neutral pH. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 286, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| P1 | P2 | P3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (h) | (mg/L) | Time (h) | (mg/L) | Time (h) | (mg/L) |
| 0 | 68.75 | 0 | 71.2 | 0 | 76.5 |
| 3 | 67.2 | 6 | 70.9 | 4 | 75.3 |
| 24 | 62.3 | 25 | 69.5 | 26 | 74.5 |
| 38 | 60.9 | 41 | 68.2 | 39 | 73.1 |
| 48 | 58.1 | 45 | 67.9 | 47 | 72.8 |
| 60 | 57.2 | 58 | 66.2 | 61 | 71.6 |
| 66 | 55.8 | 68 | 66.0 | 65 | 70 |
| 69 | 52.6 | 71 | 65.7 | 68 | 68.7 |
| 72 | 50.79 | 79 | 52.5 | 74 | 66.1 |
| 84 | 31.36 | 83 | 34.6 | 83 | 51.8 |
| 96 | 11.1 | 92 | 13.4 | 99 | 34.1 |
| 130 | 5.76 | 128 | 6.8 | 130 | 17.1 |
| Proba | t1/2, (h) | k, (h−1) |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | 72 | 9.62 × 10−3 |
| P2 | 75.2 | 9.21 × 10−3 |
| P3 | 80.1 | 8.62 × 10−3 |
| η1, % | η2, % | η3, % |
|---|---|---|
| 31.5 | 28.8 | 23.5 |
| 32.8 | 30.6 | 25.5 |
| 37.7 | 31.8 | 27.2 |
| 39.1 | 33.9 | 29.9 |
| 41.9 | 35.3 | 31.3 |
| 42.8 | 37.6 | 33.1 |
| 44.2 | 38.9 | 34.3 |
| 47.4 | 42.6 | 36.5 |
| 49.21 | 47.5 | 43.7 |
| 68.64 | 65.4 | 48.2 |
| 88.9 | 86.6 | 65.9 |
| 94.24 | 93.2 | 82.9 |
| Q, m3/s | k, m⋅s−1 | v, m⋅s−1 | K, m2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 | 0.23 × 10−2 | 1.64 × 10−4 | 2.17 × 10−7 |
| Q2 | 0.28 × 10−2 | 1.97 × 10−4 | |
| Q3 | 0.47 × 10−2 | 3.27 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orbuleţ, O.D.; Modrogan, C.; Covaliu-Mierla, C.-I. Simulating Aquifer for Nitrate Ion Migration Processes in Soil. Water 2024, 16, 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050783
Orbuleţ OD, Modrogan C, Covaliu-Mierla C-I. Simulating Aquifer for Nitrate Ion Migration Processes in Soil. Water. 2024; 16(5):783. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050783
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrbuleţ, Oanamari Daniela, Cristina Modrogan, and Cristina-Ileana Covaliu-Mierla. 2024. "Simulating Aquifer for Nitrate Ion Migration Processes in Soil" Water 16, no. 5: 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050783
APA StyleOrbuleţ, O. D., Modrogan, C., & Covaliu-Mierla, C.-I. (2024). Simulating Aquifer for Nitrate Ion Migration Processes in Soil. Water, 16(5), 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050783







