Abstract
Freshwater ecosystems provide an array of provisioning, regulating/maintenance, and cultural ecosystem services. Despite their crucial role, freshwater ecosystems are exceptionally vulnerable due to changes driven by both natural and human factors. Water quality is essential for assessing the condition and ecological health of freshwater ecosystems, and its evaluation involves various water quality parameters. Remote sensing has become an efficient approach for retrieving and mapping these parameters, even in optically complex waters such as small rivers. This study specifically focuses on modelling two non-optically active water quality parameters, dissolved oxygen (DO) and electrical conductivity (EC), by integrating 3 m PlanetScope satellite imagery with data from real-time in situ remote monitoring sensors across two small rivers in Thrace, Northeast Greece. We employed three different experimental setups using a support vector regression (SVR) algorithm: ‘Multi-seasonal by Individual Sensor’ (M-I-S) for individual sensor analysis across two seasons, ‘Multi-seasonal—All Sensors’ (M-A-S) integrating data across all seasons and sensors, and ‘Seasonal—All Sensors’ (S-A-S) focusing on per-season sensor data. The models incorporating multiple seasons and all in situ sensors resulted in R2 values of 0.549 and 0.657 for DO and EC, respectively. A multi-seasonal approach per in situ sensor resulted in R2 values of 0.885 for DO and 0.849 for EC. Meanwhile, the seasonal approach, using all in situ sensors, achieved R2 values of 0.805 for DO and 0.911 for EC. These results underscore the significant potential of combining PlanetScope data and machine learning to model these parameters and monitor the condition of ecosystems over small river surfaces.
1. Introduction
Water quality is defined as the biological, chemical, thermal, and physical characteristics of water required to maintain water-dependent activities, including drinking, irrigation, and recreation [1,2,3]. Rivers, lakes, and other inland water bodies serve as the primary resource of freshwater, providing various provisioning, regulating/maintenance, and cultural ecosystem services, yet they are exceptionally fragile ecosystems [4,5]. The domestic and industrial wastewater discharge into inland water bodies due to urban expansion and excessive use of pesticides and fertilizers in agriculture cause water pollution and consequent water quality and ecosystem degradation [6,7]. Therefore, ensuring sustainable urban and rural water supplies requires the continuous monitoring of the available water bodies quality to maintain their long-term functionality and ecological balance.
Ensuring the water quality of freshwater ecosystems is crucial for multiple reasons. Firstly, it underpins effective management strategies. Secondly, it supports accurate condition reporting, as referenced in studies [8]. Furthermore, assessing the ecosystem services these ecosystems provide, as highlighted in References [9,10], is essential. This importance is acknowledged in various policy support tools and frameworks. Among them, the System of Environmental Economic Accounting–Ecosystem Accounting (SEEA-EA) [11] stands out as a key framework guiding these efforts. Additionally, the need for such monitoring, encompassing both water quality and the ecological status of inland water bodies, is emphasized in national and European Union environmental legislation, including the EU Water Framework Directive (EU-WFD) [8]. In the context of the EU-WFD, a comprehensive evaluation has been conducted on 111,062 European surface water bodies, where 46% of these are being adequately monitored to assess their ecological status, while 23% suffer from insufficient in situ water sampling. Notably, a significant proportion of 4% remains with an unknown ecological status, warranting further investigation and attention [12,13].
The ecological status of freshwater ecosystems is assessed based on the quality of their structure and functioning, reflecting the impact of pollution and habitat degradation. This assessment relies on biological quality elements supported by physico-chemical and hydromorphological quality elements [13]. Among these, key physico-chemical parameters include turbidity, water temperature, salinity, dissolved oxygen, and electrical conductivity, which are also commonly referred to as water quality parameters [2,12,14]. Dissolved oxygen (DO), indicating the amount of molecular oxygen dissolved in rivers, lakes, or estuaries, is crucial for assessing freshwater ecosystems [15,16,17,18], with high levels indicating good water quality [15,17]. Electrical conductivity (EC) measures water’s capacity to conduct electricity, influenced by factors such as salinity and dissolved solids [2]. Each water body typically has a consistent conductivity range, providing a baseline for comparison against regular measurements. Notably, substantial increases in conductivity often signal potential water quality impairment.
Traditional point-based water quality monitoring methods, while precise, are labor-intensive, time-consuming, and costly, often failing to capture the spatial and temporal variability of water quality across extensive water surfaces [19]. In contrast, remote sensing (RS) offers an alternative for monitoring and mapping the distribution of such parameters over inland water bodies, circumventing these limitations [20]. The ongoing evolution of Earth observation (EO) data characteristics significantly reinforces this approach, particularly for optically complex waters in small and medium–large rivers, using high-spatial-resolution data [12,21,22]. Freely available, medium–high-spatial-resolution satellites, such as Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2, are commonly used for water quality monitoring due to their promising results [23,24,25,26], although their application in small water bodies like narrow rivers and small reservoirs is limited [27]. These satellites often fail to meet the necessary scientific and operational requirements for water quality parameters monitoring, which vary dynamically both spatially and temporally [28]. Currently, no freely available multispectral data provide an ideal combination of spectral and spatial resolution for small river water quality monitoring [2]. However, higher spatial resolution satellites like RapidEye and SPOT, along with the relatively new Dove/SuperDove satellites from the PlanetScope constellation, offer both high temporal and spatial resolution imagery and have shown success in monitoring small water bodies [27,29,30].
Water quality modelling through EO data hinges on the relationship between the surface reflectance and the biophysical parameters of the water. The interaction between solar radiation and optically active components alters the spectral properties of water and can be detected by satellite sensors [31]. However, determining the link between these parameters and the recorded reflectance is challenging, especially for non-optically active parameters, such as DO and EC. These parameters only minimally influence the reflectance measured by using remote sensing sensors [32,33,34]. To address this, machine learning algorithms like support vector regression (SVR) [2,15,19,35], random forests [15,35], and artificial neural networks [19,35] have been proposed to model both optically and non-optically active water quality parameters.
This study represents a significant advancement in the field of environmental monitoring by leveraging the capabilities of SuperDove satellite imagery to assess non-optically active water quality parameters in small rivers. In such ecosystems, traditional monitoring methods fall short due to their labor-intensive nature and inability to capture spatial and temporal variability. Furthermore, the spatial resolution of commonly used Earth observation (EO) sensors often fails to distinguish between land and water spectral reflectance, leading to mixed signals. Our approach overcomes these limitations, offering a more precise and efficient monitoring solution for such ecosystems.
Specifically, we focus on two small rivers in Thrace, Northeast Greece, subjected to intense anthropogenic pressures, which have been previously undermonitored in regard to their ecological status. This study is driven by two primary objectives: firstly, to develop accurate machine learning models that correlate in situ measurements of dissolved oxygen (DO) and electrical conductivity (EC) with satellite-recorded reflectance, demonstrating the capability of remote sensing in monitoring water quality parameters that are traditionally challenging to measure from space. Secondly, to investigate the impact of seasonal and locational variations on the predictive accuracy of these models, thereby assessing their robustness and applicability across different environmental conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
This study focuses on two small riverbeds, Laspias and Lissos, located in the River Basin District of Thrace region in Northeast Greece (Figure 1). The prevailing climate in the region is Mediterranean, transitioning to Mediterranean Highland in the mountainous parts of the area. The southern areas receive annual rainfall from 500 to 600 mm, while in the interior, it varies between 600 and 1000 mm [36]. The mean annual temperature is 14.5 to 16.5 °C, with a significant annual thermometric range exceeding 20 °C.
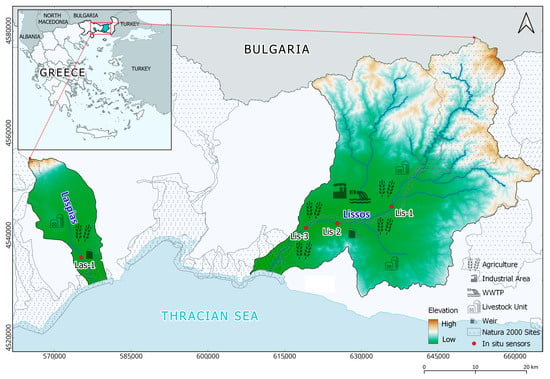
Figure 1.
Laspias River and Lissos River basins, and locations of the four real-time remote monitoring in situ sensors.
The Laspias River basin, a rural peri-urban basin in Xanthi Prefecture, covers 212 km2 and is characterized by its torrential-like character and intermittent streams. The river originates from the mountain peaks of Rhodope at altitudes up to 1300 m, flows through agricultural plains, and discharges into the Thracian Sea. Approximately 30 km in length, the Laspias River includes two heavily modified water bodies. It faces several pressures, mainly due to salinization and anthropogenic activities, including nitrate pollution, landfill waste, effluent discharge from wastewater treatment plants, as well as intense industrial and agricultural activities. This leads to contamination by nitrate (NO3), nitrite (NO2), and ammonia (NH4), as well as increased levels of conductivity (EC) and chloride ions (Cl). Despite its ecological significance, the river lacks integrated management, with only its downstream parts designated as a Natura 2000 site [36,37].
The Lissos River basin is situated in Rhodope Prefecture and covers an area of 1486 km2. The river, approximately 230 km long, includes both natural and heavily modified parts. It originates from the Eastern Rhodope mountains and discharges into the Thracian Sea, receiving contributions from numerous small rivers and streams. The entire course of the Lissos River, from its source to the estuary, is of significant economic and environmental value. It plays a crucial role in irrigating the surrounding cultivated fields, and a substantial portion of the river is protected under the Natura 2000 regime, highlighting its environmental importance [38]. Despite this, the Lissos River faces several challenges, including contamination from industrial wastes, crop pesticides, and sand extractions [36].
2.2. In Situ Sensor Measurements
For real-time remote monitoring and reference data acquisition, three in situ sensors were installed along Lissos and one along Laspias River, corresponding to four distinct sites (Figure 1). The selection of the sensor sites was based on two key criteria: the presence of anthropogenic pressures and the assurance of sufficient water quantity for reliable in situ measurements and satellite sensor detection throughout the study period. Consequently, all sensors were placed near agricultural sites, with expected pesticides and fertilizers usage, and in or adjacent to Natura 2000 sites. Additionally, Las-1 and Lis-2 sensors are located at weir structures, whereas Lis-2 is also positioned close to an industrial area and a wastewater treatment plant (Table 1). The Aqua TROLL 500 Multiparameter Sonde (In-Situ Inc, Fort Collins, CO, USA) was chosen for water quality monitoring in both rivers, equipped with onboard sensors to measure various parameters such as dissolved oxygen and conductivity, among others [39,40].

Table 1.
Location descriptions and monitoring periods for the in situ sensors in Lissos River (Lis-1, Lis-2, and Lis-3) and Laspias River (Las-1).
These sensors provided near-real-time observations of DO and EC at 30 min intervals from 25 March 2022 to 29 October 2022, covering three different seasons: spring, summer, and autumn. Data collection was facilitated by the addVANTAGE Pro 6.6 software (OTT HydroMet GmbH, Vienna, Austria), which, in conjunction with telemetry devices, constitutes the Adcon system. This system enables the measurement of specific parameters, their transmission over significant distances, and their subsequent processing for applications in agriculture, meteorology, irrigation control, water management, and environmental analysis [41]. The observation collection end date varied slightly based on each sensor's initial deployment (Table 1).
2.3. Earth Observation Data
For this study, we utilized PlanetScope Analytic Ortho Scene Product, sourced from the Planet Labs PBC (Planet Labs PBC, San Francisco, CA, USA) platform. PlanetScope constellation consists of sensors that deliver high spatial resolution and near-daily revisit frequency data across the visible to infrared spectrum. As opposed to previous PlanetScope constellations, the third Dove generation, SuperDove, delivers 8-band multispectral data, out of which 6 bands (excluding the Green I and Yellow bands) are similar and well-aligned with the spectral response functions of the Sentinel-2 bands within the visible to infrared spectrum (Table 2) [42,43,44]. The Analytic Ortho Scene Product is orthorectified and expressed as surface reflectance.

Table 2.
PlanetScope’s SuperDove sensor specifications.
Careful selection of satellite images was paramount to ensure comprehensive and consistent coverage of the study area and timeframe, as well as minimum atmospheric influence. Accordingly, SuperDove imagery, collected evenly between 25 March 2022 and 29 October 2022, was selected (Table 3). The data were then clipped to an adequate area surrounding each in situ sensor site.

Table 3.
Number of PlanetScope imagery used in this study.
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Experimental Design
Three distinct experimental setups were implemented:
- ‘Multi-seasonal by Individual Sensor’ (M-I-S). This setup incorporates data from multiple seasons, analysing observations from each of the four in situ sensors individually.
For the Lissos River sensors, two additional experiments were formulated:
- ‘Multi-seasonal—All Sensors’ (M-A-S). This approach incorporates data from all in situ measurements across three seasons, spanning from March to October.
- ‘Seasonal—All Sensors’ (S-A-S). This experiment consolidates sensor recordings on a per-season basis, separately analysing the spring period (25 March–30 May) and the summer period (2 June–31 August).
The mean pixel value within a 3 × 3 pixel window at each in situ sensor site was matched with the corresponding in situ measurement of DO and EC. Particular attention was paid to ensuring that DO and EC measurements coincided with the data and time of the satellite pass. Consequently, the dataset included eight independent variables (spectral reflectance per band) and one dependent variable (in situ DO and EC observations, respectively).
Table 4 provides a summary of the in situ observation statistics within these datasets. It should be noted that due to a dysfunction of sensor Lis-3, EC observations were not available.

Table 4.
Summary statistics for the three experimental setups: ‘Multi-seasonal by Individual Sensor’ (M-I-S), ‘Multi-seasonal—All Sensors’ (M-A-S), and ‘Seasonal—All Sensors’ (S-A-S).
2.4.2. Water Quality Parameter Modelling
The DO and EC prediction models were developed using the support vector regression (SVR) algorithm, grounded in the structural risk minimization principle introduced by Vapnik and Chervonenkis in 1974 [45]. This analysis leverages the relationship between the eight spectral bands of PlanetScope imagery (predictor variables) and the DO and EC observations (dependent variables) for each experimental setup. To derive the SVR models, parameters were optimized to enhance the generalization ability of the algorithm to unknown data [46]. These parameters were selected through a 10-fold cross-validation aiming to minimize the error rate [47]. A two-dimensional grid search method was employed to identify the most appropriate values by testing different pairs of parameters and choosing the one with the highest cross-validation accuracy. The radial basis function, a commonly used kernel function in various studies, was implemented to fit the models [48,49,50]. Prior to model execution, datasets were split into training and testing sets in a 7:3 ratio. The analysis was conducted using R programming language.
2.4.3. Accuracy Assessment
Three accuracy metrics, the coefficient of determination (R2), root-mean-square error (RMSE), and mean absolute error (MAE), were applied to assess the accuracy of the prediction models. These metrics have been incorporated in several water parameter modelling studies [2,15,19,50]. More specifically, R2 gives an approximation of the proportion of variance explained by the model, RMSE is employed for model assessment but can be strongly influenced by outliers, and MAE provides insight into the average vertical distance between predicted and observed values [50,51]. Table 5 details the mathematical formulas of the accuracy metrics used in estimating the accuracy of the water quality parameters prediction models.

Table 5.
Accuracy metrics (R2, RMSE, and MAE) for model evaluation. Here, represents observations, denotes predicted values, is the mean of the observations, and indicates the number of observations.
3. Results
3.1. ‘Multi-Seasonal by Individual Sensor’ (M-I-S) Experiment
Four models were developed for each in situ sensor across multiple seasons, separately for DO and EC. These models included three sensors from the Lissos River (Lis-1, Lis-2, and Lis-3) and one from the Laspias River (Las-1). The models’ effectiveness and their correlation with the sensor’s location were evaluated using a Taylor diagram (Figure 2) and accuracy metrics (Table 6). For the DO models, correlations ranged from 59% to 96%, indicating a strong agreement with actual values. The Las-1 sensor-based model exhibited the highest correlation at 96%, while the Lis-3 sensor-based model showed the lowest at 59%. Models using data from Lis-1 and Lis-2 sensors achieved correlations of approximately 80% (Figure 2a).
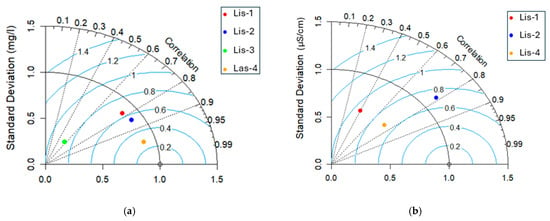
Figure 2.
Taylor diagrams of DO (a) and EC (b) of ‘Multi-seasonal by Individual Sensor’ (M-I-S) models. Distance between model and reference point is a measure of how realistically each model reproduces observations. The azimuthal angle represents the correlation between predicted and observed values, and RMSE is shown by the blue contours. The radial distance from the origin (black contours) refers to the standard deviation.

Table 6.
Accuracy metrics for ‘Multi-seasonal by Individual Sensor’ (M-I-S) model evaluation.
In contrast, the EC models demonstrated lower correlations compared to the DO models, ranging from 39% to 79%. The model based on Lis-2 sensor data had the highest correlation, while the Lis-1 sensor-based model had the lowest (Figure 2b).
3.2. ‘Multi-Seasonal—All Sensors’ (M-A-S) Experiment
Two prediction models were developed for each water quality parameter, DO and EC, considering data from multiple seasons and all sensors collectively along the Lissos River. These models utilized observations from the Lis-1, Lis-2, and Lis-3 in situ sensors, spanning from March 2022 to October 2022. The EC model outperformed slightly the DO model, achieving R2 values of 0.657 and 0.549, respectively, as illustrated in the scatter plots (Figure 3a,c). Additionally, the models’ evaluation statistics were encapsulated in Taylor diagrams (Figure 3b,d). In terms of the correlation between predicted and observed values, the models exhibited a 78% Pearson correlation for EC and 61% for DO. The EC model had an RMSE of 46.796 μS/cm, while the DO model had an RMSE of 1.813 mg/L. The standard deviation for the EC model was 61.190 μS/cm, and for the DO model, it was 1.565 mg/L. These values indicate less variability compared to the observed values, which were 74.885 μS/cm for EC and 2.350 mg/L for DO, respectively.
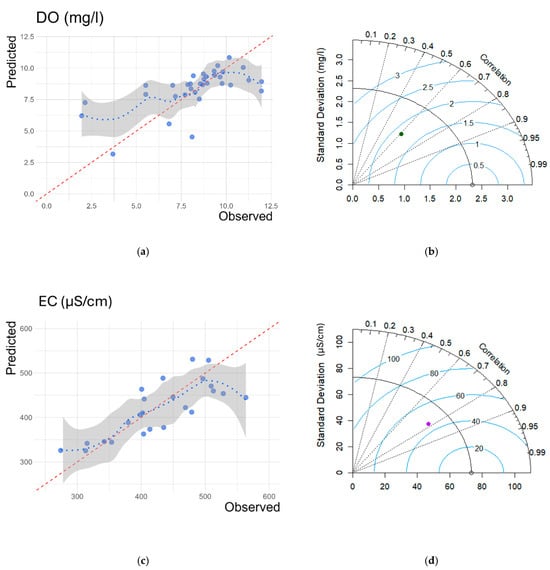
Figure 3.
Scatter plots (a,c) and Taylor diagrams (b,d) of M-A-S DO and EC models, respectively. The red dashed line is the 1:1 reference line, and the blue dotted line is the trend line considering the relationship between predicted and observed values.
3.3. ‘Seasonal—All Sensors’ (S-A-S) Experiment
For the seasonal approach using all in situ sensor observations over the Lissos River, two models were developed for each water quality parameter, focusing on the spring (March to May 2022) and summer (June to August 2022) periods. These models exhibited varying performances depending on the season. Table 7 details the accuracy metrics for these four seasonal models. Consistent with the results in Section 3.2, EC models outperformed DO models in both periods, achieving higher R2 values, as illustrated in the scatter plots (Figure 4). The DO spring model showed better performance and lower RMSE and MAE compared to its summer counterpart. On the other hand, while the EC model for spring also had higher R2 values than the summer model, it registered increased RMSE and MAE. This discrepancy is likely due to the greater variability in observed values during the spring, influenced by factors such as increased precipitation and higher water flow rates.

Table 7.
Accuracy metrics for ‘Seasonal—All Sensors’ (S-A-S) model evaluation.
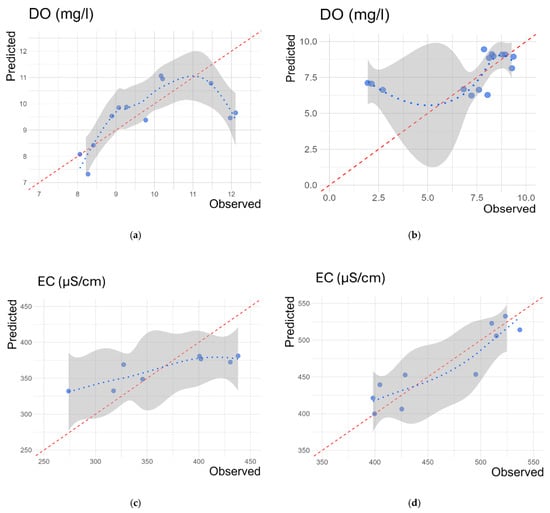
Figure 4.
Scatter plots of S-A-S DO (a,b) and EC models (c,d). Plots (a,c) refer to the spring period, and plots (b,d) refer to the summer period. The red dashed line is the 1:1 reference line, and the blue dotted line is the trend line considering the relationship between predicted and observed values.
3.4. Spatial Distribution of DO and EC
The EC and DO distribution maps were generated for the M-A-S (Figure 5 and Figure 6) and M-I-S (Figure 7 and Figure 8) models, representing data on three individual dates in the spring, summer, and autumn periods at each in situ sensor site. These maps highlighted site-specific variations in EC and DO, which were also influenced by seasonal changes.
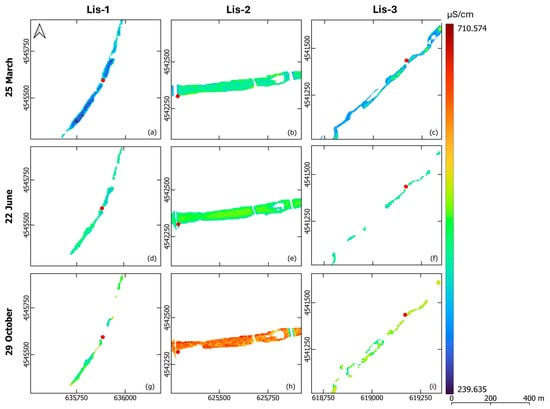
Figure 5.
Electrical conductivity distribution maps around the Lis-1 (a,d,g), Lis-2 (b,e,h), and Lis-3 (c,f,i) sites in the Lissos River on 25 March 2022 (a–c), 22 June 2022 (d–f), and 29 October 2022 (g–i) based on the M-A-S models.
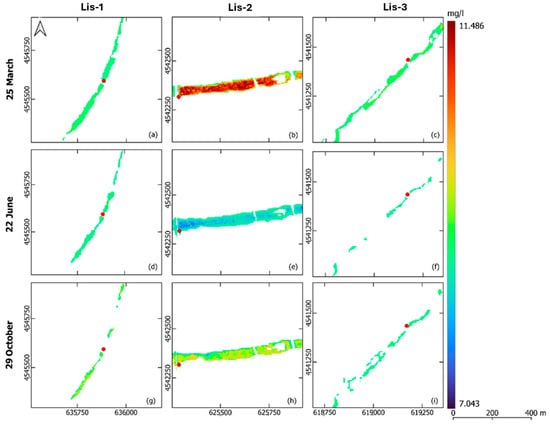
Figure 6.
Dissolved oxygen distribution maps around the Lis-1 (a,d,g), Lis-2 (b,e,h), and Lis-3 (c,f,i) sites in the Lissos River on 25 March 2022 (a–c), 22 June 2022 (d–f), and 29 October 2022 (g–i) based on the M-A-S models.
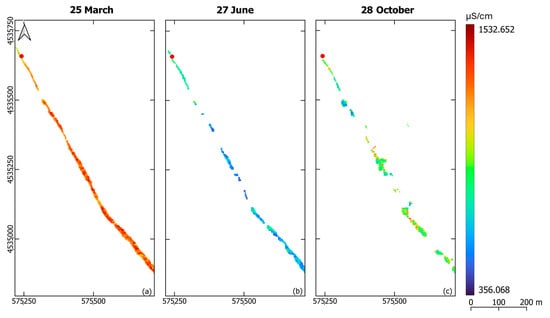
Figure 7.
Electrical conductivity distribution maps around the Las-1 site in the Laspias River on 25 March 2022 (a), 27 June 2022 (b), and 28 October 2022 (c) based on the M-I-S models.
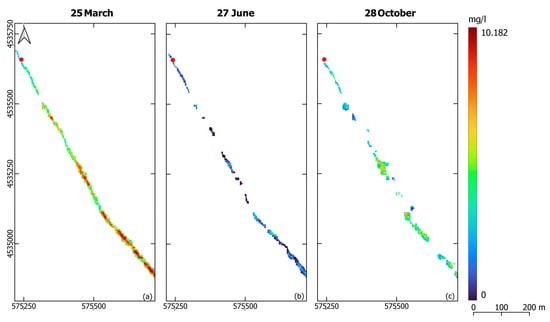
Figure 8.
Dissolved oxygen distribution maps around the Las-1 site in the Laspias River on 25 March 2022 (a), 27 June 2022 (b), and 28 October 2022 (c) based on the M-I-S models.
Levels of EC range from 239.635 to 710.574 μS/cm (Figure 5). For the EC distribution maps from the M-A-S models, lower values were observed in spring, with a slight increase in summer and the highest values recorded in autumn. Notably, EC values at the Lis-2 sensor site presented a sharp increase in October. In contrast, the M-I-S model for the Laspias River indicated EC levels between 356.068 and 1532.652 μS/cm, peaking in spring and dipping in summer (Figure 7).
The DO distribution maps consistently reflected seasonal trends across all models. The solubility of DO in freshwater, which is temperature-dependent [52], resulted in higher values in spring and lower values in summer, with a slight increase again in autumn. DO levels for the M-A-S models ranged from 7.043 to 11.486 mg/L (Figure 6), while for the M-I-S model in the Laspias River, they varied from 0 to 10.182 mg/L (Figure 8). In terms of location, DO levels at the Lis-2 and Las-1 sensor sites exhibited the most significant fluctuations, recording higher values in spring and lower values in summer.
4. Discussion
In this study, we developed prediction models to assess the water quality of two rural rivers in northeastern Greece. We synergistically used EO data, in situ observations, and the SVR algorithm to analyse the relationship between the spectral reflectance and two water quality parameters. Additionally, three experimental setups were employed to explore various modelling approaches and to determine the impact of seasonality and sampling sites on the prediction of water quality parameters. We focused on two non-optically active parameters, DO and EC, which are less studied using RS techniques. These parameters are also crucial physico-chemical quality elements within the EU-WFD framework and are integral to determining the status of water bodies [12].
Our findings indicated that the EC models generally performed well, with R2 exceeding 0.65 and comparable errors. The model developed using reference data from the Las-1 sensor exhibited the highest RMSE. This discrepancy was due to the high variation in EC observations for the Laspias River between early spring and summer. The lowest RMSE was observed in the S-A-S summer model. This aligns with other studies [26,51,53] that used regression analyses and data from Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 satellites to estimate reservoir conductivity, achieving R2 values ranging between 0.615 and 0.787. Similarly, DO models demonstrated effective results, achieving R2 above 0.69, with three models exceeding 0.80. In particular, the individual sensor models (M-I-S setup) developed with reference data from the Lis-1 and Lis-3 sensors exhibited high R2 values and the lowest errors. Comparatively, Pizani et al. [51] estimated DO with R2 values ranging from 0.69 to 0.85 using in situ data from a single date. Tian et al. [19] also estimated DO in a Chinese reservoir, using machine learning models and Sentinel-2 satellite data, achieving high accuracy (R2 > 0.70).
Our study found that the DO models consistently reflected the seasonal trends of DO concentrations, as illustrated in Figure 6 and Figure 8. In line with other research [52], we observed that DO concentrations were higher in spring when water temperatures were lower and decreased during summer and autumn due to a higher rate of biodegradation associated with higher temperatures. This seasonal variation in DO levels, with the lowest values typically in early autumn and the highest in early spring, was also noted by Boskidis et al. [54] in a study of a nearby river basin. Among our in situ sensor sites, Lis-2 exhibited the most significant seasonal fluctuations, with the highest DO levels in spring and the lowest in summer. Notably, the Lis-1 sensor site recorded the lowest DO levels, even reaching zero in June, indicating potential ecosystem disturbances from heatwaves and anthropogenic pressures. In a similar vein, Xu et al. [55] observed substantial spatiotemporal variability in water quality parameters like DO and pH across seasons and monitoring locations, particularly in areas influenced by agricultural and urban activities. Other studies [54,56] have also highlighted the impact of point and non-point source pollution and riverbed morphology on parameters such as EC and DO.
Regarding EC distribution maps, seasonal variation was again a key factor. For the Lissos River, the lowest EC values were recorded in spring, increasing to the highest in autumn. This pattern is closely tied with seasonal discharge variations: decreased river discharge and increased evaporation lead to higher mineral concentration increases [54], thereby elevating EC values. During spring, heavy precipitation leads to increased river flushing, while autumn’s reduced discharge, due to the dry season from mid-June to November, concentrates pollutants and suspended solids, affecting conductivity levels. This phenomenon also results in changes in water coloration detectable by satellites. The Lis-2 and Las-1 sites showed the most pronounced EC seasonal variations, particularly at the Las-1 site, where the highest EC values were recorded in March. Factors such as salinization and loss of natural vegetation, which contribute to increased water salinity, are strongly correlated with EC [57]. Similarly, Gonzalez et al. [26], in their study of a reservoir in Colombia, found that EC and turbidity could be linked to human impacts.
Utilizing RS data enabled the prediction of two optically inactive parameters, DO and EC, in the Lissos and Laspias Rivers. This is possible because the spectral behavior of water correlates with the presence of optically active constituents, like Chl-a and salinity. Chl-a concentration, indicative of algal biomass, reflects the trophic status of the water bodies, with increasing algal biomass typically elevating Chl-a levels and, consequently, DO levels due to enhanced photosynthesis [58]. Conversely, EC is linked to total dissolved solids and salinity; increased salinity affects the amount of radiation reflected in the visible and infrared spectrum bands [25,26]. However, modeling EC’s spatio-temporal distribution proved more challenging, likely due to its complex interplay with various optically active water components, as noted by Sagan et al. [2].
The optical complexity of the Lissos and Laspias Rivers, exacerbated by significant human activity and their narrow riverbeds, posed additional challenges in monitoring water quality parameters. Despite limited use in water quality monitoring, PlanetScope data proved to be reliable for such analysis [2,12]. The high revisit frequency of the Planet SuperDove satellites was particularly beneficial, facilitating the acquisition of cloud-free imagery and enabling near-real-time monitoring of these inland water bodies [59,60].
Data availability proved to be a challenging issue to address in this study. While the dataset covered a sufficient range of seasonal fluctuations, including the spring, summer, and autumn periods, measurements over a longer time period would contribute to better support model development. The SVR’s ability to handle limited training data sets, as was the case in our study, was a key advantage in this analysis [61,62], highlighting the relationships between the water quality parameters and the surface reflectance for near-real-time monitoring of small rivers.
5. Conclusions
The focus of this study was on two rural rivers facing similar pressures, where water quality monitoring is crucial for their sustainability. We employed a rather novel approach combining PlanetScope imagery and SVR to generate water quality prediction models. Evaluating water quality parameters is a vital process for assessing water quality, ecosystem condition, and ecosystem services, supporting the classification of water bodies’ ecological status within the framework of the EU Water Framework Directive (WFD).
This study highlights that DO and EC can serve as water quality parameters for water bodies affected by human activities and can be effectively retrieved through RS techniques. Both water quality parameters have been used as indicators of the presence of stressor factors. SEEA EA links low DO levels with excess anthropogenic nutrient inputs, affecting freshwater ecosystems. Conversely, salinity, and therefore EC, is associated with salinization and waterlogging, issues prevalent in both Lissos and Laspias Rivers. Despite successfully generating prediction models from various perspectives using EO data, the 3 m resolution posed challenges in monitoring the entire river length due to obstacles like riparian vegetation, a low summer water level, and a river width of less than 10 m. A potential solution is the use of UAVs equipped with multispectral cameras for finer resolution. However, sufficient and reliable in situ data remains essential, as evidenced by the impact of missing EC data due to sensor Lis-3 malfunction. This study also found that factors such as season and monitoring site significantly influence water quality parameters predictions and should be carefully considered in line with monitoring objectives. For comprehensive river studies, a model incorporating seasonal variations and multiple monitoring sites could reduce the impact of outliers, providing a more accurate representation. In contrast, for identifying specific pollution sources, a locality-focused model would be more suitable, while a seasonal model could isolate water quality parameter variations from seasonal changes.
Conventional in situ techniques for continuous and systematic monitoring of surface water quality are time-consuming and costly. RS offers a feasible alternative, facilitating the implementation of WFD obligations by member states. Thus, our findings can aid an increasing number of member states in establishing their water quality monitoring frameworks using RS techniques, allowing for a cost-effective and time-efficient assessment of freshwater ecosystems, taking into account their unique characteristics.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.K., C.S.A. and G.M.; methodology, K.V., S.S., C.S.A., D.L. and G.M.; software, K.V. and S.S.; validation, K.V. and S.S.; formal analysis, K.V.; data curation, K.V.; writing—original draft preparation, K.V. and S.S.; writing—review and editing, D.L., C.S.A., I.K. and G.M.; visualization, K.V. and S.S.; supervision, G.M. and S.S.; project administration, D.L.; funding acquisition, I.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Produced for Eye4Water project, MIS 5047246, implemented under the action: “Support for Research Infrastructure and Innovation” by the Operational Program “Competitiveness, Entrepreneurship and Innovation”. Co-financed by Greece and the European Union European Regional Development Fund.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to action provision.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the Planet Education and Research Program for providing access to the PlanetScope imagery used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ritchie, J.C.; Schiebe, F.R. Water Quality. In Remote Sensing in Hydrology and Water Management; Schultz, G.A., Engman, E.T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagan, V.; Peterson, K.T.; Maimaitijiang, M.; Sidike, P.; Sloan, J.; Greeling, B.A.; Maalouf, S.; Adams, C. Monitoring Inland Water Quality Using Remote Sensing: Potential and Limitations of Spectral Indices, Bio-Optical Simulations, Machine Learning, and Cloud Computing. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 205, 103187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IOCCG. Earth Observations in Support of Global Water Quality; International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group: Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grizzetti, B.; Liquete, C.; Pistocchi, A.; Vigiak, O.; Zulian, G.; Bouraoui, F.; De Roo, A.; Cardoso, A.C. Relationship between Ecological Condition and Ecosystem Services in European Rivers, Lakes and Coastal Waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, J.; Alahuhta, J.; Bini, L.M.; Cai, Y.; Heiskanen, A.; Hellsten, S.; Kortelainen, P.; Kotamäki, N.; Tolonen, K.T.; Vihervaara, P.; et al. Lakes in the Era of Global Change: Moving beyond Single-lake Thinking in Maintaining Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. Biol. Rev. 2021, 96, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Syakir Ishak, M.I.; Bhawani, S.A.; Umar, K. Various Natural and Anthropogenic Factors Responsible for Water Quality Degradation: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Saadi, A.M.; Yousry, M.M.; Jahin, H.S. Statistical Estimation of Rosetta Branch Water Quality Using Multi-Spectral Data. Water Sci. 2014, 28, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallecillo, S.; Maes, J.; Teller, A.; Babí Almenar, J.; Barredo, J.I.; Trombetti, M.; Malak, A. EU-Wide Methodology to Map and Assess Ecosystem Condition Towards a Common Approach Consistent with a Global Statistical Standard; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; D’Arge, R.; De Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The Value of the World’s Ecosystem Services and Natural Capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, J.; Teller, A.; Erhard, M.; Liquete, C.; Braat, L.; Berry, P.; Egoh, B.; Puydarrieux, P.; Fiorina, C.; Santos, F.; et al. Mapping and Assessment of Ecosystems and Their Services: An Analytical Framework for Ecosystem Assessments; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Edens, B.; Maes, J.; Hein, L.; Obst, C.; Siikamaki, J.; Schenau, S.; Javorsek, M.; Chow, J.; Chan, J.Y.; Steurer, A.; et al. Establishing the SEEA Ecosystem Accounting as a Global Standard. Ecosyst. Serv. 2022, 54, 101413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarinas, N.; Spiliotopoulos, M.; Tziolas, N.; Loukas, A. Synergistic Use of Earth Observation Driven Techniques to Support the Implementation of Water Framework Directive in Europe: A Review. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency. European Waters—Assessment of Status and Pressures; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller-Karger, F.E. Remote Sensing of Marine Pollution: A Challenge for the 1990s. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1992, 25, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, E.A.L.; Kumaran, S.S.; Partee, E.B.; Willis, L.P.; Mitchell, K. Potential of Mapping Dissolved Oxygen in the Little Miami River Using Sentinel-2 Images and Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote Sens. Appl. 2022, 26, 100759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppila, P.; Meeuwig, J.J.; Pitkänen, H. Predicting Oxygen in Small Estuaries of the Baltic Sea: A Comparative Approach. Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 2003, 57, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinebach, Y. Water Quality and the Effectiveness of European Union Policies. Water 2019, 11, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannel, P.R.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.S.; Kanel, S.R.; Khan, S.P. Application of Water Quality Indices and Dissolved Oxygen as Indicators for River Water Classification and Urban Impact Assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 132, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Guo, H.; Xu, W.; Zhu, X.; Wang, B.; Zeng, Q.; Mai, Y.; Huang, J.J. Remote Sensing Retrieval of Inland Water Quality Parameters Using Sentinel-2 and Multiple Machine Learning Algorithms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 18617–18630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, L.; Song, K.; Li, Y.; Lyu, H.; Wen, Z.; Fang, C.; Bi, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. An OLCI-Based Algorithm for Semi-Empirically Partitioning Absorption Coefficient and Estimating Chlorophyll a Concentration in Various Turbid Case-2 Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdan, Z.Y.; Kaplan, G.; Goncu, S.; Avdan, U. Monitoring the Water Quality of Small Water Bodies Using High-Resolution Remote Sensing Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, B.B.; Hu, C. Dependence of Satellite Ocean Color Data Products on Viewing Angles: A Comparison between SeaWiFS, MODIS, and VIIRS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansper, A.; Alikas, K. Retrieval of Chlorophyll a from Sentinel-2 MSI Data for the European Union Water Framework Directive Reporting Purposes. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, U.N.T.; Pham, L.T.H.; Dang, T.D. An Automatic Water Detection Approach Using Landsat 8 OLI and Google Earth Engine Cloud Computing to Map Lakes and Reservoirs in New Zealand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theologou, I.; Patelaki, M.; Karantzalos, K. Can Single Empirical Algorithms Accurately Predict Inland Shallow Water Quality Status From High Resolution, Multi-Sensor, Multi-Temporal Satellite Data? Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2015, XL-7/W3, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos González-Márquez, L.; Torres-Bejarano, F.M.; Torregroza-Espinosa, A.C.; Hansen-Rodríguez, I.R.; Rodríguez-Gallegos, H.B. Use of LANDSAT 8 Images for Depth and Water Quality Assessment of El Guájaro Reservoir, Colombia. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2018, 82, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansaray, A.S.; Dzialowski, A.R.; Martin, M.E.; Wagner, K.L.; Gholizadeh, H.; Stoodley, S.H. Comparing PlanetScope to Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 for Sensing Water Quality in Reservoirs in Agricultural Watersheds. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunar, F.; Dervisoglu, A.; Yagmur, N.; Aslan, E.; Ozguven, M. Analyzing the Retrieval Accuracy of Optically Active Water Components from Satellite Data under Varying Image Resolutions. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, XLVIII-M-1–2023, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, V.; Roy, S.; Kington, J.; Harris, T.; Tulbure, M.G.; Stone, N.; Barsballe, T.; Reba, M.; Yaeger, M.A. Monitoring Small Water Bodies Using High Spatial and Temporal Resolution Analysis Ready Datasets. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidro, C.M.; McIntyre, N.; Lechner, A.M.; Callow, I. Quantifying Suspended Solids in Small Rivers Using Satellite Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 1554–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Araujo Barbosa, C.C.; Atkinson, P.M.; Dearing, J.A. Remote Sensing of Ecosystem Services: A Systematic Review. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 52, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yi, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Remote-Sensing Estimation of Dissolved Inorganic Nitrogen Concentration in the Bohai Sea Using Band Combinations Derived from MODIS Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf El Din, E.; Zhang, Y.; Suliman, A. Mapping Concentrations of Surface Water Quality Parameters Using a Novel Remote Sensing and Artificial Intelligence Framework. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 1023–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Gu, M.; Gong, C.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; He, Z. An Advanced Remote Sensing Retrieval Method for Urban Non-Optically Active Water Quality Parameters: An Example from Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, D.; Salvador, P.; Sanz, J.; Casanova, J.L. A New Approach to Monitor Water Quality in the Menor Sea (Spain) Using Satellite Data and Machine Learning Methods. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatitsi, K.; Ioannidou, N.; Mirli, A.; Siachalou, S.; Kagalou, I.; Latinopoulos, D.; Mallinis, G. LULC Change Effects on Environmental Quality and Ecosystem Services Using EO Data in Two Rural River Basins in Thrace, Greece. Land 2023, 12, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latinopoulos, D.; Ntislidou, C.; Lazarina, M.; Papaevangelou, V.; Akratos, C.; Kagalou, I. Macroinvertebrate Community Responses to Multiple Pressures in a Peri-Urban Mediterranean River. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gikas, G.; Dimou, D.; Tsihrintzis, V. River Water Quantity and Quality Monitoring in an Agricultural Basin in North Greece. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2013, 22, 2006–2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, K.R.; Zeng, J.; Diggins, D.; Nonas-Hunter, L.; Snow, C.; Bennett, A.A. The Development and Implementation of an Automated Coastal Environment Monitoring System. In Proceedings of the Global Oceans 2020: Singapore—U.S. Gulf Coast, Virtual, 5–30 October 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqua TROLL® Sondes; In-Situ Inc.: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2023.
- AddVANTAGE Pro 6.6 User Manual; OTT Hydromet GmbH: Klosterneuburg, Austria, 2017.
- PLANET IMAGERY PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS; Planet Labs PBC: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2022.
- Tu, Y.-H.; Johansen, K.; Aragon, B.; El Hajj, M.M.; McCabe, M.F. The Radiometric Accuracy of the 8-Band Multi-Spectral Surface Reflectance from the Planet SuperDove Constellation. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 114, 103035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rösch, M.; Sonnenschein, R.; Buchelt, S.; Ullmann, T. Comparing PlanetScope and Sentinel-2 Imagery for Mapping Mountain Pines in the Sarntal Alps, Italy. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V.; Chervonenkis, A.Y. The Method of Ordered Risk Minimization, I. Avtom. Telemekh. 1974, 8, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Sallaba, F. Seminar Series Nr 220 The Potential of Support Vector Machine Classification of Land Use and Land Cover Using Seasonality from MODIS Satellite Data. Master’s Thesis, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mather, P.; Tso, B. Classification Methods for Remotely Sensed Data; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M.; Mathur, A. A Relative Evaluation of Multiclass Image Classification by Support Vector Machines. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, R.; Shaharuddin, S.; Chang, C.K.; Zakaria, N.A.; Ghani, A.A.; Chan, N.W. Prediction of Water Quality Index in Constructed Wetlands Using Support Vector Machine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 6208–6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.P.; Basant, N.; Gupta, S. Support Vector Machines in Water Quality Management. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 703, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizani, F.M.C.; Maillard, P.; Ferreira, A.F.F.; De Amorim, C.C. Estimation of Water Quality in a Reservoir from Sentinel-2 MSI and Landsat-8 OLI Sensors. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2020, V-3-2020, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Duan, L.; Wen, X.; Li, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Effects of Seasonal Variation on Water Quality Parameters and Eutrophication in Lake Yangzong. Water 2022, 14, 2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, F.; Nee Lala, M.G. Remote Estimation of Water Quality Parameters of Himalayan Lake (Kashmir) Using Landsat 8 OLI Imagery. Geocarto Int. 2017, 32, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskidis, I.; Gikas, G.D.; Sylaios, G.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Water Quantity and Quality Assessment of Lower Nestos River, Greece. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2011, 46, 1050–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Liu, R.; Ni, M.; Zhang, J.; Ji, Q.; Xiao, Z. Seasonal Variations of Water Quality Response to Land Use Metrics at Multi-Spatial Scales in the Yangtze River Basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 37172–37181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gikas, G.D. Water Quantity and Hydrochemical Quality Monitoring of Laspias River, North Greece. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2017, 52, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.I.; Vidal, T.; Gonçalves, F.J.M.; Castro, B.B.; Pereira, J.L. Challenges to Water Quality Assessment in Europe—Is There Scope for Improvement of the Current Water Framework Directive Bioassessment Scheme in Rivers? Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunlasak, K.; Chitmanat, C.; Whangchai, N.; Promya, J.; Lebel, L. Relationships of Dissolved Oxygen with Chlorophyll-a and Phytoplankton Composition in Tilapia Ponds. Int. J. Geosci. 2013, 4, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroumand-Jadidi, M.; Bovolo, F.; Bruzzone, L.; Gege, P. Physics-Based Bathymetry and Water Quality Retrieval Using PlanetScope Imagery: Impacts of 2020 COVID-19 Lockdown and 2019 Extreme Flood in the Venice Lagoon. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroumand-Jadidi, M.; Bovolo, F. Water Quality Retrieval and Algal Bloom Detection Using High-Resolution Cubesat Imagery. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, V-3–2021, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountrakis, G.; Im, J.; Ogole, C. Support Vector Machines in Remote Sensing: A Review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Kong, J.; Hu, H.; Du, Y.; Gao, M.; Chen, F. A Review of Remote Sensing for Water Quality Retrieval: Progress and Challenges. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).