Evaluation of Various Forms of Geothermal Energy Release in the Beijing Region, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
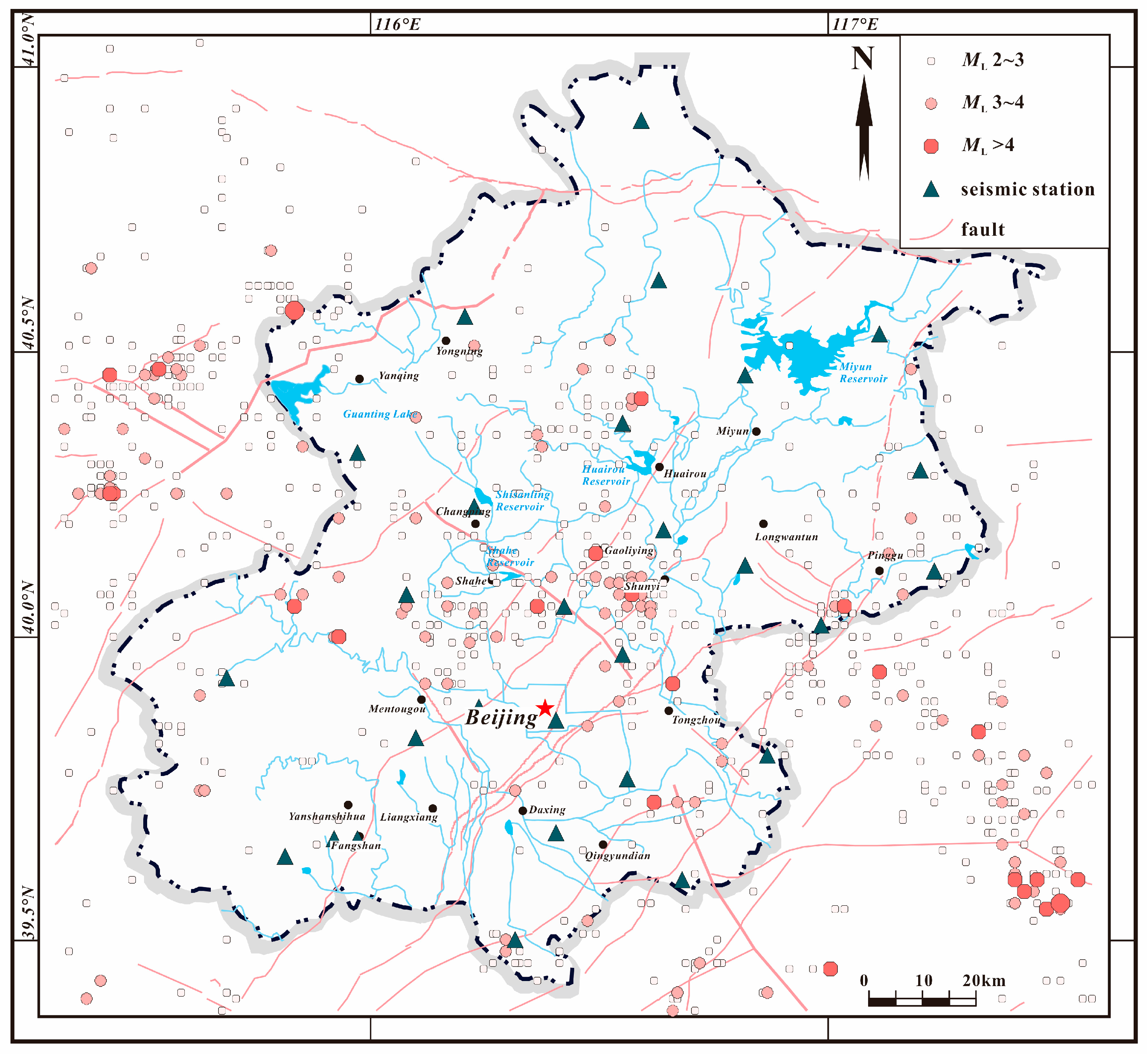
2. The Study Area
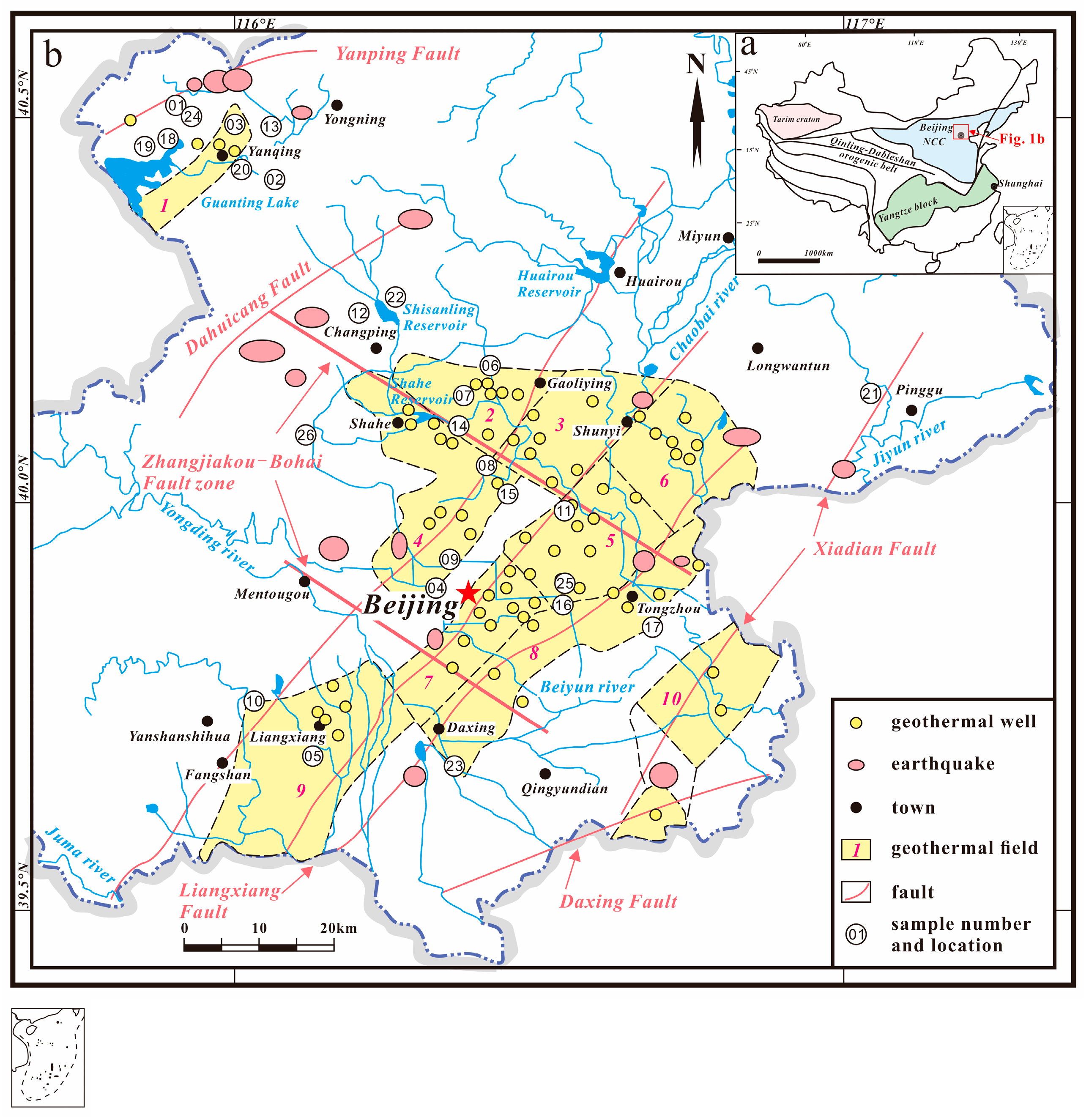
3. Sampling and Analytical Methods
3.1. Geothermal Water Samples Collection and Analysis
3.2. Geothermal Gas Samples Collection and Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
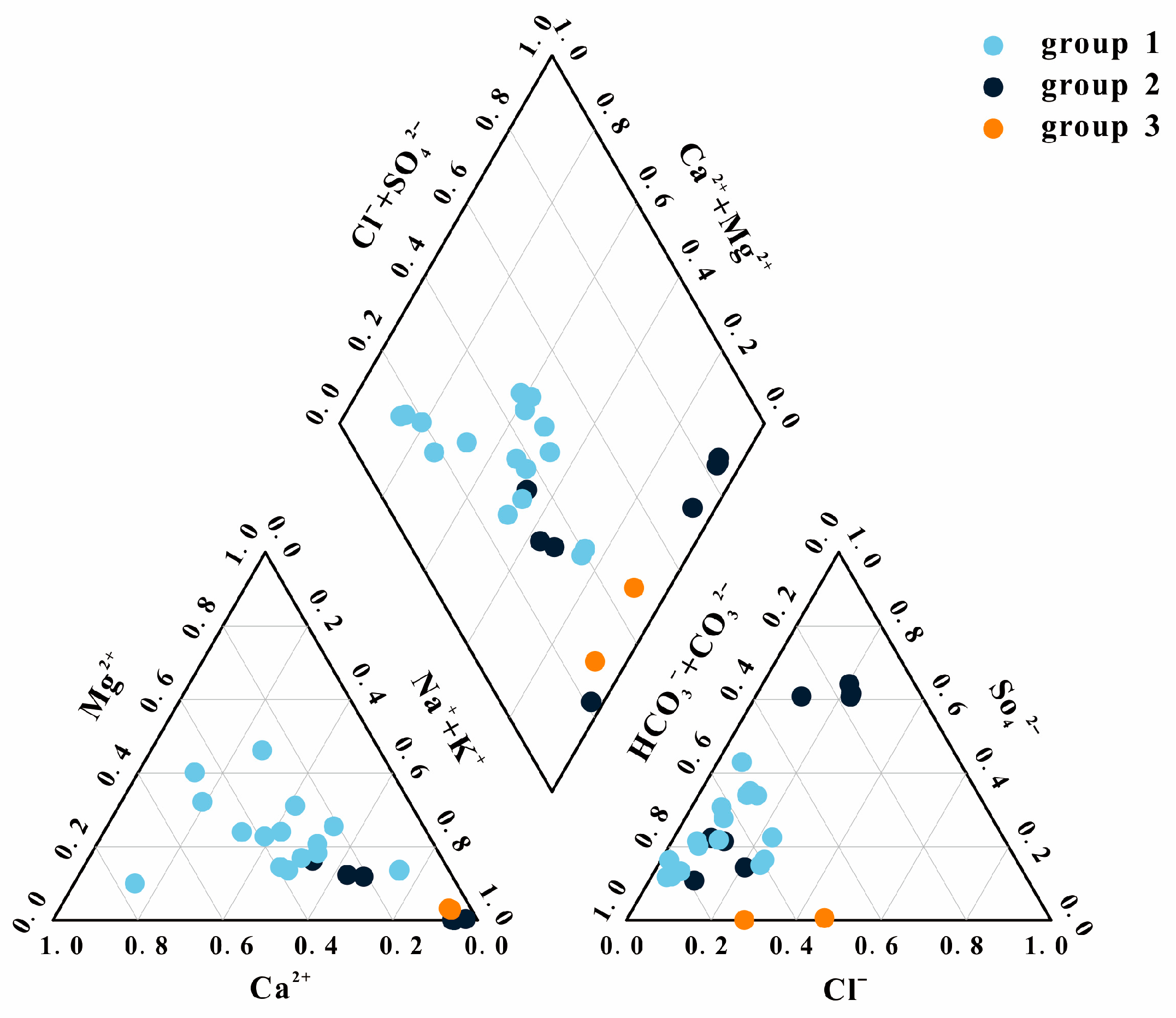
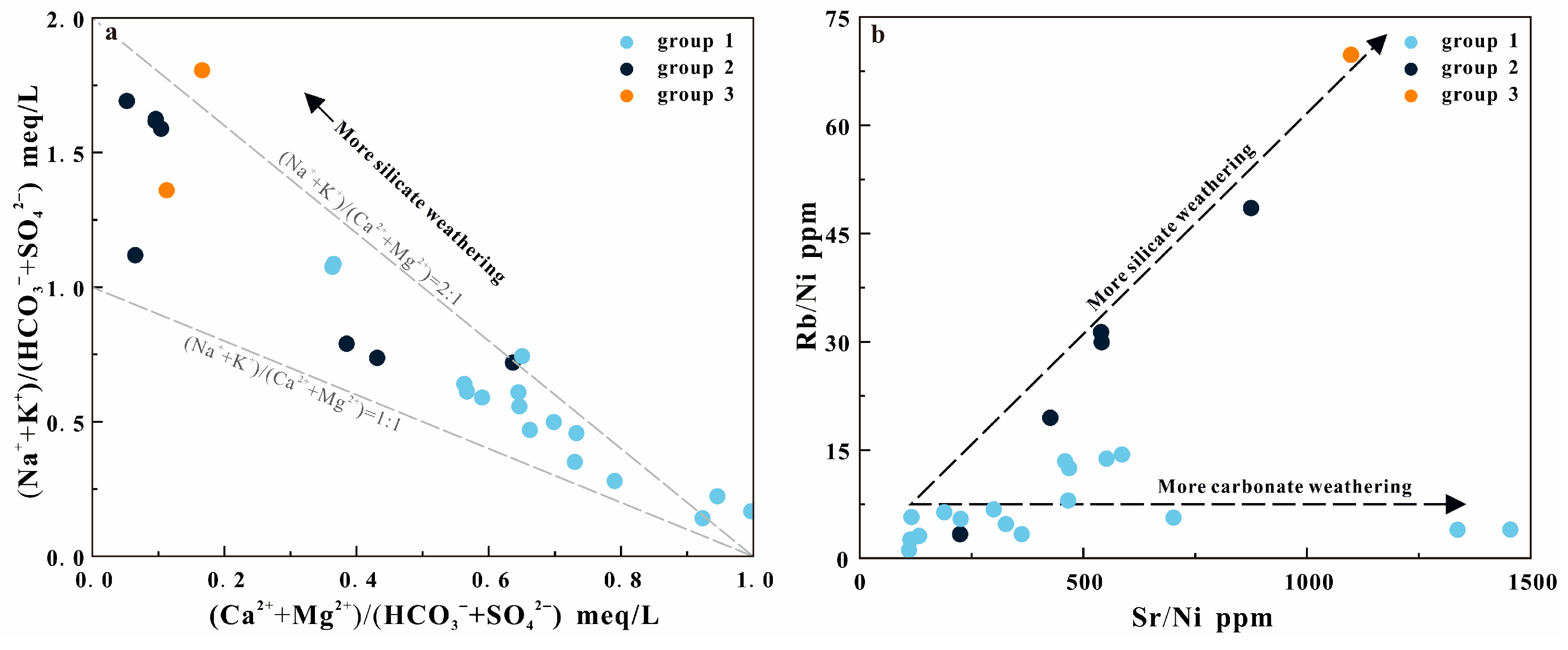
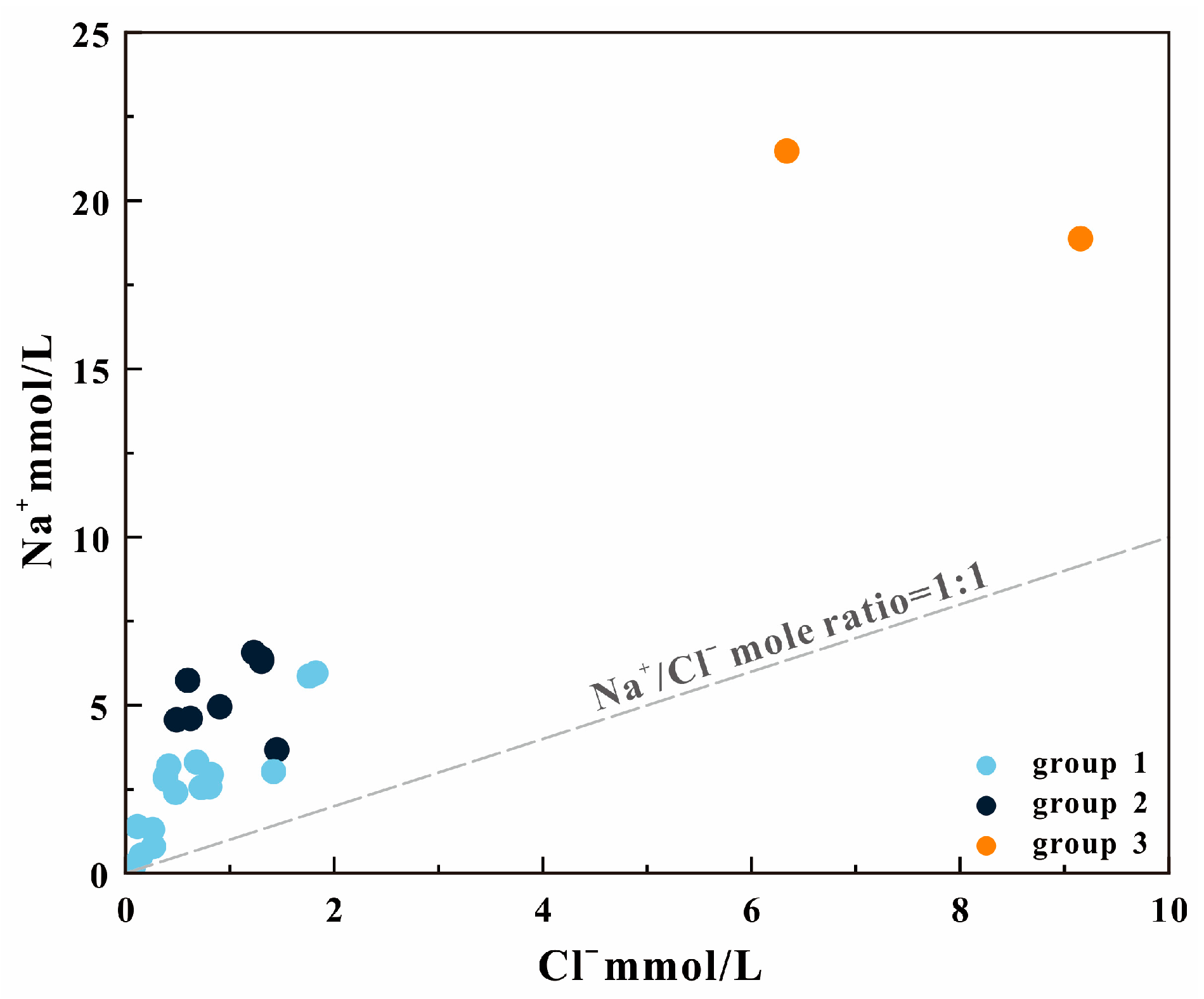
4.1. Hydrochemistry of Geothermal Waters
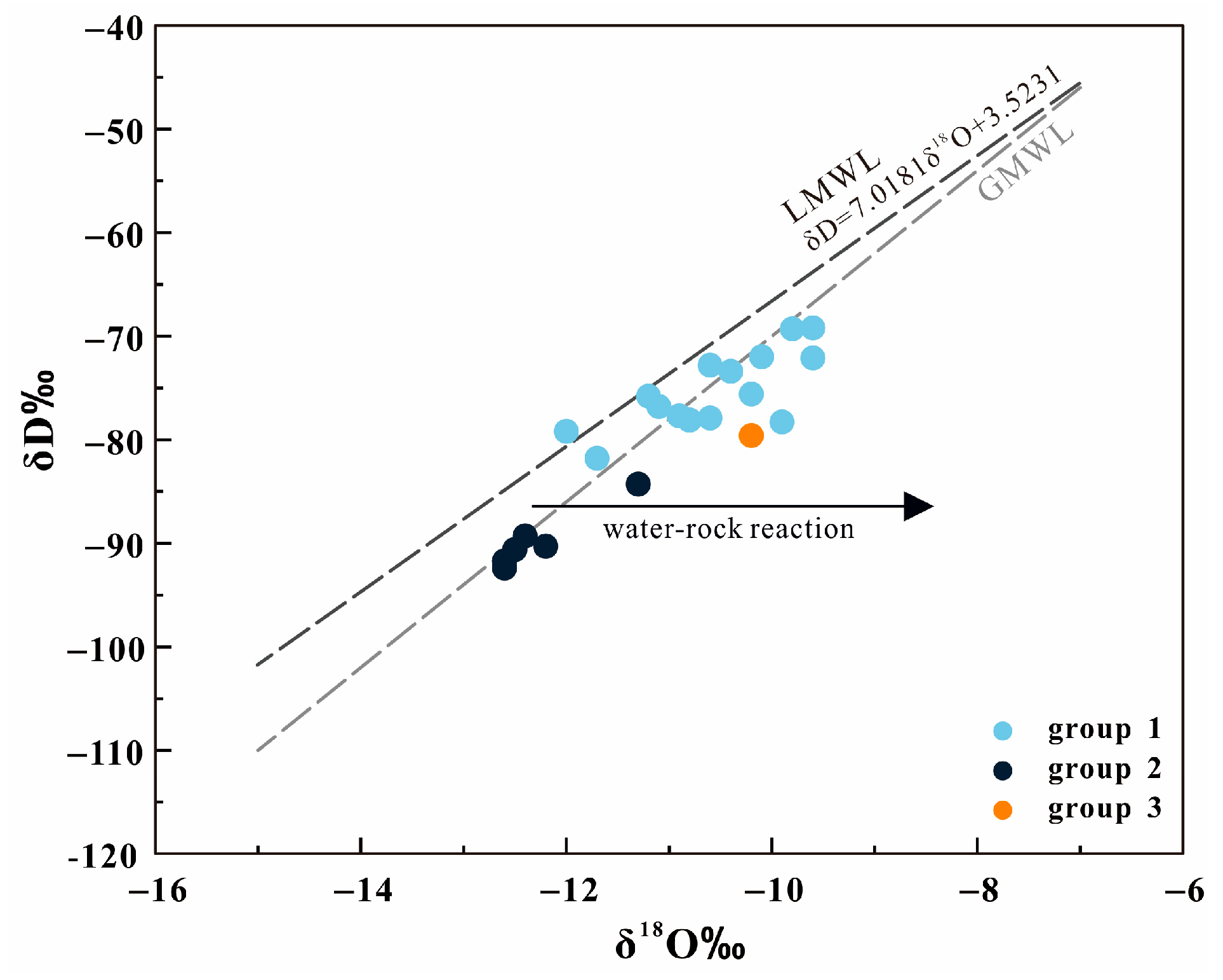
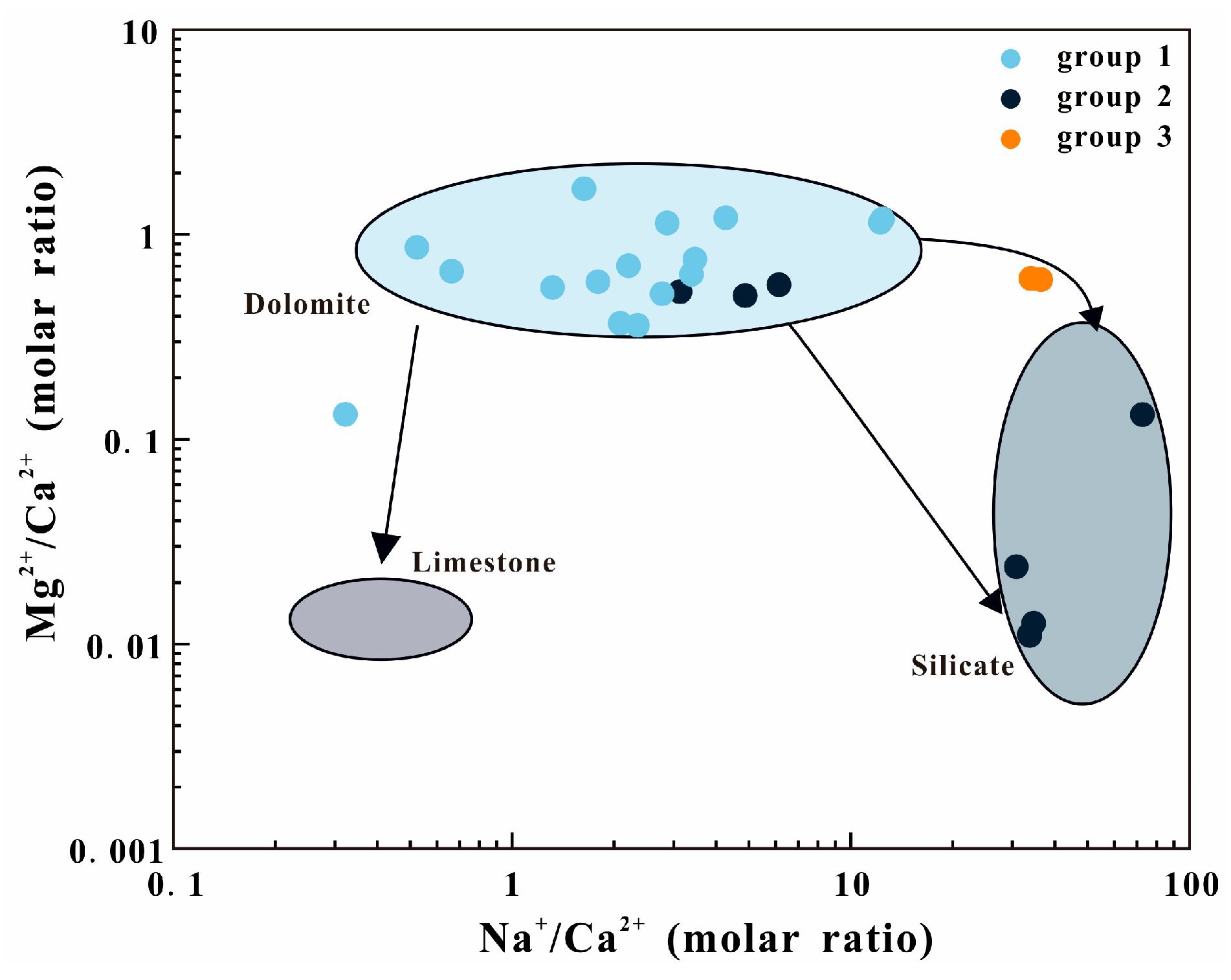
4.2. Characteristics of Heat Reservoir
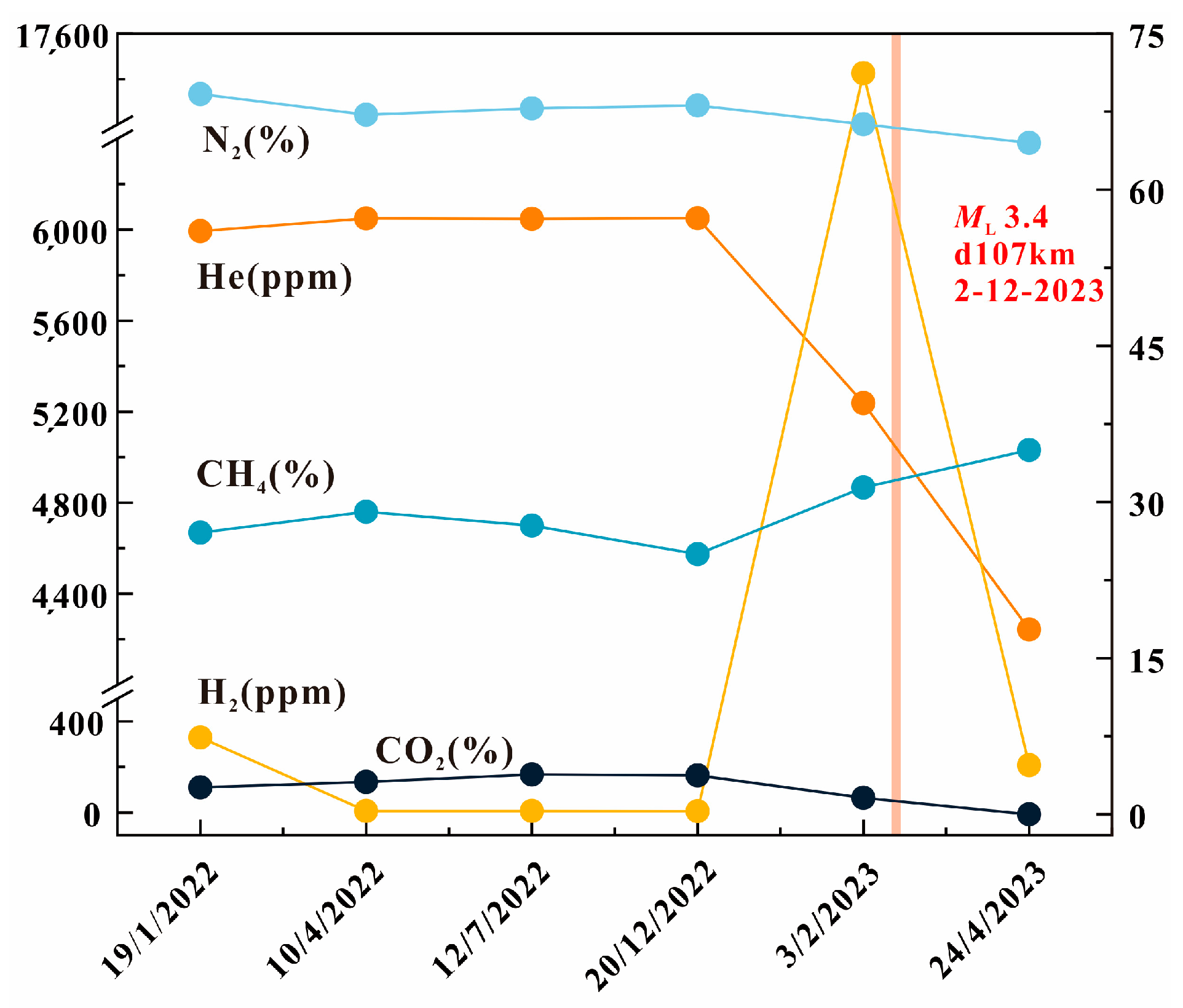
4.3. Origin of High He, H2, and CH4 Concentrations in Geothermal Gases
4.3.1. He
4.3.2. CH4
4.3.3. H2
4.4. Geothermal Water Cycle Model and Genesis of Geothermal Field
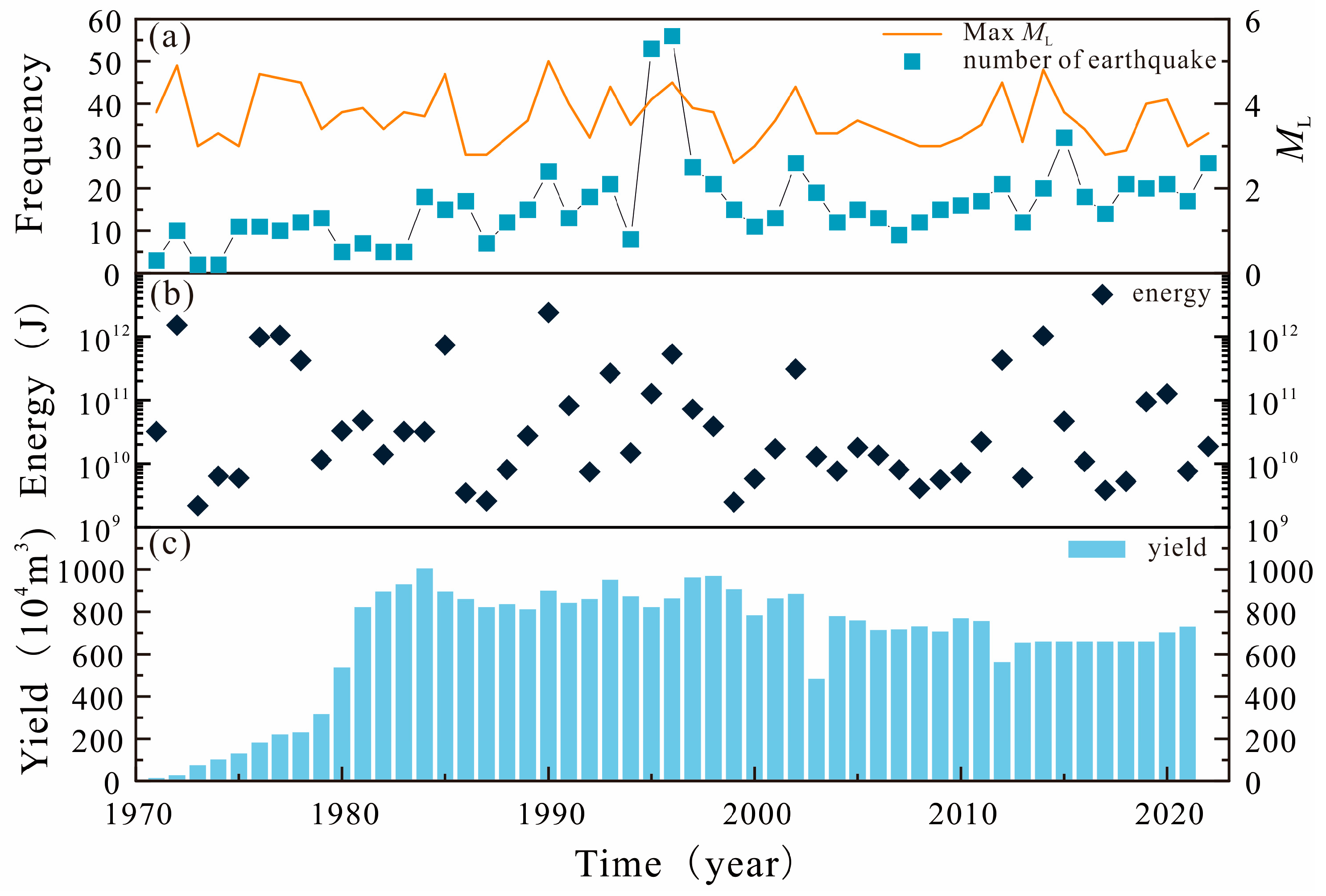
4.5. The Promotion of Geothermal Resources to Promote the Earth’s Energy Release
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alam, B.Y.C.S.S.S.; Itoi, R.; Taguchi, S.; Saibi, H.; Yamashiro, R. Hydrogeochemical and isotope characterization of geothermal waters from the Cidanau geothermal field, West Java, Indonesia. Geothermics 2019, 78, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahri, F.; Saibi, H.; Cherchali, M.-E.-H. Characterization, classification, and determination of drinkability of some Algerian thermal waters. Arab. J. Geosci. 2011, 4, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbarbary, S.; Zaher, M.A.; Saibi, H.; Fowler, A.-R.; Saibi, K. Geothermal renewable energy prospects of the African continent using GIS. Geotherm. Energy 2022, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saibi, H.; Batir, J.F.; Pocasangre, C. Hydrochemistry and geothermometry of thermal waters from UAE and their energetic potential assessment. Geothermics 2021, 92, 102061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saibi, H.; Ehara, S. Temperature and chemical changes in the fluids of the Obama geothermal field (SW Japan) in response to field utilization. Geothermics 2010, 39, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulela, H.; Amin, A.; Lashin, A.; El Rayes, A. Contribution of geothermal resources to the future of renewable energy in Egypt: A case study, Gulf of Suez-Egypt. Renew. Energy 2021, 167, 248–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rayes, A.E.; Arnous, M.O.; Aboulela, H.A. Hydrogeochemical and seismological exploration for geothermal resources in South Sinai, Egypt utilizing GIS and remote sensing. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 5631–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Pang, Z.; Liao, D.; Tian, J.; Hao, Y.; Huang, T.; Li, Y. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Genesis of Geothermal Water from the Ganzi Geothermal Field, Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Water 2019, 11, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.M.; Zhang, Q.L.; Cui, Y.L.; Shao, J.L.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, J.X. Hydrogeochemistry and Genesis Analysis of Thermal and Mineral Springs in Arxan, Northeastern China. Water 2017, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Lin, W.; Xing, L.; Chen, L. The Estimation of Geothermal Reservoir Temperature Based on Integrated Multicomponent Geothermometry: A Case Study in the Jizhong Depression, North China Plain. Water 2022, 14, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Tian, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, H.; Yang, X. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Geothermal Water in Ancient Deeply Buried Hills in the Northern Jizhong Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Water 2023, 15, 3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Jiang, C.; Zhai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Lai, G.; Zhu, A.; Yin, F. Review of induced seismicity and disaster risk control in dry hot rock resource development worldwide. Chin. J. Geophys. Chin. Ed. 2021, 64, 3817–3836. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, K.; Yi, L.; Asanuma, H.; Okabe, T.; Abe, Y.; Tsuzuki, M. Triggering processes of microseismic events associated with water injection in Okuaizu Geothermal Field, Japan. Earth Planets Space 2018, 70, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, E.E.; Lajoie, L.J. Anthropogenic Seismicity Rates and Operational Parameters at the Salton Sea Geothermal Field. Science 2013, 341, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruenthal, G. Induced seismicity related to geothermal projects versus natural tectonic earthquakes and other types of induced seismic events in Central Europe. Geothermics 2014, 52, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi, Y.; Cappa, F.; Avouac, J.P.; Henry, P.; Elsworth, D. Seismicity triggered by fluid injection–induced aseismic slip. Science 2015, 348, 1224–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trutnevyte, E.; Wiemer, S. Tailor-made risk governance for induced seismicity of geothermal energy projects: An application to Switzerland. Geothermics 2017, 65, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, X.; Yan, Y.; Ouyang, S.; Liu, F. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Hot Springs and Their Short-Term Seismic Precursor Anomalies along the Xiaojiang Fault Zone, Southeast Tibet Plateau. Water 2021, 13, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, Y.; Ouyang, S.; Liu, F.; Zhong, J. Hydrogeochemistry and Precursory Anomalies in Thermal Springs of Fujian (Southeastern China) Associated with Earthquakes in the Taiwan Strait. Water 2021, 13, 3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majer, E.L.; Baria, R.; Stark, M.; Oates, S.; Bommer, J.; Smith, B.; Asanuma, H. Induced seismicity associated with enhanced geothermal systems. Geothermics 2007, 36, 185–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haering, M.O.; Schanz, U.; Ladner, F.; Dyer, B.C. Characterisation of the Basel 1 enhanced geothermal system. Geothermics 2008, 37, 469–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Ree, J.-H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.; Kang, S.Y.; Seo, W. Assessing whether the 2017 Mw 5.4 Pohang earthquake in South Korea was an induced event. Science 2018, 360, 1007–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, L.V.; Wood, C.K.; Yeck, W.L.; King, V.M. The 24 January 2013 M-L 4.4 Earthquake near Paradox, Colorado, and Its Relation to Deep Well Injection. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2014, 85, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Yu, J. Influence and controlling of fluid in the crust on earthquake activity. Recent Dev. World Seismol. 2014, 8, 1–9, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ellsworth, W.L. Injection-Induced Earthquakes. Science 2013, 341, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.M. Denver area earthquakes and the Rocky Mountain Arsenal disposal well. Mt. Geol. 1966, 3, 23–36. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, S. Disposal of Hydrofracking Waste Fluid by Injection into Subsurface Aquifers Tiggers Earthquake Swarm in Central Arkansas with Potential for Damaging Earthquake. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2012, 83, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keranen, K.M.; Savage, H.M.; Abers, G.A.; Cochran, E.S. Potentially induced earthquakes in Oklahoma, USA: Links between wastewater injection and the 2011 Mw 5.7 earthquake sequence. Geology 2013, 41, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keranen, K.M.; Weingarten, M.; Abers, G.A.; Bekins, B.A.; Ge, S. Sharp increase in central Oklahoma seismicity since 2008 induced by massive wastewater injection. Science 2014, 345, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.Y. Induced seismicity associated with fluid injection into a deep well in Youngstown, Ohio. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2013, 118, 3506–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarr, A. Maximum magnitude earthquakes induced by fluid injection. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014, 119, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaucher, E.; Schoenball, M.; Heidbach, O.; Zang, A.; Fokker, P.A.; Wees, J.D.V.; Kohl, T. Induced seismicity in geothermal reservoirs: A review of forecasting approaches. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 1473–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Rudnick, R.L.; Yuan, H.L.; Liu, X.M.; Liu, Y.S.; Xu, W.L.; Ling, W.L.; Ayers, J.; Wang, X.C.; Wang, Q.H. Recycling lower continental crust in the North China craton. Nature 2004, 432, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.C.; Sun, M.; Wilde, S.A.; Li, S.Z. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton: Key issues revisited. Precambrian Res. 2005, 136, 177–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, M.X.; Li, Y.; Ding, X.; Teng, F.Z.; Yang, X.Y.; Fan, W.M.; Xu, Y.G.; Sun, W.D. Destruction of the North China Craton Induced by Ridge Subductions. J. Geol. 2013, 121, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Xu, Y.; Gao, S.; Zheng, J. Lithospheric thinning and destruction of the North China Craton. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2008, 24, 1145–1174, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.; Chen, L.; Wu, F.; Liu, J. Timing, scale and mechanism of the destruction of the North China Craton. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, H.; Xia, Q.; Zheng, T. Destruction of the North China Craton. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 1565–1587, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.X.; Xu, Y.G. The subduction of the west Pacific plate and the destruction of the North China Craton. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 1340–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.B.; Liu, G.P.; Liu, Z.; Ma, J.C.; Li, L.W.; Wang, Z.G.; Hua, P.X.; Xing, L.T.; Sun, X.R.; Han, K.Y.; et al. Geochemical characteristics of geothermal and hot spring gases in Beijing and Zhangjiakou Bohai fault zone. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 933066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Z. Research on activity of Zhangjiakou-Bohai fault zone based on GPS observations. Seismol. Geol. 2020, 42, 95–108, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, W.; Lin, W.; Liu, F.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Research on formation mode and development potential of geothermal resources in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Geol. China 2017, 44, 1074–1085, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Wang, S.; Sun, Y.; Cui, W.; Zhu, D. Characteristics and regionalization of geothermal resources in Beijing. Geol. China 2017, 44, 1128–1139, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Zhou, X.; He, M.; Liang, J.; Li, J.; Dong, J.; Tian, J.; Yan, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; et al. Earthquakes evoked by lower crustal flow: Evidence from hot spring geochemistry in Lijiang-Xiaojinhe fault. J. Hydrol. 2023, 619, 129334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.Z.; Wang, J.S.; Zhang, Y.; Teng, Y.G.; Zuo, R.; Huan, H. Hydrochemical and isotopic investigation of atmospheric precipitation in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 456, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.X.; Zhou, X.R.; Li, S.H.; Zhang, N.D.; Ji, L.; Lu, H. Mechanism Study of Hydrocarbon Differential Distribution Controlled by the Activity of Growing Faults in Faulted Basins: Case Study of Paleogene in the Wang Guantun Area, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Lithosphere 2022, 2021, 7115985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.H. Hydrogeochemistry of high-temperature geothermal systems in China: A review. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Kong, Y.; Wang, K.; Ren, Y.; Pang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wen, D.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Q.; Zhu, G.; et al. Magmatic origin of geothermal fluids constrained by geochemical evidence: Implications for the heat source in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.L.; Liu, C.Q. Water geochemistry controlled by carbonate dissolution: A study of the river waters draining karst-dominated terrain, Guizhou Province, China. Chem. Geol. 2004, 204, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouillac, C.; Michard, G. Sodium/lithium ratio in water applied to geothermometry of geothermal reservoirs. Geothermics 1981, 10, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, R.O. Chemical geothermometers and mixing models for geothermal systems. Geothermics 1977, 5, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, Z.; Yi, L.; Liu, L.; Xie, C.; Cui, Y.; Du, J.; Cheng, J.; Yang, L. Hot Spring Gas Geochemistry in Western Sichuan Province, China after the Wenchuan Ms 8.0 Earthquake. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2015, 26, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.C.; Yan, Y.C.; Fang, W.Y.; Wang, W.L.; Shi, H.Y.; Li, P.F. Short-Term Seismic Precursor Anomalies of Hydrogen Concentration in Luojishan Hot Spring Bubbling Gas, Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 8, 586279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudry, P.; Stefansson, A.; Fiebig, J.; Rhim, J.H.; Ono, S. High temperature generation and equilibration of methane in terrestrial geothermal systems: Evidence from clumped isotopologues. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2021, 309, 209–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etiope, G.; Lollar, B.S. Abiotic methane on earth. Rev. Geophys. 2013, 51, 276–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etiope, G.; Schoell, M. Abiotic Gas: Atypical, But Not Rare. Elements 2014, 10, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etiope, G.; Schoell, M.; Hosgormez, H. Abiotic methane flux from the Chimaera seep and Tekirova ophiolites (Turkey): Understanding gas exhalation from low temperature serpentinization and implications for Mars. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 310, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etiope, G.; Tsikouras, B.; Kordella, S.; Ifandi, E.; Christodoulou, D.; Papatheodorou, G. Methane flux and origin in the Othrys ophiolite hyperalkaline springs, Greece. Chem. Geol. 2013, 347, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, F.; Grozeva, N.G.; Seewald, J.S. Abiotic methane synthesis and serpentinization in olivine-hosted fluid inclusions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 17666–17672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, J.M.; Seewald, J.S.; German, C.R.; Sylva, S.P. Pathways for abiotic organic synthesis at submarine hydrothermal fields. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7668–7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proskurowski, G.; Lilley, M.D.; Seewald, J.S.; Fruh-Green, G.L.; Olson, E.J.; Lupton, J.E.; Sylva, S.P.; Kelley, D.S. Abiogenic hydrocarbon production at Lost City hydrothermal field. Science 2008, 319, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, E.P.; Fiebig, J. Abiotic Synthesis of Methane and Organic-Compounds in Earth’s Lithosphere. Elements 2020, 16, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciarra, A.; Saroni, A.; Etiope, G.; Coltorti, M.; Mazzarini, F.; Lott, C.; Grassa, F.; Italiano, F. Shallow submarine seep of abiotic methane from serpentinized peridotite off the Island of Elba, Italy. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 100, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, R.M.R.; Camarda, M.; Gurrieri, S.; Valenza, M. Continuous monitoring of hydrogen and carbon dioxide at Mt Etna. Chem. Geol. 2013, 357, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hirose, T.; Kawagucci, S.; Suzuki, K. Mechanoradical H2 generation during simulated faulting: Implications for an earthquake-driven subsurface biosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L17303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameda, J.; Saruwatari, K.; Tanaka, H. H2 generation in wet grinding of granite and single-crystal powders and implications for H2 concentration on active faults. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakita, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Kita, I.; Fujii, N.; Notsu, K. Hydrogen release: New indicator of fault activity. Science 1980, 210, 188–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Du, J.; Chen, Z.; Cheng, J.; Tang, Y.; Yang, L.; Xie, C.; Cui, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; et al. Geochemistry of soil gas in the seismic fault zone produced by the Wenchuan Ms 8.0 earthquake, southwestern China. Geochem. Trans. 2010, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Shang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, W.; Liu, X. Effect of Fluid Salinity on Reaction Rate and Molecular Hydrogen (H2) Formation during Peridotite Serpentinization at 300 °C. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2023, 128, e2022JB025218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, A.; Andren, M.; Kristmannsdottir, H.; Stockmann, G.; Morth, C.-M.; Sveinbjoernsdottir, A.; Jonsson, S.; Sturkell, E.; Gudorunardottir, H.R.; Hjartarson, H.; et al. Changes in groundwater chemistry before two consecutive earthquakes in Iceland. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Z.; Yang, M.; Zhou, X.; Liu, G.; Liang, J.; Liu, Z.; Hua, P.; Ma, J.; Hu, L.; Sun, X.; et al. Evaluation of Various Forms of Geothermal Energy Release in the Beijing Region, China. Water 2024, 16, 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040622
Luo Z, Yang M, Zhou X, Liu G, Liang J, Liu Z, Hua P, Ma J, Hu L, Sun X, et al. Evaluation of Various Forms of Geothermal Energy Release in the Beijing Region, China. Water. 2024; 16(4):622. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040622
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Zebin, Mingbo Yang, Xiaocheng Zhou, Guiping Liu, Jinlong Liang, Zhe Liu, Peixue Hua, Jingchen Ma, Leyin Hu, Xiaoru Sun, and et al. 2024. "Evaluation of Various Forms of Geothermal Energy Release in the Beijing Region, China" Water 16, no. 4: 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040622
APA StyleLuo, Z., Yang, M., Zhou, X., Liu, G., Liang, J., Liu, Z., Hua, P., Ma, J., Hu, L., Sun, X., Cui, B., Wang, Z., & Chen, Y. (2024). Evaluation of Various Forms of Geothermal Energy Release in the Beijing Region, China. Water, 16(4), 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16040622





