Abstract
Rice terraces are crucial for agriculture in China’s southern mountainous regions. Land use and land cover change (LUCC) in these areas impact hydrology, but our understanding is limited. In this study, we applied the hydrological assessment tool SWAT to a selected small watershed in the rice terrace-dense area of central Hunan province, China. This study covered four LUCC periods over the past 40 years and was simulated at annual and monthly scales. The results showed that from 1980 to 2020, the areas of paddy fields and drylands decreased by 4.19% and 5.76%, respectively, while the areas of forests and construction land increased by 1.14% and 92.48%, respectively. During the past period, LUCC led to a decrease of 1.77% and 2.49% in runoff and infiltration, respectively, and an increase of 1.03% in ET. However, the water yield remained almost unchanged, indicating that the rice terrace plays a positive role in maintaining stable watershed water yield under LUCC. The results of the sub-basin analysis indicated that the transformation of paddy fields and forests directly determines the trend of hydrological changes. Land use type had the most significant impact on the runoff of the rice-terrace watershed, with the proportions of paddy fields and forests being the most influential factors. Paddy fields significantly influenced the stability of runoff at the watershed scale, suggesting that a high paddy field ratio doesn’t ensure sustainability. This study offers valuable insights for managing small watershed terraces, land use planning, and achieving sustainable development in the watershed.
1. Introduction
As one of the key factors affecting economic and social development, water scarcity has become a universal issue that troubles people around the world [1]. The availability of water resources is closely related to hydrological processes, and climate and land use changes are considered to be two major factors influencing watershed hydrological processes [2,3,4]. Land use change refers to the alteration of land cover and land use caused by human activities. It can modify the physical properties of the land surface, affecting hydrological processes such as infiltration, evaporation, and runoff [5]. Improper land use and management practices can have adverse effects on hydrological processes and water cycling, thereby threatening regional water resource security [6,7]. The study of land use change and its hydrological responses has become one of the hot topics in the field of environmental change [8,9].
Terraced fields are strip-shaped, step-like, or wave-like fields built along contour lines in mountainous and hilly areas. The main purpose is to maximize the utilization of land resources on steep slopes and increase the planting area of crops. As a unique way to adapt to mountain ecosystems and an important carrier of the small-scale agricultural economy in the long-term struggle between human society and harsh natural conditions, terraced fields have influenced the processes of soil, hydrology, and topographic changes in the form of vitality for thousands of years, making remarkable contributions to people’s livelihoods, food security, and ecological benefits [10,11,12]. However, in recent years, with economic development and rapid urbanization, there has been frequent land cover conversion in the rice-terraced systems. The changes in land use patterns of rice terraces and the drying up, abandonment, and disappearance of terraced fields will inevitably lead to corresponding hydrological responses, thereby affecting the entire agricultural ecosystem [13]. Therefore, it is necessary to discuss in detail the hydrological responses of land cover conversion in rice terraces.
Currently, research on hydrological responses caused by LUCC has become one of the hot topics in related fields, and the rice-terrace system, as an important agricultural cultural heritage, is receiving increasing attention. Regarding the former, research mainly focuses on different scales, such as national, regional, urban, and watershed levels. For example, Zhang et al. studied the impact of afforestation on watershed runoff in the North Johnstone River Basin, and the results showed that under the same rainfall, slope, and soil texture conditions, total runoff from evergreen forests was generally less than that from pasture and built-up use [14]. Hu et al. studied the Loess Plateau and found that land use changes in the Loess Plateau over the past thirty years have resulted in a 5.3% decrease in water yield and a 6.2% increase in soil moisture, while evaporation remained relatively unchanged [15]. As for research on rice terraces, it mainly focuses on the structure and types of rice-terraced systems. For example, Wei et al. conducted a global review of the classification, distribution, benefits, and issues of terraced fields [16]. Despite decades of global research on terraced hydrology, the conclusions from these small-scale studies are inconsistent [12]. Many studies indicate that terracing plays a positive role in soil and water conservation. Compared to the original slope, terracing can significantly reduce sediment and runoff by decreasing slope length and gradient, increasing surface roughness and vertical relief, enlarging the catchment area, and altering the flow direction [17,18,19]. It also enhances infiltration, soil moisture, and soil water-holding capacity [16], resulting in an increase in soil moisture by 4.24% to 12.9% [20]. By improving runoff discharge efficiency [21,22], terracing enables better utilization of soil moisture and thermal energy, enhancing the efficiency of soil moisture utilization [23,24,25]. However, some studies have highlighted drawbacks or potential negative effects of terracing. For instance, Zhang et al. pointed out that in the soil profile of 0–200 cm, slopes compensate for insufficient soil water storage more effectively than terraced fields [26]. Additionally, abandoned and newly built terraces may lead to soil deterioration [27]. Moreover, existing studies have often treated terraced watershed systems as static systems, lacking a comprehensive understanding of the dynamic responses of rice-terrace systems to hydrological changes in the context of land use changes [28,29,30]. Due to limitations in available data and information, coupled with the inherent variations in natural conditions across different watersheds, understanding how land use changes in rice-terrace systems affect hydrological mechanisms at the small watershed scale remains a challenging aspect of current research [31]. Therefore, evaluating the hydrological responses of rice-terrace LUCC becomes crucial for more accurate watershed management.
The rice-terrace system in southern China is a significant agricultural cultural heritage. The construction and maintenance of rice terraces were once the primary source of livelihood for residents. However, since the 1980s, with the rapid economic development, many terraced fields have been abandoned and left fallow, leading to the threat of imbalance and unsustainability in the hydrological cycle of the rice-terrace system. In recent years, as the livelihood and ecological effects of the rice-terrace system have gained more attention, some regions have initiated efforts to protect and restore these systems. The implementation of policies, such as the “retirement of forests and resumption of farming” and the concentration of land use by agricultural production cooperatives, have led to the conversion of relatively productive fallow land and forested areas back into rice paddies. Meanwhile, higher-altitude areas with less favorable production conditions are designated as permanent forest land. Under the frequent changes in land use, the hydrological changes in the rice-terrace system exhibit unique characteristics and typical patterns.
In this study, a small watershed in southern China, which included a rice-terrace system, was selected. The calibrated and validated SWAT hydrological model was used to determine the hydrological response of the watershed under different land use scenarios in the past, including four LUCC periods over the past 40 years. The objectives of this study are as follows: (1) to analyze the overall characteristics of LUCC patterns and compare the variations among different sub-basins; (2) to explore the spatiotemporal differences in hydrological responses to land use changes and identify key influencing factors; (3) to investigate the hydrological impacts of land use changes in the rice-terrace system. The research findings can provide support for decision-makers and planners in formulating appropriate management measures for land and water resource allocation and proposing effective strategies for achieving sustainable and coordinated development between humans and the environment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Xinhua Basin (Hunan Province, China) is located between 110.7° E and 111.8° E and between 27.4° N and 28.2° N, with a total area of approximately 471,977.45 hectares (Figure 1). The watershed has an average annual temperature ranging from 15 °C to 23 °C and an average annual rainfall of 1455.9 mm. It belongs to a subtropical monsoon climate. The topography of the watershed is characterized by higher elevation in the west and lower elevation in the east, with a wide area of hilly terrain. Terraced fields are widely distributed and have a long history in the watershed. Terraced fields are widely distributed in the watershed, with a long history dating back approximately 2000 years. As of 2020, the area covered by terraced fields in the watershed was approximately 117,593.76 hectares, accounting for about 25% of the total watershed area and 76% of the cultivated land area. The distribution of cultivated land highly overlaps with terraced fields, with paddy fields being the primary farming method. In the rice-terrace system, villages are often situated on the mountainside, forming a three-dimensional ecological landscape pattern together with the forest in the upper part of the village, the rice fields in the lower part, and the river at the base of the mountain (Figure 2a). Therefore, compared with other systems, its hydrological processes also show unique characteristics (Figure 2b). Influenced by economic development and national policies, there has been frequent conversion between different land use types in the watershed over the past few decades, leading to noticeable phenomena such as paddy field abandonment and desiccation. This may affect the hydrological processes in the terraced region, introducing uncertainty into the current hydrological management of the terraced fields. The hydrological changes in the Xinhua Basin under land use variations reflect the impact of rice-terrace land use conversion on hydrological elements at the small watershed scale.
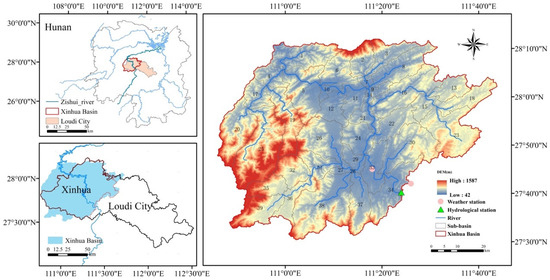
Figure 1.
Slope classes and river network of the Xinhua Basin and its location in China.
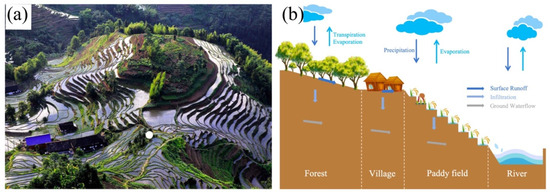
Figure 2.
The land use patterns (a) and the hydrological cycle process (b) of Xinhua Basin.
2.2. The SWAT Model
The SWAT model is a distributed hydrological model consisting of a constant time-step simulation tool. It objectively predicts the impact of land management practices on water. The SWAT model demonstrates high computational efficiency, making it suitable for assessing the effects of various land uses and management practices on water quantity and quality over extended periods [32,33,34,35,36]. All hydrological processes in the model are simulated based on the following water balance equation [37]:
where SWt (mm) is the final soil moisture content at time t (days), and SW0 (mm) is the initial soil moisture content on the ith day. Rday (mm) is the precipitation on the ith day. Qsurf (mm) is the surface runoff on the ith day. ETa (mm) is the evapotranspiration (ET) on the ith day. Wseep (mm) is the percolation at the bottom of the soil profile on the ith day. Qgw (mm) is the water returning to the groundwater on the ith day.
The terrace module of the SWAT model, developed based on the physical processes of terrace watershed hydrology, addresses the previously existing gap in the SWAT model for simulating terraced measures in watershed studies [38]. It achieves this by adjusting erosion and runoff parameters to simulate terraced fields, specifically by modifying the Universal Soil Loss Equation conservation factors (USLE P-factor), slope length factor, and the SCS curve number (CN2) to capture the influence of terraced fields. Simulation validation results from various regions demonstrate that the terrace module can effectively simulate water and sediment processes at both slope and watershed scales [35,38,39,40,41,42,43].
For the calibration, validation, sensitivity analysis, and uncertainty analysis of SWAT, the calibration and uncertainty program SWAT-CUP is commonly employed. In this study, the SUFI-2 (Sequential Uncertainty Fitting Version 2) algorithm, an embedded sequential uncertainty fitting algorithm within the SWAT-CUP (2012) software, was chosen for the calibration and adjustment of model parameters for the Swat project [44,45]. The performance evaluation for different climate change and land-use change scenarios used in this study is represented by the determination coefficient (R2) and the Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency coefficient (NSE) as follows:
where Qm,i is the simulated values of the SWAT model; Qs,i is the observed values, and and are the mean values of the simulated and observed values, respectively. n is the length of the observed values in time. Generally, it is considered that the SWAT model simulation is good and significant when R2 > 0.6 and NSE > 0.5 [18,46].
2.3. Data Sources
In this study, the input data for the SWAT model mainly include DEM (Digital Elevation Model), land use, soil type, and meteorological, hydrological, and terrace distribution data. The 30 m resolution DEM data is obtained from the National Earth System Science Data Center (http://www.geodata.cn (accessed on 11 July 2022)) and is used for extracting basin topography, river network, and channel parameters, as well as delineating sub-basins. The 30 m resolution land use data is sourced from the Resource and Environment Science Data Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (https://www.resdc.cn, (accessed on 26 July 2022)), and the 1 km resolution soil data is from the Cold and Arid Regions Science Data Center of Lanzhou (http://westdc.westgis.ac.cn, (accessed on 9 November 2022)). These datasets are utilized for delineating hydrological response units (HRUs) within sub-basins. The terrace distribution data for the basin is derived from the Chinese 30 m Terrace Map [47] and field surveys. Meteorological and hydrological data required for establishing and calibrating the SWAT model are obtained from the meteorological and hydrological bureaus of Xinhua County, covering continuous daily data from 1990 to 2009. Meteorological data include daily precipitation, average temperature, average air pressure, average wind speed, average relative humidity, small evaporation, large evaporation, and sunshine hours, collected from two meteorological stations, Xinhua Station and Lengshuijiang Station. Hydrological data consist of daily runoff data from the Lengshuijiang hydrological station.
2.4. Model Calibration and Validation
The study area, divided into 39 sub-basins and 4275 HRUs using the SWAT model, excluded the 28th sub-basin due to its small size (only 6.32 hectares) and stable land use during the study period. To investigate the hydrological response of the rice-terrace watershed under different land use change scenarios, we fixed the SWAT model inputs, including DEM and weather data, and introduced five past land use scenarios (S1980, S1990, S2000, S2010, and S2020) into the model. Considering the actual distribution of terraced fields, corresponding terrace management measures were incorporated at the hydrological response unit level within each sub-basin. Ultimately, simulations were conducted to obtain annual and monthly hydrological results for different land use scenarios. Four key indicators closely related to watershed hydrological cycles—runoff, infiltration, water yield, and actual evapotranspiration—were selected from the simulated hydrological data.
The SUFI-2 algorithm was employed to calibrate and adjust model parameters for the Swat project before and after the introduction of the terrace management measures. The hydrological data used for calibration and validation spanned 20 years (1990–2009). The data from 1990–1991 served as a model warm-up; the 1992–2001 data were used for model simulation, and data from other years were used for model validation.
2.5. Land Use Scenarios
This study utilized land use data from five time periods: 1980; 1990; 2000; 2010; and 2020 (Figure 3). Based on the actual conditions and modeling requirements of the SWAT model, the land use in the watershed was classified into eight categories: paddy field; dryland; forest; orchard; grassland; water bodies; built-up area; and unused land. The land use conversion status in the watershed at five time points from 1980 to 2020 was analyzed using the land use transfer matrix method. The analysis focused on two aspects: (1) overall changes in land use; and (2) heterogeneity of land use changes in sub-basins. The formula for calculating the magnitude of land use change is as follows:
where Q represents the magnitude of land use change, while Wa,i and Wb,i denote the area quantities of land use type i at the initial and final stages of the study, respectively.
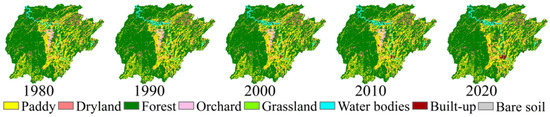
Figure 3.
Land use maps for five periods (1980, 1990, 2000, 2010, and 2020) in the Xinhua Basin.
3. Results
3.1. Model Performance
This study chose 14 parameters closely linked to watershed runoff and utilized SWAT-CUP for iterative calibration and validation until satisfactory model parameters were obtained. The calibration results revealed that the most sensitive parameters for hydrological formation in the Xinhua Basin were, in order, the average slope, soil evaporation compensation coefficient, main channel Manning coefficient, SCS model runoff curve number, and soil saturated hydraulic conductivity. This suggests that runoff in the study area is sensitive to factors such as surface water–groundwater–atmospheric water exchange, land cover changes, and terrain. Figure 4 illustrates the visual and numerical comparisons of simulated monthly streamflow (a) and ET data (b) from the calibration period (1992–2001) and validation period (2002–2009) at the Lengshuijiang hydrological station. The R2 values for the calibration and validation periods were 0.71 and 0.66, respectively, while the NSE values were 0.71 and 0.66, respectively, and the R2 and NSE of the ET simulation results were both greater than 0.8 during both the calibration and validation periods. Generally, when R2 > 0.6 and NSE > 0.5, the SWAT model is considered to have good and significant simulation performances. Therefore, based on the evaluation, the model can be used for simulation purposes.
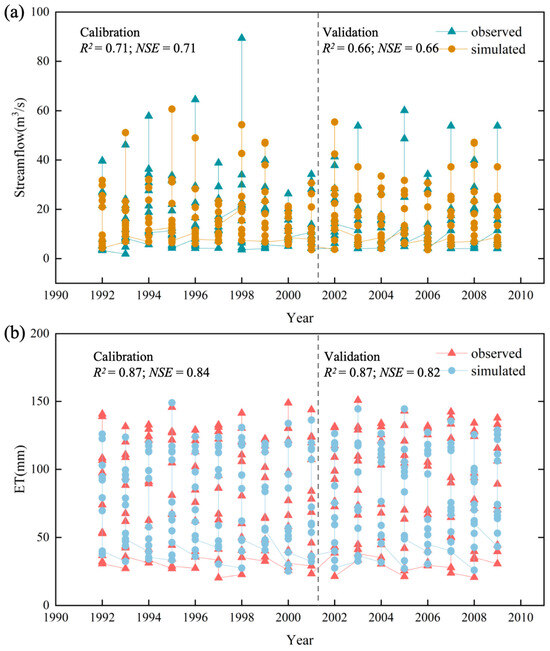
Figure 4.
Monthly simulation at Lengshuijiang Hydrological Station (a) streamflow; (b) ET.
3.2. LUCC in the Xinhua Basin from 1980 to 2020
3.2.1. Total Land Use Change
Figure 3 and Figure 5, respectively, illustrate the land use distribution and their proportions in the Xinhua Basin at different time periods. The results indicate that forests, paddy fields, and drylands are the predominant land use types in the Xinhua Basin, constituting 66%, 21%, and 8% of the total watershed area, respectively. Figure 6 provides land use transition matrices for four stages (1980–1990, 1990–2000, 2000–2010, and 2010–2020). It is evident that the periods 1980–1990 and 2010–2020 experienced more pronounced land use transformations, whereas during the period from 1990 to 2010, the land use within the watershed remained relatively stable.
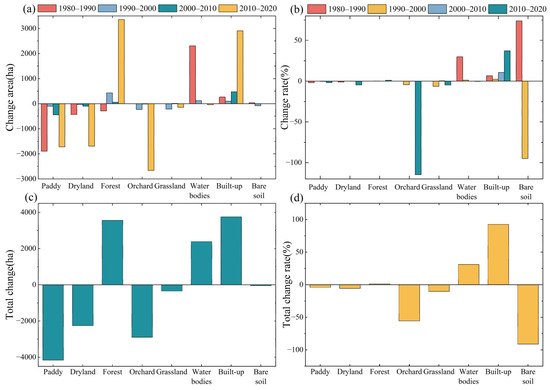
Figure 5.
Change area of different land use types over the study period (a) and their change rate (b), total change area (c), and total change rate (d).
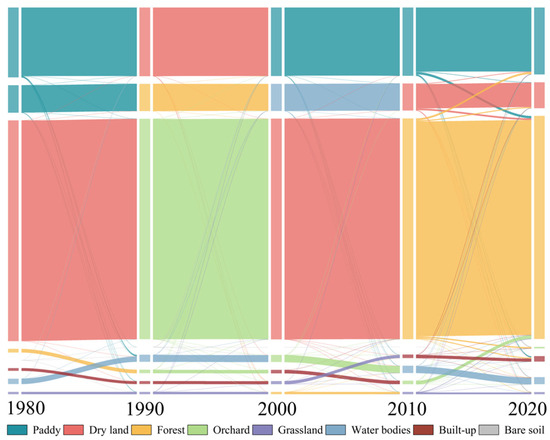
Figure 6.
Direction of land use transfer in Xinhua Basin in different periods.
Overall, except for the initial stage when the primary land use transition was toward water bodies, in the past several decades, the Xinhua Basin has seen a general trend of decreasing paddy fields and drylands, with increasing areas of forests and construction land. Additionally, there have been mutual conversions between various land use types, such as forests to paddy fields, forests to drylands, paddy fields to drylands, and forests to orchards. Under this transition trend, over the past forty years, the areas of paddy fields, drylands, orchards, and grasslands have decreased by 4.19%, 5.76%, 55.59%, and 10.27%, respectively. In contrast, the areas of forests, construction land, and water bodies have increased by 1.14%, 92.48%, and 30.99% hectares, respectively. The land use transition process and outcomes reflect human needs and socio-economic development trends. In this process, agricultural land has consistently decreased and become more concentrated, and in some high-altitude areas, agricultural land has been converted into permanent forest land.
3.2.2. Land Use Changes in Sub-Basins
At the sub-basin scale, most of them have forested land and paddy land as the main land use types, and land use changes are mainly reflected in paddy land, dry land, forested land, and construction land. Paddy fields showed a decreasing trend in 35 sub-basins. Nine of them showed a decrease in the area of paddy fields in the range of 1–2%, 10 in the range of 2–10%, and 5 with a decrease of more than 10%, with a decrease of up to 53.9% (sub-basin No. 10). Paddy fields in the sub-basins showed a decreasing trend until 2010, when nine sub-basins started to show an increase in paddy fields, with an increase of up to 3.93%. In terms of drylands, 32 sub-basins showed a decreasing trend, with 9 sub-basins experiencing a decrease of more than 10%, with a maximum decrease of 49.7% (sub-basin No. 12). The decrease in drylands was mainly in the period of 2010–2020 when they were either converted to paddy land for reuse or to forest land, while the increase in drylands was mainly due to the drying out of paddy land in the period of 1990–2010. Regarding forested land, there are significant variations in forested land area changes among the sub-basins. Out of these, forested land area decreased in 25 sub-basins, with the highest reduction being 14.02% in the 9th sub-basin. Simultaneously, 13 sub-basins experienced an increase in forested land area, with the highest increase of 61.94% in the 12th sub-basin, and these increases were notably substantial. The increase in forested land within these sub-basins primarily resulted from the conversion of areas such as orchards, drylands, and paddy fields into forested land. Conversely, the decrease in forested land was primarily due to conversions into dryland and built-up. These changes in forested land area were most significant during the period from 2010 to 2020 within these sub-basins. In conjunction with the reduction in paddy fields and drylands, 36 sub-basins showed an increase in built-up areas. Among these, 13 sub-basins saw built-up areas increase by over 100%, with the highest rate of change reaching 1158.13%. The built-up area has shown a consistent upward trend over the years, with significant large-scale increases occurring primarily after 2000. Although the built-up area within the sub-basins is considerably smaller compared to forested land, paddy fields, and drylands, the rate of change in the built-up area stands out as the most significant among the different land use types when compared to the initial period of this study.
3.3. Hydrological Impacts of LUCC
3.3.1. Total Hydrological Response
Figure 7 illustrates the annual average rate of change in various hydrological indicators for the Xinhua Basin compared to the conditions in 1980, as well as the extent to which different land use scenarios have influenced these indicators. We observe that historical LUCC has led to a 1.77% reduction in runoff and a 2.49% decrease in infiltration, while ET has increased by 1.03%. However, water yield has remained nearly unchanged. Regarding the impact of different land-use scenarios on hydrological results, it can be observed that the basin’s runoff reached its highest point under the land-use conditions of 1980. Subsequently, it fluctuated with periods of decrease and increase, although the increase was much smaller than the decrease. Overall, the runoff showed a decreasing trend, with the most significant changes occurring between 1980 and 1990, resulting in a 1.78% decrease. Over the past four periods, the infiltration exhibited a trend of decrease–decrease–increase–decrease. Although there was a slight recovery during the third period, the infiltration consistently showed a significant decrease compared to the initial conditions. For ET at the basin level, there was an increasing trend. It increased by 1.03% compared to the initial period, with the most significant increase observed between 1980 and 1990 and between 2010 and 2020.
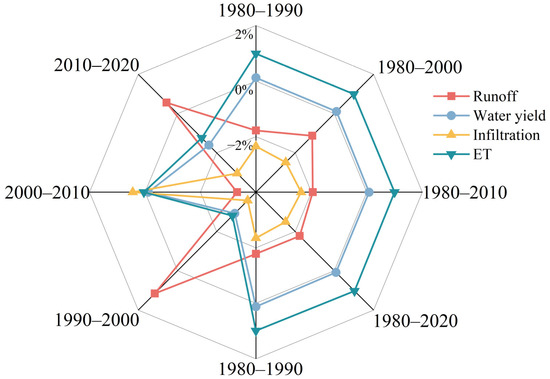
Figure 7.
Changes in runoff, water yield, infiltration, and ET under different land-use conversion scenarios.
3.3.2. Hydrological Response in Sub-Basins
Different sub-basins exhibit varying hydrological responses due to differences in the direction and scale of land use changes, and the differences in hydrologic responses between them are shown in Figure 8.
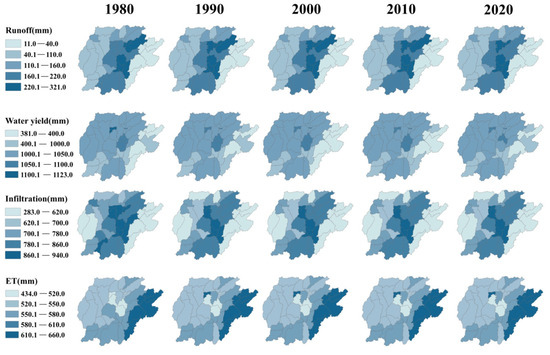
Figure 8.
Simulated runoff, water yield, infiltration, and ET under the different land use scenarios.
Sub-basins where forest, grassland, and water bodies decreased while paddy fields and built-up areas increased experienced an increase in runoff. Only four sub-basins showed increased runoff during the study period, specifically sub-basins 7, 9, 11, and 24, with increases ranging from 0.20% to 11.53%. Conversely, sub-basins where water bodies and forests increased saw a decrease in runoff, with 34 sub-basins exhibiting a decreasing trend in runoff, most notably sub-basins 12, 16, and 23, which decreased by 8.59%, 6.29%, and 15.71%, respectively.
There was not a significant difference in water yield among sub-watersheds. Sub-basins with continuous expansion of built-up areas showed an increasing trend in water yield, with approximately 82% of sub-basins experiencing an increase in water yield during the study period. However, the magnitude of the increase was relatively small, with growth rates ranging from 0.05% to 0.73%.
Sub-basins, where paddy fields, drylands, and forests were converted into built-up areas, experienced a decrease in baseflow. Apart from sub-watershed 10, which showed a slight increase in baseflow, the remaining sub-basins exhibited a decreasing trend in baseflow, with reductions ranging from 0.71% to 6.75%. Sub-basins 20 and 25 demonstrated the most significant baseflow reduction, with decreases of 6.45% and 6.42%, respectively.
ET decreased in all 34 sub-basins, but the reduction rates were all within 1%. Only in the sub-basins where paddy fields were converted into forests and built-up areas (Sub-basins 9, 10, 11, and 14) ET showed an increasing trend. In these sub-basins, the rate of paddy field conversion exceeded 20%, resulting in a significant increase in ET, with the highest increase observed in sub-watershed 10, reaching 51.6%.
In general, the most pronounced hydrological changes occurred in sub-basins where there were significant alterations in the extent of paddy fields or forests. The direction of conversion between paddy fields and forests played a pivotal role in determining the hydrological change trends in these sub-basins. Although the proportion of built-up areas within the sub-basins was relatively small, their rapid expansion in recent decades has had a substantial impact on the hydrological characteristics of these sub-basins.
3.4. Hydrological Impacts of Land Use Types
In this section, to investigate the influence of land use combinations in the paddy terrace system on sub-basin hydrology, areas with smaller proportions, such as orchards, grasslands, water bodies, and unused land, are collectively referred to as “Other”, based on their respective areas and their proportions within the watershed. Utilizing Pearson correlation analysis, a correlation analysis was conducted between the proportions of different land use types and runoff, water yield, infiltration, and ET. The results (Figure 9) indicate that land use types have the most significant impact on runoff in the hydrological cycle. There are correlations between all land use types and runoff. Runoff is highly correlated with paddy, dryland, forest, and built-up areas (correlation coefficients of 0.65, 0.53, −0.68, and 0.55, respectively) and significantly correlated with “Other” land use types with a correlation coefficient of 0.16. Regarding the proportion between paddy and forest, the paddy–forest ratio is highly correlated with runoff, with a correlation coefficient of 0.75. This suggests that during the study period, the proportion of forest land and paddy fields in the sub-basin had a significant influence on runoff. A higher proportion of forest leads to lower runoff, while a higher proportion of paddy, dryland, built-up areas, and “Other” land use types leads to higher runoff. In addition, there is a significant correlation between infiltration and “Other” land use types, with a correlation coefficient of 0.19. A higher proportion of “Other” land use types results in greater infiltration in the sub-basin. There were no significant correlations observed between water yield, ET, and the various land use types.
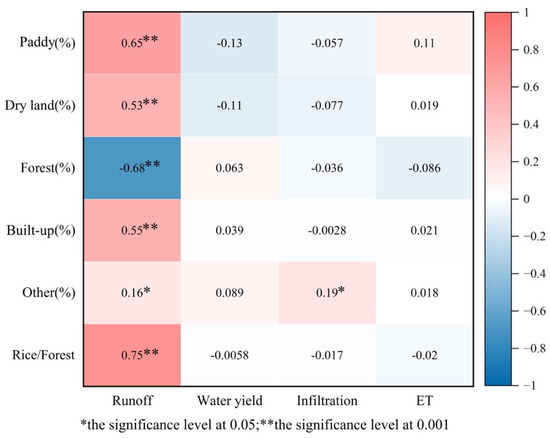
Figure 9.
The correlation between land use proportions and hydrological indicators.
By using stepwise regression analysis, a linear relationship was established between paddy, dryland, forest, built-up areas, “Other” land use types, and runoff. The results (Figure 10, Table 1) indicate that the proportions of paddy, forest, and built-up areas in the basin are the main factors influencing sub-basin runoff. They can explain 45.3% of the spatial variation in runoff. Dryland and “Other” land types, either individually or in combination with paddy, forest, and built-up areas, also have an impact on runoff. The linear relationship between infiltration and “Other” land types (including orchards, grassland, water bodies, bare soil) can be represented as Infiltration = 648.483 + 367.729 × Other (%) (R2 = 0.033, p < 0.05). However, due to the relatively small proportion of “Other” land types in each sub-basin, their explanatory power for variations in infiltration is limited. Meanwhile, no significant linear relationships have been established between infiltration and paddy, dryland, forest, and built-up areas (Figure 10).
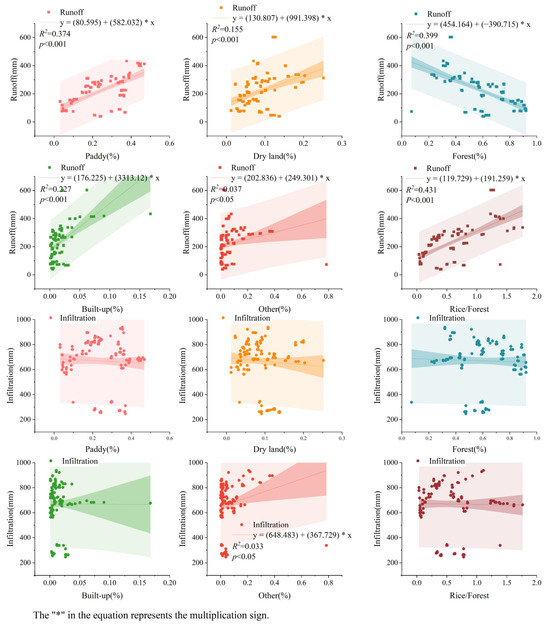
Figure 10.
The relationship between land use proportions and runoff and infiltration.

Table 1.
The stepwise regression analysis of land use proportions and runoff.
4. Discussion
4.1. Driving Forces of LUCC
LUCC provides a vivid reflection of the evolving interplay between human activities and natural factors over time [48]. The 1980s marked the initial phase of China’s economic reform and opening-up, a period when significant transformations occurred in the land use patterns of the Xinhua Basin. The implementation of the household responsibility system and the introduction of market-oriented economic policies gradually steered land utilization toward more economically favorable crops and agricultural practices, such as rice–fish farming, rice–shrimp cultivation, and integrated rice–duck farming. Concurrently, rural residents began constructing homes on arable land, leading to the conversion of paddy fields and drylands into water bodies and areas designated for urban development during the 1980s and 1990s. The period from 1990 to 2010 witnessed relatively stable land use changes within the watershed. The primary shifts in land utilization were directed toward urban development and afforestation. This era was characterized by the ongoing industrialization and urbanization processes in the watershed, with substantial land allocations for factory construction, urban expansion, and residential development. In contrast, the most pronounced transformations in land use occurred from 2010 to 2020. On the one hand, a significant outflow of the watershed’s population resulted in the gradual desiccation of poorly maintained paddy fields, leading to their transformation into drylands or forested areas. Simultaneously, the continued expansion of industrialization and urbanization contributed to the persistent increase in built-up areas. On the other hand, Xinhua County intensified its efforts in ecological and environmental conservation during this period. Ecological projects aimed at reforestation and grassland restoration were implemented, resulting in the expansion of forested land. Moreover, some regions leveraged terraced landscapes for the development of eco-tourism. In their pursuit of continuous and aesthetically appealing terraced landscapes, certain areas repurposed lower-altitude drylands and forests as rice paddies. As a result, while the overall area of paddy fields continued to decline during this period, a significant conversion from forested, dryland, and other land types to paddy fields was also observed.
In general, between 1980 and 2020, the prevailing trend in land use has been the continuous reduction in paddy fields and drylands, coupled with the consistent expansion of built-up areas and forests. Paddy field acreage has diminished, with distant rice paddies often abandoned or replaced by forests, while those nearer to villages have frequently been converted into built-up areas or other land types. The increase in forested land has resulted in a significant rise in vegetation cover, which has proven advantageous in mitigating soil erosion in vulnerable regions. It is evident that land cover in the watershed has become increasingly concentrated during past periods, and both production structures and land utilization patterns have continually improved. This, in turn, promotes the harmonious development of the relationship between humans and the environment.
4.2. Hydrological Impacts of the Terrace System
4.2.1. Hydrological Impacts of Rice-Terrace Structures
The impact of land use changes on the hydrological balance within the Xinhua Basin is relatively small, and the changes in various hydrological indicators are not very significant. Especially concerning the water yield, it remains almost unchanged against the background of land use changes. This is due to the inherent ability of the rice-terrace system to play a proactive role in the hydrological cycle of the small watershed. Constructing terraces can reduce slope length and steepness, resulting in reduced sediment and runoff, as well as soil conservation [49]. Furthermore, the construction of terraces changes the original runoff pathways, reduces hydrological connectivity, and expands the catchment area [50], effectively intercepting rainfall, increasing infiltration, and improving soil moisture and water-holding capacity. Research on terraced fields in the Loess Plateau by Ran et al. showed that well-maintained terraces can reduce runoff by up to 100%, and even terraced fields without ridges can reduce runoff by 28%. Similarly, a study by Mai et al. on rice terraces in Tam Duong, Vietnam, demonstrated that the presence of terraces can reduce surface runoff by 75% [51]. We used the SWAT model to compare the hydrological performance of the Xinhua Basin with and without terraces, and the results showed that the construction of the terraces resulted in a 52.5% decrease in surface runoff and a 5.83% decrease in water yield. This indicates that regardless of the land use types present in terraced watershed areas, the presence of terrace systems alone can reduce runoff. Based on this, the terrace system can provide a certain buffering effect on hydrological changes in the watershed under conditions of land use change, reducing the magnitude of those changes.
4.2.2. Hydrological Impacts of Rice-Terrace Land Use
The hydrological impact of land use in the rice-terrace system is crucial for its overall sustainability. In the vertical structure of forest–village–paddy-field–river, the presence of forests and paddy fields is essential. Forests are typically located at the top of the system, intercepting rainfall and facilitating its gradual infiltration into the soil, forming a significant “water reservoir” underground. As a result, even though rivers are at the bottom of the system, irrigation systems are rarely constructed in the rice-terrace system, relying primarily on the natural flow of water to irrigate the entire system. The utilization and management of paddy fields are the main source of livelihood in the rice-terrace system and have always been considered the core of the entire system.
Figure 7 and Figure 8 indicate that with the conversion of land use within the watershed, there has been a reduction in runoff and infiltration but an increase in water yield and ET. This is closely related to the reduction in paddy fields, the increase in forestland, and built-up land during the study period. Since forestland has a higher water consumption rate than other land use types, the increase in forestland area results in a reduction in runoff. Additionally, the forest canopy and litter layer have excellent water interception and retention capabilities, reducing infiltration and increasing evaporation. Furthermore, the increase in built-up land not only contributes to reduced infiltration and increased evaporation but also compensates for the loss of water provisioning services from other land use types, making it the primary reason for the increase in water yield.
Results indicate that land use patterns have the most significant impact on runoff within the rice-terrace system’s hydrological cycle, and the correlation between runoff and the proportion of paddy fields and forestland, as well as the combination of the two, is the closest. The larger the proportion of paddy fields, the greater the watershed runoff. Building on this, further assessment of the influence of land use patterns on the coefficient of runoff variation (CV of Runoff) reveals that there is a power function relationship between land use types and CV of runoff, in which the combination of paddy fields and forestland have the most significant impact on the stability of watershed runoff (Figure 11). The presence of forestland can significantly reduce runoff and enhance the stability of runoff in the small watershed. Unlike the relatively stable forestland, paddy fields exhibit different runoff efficiencies in different seasons. During the months when rice is planted, and the paddy fields are filled with water, any precipitation at this time will turn into runoff due to the reservoir being full. In other seasons, when the paddy fields are without water, there is a significant increase in infiltration, reducing runoff. As the months of rice cultivation often coincide with the rainy season, this inevitably leads to larger areas of waterlogged paddy fields in the watershed, resulting in higher runoff and lower runoff stability in the watershed. This finding is similar to the conclusions drawn by Han et al., who demonstrated that the presence of farmland significantly reduced the stability of runoff in watersheds with less groundwater disturbance [52]. This emphasizes the importance of forestland in the hydrological balance of the system. Despite traditionally considering paddy fields as the core for the overall sustainable development of the system, it is not necessarily the case that more paddy fields are better.
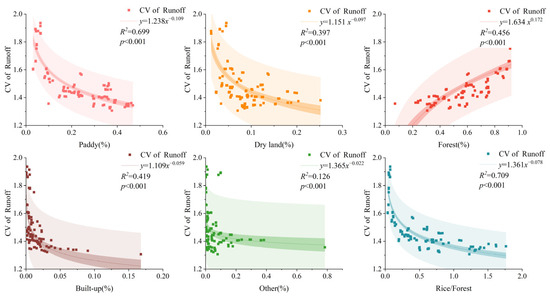
Figure 11.
The relationship between land use proportions and the coefficient of runoff variation (CV of Runoff).
4.3. Comprehensive Understanding
Quantitative research has demonstrated the significant role of the terraced rice paddy system in conserving water resources. Against the backdrop of land use changes, it has a positive impact on maintaining hydrological stability within small basins. However, the hydrological cycle in a basin is a complex mechanism influenced by various factors. Therefore, attention should be paid to the impact of terraced fields on hydrological processes [53].
Due to variations in natural environmental conditions, the benefits of soil and water conservation in terraced fields vary across different regions. In comparison to the hydrological differences resulting from the conversion between dryland and forest in arid areas, the hydrological changes arising from the conversion between paddy fields and forest in humid regions are much less pronounced. Yang and Lu (2018) found that the conversion of farmland to Forest in the Yanhe River Basin led to a 13.8% decrease in runoff [54,55]. However, in the humid Xiangxihe River Basin in southern China, where paddy fields were extensively converted to forest, the simulated runoff only decreased by 0.7% [55]. Even within the same region, the efficiency of terraced fields in performing their functions varies due to differences in the combination of land use practices. Further research on the hydrological response of terraced fields to rice cultivation needs to take into account the differences in plant growth stages associated with different land use practices. Specifically, this includes variations in runoff efficiency in paddy fields during the rice growing and harvesting seasons, as well as differences in the water retention capacity provided by forestland at different levels of density.
The functionality of terraced fields relies on careful management by farmers. The farmers’ cultivation choices determine the land allocation in terraced fields. If the cultivation area increases, the water consumption for rice cultivation will also increase [56]. In other words, if the proportion of paddy fields within the terraced rice paddy system exceeds a certain level, the water demand for rice cultivation may exceed the water stored in the system’s internal forests. This could potentially challenge the basin’s hydrological balance [57]. If the forestland coverage area increases, the reduction in basin runoff will also increase. Due to the reduction in hydrological connectivity by terraced fields, there is a weakening of the connection between basin runoff and rivers within the basin [58,59]. Reduced runoff can potentially affect the dynamic balance of water resources among different regions, potentially leading to conflicts in water resource needs between regions. When farmers are insufficiently engaged over the long term, terraced fields lacking proper management will gradually be abandoned, leading to concentrated runoff and an overall decrease in water resource availability [60,61]. Research indicates that the runoff coefficient of abandoned terraced fields is between 20% and 40%, resulting in runoff volumes more than three times that of well-managed terraced fields [62,63,64]. This underscores the importance of paying attention to the role of humans, implementing reasonable measures to mitigate the impact of human activities, exploring appropriate proportions of paddy fields and forestland in terraced fields, and focusing on hydrological balance on a larger scale. This ensures the optimal functionality of mountainous terraced fields.
5. Summary and Conclusions
This study centers on the theme of the impacts of land use patterns and their changes on watershed hydrology in rice-terrace watersheds, and a sub-watershed containing rice terraces was selected as the study area of this paper. First, land use data for 1980, 1990, 2000, 2010, and 2020 were selected to elucidate the land use change trends and their dynamic processes in the rice-terrace watershed using the land use transfer matrix; second, the hydrological response of the watershed under the past land use scenarios was obtained by using the SWAT model to simulate the hydrological response of the watershed and to assess the impacts of the land use practices and the changes in land use on key hydrological components of the rice-terrace watershed. The above study led to the following conclusions:
- (1)
- Land use changes in the study area during the past period were significant. Overall, the area of forest land and built-up areas increased, while paddy fields and dryland decreased;
- (2)
- LUCC resulted in a reduction of 1.77% in runoff, a decrease of 2.49% in infiltration, and an increase of 1.03% in ET in the previous period. Water yield remained almost unchanged;
- (3)
- Among the land use types in the rice-terrace system, the proportion of paddy fields, forests, and their combination had the most significant influence on runoff in the small watershed. The larger the proportion of paddy fields, the greater the runoff, but with lower runoff stability;
- (4)
- Hydrological changes in the study area were relatively small, indicating that rice-terrace systems had a positive role in maintaining hydrological stability in the watershed under land use changes. For sustainable development of rice-terrace systems, it is not necessarily better to have a higher proportion of paddy fields.
This study provides useful information for land use planning and soil and water conservation of rice-terrace systems. The quantitative assessment of LUCC and its impact on hydrology can provide valuable information for small watershed terrace management, land use planning, and, ultimately, sustainable development of the watershed. This information can be the basis for the analysis and formulation of new land use schemes, for example, exploring the rational land use ratio of rice terraces according to the water balance, combining water supply and water demand in the basin.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and formal analysis, C.D.; investigation and writing original draft, Y.L. (Yaqun Li); data curation and visualization, C.L. and G.Z.; Methodology and supervision, Y.L. (Yaojun Liu). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42171258; U22A20611; 42377336) and the Research Foundation of the Department of Natural Resources of Hunan Province (No. 20230110GH).
Data Availability Statement
Due to the data policies of data agencies in China, the meteorological data and streamflow data used in this research cannot be made publicly available. Other data can be downloaded from the corresponding websites marked in the text.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42171258; U22A20611; 42377336) and the Research Foundation of the Department of Natural Resources of Hunan Province (No. 20230110GH).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jiang, Y. China’s Water Scarcity. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3185–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bakri, J.T.; Salahat, M.; Suleiman, A.; Suifan, M.; Hamdan, M.R.; Khresat, S.; Kandakji, T. Impact of Climate and Land Use Changes on Water and Food Security in Jordan: Implications for Transcending “the Tragedy of the Commons”. Sustainability 2013, 5, 724–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Franczyk, J. Climate Change, Land-Use Change, and Floods: Toward an Integrated Assessment. Geogr. Compass 2008, 2, 1549–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praskievicz, S.; Chang, H. Impacts of Climate Change and Urban Development on Water Resources in the Tualatin River Basin, Oregon. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2011, 101, 249–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Shibata, H. Simulation of Watershed Hydrology and Stream Water Quality under Land Use and Climate Change Scenarios in Teshio River Watershed, Northern Japan. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 50, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentine, P.; Troy, T.J.; Lintner, B.R.; Findell, K.L. Scaling in Surface Hydrology: Progress and Challenges. J. Contemp. Water Res. Educ. 2012, 147, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tian, H.; Yang, Q.; Yang, J.; Song, X.; Lohrenz, S.E.; Cai, W.J. Long-Term Trends in Evapotranspiration and Runoff over the Drainage Basins of the Gulf of Mexico during 1901–2008. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1988–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Tian, H.; Friedrichs, M.A.M.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Yang, J. Hydrological Responses to Climate and Land-Use Changes along the North American East Coast: A 110-Year Historical Reconstruction. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2015, 51, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán-Tejeda, E.; Ceballos-Barbancho, A.; Llorente-Pinto, J.M. Hydrological Response of Mediterranean Headwaters to Climate Oscillations and Land-Cover Changes: The Mountains of Duero River Basin (Central Spain). Glob. Planet Chang. 2010, 72, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araral, E. What Makes Socio-Ecological Systems Robust? An Institutional Analysis of the 2000 Year-Old Ifugao Society. Hum. Ecol. 2013, 41, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, C.H.M.; Altoveros, N.C.; Borromeo, T.H.; Dayo, M.H.F.; Koohafkan, P. Traditional Rice-Based Agroecosystem in Kiangan, Ifugao, Philippines: Drivers of Change, Resilience, and Potential Trajectories. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 45, 296–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wei, W.; Chen, L. Effects of Terracing Practices on Water Erosion Control in China: A Meta-Analysis. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevan, A.; Conolly, J. Terraced fields and Mediterranean landscape structure: An analytical case study from Antikythera, Greece. Ecological Modelling. 2011, 222, 1303–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, B.; Liu, D.L.; Zhang, M.; Leslie, L.M.; Yu, Q. Using an Improved SWAT Model to Simulate Hydrological Responses to Land Use Change: A Case Study of a Catchment in Tropical Australia. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, P.; Zhao, F.; Jin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, L.; Lian, Y. Impacts of Land-Use Conversions on the Water Cycle in a Typical Watershed in the Southern Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Chen, D.; Wang, L.; Daryanto, S.; Chen, L.; Yu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Sun, G.; Feng, T. Global Synthesis of the Classifications, Distributions, Benefits and Issues of Terracing. Earth Sci. Rev. 2016, 159, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.H.; Cai, C.F.; Ding, S.W.; Wang, T.W.; Chow, T.L. Soil Conservation Planning at the Small Watershed Level Using RUSLE with GIS: A Case Study in the Three Gorge Area of China. Catena 2004, 55, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Chen, X.; Hong, Y.; Ye, S.; Gao, J. Impacts of Terracing on Hydrological Processes: A Case Study from the Loess Plateau of China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 125045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fashaho, A.; Ndegwa, G.M.; Lelei, J.J.; Musandu, A.O.; Mwonga, S.M. Effect of Land Terracing on Soil Physical Properties across Slope Positions and Profile Depths in Medium and High Altitude Regions of Rwanda. S. Afr. J. Plant Soil 2020, 37, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wei, W.; Chen, L. How Can Terracing Impact on Soil Moisture Variation in China? A Meta-Analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 227, 105849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Ren, Z.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z. Temporal Persistence and Stability of Soil Water Storage after Rainfall on Terrace Land. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, C.; Frampton, A.; Hvidtfeldt Christiansen, H. Soil Moisture Redistribution and Its Effect on Inter-Annual Active Layer Temperature and Thickness Variations in a Dry Loess Terrace in Adventdalen, Svalbard. Cryosphere 2017, 11, 635–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damene, S.; Tamene, L.; Vlek, P.L.G. Performance of Exclosure in Restoring Soil Fertility: A Case of Gubalafto District in North Wello Zone, Northern Highlands of Ethiopia. Catena 2013, 101, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolka, K.; Mulder, J.; Biazin, B. Effects of Soil and Water Conservation Techniques on Crop Yield, Runoff and Soil Loss in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Review. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 207, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.A.; Li, F.R.; Zhou, L.M.; Zhang, R.H.; Yu-Jia; Lin, S.L.; Wang, L.J.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Li, F.M. Effect of Organic Manure and Fertilizer on Soil Water and Crop Yields in Newly-Built Terraces with Loess Soils in a Semi-Arid Environment. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 117, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang Beiying, X.X.L.W. Soil Water Condition under Different Measures of Soil and Water Conservation in Loess Hilly and Gully Region. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2009, 25, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Calsamiglia, A.; Fortesa, J.; García-Comendador, J.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Calvo-Cases, A.; Estrany, J. Spatial Patterns of Sediment Connectivity in Terraced Lands: Anthropogenic Controls of Catchment Sensitivity. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1198–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Spek, D.; Van Arendonk, J.A.M.; Bovenhuis, H. Genome-Wide Association Study for Claw Disorders and Trimming Status in Dairy Cattle. J Dairy Sci 2015, 98, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruins, H.J.; Bithan-Guedj, H.; Svoray, T. GIS-Based Hydrological Modelling to Assess Runoff Yields in Ancient-Agricultural Terraced Wadi Fields (Central Negev Desert). J Arid Environ 2019, 166, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelifa, W.; Ben; Hermassi, T.; Strohmeier, S.; Zucca, C.; Ziadat, F.; Boufaroua, M.; Habaieb, H. Parameterization of the Effect of Bench Terraces on Runoff and Sediment Yield by Swat Modeling in a Small Semi-Arid Watershed in Northern Tunisia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 1568–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Nie, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhu, D. Advantages and Disadvantages of Terracing: A Comprehensive Review. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2021, 9, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, M.; Everson, C.S. Modelling Streamflow from Two Small South African Experimental Catchments Using the SWAT Model. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévesque, É.; Anctil, F.; Van Griensven, A.; Beauchamp, N. Evaluation of Streamflow Simulation by SWAT Model for Two Small Watersheds under Snowmelt and Rainfall. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2008, 53, 961–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, J.; Gosain, A.K.; Khosa, R. Prediction of Land Use Changes Based on Land Change Modeler and Attribution of Changes in the Water Balance of Ganga Basin to Land Use Change Using the SWAT Model. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanowicz, A.A.; Vanclooster, M.; Rounsevell, M.; La Junesse, I. Sensitivity of the SWAT Model to the Soil and Land Use Data Parametrisation: A Case Study in the Thyle Catchment, Belgium. Ecol. Model. 2005, 187, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas-Mankin, K.R.; Srinivasan, R.; Arnold, J.G.; Raghavan Srinivasan, K.; Member, A.; Douglas-Mankin, K.R. Soil and water assessment tool (SWAT) model: Current developments and applications. Trans. ASABE 2010, 53, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Moriasi, D.N.; Gassman, P.W.; Abbaspour, K.C.; White, M.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Santhi, C.; Harmel, R.D.; Van Griensven, A.; Van Liew, M.W.; et al. SWAT: Model use, calibration, and validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1491–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Baffaut, C.; Gao, J.E.; Nelson, N.O.; Janssen, K.A.; Pierzynski, G.M.; Barnes, P.L. Development and Application of Algorithms for Simulating Terraces within SWAT. Trans. ASABE 2013, 56, 1715–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Lim, K.J.; Kim, J.; Shin, M.; Park, Y.S. Modification and Application of SWAT Model to Simulate a Submerged Rice Paddy Field. Paddy Water Environ. 2023, 22, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Fohrer, N. SWAT2000: Current Capabilities and Research Opportunities in Applied Watershed Modelling. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.R.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Gassman, P.W.; Green, C.H. History of Model Development at Temple, Texas. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2008, 53, 948–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassman, P.W.; Reyes, M.R.; Green, C.H.; Arnold, J.G.; Gassman, P.W. The soil and water assessment tool: Historical development, applications, and future research directions invited review series. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 1211–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Bruijnzeel, L.A. Runoff and Soil Loss from Bench Terraces. 1. An Event-Based Model of Rainfall Infiltration and Surface Runoff. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2004, 55, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Bruijnzeel, L.A. Runoff and Soil Loss from Bench Terraces. 2. An Event-Based Erosion Process Model. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2004, 55, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C. SWAT-CUP 2012: SWAT Calibration and Uncertainty Programs—A User Manual. Sci. Technol. 2014, 106, 20–81. [Google Scholar]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Vejdani, M.; Haghighat, S. SWAT-CUP Calibration and Uncertainty Programs for SWAT. In Proceedings of the MODSIM07—Land, Water and Environmental Management: Integrated Systems for Sustainability, Proceedings, Christchurch, New Zealand, 10–13 December 2007; pp. 1596–1602. [Google Scholar]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Yu, L.; Naipal, V.; Ciais, P.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, W.; Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Gong, P. A 30 m Terrace Mapping in China Using Landsat 8 Imagery and Digital Elevation Model Based on the Google Earth Engine. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 2437–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kuang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Qin, Y.; Ning, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; et al. Spatiotemporal Characteristics, Patterns, and Causes of Land-Use Changes in China since the Late 1980s. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerkerk, A.L.; van Wesemael, B.; Bellin, N. Application of Connectivity Theory to Model the Impact of Terrace Failure on Runoff in Semi-Arid Catchments. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 2792–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, V.T.; van Keulen, H.; Hessel, R.; Ritsema, C.; Roetter, R.; Phien, T. Influence of Paddy Rice Terraces on Soil Erosion of a Small Watershed in a Hilly Area of Northern Vietnam. Paddy Water Environ. 2013, 11, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.F.; Wang, X.S.; Wan, L.; Kuang, X. Croplands Decreased Stability of Streamflow with Changing Climate: An Investigation of Catchments in Illinois. J. Hydrol. 2022, 606, 127461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higson, J.L.; Singer, M.B. The Impact of the Streamflow Hydrograph on Sediment Supply from Terrace Erosion. Geomorphology 2015, 248, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, K.; Lu, C. Evaluation of Land-Use Change Effects on Runoff and Soil Erosion of a Hilly Basin—The Yanhe River in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieger, K.; Hörmann, G.; Fohrer, N. The Impact of Land Use Change in the Xiangxi Catchment (China) on Water Balance and Sediment Transport. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2015, 15, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yu, C.; Xiong, L.; Chang, Y. How Can Agricultural Water Use Efficiency Be Promoted in China? A Spatial-Temporal Analysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 145, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Cheng, W.; Fu, B.; Lü, Y. The Role of Climatic and Anthropogenic Stresses on Long-Term Runoff Reduction from the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesschen, J.P.; Schoorl, J.M.; Cammeraat, L.H. Modelling Runoff and Erosion for a Semi-Arid Catchment Using a Multi-Scale Approach Based on Hydrological Connectivity. Geomorphology 2009, 109, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.E.; Jacobson, P.J. Water and Nutrient Discharge to a High-Value Terrace–Floodplain Fen: Resilience and Risk. Ecohydrology 2016, 9, 1196–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulouri, M.; Giourga, C. Land Abandonment and Slope Gradient as Key Factors of Soil Erosion in Mediterranean Terraced Lands. Catena 2007, 69, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, M.A.; Herath, S. Quantifying the Role of Traditional Rice Terraces in Regulating Water Resources: Implications for Management and Conservation Efforts. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 42, 885–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnoletti, M.; Errico, A.; Santoro, A.; Dani, A.; Preti, F. Terraced Landscapes and Hydrogeological Risk. Effects of Land Abandonment in Cinque Terre (Italy) during Severe Rainfall Events. Sustainability 2019, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnáez, J.; Lana-Renault, N.; Lasanta, T.; Ruiz-Flaño, P.; Castroviejo, J. Effects of Farming Terraces on Hydrological and Geomorphological Processes. A Review. Catena 2015, 128, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesschen, J.P.; Cammeraat, L.H.; Nieman, T. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms Earth Surf. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2008, 33, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).