Effect of Combined Application of Lanthanum-Based Capping Material and Biochemical Oxidant on Control of Internal Phosphorus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Sample Collection
2.2. Experimental Core Microcosm Setup
2.3. DO Measurements by Planar Optode
2.4. Chemical Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
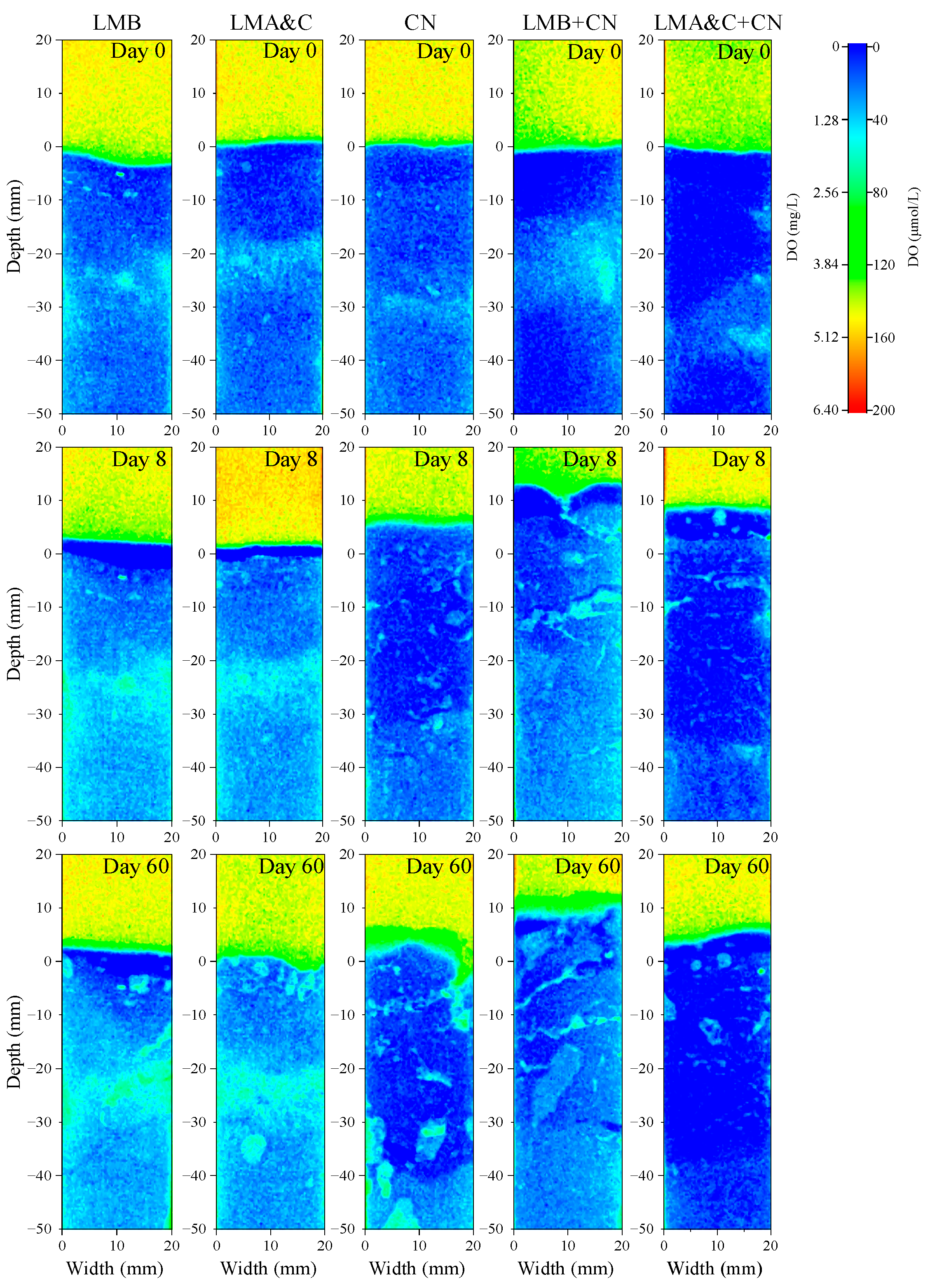
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Variations in DO at the Sediment–Water Interface
3.2. Variations in DGT-Labile Sulfide Flux in the Sediment–Water Profile
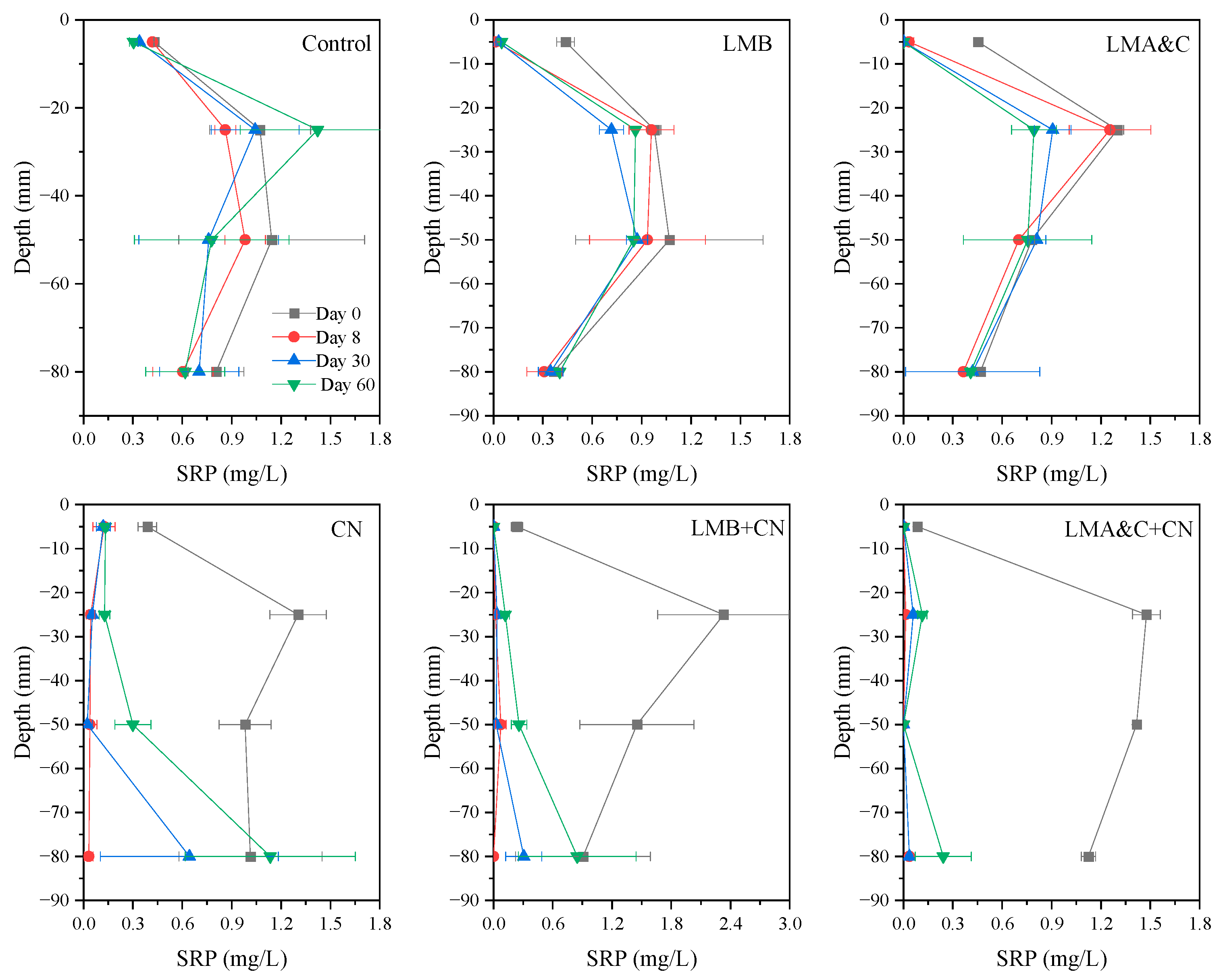
3.3. Variations in SRP Concentration in Pore Water
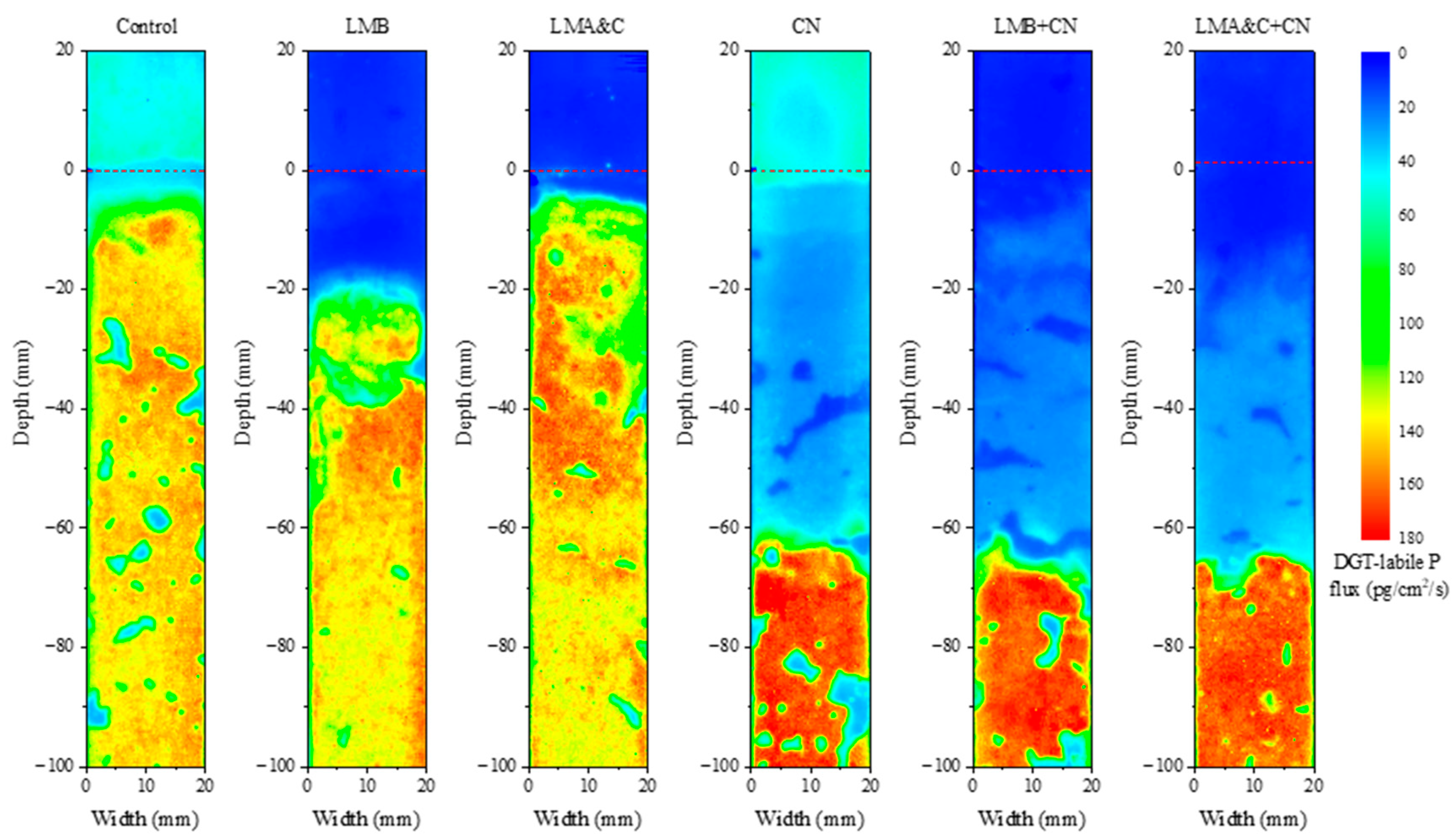
3.4. Variations in DGT-Labile P Flux in the Sediment-Water Profile
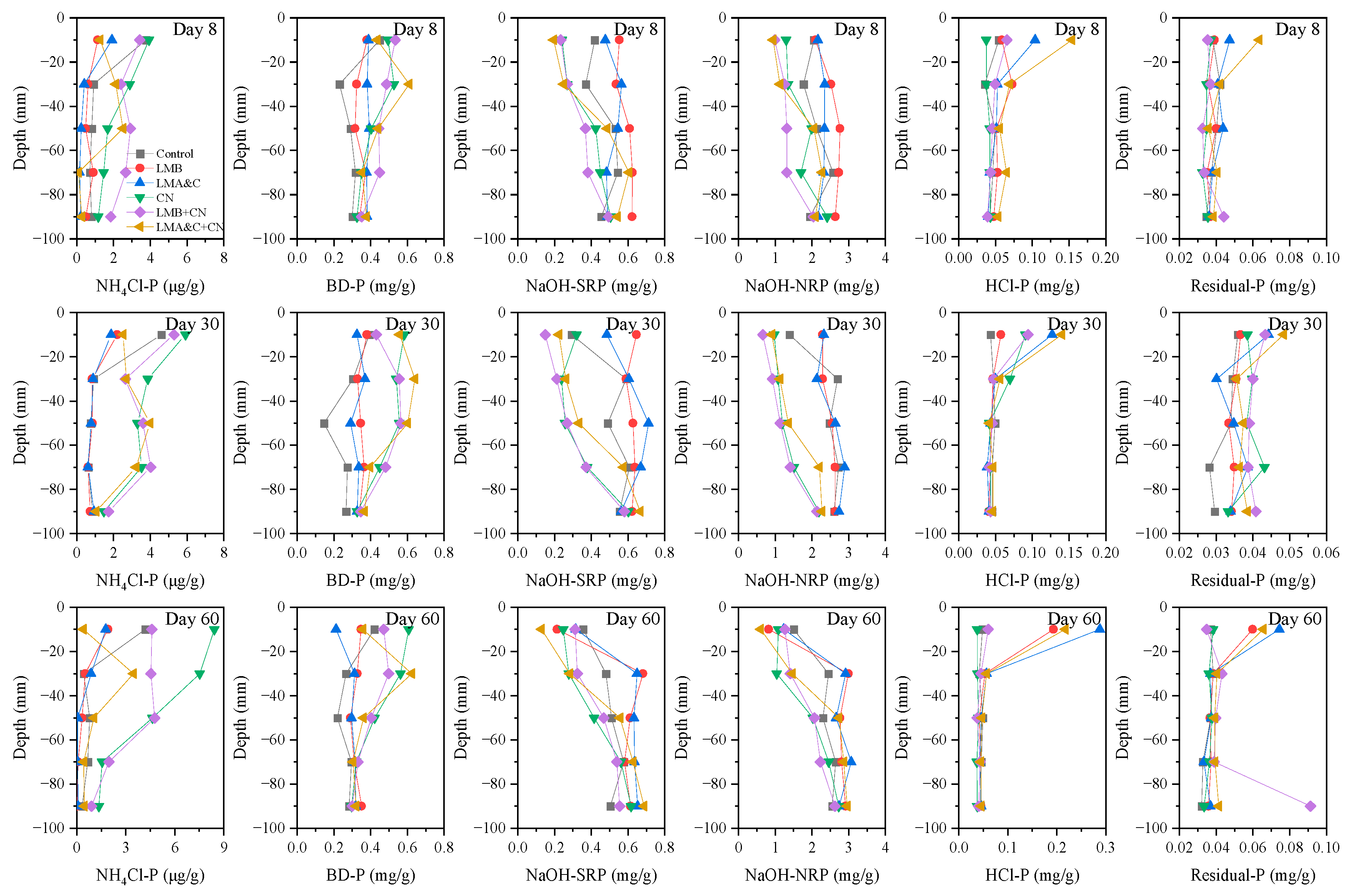
3.5. Variations in P Fractionation in Sediment
3.6. Implication for the Combined Application in the Control of Internal P
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- LMB and LMA&C decreased the SRP concentration to <0.05 mg/L at depths of −5 mm after 8, 30 and 60 days. CN, LMB+CN and LMA&C+CN decreased SRP concentrations to <0.13 mg/L at depths of −5, −25, −50 and −80 mm on days 10 and 30, but on day 60, SRP at −80 mm rebounded to some extent. The SRP removal rates of the two combined groups were much higher than that of LMB and LMA&C alone at −25, −50 and −80 mm, and higher than that of CN alone at −5 and −80 mm.
- (2)
- LMB decreased DGT-labile P flux in the overlying water and 40 mm surface sediment, and LMA&C decreased DGT-labile P flux in overlying water and 10 mm surface sediment. CN decreased DGT-labile P flux in surface 65 mm sediment but had no obvious effect on DGT-labile P in the overlying water. LMB+CN and LMA&C+CN decreased DGT-labile P flux in overlying water and surface 65 mm sediment. The control effect on DGT-labile P by the two combined groups was much better than that of LMB, LMA&C and CN alone.
- (3)
- NH4Cl-P, BD-P, NaOH-SRP and NaOH-NRP in the surface 20 mm were transformed into HCl-P and Residual-P by LMB and LMA&C on day 60. The NaOH-NRP removal might be attributed to the improved microenvironment in the SWI, which was favorable for microbial growth. CN transformed NaOH-SRP and NaOH-NRP to BD-P through the formation of Fe hydroxide and resulted in the increase in NH4Cl-P. In the LMB+CN and LMA&C+CN groups, the sequestered P in the surface 20 mm was mainly passivated to HC-P and Residual-P, and in −20~−60 mm was passivated to Fe-hydroxide-bound P.
- (4)
- Both the two combined methods in our study were effective for SRP and DGT-labile P removal in at least 60 mm of sediment. The “transition layer” (−20~−60 mm) rich in Fe hydroxide and the capping layer (surface 20 mm) rich in La effectively prevented the release of internal P.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, L.; Haasler, S.; Mucci, M.; Korving, L.; Dugulan, A.I.; Prot, T.; Waajen, G.; Lürling, M. Comparison of dredging, lanthanum-modified bentonite, aluminium-modified zeolite, and FeCl2 in controlling internal nutrient loading. Water Res. 2023, 244, 120391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Johansson, L.S.; Jeppesen, E. Nitrogen or phosphorus limitation in lakes and its impact on phytoplankton biomass and submerged macrophyte cover. Hydrobiologia 2017, 791, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.B.; Yang, P.; Kong, M. Effects of different chemical agents on changes in sediment phosphorus composition and the response of sediment microbial community. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.H.; Jiang, H.L. Chemicals used for in situ immobilization to reduce the internal phosphorus loading from lake sediments for eutrophication control. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 947–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.H.; Qiu, B.; Lin, J.W. Effect of common ions aging treatment on adsorption of phosphate onto and control of phosphorus release from sediment by lanthanum-modified bentonite. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 341, 118109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copetti, D.; Finsterle, K.; Marziali, L.; Stefani, F.; Tartari, G.; Douglas, G.; Reitzel, K.; Spears, B.M.; Winfield, I.J.; Crosa, G.; et al. Eutrophication management in surface waters using lanthanum modified bentonite: A review. Water Res. 2016, 97, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waajen, G.; Van Oosterhout, F.; Douglas, G.; Lurling, M. Management of eutrophication in Lake De Kuil (The Netherlands) using combined flocculant—Lanthanum modified bentonite treatment. Water Res. 2016, 97, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhen, W.; Cui, S.; Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Q.; Jeppesen, E.; Liu, Z. The effects of different doses of lanthanum-modified bentonite in combination with a submerged macrophyte (Vallisneria denseserrulata) on phosphorus inactivation and macrophyte growth: A mesocosm study. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 352, 120053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripl, W. Biochemical oxidation of polluted lake sediment with nitrate: A new lake restoration method. Ambio 1976, 5, 132–135. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.L.; Zheng, X.J.; Zhang, K.; Wu, B.L.; Pei, X.; Chen, W.S.; Wei, X.L.; Luo, Z.F.; Li, Y.T.; Zhang, Z. Sustained-release nitrate combined with microbial fuel cell: A novel strategy for PAHs and odor removal from sediment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 455, 131610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.Y.; He, Z.L.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Guo, J.; Sun, G.P.; Zhou, J.Z. Responses of aromatic-degrading microbial communities to elevated nitrate in sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12422–12431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.S.; Chen, Z.T.; Wang, A.; Zhang, S.R.; Li, N.; Liang, Z.Y.; Lai, J.T.; Kang, P.L.; Liang, Y.H.; Yu, G.W. Remediate black-odorous sediment by slow-release calcium nitrate: Migration, transformation and microbial succession. J. Clean Prod. 2023, 413, 137458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.H.; Huang, R.; Liang, Y.H.; Yu, G.W.; Chong, Y.X.; Wang, L. Index for nitrate dosage calculation on sediment odor control using nitrate-dependent ferrous and sulfide oxidation interactions. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 226, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.M.; Sueitt, A.P.E.; Beraldo, D.a.S.; Botta, C.M.R.; Fadini, P.S.; Nascimento, M.R.L.; Faria, B.M.; Mozeto, A.A. Calcium nitrate addition to control the internal load of phosphorus from sediments of a tropical eutrophic reservoir: Microcosm experiments. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6463–6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.H.; Wu, X.L.; Lin, J.W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y. Combined use of calcium nitrate addition and anion exchange resin capping to control sedimentary phosphorus release and its nitrate nitrogen releasing risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.A.; Zhong, M.; Pu, J.; Liu, C.Z.; Luo, H.; Xu, M.Y. Risk control and assessment of sulfide-rich sediment remediation by controlled-release calcium nitrate. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Qiu, P.H.; Yan, X.J.; Xiong, X.; Jing, L.D.; Wu, C.X. Effectiveness and mode of action of calcium nitrate and Phoslock (R) in phosphorus control in contaminated sediment, a microcosm study. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Bian, S.; Liang, X.; Sondergaard, M.; Jeppesen, E. Effects of nitrate on phosphorus release from lake sediments. Water Res. 2021, 194, 116894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Lin, J.; Cao, J.; Li, C.; Shi, D.; Gao, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ding, S. A new method to overall immobilization of phosphorus in sediments through combined application of capping and oxidizing agents. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.R.; Sun, Q.; Wang, J.H.; Ding, S.M. Investigation of the combined use of capping and oxidizing agents in the immobilization of arsenic in sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdi, F.; Anbia, M.; Sepehrian, M. Recent advances in removal of inorganic anions from water by chitosan-based composites: A comprehensive review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 320, 121230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.H.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, X.; Fan, P.D.; Song, R. La(III)-bentonite/chitosan composite: A new type adsorbent for rapid removal of phosphate from water bodies. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 190, 105547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Cui, H.; Liu, B.J.; Gao, X.; Wang, D.F.; Liang, P. La(III)-loaded bentonite/chitosan beads for defluoridation from aqueous solution. J. Rare Earths 2014, 32, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ding, S.M.; Chen, M.S.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhong, Z.L.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Wang, Y. Mechanistic insights into trace metal mobilization at the micro-scale in the rhizosphere of Vallisneria spiralis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEPC. Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 4th ed.; Chinese Environmental Sciences Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rydin, E.; Huser, B.; Welch, E.B. Amount of phosphorus inactivated by alum treatments in Washington lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhu, C.G.; Zhang, C.S. Gel-based coloration technique for the submillimeter-scale imaging of labile phosphorus in sediments and soils with diffusive gradients in thin films. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7821–7829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, S.M.; Ren, M.Y.; Li, C.; Xu, S.W.; Sun, Q.; Xu, L.G. Enhanced DGT capability for measurements of multiple types of analytes using synergistic effects among different binding agents. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glud, R.N.; Ramsing, N.B.; Gundersen, J.K.; Klimant, I. Planar optrodes: A new tool for fine scale measurements of two-dimensional O2 distribution in benthic communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. 1996, 140, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Fu, Z.; Yao, J.W.; Wei, X.; Wang, D.; Ning, D.L.; Chen, M.S. Behavior of iron and other heavy metals in passivated sediments and the coupling effect on phosphorus. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopel, K.; Gibbs, M.; Hickey, C.W.; Quinn, J. Modification of sediment-water solute exchange by sediment-capping materials: Effects on O-2 and pH. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2008, 59, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teasdale, P.R.; Hayward, S.; Davison, W. In situ, high-resolution measurement of dissolved sulfide using diffusive gradients in thin films with computer-imaging densitometry. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 2186–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Liu, M.; Zhuang, S.; Geng, B.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Chen, M. Effects on the migration and speciation of heavy metals by combined capping and biochemical oxidation during sediment remediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 162055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dithmer, L.; Lipton, A.S.; Reitzel, K.; Warner, T.E.; Lundberg, D.; Nielsen, U.G. Characterization of phosphate sequestration by a lanthanum modified bentonite clay: A solid-state NMR, EXAFS, and PXRD study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4559–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.B.; Zhu, J.C.; Tang, W.Y. Management of nitrogen and phosphorus internal loading from polluted river sediment using Phoslock (R) and modified zeolite with intensive tubificid oligochaetes bioturbation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, S.M.; Wang, D.; Sun, Q.; Lin, J.; Shi, L.; Chen, M.S.; Zhang, C.S. Static layer: A key to immobilization of phosphorus in sediments amended with lanthanum modified bentonite (Phoslock (R)). Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 325, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Fu, Z.; Ding, S.M.; Ren, M.Y.; Gao, S.S. Laboratory investigation on calcium nitrate induced coupling reactions between nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, and metals in contaminated sediments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 25866–25877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiserli, A.; Voutsa, D.; Samara, C. Phosphorus fractionation in lake sediments—Lakes Volvi and Koronia, N. Greece. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozerski, H.P.; Kleeberg, A. The Sediments and Benthic-pelagic Exchange in the Shallow Lake Müggelsee (Berlin, Germany). Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 1998, 83, 77–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.B.; Yang, C.H.; Yang, P.; Kaksonen, A.H.; Douglas, G.B. Contrasting effects and mode of dredging and in situ adsorbent amendment for the control of sediment internal phosphorus loading in eutrophic lakes. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dithmer, L.; Nielsen, U.G.; Lundberg, D.; Reitzel, K. Influence of dissolved organic carbon on the efficiency of P sequestration by a lanthanum modified clay. Water Res. 2016, 97, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhong, Y.F.; Fan, H.; Song, C.F.; Yu, C.; Gao, Y.; Xiong, X.; Wu, C.X.; Liu, J.T. Chemical treatment of contaminated sediment for phosphorus control and subsequent effects on ammonia-oxidizing and ammonia-denitrifying microorganisms and on submerged macrophyte revegetation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Geng, B.; Wu, G.; Si, J.; Liu, Y.; Ning, D.; Lin, J. Effect of Combined Application of Lanthanum-Based Capping Material and Biochemical Oxidant on Control of Internal Phosphorus. Water 2024, 16, 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050641
Liu Y, Geng B, Wu G, Si J, Liu Y, Ning D, Lin J. Effect of Combined Application of Lanthanum-Based Capping Material and Biochemical Oxidant on Control of Internal Phosphorus. Water. 2024; 16(5):641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050641
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yvlu, Bing Geng, Guoyi Wu, Jingyi Si, Yi Liu, Dongliang Ning, and Juan Lin. 2024. "Effect of Combined Application of Lanthanum-Based Capping Material and Biochemical Oxidant on Control of Internal Phosphorus" Water 16, no. 5: 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050641
APA StyleLiu, Y., Geng, B., Wu, G., Si, J., Liu, Y., Ning, D., & Lin, J. (2024). Effect of Combined Application of Lanthanum-Based Capping Material and Biochemical Oxidant on Control of Internal Phosphorus. Water, 16(5), 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050641





